The Study of Trans
Novel
Submitted as Partial English Department F
FAC STATE ISLAM
f Translation Shifts in English-Indonesian Tr
ovel
Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows
THESIS
artial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Sarja ment Faculty of Arts and Humanities State Islamic
Sunan Ampel Surabaya
by:
Novi Lely Saputri Reg Number : A33213070
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF ARTS AND HUMANITIES ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY SUNAN AMPEL SURA
2017
ian Translation of
lows
Sarjana Degree of lamic University of
ABSTRACT
Lely Saputri, Novi. 2017. The Study of Translation Shifts in English-Indonesian Translation of Novel Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows. Thesis. Surabaya: English Letters Department, Letters and Humanities Faculty, State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel.
The Advisor : Roudlotul Jannah M. App. Ling Keywords: translation shift, translation, novel
The objective of this research is to find out the kinds of translation shift in English-Indonesian translation. Also, the purpose of this research is to figure out what are the factors that can cause or affect each kinds of translation shift. The theory of translation shift used in this research based on theory of J.C. Catford. This research is conducted the kinds of translation shift analysis, a novel by J. K. Rowling, Harry potter and The Deathly Hallows and its Indonesian translation, Harry Potter dan Relikui kematianby Listiana Srisanti.
The methodology used in this research is qualitative descriptive method. The research is accomplished by the writer by reading and comparing the English text and the Indonesian text. Then the writer compared the data where translation shifts from source language (SL) to target language (TL) occurred. The data are classified according to each kinds of translation shift and the factors that can be caused in translation shift are found after the classification.
The kinds of translation shift found in the translation of Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows to Harry Potter dan Relikui Kematian are lexical shift and category shift. In lexical shift only one kind but in category shift divided into four kinds: structure shift, class shift, unit shift, and intra-system shift.
INTISARI
Lely Saputri, Novi. 2017. The Study of Translation Shifts in English-Indonesian Translation of Novel Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows. Skripsi. Surabaya: Sastra Inggris, Fakultas Adab dan Humaniora, Universitas Islam Negeri Sunan Ampel.
Dosen Pembimbing : Roudlotul Jannah M. App. Ling Kata kunci: pergeseran susunan kata, penerjemahan, novel
Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk menemukan jenis-jenis pergeseran susunan kata yang terjadi pada penerjemahan English-Indonesian. Juga untuk memberikan gambaran, apa saja faktor-faktor yang menyebabkan terjadinya pergeseran susunan kata. Teori penerjemahan dari Catford juga digunakan dalam penelitian ini. Penelitian ini diadakan untuk menganalisis jenis-jenis pergeseran susunan kata yang terjadi pada novel J. K. Rowling yang berjudul Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows dan terjemahannyaHarry Potter dan Relikui Kematian oleh Listiana Srisanti.
Penelitian ini menggunakan metode kwalitatif deskripsi. Penelitian ini diselesaikan oleh penulis dengan membaca dan membandingkan teks bahasa Inggris dan teks bahasa Indonesia. Kemudian penulis membandingkan datanya, dimana pergeseran susunan kata terjadi pada bahasa sumber dan bahasa target. Data diklasifikasikan berdasarkan jenis-jenis pergeseran susunan kata dan menemukan faktor-faktor yang menyebabkannya.
Jenis-jenis dari pergeseran susunan kata yang ditemukan dalam novelHarry Potter and the Deathly Hallows yang diterjemahkan menjadi Harry Potter dan relikui kematian adalah pergeseran leksikal dan kategori penerjemahan. Hanya ada satu jenis dalam pergeseran leksikal sedangkan pada kategori pergeseran dibagi menjadi empat jenis: struktur, kelas, unit, dan intra system.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Inside Cover Page ... i
Inside Title Page... ii
Declaration Page ... iii
Motto... iv
Dedication Page ... v
Advisor’s Approval Page... vi
Examiner’sApproval Page... vii
Acknowledgement ... viii
Table of Contents ... ix
Abstract ... xii
Intisari ... xiii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION... 1
Background of the Study ... 1
Statement of the Problems ... 6
Objectives of the Study... 7
Significance of the Research... 7
Scope and Limitation ... 7
Definition of the Key Terms ... 9
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW ... 10
2.1 Theoretical Framework ... 10
2.1.1 Translation... 10
2.1.2 Procedure of Translation ... 11
2.1.3 Transposition... 12
2.1.4 Grammatical Hierarchy... 15
a. Morpheme ... 16
b. Word... 17
c. Phrase ... 18
d. Clause... 20
e. Sentence ... 21
2.1.5 Pattern of Translation Shifts... 22
1. Level Shift... 22
a. Structure Shift ... 23
b. Unit Shift... 23
c. Class Shift ... 24
d. Intra-system Shift... 24
2.1.6 Cause of Translation Shift... 24
2.2 Review of Related Studies ... 25
CHAPTER III ... 28
3.1 Research Design... 28
3.2 Data Collection ... 29
3.2.1 Data and Data Source... 29
3.2.2 Research Instrument... 29
3.2.3 Techniques of Data Collection ... 29
a) Browsing and Downloading ... 29
b) Close Reading... 29
c) Knowing the Grammatical Hierarchy... 30
d) Selecting the Data ... 31
3.3 Data Analysis ... 32
3.3.1. Identifying the selected data ... 32
3.3.2. Classifying the identified data ... 32
3.3.3. Describing and concluding the data ... 33
CHAPTER IV FINDING and DISCUSSION ... 34
4.1 Finding ... 34
4.2 Discussion ... 35
4.2.1 Grammatical Hierarchy... 35
a) Morpheme ... 35
b) Word ... 37
c) Phrase or Groups... 38
d) Clause ... 40
e) Sentence ... 41
4.2.2 Procedure Translation ... 42
4.2.3 Translation Shift... 43
A. Level Shift... 43
2. Unit Shift... 47
3. Class Shift ... 49
4. Intra-system Shift... 50
4.3 The Factors that caused of Translation Shifts ... 54
(a) Intra-Linguistic ... 54
(b) Extra-Linguistic... 56
CHAPTER V ... 58
A. Conclusion ... 58
B. Suggestion... 59
BIBLIOGRAPHY... 60
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter consists of background of the study, statement of the problems, objectives of the study, significance of the study, scope and limitation, and definition of the key terms.
1.1Background of the study
There has been a great development in this globalization era, such as technology, economy, culture, and so on. Globalization also concentrates in many kinds of race, language, religion, culture and other. Those development causes an insistence of the available informational access grow higher, as in communication aspect for instance. Communication becomes an important thing because every kind of activities needs a good communication to get the advantageous purpose. Therefore, the across language communication is always happen. In a fact, not all of people can understand about another language. Hence, translation becomes bridge between those languages to getting a good understanding.
2
writer can conclude that translation is not only translating but also replacing. There is one process of translation called replacement. From the phrase equivalent textual material, it can be understood that replacing word will refer to the information that will inform the text. Because of that, the information from will understood completely.
In the process of translation, the role of translator is important.Translator is a person who takes written text in one language and converts it into written text with the same meaning in another language. Translator is different with interpreter. Interpreter is a person who listens to a spoken message in one language and converts it into a spoken message with the same meaning in another language. They are having same task, but in different way. Because, interpretation is the process of listening to a spoken message in one language and it will converts into a spoken message with the same meaning in another language. Hence, translation and interpretation is a method to extend information or a message from SL into TL. In this study, the writer focuses on translation process.
When translator is translating the text, it might be changed the structure of the sentence,because every language has different structures. The main Indonesian sentence structure is SVO (subject-verb-object), and this arrangement coincides with the composition in English. For example: “Hindun brings a book” while it replacement into Indonesia “Hindunmembawabuku”. Other languages do not necessarily follow this SVO system. For example, in Arabic which is commonly used
arrangement is VSO, for example:
ب<=>?ا ABھ DEFG, when it replacements into
3
translation like “Hindun brings a book”. The process of changing the structure above is called shifts.This is the reason why a translator is needed to shift the structure of language when translating from one language to another.
In the process of shifts, it is not only change the structure, word class, but also about grammar and lexis. Grammar of a language is the set of rules that govern its structure. Based on oxford dictionary, Grammar determines how words are arranged to form meaningful units. Grammar and structure is unity, and to make a good sentence based on the language structure must be include many words.While lexis itself is all of the words in a language or all word forms having meaning or grammatical function. Thus, in the process of shifts, many forms of words are involved. Because, the structure of two languages are same but form of the word will be different. Therefore, the writer wants to know the shifts by saw the process of translation shift.
4
Hestated that by shift of level he means that a SL item at one linguistic level has a TL translation equivalent at a different level. For example “Tomihas eaten” become “Tomisudahmakan”. From the text in the source language above, it is found that the grammatical item has + V3 (pattern of Past participle tense in English) in the source language is translated into sudah in the target language. So, the level shift in the translation is indicated by grammar in the source language which is translated into lexis in the target language.
Then the type of translation shifts is category shift. Category shifts are departures from formal correspondence in translation. In order to understand more about category shifts, it should be discussed about the classification of category shifts. First of all are structure shifts, it is indicated by a situation when there are two languages which have different element of structure. For example is “I(S) wash(V) myself(O)” becomes “saya(S) mandi(P)”. In the example above, it can be found that the source language has different structure of sentence level and phrase level with the target language. Its translation has different sentence structure in the target language, and from its translation it can be seen that one element that is object myselfin the SL is not translated in TL.
The next is class shift, the word classes might change along with the structure of the word. Here is the example of class shift “they are working slowly” becomes “merekabekerjadenganlambat”. From the example above, the word slowly in SL works as an adverb, and the word lambat in the TL works as an adjective. So the translation equivalent of the adverb slowly in the SL is the adjective in TL.
5
of rank. As we see, the word watch (in low rank) in the SL is translated into a phrase
jam tangan(in higher rank) in TL. The last is Intra-system shifts, there aredifference systems in this shifts. Moreover, in each language, the system is one of two terms, they are singular and plural and the terms are also regarded as formally corresponding. Below is the example of intra system shift: “Balinese people go to exhibition” becomes “Orang Bali menontonpertunjukanitu”. There is a corresponding plural form for people through a repetition of the word orang (orang-orang) in Indonesian, but the Indonesian language system shows it in a singular form orang.
Recently,the areas of study about translation shifts in many fields and have been receiving many attentions of some researchers above. Like the study of Pramuaji (2011) and Yuhezmi(2012) whichanalyzing about translation shift of prepositional phrases, Hariyanti et al. (2015) whose focused on adjective phrases, and Wulandari (2010) who has focused on identifying about the translation shift of noun and noun phrase. Then,this present study intended to followthe previous researchers above with different focus, which mainly explained about phrases. Hence, the writer focuseson the process of translation shift also untranslatability and knowing the rank of translation shift.
Translation shifts can be happened in many fields, such as: movie, novel, poem, lyrics of the song, etc. In this study, the writer will chose one novel of J.K. Rowling with the tittle Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows and its translation as an object. The novel was translated by ListianaSrisanti. There are many problems of shifts in this novel. Such as, A handsome manor house grew out of the darkness at the end of the straight drive, lights glinting in the diamond-paned downstairs windows.
Those sentence will be translated
6
darilurusjalan, cahaya-cahayakilauanpadaberlianmencelaruangbawahjendela, if the translator only replacement.
The text of replacement above was so difficult to be understood, because the structure was so different with Indonesian’s structure. Thus, ListianaSrisanti needs translation shift to treat the translation same as Indonesian structure. Like this sentence, sebuahgedungmegahmunculdarikegelapan di ujungjalankereta yang lurus,
cahayaberkilaupadakaca-kacajendelalantaibawah yang berbentukwajik. She use three kinds of shifts first of all is structure shift, a handsome manor house becomes sebuahgedungmegah. Secondly is unit shift, from higher rank grew out to low rank muncul. The last is intra system-shift, from lightsand windowsbecomescahayaand jendela. She is not only changing the form of the structure, but also including the new term to clearly the translation. Therefore, if Indonesian people read the translation, they will understand completely. That is the reason why the writer uses this novel as her object to be analyzed translation shifts, with the title “The study of Translation Shift in English-Indonesian translation of Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows”.
1.2Statement of the Problems
This study is conducted to answer the problems formulated in the following questions: 1. What kinds of translation shift that found in novel Harry Potter and The Deathly
Hallows?
2. What are the factors that cause of translation shift in novel Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows?
7
Based on the problems above, the objectives of the study are:
1. To know the kinds of translation shift that found in novel Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows.
2. To know the factors that cause of translation shifts innovel Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows.
1.4Significance of the Research
This study has prospect to be one of the resources in translation studies and gives more knowledge about translation shifts that used the theory from Catford. Therefore, the writer hopes that this study is useful for other linguistics researchers whom are interested in studying translation shifts.
Then, this study also gives some information about translation shift and helps the reader to understand aboutthe kinds of translation shift which found in novel Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows and its translation Harry Potter danRelikuiKematian. Especially, for linguist and non-linguist students, they should know that there are many factors that cause of translation shifts.
1.5 Scope and Limitation
The scope of this study will focus on analyzing the kinds of translation shifts. Also to know the factors that cause of translation shifts which found in novel Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows and its translation. This study will be limited by using Catford’s theory as the main theory of translation shifts.
8
important,(Machali,2009). The procedures that must be exceeded are transposition, modulation, adaptation, contextual conditioning, and footnote.
Transposition (Shift) is a procedure of translation that involve to changing the grammatical form for source language into target language. There are two kinds of shifts: they are level shift and category shift. Modulation is the changing of meaning from SL to TL caused by the differences of perspective or point of view or another meaning. For example “environmental degradation” becomes “penurunanmutulingkungan” (the word mutu is implicit in SL). Adaptation is the way to get some meaning between two culture situations. Example “Dear Sir” becomes “DenganHormat” why it is not translating as Tuan
yang terhormat because the culture in Indonesia for opening letter is DenganHormat not Tuan yang Terhormat.
Contextual conditioning is adding information in a context to get clearly meaning for the reader. “hariiniadalahempat-puluhhariibunya Bu Mina. The underlined phrases above cannot be translated to(the eve of) the fortieth day without enclosing the context, that is “of her mother’s death”. Footnote is same with contextual conditioning, but in here there is a note to clear the understanding of reader. For example “Doodgeridoo is a traditional musical instrument used by the Aborigines” becomes “Doodgeridooadalahalat music tradisional yang digunakanoleh orang Aborigin” (catatan:
Doodgeridooadalahalat music yang
bentuknyasepertisulingpanjangdenganujungnyamelengkung, danmengeluarkanbunyisepertisirenekapallaut yang akanberangkat).
9
chooses her analysis in J. K. Rowling’s novel, Harry Potter and The Deathly
Hallows published in 2007.
1.6 Definition of the key terms
The writer gives some the definition of key terms to make clear and to avoid misunderstanding.
1. Translation
Translation is the replacement of textual material in one language or source language (SL) by equivalent textual material in another language or target language (TL) Catford (1965). Translation is not change, but it is replacing the SL into TL. The translator was replacing the word to getting same message. Hence, the translator will change the language but not for the contents.
2. TranslationShifts
Translation Shiftsare departures from formal correspondence in the process of going from the SL to the TL. It is the one of procedure in translation process which is involving the chance of grammatical form from SL into TL. So, in shift or translation, it is only the form that is changed.
3. Harry Potter Novel
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Theoretical Framework 2.1.1 Translation
The translator must understand the definition of translation. There are many definitions of translation taken from many sources that all given by the theorist of it among others is as (Nida, 1969) stated that translation consists of reproducing in the receptor language the closest natural equivalence of the source language message, first in terms of meaning and secondly in terms of style. Another definition from Catford (1965), he explained that translation is the replacement of textual material in one language or source language (SL) by equivalent textual material in another language or target language (TL).The last definition is from Newmark (1988), states that translation is rendering the meaning of a text into another languages in the way that the author intended the text.
11
2.1.2 Procedures of Translation
In the process of translation, the translator must pay attention the procedures of translation. Procedure is the act or manner of proceeding in any action or process. In translation process, there is a procedure that used by translator to transferring the messages. Newmark (1988) stated that translation procedures are used for sentences and smaller unit of language. When we study about fourteen procedures of translation by Newmark, but not all of those procedures are relevant for Indonesian translator. Machali (2009) stated that only five procedures that relevant for translator who is involving Indonesian language as source language (SL) or target language (TL), they are: transposition, modulation, naturalization, contextual condition, and footnote.
Transposition was called shift by Catford. It was a translation procedure which is involving a grammatical changing from source language to target language. Modulation was a translation procedure to define a variation through a change of viewpoint, of perspective and very often of category of though. There are two kinds of modulation, standard modulation and free modulation. Standard modulations are recorded in bilingual dictionaries. It used when the word or phrase of source language does not equivalent, like active become passive or general become specific and vice versa. For example family become keluarga. As we know that in British when talk family, it means father, mother, and brother or sister. It difference with Indonesian, keluarga is not only father, mother, and brother or sister, but also uncle, aunt, nephew, and others.
12
Naturalization is the procedure which succeeds transference and adapts the source language (SL) word first to the normal pronunciation then to the normal morphology (word form) of the target language (TL). For example: the word police in English then it naturalize with Indonesian language becomes polisi. Naturalization was like borrowing.
Contextual conditioning was adding information in the context to clarify the meaning. For example the word mustang, it is like horse. Then need a new word to clarify. The mustang was the fastest in the race becomes kuda mustangituadalah yang tercepatdalampertandingantersebut. Footnote used when there is no equivalent or term that used to explain in the target language. Translator must give a little explanation, like the name of traditional food, traditional term, and so on. Like gado-gado, sarung, batik, jarik, kebaya, and others.
2.1.3 Transposition
Transposition is the term that given by Catford as shift in translation procedure which involving a change in the grammar from source language (SL) to target language (TL). Translation shift is the term that given by Vinay and Darbalnet, it can be known as transposition which involves replacing one word class with other without changing the meaning of the message. In transposition there are two types:
13
2. Optional transposition, translation shift which occur because of the translator’s discretion. In shifts like these, there are formal correspondences, but the translator in light of interpersonal has selected something else.
The translator faces many problems to translate the source language (SL) text into target language (TL) text. There are two kinds of linguistic problems which are faced by Indonesian translators. They are intrinsic difference among the two languages and special problem relating to the standardization process of Indonesian language currently as relative young and developing languages. When translation cannot be carried out closely to the linguistic form of the source text or textual equivalence is achieved in the text, then Catford calls translation shift. From Catford, the concept of shifts is defined in term of departures from formal correspondence in the process of going from the source language (SL) to the target language (TL). He also divides shifts into two major types: level shifts and category shifts.
1. Level shift is SL item at one linguistic level has a TL translation equivalent at a different level. It would be something which is expressed by grammar in one language and lexis in another. Example of shift in linguistic level is the shift from grammar to lexis. Actually, this kind of shift frequently occurs in translation.
For example: SL: Tomy has eaten. TL: Tomy sudah makan
14
2. Category shift is a departure from formal correspondence in translation. Category shift occurs if the source language (SL) has different forms from the target language (TL). This shift is subdivided into four kinds:
a.Structure shift is to be the most common form of shift and involve mostly a shift in grammatical structure. For instance, in SL structure consists of subject, predicate, object while in TL structure consists of predicate, subject, object. That is very different structure.
For example: SL: She is beautiful TL: Diacantik
b. Class shift occurs when the translation equivalent of SL item is a member of a different class from the original item. This comprises shift from one part of speech to another.
For example: SL: medical student (adjective + noun) TL: mahasiswakedokteran (noun + noun)
In the example above, the word medical in SL (English) is an adjective, while its translation in Indonesiaankedokteran is a noun. Here, the translation equivalent has different class from the original item.
c.Unit-shift means change of rank – that is, departures from formal correspondence in which the translation equivalent of a unit at one rank in the SL, is a unit at a different rank in the TL. ‘Rank’ here refers to the hierarchical linguistic units of sentence, clause, group, word and morpheme.
For example: SL: after getting the job, ……
15
In the SL, after getting the job is a group of words, while its translation equivalent in Indonesia, setelahdiamendapatkanpekerjaanitu is a clause, since it has a subject (dia) and a predicat (mendapat).
d. Intra-system shift occurs internally, within a system; that is, for those cases where SL and TL possess systems which approximately correspond formally as to their constitution, but when translation involves selection of a non-corresponding term in the TL system. For instance, both Indonesia Language and English Language have a system of number, but the numerical system is not essentially the same. Some nouns in English are always in plural form, but their equivalent translation in Indonesian language may take form of singular noun.
For example: SL: This is the place for rabbits. TL: Ini tempat untuk kelinci.
Exactly, the word of rabbits can translate uses kelinci-kelinci, but in this case translator uses kelinci not kelinci-kelinci. It means in the discretion of translator which one is they like to use those verb in their work. In a significant cases, it is called intra system-shifts (plural become singular or just the opposite).
2.1.4 Grammatical Hierarchy
In the point of translation shift above, the writer has explained about the kinds of translation shift and its process. In this section, the writer is going to recover further about the elements that related with translation shift and as well, also about grammatical hierarchy and rank scale.
16
grammatical hierarchy, from the larger units being made up of smaller units or vice versa. They form a scale of units with different rank that is called rank scale.
In English grammar, there are five units; sentences, clause, group, word and morpheme. Sentence is the highest on the rank scale and morpheme is the smallest on the rank scale. Both those, there is clause, group and word. By placing these in this order on the rank scale, it can be conclude that every sentence consist of more than one clause, every clause of one or more group, every group can be followed by one or more word, and every words of one or more than one morpheme.
In addition, in explaining about grammatical hierarchy and units of English, those need to be explained more. Actually there is no difference between English/Indonesian Grammatical and units. Indonesian grammatical hierarchy also has five units, morfem (morpheme), kata (word), frasa (phrase/group), klausa (clause), and kalimat (sentence). Hence, for grammatical hierarchy of English and Indonesia is closely same.
a. Morpheme
Morpheme is the smallest part of words. Whereas the area of grammar concerned with the structure of words and with relationships between words that involving the morphemes that compose them is technically called morphology (Carstairs&Carthy, 2002). There are two kinds of morphemes, bound and free. Bound morpheme is the morpheme that cannot stand on their own, while free morpheme is the morphemes that can stand on their own. In Indonesian language free morpheme is called morfembebas and bound morpheme is called morfemterikat (Chaer, 2008).
17
which are occur only before other morphemes and it called prefix. In Indonesian language also have prefix which is called prefiks, like me- (mengenal), ber- (berlari), pe- (pembaca and pelajar), and so on.
Other morphemes occur only as suffixes that following by other morphemes. The examples of English suffix are: -er (singer, reader, writer, player, and so on), -ist (pianist, novelist, linguist, and so on), and –ly (friendly, beatifully), to mention only few. In Indonesian also has suffix which is called sufiks. –an (permainan, tontonan, bisikan), -kan (kembalikan, ambilkan, kerjakan), and –I (guntingi, potongi, sirami), etc.
Indonesian language also has bound morpheme that is called konfiks, that is coming together in the beginning and the end of the word. For the example of konfiks are ke - an (keterampilan, ketakutan, kelihatan), ber - an (bermandikan, berlumuran, bercucuran), etc.
Those prefixes and suffixes also konfiks in Indonesian language are bound morphemes because they cannot occur unattached. It is different with some morphemes like friend, magic, fly, cool, and so on. Those morphemes are called free morphemes, while in Indonesian language those are sekolah, rajin, senang, and others.
b. Word
18
Verbs
Verbs is the word which indicates the activity that doing by subject, or as a connected between subject and complement. Example of verbs in English are eat, sleep, drink, see, etc. while example of Verbs in Indonesian language are makan, minum, tidur, etc.
Nouns
Noun is a part of speech that identifies a person, place, thing, or idea. For the example is man, flower, shoe, mountains, etc. while in Indonesian is sinta, tikus, rumah, meja, kursi, etc.
Pronouns
Pronoun is a word that is used instead of a noun or noun phrase. Example pronoun in English is them, you, it and so on. In Indonesian language also has a pronoun, like –nya in a word bukunya.
Adjectives
Adjective is the word that describes or clarifies a noun. Adjectives describe nouns by giving some information about an object’s size, shape, age, color and so on. Like in this example, a very tall man. While in Indonesian language is,bungamawaryang indah.
Adverbs
Adverb is a word that describes or modifies as grammarians put it in a verb, an adjective or another adverb. Like in sentence, a very pretty girl was in the car. Example in Indonesian Rani bekerja di rumahsakit,diajugabekerjadengangiat. c. Phrase or groups
Phrase is a group of words which has a relation without a subject and a predicate, like the man, on the table, with one of word has a functional as a parts of speech.
19
A noun phrase consists of a noun and all the word groups that belong with the noun and cluster around it. The noun itself is called head, and the other words and words groups are modifiers of the noun. For the example in the word blackboard: the white cat.
In the noun phrase, commonly use one modifier of a head, a determiner as: the white cats are eating and a white cat is eating. Determiner are the anda, which are the most common first elements in noun phrases. But, commonly modifiers of nouns are adjectives. The pattern is determiner + adjective + noun which is a very familiar in noun phrase. As in a tall girl, the old man, the handsome boy. In Indonesian language also has noun phrase like: bajubaru (baju as a head and baru as a modifier).
Verb Phrase
The special kind of construction made up of a main verb and certain other elements from a list of auxiliaries that is called verb phrase. The example of verb phrase is Nothing has been decided, has been decided is a verb phrase. While in
Indonesian language, example of verb phrase is
mulaibesukandasudahbolehbekerja, sudahbolehbekerja is a verb phrase. Adjective phrase
In adjective phrase is any phrase which modifies a noun or pronoun. Example in English of adjective verb is Nina is a beautiful girl,beautiful girl is an adjective phrase. While in Indonesian language Amaliamemetik manga yang belummasak, yang belummasakis an adjective phrase.
20
Adverb phrase is a group of words which gives an additional detail about the meaning of a verb or an adjective or another adverb. For example is my grandmother came to my house two days ago, two days ago, explains the word came. In Indonesia also has adverb of phrase, example is kami makanikanbakardi sebuahrestoran.
d. Clause
Clause is a group of words which has a relation that is consist of subject and predicate. There are two kinds of clause, independent clause and dependent clause. Independent clause is a complete sentence that contains the main subject and verb of a sentence. It also called main clause. Dependent clause is not a complete sentence and it must be connected to dependent clause. For example, Agathon has always been a good student (independent clause). Unless you have a better idea, I suggest that we follow the original plan. Unless you have a better idea andthat we follow the original planare called dependent clause.
There are three kinds of dependent clause: Adjective clause
Adjective clause is a dependent clause that modifies a noun or pronoun. It will describe, identify, or give further more information about a noun or pronoun. It also called a relative clause.
21
Adverb clause
Adverb clause is a clause that does the work of an adverb. Like this examples it was cold, when we went out. Before I left for work, I ate breakfast. The clause before I left for work is explains word ‘ate’. The example of adverb clause in Indonesian language is Ratihmakansebelumpergikesekolah.
Noun clause
Example when noun clause as a subject, what he does is his business. Example when noun clause as an object is I believe that you have met maydia.
Example of noun clause in Indonesian language as a subject is siapa yang menirukanataumemalsukanuangakan di tuntut di pengadilan. While example of noun clause function as an object is pemerintahmengumumkanbahwaharga BBM akannaik.
e. Sentence
Sentence is a grammatically complete construction and it does not need the help of other construction to make its grammatical meaning clearly. Carstairs and Carthy stated that sentences come later when words are strung together meaningfully. That is not to say that a sentence must always consist of more than one word.
According to its structure, sentence will divide into three classes: Simple sentence
22
Compound sentence
Compound sentence is the sentence which is consists of one or more dependent clause. Like the example, the moon was bright and we could see our way.
Example of Indonesian compound sentence is
andadatangkerumahsayaatausayadatangkerumahanda. Complex sentence
Complex sentence is the sentence that consist of one independent clause and one or more dependent clause. Example of complex sentence in English is since no one else is here, I shall do whatever is necessary myself. While example of complex sentence in Indonesian language is Dian barusajamenonton film yang menempatiurutanteratas di box office mingguini.
2.1.5 Pattern of Translation Shifts
As the writer explains above based on Catford’s theory there are two kinds of translation shifts. Those are level shifts and category shifts. Every kinds of shift have different pattern, like the picture below.
Level Shift
Source Language (English) Grammar of SL
Target language (Indonesian Language) Lexis in TL
To be + verb + ing Sedang
Had/ has/ have + verb3 -telah
-sudah
23
Category Shifts
Category shifts are departures from formal correspondence in translation. It divided into four kinds of category shifts.
a. Structure Shifts
Structure shift is the shift that occurs in the structure or arrangement of sentence or a clause, sometimes also find in a group.
b. Unit Shifts
In unit shifts, it means that changes of the rank which is departures from formal correspondence in which the translation equivalent of a unit at one rank in the SL is a unit at a different rank in the TL.
Downward rank Shift
Source Language (English) Target Language (Indonesian language)
Clause Phrase
Phrase Phrase
Phrase Word
Upward rank Shift
Source Language (English) Target Language (Indonesian Language)
Word Phrase
Phrase Phrase
Phrase Clause
c. Class Shifts
Class Shifts is the shift when the translation equivalent of a SL item is a member of a different class from the original item.
Source Language (English) Target Language (Indonesian language)
S+V+O S+V
S+V+O V+S+O
Modifier + Head Modifier + Head + Qualifier
24
Source Language (English) Target Language (Indonesian language)
Adjective Noun
Noun Verb
Noun Adjective
Verb Noun
d. Intra-system Shifts
Source Language (English) Target Language (Indonesian language)
Singular Plural
Plural Singular
Intra-system shift is only could the mean departure from formal correspondence in which one system in the SL has as its translation equivalent a different non corresponding-system in the TL.
2.1.6 Cause of Translation Shift (a) Intra-linguistic
1. Grammatical construction between the source language SL and target language (TL) vary. In source language (SL) using tenses to indicate the time of event, but target language (TL) does not use tenses. For example: he had been thinking::diatadisedangmemikirkanalmarhumkepalasekolahnya.
2. Sentence organization between the source language (SL) and target language (TL) was different. Sometimes in the target language can be adding a new word and it will disappearance a part of sentence, and so on. For example: he had imaged :: diamembayangkannya.
25
Larson’s theory about this cause of translation shift goes along with Catford’s theory about translation shift itself.
(b)Extra-linguistic
It was consist of cultural diversities and translators choices. Like the differences of pluralities concept of certain word that happened in intra-system shift.
2.2 Review of the Related Studies
There are some studies supporting this research that have relation to translationshifts theory. First is study is from Suhaila (2010). She studied about unit shift then the objective of her research is to find out the patterns of unit shift in English Indonesian translation. The purpose of her research is to figure out what are the factors which can cause or affect each unit shift. The theory of unit shift used in her research is based on translation shift theory by J. C. Catford. She used qualitative descriptive method to explain her research. There are two results of this research. First is, based on the theory J. C. Catford, the patterns of the unit-shifts found by hers in the unit analysis are: morpheme to word, word to phrase, phrase to word, phrase to clause, clause to word, clause to phrase, and clause to sentence. Second is, she also analyzed the cause of unit shifts based on characteristics by Mildred L. Larson. Some of the shifts like combative: sukabertempur, son: anaklaki-laki, oldest brother: sulung, occurs because the lexical aspects.
26
of Harry Potter and the Philosopher’s stone into Indonesia subtitle, what is the dominant category shift found in the movie of Harry Potter and the Philosopher’s stone into Indonesia subtitle. The data of his research were taken from the movie subtitle of Harry Potter from English into Indonesia by Togap. The result of his study was founding all kinds of category shifts in the subtitle of Harry Potter and the Philosopher‟s stone Movie. The category shifts used are: unit, structure, class, and intra-system shifts. Then, the researcher also founds that the dominant category shifts used in the subtitle of Harry Potter and the Philosopher‟s stone movie subtitle is Unit Shift. It can be seen by him in counting the shifts from the subtitle of Indonesia byTogap. The next dominant is structure shifts.The most difference between Indonesia and English language is the position of Head-Modifier and Modifier-Head.
27
Structure Shift with 59 phrases with 55,7%; the second level is Unit Shift with 23 phrases or 21,7%, the third level is Intra System Shift with 16 phrases with 15,1%, furthermore the forth level is Class Shift with 8 phrases or 7%.
The last is study about translating demonstrative by Novianti (2009).This study aims to find out the strategies applied by the translator in translating the demonstrative references in the novel. The data source of her research is the whole text of Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets, written by J.K Rowling and its translated version by ListianaSrisanti. The result of the analysis shows that there are five strategies applied to render the demonstrative reference in the novel, they are; literal translation, structural adjustment, shifting, amplification, and deletion. She also found those percentages.
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter describes the research methodology that used to conducting the
study. It consists of research design used, including: data and data sources,
instruments, technique of data collection and techniques of data analysis.
3.1 Research Design
Based on the purpose of the study, this study aims to find the kinds of
translation shifts which find out in novel of Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows
and its translation Harry Potter danRelikuiKematian and the factors that caused of
translation shifts that found in the novel. This study used content analysis.
Krippendorff (2014) stated that content analysis is techniques of analyze texts in order
to make inferences concerning the texts through the context of its use. There are some
classifications of content analysis design in term of inferences, they are: explorations,
standards, indices and symptoms, linguistic representation, and conversation. In this
study, the researcher focused on linguistic representation which concern on one of
translation problem. Then the writer applied data language data component of content
analysis to explain the conclusion.
Based on Krippendorff there are three criteria of applying data language
component in content analysis. Those criteria are: (1) data languages should not
consist of syntactical ambiguities and inconsistences, (2) it should fulfill the
requirements of analytical techniques, and (3) it must consist of information related to
the issue of phenomena so that the researcher can get satisfaction toward the research
conclusion. Hence, content analysis design was the reasonable technique of research
29
problem of translation especially in translation shift of J.K. Rowling’s novel entitled
“Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows”.
3.2 Data Collection
3.2.1 Data and Data Source
The data source of this study was literary work that is the novel of J.K.Rowling,
Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows. It was the last novel of J.K.Rowling and it
was published on July, 2007. The novel was downloading on
www.download-3204605-book.7.deathly.hallows.pdf. Meanwhile, the data were sentences and the
kinds of translation shift that is described in it translation.
3.2.2 Research Instrument
The research instruments for this research is human because she will fully collect
and analyze the data by herself. Moreover, she will also use some supporting tools,
such as: computer, papers, pen, and so on.
3.2.3 Techniques of Data Collection
The data will be collected from the novel of J. K. Rowling with the title Harry
Potter and The Deathly Hallows and its translation. There are some steps that the
researcher will do in collecting the data:
a) Browsing and downloading
Since the novel was form of PDF, the researcher firstly browsed and downloaded in
the website address of digital library,
www.download-3204605book.7.-deathly.hallows.pdf
b) Close reading
After the novel was downloading the researcher was reading carefully and repeatedly
30
c) Knowing the grammatical Hierarchy
1. Morpheme
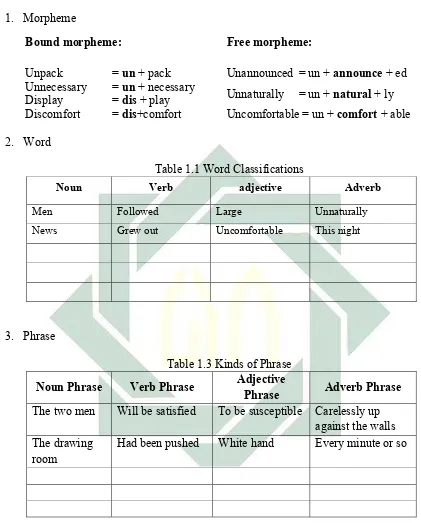
Bound morpheme:
Unpack = un + pack Unnecessary = un + necessary Display = dis + play Discomfort = dis+comfort
Free morpheme:
Unannounced = un + announce + ed
Unnaturally = un + natural + ly
Uncomfortable = un + comfort + able
[image:40.595.88.509.88.611.2]2. Word
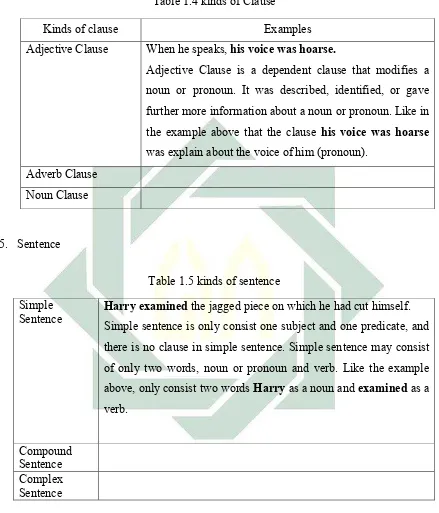
Table 1.1 Word Classifications
Noun Verb adjective Adverb
Men Followed Large Unnaturally
News Grew out Uncomfortable This night
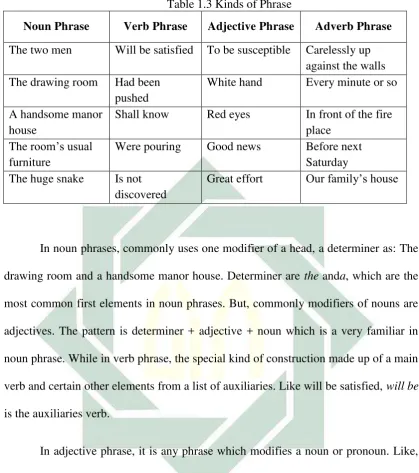
3. Phrase
Table 1.3 Kinds of Phrase
Noun Phrase Verb Phrase Adjective
Phrase Adverb Phrase
The two men Will be satisfied To be susceptible Carelessly up against the walls The drawing
room
31
[image:41.595.94.533.115.628.2]4. Clause
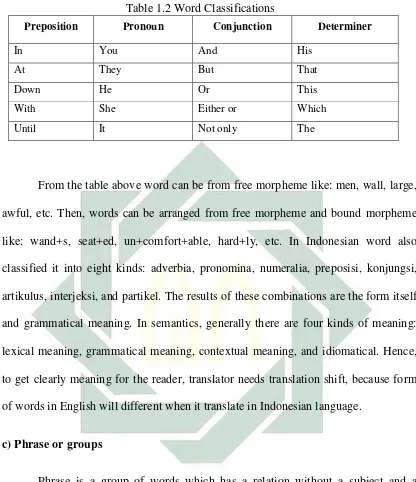
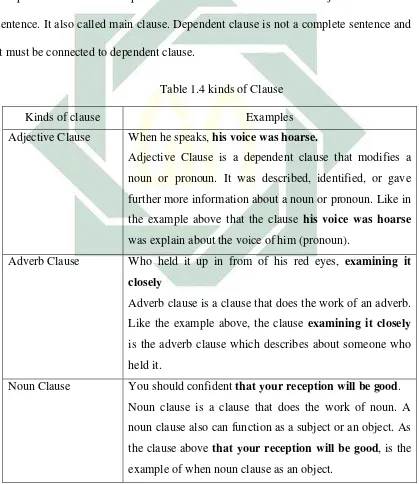
Table 1.4 kinds of Clause
Kinds of clause Examples
Adjective Clause When he speaks, his voice was hoarse.
Adjective Clause is a dependent clause that modifies a
noun or pronoun. It was described, identified, or gave
further more information about a noun or pronoun. Like in
the example above that the clause his voice was hoarse
was explain about the voice of him (pronoun).
Adverb Clause
Noun Clause
5. Sentence
Table 1.5 kinds of sentence
Simple Sentence
Harry examined the jagged piece on which he had cut himself.
Simple sentence is only consist one subject and one predicate, and
there is no clause in simple sentence. Simple sentence may consist
of only two words, noun or pronoun and verb. Like the example
above, only consist two words Harry as a noun and examined as a
verb.
Compound Sentence Complex Sentence
d) Selecting the data
After understanding the story, the researcher then selected the data, kinds of
translation shifts which happen in the novel. In this part, the writer uses two kinds of
32
The data of translation shifts were selected by underline, and
The data of untranslatability were selected by highlighting
The selecting data were like this example:
3.3 Data Analysis
To analyze the data, the writer will use the following steps:
1.3.1 Identifying the selected data
After all the data were selected, then the writer identified the data that indicated the kinds
of translation shifts. This step is conducted to answer problem number one that is to
know the process of changing the SL into TL. In this case, the writer focuses on four
kinds of category shifts based on Catford theory. The four kinds of category shifts
includes: structure shift, unit shift, class shift, and intra-system shift.
The data identification was done by coding the selected texts. The coding used
abbreviations that indicate each process. The abbreviation LS was for level shift, SS was
for structure shift, US was for unit shift, CS was for class shift, and IS for Intra system
shift. Below was picture for the example of coding.
1.3.2 Classifying the identified data.
In this step, the researcher presents the rank shift category based on Catford’s
framework (1965) used in novel Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows and its
33
level is intra system shift, and then the forth level is class shift. The table of frequency of
distribution of each kind of shift category used in novel Harry Potter and The Deathly
Hallows, can be seen as follows:
The tables of data classification will be completely shown in appendixes.
Meanwhile, the analyzed of data will explain in this section by the writer. She will
explain the process of translation shift and the term which cannot translate by the
translator.
1.3.3 Describing and concluding the data
The next step is describing and explaining the whole data to infer and to validate the
data. Then, the inferences of the data will be related effect analyzed. Thus, the
conclusion will result valid and detail explanation. USS
CHAPTER IV
FINDING AND DISCUSSION
This chapter explains the finding data of the research and the discussion
concerning the result of analysis. It deals with the dominant shifts and the process of translation shifts by ListianaSrisanti in the Harry Potter’s novel.
4.1 Finding
Based on the analysis, the writer finds all of the kinds of translation shifts, they are: Lexical Shift, Category Shift (Structure Shift, Unit Shift, Class Shift, and
Intra-system Shift). Those two kinds are one of procedure translation that is used by translator to translate the novel. In addition, the writer also finds the process of translation shifts and the words which cannot translate or untranslatability, like
magical terms.
In this study, the writer divides the findings into two sub points that are
appropriate to answer each problem, these are. First, sub point explains the kinds of translation shift that found in the novel. The second point explains the factors that
cause of translation shifts.
Translation shifts can be indicated from the small linguistic changes that occur between source language (SL) and target language (SL). Two kinds of translation
shifts as the researcher explain above: level shift and category shift. Moreover, there are two kinds of translation shifts: lexical shift and category shift according to Catford
35
kinds and the process of translation shift can be found by understanding the grammatical hierarchy of the two languages. Therefore, the writer firstly must
understand about grammatical hierarchy between English as source language (SL) and Indonesian as (target language), later the writer finds the factors that cause of
translation shifts in novel Harry Potter and The deathly Hallows.
4.2 Discussion
4.2.1 Grammatical Hierarchy
Before going to analyzing the translation shift, for the first, the writer must understand about grammatical hierarchy. In English grammar, there are five units: sentence, clause, group, word and morpheme. Sentence is the highest on the rank
scale and morpheme is the smallest on the rank scale. Both those, there is clause, group and word. By placing these in this order on the rank scale, it can be concluded
that every sentences consist of more than one clause, every clause of one or more group, every group can be followed by one or more word, and every words of one or
more than one morpheme.
a) Morpheme
Morpheme is the smallest part of words. Whereas the area of grammar concerns with
the structure of words and relationships between words that involving the morphemes that compose them is technically called morphology (Carstairs&Carthy, 2002). There are two kinds of morpheme: bound morpheme and free morpheme. Let see the
examples bellow:
Bound morpheme:
36
Display (p.50) = dis + play Discomfort (p.52) = dis + comfort
From the examples above, the bold words were bound morpheme, because they
cannot stand on their own.
Free morpheme:
Unannounced (p.33) = un + announce + ed Unnaturally (p.43) = un + natural + ly Uncomfortable (p.52) = un + comfort + able
While the examples above, the bold words are free morpheme because they can stand on their own. In Indonesian language, free morpheme is called
morfembebas and bound morpheme is called morfemterikat (Chaer, 2008).
Morfembebas (free morpheme):
“Kedualaki-lakiitumunculbegitusaja, berjarakbeberapa meter di jalankecildisinaricahayabulan.” (p.11)
Free morpheme is the morpheme that there is no relevance with other morpheme and it can use in linguistic function, stated by (Chaer, 2008). From the example above the
bold word is free morpheme or morfembebas: muncul, jarak, jalan, and sinar.
Morfemterikat (bound morpheme):
“SnapedanYaxleydiamsejenak di
37
Based on Chaer’s statement that bound morpheme is the morpheme that it cannot use
in linguistic form without adding another morpheme. Like this examples bellow:
- menyesuaikan = menye + sesuai + kan - ketiadaan = ke + tiada + an - pandangan = pandang + an - tertarik = ter + tarik - keatas = ke + atas - sesosok = se + sosok - tergantung = ter + gantung - bayangannya = bayang + an + nya
From the examples above, the bold words are bound morphemes because they cannot stand on their own. In other word bound morpheme same with affixation.
b) Word
The second unit of grammatical hierarchy is word. Word is combination from bound morpheme and free morpheme. Free morpheme is the morphemes that can stand on their own. In other word free morphemes constitute words by themselves, it
can be concluded that word is free morpheme. Based on the kinds and combinations of morphemes which is composed them, based on the function of the word or word
[image:47.595.113.528.138.536.2]classes, it is divided into eight kinds: noun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, pronoun, conjunction, and determiner. Let see the table bellows.
Table 1.1 Word Classifications
Noun Verb adjective Adverb
Men Followed Large Unnaturally
News Grew out Uncomfortable This night
Wands Seated Awful Excitedly
Wall Took Anxious Hardly
[image:48.595.106.522.91.573.2]
38
Table 1.2 Word Classifications
Preposition Pronoun Conjunction Determiner
In You And His
At They But That
Down He Or This
With She Either or Which
Until It Not only The
From the table above word can be from free morpheme like: men, wall, large, awful, etc. Then, words can be arranged from free morpheme and bound morpheme like: wand+s, seat+ed, un+comfort+able, hard+ly, etc. In Indonesian word also
classified it into eight kinds: adverbia, pronomina, numeralia, preposisi, konjungsi, artikulus, interjeksi, and partikel. The results of these combinations are the form itself
and grammatical meaning. In semantics, generally there are four kinds of meaning: lexical meaning, grammatical meaning, contextual meaning, and idiomatical. Hence, to get clearly meaning for the reader, translator needs translation shift, because form
of words in English will different when it translate in Indonesian language.
c) Phrase or groups
Phrase is a group of words which has a relation without a subject and a
[image:49.595.104.524.75.549.2]
39
Table 1.3 Kinds of Phrase
Noun Phrase Verb Phrase Adjective Phrase Adverb Phrase The two men Will be satisfied To be susceptible Carelessly up
against the walls The drawing room Had been
pushed
White hand Every minute or so
A handsome manor house
Shall know Red eyes In front of the fire place
The room’s usual furniture
Were pouring Good news Before next Saturday The huge snake Is not
discovered
Great effort Our family’s house
In noun phrases, commonly uses one modifier of a head, a determiner as: The drawing room and a handsome manor house. Determiner are the anda, which are the
most common first elements in noun phrases. But, commonly modifiers of nouns are adjectives. The pattern is determiner + adjective + noun which is a very familiar in
noun phrase. While in verb phrase, the special kind of construction made up of a main verb and certain other elements from a list of auxiliaries. Like will be satisfied, will be is the auxiliaries verb.
In adjective phrase, it is any phrase which modifies a noun or pronoun. Like, to be susceptible and white hand. Susceptible and white are an adjective. Meanwhile, adverb phrase is a group of words which gives an additional detail about the meaning
of a verb or an adjective or another adverb.
In Indonesian structure also have four kinds of phrase: frase nominal, frase
verbal, fraseajektifal, and frasepreposisional. Same with English, frase nominal is phrase which takes position as a subject or an object in the clause, like: ayah ibu, sawahladang, etc. Frase verbal is phrase which takes position as a verb (ptedikat) in
40
phrase which takes position as a verb (predicat) in the adjctive clause, like: jauhdekat, ramahdansopan, sangatindah. Then frasepreposisional is phrase which takes position
as an adverb in the clause, like: di pasar, dengantongkatnya, padaMuggle.
d) Clause
Clause is a group of words which has a relation that consists of subject and predicate. There are two kinds of clause, independent clause and dependent clause. Independent clause is a complete sentence that contains the main subject and verb of a
[image:50.595.112.531.268.752.2]sentence. It also called main clause. Dependent clause is not a complete sentence and it must be connected to dependent clause.
Table 1.4 kinds of Clause
Kinds of clause Examples
Adjective Clause When he speaks, his voice was hoarse.
Adjective Clause is a dependent clause that modifies a noun or pronoun. It was described, identified, or gave further more information about a noun or pronoun. Like in the example above that the clause his voice was hoarse was explain about the voice of him (pronoun).
Adverb Clause Who held it up in from of his red eyes, examining it closely
Adverb clause is a clause that does the work of an adverb. Like the example above, the clause examining it closely is the adverb clause which describes about someone who held it.
41
Whereas in Indonesian also have many kinds of clause: verb clause (klausa verbal), noun clause (nominal clause), adjective clause (klausaajektifal), and
prepositional clause (klausapreposisional).
e) Sentence
Sentence is a grammatically complete construction and it does not need the help of other construction to make its grammatical meaning clearly. Carstairs and Carthy stated that sentences come later when words are strung together meaningfully.
[image:51.595.108.531.251.731.2]It does not say that a sentence must always consist of more than one word, based on its structure sentence will divide into three kinds:
Table 1.5 kinds of sentence Simple
Sentence
Harry examined the jagged piece on which he had cut himself. Simple sentence is only consist one subject and one predicate, and there is no clause in simple sentence. Simple sentence may consist of only two words, noun or pronoun and verb. Like the example above, only consist two words Harry as a noun and examined as a verb.
Compound Sentence
He not only won every prize of note that the school offered, he was soon in regular correspondence with the most notable magical names of the day.
Compound sentence is the sentence which is consists of one or more dependent clause. He not only won every prizeand he was soon in regular correspondence.
Complex Sentence
She was angry with Harry about the limited amount of time she was allowed out of her cage at the moment.
42
In generally, Indonesian language and English has same grammatical hierarchy. They have morpheme, word, phrase, clause, and sentence. But, the way to
arrange word, phrase, clause, and sentence can be different. For translator, conveying the message is the first point that they must do, the best message is cannot see by the best translation. Therefore, translator must change the grammatical structure, the
arrangement of word form, or word classes to get the best message and their translation can acceptance by people who use target language (Indonesian), then
procedure translation takes play role.
4.2.2 Procedure Translation
As the translator, they must work hardly to get the message from source
language (SL) and then convey it by rewrote into target language (TL). To rewrite again the texts, the translator need a procedure of translation. As the writer was
explained above there are five procedures that that relevant for translator who is involving Indonesian language as source language (SL) or target language (TL), they are: transposition, modulation, naturalization, contextual condition, and footnote.
(Machali,2009). In this study, the writer only focus on first procedure, that is transposition.
Transposition is the shiftiest in translation procedure which involving a change in the grammar from source language (SL) to target language (TL). There are two
kinds of transpositions: obligatory transposition and optional transposition. Obligatory transposition, translation shift which occur because of the discrepancies in the lexical grammatical system between SL and TL, the compensatory device for the discrepancy
43
While optional transposition is the translation shift which occurs because of the translator’s discretion. In shifts like these, there are formal correspondences, but
the translator in light of interpersonal has selected something else. And when translation cannot be carried out closely to the linguistic form of the source text or textual equivalence is achieved in the text, then Catford calls translation shift. Hence,
the writer used second types of procedure translation as the case in this study, which analyze translation shift.
4.2.3 Translation shift
Translation shift is one of translation problem, when translation cannot be carried out closely to the linguistic form of the source text or textual equivalence is
achieved in the text. As the writer explains above, there are two kinds of translation shift: level shift and category shift that found in novel Harry Potter and The Deathly
Hallows.
A. Level Shift
The writer have already pointed out that level in level shift mean a source
language (SL) item at one linguistic level has a target language (TL) translation equivalent at a different level. Because translation between the levels of phonology
and graphology, or between either of these levels and the levels it was of grammar and lexis is impossible. Hence, translator needs level shifts in translation shift.
Level shift is the shift which happened from level of grammar into lexis or
vice versa. It means that a grammatical of language (like in English which has pattern Have+V3), because every language has different grammar. As we know that in
44
does not know about tenses. Then, to solve the problem of the differences pattern between English and Indonesia, translator needs a change of grammatical pattern.
Like level shift, if in English has grammatical pattern (have/has/had+V3/V+ing) and it
must translate become word (lexis) of another language, as in Indonesia using word “telah” or “sudah”. (Machali,2009)
(Data 1)
SL : there was no other explanation; imagined it, because he had been thinking of his dead headmaster. (p.29)
TL : taka da penjelasan lain; membayangkannya karena dia tadi sedang memikirkan almarhum kepala sekolahnya. (47)
If in the first example, the sentence show that the activity start in the past and still do
until now or called past perfect continuous tense. The pattern is (Had+been+V+ing)
“had been thinking”, and it has translated become “sedang” because in that time still
happened.
(Data 2)
SL : You and your aunt and uncle are going your separate ways tonight, in the full understanding that you’re never ………. (p.46)
TL : Kau dan bibi dan pamanmu telah berpisah jalan malam ini, dengan pengertian penuh bahwa ………. (p.71)
In the Data 2, the sentence shows that the activity was temporary activity, it may happen before the speaker speaks. In English pattern it called present continuous tense
with pattern (to be + V+ing). If it was in the example above “are going your separate”
45
(Data 3)
SL : Two figures had appeared in the yard, and as Harry ……. (p.66) TL : Dua sosok telah muncul di halaman dan ketika harry …… (p.102)
From the example above, “had appeared” is the pattern of past perfect (had+V3)
which is showing that the activity has been done. Because the activity has been done, then in target language (TL) has translated become lexis “telah”.
All of the sentences above can conclude that they have different pattern but it was a grammar. Since in level shift need the change from grammar to lexis and those
grammar was translated become lexis (there is lowering level) also. Hence, whatever the structure, if it was translated become lexis, it was called level shift.
B. Category shift
The second kind of translation shift was category shift. It was happened when the shift of tran