Stem Cell Oncology – Adella (Ed.) © 2018 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-0-8153-9272-9
The CYP2A13 Arg257Cys polymorphism and its relationship
to lung cancer
N.N. Soeroso & B.Y.M. Sinaga
Department Pulmonology and Respiratory Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, North Sumatera, Indonesia
R. Zain-Hamid
Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, North Sumatera, Indonesia
A.H. Sadewa
Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
E. Syahruddin
Department Pulmonology and Respiratory Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Medan, North Sumatera, Indonesia
ABSTRACT: A common polymorphism, Arg257Cys of CYP2A13 gene, is associated with lung cancer in several populations. The aim of this study was to analyse the relationship between this polymorphism and lung cancer in several ethnics of the Indonesia population. Consecutive sampling and case-control study were applied. The PCR-RFLP assay was employed to geno-type. The chi-square test with p < 0.05 considered as significant. Of all 50 subjects, 26 (13%) indi-viduals were heterozygotes, and 37 (74%) were homozygote for the 257Cys allele. The frequency distributions among ethnics were Acehnese two (5.4%) homozygote, Malay two (5.4%) homozy-gote, Chinese one (7.7%) heterozyhomozy-gote, 20 (54%) homozygote and six (46.1%) heterozygotes in Batak, 13 (35.1%) homozygote and six (46.1%) heterozygotes in Javanese. The CYP2A13 Arg-257Cys variant represents a common polymorphism in Batak and Javanese ethnics. There is no association between Arg257Cys polymorphism of CYP2A13 and lung cancer.
Keywords: CYP2A13 gene, PCR-RFLP, lung cancer, Indonesia population
1 INTRODUCTION
Lung cancer is the most common cancer in the world, representing approximately 1.2 million lung cancer patient annually, which is leading cause of cancer death (Parkin et al., 2001). Lung cancer deaths contribute to more than 1 million deaths with the prediction of approximately 1.4 million people (Globocan, 2012). Since 1950, tobacco smoke has been recognised as the main cause of lung cancer and smoking has also become a life style. Lung cancer will be the health problem in the future (Medical Research Council, 1957). In Indonesia, tobacco smoke and smokeless tobacco is used by approximately 67.4% of the male and 4.5% of the female population. It means Indonesia has the most common tobacco use, approximately 61.4 mil-lion people (31.1% of the population), (Global Adult Tobacco Survey, 2011).
266
are homozygous for the Cys257 allele because the Cys257 variant had a > 2-fold less catalytic efficiency for Nicotine-derived Nitrosamine Ketone (NNK). However, this relationship is still controversial, and further study is needed in several ethnics (Cheng et al., 2004).
So far, there is still limited data regarding the Arg257Cys polymorphism of CYP2A13 in the Indonesia population. Therefore, the aim of this study is to identify this polymorphism and its relationship to lung cancer in the Indonesia population.
2 METHOD
2.1 Subjects
50 male subjects with a history of cigarette smoking were recruited in the study, 25 subjects with lung cancer compared with 25 healthy subjects. All subjects were patients in Adam Malik General Hospital. This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, and obtained informed consent from each participant.
2.2 Blood acquisition and DNA isolation
3 ml of venous blood was collected from the mediana cubiti vein in a sterile tube containing EDTA and stored at 4°C in the refrigerator (Sambrook et al., 1989).
2.3 PCR-RFLP assay for genotyping
Exon 5 of the CYP2A13 gene was amplified using a forward primer 5’- CCTGGACAGAT-GCCTTTAACTCCG-3’ paired with a reverse primer 5’- TGGCTTTGCACCTGCCT-GCACT-3’. PCR amplification was performed in a Bio-Rad DNA Model T-100 thermal cycler in a total volume of 25 µl containing approximately 200 ng of genomic DNA, 2.5 µl × PCR buffer 2 mmol/l MgCl2, 0.2 mmol/l of each dNTP, 0.28 µmol/l of each primer, and 2 U of Taq DNA polymerase. The PCR conditions involved an initial denaturation at 95°C for three minutes, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 63°C for 45 seconds, and extension at 72°C for 30 seconds, with a final extension at 72°C for five minutes. After amplification, the PCR products (332 bp) were digested with HhaI restriction. Endonuclease at 37°C for at least four hours. Digested products were analysed by electro-phoresis on a 2% agarose gel in the presence of ethidium bromide (Zhang et al., 2003).
2.4 Statistical analysis
The chi-square test was used to compare genotypic frequencies between the case and control. The OR and 95% CI were calculated to determine the association between variables and the risk of lung cancer regarding the Arg257Cys polymorphism in both cases and controls. Statistical analyses were conducted using statistical software SPSS 17.0 for PC A p-value of < 0.05 was required for statistical significance.
3 RESULT
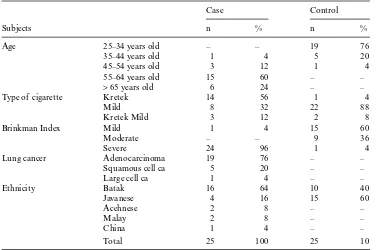
The characteristic of subject is shown in Table 1. Of all 50 participants, the overall frequency of genotype CC, CT and TT was 72%, 26%, and 2% respectively. The frequency of allele homozy-gote was 74%, while the heterozyhomozy-gote was 26%. Genotype distribution based on six groups of ethnicity revealed that Javanese and Batak had the highest frequency of CT genotype, 31.5%, and 23% respectively of Chinese participated in this study. The TT genotype was detected in one sample only (Table 2). The genotype distribution was in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
This research failed to confirm the association between genetic polymorphism of CYP2A13 Arg257Cys and lung cancer susceptibility. Of all 25 cases and 25 controls, the
ISCOC17_Book.indb 266
combined genotype frequency of CT and TT was found to be 32% and 24% respectively (Table 2). Chi-square analysis revealed that there was no significant association between genetic polymorphism CYP2A13 Arg257Cys and lung cancer susceptibility (OR 0.67; 95% CI 0.19–2.32; p = 0.52). Figure 1 shows that the Arg257Cys mutation eliminates an HhaI
cleavage site (Cheng et al., 2004).
Figure 1. PCR-RFLP analysis of the CYP2A13 Arg257Cys polymorphism with Hha I. M: DNA Marker, lane 6 was genotype with Cys/Cys at 257; lanes 7 and 10 were genotype with Arg/Cys at 257; lanes 1–5, 8, 12–15 were genotype with Arg/Arg at 257.
Table 1. The characteristics of the subjects.
Subjects
Case Control
n % n %
Age 25–34 years old – – 19 76
35–44 years old 1 4 5 20
45–54 years old 3 12 1 4
55–64 years old 15 60 – –
> 65 years old 6 24 – –
Type of cigarette Kretek 14 56 1 4
Mild 8 32 22 88
Kretek Mild 3 12 2 8
Brinkman Index Mild 1 4 15 60
Moderate – – 9 36
Severe 24 96 1 4
Lung cancer Adenocarcinoma 19 76 – –
Squamous cell ca 5 20 – –
Large cell ca 1 4 – –
Ethnicity Batak 16 64 10 40
Javanese 4 16 15 60
Acehnese 2 8 – –
Malay 2 8 – –
China 1 4 – –
Total 25 100 25 10
Table 2. CYP2A13 polymorphism and lung cancer.
Case Control
p-value OR 95% CI
n % n %
CC 17 34.0 19 38.0 0.529 0.671 0.193–2.329
CT&TT 8 16.0 6 12.0
268
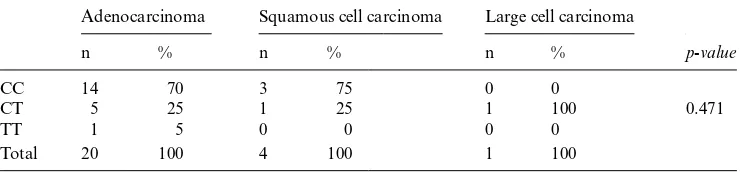
Furthermore, we evaluated the association of genetic polymorphism CYP2A13 Arg-257Cys and histologic type of lung cancer. Of the 25 lung cancer patients, the highest rate of type was adenocarcinoma, in which the frequency of CC, CT, and TT was 70%, 25% and 5% respectively (Table 3). There was no relationship between genetic polymorphism of CYP2A13 Arg257Cys and histologic type of lung cancer (p = 0.42).
4 DISCUSSION
We found that the most predominant ethnicity in this study was Batak (52%) compared with four other ethnics in Indonesia. There is a tradition in Batak culture to serve cigarettes in several traditional ceremonies, and smoking habits are very common among the Batak popu-lation. Furthermore, Batak ethnics are well known to have a pure genetic heritance due to its culture in marriage and thus will provide a better model for genetic polymorphism to identify its effect on Tobacco-Specific Nitrosamine (TSNA) contained in cigarettes.
Each cigarette contains a mixture of carcinogen, including a small dose of Polycyclic Aro-matic Hydrocarbons (PAH) and 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1 butanone (NNK/ Nicotine-derived Nitrosamine Ketone) among other lung carcinogens, tumour promoters and co-carcinogens. The metabolism of TSNA needs a CYP2A13 in phase 1 metabolism (Su et al., 2000, Wang et al., 2003).
Arg257Cys CYP2A13 variant has been detected at frequencies of 1.9%, 14.4% and 7.7% in the white, black and Asian population respectively. Functional analysis has shown that the Cys257 variant is some 37–56% less active than the wildtype Arg257 form of the CYP2A13 protein in all subtracts tested. Heterozygosity and homozygosity for the Cys257 variant have been found to be associated with the Chinese population with the significantly reduced risk of lung adenocarcinoma (OR 0.41, 95% CI 0.23–0.71). On this basis, it might seem reason-able to surmise that individuals possessing a significantly reduced level of CYP2A13 may manifest sensitivity reduction to xenobiotic toxicity resulting from the CYP2A13 mediated metabolic activation of procarcinogens in the respiratory tract (Zhang et al., 2003).
CYP2A13-catalysed metabolic activation in situ may play a critical role in human lung carcinogenesis related to cigarette smoking. It is reasonable to further speculate that func-tional genetic polymorphisms of CYP2A13 may have a significant impact on human sus-ceptibility to lung cancers related to NNK. Single nucleotide polymorphism CYP2A13 in 5 exons with the variant of C/T had been identified with Arg257Cys amino acid alteration in this study. This study found wild-type Arg257 allele could be cut to yield two fragments of 99 and 233bp in length, whereas the variant Cys257 allele gave only a 332bp band, C/C about 36 persons (72%), C/T about 13 persons (26%) and T/T about one person (2%). Genetic polymorphism analysis of CYP2A13 in lung cancer patients revealed C/T in about seven persons (58.8%), C/C in about 17 persons (47.2%) and T/T in about one per-son (1%). In contrast to Zhang et al., (2003), statistical analysis of this study showed that there was no significant relationship between CYP2A13 gene with lung cancer, OR = 0.67 (95% CI = 0,193–2,329).
Table 3. CYP2A13 polymorphism and histologic type of lung cancer.
Adenocarcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Large cell carcinoma
p-value
5 CONCLUSION
The CYP2A13 Arg257Cys variant represents a common polymorphism in the Indonesia population, particularly in Batak and Javanese ethnics. There is no association between Arg-257Cys polymorphisms of CYP2A13 and lung cancer.
REFERENCES
Cheng, X.Y., Chen, G.L., Zhang, W.X, Zhou, G., Wang, D. & Zhou, H.H. (2004). Arg257Cys Polymor-phism of CYP2 A13 in a Chinese population. Clinica chimica acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry, 343, 213–216.
Global Adult Tobacco Survey. Indonesia Report, (2011). World National Institute of Health Research and Development Ministry of Health.
Globocan. (2012). Estimated cancer incidence. Mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012.
Medical Research Council. (1957). Tobacco smoking and cancer of the lung. British Medical Journal, 1 (5034), 1523–1524.
Nakajima, M., Yamamoto, T., Nunoya, K., Yokoi, T, & Nagashima, K. (1996). Role of human cyto-chrome P4502 A6 in C-oxidation of nicotine. Drug metabolism and disposition: The Biological Fate of Chemicals, 24, 1212–1217.
Parkin, D.M., Bray, F.I. & Devesa, S.S. (2001). Cancer burden in the year 2000. The global picture. European Journal of Cancer, 37(8), 54–66.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual (2nd ed). Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, pp. 16–19.
Su, T., Bao, Z., Zhang, Q.T., Smith, T.J/, Hong. J/Y. & Ding, X. (2000). Human cytochrome p450 CYP2 A13: predominant expression in the respiratory tracts and its high-efficiency metabolic acti-vation of a tobacco-specific carcinogen, 4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-Pyridyl)-1-butanone. Cancer Research, 60(18), 5074–5079.
Wang, H., Tan, W.M., Hao, B., Miao, X., Zhou, G. & He, F. (2003). Substantial reduction in risk of lung adenocarcinoma associated with genetic polymorphism in CYP2A13, the most active cytochrome p450 for the metabolic activation of tobacco-specific carcinogen NNK (Nicotine- derived Nitro-samine Ketone), Cancer Research, 63(22), 8057–8061.