DEPAR THE FACULTY S
By:
Nur Djumadil Iman 207014000286
ARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION Y OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS’ TRAIN
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
JAKARTA 2013
i
that the ‘Skripsi’ (Scientific Paper) entitled “ THE CORRELATION BETWEEN STUDENTS’ANXIETY AND THEIR ENGLISH LEARNING ACHIEVEMENT” (A Study Research at First Year Students of SMP BAKTI MULYA 400), written by NUR DJUMADIL IMAN, student’s registration number:207014000286, was examined by the committee on May, 22th 2013, The ‘Skripsi’ was declared to have passed and, therefore, fulfilled one of the
requirements for the academic title of ‘S.Pd. (Bachelor of Arts)’ in English Language Education
at the Department of English Education.
Jakarta, May, 22th2013.
Examination Committee
CHAIRMAN :Drs. Syauki, M.Pd ( )
NIP. 1964121 299103 1 003
SECRETARY :Neneng Sunengsih, M.Pd. ( )
NIP. 19730625 199903 2 001
EXAMINERS : 1.Dra. Fachriany, M.Pd. ( )
NIP.19700611 199101 2 001
2.Neneng Sunengsih, M.Pd. ( )
NIP. 19730625 199903 2 001
Acknowledged by
Dean of the Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers’Training
ii
Abstract
Iman, Nur Djumadil (NIM: 207014000286), THE CORRELATION BETWEEN
STUDENTS’ ANXIETY AND THEIR ENGLISH LEARNING
ACHIEVEMENT, at the first year students of SMP BHAKTI MULYA 400. A Skripsi of English Education at The Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers’ Training of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta, 2013.
Advisor : Drs. Syauki, M.Pd.
Keywords:Students’ Anxiety, English Learning Achievement
The purpose of this study is aimed to investigate the correlation between
students’ anxiety in English learning and their English achievement. The study was conducted at the first year students of SMP BAKTI MULYA 400. The populations of this study were all the first year students of SMP BAKTI MULYA 400 2012-2013. There were 109 students as the sample of population and 40 of them were used as the sample of study. There were two variables investigated in this study, namely: students’
anxiety in English learning and English achievement.
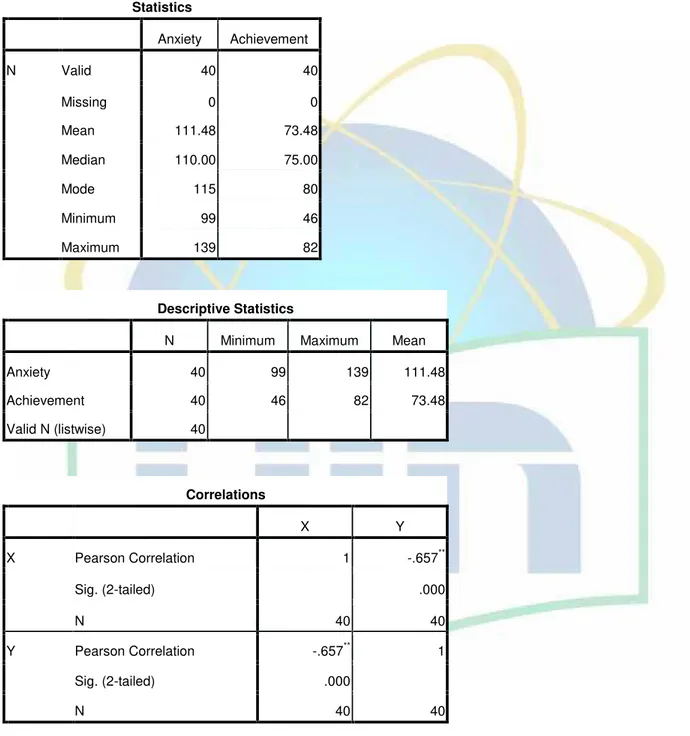
The method used in this research is quantitative research through correlation technique. In collecting the data the writer did two kinds of instrument which were a questionnaire and the result of the test. The questionnaire aimed to know about anxiety in teaching learning process that was done in the classroom, and the result of the test is aimed to know the students achievement after learning English. The data was analyzed by using SPSS. From the calculation of statistic by applying SPSS program, it was known that the value of coefficient correlationrxy= - 0.657. It is in the interval of 0.41– 0.70, this means that the correlation belongto “medium correlation”in negative range. In other words, there is a correlation between variable X and variable Y.
The result showed that the correlation between students’ anxiety and students’
English learning achievement is significant (rxy = - 0.657). Because of the value of significant lower than level of significant and it is negative (- 0.657 < 0.05), it means that
students’ anxiety has negative correlation and it’s significant to their English
iii
SISWA DENGAN HASIL BELAJAR BAHASA INGGRIS,di SMP BAKTI
MULYA 400, Skripsi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris di Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah, Jakarta, 2013.
Pembimbing : Drs. Syauki, M.Pd.
Kata Kunci:Kecemasan Siswa, Hasil Belajar Bahasa Inggris
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui korelasi antara kecemasan siswa dalam belajar bahasa Inggris dan hasil belajar bahasa Inggris. Hal ini dimaksudkan untuk mengetahui apakah terdapat korelasi antara kecemasan siswa dengan hasil belajar bahasa Inggris mereka dan membicarakannya dalam skripsi penulis, Penelitian ini dilaksanakan di kelas satu SMP BAKTI MULYA 400. Populasi penelitian ini adalah semua siswa kelas satu SMP BAKTI MULYA 400 2012-2013. Terdapat 109 siswa sebagas sample populasi dan 40 sample dijadikan sample dalam penelitian ini. Ada dua variable yang diteliti dalam penelitian ini, yaitu kecemasan siswa dalam bahasa Inggris dan hasil belajar bahasa Inggris.
Metode yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah penelitian quantitatif melalui teknik korelasi. Dalam mengumpulkan data, penulis melakukan dua macam instrumen yakni kuesioner dan hasil tes bahasa Inggris siswa. Kuesioner ditujukan untuk mengetahui kecemasan siswa dalam proses belajar mengajar dalam kelas, dan hasil tes bahasa Inggris ditujukan untuk mengetahui hasil belajar siswa setelah belajar bahasa Inggris. Data dianalisa menggunakan SPSS. Dalam perhitungan statistik dalam mengaplikasikan program SPSS, diketahui nilai koofisien korelasi rxy = - 0.657. ini berada antara 0.41– 0.70, arti korelasinya adalah “korelasi sedang” dalam nilai negatif. Dengan kata lain, terdapat korelasi antara variable X dan variable Y.
iv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of Allah SWT, the Beneficent, the Merciful.
All praises be to Allah, the Lord of the world, who always gives His mercy
and blessing upon the writer in completing this skripsi. Praying and greeting
always be upon His messangger, our prophet Muhammad SAW, his family and
his followers, who has spread Islam all over the world.
Firstly, the writer would like to express his deepest gratitude to his
beloved parents, (the late father) Drs. Djamil, L. and especially his mother Artini
S,Pd., who always support and give charity with a deep caring and loving to the
writer. And for all her family (who always give support).
And also, all persons who have helped him in finishing this skripsi,
particularly to:
1. Prof. Dr. H. Rif’at Syauqi Nawawi, M.A., the Dean of Faculty of Tarbiya. 2. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd.as the head of English Education Department. And
Neneng Sunengsih, S.Pd, the secretary of English Education Department.
3. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd, also as his advisor who patiently guided him in writing
this skripsi. And All Lecturers at English Education Department, who have
guided and given him valuable knowledge and chances in finishing his
study.
4. Dr. Hadi Suwarno as the Headmaster of SMP BAKTI MULYA 400, who
has allowed him, doing the research of this skripsi at the institution he
leads.
5. All Teachers at SMP BAKTI MULYA 400, especially English Teachers
who has helped hi in conducting the research. And also, The first year
students of SMP BAKTI MULYA 400, who have assisted in collecting the
data during the research.
6. His lovely family, who always give him support and always take care of
v
their any contribution to her during finishing her study.
8. The staffs of libraries whose books he used for the references of this
research; main library Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University, library
Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training, andNational Library.
“May Allah SWT,blessyouall…”
This ‘skripsi’ is presented to English Department of Faculty of Tarbiyah
and Teachers’ Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Isamic University Jakarta as
partial fulfillment of the requirement for the Degree of Strata-1 (S1).
Finally, yet importantly, the writer realized that ‘skripsi’ still has some weakness and mistakes. Therefore, he would be grateful to accept any suggestion
and correction from anyone for the better writing. And then, he hopes that this
‘skripsi’ could be valuable writing. “Amiin…”.
Jakarta, February, 22th2013
ix
LIST OF TABLES
Table 3.1 The Score of Instruments………...32
Table 3.2 Instrument Indicators………33
KEMENTERIAN AGAMA
FORM (FR)
No. Dokumen : FITK-FR-AKD-063
UIN JAKARTA Tgl. Terbit : 1 Maret 2010
FITK No. Revisi: : 01
Jl. Ir. H. Juanda No 95 Ciputat 15412 Indonesia Hal : 1/1
SURAT PERNYATAAN KARYA SENDIRI
v
Saya yang bertanda tangan dibawah ini:
Nama : Nur Djumadil Iman
NIM : 207014000286
Tempat/Tgl. Lahir : Biak, 11 Januari 1990
Jurusan : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
MENYATAKAN DENGAN SESUNGGUHNYA
Bahwa skripsi yang berjudul The Correlation between Students’ Anxiety and Their English Learning Achievement (A Study Research at the First Year Students of SMP BAKTI MULYA 400 Jakarta Selatan) adalah benar hasil karya sendiri dibawah bimbingan dosen:
Nama Dosen Pembimbing : Drs. Syauki, M.Pd.
NIP :1964121 299103 1 003
Jurusan/Program Studi : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Demikian surat pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sesungguhnya dan saya siap
menerima segala konsekuensi apabila terbukti bahwa skripsi ini bukan hasil karya
sendiri.
Jakarta, 22 Mei 2013
Yang Menyatakan
NUR DJUMADIL IMAN
vii
ENDORSEMENT SHEET ………. i
ABSTRACT ……….………..ii ABSTRAK ……….iii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... iv
PERNYATAAN KARYA SENDIRI ... vi
TABLE OF CONTENTS ……..……….………..…vii
LIST OF TABLES ………..ix
LIST OF APPENDIXES ……….x
CHAPTER I INTORDUCTION A. Background of the Study …... 1
B. The Limitation of the Study…..……... 3
C. The Statement of the Study ...4
D. The Purpose of the Study ... 4
E. Significance of the Study...4
CHAPTER II THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK A. Theoritical Description...5
1. Definition of Learning ...5
2. Learning Theory ...8
3. Definition of Achievement ...17
4. Definition of Anxiety ...23
B. Conceptual Framework...26
C. Hypothesis ...27
viii
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. The Method of the Research ...28
B. Variables………..28
C. The Place and time of the Research ...29
D. Population, Sample and Sampling ...29
E. Data of Research ...30
F. Technique of Collecting Data and Research Instrument...31
G. Technique of Data Analysis ...35
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDING A. The Description of Data ...36
B. The Finding ………36
1. Students’Anxiety Scores……..………..36
2. Students’English Scores ……..……….36
C. Data Analysis...37
D. The Test of Hypothesis……….37
E. Interpretation of Data ……….38 CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ...39
B. Suggestion ...40
BIBLIOGRAPHY ………...41
x
Appendix 1. Blue PrintKalkulasi Statistik ‘Students’ Anxiety Score
and Students’ English Score dengan menggunakan SPSS ……..45
Appendix 2. Blue Print of Table ofStudents’ Anxiety Score
and Students’ English Score ……….46
Appendix 3. The Result of Instrument Validity……….…………47
Appendix 4. Angket untuk Siswa ……….………48
Appendix 5. Blue Print of Table of Studensts’ Anxiety Scores ….………..56
Appendix 6. Blue Print of Table of Studensts’ English Scores……….58
Appendix 7. Blue Print of Table ofThe Result of Students’ Anxiety
and English learning achievement by Product Moment Table…..60
1
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the study
English is very important subject in the human life to learn today; it’s
caused by developing of science. It may be true to say that English now is the
most important language in the world. English is one of foreign language that
has been used widely in the world as means of communication and as a tool
in gathering information. According to estimation, there are about a billion
people in the world today learning English as a foreign language.1 English is
also commonly used in the writing of many books of science and technology.
And now English as second language in Indonesia. Unfortunately, the
English mastery of Indonesia people is generally bad. To change this, of
course we must improve our English, through formal education at school over
Indonesia the teaching of English is aimed to prepare youngest Indonesia in
facing the rapid progress of science and technology to be more confident to
get involved in international relation as part of the world society.
In Indonesia, English has been taught to the students from the elementary
school up to university. Studying English is very important for them, because
there are many books needed to increase their knowledge, written in English.
Their good mastery in English, therefore, will make them easier to
comprehend those books. One of important factor that is able to increase their
knowledge is motivation in teaching English; teacher should realize about
student’s motivation, teacher should understand student’s needs.
In fact, we have known that among students who had graduated from
university has not enough yet competence in English. It can be seen from the
fact that the students have low ability in mastering the language and they also
have little knowledge of English.2
1
Keith Johnson,An Introduction to Foreign language Teaching and, (Pearson Education Limited: 2001):p.3.
2
Since this language has been taught in Indonesian school, some problems
which are found by teachers or students arisen concerning with the lesson of
English. This can be seen that the most of students are not able to
communicate well orally or in written, and it also can be seen from their
English scores that are still categorized low.
The writer argued that the low English scores may be caused by students
of English as a billingual difficult lesson, that English is a foreign language
and it is very far different from their mother tongue. The foreign language
also contain different aspects that have to be understood by the English
learner. Those things burdened most students in English teaching-learning
process.
Those things are called Language anxiety. As Skehan stated that
“Language anxiety, a type of anxiety specifically associated with L2 learning
contexts, can arise from many kinds of sources, according to the learners'
individually unique frame of reference.”3
Because of those things burden the students, some of students has
experience of anxiety in the English classroom while trying to learn English,
neither they’re doing English exercise on the class, having a homework, or having an examinaton. Horwitz have stated that, The subjective feelings,
psycho-physiological symptoms, and behavioral responses of the anxious
foreign language learner are essentially the same as for any specific anxiety.
They experience apprehension, worry, even dread. They have difficulty
concentrating, become forgetful, sweat, and have palpitations. They exhibit
avoidance behavior such as missing class and postponing homework. 4
The writer figure out language anxiety happens among students. Anxiety
often arise which is related with anxiousness in facing situation that never be
worried before. Zeidner said that “Anxiety tends to bother teaching-learning
process and achievement in education, even bother attention, working
3
Kota Ohata, Potential Sources of Anxiety for Japanese Learners of English: Preliminary Case Interviews with Five Japanese College Students in the U.S., TESL-EJ Journal, Vol.9, No.3, (Tokyo, Japan, International Christian University, Des. 2005): p.1.
4
3
memory, and retrieval.”5For example, 'Speaking in front of others' is rated as the biggest cause of anxiety followed by 'worries about grammatical
mistakes', 'pronunciation' and 'being unable to talk spontaneously'. And they
think English is difficult to learn. These situation and condition can affect
learners’English learning achievement indirectly.
English learning achievement as a determiner of learner’s achievementis
influenced by such factors as learner’s capability, learner’s interest, and anxiety which has been around the students. Their English achievement was
measured through their final standardized English exam administered by the
school.
Based on the background of the study previously, the writer argued that
one of important think that can affect learners in mastering English is
learners’ anxiety. The student’s anxietyin language learning aslo affect their English score. It is approved that the students who have low English
proficiency and difficulties’ belief can arise anxious personality. To ensure the success of English education, language anxiety is a significant issue
which cannot be ignored. Then, the writer assumes that anxiety is regarded as
one of dominant factors that can affect the students’ English learning achievement.
The writer stated that it is such an interesting study to have a research on
what have been mentioned above in order to find whether the students’
anxiety has any correlation with their English learning achievement. It is
expected that this study may support the English Teaching-Learning process
to improve the quality of study.
B. The limitation of the study
In this paper, the writer limits the study on the discussion of students’
anxiety in correlation with their English learning achievement. In this
research, the object of this study is limited on student’s anxiety of the first year students of SMP BAKTI MULYA 400.
5
C. The Statement of the Study
Based on the limitation of the studyabove, the statement problem is: “is there any correlation between students’ anxiety and their English learning achievement?”
D. The Purpose of study
This study aims to know whether anxiety has any correlation with
students’ English learning achievement. The writer hopes that this research
will help to figure outhow students’ anxiety can affect their English learning
achievement.
E. The Significant of the Study
1. Theoretically
Theoretically the result of this study will answer the question at the
formulation of the problem whether the student’s anxiety in learning
English is really important factor in English achievement.
2. Practically
It is expected that the result of the study will be useful for:
a. Headmaster: As feed back to the institution to improve for
improving the system of education and facilitating what the
teacher needs.
b. Students: to get an information about correlation between
students’ anxiety and their english learning achievement. In order
they can stimulate themselves to increase their english
achievement.
c. Teacher: to give an encouragement to the students in order that
he/she can improve the students’ english learning achievement.
d. Other researchers: the result of this research can give information
about the correlation between students’ anxiety and their english
learning achievement that can be used to basic consideration and
basic information to increase learning achievement especially
5 CHAPTER II
THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter discusses about definition of learning, the learning theories,
definition of achievement, definition of anxiety, types of anxiety and conceptual
framework.
A. Theoretical Description 1. Definition of Learning
Learning has an important role in people life. The most
development process is through learning activity directly. According to
Santrock, Learning is a relatively permanent influence on behavior,
knowledge, and thinking skills, which comes about through experience. For
example: when children learn how to use computer, they might make some
mistakes along the way, but at a certain point they will get the knack of the
behaviors required to use the computer effectively. The children will
change from being individuals who cannot operate a computer into being
individuals who can.1 It means learning is always about changes of
individual who learns whether its head for good or bad, planned or not.
Another thing which is always concerning about learning is experience,
experiencethat’s classified with other people or the environment.
Some expert has explained about learning, such as Witherington, he
explained that learning is changes of personality, which manifestation as
pattern of new responses which are skill, attitude, and knowledge.
The closest opinion has defined by Hilgard quoted by Sukmadinata,
he said that learning is a process where an attitude arises or changes,
because of there are responses to the situation.2
1
John W. Santrock, Educational Psychology: Classroom Update; Preparing for Praxis and Practice, second edition, (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2001),p.210.
2
Another definition that has to be informed here such as Kingsley
quoted by Soemanto. He stated that Learning is the process by which
behavior (in the broader sense) is originated or changed through practice or
training.3
Then, De Cecco also explained in his book about learning.
“Learning is a relatively permanent change in a behavioral tendency and is
the result of reinforced practice.”4
Likewise,Morrison, he stated that “Learning refers to the cognitive and behavioral changes that result from experiences.” The experiences that make up the curriculum are at the core of the learning process, and an
experience which is provided for children should be based on theory or
theories of how children learn.5
Psychologists have many different ways to explain the definitions of
learning. But, either explicit or implicit, finally it has the similar meaning
from the definition of learning which always directed to a process of
someone behavior’schange based on practice or certain experience.
Based on the description above, the writer tries to synthesize them
to gain general meaning about learning. Learning is an effort in developing
individual personality, either physical aspect or physiological. Learning is
an activity that has purpose to make a change of behavior, attitude,
habitual, knowledge, skill, etc, as a result of individual experience of
interaction with the environment.
Many learning definitions have been defined above. Some of them
are different but there also have the same concept. The same concept looks
as the learning principle.
Some of learning principle has explained in the following;
1. Learning as a part of development
2. Learning long live
3
Wasty Soemanto, Psikologi Pendidikan Landasan Kerja Pemimpin Pendidikan, (Jakarta: PT RINEKA CIPTA, 2006),p.104.
4
John P. De Cecco,The Psychology of Leaning and Instrucition:Educational Psychoogy, (New Jersey: Prentice Hall, INC.,1968), p.243.
5
7
3. Learning achievement affected by bring factors, environment,
mature and also effort from self-individual
4. Learning includes the whole aspect of life
5. Learning activity occur in every place and every time
6. Learning happens with or without a teacher
7. Learning scheduled and with intentional gain high motivation
8. Learning act varieties from simple to complex
9. In learning occur the inhibitions
10. In the certain learning activity is needed help or guide from other
people.6
Learning is continuing process and long live education, occurs in
house, school, even in society environment. In facing and adapting the
requirement of world development, UNESCO formulated four pillars of
education, they are;
a. Learning to know, it may be regarded as both a means and an end
of human existence. People have to learn to understand the world
around them. To provide the cognitive tools required to better
comprehend the world and its complexities, and to provide an
appropriate and adequate foundation for future learning.
b. Learning to do, Learning must transform certified skills into
personal competence. It is assessed by looking at a mix of skills
and talents, social behavior, personal initiative and a willingness
to work. To provide the skills that would enable individuals to
effectively participate in the global economy and society.
c. Learning to live together, Education should help in inculcating a
spirit of empathy in students so that it can have a positive effect
on their social behavior throughout their lives. Understanding
each other, resolving conflicts through dialogue and discussion
should be the essential tools of present day education.
6
d. Learning to be, the aim of development is the complete
fulfillment of man and his development in a holistic way as an
individual, member of a family and community and as a
responsible citizen.7
In Monitoring learning, learning achievement means assessing the
knowledge, skills, and attitude values of pupils. One of parameter that is
used to measure level of education success is students learning achievement.
If the students show good learning achievement, it means that the education
process is success. But when students show bad learning achievement, it
means that the education process has failed.
Therefore, considering the important role of students learning
achievement to determine the success of education, so learning process
should be directed toward the increasing of students learning achievement.
But, firstly the writer tries to explain the learning theoryes.
2. Learning Theory
Learning theories are conceptual frameworks that describe how
information is absorbed, processed, and retained during learning. Learning
brings together cognitive, emotional, and environmental influences and
experiences for acquiring, enhancing, or making changes in one's
knowledge, skills, and values. There are three main categories of learning
theory: behaviorism, cognitive, and constructivism.
a. Behaviorism
Behaviorism theory is one of experimental psychology
which is adopted by education. Even though in the last twentieth
century, another theory has reaction with behaviorism, but
behaviorism had dominated the learning phenomenon.
Behaviorism is thus the study of the relation between people’s
environments and their behavior, without appeal to hypothetical
7
9
events occurring within their heads.8 It means Behaviorism is the
view that behavior should be explained by observable
experiences, not by mental processes.
In the following explanations, the writer tries to describe
behaviorism psychologists and their approach. They are Ivan
Petrovich Pavlov, Edward Thorndike, Watson, and Skinner. Their
theories are the most referenced in education.
1.) Classical Conditioning Theory by Ivan Pavlov
Ivan Pavlov is one of psychology’s most recognizable
figures, the Russian physiologist who developed the concept which
had been widely known as Classical Conditioning. Morris and Maisto had explained it in their book. Pavlov (1849-1936)
discovered Classical Conditioning almost by accident. He was
studying with dog salivates experimental. Classical (or Pavlovian)
conditioning refers to the type of learning in which a response
naturally elicited by one stimulus comes to be elicited by a
different, formerly neutral stimulus. There are four elements of
classical conditioning. (1) The unconditioned stimulus, (2) the
unconditioned response, (3) the conditioned stimulus, (4) the
conditioned response. The unconditioned stimulus is an event that
automatically elicits a certain reflex reaction, which is the
unconditioned response. The conditioned stimulus is an event that
is repeatedly paired with the unconditioned stimulus. The learned
reaction elicited by repeatedly paired is the conditioned response.9
2.) Operant Conditioning Theory by Skinner
Skinner’s learning theory had widely known as Operant Conditioning Theory (also called instrumental conditioning). This
8
Neil R. Carlson & William Buskist, Psychology the Science of Behavior, 5thedition, (U.S.A.: Allan and Bacon, 1997), p.15.
9
is a form of learning in which the consequences of behavior
produce changes in the probability that the behavior will occur.
The consequences -reinforcement or punishment- are contingent on
the organism’s behavior. Reinforcement (reward) is a consequence that increases the probability that a behavior will occur. In contrast,
punishment is a consequence that decreases the probability a
behavior will occur.10
3.) Connectionism theory by Edward Thorndike
Learning theory of Edward Thorndike is also called by
Connectionism Theory. According to Connectionism Theory,
Learning is the result of associations forming between stimuli and
responses. Such associations or "habits" become strengthened or
weakened by the nature and frequency of the S-R pairings. The
paradigm for S-R theory was trial and error learning in which
certain responses come to dominate others due to rewards.11
Thorndike characterized the two most basic intelligences as
Trial-and-Error and Stimulus-Response Association. It means changing
of learning behavior can be seen as observable behavior and hidden
behavior).
4.) Behaviorism theory by Watson
Watson was one of the behaviorists which came after
Thorndike. John B. Watson was an important contributor to
classical behaviorism, who paved the way for B. F. Skinner's or
operant behaviorism. Watson coined the term "Behaviorism" in
1913. Behaviorism assumes that behavior is observable and can be
correlated with other observable events. Thus, there are events that
precede and follow behavior. Behaviorism's goal is to explain
relationships between antecedent conditions (stimuli), behavior
(responses), and consequences (reward, punishment, or neutral
10
Neil R. Carlson & William Buskist,Psychology the Science of Behavior, pp.165-166.
11
11
effect). Watson's theory was more concerned with effects of
stimuli. He derived much of his thinking from Pavlov's animal
studies (classical conditioning). This is also referred to as "learning
through stimulus substitution," a reference to the substitution of
one stimulus for another.12
Underlying the behaviorist perspective are several key
assumptions:
a) People’s behaviors are largely the result of their experiences with environmental stimuli. As teachers, we must keep in mind very significant effect that students’
past and present environments are likely to have on their
behaviors. We can often use this basic principle to our
advantage: by changing the classroom environment, we
may also be able to change how students behave.
b) Learning involves a behavior change. We might define learning as a change inbehaviordue to experience. Such a view of learning can be especially useful in classroom.
Consider the scenario: “your students look at you attentively as you explain a difficult concept. When you
finish, you ask “Any questions? You look around the
room, and not a single hand is raised. “Good”, you think, “the all understand.”
But do your students understand? On the basis of what you’ve just observed, you really have no idea whether they do or don’t. Only observable behavior
changes-perhaps an improvement in achievement test
scores, a greater frequency of independent reading, or
reduction in off-task behavior that tell us learning has
occurred.
12
c) Learning involves forming associations among stimuli and responses. By and large, behaviorist principles focus on relationships among observable events.
d) Learning is most likely to take place when stimuli and responses occur close together in time. When to events occur at more or less the same time –perhaps two stimuli or perhaps stimulus and a response – we say that there is Contiguity between them.
e) Many species of animals including human beings learn in similar ways. Many behaviorist principles have been derived from research with nonhuman animals. For
instance, as seeing the moment, our knowledge about
classical conditioning first emerged from Ivan Pavlov’s
early work with dogs. And another well-known
behaviorist B. F. Skinner, worked almost exclusively with
rats and pigeons. The fact is that behaviorist principles
developed from the study of nonhuman animals are often
quite helpful in explaining human behavior.13
5).Social Learning Theory by Albert Bandura
Social learning theory is a major growth of the behavioral
learning theory tradition. Developed by Albert Bandura, social
learning theory accepts most of the principles of behavioral
theories but focuses to a much greater degree on the effects of cue
on behavioral and on internal mental processes, emphasizing the
effects of thought on action on thought (Bandura, 1986).
Bandura’s analysis of observational learning involves four
phases: attentional, retention, reproduction, and motivational
phases.
a). Attentional phase. The first phase in observational learning is paying attention to a model. In general, students
13
13
pay attention to role models who are attractive, successful,
interesting, and popular.
b). Retention phase. One teacher has students’ attention, it is
time to model the behavior they want students to imitate
and then give students a chance to practice or rehearse.
c). Reproduction. During the reproduction phase, students try to match their behavior to the models. In the classroom the
assessment of students learning takes place during this
phase.
d) Motivational phase. The final stage in the observational learning process is motivation. Students will imitate a
model because they believe that doing so will increase their
own chances to be reinforced. In the classroom the
motivational phase of observational learning often entails,
praise or grades given for matching your model.14
b. Cognitive Learning Theory
Cognitive learning theory focuses on internal mental
processes and their learning role. Its primary concern is with
making meaning out of information and experience (Brunner,
1990). According this approach, learning is defined as the
acquisition of new information. This is achieved through the
processing and storing of knowledge and skills in one’s mind in
such a way that they can be recalled and used at a later time when
we needed (Cooper, 1998).15
Constructivism is a cognitive theory of development and
learning based in the ideas of Jean Piaget, and Lev Vygotsky. The
constructivist approach supports the belief that children actively
seek knowledge; it explains children’s cognitive development,
14
Robert E. Slavin, Educational Psychology Theory and Practice, tenth edition, (New Jersey: Pearson, 2009),pp.132-133.
15
provides guidance for how and what to teach, and provides
direction for how to arrange learning environments.
1) Piaget’sTheory of Cognitive Development
In the early 1920s, the Swiss biologist Jean Piaget began
studying children’s responses to problem of this nature. He used an approach he called the clinical method, in which an adult presents a task or problem and asks a child
a series of questions about it, tailoring later questions to
the child’s responses to previous ones. Piaget introduced a number of ideas and concepts to describe and explain the
changes in logical thinking he observed in children and
adolescents:
a. Children are active and motivated learners
b. Children construct rather than absorb knowledge
c. Children learn through a combination of
assimilation and accommodation
d. Interactions with one’s physical and social
environments are essential for cognitive
development
e. The process of equilibration promotes
progression toward increasingly complex
thought.
f. In part as a result of maturational changes in
brain, children think in qualitatively different
ways at different ages.
2) Vygotsky’s Theory of Cognitive Development
Lev Vygotsky’s theory contrast with Piaget, he believed that adults in any society foster children’s cognitive
development in an intentional and somewhat systematic
15
adult instruction and guidance for promoting cognitive
development – and, more generally, because he emphasized the influence of social and cultural factors in
children’s cognitive growth – his perspective is known as asocialcultural theory.16
c. Humanism Learning Theory
Humanistic, humanism and humanist are terms in psychology
relating to an approach which studies the whole person, and the
uniqueness of each individual. Essentially, these terms refer the
same approach in psychology. Humanism is a psychological
approach that emphasizes the study of the whole person.
Humanistic psychologists look at human behavior not only through
the eyes of observer, but through the eyes of the person doing the
behaving. Humanistic psychologists believe that an individual’s
behavior is connected to their inner feelings and self concept. The
humanistic approach in psychology developed as a rebellion
against what some psychologists saw as limitations of the
behaviorist and psychodynamic psychology. The humanistic
approach is thus often called the ‘third force’ in psychology after
psychoanalysis and behaviorism (Maslow, 1968).17
Here two highly influential theories by Carl Rogers and
Abraham Maslow.
1. Rogers’ Theory of the Self
Carl Rogers (1902-1987), a clinical psychologist,
developed his theory of personality from observations the
made while practicing psychotherapy. Rogers found that
most people are constantly struggling to become their
“real” selves. Rogers concluded that the overriding human motivation is a desire to become all that one truly
is meant to be – to fulfill one’ capabilities and achieve
16
Jeanne Ellis Ormrod,Educational Psychology Developing Learners,pp.38-39
17
one’ total potential. This powerful, lifelong motive Rogers called a striving toward self-actualization
(Rogers, 1970, 1971).
2. Maslows’ Self-Actualization Person
Like Carl Rogers, psychologist Abraham Maslow
(1908-1970) began with the assumption that people are
free to shape their own lives, and they are motivated by a
desire to achieve self-actualization. According to
Maslow, a self-actualized person finds fulfillment in doing the best that he or she is capable of, not in competition with others but in an effort to become “ the best me I can be” (Maslow, 1971a, 1971b).
One of Maslow’s key concepts is the hierarchy of needs. Maslow believed that all humans face a series of needs, and that basic needs must be met before a person
can fulfill higher level need. At the bottom are
fundamental needs: those associated with physical needs, such as thirst and hunger, and those related to obtaining a
safe and secure environment. At the above are
psychological needs, including both the need of sense of belonging and the need to achieve competence,
recognition, and high self-esteem. Once all the
fundamental needs and psychological needs have been
met, a person can begin to fulfill the need for
self-actualization.18
Behavioral and cognitive theories agree that differences among
learners and the environment can affect learning, but they diverge in
the relative emphasis they give to these two factors. Behavioral
theories stress role of the environment-specifically, how stimuli are
18
17
arranged and presented and how response are reinforced. Behavioral
theories assign less importance to learner differences than do
cognitive theories. Two learner variables that behavioral theories
consider arereinforcement history (the extent to which the individual was reinforced in the past for performing the same or similar
behavior) and developmental status(what the individual is capable of doing given his or her present level of development).
Cognitive theories acknowledge the role of environmental
conditions as influences on learning. Teachers’ explanations and
demonstrations of concepts serve as environmental inputs for students.
Student practice of skill, combined with corrective feedback as
needed, promote learning. Cognitive theories emphasize that role of
learner’s thoughts, beliefs, attitudes, and values. Learners who doubt their capabilities to learn may not properly attend to the task or may
work halfheartedly on it, which retards learning.19
3. Definition of Achievement
In general, every teaching-learning process will optimally succeedd
as expected especially English. i.e., it’s taken by high or low score
achievement. It is important know what learning achievement is.
Achievement term came from Dutch ‘prestatie’ and then in Indonesian become ‘Prestasi’. Achievement is always related with certain activity, e.g. learning. Syah (1997) had explained that, “Prestasi belajar merupakan taraf keberhasilan siswa dalam mempelajari materi pelajaran di sekolah yang dinyatakan dalam bentuk score yang diperoleh dari hasil tes mengenai sejumlah materi pelajaran tertentu.”20 (Learning achievement is the learners’ successful value in studying the material at school which is said by score and which is obtained from the final test about specific
19
Dale H. Schunk, Learning Theories An Educational Perspective, Sixth edition, (Boston, Pearson, 2008),p.22
20
material). This means that achievement is the result that students obtain
after following a teaching-learning process in certain period of time.
The other definition of achievement in Cambridge Advanced
Learner’s Dictionary is “something very good and difficult that you have succeeded in doing.”21
Another expert’s opinion such as Hornby about achievement is a thing
done successfully, especially with an effort and skill.22
Based on the description above, the writer tries to synthesize them to
gain general meaning about achievement. According to the writer,
achievement is the final result of students’ ability in learning English after they have followed a teaching-learning process in period of time.
A student who learned English is he or she who wants to develop and
gain their knowledge in mastering English well, by doing practices and
exercises continuously. So, English learning achievement is the ability that
students obtain in learning English after they have learned in teaching
learning process in a particular period of time.
z
y As Sukmadinata quotedthat, “Tingkat penguasaan pelajaran atau hasil belajar dalam mata pelajaran dilambangkan dengan angka-angka atau huruf, angka-angka 0-10 pada pendidikan dasar dan menengah dan huruf A, B, C, D pada pendidikan tinggi”. (Achievement of the lesson can be signed with number or letter. The number 0-10 is for elementary until
middle of education, and the letter of A, B, C, D, to the high of education).23
It means that achievement is not only a mastery of knowledge, but also
capability and skillful of students in schools that is expressed in numerical
value.
21
Cambridge Advanced Learner’s Dictionary, Third Edition, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press),p.20.
22
A.S. Hornby, Oxford Advanced Learner Dictionary, (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1995),p.10.
23
19
To promote student’s achievement many teachers use strategies of teaching as Keith Johnson said “Many teachers intuitively use strategies that promote the achievement and cognitive growth of student”.24
Richard Kindvatter has found three strategies that have positive effect
on students’ achievement. They are: direct teaching, mastery learning, and
cooperative learning.
But he also said that three is not a single teaching strategy that is the
best approach as he said “there is not one single strategy that is the best approach but certain strategies, used in certain context have been
documented by writer as improving achievement”.25
Based on Richard points of view, we know that the main print in
teaching is appropriate strategies and instruction to help learner understand
the lesson. In choosing strategies the teacher must consider the students,
their development level, cultural background, academic abilities, and social
economic background.
Concerned with many factors that can inhibit English learning
achievement are obtained by students.
Muhibbin syah globally has divided some factors influencing
student’s achievement to be: internal factors, external factors, and approach to learning.
A. Internal factors
Internal factors are “factors from the inside of student themselves”. It is included two factors: physiological and psychological factors.26
1. Physiological factors
It is included general physical condition and specific
physical condition of life. It means the condition of eyes and ear.
24
Keith Johnson,Educational Psychology For Effective Teaching,(Toronto:Thompson Publishing Company, 1999),p.76
25
Richard Kindsvatter, William Willen, Margareth Ishler,Dynamic Of Effective Teaching.,p.135
26
“Briefly to help student whose eyes or ear are not good enough
teacher move them to the forward seat”.27
Giving vitamins to our students preventively can help them
protect their physical condition in this case; teacher can cooperate
with student’s parents.
2. Psychological factors
Generally among psychological factors of the student that
seem essential are “intelligent of student, attitude, aptitude, interest and motivation”.28
a. Intelligent
“……intelligent is one of human abilities to do activity and it
is had been exist where ha was born”.29
The quality of student intelligent cannot be doubted. It is
influence student success in learning. It means that higher
student’s intelligent bigger opportunities. They will be success in contrast lower student’s intelligent smaller opportunity they
have.
All teachers must realize that student’s intelligent superior or borderline generally will make our students get difficulty in
learning. The smart students, they will be boring if the lessons
are easy for them whilst the lower students will by very tired if
the lesson too hard for them.
b. Attitude
“Attitude is internal phenomenon that have effective
dimension tendency to response (response tendency) with
stabile method toward object negatively or positively….”30 The teachers have to able to manage the students, lessoned
and also themselves in order to make positive attitude of the
Cronbach in Sardirman, Interaksi dan Motivasi Belajar Mengajar,(Jakarta: PT Raja Grafindo Persada, 2003), p.46
30Ibid.
21
students and avoid negative attitude of students. It aims to
avoid negative attitude of our students and our profession as
teacher. The teacher not only master the lesson, but also able
to make the students sure that the lesson will be useful for
them.
c. Aptitude
“Generally aptitude is the ability of human to get the goal
or success in the future…..”.31
Based on this definition, we may state aptitude will
influence high and low of our student’s achievement, in
specific lesson. So that it is not a brief treatment if we and
parents force our students to go to specific skill school without
knowing our children aptitude. Foreign our student will give
bad influence to the achievement of our students.
d. Interest and Motivation
About interest and motivation have been discussed that
interest and motivation have correlation each other. Motivation
and interest caused by same thing. “Motivation comes because of the need of human and interest is also like it”.32
Interest is the basic motivational elements. The process of
learning will be run well if the students have good interest in
the lesson, because they have motivation from their self.
b. External factors
Muhibbin Syah gives external factors influencing student’s
achievement to be social environment, national environment, learning
approach factor.33
31
Sudirman AM,Interaksi dan Motivasi,.p.150
32Ibid,.
p.94
33
1. Social environment
Social environment such as school, teacher, staff
administration, and friends can influence spirit of learning of the
students.
2. National environment
Factors included in national environment are school building
and the place, houses of the students, learning tools, season, and
the time of learning. This factor considered has great influence in
our students.
3. Approach to learning
Approach of learning can be considered as all method or
strategies. Used by our students in improving effectiveness and
efficiency of learning process. In this case learning approach
means a set of operational theory to solve the problems to get goal
of special learning.34
Beside internal and external factors, approaches to learning also
considered have great influence in the success of our students in
learning. A student who use deep approach maybe has greater
opportunity to get better achievement than who whose surface
approach or reproductive approach35
As Sabri have stated in his book, that Psychological factor involves
interest, motivation, intelligence, perception, think, and memory.36 Their
perception that English as a foreign language, then they think English is
difficult to learn. This condition can affect learners’ English learning achievement and arising anxiety indirectly. It can be said that English
learning achievement will be different depend on what the kinds of anxiety
of the learner has.
Although English learning achievement can be depended into the
learner within his anxiety, in education or learning system, learning
34
Larso in Muhibbin,Psikologi,.p.155
35Ibid.,
p.155
36
23
achievement have to be measured. Curriculum or syllabus in learning shows
the general achievement called standard competences. It shows minimum
target of learner which is explained by affective, cognitive, and
psychomotor standard. Those standards are appropriate with the educational
theory used by the nation. In conclusion, learning achievement is target
measured by competences of the learner in learning which are shown by
score as a sign and score.
4. Definition of Anxiety
If someone is deal with something, and this certain thing can threat
him/her or, at least, can cause unpleasant thing to him/herself which inhibit
emotion or physiological, then he/she can be said have an anxiety.
Talking about anxiety, Anxiety is one of dominant factor that can
affect students learning. Commonly, learners have anxiety, when he/she
faces the difficult lesson, oriented to get the high scores, pressure from
teacher in teaching and also having anxiety in test.
According to Spielberger (1983) quoted by Sara Atef-Vahid and
Alireza Fard Kashani, Anxiety can be described as the subjective feelings
of tension, apprehension, nervousness, and worry associated with an arousal
of the autonomic nervous system. 37
The other psychologist tries to make a general definition of anxiety
like Branca. He mentions that, Anxiety is “best defined and described by
comparing it to fear. The feeling-tone of anxiety is very similar to the
feelings experienced in fear.”38
Similarly with Kowalski (2000) stated that the basic meaning of
anxiety, “Anxiety involves a vague, highly unpleasant feeling of fear and apprehension.”39 It means that anxiety is normal thing or an emotion condition that will happen to any individual. This common reaction also
37
S. Atef-Vahid and A. Fard Kashani,The Effect of English Learning Anxiety on Iranian High-School Students’ English Language Achievement,p.2.
38
Albert A. Branca, PSYCHOLOGY the Science of Behavior, (U.S.A: Allyn and Bacon, INC.,1964),p.432.
39
happen in classroom activities especially English classroom. Because of it
can inhibit new learning behavior and performance which had been learned
previously by all students.
Anxiety is believed to consist of two components:
1. Cognitive anxiety which refers to the mental aspect of anxiety
experience including negative expectations, preoccupation with
performance and concern about others’ perceptions.
2. Somatic anxiety which refers to learners’ perceptions of the
psychological effects of the anxiety experience as reflected
arousal and unpleasant feeling states such as nervousness, upset
stomach, pounding heart, sweating, and tension (Morris, Davis
and Hutchings 1981).
To some researchers (Lang 1971; Cheng 2004) anxiety has three
different components rather than two: cognitive, physiological (somatic),
and avoidance behavior (behavioral). It is believed to involve a variety of
dysfunctional thoughts, increased physiological arousal and maladaptive
behaviors. Some studies find somatic anxiety and cognitive anxiety covary
and are hard to separate. Learners experience apprehension, worry and
dread. They exhibit behavior such as missing the class and postponing the
work or assignment. The relations among anxiety, cognition and behavior
are best seen as recursive or cyclical where each influences the other. A
demand to answer a question in a foreign language class may cause learners
to become anxious and anxiety leads to worry and rumination. Cognitive
performance is diminished because of the divided attention and therefore
performance suffers, leading to negative self evaluations and more self
deprecating cognition which further impairs performance. In an educational
setting anxiety may impair the ability to take in information, process it and
retrieve it, can limit the use of both short and long term memory.40
From the definition above, they could be concluded that anxiety is
an unpleasantcondition that can’t be ignored by anybody as a response from
40
25
any situation which threats the forthcoming marked by complaints such as:
worry, apprehensive, and fear.
Every learner has different rates of anxiety. This anxiety can be
observed directly. As Michael W. Passer mentioned that anxiety responses
have four components. They are:
1. A Subjective-emotional component, including feelings of tension and apprehension,
2. ACognitive component,including worrisome thoughts and a sense of inability to cope,
3. Physiological responses, including increased heart rate and blood pressure, muscle tension, rapid breathing, nausea, dry mouth and,
4. Behavioral responses, such as avoidance of certain situations and impaired task performance.41
English anxiety also called a foreign language anxiety that is a
situation or reaction to learners in facing inconvenient condition when
they’re in English teaching-learning process. Actually this anxiety is less than anxiety of English test. This anxiety, considered as a one of resistor
factor in teaching-learning process, which bothers learners performance of
cognitive functions, such as concentration, remember, concept form, and
problem solving (Sieber, 1977).42Besides, English lesson is ‘scary’;anxiety
also can arise by teaching system, teachers’ capability and students’
academic ability.
There are three main types of foreign language anxiety on which all
practitioners agree:
1. Communication apprehension is a type of shyness characterized by
fear of and anxiety about communicating with people. Difficulty in
speaking in public, in listening or learning a spoken message is all
manifestations of communicative apprehension.
41
Michael W. Passer and Ronald E. Smith,PSYCHOLOGY The Science of Mind and Behavior, second edition, (New York: McGraw Hill, 2004),p.513.
42
2. Test anxiety refers to a type of performance anxiety stemming from
a fear of failure. Test anxious students often put unrealistic demands
on themselves.
3. Fear of negative evaluation, apprehension about others’ evaluations,
and avoidance of evaluative situations. Learners may be sensitive to
the real evaluations or imagined of their peers.43
English anxiety is usually similar with students’ disbelief in learning English. They think English is difficult and fright which arisen because
they’re not sure with their ability, attitude, and hopeless. It will affect
learners’ learning development. According to Sabri, definition of
‘development’ is changes of qualitative and quantitative which concerns aspects of human mental-psychology.44 It means individual conditioning
from child (always be forced by parents to learn English and must get best
score), with having this experience will cause anxiety, or having
mental-conflict in choosing lesson which is liked by students, but inappropriate
with they hope or will.
B. Conceptual Framework
According to Sabri, Students’ learning achievement can be influenced by some factors, come from internal and external factors of the students.
One of internal factor is psychological term that can affect the students’
learning achievement are IQ, talent, interest, and cognitive ability, including
anxiety.45
Students’ achievement is signed by their final scores. It is resulted
from the average of their daily scores (formative scores) and their final test
score.
Students’ anxiety especially in learning English as one factor that is
assumed can interfere the students’ learning achievement in English by the
following reason :
43
Feryal Cubukcu,Foreign Language Anxiety,p.3.
44
H. M. Alisuf Sabri,Psikologi Pendidikan, p.11.
45Ibid
27
Students who have anxiety in learn English will drive their self not to
learn. In other words, they will unenjoy in their learning process.
Students who have high level of anxiety and worry constantly can
significantly impair their ability to achieve.
Students who have high levels of anxiety can discourage students
from participating in classroom activities or studying at home, and may
even cause them to lose their self-confidence and motivation for learning
English.
Students who have higher achievement usually have lower anxiety
significantly than students who have lower achievement.
Students’ anxiety doesn’t only come from inside, but also comes from
outside, such as, teacher, parents, environment.
Finally, it can be concluded that the higher anxiety the students have,
the worst English achievement they will get. But, the lower anxiety students
have, the better English achievement they will get. In other words, there is a
correlation between students’ anxiety and English learning achievement.
C. Hypothesis
Based on theoretical and conceptual framework stated before, the
writer formulated the hypothesis of this study namely: there is a correlation
between students’ anxiety and English Learning achievement.
D. Statistical Hypothesis
Statistically, the formulation of hypothesis as follows:
- Ho = There is no correlation between students’ anxiety and their English learning achievement
- Ha = There is a correlation between students’ anxiety and their
28
Research is an important way to get fact of a problem. Research
methodology, more over, is the most significant aspect in conducting a research.
In this chapter, the researcher discusses, The Method of the Research, Variables,
The Place and Time of the Research, Population, Sample and Sampling, Data of
Research, Technique of collecting Data, and Technique of Data Analysis.
A. The Method of the Research
In doing this research, the writer used a survey method through correlation
techniques.
The method used in this study is the correlation research. According to
Gay, Correlational research is a research study that involves collecting data in
order to determine whether and to what degree a relationship exists between two
or more quantifiable variables.1 It means this study is focusing on knowing
correlation between two variables.
B. Variables
In education study, the correlational research is usually used to search
some variables which are estimatable that has a significant role in achieving
successful of teaching-learning process.
According to Suharsimi variable is “everything that will be objects of research or factors that have influence in the phenomena studied.2
Ary states that “Variable is an attribute that is regarded as reflecting or
expressing some concept or construct.3
For example, about achievement and internal motivation, strategy learning,
college attendance intensity, and including anxiety.4
1
Sukardi,Metodologi Penelitian Pendidikan, (Jakarta: PT Bumi Aksara, 2003),p.166.
2
Suharsimi Arikunto,Prosedur Penelitian,(Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta, 1996), p. 99
3
Donald Ary,Introduction to Research in Education;6 th ed, (USA: Wadsworth Group Thomson Learning Inc, 2002),p.30
4
2
The dependent variable of this research is English learning achievement
(variable Y), and the independent variable is students’ anxiety (variable X). In this case, that anxiety in learning English (variable X) is regarded as a factor that
influence students’ English learning achievement (Variable Y). Finally, he tried to correlate both variables.
X Y
Notes:
X = Students’ anxiety in learning English (Independent variable) Y = Students’ English learning achievement (Dependent variable)
= Correlation
C. The Place and Time of the Research
This research was conducted at SMP BHAKTI MULYA 400 Jakarta
Selatan. The research started on January, 11thand was done on January, 12th2013.
D. Population, Sample and Sampling
a. Population
LR Gay in educational research stated “a population is a group to which writer would like to result of study to be generalizable.”5
Suharsimi Arikunto stated that population is “all object of research.”6
And in encyclopedia of educational evaluation stated that population is a set
(a collection) of an elements possessing one or more attributes of interest.7 In
this research, the researcher take all of the first year students of SMP
BHAKTI MULYA 400 Jakarta Selatan. There are fifth classes. The totals of
first year students are 109 students.
5
LR Gay,Education Research,(New York: Macmillian Publishing Company, 1992),p.140
6
Arikunto,Prosedur,.p.115
7Ibid,
Arikunto said that “sample is part population that researched.8Based on this statement the writer took of population to be sample. Furthermore,
Arikunto explained that if the subject is changed, the writer takes 11%. The
researcher took 40 students from 109 students of the sample. They are the
first year students of SMP BHAKTI MULYA 400 Jakarta Selatan.
c. Sampling
The sample is taken using random sampling techniques. Ary said that
random sampling is the best known of the probability sampling procedures
that has basic characteristic is that all members of the population have an
equal and independent chance of being included in the sample.9
Also, Ahmad Tanzeh said that Sampling is the technique to removal of
sample.10
Sampling is the process of selecting units from population of
motivation so that by studying the sample we may fairly generalize result
back to the population from which they were chosen.11
The writer only took 40 respondents as samples that were selected
randomly. The writer gives the questionnaire to all class. Then, the writer
took the questionnaire from every eight students from each class.
E. Data of Research
According to Suharsimi Arikunto his book “ Prosedur Penelitian” he states
that “Data is the result of writer investigation number as fact.”12
Data is the important factor within a research. It is needed by the
researcher to solve problems in his/her investigation. It is some information or fact
to be analyzed by the researcher 13. It mean that data is all information needed by
researcher to find the answers of the research problems. There were two kinds of
8
Arikunto,Prosedur,.p.109
9
Ary,Introduction,.p.141
10
Ahmad Tanzeh,Metode Penelitian Praktis,(Tulungagung :P3M STAIN, 2004), p.57
11
http://www.Social Research Method, Net/kb/sampling.php
12
Arikunto,Prosedur,.p.99
13