AN ANALYSIS OF STUDENTS’ TRANSLATION PRODUC
T OF
A DESCRIPTIVE TEXT ENTITLED OCTOPUS
(A case study of eight grade students in one State Junior High School in Bandung)
A RESEARCH PAPER
Submitted to the English Education Department of FPBS UPI
as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
By
ASEP SURAHMAN
0906229
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
Analisis Hasil Terjemahan Siswa Berupa Teks Deskiptif yang Berjudul Octopus
Oleh
Asep Surahman
Sebuah skripsi yang diajukan untuk memenuhi salah satu syarat memperoleh gelar
Sarjana pada Fakultas Pendidikan Bahasa dan Seni
© Asep Surahman 2013
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
Oktober 2013
Hak Cipta dilindungi undang-undang.
Skripsi ini tidak boleh diperbanyak seluruhnya atau sebagian,
ASEP SURAHMAN
AN ANALYSIS OF STUDENTS’ TRANSLATION PRODUCT OF A DESCRIPTIVE TEXT ENTITLED OCTOPUS
(A case study of eight grade students in one State Junior High School in Bandung)
APPROVED BY:
First Supervisor,
Hj. Emi Emilia, M.Ed., Ph.D.
NIP. 196609161990012001
Second Supervisor,
Rojab Siti Rodliyah, S.Pd., M.Ed.
NIP. 197308062002122001
Head of English Education Department
Prof. Dr. H. Didi Suherdi, M.Ed
ABSTRACT
This research, entitled “An Analysis of Students’ Translation Product of a Descriptive Text Entitled Octopus” was conducted in one state Junior High School in Bandung involving six eight grade students. This research aims to find
out students’ translation strategy, students’ problems in translating, and students’
translation quality. It applies a qualitative case study with data collected from documents of students’ translation works and interview. The students’ translations were analyzed by using translation strategy theory of Vinay and Darbelnet in Fawcet (1997), Newmark (1988) and method of translation test assessment by National Accreditation Authority for Translators and Interpreters (NAATI) concerning the quality of translation. The interview was analyzed through textual descriptive analysis to find out students’ translation problems. The findings reveal that the translation strategies found in students’ translation works were Transposition (46%), Reduction (39%), Literal (21%), Expansion (8%), Couplets (8%), Naturalization (3%), Equivalence (3%) and mistranslation about 18%. The problems found were vocabulary problem, lexical problem, and syntactic problem. And for the quality, three translation works were categorized as acceptable translations, since the scores were more than 70. It is recommended that further research can be conducted in different group of students, places, and
text types to give more information about students’ translation.
Key words: Students’ translation, translation strategies, translation problems,
ABSTRAK
Penelitian ini, berjudul “Analisis Hasil Terjemahan Siswa Berupa Teks Deskiptif yang Berjudul Octopus” yang dilaksanakan di satu Sekolah Menengah Pertaman Negeri di Bandung yang melibatkan enam siswa kelas delapan. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menemukan strategi siswa dalam menerjemahkan, permasalahan siswa dalam menerjemahkan, dan kualitas dari hasil terjemahan siswa. Penelitian ini menerapkan sebuah studi kasus kualitatif dengan data diperoleh dari dokumen-dokumen hasil terjemahan siswa dan wawancara. Hasil terjemahan siswa dianalisis dengan menggunakan teori strategi penerjemahan dari Vinay dan Darbelnet pada Fawcet (1997), Newmark (1988) dan metode penilaian ujian penerjemahan dari Otoritas Akreditasi Nasional untuk Para Penerjemah dan Penafsir (NAATI) yang berfokus pada kualitas terjemahan. Hasil dari wawancara dianalisis melalui analisis teks secara deskriptif untuk mengetahui permasalahan-permasalahan siswa dalam menerjemahkan teks bahasa Inggris. Penelitian ini menemukan bahwa strategi-strategi penerjemahan yang ditemukan pada hasil terjemahan siswa adalah Transposition (46%), Reduction (39%), Literal (21%), Expansion (8%), Couplets (8%), Naturalization (3%), Equivalence (3%) dan kesalahan dalam menerjemahkan sebanyak 18%. Permasalahan-permasalahan yang ditemukan adalah masalah kosakata, masalah bahasa yang berkaitan dengan makna kata, dan masalah sintaktis. Dan untuk kualitas, tiga hasil terjemahan siswa ditetapkan sebagai hasil terjemahan yang bisa diterima, karena nilainya lebih dari 70. Direkomendasikan untuk penelitian selanjutnya dapat dilaksanakan pada kelompok siswa yang berbeda, tempat yang berbeda, dan jenis teks yang berbeda untuk memberikan lebih banyak informasi mengenai penerjemahan yang dilakukan siswa.
Kata Kunci: Terjemahan siswa, strategi-strategi penerjemahan, permsalahan-permasalahan penerjemahan, kualitas terjemahan.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page of Approval...
Statement ... i
Preface ... ii
Acknowledgment ... iii
Abstract ... iv
Table of Contents ... v
List of Tables... viii
List of Chart ... ix
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION 1.1 Background of the Research ... 1
1.2 Research Questions ... 3
1.3 Aims of the Research ... 3
1.4 Scope of the Research ... 3
1.5 Significance of the Research ... 3
1.6 Organization of the Paper... 4
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FOUNDATION 2.1 Definition of Translation ... 5
2.2 Translation Process ... 5
2.3 Translation Strategies ... 6
2.4 Problems in Translation ... 13
2.5 Quality of Translation ... 14
2.5.1 Criteria of Good Translation ... 14
2.5.2 Quality Assessment of Translation ... 16
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Purposes of the Study and Research Questions ... 19
3.2 Research Design ... 19
3.3 Site and Participant ... 20
3.4 Data Collection... 21
3.4.1 Documentation ... 22
3.4.2 Interview ... 22
3.5 Data Analysis ... 23
3.5.1 Data from Documents or Students’ Translation Works ... 23
3.5.2 Data from Interview ... 25
3.6 Summary of Research Methodology ... 25
CHAPTER IV FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION 4.1 Students’ Translation Strategies ... 26
4.1.1 Discussion of the Students’ Translation Strategies ... 27
4.2 Students’ Translation Difficulties ... 36
4.2.1 Vocabulary Problem ... 36
4.2.2 Lexical Problem ... 38
4.2.3 Syntactic Problem ... 40
4.2.3.1 Problem of Word Order ... 40
4.2.3.2 Problem of Grammatical Aspects ... 41
4.2.4 Data From Interview ... 42
4.3 Students’ Translation Quality ... 43
4.5 Summary of Findings and Discussion... 50
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS 5.1 Conclusions ... 51
Bibliography
Appendix
Students’ Translation Sheets
Students’ Translation Strategy
Students’ Translation Quality
Interview
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1 The Example of NAATI Marking for Translation Errors ... 17
Table 3.1 Example Table of the Result of Analyzing the Strategy Used ... 23
Table 3.2 Example Table of the Result of Analyzing the Quality of Students’ Translation Work ... 25
Table 4. 1 Percentages of Students’ Strategies in Translating the Text ... 26
Table 4.2 Examples of Transposition Translation Strategy ... 28
Table 4.3 Examples of Reduction Translation Strategy ... 29
Table 4.4 Examples of Literal Translation/Word for Word Translation Strategy. .... 30
Table 4.5 Examples of Expansion Translation Strategy ... 32
Table 4.6 Examples of Couplets Translation Strategy ... 33
Table 4.7 Examples of Naturalization, Equivalence, and Modulation Translation Strategies. ... 33
Table 4.8 Examples of Mistranslation Cases ... 35
Table 4.9 List of Difficult Words ... 36
Table 4.10 Examples of Out of Context Meaning of Words ... 38
Table 4.11 Examples of Incorrect Translation ... 43
Table 4.12 Examples of Incorrect Word Order ... 41
Table 4.13 Examples of Grammatical Aspects Errors ... 42
Table 4.14 the Result of Analyzing the Quality of Students’ Translation Work. ... 43
LIST OF CHARTS
Chart 3.1 the Result of Analyzing the Strategy Used ... 24
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents the general description of the research, covering
background of the research, research questions, aims of the research, scope of the
research, significance of the research, and organization of the paper.
1.1 The Background
people in helping them to get information which is written in English. Regarding
this, Weber (1984, p.3) says translation is the process of transposition of a text
which is written in a source language into target language. It can be said that
translation product can help people who do not understand English to get
information from the English text.
Unfortunately, people cannot always rely on the translation products since
they are still limited. Although currently translation services are offered by many
institutions or individuals, but the cost is quite expensive and the quality is also
sometimes unsatisfied. For that reason, to full fill personal need actually someone
can be a translator for himself. It is because the translation skills can be learned
and trained.
Basically, according to Catford (1965, p.20) the ability for being translator
is comprehanding both Source Language (SL) and Target Language (TL) as long
as someone can find the replacement of textual material in one language (SL) by
the translation product, it will be defined by translator’s knowledge about SL and
TL, and also by translator’s skills in putting the knowledge into the practice of
analysis, discovery, transfer, and re-expression of the meaning (Choliludin, 2005,
p.38). It can be said that educational background related to theory of translation
and experiences in translation field determine the quality of translation work.
To train translation skill is actually can be started in Junior High School. It
is because at that time the students are starting to learn some genre of texts for
examples procedure, descriptive, narrative, and recount. Later, in Senior High
School the students learn more complex texts. This situation can be an
opportunity for students to train their translation skill before they know about the
theory of translation.
Students’ translation work is an interesting object for research. Supangkat (2009) has investigated the students’ method, strategies, and difficulties in translating English texts into Indonesia in the level of Senior High School. Jayanti
(2010), Infiani (2011), and Ahmad (2011) have conducted research about
students’ translation strategy in the level of college students. Different from those
studies, this study attemps to explore the Junior High School students’ translation
product. On the other words, the participants of this research are beginer learners
of English.
This research analyzed the documents of students’ translation work to find
out the quality of its translation. The students’ strategies in translating text have been disclosed and also their difficulties has been discussed. The result of the
research revealed the potential ability of Junior High School Students’ in
translating an English text into Indonesian as well as the difficulties faced in their
translation activity which can be considered as their weakness in understanding an
1.2 Research Questions
According to the background above, there are three reaearch questions to
be answered. The research questions are formulated as follows:
1. What strategies do students apply in translating a descriptive text?
2. What difficulties or problems do the students face in translating the text from
English to Indonesia?
3. What is the quality of students’ translation product?
1.3 Aims of the Research
Based on the research questions above, basically this research has aims to:
1. Identify the strategies used by students in translating an English descriptive
text into Indonesian.
2. Find out the difficulties faced by students in their translation activity.
3. Find out the quality of students’ translation product.
1.4 Scope of the Research
This research focuses on identifying the quality of students’ translation of
a descriptive text. The study is concerned with the strategies used by students in
translating text as well as the difficulties faced by them in translation activity.
1.5 Significance of the Research
researches to find out new theory about translation.
Secondly, this research reveals some difficulties faced by students in
translating a text especially in understanding message from the text. This situation
give important information for teachers to conduct the best strategy in helping
1.6 Organization of the Paper
This paper is organized into five chapters. The description is as follows:
Chapter I Introduction
This chapter involves background of the research, research questions, aims
of the research, scope of the research, significance of the research, and
organization of the paper.
Chapter II Theoretical Foundation
This chapter contains the related theories from the experts. It involves
definition of translation, translation process, strategies or procedures in
translation, problems in translation, quality of translation, and previous research.
Chapter III Research Methodology
This chapter describes the methodology of the research that covers
purposes of the study and research questions, research design, site and participant,
data collection, data analysis, and summary of research methodology.
Chapter IV Findings and Discussion
This chapter consists of the result and finding of the research.
Chapter V Conclusion and Recomendation
This chapters states the conclusion of the research and presents
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents the aspects of methodology of the research which
cover purposes of the study and research questions, research design, site and
participant, data collection, data analysis, summary of research methodology.
3.1Purposes of the Study and Research Questions
The purposes of this research are first to identify the strategies used by
students in translating an English descriptive text into Indonesian. Second, to find
out the difficulties faced by students in their translation activity. And third, to find
out the quality of students’ translation works. Actually those purposes are in line with the research questions of this study, “What strategies do students apply in their translation activity?”, “ What difficulties or problems do the students face in
translating the text from English to Indonesia?”, and “What is the quality of
students’ translation produict?”.
3.2Research Design
This research was a qualitative case study which investigated students’ translation works. According to Fraenkel & Wallen (2012, p.426) the research
studies that investigate the quality of relationships, activities, situations, or
materials are frequently refer to as qualitative research. Sugiyono (2013, p.1) adds
the qualitative method is focused on natural object, the main instrument is the
researcher, the data are inductive, and the result focuses on the meaning rather
than generalization.
This research was descriptive because the researcher analyzes the data
descriptively and the presentation of the result was in form of explanation of
words which would be supported by data in the tables. Suryana (2010, p.14) says
that descriptive study has aim to make a description sistematically and accuratelly
The approach of this research was case study. It was because this research
was conducted in a class which involved students as participants. It meant that the
result of this research might be different if it was conducted in other places. It was
in line with what Fraenkel & Wallen (2012, p.434) said that case study comprises
just one individual, classroom, school, or program.
3.3Site and Participant
The site of this research was a State Junior High School in Geger Arum
Bandung. There were two main reasons why this school was chosen. First, the
location is near with University where the researcher studies. Second, this school
has good relationship with the University. Every semester some students from the
University do teaching practice there. So it helped researcher in arranging the
research from making permission until collecting the data.
The participants of this research were students of Junior High School.
There were some reasons why Junior High School Students were chosen as
participants. First of all there was willingness of the researcher to find out basic
ability of beginer learners of English in making translation. Second, through this
research some difficulties were found related to translation process which could
be considered as their weakness in understanding an English text. It is importat
because in their examination, almost all of the questions are based on text
(descriptive, procedure, recount, and narrative). The information about students’ difficulties was an input for teachers to help their students in understanding text.
Third, lack of information about translation theory was a good point for
participants because the result was more natural and it could be good invention
when they could apply intuitively some strategies which were proposed by
experts.
The research was speciffically conducted in class 8L. This class was
recommended by English teacher who held some classes in grade eight. Thirty six
from the English teacher as well as consideration from the writer. According to
Kothari (2004, p.59) this kind of sample is called as non-probability sampling
because they were chosen by the researcher.
3.4Data Collection
As stated before that this research was conducted to find out the students’ strategies in translation, problems that they faced in translation activity, and the
quality of their translation works. It meant that the main source data of this
reaserch was document or students’ translation work and it supported by the information from interview. For that reason, this study employed two types of
data collection techniques, they were documentation and interview.
The text given to participant was a descriptive text which was taken from
Buku Elektronik Sekolah (BSE) English Focus for eight grade. The descriptive
text was chosen because it was the first text that they have learned since they were
in seven grade. So they should have good comprehension about this text. A text
from BSE was chosen because students in Indonesia generally learned that kind of
text. They generally did not learn original English text.
The text is as below:
Octopus
The Octopus is a sea animal with eight powerful feet which it uses as
hands. These are called tentacles. The word “Octopus” comes from two Greek words that mean “eight feet”.
The octopus, the squid and the cuttlefish belong to the same family that
has no outside shells. Their bodies are covered entirely with skin.
Therefore the body of an octopus is soft. It looks like a big balloon. A
fully-grown octopus can be as large as 8,5 meters from the tip of one
tentacles to the tip of another. It can weigh as much as 45 kilograms.
Besides using its tentacles to catch small fish, sea plants, crab and lobsters,
the octopus also uses them against its enemies. The octopus wraps its
The octopus escapes from its enemies by giving out a thick dark fluid to
darken the water. It can also change the color of its body to match its
surroundings. It hides from its enemies by doing this.
(Adapted From: Target UPSR Citra Pintar Bahasa Inggris which is written
in English Focus for Grade VIII.)
3.4.1 Documentation
To collect the documents or students’ translation works, the researcher did some steps as follows:
1. Chosing a classroom as place of data collection.
All of the students in the class would be involved in translation activity.
2. Telling the rule of the translation activity.
3. Distributing the texts and also the sheets to write down their translation.
4. Distributing English-Indonesia dictionaries.
5. Starting the translation activity.
6. Collecting the sheets or students’ translation works.
Translation activity was not an easy process, moreover for beginer learners
of English. For that reason, the time for conducting the activity was 100 minutes.
It should be enough to translate a text which contained 172 words. Almost all of
the words were simple words. The participants were also asked to write down
some English words that they did not know the meaning and forced them to open
dictionary.
3.4.2 Interview
Interview was conducted after the documentation finished. Just three of
participants were selected as representatives to be explored in the interview
session. There were nine questions delivered to the participants. The form of
interview was semistructured interview which consisted of a series of questions
conducted to find out what was actually on participants’ minds – what they thought or how they felt about something (Fraenkel & Wallen, 2012, p.451).
Mainly the focused of the interview was to find out participants’ difficulties or problems in translating activity. Then the data were analyzed by the
problems of translation which were stated in chapter II.
3.5Data Analysis
There were two kinds of data that have been analyzed in detail. The first
was students’ translation works or documents, and the second was interview. The
result of the data analyzing process was the answers of the research questions of
this study.
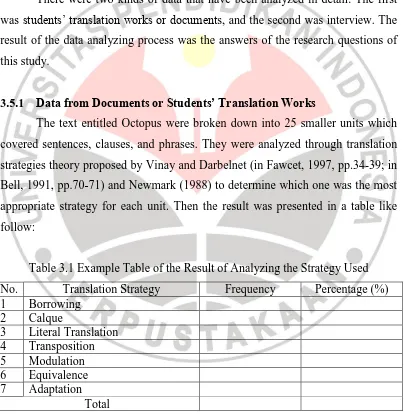
3.5.1 Data from Documents or Students’ Translation Works
The text entitled Octopus were broken down into 25 smaller units which
covered sentences, clauses, and phrases. They were analyzed through translation
strategies theory proposed by Vinay and Darbelnet (in Fawcet, 1997, pp.34-39; in
Bell, 1991, pp.70-71) and Newmark (1988) to determine which one was the most
appropriate strategy for each unit. Then the result was presented in a table like
follow:
Table 3.1 Example Table of the Result of Analyzing the Strategy Used
Where :
P = Number of percentage
F = Frequency of strategies or rocedures
N = Number of whole samples
In a conclusion it could be presented in a chart like follows:
Chart 3.1 the Result of Analyzing the Strategy Used
For the quality of the students’ translation work, this research adapted the
NAATI’s method in assessing translation work. And in the discussion, it also has been examined by the criteria of good translation proposed by Larson (1984),
Enani (in Abdellah, 2002), Tylter (in Bassnett, 2002, p.69), and Massoud (in
Abdellah, 2002).
The maximum score was 100. It would be deducted by errors found in the
translation work. The minimum score was 70. It meant that the deduction should
not be more than 30 points to get judgment as an acceptable translation. The
Student 1 Student 2 Student 3 Student 4 Student 5 Student 6
The result of analyzing the quality of students’ translation work would be presented as in the table below:
Table 3.2 Example Table of the Result of Analyzing the Quality of Students’ Translation Work
participant. The answers were analyzed through theory of translation problems by
Miremadi in Owji (2013) to determine the difficulties faced by participants in translating a text as well as through the theory of good translation proposed by
Larson (1984), Enani (in Abdellah, 2002), Tylter (in Bassnett, 2002, p.69), and
Massoud (in Abdellah, 2002).
Actually the process of identification the difficulties or problems has been
started since examining the strategies. The data from the interview were as
addition to strengthen the finding of difficulties in examining the strategies.
3.6 Summary of Research Methodology
This chapter has explained the methodology of this study. This research was descriptive qualitative study which examined students’ translation works. Students translation works or documents were the main data which have been
strengthened by the result of interview to answer the research questions. Since this
study was descriptive qualitative, the result of the data were presented in form of
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATION
This chapter consists of conclusions of the research and the researcher’s
recommendation in the field of translation and education.
5.1Conclusions
As stated in the first chapter, this research has three aims. The aims are to
identify the strategies used by students in translating an English descriptive text
into Indonesian, to find outthe difficulties faced by students in their translation
activity, and to find out the quality of students’ translation product.
Based on the findings and discussion sessions, the research actually
reaches its aims. For the strategies used by students in translating a descriptive
text, it was found from the highest to the lowest percentages; Transposition
(46%), Reduction (39%), Literal/Word for word (21%), Expansion (8%), Couplets
(8%), Naturalization (3%), and Equivalence (3%). In their translation also were
found some cases of mistranslation which reached 18%. The result was in line
with what Ahmad (2011) and Infiani (2011) found in their research which stated
that students’ translation were dominated by Transposition, Literal/Word for
word, and Reduction translation strategy.
Transposition or Shift was the mostly used translation strategy by students
in translating the text. It suggested that students have already recognized that
Indonesian and English have different rule especially in word order. However
some inappropriate or out of context meaning of words were still found. The
second mostly used translation strategy was reduction. Unfortunately the
reduction cases generally happened because of their translation errors like
ignoring article, ignoring pronoun, and skipping difficult word.
The next translation strategy mostly used was Literal/Word for word
translation. Basically the students have already known about the grammatical
text singly word by word with out of context meaning of word. In line with that
case, some cases in expansion strategy also happened because of the errors of
students. They added unimportant words to their translation product which
changed the original meaning.
The next translation strategy found in students work was couplets. It
showed that some of them have ability to use more than one strategy in translating
a text. Unfortunately this only happened rarely. In line with that, equivalence
strategy also was rarely found in students translation work. It was because their
knowledge of especially source language was not adequate.
Mistranslation also happened in students’ translation work. The percentage
was not too big, but it showed that some of the students did crucial problem in
translation. Mistranslation means the message is not accurately delivered to the
reader. In the other words, the message which is delivered contains wrong
information. However, since the translators were beginner learners of English, the
problem could be considered as usual error.
The next finding was difficulties faced by students in translating a text. It
could be said that generally the problems were categorized as vocabulary
problem, lexical problem, and syntactic problem. The biggest problem was
vocabulary problem. The students did not know the meaning of 23% words in the
text. It generated the next problem which was lexical problem. Many of the
difficult words were translated to the out of context target language. Even some of
them were wrongly translated.
Students’ problems in translating the text influenced their translation
quality. Three students’ translation works were categorized as acceptable
translation, since the scores were more than 70. The other three were
unacceptable. The scores were 58, 66, 68, 72, 76.5, and 79.5. It can be seen that
actually the range of the scores are not significantly different. Since the minimum
score to pass is 70, all of the students basically have opportunity to get pass if they
5.2Recommendation
This research is actually in form of case study which means that the result
of this research cannot be generalized as universal finding. However this research
has revealed that basically Junior High School Students have ability to translate an
English text especially a descriptive text. Even they successfully applied some
translation strategies to their translation work. This potential ability actually needs
to be developed. The stage of development should be monitored. So it will be
better if there are other studies which examine students’ ability in translating text
in the higher level.
This research also reveals difficulties or problems faced by students in
translating text. The problems can be stated as their weakness in understanding an
English text. So the finding of the problems can be an input for teachers to help
their students in understanding English text. However because of the limitation of
this research, the other studies are needed to find out more information about
students difficulties in translating an English text.
This research finds that only half of students’ translation works are categorized as acceptable translation. However it cannot be generalized since this
research was conducted in a middle cluster Junior High School in Bandung. It
would be better if there are other studies which are conducted in different places,
different group of students and different text types.
As the last recommendation, the writer suggests to the English teachers to
give opportunity to their students to develop their students’ translation ability by
giving translation activity. It is because the writer found that translation activity is
an interesting activity for students. Moreover, if the texts are interesting and easy
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Abdellah, A. S. (2002). “What Everey Novice Translator Should Know”. Translation Journal. Vol 7 No 3. Online Available at: www.translationjournal.net/journal/21novice.htm
Ahmad, M. (2011). Students’ Strategies in Translating an English Text into Bahasa Indonesia. A Thesis of SPS UPI Bandung: Unpublished.
Bassnett, S. (2002). Translation Studies. London: Routledge.
Bell, R. T. (1991). Translation and Translating: Theory and Practice. London: Longman.
Brown, H. D. (2001). Teaching by Principles an Interactive approach to Language Pedagogy. New York: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.
Catford, J. C. (1965). A Linguistic Theory of Translation. London: Oxford University Press.
Choliludin. (2005). The Technique of Making Idiomatic Translation. Jakarta: Kesiant Blanc.
Fawcett, P. (1997). Translation and Language Linguistic Theories Explained. Manchester: St. Jerome Publishing.
Fraenkell, J. R, & Wallen N.E. (2012). How to Design and Evaluate Research in Education (Eight Ed.). New York: Mc. Graw-Hill International Edition.
Gerding-Salas, C. (2000). “Teaching Translation Problems and Solutions”. Translation Journal. Vol 4 No 3. Online Available at: www.translationjournal.net/journal/13edu.htm
Hale, S. B. (2007). Community Interpreting. Hampshire: Macmillan Distribution Ltd.
Hurtado, A. (2008). “The Problem Of Translation In Cross-Cultural Research
On Emotion Concepts (Commentary On Choi & Han)”. International
Journal for Dialogical Science. Vol. 3, No. 1, 241-248.
Iida, A. (2008). “Individual Differences in the Translation Process: Differences in
Infiani, I. T. (2011). An Analysis of the Students’ Translation of an Online Advertisment in Terms of Methods and Quality. A Paper of English Education Department of FPBS UPI Bandung: Unpublished.
Jayanti, I. (2010). An Analysis of Students’ English-Indonesian Translation of Two Robert Frost’s Poetries. A Paper of English Education Department of FPBS UPI Bandung: Unpublished.
Larson, M. L. (1984). Meaning-Based Translation. New York : University of America.
McPake, J. & Johnstone, R. (2002). Translating, Interpreting and Communication Support Services Across the Public Sector in Scotland. Edinburgh: The Stationery Office Ltd.
NAATI. (2013). Booklet A: Accreditation by Testing. Online Available at: www.naati.com.au/testing.html
Nababan. (2008). Equivalence in Translation: Some Problem-Solving Strategies. Online Available at: http://www.proz.com/doc/2071
Newmark, P. (1988). A textbook of Translation. Hertfordshire: Prentice Hall International (UK) Ltd.
Ordudari, M. (2007). “Translation Procedures, Strategies and Methods”. Translation Journal. Vol 11 No 3. Online Available at: www.translationjournal.net/journal/41culture.htm
Owji, Z. (2013). “Translation Strategies: a Review and Comparison of Theories”.
Translation Journal. Vol 17 No 1. Online Available at: www.translationjournal.net/journal/63theory.htm
Sugiyono. (2013). Memahami Penelitian Kualitatif. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Supangkat. (2009). An Investigation of the students’ Methods, Strategies, and Difficulties in Translating English Texts into Indonesian. A Thesis of SPS UPI Bandung: Unpublished.
Suryana. (2010). Metode Penelitian Model Praktis Penelitian Kuantitatif dan Kualitatif. Buku Ajar Perkuliahan. Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia. Bandung: Unpublished.
Weber, W. K. (1984). Training Translation and Conference Interpreters. New Jersey: Prentice Hall Regents.
Williams, M. (2009). “Translation Quality Assessment”. Mutatis Mutandis. Vol 2,
No 1. 2009. pp. 3 – 23.