CHAPTER 1
THE PROBLEM AND ITS BACKGROUND
INTRODUCTION
The first years of life are important, according to Harvard (2009), because what happens in early childhood can matter in a lifetime. Every Filipino child now has access to early childhood education through Universal Kindergarten. At 5 years old, children start schooling and are given the means to slowly adjust to formal education. Research shows that children who underwent Kindergarten have better completion rates than those who did not. Children who complete a standards-based Kindergarten program are better prepared, for primary education. Education for children in the early years lays the foundation for lifelong learning and for the total development of a child. The early years of a human being, from 0 to 6 years, are the most critical period when the brain grows to at least 60-70 percent of adult size. (K to 12 Toolkit)
On the 20th day of January in the year of our Lord, Two Thousand and Twelve (12), President Benigno “Noynoy” Aquino III signed into law the Republic Act No. 10157 also known as the Kindergarten Education, the policy statement of the new law where it provides an equal opportunities for all children to avail of accessible mandatory and compulsory kindergarten education that effectively promotes physical, social, intellectual, emotional, and skills stimulation and values formation to sufficiently prepare them for formal education. Department of Education believes that a Mandatory Kindergarten is an important step of the child. It will help them learn skills that they will build on throughout their life. The Department of Education having been a strong advocate of early childhood education has implemented various programs for preschoolers for decades now. The Department further strengthens this through the inclusion of kindergarten in the K to 12 basic education curriculum in the country.
The K-12 program has been implemented by the Department of Education throughout the whole country through Republic Act No. 10533 series 2012 also known as the Enhanced Basic Education Act of 2013 which was signed into law on the 15th day of May in the year of our Lord, two thousand thirteen (2013). It restructures the basic education in the country by requiring Filipino students to undergo one year in Kindergarten, six years in primary school, four years in junior high school and two years in senior high school. The primary aim of this program is to provide sufficient time for mastery of concepts and skills, develop lifelong learners, and prepare graduates for tertiary education, middle-level skills development, employment and entrepreneurship as Department of Education stated.
specialized upper secondary education wherein students may choose a specialization based on aptitude, interests, and school capacity. In SHS, students will go through a core curriculum and subjects under a track of their choice. Department of Education stated that in school year 2012-2013, there are 33 public high schools, public technical-vocational high schools, and higher education institutions (HEIs) that have implemented Grade 11. This is a Research and Design (R&D) program to simulate different aspects of Senior High School in preparation for full nationwide implementation in school year 2016-2017. Modelling programs offered by these schools are based on students’ interests, community needs, and their respective capacities. After going through Kindergarten, the enhanced Elementary and Junior High curriculum, and a specialized Senior High program, every K to 12 graduate will be ready to go into different paths such as education, employment, or entrepreneurship. Every graduate will be equipped with: information, media and technology skills; learning and innovation skills; effective communication skills and; life and career skills.
K to 12 is no longer an option. It is a necessity! The focus in education in recent years has been on preparing students for the global economy by equipping them with 21st century skills, such as information and communication technology skills and problem-solving skills. Using K-12 education will make a school more competitive and help the students learn better. A 12-year program is found to be the best period for learning under basic education. It is also the recognized standard for students and professionals globally.
international standard. With the new K-12 program, Filipino students are at the same league with the rest of the world. It is also supposed to teach students vocational college bound subjects expected to help students attain intellectual competencies, personal and civic responsibilities, and practical skills that will be useful in terms of college readiness and employment demands.
Along the cited changes are the challenges, issues, concerns and reactions associated with the said program. When the K–12 program was first brought up, those who opposed it raised concerns. Especially on the part of the parents and students who are the primary affected. The additional two (2) years burden will add to the financial problem of the family so parents have to spend out more money for the education of their children. Although Department of Education assured that the government will basically shoulder most of the education cost. Some groups say that we need a better education and not more education. The drop-out rate will increase, because of the two extra years.
courses, (3) Higher Education Institution faculty, and (4) Practitioners will be allowed.
On the other hand, the lack of facilities and equipment are also the main problem of this program, considering the fact that K-12 program promotes a globally competitive education that internationally recognized and comparable. Therefore, the schools, both public and private who are offering the said program must provide enough technological equipment to the number of students, e-library and internet connection, computer laboratory and conducive classrooms that suited to the said program.
“We need to add two years to our basic education. Those who can afford pay up to fourteen years of schooling before university. Thus, their children are getting into the best universities and the best jobs after graduation. I want at least 12 years for our public school children to give them an even chance at succeeding.” (Aquino III, 2011)
The Aquino Administration believes that adding more years to basic education in the Philippines will help solve the problems of unemployment, keep with global standards, and help Filipino students to have more time to choose the career that best suits their skills. It’s given fact that the Aquino Administration has good intensions in implementing this K-12 plan. But no matter how good these intensions are, there would still be part of the society who would give them a criticisms and concerns.
BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY
Lacorte (2013) explains that Philippine basic education has been undergoing series of changes, modifications and improvement in the curriculum areas. Changes within the educational system have been constantly implemented by the Department of Education to adopt the Philippine educational system to the needs and demands of globalization. These were experienced by the elementary and secondary teachers, especially of public schools. Some of these changes were manifested in curriculum programs and activities, which include the use of different approaches and teaching strategies such as the Cooperative Learning strategy, the Four Pronged Approach, UBD in the secondary level and the change of the time allotment in the teaching of different subject areas, and lately the inclusions of the use of both English and the Mother Tongue as the medium of instruction, of which was included the Double Exposure in Mathematics. This program was included in the implementation of the Mother Tongue-Based Multilingual Education (MTB-MLE). And most recently, the implementation of K to 12 initiated in the school year 2012-2013 was considered the most astounding among the series of changes in the Philippine educational system.
Corpuz, in her writings “The K to 12 Curriculum” averred that the proposal to expand the basic education dates back to 1925. K-12 is not new, it has been studied since 1925 but there is no political will to do it so we need to be more competitive. A 12-year pre-university education has become the international standard. The Washington Accord prescribes a minimum of 12 years of basic education as an entry to recognition of engineering professional. The Bologna Process requires 12 years of education for university admission and practice of profession in European countries. On account of the Bologna Accord, starting 2010, undergraduate degrees in the Philippines are no longer recognized in most European countries.
employment in a rapidly changing and increasingly globalized environment (7) produce graduates who possess skills and competencies that will allow them to be productive members of the society or pursue higher education (8) through coordination between the academic and business sectors, to change industry hiring practices into account the enhance skills and competencies of K-12 graduates. (Discussion Paper, 2010)
What is most pleasing and interesting about this study is the popularity, the relevance to researcher’s course since the researchers are educators who will teach in the future that for sure will undergo the said curriculum, and its national trend. K to 12 has been one of the greatest issues in the country ever since it was implemented; the only research that could be conducted currently about this K to 12 Program inside the country is its implementation and the reactions of people towards it.
opportunity that can help in their research study. The result of this study may prove beneficial for the school because the researchers believe that Balara High School students are not an exemption on this problem.
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
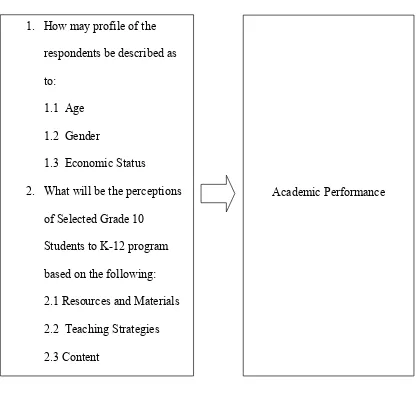
Figure 1 shows the paradigm of the study. It consists of two frames namely Independent Variable (profile and perceptions of the respondents) and Dependent Variable (Academic Performance).
This study was premised from the concept that the academic performance of the students can affect their perceptions towards K-12 Program.
The Social Learning Theory of Albert Bandura anchored on this study. People learn through observing others’ behavior, attitudes, and outcomes of those behaviours. “Most human behavior is learned observationally through modeling: from observing others, one forms an idea of how new behaviors are performed, and on later occasions this coded information serves as a guide for action.” (Bandura).
The law of readiness by Thorndike is pertinent on this study. The law of readiness describes those situations in which the person who learns either invites the object of his learning or rejects it. Readiness includes all those preparatory adjustments which immediately precede the action. This law relates with the topic of the present study which is on the readiness of the teachers and the schools in the implementation of K to 12 curriculum program.
was a fixed trait, and regarded cognitive development as a process which occurs due to biological maturation and interaction with the environment.
He suggested that the adult’s role in helping the child learn was to provide appropriate materials for the child to interact and construct.
PARADIGM OF THE STUDY
Independent Variable Dependent Variable
Figure 1. Conceptual Paradigm
Academic Performance 1. How may profile of the
respondents be described as to:
1.1 Age 1.2 Gender
1.3 Economic Status
2. What will be the perceptions of Selected Grade 10
STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
This study aimed to determine the perceptions of selected Balara High School Grade 10 students towards K-12 Program. This study hoped to gather data that may be used as basis for the enhancement of the curriculum program.
Specifically, it sought answer to the following questions:
1. How may profile of the respondents be described as to: 1.1 Age
1.2 Gender
1.3 Economic Status
2. What will be the perceptions of Selected Grade 10 Students to K-12 program based on the following:
2.1 Resources and Materials 2.2 Teaching Strategies 2.3 Content
3. What is the academic performance of the Grade 10 students?
ASSUMPTION
The whole Philippines will benefit the said program. The country’s economy will absolutely increase and experience accelerated growth in long run. Our educational system will level with the international standards for sure. There will be a long term socio – economic development because the Philippines will be a better educated society. The graduates will be able to earn higher wages or better prepared to start business for their own, possess competencies and skills relevant to the job market, employable and globally competitive, and can recognized abroad. They will be prepared for higher education. Because of the enhanced curriculum that will provide relevant content and attuned with the changing needs of the times, basic education will ensure sufficient mastery of core subjects to its graduates such that graduates may opt to pursue higher education if they choose to. An immediate work after high school, without needing an extra TESDA certificate or passing college requirements such as National Service Training Program (NSTP) and board examinations will wait them. More job openings for work that previously required a two-year college course.
the 10 years curriculum to 12 years curriculum without improving the content such as lack of teachers and classrooms. The problem is the content, not the length, of basic education. We need to have better education, not more education. There are also some schools and institutions that are offering K-12 program but not yet ready and globally competitive for the said curriculum due to lack of facilities and equipments as well as the incapable teachers who are not well-trained. For schools to be able to shift to the K-12 program, administrators have to make adjustments to the movement of faculty, as well as resources. Another issue has cropped up its effect on the teachers. The transition from the 10-year Basic Education program to the 12 years of the K to 12 programs is also critical to teachers as these professionals will also need to upgrade their skills so they will not be left behind.
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE STUDY
The study is considered significant because it discusses the K-12 Program for the students who will benefit from the additional two years. And also this will provide better understanding about the said program.
The result of the study will be beneficial to the following people as it will give them a clearer view about K-12 Program.
The School Administrators. The result of the research may serve as a basis for them. They will be gaining insights as to what measures are appropriate to help the teachers orient both students and teachers regarding the K-12 program.
The Students. The students will be greatly benefited by the present study as they will be exposed and be familiarized to the issues and open to the solutions needed. This research may enlighten them and help them for their future career, for the improvement of their community and for the development of the country.
The Teachers. This study will help teachers to be prepared themselves to handle both skills-based and academic subjects. The teachers will become more productive and efficient in developing their teaching skills in the field of recent curriculum.
The Community. They play a vital role in the development of every learner. The school is part of the community se every parent of the learner must know what the problems of the school are. So that they will understand what is happening and what is the good solution to that problem.
The Government Agencies. This study will help them who are concerned with the development of young minds specially the Department of Education which continuously shapes the country’s future. In this study, the agency is benefited for it will gain wisdom in providing quality service to everybody particularly t the secondary students through the realization of the K-12 program.
SCOPE AND LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY
The researchers conducted this study to know what will be the perceptions of selected Grade 10 students of Balara High School towards K-12 program and how this program will benefit them. Additionally, the researchers seek to answer if there is a significant relationship between the perceptions of students towards K-12 program and impact on their academic performance.
The study will be conducted at Balara High School located at H Ventura St., Balara Filters, Diliman, Quezon City. The attainment of the objectives of the study is dependent on the response of section St. Augustine with forty-six (46) Grade 10 students-respondents of Balara High School.
The scope of the study will be from the School Year 2016-2017. The school itself has enough population and continue to increase and progress in the succeeding years. The researchers are very glad and thankful to take that opportunity which can help in the researchers’ study.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
The following terms are defined conceptually and operationally for their better understanding.
Academic Achievement (Academic Performance) – The extent to which a student, teacher or institution has achieved their educational goals. It refers to the academic achievement of the pupils as evidenced by test results or marks given by the teacher based from the criteria such as: periodical test, written outputs, and participation or recitation.
Education – in its broadest, general sense education is the means through which the aims and habits of a group of people lives on from one generation to the next. Generally, education occurs through any experience that has a formative effect on the way one thinks, feels, or acts. In its narrow, technical sense, education is the formal process by which society deliberately transmits its accumulated knowledge, skills, customs and values from one generation to another, e.g. instructions in schools.
Curriculum – The term curriculum refers to the lessons and academic content taught in a school or in a specific course or program. In dictionaries, curriculum is often defined as the courses offered by a school, but it is rarely used in such a general sense in schools.
Impact – have a strong effect on someone or something.
Kindergarten – Department of Education believes that Kindergarten is a transition stage between informal literacy and formal literacy (grade 1-12). This is the period of greatest growth and development, when the brain develops most rapidly, almost at its fullest. It is a period when walking, talking, self- esteem, vision of the world and moral foundations are established. Children at this stage should be immersed with activities, games, and plays to naturally acquire the skills/competencies appropriate for their holistic development as emergent literates and be ready for formal school.
Parent – The one that begets or brings forth offspring, a person who brings up and cares for another.
Perception – The ability to understand or notice something easily. It is the process of attaining awareness or understanding of the environment by organizing and interpreting sensory information.
Profile – Refers to the respondent’s age, gender and economic status.
Program – Refers to the listing of the order of the pertinent activities or plan by the Department of Education which is essentialists for the development of the department as well as the learners.
Private School – School that is established, conducted, and primarily supported by a nongovernmental agency.
Public School – A free tax-supported school controlled by a local governmental authority.
Senior High School (SHS) – Covers the last two years of the K-12 program and includes Grades 11 and 12. In SHS, students will go through a core curriculum and subjects under a track of their choice.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND STUDIES
This chapter must compose of related literatures and studies. The researchers have gone through intensive readings of materials, both printed and downloaded through internet which has a great significance to problem during the course of thesis writing.
This chapter also shows and discusses the relevance of the reviewed literature and studies to the present study.
LOCAL LITERATURE
Shahani (2015) in her article on The Philippine Star “The challenges of basic education: dealing with K-12”. She discussed about the nature of the K-12 curriculum and how it differs from the previous 10-year basic education curriculum. She also mentioned some problems of the program in terms of content such as lack of teachers, classrooms, facilities and equipments and the additional cost to parents for food and transportation expenses to send their children for two more years of high school
superficial solution and does not truly address the more fundamental problems of the educational system.” And the opportunities waiting for us as a whole country which DepEd strongly believes that K-12 program is the best solution to our main problems.
According to the International Journal of Education and Research, Montebon (2014) in her journal “K12 Science Program in the Philippines: Student Perception on its Implementation” it determined the perception of students on the new science curriculum in terms of the concepts they learn, the skills they acquire, and the values and attitude they develop. This journal also aims to assess how judicious science teachers implement the new curriculum and seeks to evaluate if the goals in the different learning domains in the new science curriculum are being met as perceived by the students.
FOREIGN LITERATURE
Omoruyi (2014), in her European Journal of Educational and Development Psychology entitled “Influence of Broken Homes on Academic Performance and Personality Development of the Adolescents in Lagos State Metropolis” revealed that broken homes, single parenting and socio- economic status of the parents are determinant of adolescents’ academic achievement in schools. The study was conducted in Nigeria.
Guo, Linyuan (2012) “New Curriculum Reform in China and its Impact on Teachers” discussed the transformation of China’s education system through a nation-wide curriculum reform and the impact of the new curriculum on teachers through understanding what the new curriculum reform meant to them.
Aloraini (2012) in her journal on Journal of King Saud University – Languages and Translation “The impact of using multimedia on students’ academic achievement in the College of Education at King Saud University” pointed out the impact of using multimedia on students’ academic achievement in the “computer & its use in education” curriculum. At the end of her study, she recommended to use multimedia in theoretical faculties, expansion in using multimedia in teaching other theoretical curriculums and stressing the use of computer as an educational tool in teaching. She also recommended giving training courses to computer teachers regarding the use of multimedia in teaching educational subjects and conducting more studies on using multimedia in the academic curriculum in the University atmosphere.
Zellman, Constant & Goldman (2012) in their “K-12 Education Reform in
Qatar” talked about a reform of education for a new era because the leadership of the
progress. This study is one of a RAND’s studies that trace and document the reform
process in Qatar, was designed to assess progress made in the first year of the K-12
reform’s implementation in Qatar’s schools and the perception of the teachers,
parents, students and school administration on the implementation of the K-12
program.
LOCAL STUDIES
Lacorte (2013) conducted a study “Readiness of the Teachers on the Implementation of K-12 Program in selected Private and Public Schools in Lucban, Quezon City” she indicated that the schools in Lucban, Quezon City are adequately prepared in the implementation of K to 12 in terms of curriculum adjustment, school plant and facilities and administration and management. The teachers are likewise adequately prepared in the implementation of K to 12 in terms of teaching competencies, teaching strategies and instructional materials. The problems the teachers encountered in the implementation of K to 12 are of average gravity and they are manageable.
Parica (2012) in her related study “The Reaction of the Grade VII Parents on K–12 Implementation” discussed on how and where parents learn the information about the K–12 program. It aims to recognize the parents reactions based from the rationale. The study also likes to know the parents perception about the K – 12 program in terms of personal and student’s welfare. Problems which perceived by the parents in regards to the implementation of K-12 program were enumerated.
The study of Jinnu et.al (2014) “Effectiveness of K-12 assessment to Grade 7 to 9 high school students of Living Stone International School” relates to the researhers’ study with its aimed to answer if K-12 can make the academic performance of the students better. They tend to measure also the students’ thoughts/opinions on the effectiveness of K-12 assessment.
FOREIGN STUDIES
In the study of VanderJagt (2013) “The Student Thoughts and Perceptions on Curriculum Reform” he examined how students experience and respond to Michigan’s increased graduation requirements, the impact of school reform by eliciting the voices of students relative to a state-sponsored reform that directly impacts the way students experience and make decisions about their high school program. Additionally, this study engaged focus groups of one or more parents of the participating students and a cross-section of teaching, counseling, and administrative staff from the case study site.
On the other hand, Brown (2011) concluded that technology in the classroom is already a reality in most schools. The extent to which technology is integrated into curriculum is likely to increase exponentially as technological advances continue and the cost of technology decreases, he cited. This meta-analysis sought to understand if technology could enhance students‟ learning experience and overall academic performance, as well as to provide additional understanding of the role of technology enhanced learning (TEL) programs in curriculum.
some similar studies, however, and analyzing the results of my survey, my study revealed that PATHS faces the same issues and barriers that plague other schools. The issues are not a simple matter of resources and funding; they runs deep into the foundation of the pedagogy and attitudes of the teachers.
Sha Li (2013) in her comparative study of K-12 foreign language education in American and Chinese public schools: a case study of six foreign language teachers. The study concluded that it has contributed knowledge for a more complete picture of how the U.S. and China have developed their foreign language education— specifically in secondary public schools. It has shown the similarities and differences that China and America have in developing each foreign language education through an analysis of three fundamental/essential elements--social/political investment, teachers’ professional development, and curriculum and instruction, which are considered as the most important factors to successful K-12 foreign language environments. Besides these necessary elements for successful K-12 foreign language curriculum, parental influence is another important factor put forward by the teachers in the focused group interview.
RELEVANCE OF THE REVIEWED LITERATURE AND STUDIES TO THE PRESENT STUDY
Generally, the foregoing literatures and studies, both local and foreign were supportive of the variables used in this study, which include the following: the perceptions of students towards K-12 Program in terms of content, materials and teaching agency; the reaction of students towards the same; the academic performance of the students; the relationship between the academic performance of the students and their perceptions; and the effects of these issues and concerns. More of the related studies were not directly discussed and focused on K to 12 Program, but they reflected the other variables within the study which is really helpful and useful.
METHODOLOGY OF RESEARCH
This chapter deals with the procedural operation on how the research problems were answered. It includes the research design to be used, respondents of the study, sampling techniques, research instrument, construction of the instrument, validation of the instrument, administration and retrieval of the instrument and statistical treatment of data.
RESEARCH DESIGN
Carague, O., Castolo C., and Nava, V. (2009) defined research design as a plan, structure and strategy of the research investigation.
In this study, the researchers used the Survey Research to assess the profile of the respondents such as age, gender, and financial status. It is a strategy that tackles the occurrence of events in varying situation and circumstances. It involves gathering and analyzing data about the issue rather than about individuals and involves collection of data in order to test the hypothesis or answer questions concerning the current status of the study. The broad area of Survey Research encompasses any measurement procedures that involve asking questions of respondents. Survey research is a method for collecting and analyzing social data via highly structured questionnaires in order to obtain information from large numbers of respondents presumed to be representatives of a specific population.
This study involved a total of forty-six (46) Grade Ten (10) students of Balara High School.
Table 1
Frequency and Percentage Distribution of Respondents by Gender
Gender Frequency Percentage
Male 31 67.39
Female 15 32.61
Total 46 100.00
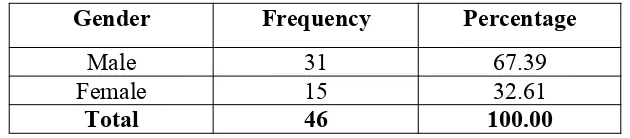
Table 1 shows that out of 46 students-respondents, 31 or 67.39 % are males and 15 or 32.61 % are females with a total of 100. The finding shows that most of respondents are male students.
SAMPLING TECHNIQUES
The attainment of the objectives of the study is dependent on the response of selected Grade 10 students of Balara High School particularly section St. Augustine with forty-six (46) students for the school year 2016-2017.
There are 10 sections of Grade 10 in Balara High School. Through a fish bowl technique, class random sampling was utilized. It was used in this study to minimize the number of students-respondents. Every section has an equal chance of inclusion in the sample. Grade 10 – section St. Augustine was chosen.
INSTRUMENTS USED
students regarding the K-12 Program. It was used as the primary data gathering instrument with focus on the perceptions of the students towards K-12 Program in terms of resources and materials, teaching strategies and content.
CONSTRUCTION OF THE INSTRUMENT
A researchers’ made questionnaire was designed personally by the researchers. Revisions were noted to improve the phrasing of the questionnaire items before the instrument was finally administered to the actual respondents of the study. Questionnaires consisted of two (2) parts to be utilized by the researchers for data gathering.
a. The cover letters (respondents) describe the study and its purpose, and indicating the confidentiality of the information that may be given out by the respondents.
b. Perceptions of selected Grade 10 students of Balara High School towards K-12 Program. This consisted of three (3) questions where student-respondents were asked to rate using five-point Likert type Scale.
VALIDATION OF THE INSTRUMENT
run of the instrument was conducted to different undergraduate researchers of a school not covered by the study. They were not included as actual respondents but were used only for validation purposes to determine whether the contents of the questionnaire are comprehensible and reliable.
ADMINISTRATION AND RETRIEVAL OF THE INSTRUMENT
The researchers made a request letter for the copy of grades of the students in first quarter and second quarter. The request letter also included to conduct the said survey. Upon approval, the researchers asked the assistance of the adviser of the Grade10 Section St. Augustine. The researchers personally asked and obtained the questionnaires. A copy of the letter addressed to the respondents and the questionnaires to be distributed.
The researchers personally distributed the questionnaire to the respondents in Balara High School during a classroom meeting. In the cover letter, a clear explanation stated that the researchers were respectfully asking about ten (10) minutes of the respondents’ time to complete the attached questionnaire. The purpose and objectives of the study have also been indicated. Confidentiality was given in order to assure cooperation and to avoid inhibitions from the respondents in accomplishing the questionnaire.
STATISTICAL TREATMENT OF DATA
After data gathering, the researchers tallied the scores and applied the appropriate statistical treatment and analyses were employed. Students’ responses to the questionnaire were statistically analyzed with the use of the following instruments.
Percentage was used to describe the respondents’ profiles. It is a proportion expressed either in decimal or fractional form that can be computed into percentage by multiplying the proportion by 100 and affixing the percentage symbol (%).
The formula for computing this statistics is as follows: Percentage (%) = f / N x100
Where: P = computed percent
F = Frequency for each class or category
N = Total number of respondents
100 = constant multiplier to change the decimal into percentage value
Stratified Sampling was used to reflect randomly samples from the different strata of the population.
related. In a more general sense, it test to see whether distributions of categorical variables differ from each another using the formula:
Add: Mean, Standard Deviation
´
x=´xo+Σ fdn sd=c
√
n Σ fd2
−(Σ fd)2
n
Weighted Mean was used to measure the extent by which the respondents assessed the given research variables, which include schools’ and teachers’ readiness and problems encountered in the implementation of K to 12.
The formula for computing this statistics is as follows:
WM = ∑FW / N Where:
WM = Computed Weighted Mean ∑ = Summation symbol
F = Frequency for each option W = Assigned weight
N = Total number of frequencies
The following interpretations were used to describe the weighted mean obtained.
Ranges Scale Verbal Interpretation
4.2-5.0 5 Strongly Disagree
3.4-4.1 4 Moderately Agree
2.6-3.3 3 Agree
1.8-2.5 2 Disagree
1.00-1.7 1 Strongly Disagree
CHAPTER IV
PRESENTATION, ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF DATA
be presented, discussed and interpreted according to the perimeters of this research to answer the problem sought for this study.
1. How may profile of the respondents be described as to: 1.1. Age
1.2. Gender
1.3. Economic Status
2. What will be the perceptions of Selected Grade 10 Students to K-12 program based on the following:
2.1. Resources and Materials 2.2. Teaching Strategies 2.3. Content
3. What is the academic performance of the Grade 10 students?
4. Is there a significant relationship between the perceptions of students towards K-12 program on their academic performance?
1. How may profile of the respondents be described as to:
Age of the Respondents Table 1.1
Age Frequency Percentage (%)
16 9 19.57
18 9 19.57
19 2 4.35
20 1 2.17
21 1 2.17
Total 46 100.00
Table 1.1 shows the age profile of the respondents, with age 17 posts the highest frequency of 24 or 52.17 percent of the total 46 respondents. The other ages posted the following frequencies: 9 or 19.57 percent for ages 16 and 18; 2 or 4.35 percent for age 19; and 1 or 2.17 percent for ages 20 and 21.
As a whole, Grade 10 St. Augustine students-respondents are mostly 17 years old.
Gender of the Respondents Table 1.2
Gender Frequency Percentage (%)
Male 31 67.39
Female 15 32.61
Table 1.2 shows that out of 46 students-respondents, 31 or 67.39 % are males and 15 or 32.61 % are females with a total of 100. The finding shows that most of respondents are male students.
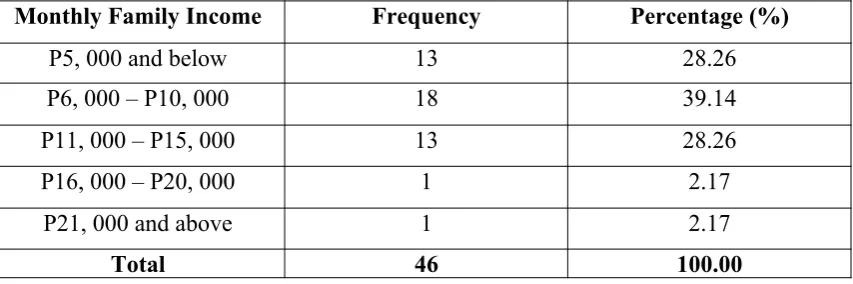
Economic Status of the Respondents Table 1.3
Monthly Family Income Frequency Percentage (%)
P5, 000 and below 13 28.26
P6, 000 – P10, 000 18 39.14
P11, 000 – P15, 000 13 28.26
P16, 000 – P20, 000 1 2.17
P21, 000 and above 1 2.17
Total 46 100.00
The data presented in Table 1.3 shows the assessment on the respondents profile in terms of the combined income of family members. Most of the students of Grade 10 St. Augustine with the percentage of 28.26 %, their families receive an income of P5, 000 and below only. While the 39.14 receives P6, 000 – P10, 000 per month. 28.26 receives P11, 000 – P15, 000 monthly, 2.17 both receives P16, 000 – P20, 000 monthly and P21, 000 and above.
2. What are the perceptions of Selected Grade 10 Students to K-12 program based on the following:
Table 2.1
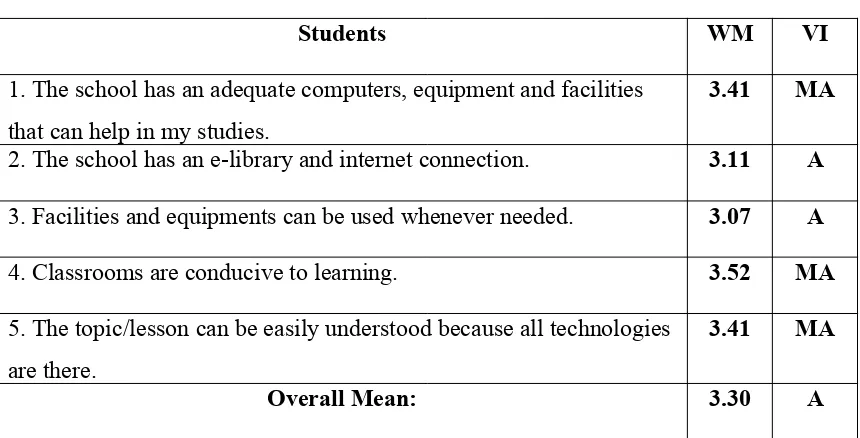
Students WM VI
1. The school has an adequate computers, equipment and facilities that can help in my studies.
3.41 MA
2. The school has an e-library and internet connection. 3.11 A 3. Facilities and equipments can be used whenever needed. 3.07 A 4. Classrooms are conducive to learning. 3.52 MA 5. The topic/lesson can be easily understood because all technologies
are there.
3.41 MA
Overall Mean: 3.30 A
Legend: WM = weighted mean; VI = verbal interpretation; MA = moderately agree; A = agree
Table 2.1 shows the perceptions of students to K-12 Program in terms of Resources and Materials. Item number 1, which says that the school has adequate computers equipment and facilities that can help in my studies garnered 3.41 weighted mean interpreted as Moderately Agree. While item number 2, which says that the school has an e-library and internet connection garnered 3.11 weighted mean interpreted as Agree. On the other hand, item number 3 which says that facilities and equipments can be used whenever needed garnered 3.07 interpreted as Agree. Meanwhile, item number 4 which says classrooms are conducive to learning garnered 3.52 interpreted as Moderately Agree. Finally, in item number 5 which says that the topic/lesson can be easily understood because all technologies are there garnered 3.30 interpreted as Agree.
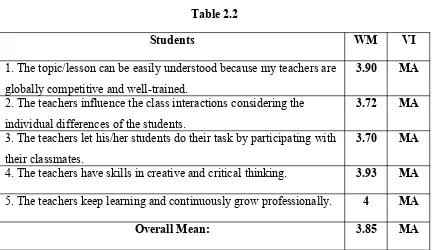
Teaching Strategy Table 2.2
Students WM VI
1. The topic/lesson can be easily understood because my teachers are globally competitive and well-trained.
3.90 MA
2. The teachers influence the class interactions considering the individual differences of the students.
3.72 MA
3. The teachers let his/her students do their task by participating with their classmates.
3.70 MA
4. The teachers have skills in creative and critical thinking. 3.93 MA 5. The teachers keep learning and continuously grow professionally. 4 MA
Overall Mean: 3.85 MA
Legend: WM = weighted mean; VI = verbal interpretation; MA = moderately agree
Table 2.2 shows the perceptions of students to K-12 Program in terms of Teaching Strategy. The above findings with a unanimous weighted mean 3.85 found out that the respondents are moderately agreed that the teachers in their school are globally competitive and well-trained, influence the class interactions considering the individual differences of the students, let his/her students do their task by participating with their classmates, have skills in creative and critical thinking, and keep learning and continuously grow professionally in perceiving K-12 Program.
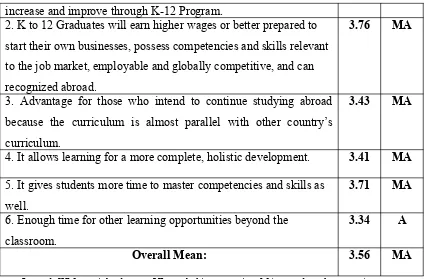
Content Table 2.3
Students WM VI
increase and improve through K-12 Program.
2. K to 12 Graduates will earn higher wages or better prepared to start their own businesses, possess competencies and skills relevant to the job market, employable and globally competitive, and can recognized abroad.
4. It allows learning for a more complete, holistic development. 3.41 MA 5. It gives students more time to master competencies and skills as
well.
3.71 MA
6. Enough time for other learning opportunities beyond the classroom.
3.34 A
Overall Mean: 3.56 MA
Legend: WM = weighted mean; VI = verbal interpretation; MA = moderately agree; A = agree
Moderately Agree. Finally, item number 6 which utters that enough time for other learning opportunities beyond the classroom gathered 3.34 interpreted as agree.
As a whole, the above findings with a total weighted mean 3.56 found out that the respondents are moderately agreed in terms of Content in perceiving K-12 Program.
3. What is the academic performance of the students?
Table 3.1
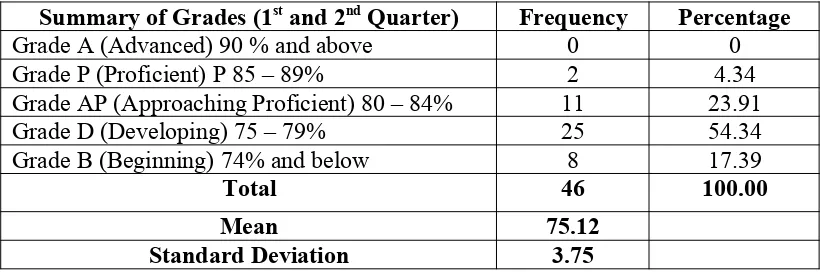
1st and 2nd Quarterly Average Academic Performance of Students in all Subject Areas based on the Code and Equivalent Numerical Values of Grades in K-12
Summary of Grades (1st and 2nd Quarter) Frequency Percentage
Grade A (Advanced) 90 % and above 0 0
Grade P (Proficient) P 85 – 89% 2 4.34 Grade AP (Approaching Proficient) 80 – 84% 11 23.91
Grade D (Developing) 75 – 79% 25 54.34
Grade B (Beginning) 74% and below 8 17.39
Total 46 100.00
Mean 75.12
Table 3.1 shows the First and Second Quarterly Average Academic Performance of the students in all subject areas based on the Code and Equivalent Numerical Values of Grades in K-12 Curriculum. The data shows that the frequency of 2 students-respondents or 4.34 percent belong to 85 – 89% categorized as P (Proficient). 11 students or 23.91 percent belong to Grade AP (Approaching Proficient) who got 80 – 84 %. 8 students or 17.39 percent got 74% and below belong to Beginning. None of the students got 90% and above.
Finally, most of the students who are in Section St. Augustine are on Developing level which has 25 students or 54.34 percent. The above findings indicate that the respondents who are in a lower section, whether heterogeneous or not, have poor academic performance.
4. Is there a significant relationship between the perceptions of students towards K-12 program on their academic performance?
Table 4.1
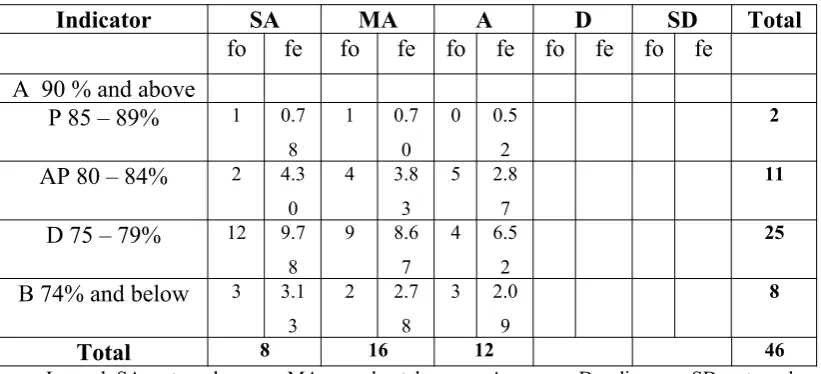
Correlation of Academic Performance of the Students to their Perception in Resources and Materials
Indicator SA MA A D SD Total
fo Fe fo fe fo fe fo fe fo Fe
Table 4.1 shows the frequency answer of students in terms of Resources and Materials. Based on the findings, most of the answers of respondents categorized as A (Agree) with a frequency of 21, while the second highest frequency is in category MA (Moderately Agree) which is 16. Students who answered in category SA (Strongly Agree) are 5. Finally, only 4 students answered D (Disagree) and none of the students answered SD (Strongly Disagree).
Table 4.2
Correlation of Academic Performance of the Students to their Perception in Teaching Strategies
Indicator SA MA A D SD Total
fo fe fo fe fo fe fo fe fo fe
Legend: SA = strongly agree; MA = moderately agree; A = agree; D = disagree; SD = strongly disagree
Table 4.3
Correlation of Academic Performance of the Students to their Perception in Content
Indicator SA MA A D SD Total
fo fe fo fe fo fe fo fe fo fe
Legend: SA = strongly agree; MA = moderately agree; A = agree; D = disagree; SD = strongly disagree
Strongly Agree. Only one student answers D (Disagree) and none of the students answers SD (Strongly Disagree).
Table 4.4
CORRELATION: Chi Square Test for Significant Relationship between the Academic Performance of the Students and their Perceptions
Indicator Chi – Square Distributio
Content, since the computed Chi – square is 13.50 which is greater than Distribution, we cannot reject the hypothesis. But in terms of Resources and Materials, and Teaching Strategies, our computed Chi – Square is less than the level of Distribution, we can conclude that there is no significant relationship between the academic performance of the students and their perceptions to K-12 Program.
CHAPTER V
SUMMARY OF THE STUDY, CONCLUSIONS, AND RECOMMENDATIONS
This chapter presents the summary, findings, and conclusions taken from the results of the study. It also provides recommendations drawn from the conclusions which are deemed important.
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
The data were analyzed and the following findings were formulated in accordance with the specific questions given under the statement of the problem:
group. In terms of Economic Status, 18 or 39.14 percent of the respondents are averaging P6, 000 – P10, 000.
2. The respondents are agreed that there are Resources and Materials in their school with a weighted mean 3.30. While the respondents found out that they are moderately agreed in terms of Teaching Strategy with a weighted mean 3.85. At last, in terms of Content, the respondents are also moderately agreed with a weighted mean 3.56.
3. The Academic Performance of the whole respondents from first quarter to second quarter is averaging 74.36 percent. The computed mean is 75.12 while the computed standard deviation is 3.75.
CONCLUSIONS
On the basis of the findings, the following conclusions were drawn:
1. In general, the respondents posts 17 years old.
2. The above findings found out that the respondents perceived K-12 Program evidently high.
3. There is no significant relationship between the perceptions of the students to K-12 Program and their academic performance.
4. Obviously, there are no impacts of perceptions of the students to K-12 program to their academic performance.
5. Based on the findings, most of the students who are in lower section whether heterogeneous or not have poor academic performance.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Based on the findings and conclusions drawn, the following recommendations are humbly offered:
1. The Government must keep on helping those people who are in poverty lane, and financially incapable. Enhance their services, projects, and programs (e.g. Voucher Program) so that everyone can pursue their studies that will end-up to a well-educated and globally competitive society.
2. The Department of Education or the school itself should come up with different orientations, seminars, and trainings for the sake of the students and parents to have a clearer view and better understanding about K-12.
4. The teachers should also maintain and strengthen further their skills and competencies through attending more in-service training and seminars related to K to 12 Program.
5. The Guidance Office or school heads should keep on giving pieces of advice and information to the students and parents about current issues through conferring them by institutionalizing a program where a regular orientation, and consultation not only with the students but also with other stakeholders, particularly the parents.
6.
Future researchers should conduct the same study undertaken with the same methodologies but in different setting and bigger samples.BIBLIOGRAPHY
BOOKS
Carague, O, Castolo C., and Nava, V. (2009) Modules On RSH 630: Research Seminar 1. Philippines: PUP
PUBLISHED/UNPUBLISHED MATERIALS
J. Mariah Brown (December 2011)“Presented to the Faculty in Communication and Organizational Leadership Studies School of
Professional Studies” (Doctoral Dissertation, Educational Leadership,
Lacorte, Emelita A. (2013) “Readiness of the Teachers on the Implementation of
K-12 Program in selected Private and Public Schools in Lucban, Quezon City” Unpublished Thesis. Polytechnic University of the Philippines.
Lee, Jee Young (2013) “Multicultural Education in the Republic of Korea: How Elementary School Teachers Interpret Multicultural Education and Its Practical Use in Classrooms” Unpublished doctoral dissertation. University of California.
Li, Sha (2013) “A Comparative Study Of K-12 Foreign Language Education In American And Chinese Public Schools: A Case Study Of Six Foreign Language Teachers” Unpublished Master’s Thesis. University of
Akron.
Martinez, Kaitlin (2012) “Technology Implementation in K-12 Schools: A Research Study of Perceptions and Practice” Unpublished Master’s Thesis. University of Central Florida.
VanderJagt, Douglas D. (April 2013) “The Student Thoughts and Perceptions on Curriculum Reform” (Doctoral Dissertation, Educational Leadership, Research and Technology Western Michigan University) Dissertation Abstracts International, Paper 154.
ELECTRONIC REFERENCE/WEBSITE
Cognitive Theory | Simply Psychology. Saul McLeod. Retrieved January 1,
2017 from: https://www.simplypsychology.org/piaget.html
K12philippines. “K-12 Basic Education Curriculum| K12 Philippines”. (Retrieved January 1, 2017 from: http://k12philippines.com/)
K12 research paper. “K12 research paper”. (Retrieved January 1, 2017 from:
http://katherine-thecrescentmoon.blogspot.com/2011/11/k12-research-paper.html)
Learning Theories. “Social Learning Theory Bandura Social Learning Theory”. (Retrieved January 1, 2017 from: https://www.learning-theories.com/social-learning-theory-bandura.html)
Official Gazette| Department of Education. K-12 Program. (Retrieved January
1, 2017 from: http://www.gov.ph/k-12/
PublishYourArticles.net - Publish Your Articles Now. “What is S-R Bond Theory of Thorndike?” (Retrieved January 1, 2017 from: http://www.
publishyourarticles.net/knowledge-hub/education/what-is-s-r-bond-theory-of-thorndike/5274/)
Quintas, K., and Miasco, M. (April 26, 2016) “K TO 12 Are we ready for Senior High? (CONCLUSION)”. The Freeman. (Retrieved January 1,
2017 from: philstar.com)
Rate Limited. “Balara High School”. (Retrieved January 1, 2017 from:
http://publicschools.findthebest.com.ph/l/3518/Balara-High-School-in-Quezon-City-NCR)
Shahani, Lila R.(June 15, 2015). “The challenges of basic education: dealing
with K-12”. The Philippine Star. (Retrieved January 1, 2017 from: philstar.com)
JOURNALS/SERIALS/PERIODICALS
Cabansag, Marie Grace S. (April 2014). “Impact Statements on the K-12 Science Program in the Enhanced Basic Education Curriculum in Provincial Schools”. ResearchersWorld -Journal of Arts, Science & Commerce ■E-ISSN 2229-4686 ■ISSN 2231-4172.
Constant, Louay, Goldman, Charles, and Zellman, Gail L. (2012) “K-12 Education Reform in Qatar”. RAND Corporation.
Corpuz, Brenda (2014). The K to 12 Curriculum.
EY Ernst & Young publication (March 2014). “Private sector’s contribution to K-12 education in India Current impact, challenges and way forward”. EYIN1403-024
Guo, Linyuan (2012) “New Curriculum Reform in China and its Impact on Teachers,Canadian and International Education” / Education canadienne et internationale: Vol. 41: Iss. 2, Article 6.
Omoruyi, Igbinosa Victor (September 2014). “Influence of Broken Homes on Academic Performance and Personality Development of the Adolescents in Lagos State Metropolis”. European Journal of Educational and Development Psychology, Vol.2,No.2, pp.10-23
Oteyza, Kristine Carla O. (December 2012). “Enhanced K to 12 Basic Education Program: opportunities and challenges”. Economic Issue of the Day, Vol. XII No. 2.
Commonwealth Ave., Rd. 44 Diliman Quezon City 436-4468/ 434-7192
QUESTIONNAIRE
February 2017
Dear Respondents:
The undersigned is currently working on a study entitled “The Impact of Perceptions of the Selected Grade 10 Students to K-12 Program to their Academic Performance of Balara High School School Year 2016-2017” in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Science in Secondary Education (BSED) Major in English.
Rest assured that your participation on this will be completely anonymous as no identifying information will be collected. The data that you will be used for research and educational purposes only.
Truly Yours,
MARICAR F. SULAT JULEOS I. MAGBANUA RAYMOND R. TINDUGAN
RACHELLE S. MACADANGDANG
THE IMPACT OF PERCEPTIONS OF THE SELECTED GRADE 10 STUDENTS TO K-12 PROGRAM TO THEIR ACADEMIC PERFORMANCE
OF BALARA HIGH SCHOOL SCHOOL YEAR 2016-2017
1. Reminder: All information given by you will be kept confidential. Please answer honestly and precisely. Kindly leave no blank spaces.
I.1 Age (please check ) (__) 14-20 years old (__) 21-25 years old (__) 26 and above
1.2 Gender (please check) (__) male
(__) female
1.3 Economic Status of the family (please check) (__) P5, 000 and below
(__) P11, 000 – P15, 000 (__) P16, 000 – P20, 000 (__) P21, 000 and above
2. Please indicate the level of your agreement / disagreement to the following statements. Please check () on the appropriate box.
SA – Strongly Agree MA – Moderately Agree
A – Agree D – Disagree
SD – Strongly Disagree
Resources and Materials SA MA A D SD
1. The school has an adequate computers,
equipments and facilities that can help in my studies. 2. The school has an e-library and internet
connection.
3. Facilities and equipments can be used whenever needed.
4. Classrooms are conducive to learning.
5. The topic/lesson can be easily understood because all technologies are there.
Teaching Strategies SA MA A D SD
1. The topic/lesson can be easily understood because my teachers are globally competitive and well-trained.
2. The teachers influence the class interactions considering the individual differences of the students.
3. The teachers let his/her students do their task by participating with their classmates.
4. The teachers have skills in creative and critical thinking.
Content SA MA A D SD 1. The economy and the quality of education in the
Philippines will increase and improve through K-12 Program.
2. K to 12 Graduates will earn higher wages or better prepared to start their own businesses, possess competencies and skills relevant to the job market, employable and globally competitive, and can recognized abroad.
3. Advantage for those who intend to continue studying abroad because the curriculum is almost parallel with other country’s curriculum.
4. It allows learning for a more complete, holistic development.
5. It gives students more time to master competencies and skills as well.
Commonwealth Ave., Rd. 44 Diliman Quezon City 436-4468/ 434-7192
January 16, 2017
NIMFA BONGALING Principal
Balara High School
H. Ventura St, Quezon City, Metro Manila
Dear Madam: Warmest Greetings!
The following undersigned are 4th year students of Mary the Queen College of Quezon City taking up Bachelor of Secondary Education major in English and presently conducting a research entitled “The Impact of Perceptions of the Selected Grade 10 Students to K-12 Program to their Academic Performance of Balara High School School Year 2016-2017”.
We appreciate your prompt attention to this matter, as these documents are a requirement/ data needed on our research. By receiving this documentation quickly, we will be able to organize our research with the correct paperwork in hand.
Thank you very much and God bless.
Respectfully yours,
Maricar F. Sulat Juleos I. Magbanua Raymond R. Tindugan Rachelle S. Macadangdang
Noted by:
ROHANNA C. COMBO Head Teacher-English
EDNALYN A. LACERNA Thesis Adviser
WILSON D. GETALADO Ph. D Dean, College of Education
NIMFA BONGALING Principal, Balara High School
First and Second Quarterly Average Grades of Grade 10 Students – Section St. Augustine in all Subject Areas
FIL ENG MATH SCI AP EP TLE MAPEH FG
83.5 82 81.5 82 88 86.5 83 80 83.31
70.5 75.5 75 77.5 78.5 72.5 73.5 72.5 74.43
70 74.5 72.5 75 78.5 71.5 71.5 71.5 73.12
70 82 74.5 78.5 75 75 71.5 73.5 75
70 79 78.5 79 75 75 78.5 78 77
75 81.5 77 77.5 78 75.5 80 77.5 78
84 81 74.5 77.5 79 75.5 79.5 72.5 78
77.5 87.5 78.5 78.5 80 76 80.5 77 79.43
73 77 71 76 77 72.5 71.5 74.5 74.06
82.5 87 85.5 89 89 83.5 78.5 81.5 85
Chi-Square Distribution Table
CURRICULUM VITAE
RAYMOND REFALPA TINDUGAN
08 Sitio Kaliwa 1, Batasan Hills, Quezon City Mobile no. 09121867587
Email address: emonemph@gmail.com
PERSONAL INFORMATION
Age: 20 years old
Date of Birth: September 13, 1996 Civil Status: Single
EDUCATIONAL BACKGROUND
Tertiary : MARY THE QUEEN COLLEGE OF QUEZON CITY INC. Commonwealth Ave., Rd. 44 Diliman, Quezon City
2013 – 2017
Course : BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN SECONDARY EDUCATION MAJOR IN ENGLISH
Secondary : BATASAN HILL NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL Batasan Hills, Quezon City
2002 – 2008
Primary : BATASAN HILLS ELEMENTARY HIGH SCHOOL San Mateo Road, Batasan Hills Quezon City
TRAININGS AND PROGRAMS ATTENDED
21st Century Skills of Pre-Service Teachers Sept. 17, 2015 A Look on Understanding By Design Sept. 17, 2015 Effective Methods in Teaching Sept. 8, 2014 Freedom in Achievement: Path to Learning Sept. 8, 2014 Demo Teaching August – November 2016
ROHANNA C. COMBO Head Teacher, English Dept. Balara High School
09365345117
LAARNIE R. PALERMO Secretary, Denji Marketing
09077467933
RACHELLE SORIANO MACADANGDANG
15-A Presidential Road, Batasan Hills, Quezon City Mobile no. 09502322937
Email address: rachellefhanget@gmail.com
PERSONAL INFORMATION
Age: 21 years old
Date of Birth: February 6, 1996 Civil Status: Single
Citizenship: Filipino
Tertiary : MARY THE QUEEN COLLEGE OF QUEZON CITY INC. Commonwealth Ave., Rd. 44 Diliman, Quezon City
2013 – 2017
Course : BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN SECONDARY EDUCATION MAJOR IN ENGLISH
Secondary : BATASAN HILL NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL Batasan Hills, Quezon City
2002 – 2008
Primary : SAN DIEGO ELEMENTARY SCHOOL Luzviminda, Batasan Hills Quezon City
TRAININGS AND PROGRAMS ATTENDED
21st Century Skills of Pre-Service Teachers Sept. 17, 2015 A Look on Understanding By Design Sept. 17, 2015 Effective Methods in Teaching Sept. 8, 2014 Freedom in Achievement: Path to Learning Sept. 8, 2014 Demo Teaching August – November 2016
CHARACTER REFERENCES
Call Center Agent at Concentrix 09364222473
MRS. JEAN T. MATALICIA Teacher 1 at Culiat High School 09469058806
JULEOS IBANEZ MAGBANUA
14 M Maayusin ext. Barangay San Vicente Diliman, Quezon City Mobile no. 09066965148
Email address: presie_kyo_08@yahoo.com
PERSONAL INFORMATION
Age: 29 years old
Date of Birth: June 20, 1987 Civil Status: Single
EDUCATIONAL BACKGROUND
Tertiary : MARY THE QUEEN COLLEGE OF QUEZON CITY INC. Commonwealth Ave., Rd. 44 Diliman, Quezon City
2013 – 2017
Course : BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN SECONDARY EDUCATION MAJOR IN ENGLISH
Secondary : QUEZON CITY HIGH SCHOOL Ybardolaza, Kamuning Quezon City
2006 – 2007
Primary : SAN VICENTE ELEMENTARY SCHOOL
Barangay San Vicente Elementary School Quezon City
TRAININGS AND PROGRAMS ATTENDED
CHARACTER REFERENCES
EFREN ADVICULA
Teacher 1 at Culiat high School 09485097662
KRISTHINE DEL ADRANEDA- ADVINCULA Barangay Captain, Barangay San Vicente
09502755747
MARICAR FUNA SULAT
#32 Carter St. Freedom Park IV Batasan Hills Quezon City Mobile no.09123538192
Email address:maricar.sulat@gmail.com
PERSONAL INFORMATION
Age: 22 years old
Date of Birth: February 17, 1995 Civil Status: Single
EDUCATIONAL BACKGROUND
NC II : FRONT SERVICES II
Commonwealth Ave., Rd. 44 Diliman, Quezon City
Tertiary : MARY THE QUEEN COLLEGE OF QUEZON CITY INC. Commonwealth Ave., Rd. 44 Diliman, Quezon City
2013 – 2017
Course : BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN SECONDARY EDUCATION MAJOR IN ENGLISH
Secondary : BATASAN NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL IBP Rd. Batasan Hills Quezon City
Primary : COMMONWEALTH ELEMENTARY SCHOOL Brgy. Commonwealth Quezon City
TRAININGS AND PROGRAMS ATTENDED
CHARACTER REFERENCES
GENE KENU ROVIRA Service Engineer at Asianic 09094717265