i
DEPARTMENT OF IAIN SURAKARTA
THESIS
By:
AMBARWATI
SRN. 143221179
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
CULTURES AND LANGUAGES FACULTY
THE STATE ISLAMIC INSTITUTE OF SURAKARTA
iv
This thesis proudly dedicated to:
1. The researcher‟s beloved parents (Bapak Ngadiman and Ibu Masiyem) who always give their loves, supports, and motivations
2. My second parents Drs. K. H. M. Ismail Thoyib, M. Pd and Ibu Nyai Nur Fauziah in Al-Istiqomah Islamic Boarding House Kartasura and also K. H. Minanul Aziz Asy-Syathori, M. Pd and Ibu Nyai Indiana Ajeng Putri in An-Najah Gondang Islamic Boarding House
v
Every single person has their advantages and disadvantages. Kami tidak bisa berimajinasi
Kami tidak punya khayalan
Kami tak bisa bersosialisasi
Namun, bukan kami bodoh
Mama Papa jangan sedih
Kumampu berprestasi
Teman, jangan kecil hati
Ayo buktikan
Mungkin cara Tuhan beri kita keganjilan
Tunjukkan pada dunia tentang Maha Kuasa-Nya
(piece of song entitled “Autisme”, created by The Head of SLB Negeri Semarang,
vii
Alhamdulillahirabbil‟alamin, all praises be to Allah, the single power, the
Lord of the universe, master of Day of Judgment, for all blessing and mercies so
the researcher was able to finish this thesis entitled “Profile of Autism Student in
Reading Comprehension at English Education Department of IAIN Surakarta”. Peace be upon Prophet Muhammad SAW, the great leader and good inspiration of the world revolution.
The researcher is sure that this thesis would not be completed without the helps, supports, and suggestions from several sides. Thus, the researcher would like to express her deepest thanks to all of those who had helped, supported, and suggested her during the process of writing this thesis. This goes to:
1. Dr. H. Mudofir, S. Ag., M. Pd., as the Rector of the State Islamic Institute of Surakarta
2. Dr. H. Giyoto, M. Hum., as the Dean of Cultures and Languages Faculty of the State Islamic Institute of Surakarta
3. Dr. Imroatus Solikhah, M. Pd., as the Head of the English Education Department in Cultures and Languages Faculty and as Advisor for her guidance, preciously advice, and motivations for the researcher
ix
B.Limitation of the Problem ... 9
x
D.Learning Style of Autism ... 33
E. WCC (Weak Central Coherence) ... 34
F. Testing of Reading Comprehension ... 37
G.Biography of Subject ... 40
H.Inclusive Education ... 42
I. Previous Study Related to The Topic ... 44
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
F. Technique of Collecting Data ... 51
G.Technique of Analyzing Data ... 52
H.Trustworthiness of the Data ... 54
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION A.Research Findings ... 56
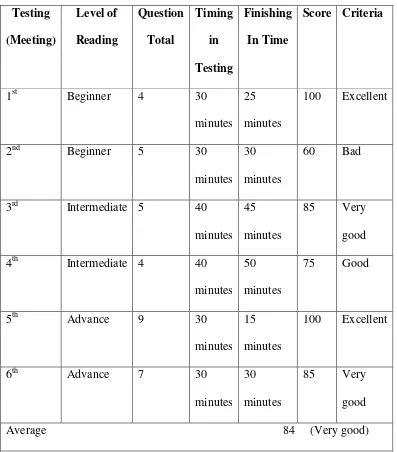
1. Result of First Meeting in Testing Reading Comprehension ... 58
2. Result of Second Meeting in Testing Reading Comprehension ... 60
3. Result of Third Meeting in Testing Reading Comprehension ... 63
4. Result of Fourth Meeting in Testing Reading Comprehension .... 71
5. Result of Fifth Meeting in Testing Reading Comprehension ... 79
6. Result of Sixth Meeting in Testing Reading Comprehension ... 81
B.Discussion ... 83
1. Result of First Meeting in Testing Reading Comprehension ... 84
2. Result of Second Meeting in Testing Reading Comprehension ... 88
3. Result of Third Meeting in Testing Reading Comprehension ... 90
4. Result of Fourth Meeting in Testing Reading Comprehension ... 93
xi
A.Conclusion ... 99
B.Suggestion ... 100
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 102
xii
ABSTRACT
Ambarwati. 2014. Profile of Autism Student in Reading Comprehension at English Education Department of IAIN Surakarta. Thesis, Surakarta: English Education Department, Cultures and Languages Faculty.
Advisor : Dr. Imroatus Solikhah, M. Pd
Key words : Autism, Reading Comprehension, Testing Reading Comprehension
This research aims at giving a description about the Reading Comprehension of Autism Student. The subject of this research is Yn, the student of IAIN Surakarta in English Education Department with Autism IAIN Surakarta. This campus is one of Inclusive education, because it is indirectly has some students with disability. One of them is Yn, student with Autism.
The researcher used the descriptive qualitative research. The research was conducted from September until November 2018 in English Education Department program of IAIN Surakarta. The researcher collected the data from testing, observation, documentation, and interview. This research did six meetings in testing and also did observation while Yn was doing the testing. The researcher did interview with mother of Yn and her therapist. In this research, the researcher was as participant observation (the researcher interacts with the participant and becomes one of them to observe and record behavior). The researcher did three steps to analyze the data such as; reduction the data, display the data and verification or drawing conclusion, the researcher used theory by Miles and Huberman (2002). To prove the trustworthiness of the data, it used the triangulation especially methodological triangulation that developed by Moleong (2002).
xiii
LIST OF FIGURES
xiv
LIST OF TABLES
xv
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1 Field Note ...106 Appendix 2 Students‟ Worksheet
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents about introduction of the research. It consists of five sections involving: (1) background of the study, (2) limitation of the problem, (3) problem formulation, (4) the objectives of the study, (5) the benefits of the study.
A.Background of The Study
Education is a right by each people. It means education is done in the same, not underestimate each people from religion, race, ethnic, physical or nation. From this physical case, not all people capable acquire education rightfully. (Nastiti in her thesis, 2015: 1). This cases which concerned with difable student. According to UNICEF executive summary concerning the condition of children in the World 2013, difable students susceptible towards discrimination in society and also didn‟t obtain education service rightly, so that they got underestimate than the other students. In other way, Stubbs in Nastiti said that there are some international documents which discusses about all circles included difable students, but not all discusses its implication straightaway, that is, the realization of inclusive education for difable student. One of the international documents is Education For All or EFA. According to Peraturan Menteri Number 5 a and b, Year 2011 about the equality of Children Education in Indonesia. It mentions that; a) every single children have gotten education and teaching of individual development and intelligent degree appropriate with talent and interest, b) that Pasal 11 ayat (1) Undang-Undang Number 20 Year 2003
about Sistem Pendidikan Nasional obligates Government and Region Government for giving easy and serve, and also certify in doing quality education for every societies without discrimination.
From regulations above, our country has facility to give education for all society, such as disabilities children. It comes from Elementary School till Senior High School, but not for university degree. It makes as discrimination as for getting education in all degree, why government not makes like “SLB (Sekolah Luar Biasa)” in university degree? They did not get the right like the others just
because they have weakness whereas they have strength in each individual. Finally, the disability student enters university, the rightly they should get education according their portion. These are same with some university which receives the disabilities student not intentionally. Because the selection in university doesnot yet use face to face interview, but just using written test. It effects the university as inclusive class which the college students are normally and disabilities students. According to the researcher, the university as UIN Sunan Kalijaga Jogjakarta, UIN Walisongo Semarang, and IAIN Kudus has disabilities student. It is also IAIN Surakarta receives disabilities besides normal students, it is proven by there is a program especially for disability students, it is PSLD (Pusat Studi dan Layanan Disabilitas). This program actually, does not
yet realize but it is prepared to be realized by Mr. HS as the chairman of PSLD. According to Government regulation of Republic Indonesia no. 70 in 2009 about
(1) Any student who has a physical, emotional, mental, and social or have the intelligence and/ or special talents eligible for inclusive education in educational unit. According to the particular needs and abilities, (2) students who have disorder as define in paragraph, (1) shall consist of; (a) blind, (b) hearing impairment, (c) mental retardation, (d) quadriplegic, (e) learning disabilities, (f) autism, and (g) motor disorder.
Those government regulations explain that inclusive education means every single child has opportunities to learn at school in his/her neighborhood. Inclusive education concentrates in implementing best practices for children with special needs within regular classroom. By using inclusive classrooms, all students have occasion to interact with and learn from their peers. Moreover, it can be said that inclusive education is an educational service admitting disable, gifted, talented student, and autistic student into curriculum. Inclusive environments can provide opportunities for children with autism to increase their social interaction and improve their social skills. Inclusive education give chance for Autistic student to interact with peers and gives students with Autism a chance to practice communication skills, develop friendships, and see how peers behave in day to day situations. In IAIN Surakarta, in real condition there are some disable students who include in the campus, such as blind and autism. The campus to handle the problem faces, rector makes a unit for handling the disable students above, the name is PSLD (Program Studi dan Layanan Disabilitas).
The researcher found a student with Autism in IAIN Surakarta and has good ability in reading. Reading is language ability. The raw material of reading sounds, words, sentences, communicative intentions in much the same as that of language in general. Thus, over the years, reading has been described as
to read have some parallels. People who currently use the term “whole language”
acknowledge that reading is language ability and should be taught in close and meaningful connection with the whole spectrum of language abilities including talking, listening, writing, and thinking. (Gillet and Temple, 1994: 3). In addition, reading is one of the most important in language skill beside listening, writing, and speaking. Because with reading someone can open the world, its better reading books, book is window of the world. The complex process of
learning to read is a fundamental task in children‟s development; a life skill:
“The ability to read is essential for successful functioning society and therefor is one of the most “survival” to teach our children. In virtually, all instances the goal of reading
is to identify the meaning or the message of the text at hand. Doing so involves the
execution and integration of the processes”.
(Van den Broek, Kendeou, Kremer, LYnch, Butler & White cited in Paris & Stahl, 2005 p 107),cited in Robbertss‟ Thesis.
The nature of reading has many sides of activities as being stated by Bamman in Arifin (2014: 12). It shows that reading can be described as mode of thinking. As thinking, reading requires that the reader follows the line of thought, which the writer has expressed. The process of reading therefore must (1) recall pertinent previous experiences and already learned facts that will help him
understand the printed material; (2) follow the writer‟s development and,
organization of ideas; (3) evaluate the accuracy and appropriateness of information and conclusion; (4) see how the printed data can apply a problem the reader may be trying to solve; (5) select the fact that is important to his purposes,
and so on. Unless the reader understands the writer‟s message and thinks along
Thus, reading can be seen as the processing of information. The reader brings to texts his own store of general information derived from his native culture, education, personal experience, and normally some specific knowledge of the topic of the written text. At the same time, the reader also possesses a linguistic competence including knowledge of words (lexis), of how these, words are developed according to the linguistic system in order to form sentence (syntax), and of rhetorical patterns and linguistic convention which characteristics different types of text (Haarman et. Al., 1988: vii cited in Arifin (2014: 12)).
Darland (1996) in Sastra (2011: 134) stated that Autism is from Greece language auto, means own self. The condition of autism is held by the thought or behavior leaning to own self and subjective. Beside, autism has communication disorder and behavior seriously. Furthermore, Bashir in his thesis, autism is a developmental disability that affects the normal functioning of the brain. Autism presents from birth and has an effect on how an individual learns. It is usually diagnosed by three years of age and continuous through adulthood. Individuals with autism often have difficulty with communication skills, social skills, and reasoning. From statements of scientist above, we can conclude that autism is a child disorder, usually appear since three years old which the autism children has complex disorder in communication, interest with their own world so they usually individualistic.
in English Education Department. The result of the interview (1) with the
lecturer, Miss MW (Academic Readings‟ lecturer in third semester of the object)
in July 25th, 2017 said that the autism student always active when teaching and learning process in the classroom, especially in her class. She said that this autism student when there was a student reading a text, she will make more
intention with her friends‟ reading. Therefore, she feels there is something that
she knows about the text, she cut the readings‟ friend, she asked something that
she didn‟t know or she shared something which has correlation about the text.
Moreover, when she is asked to reading a text in the classroom, she is actively to make something that having correlation with the text, and also she made the structure of the text with grammar session. The teaching and learning classroom is same like have two block students, the normal student and the disable student, cause miss MW must make more intention with the autism student when she is asking something related with the text (outside the material), if Miss MW didn‟t respond her, she would be angry and also make chaos the class, so Miss MW must respond first than carry on the next materials with the all students in the class. (2) With the therapist, Miss DW, she have said that YN is Autism with high level (Asperger) has strong memory to memories what they see, what they read, because their IQ are so high. In step with the object of this study, the researcher will study how the reading comprehension of an autism English Education Department student in IAIN Surakarta.
In other research related to the topic above are from the thesis of
Bridging theory, Research and Practice”. This research is divided into two
sessions; first the researcher researched 24 children ASC (Autism Spectrum Condition) of their reading, cognitive, and receptive language ability. The findings are the heterogeneity of reading and cognitive profiles and receptive language abilty of them. To make easier in learning process, the researcher gave intervention in each level. Study Two involved the development of a reading comprehension intervention involving three children from Study One, in their first term of secondary education. Findings are discussed with reference to the theories of autism and implications for parents, teachers and Educational
Psychologists supporting the learning of children with ASC‟s.
For second research in the same topic is from Melissa L. Ball-Erickson
with the title “Effective Reading Comprehension Strategies For Students With
Autism Spectrum Disorders In The Elementary General Education Classroom”.
This study focuss on the research centered on effective reading comprehension strategies for students with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) in the elementary general education classroom. The result and conclusion of this study indicated all of the discussed strategies proved to be effective to the various small groupings of participants. Recommendations for improving effectiveness of reading comprehension strategies for students with ASD in the elementary general education classroom include the concept that no single isolated reading diagnosis can be given to all children with ASD.
For next same research is about “Reading Comprehension Interventions
El Zein et. al. The researcher investigated the reading intervention studies conducted between 1980 and 2012 with K-12 students identified with autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Nine single-subject design studies, one quasi-experimental study, and two single-group design studies met the criteria for inclusion. Findings from the studies indicate that modifying instructional interventions associated with improved comprehension for students with reading difficulties may improve reading comprehension in students with ASD.
Four studies implemented strategy instruction that included (a) question generation; (b) graphic organizers; and (c) making predictions. Two studies utilized anaphoric cueing instruction, three implemented explicit instruction, and three examined student grouping practices. Among the reviewed studies, the majority (n = 9) measured reading comprehension through researcher-developed probes, and two studies reported results from standardized measures.
The last is from ThereseAnne Carberry “Teaching Reading
Comprehension to Students with High Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorder: A
Review of the Literature”. The researcher reviewed the literature surrounding
approaches that have proven to be beneficial in studies for students with ASD. Educators should examine, consider, and even combine strategies based individually on student need, and how successful students could be using the approach to improve their reading comprehension skills.
From some statements above, the researcher will investigate how the autism student of English Education Department, because Miss DW said that she has high IQ, Asperger Autism, which if someone has high IQ, so they will have high
capable to memories something. In line with the reading lecturers‟ statement,
Miss MW said that she has high ability in memories something, especially in reading, which she got high score though she has autism diagnosed, but she has capability to take on the education especially in scholarship. She has detail focus,
in line with Ericksons‟ statement cited in Carberry said that ASD are often
detached and very detailed-focused” (2014: 22). Although, she has weakness, as Autism, explained some experts above she cannot be society with around kindly. Based on the description above, the researcher conducted the research focused on PROFILE OF AUTISM STUDENT IN READING COMPREHENSION AT ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT STUDENT OF IAIN SURAKARTA.
B.Limitation of the Problem
this research, the researcher limited the scope of how the reading comprehension skill of Autism English Education Department student at IAIN Surakarta.
C.The Problem Formulation
Based on the background of the study and limitation of the problem, the research problem is how the profile of Autism student in Reading Comprehension at English Education Department of IAIN Surakarta, especially in level of Reading Comprehension and behavior during reading test?
D.The Objective of The Study
Based on the problem formulation above, the objective of the study is to describe the profile of Autism student in Reading Comprehension at English Education Department of IAIN Surakarta, especially in level of Reading Comprehension and behavior during reading test.
E.The Benefits of The Study
of autism student. This research can also give benefit for the researcher so that she gets new experience in communicating with autism.
F. Definition of Key Terms 1. Reading Comprehension
Comprehension is a multifaceted process affected by a variety of factors. The reading process is a dynamic one, requiring active, meaningful communication between the author and the reader. Reading without meaning is an unsatisfying and inconsequential exercise. The goals of reading program
should be aimed toward furthering children‟s comprehension abilities
(Heilman et. al.: 1981: 236). 2. Autism
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL REVIEW
A. The Nature of Reading
Reading is language skill. The raw material of reading sounds, word, sentences, communicative intensions is much the same as that of language in general. Thus over the years, reading has been described as psycholinguistic
guessing game”. The processes of learning to talk and learning to read have
some parallels. People who currently use the term “whole language”
acknowledge that reading is language ability and should be taught in close and meaningful connection with the whole spectrum of language abilities including talking, listening, writing, and thinking. (Gellet and Temple in Arifin, 2014: 11)
Harmer (2005: 6) stated that reading is useful for other purposes too: any exposure to English (provided students understand it more or less) is a good thing for language students. In addition, Heilman et. al. (1981: 2) said, reading is one of the basic communicative skills, but it is a very complex process. It is difficult to arrive at a precise definition of the reading process.
Related to the description above, Bamman in Arifin (2014: 12) suggested that the nature of reading has many sides of activities. It shows that reading can be described as a mode of thinking. As thinking, reading requires that the reader follows the line of thought, which the writer has expressed. The process of reading therefore must (1) recall pertinent
previous experiences and already learned facts that will help him understand
the printed material; (2) follow the writer‟s development and, organization
of ideas; (3) evaluate the accuracy and appropriateness of information and conclusion; (4) see how the printed data can apply a problem the reader may be trying to solve; (5) select the fact that is important to his purposes, and so on. Unless the reader understands the writer‟s message and thinks along with him, there is actually little or no reading. Mere word calling is not reading.
From some statements from experts above, the researcher concludes that reading is a basic communication skill which very complex process and also it is as a mode of thinking. Reading should be taught in whole language abilities such as; speaking, listening, writing, and thinking. For this, the subject YN has this basic skill and very complex, though she is diagnosed as autism but she gets this skill good enough from education levels before with the effective method in teach her.
Edmund Huey, a pioneer in research on reading, wrote in early 1900s in Heilman et. al. (1981: 4):
And so to completely analyze what we do when we read would almost be the acme of
a psycholinguist‟s achievements, for it would be to describe very many of the most
intricate workings of the human mind, as well as to unravel the tangled story of the most remarkable specific performance that civilization has learned in all its history.
Heilman et. al. (1981: 4) stated that reading is currently available to help plan for reading instruction, there are some aspects of reading:
b. The product of interacting with the printed language should be comprehension
c. Reading ability is closely related to oral language ability.
d. Reading is an active and ongoing process that is affected directly by an
individual‟s interaction with his environment.
1. The Kind of Reading
Broughton et. al. in Arifin (2014: 13) suggests that the word
„reading‟ has a number of interpretations. It means reading aloud a very
complex skill, which involves understanding the black marks first, and then the production of the right noises. It must be recognized that reading aloud is primarily an oral material and for those who teach a foreign language, it is closer to pronunciation than it is to comprehension.
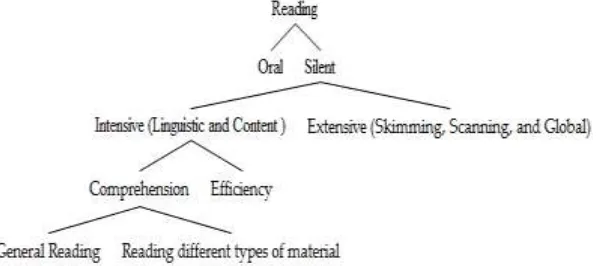
According to Sonka in Arifin (2014: 14-15), intensive and extensive reading has two major components: efficiency and comprehension, both
of which need readers‟ good understanding of the organization of text.
The division of Reading thus can be described as follows:
Figure 1 The Divison of Reading
The efficiency requires the reader to be able to recognize and use the organization provides the reader with a rough mental outline, which he then completes by reading. It gives him a basis for anticipating what follows, and thus establish the appropriate mental set for understanding an assimilation of new material (Sonka, 1979 in Arifin, 2014: 15). Then, Dwyer in Arifin (2014: 15) said that the efficiency also can be supported by reading by phrases rather than by words. This can be achieved successfully only by having well developed knowledge of grammar, especially, its SYntactic components by which he can guess or predict unfamiliar words.
2. The Model of Reading
a process of decoding written symbols, working from smaller units (individual letters) to larger ones (word, clauses, and sentences). In other word, readers use strategies to decode written forms in order to arrive at meaning. The bottom up model of reading has come in some rather severe criticism over the years. Smith (1978), as being rioted by Nunan (1995: 33), in fact, argues that reading actually works in the reverse order from that proposed by the bottom up model. In other words the readers need to comprehend meaning in order to identify words and that they generally need to identify words in order to identify letters. This model is called top-down model of reading.
The other research indicates that both bottom-up and top-down strategies may be used in learning to read and that efficient reading may require the integration of both bottom-up and top-down strategies (Stanovic, 1980 in Nunan, 1989: 33). Dubin Bycina (1991) calls this
model as „interactive‟ model of reading. It stresses the interplay of all
previous experience, prediction is made about the content of the text, which, upon further sample of the data, is either confirmed or revised (Dubin and Bycina, 1991: 197).
Finally, there are three models of reading: bottom-up, top-down, and interactive, each of which has its own effectiveness according to whom the models are implemented. The implementation of those three models are based the need of the readers.
B. Reading Comprehension 1. Reading Comprehension
Comprehension is a multifaceted process affected by a variety of factors. The reading process is a dynamic one, requiring active, meaningful communication between the author and the reader. Reading without meaning is an unsatisfying and inconsequential exercise. The
goals of reading program should be aimed toward furthering children‟s
comprehension abilities (Heilman et. al.: 1981: 236). The comprehension process is the realization that it is an internal, mental process that cannot be observed or studied directly. The tremendous expert who has influence on American education, Thorndike defined reading as thinking. He stated in Heilman et. al. (1981: 238):
Although direct observation of the comprehension process cannot be made, numerous research studies, theories, and models have been advanced to provide probable explanations relating to its components and development. Most of these hypothesized explanations view reading comprehension as composed of a multiple number of skills and abilities that are interrelated and interdependent.
The researcher can conclude that reading comprehension is a realization in internal of human, which as a mental process for analyzing as does thinking includes; attention, association, abstraction, generalization, concentration, and deduction.
Goodman in Heilman et. al. stated a crucial factor affecting
comprehension is the importance of the reader‟s background of
experience. One important area of a child‟s background of experiences is
that related to language development and growth. The following factors are among those that affect the comprehension of written material:
a. Oral language development related to real objects, experiences, and pictures.
b. Ability to listen with understanding to stories read aloud c. Firsthand experiences with people, objects, and places
e. Oral language development of sYntactic and semantic features of our language.
2. Components of Comprehension
A study by Davis cited in Heilman (1981: 241) is generally regarded as the significant attempt to delineate separate comprehension skills. His analysis showed the following five comprehension skills: a. Recalling word meanings (vocabulary knowledge)
b. Drawing inferences from content c. Following the structure of a passage
d. Recognizing a writer‟s purpose, attitude, tone, mood
e. Finding answers to questions answered explicitly or in paraphrase. In addition, Heilman et. al. (1981: 243) mentioned the summary of
five Barret‟s Taxonomy of Cognitive and Affective Dimentions of
Reading Comprehension: a. Literal comprehension
This dimension focuses on ideas and information explicitly stated in the selection. Purpose for reading may range from simple to complex, encouraging recognition and recall of simple or detailed facts.
b. Reorganization
It requires the student to analyze, sYnthesize and/or organize ideas and information explicitly stated in the selection. He may utilize verbatim
statements. Reorganization tasks are: Classifying, Outlining, Summarizing, and SYnthesizing.
c. Inferential comprehension
It is stimulated by purposes for reading and teacher‟s questions which
demand thinking and imagination that goes beyond the printed page. Here the pupil uses the ideas and information explicitly stated, his intuition, and personal experiences as a basis for conjecturing and hypothesizing.
d. Evaluation
Evaluation deals with judgment and focuses on qualities of accuracy, acceptability, worth, or probability of occurrence. There are five judgments as follow:
1) Judgment of Reality or Fantasy. Could this reality happen? This judgment is based on experience.
2) Judgments of Fact or Opinion. Does the author provide adequate support for his conclusion? Is he attempting to sway your opinion? This required analyzation and evaluation of the reader‟s
knowledge as well as the author‟s and the intent of the author.
4) Judgments of Appropriateness. What part of the story best describes the main character? This requires judging relative adequacy of different parts of the selection to answer the question. 5) Judgments of Worth, Desirability and Acceptability. Was the
character right or wrong in what he did? Was his behavior good or bad? How would you have handled the situation? Such questions call for judgments or moral codes and value systems.
e. Appreciation
Appreciation involves all the previously cited cognitive dimensions, for it deals with the psychological and aesthetic impact of the selection. Appreciation includes the knowledge of and emotional response to literary techniques, forms, styles, and structures.
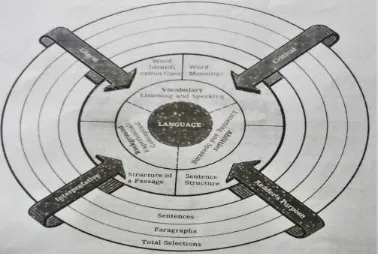
3. Comprehension Processes
Figure 2 The Comprehension Process
Reading comprehension is a process of making sense of written ideas through meaningful interpretation and interaction with language. Reading comprehension is best viewed as a multifaceted process affected by several thinking and language abilities.
are representing conceptual experiences with concrete objects, firsthand experiences, pictorial aids, vicarious experiences. The other hand, specific abilities counted the continuous development of word meanings (semantic), the ability to identifying the word cues, to establish topic sentence in detail, sequence, and comparison, and the ability to understand sentence structure (sYntax) of the written.
Each components of the figure are interacts. It shows that the level of thinking (literal, interpretative, and critical) can be used to apply in writing and oral language. Heilman et. al. (1981: 242-246) identify three levels of comprehension as follow:
a. Literal Comprehension
Understanding the ideas and information explicitly stated in the passage.
Abilities:
1) Knowledge of word meanings
2) Recall of details directly stated or paraphrased in own words 3) Understanding of grammatical clues-subject, verb, pronouns,
conjunctions, and so forth
4) Recall of main idea explicitly stated
5) Knowledge of sequence of information presented in passage. b. Interpretative Comprehension
Abilities:
1) Reason with information presented to understand the author‟s tone, purpose, and attitude
2) Infer factual information, main ideas, comparisons, cause-effect relationships not explicitly stated in the passage.
3) Summarization of story content c. Critical Comprehension
Analyzing, evaluating, and personally reacting to information presented in a passage.
Abilities:
1) Personally reacting to information in a passage indicating its meaning to the reader
2) Analyzing and evaluating the quality of written information in terms of some standards.
The conclusion is the depth of understanding is affected the
recognition of how a readers‟ acquire from reading a sentence,
paragraph, or total selection depends on the expressed purpose for reading.
Strategic Intervension (SI), (2) On-Level (OL), (3) Advanced (A). A code at the bottom of each page tells the level of each test. In this Beginner level, Yn was given in page of SI (SI also means for Beginner level). (unyear: v). In Beginner questions of this book, included Literal and Inferential level Reading Comprehension, which the specificly of each number was in the chapter IV.
The Intermediate level was taken from Real Reading 3, the book of Liz Driscoll (2002: 7). In introduction, she said that this book is for Intermediate or upper-intermediate level of Reading. So, the researcher took this book for giving test in Intermediate level. Intermediate level contained literal, inrerrential, and some little of critical level of Reading Comprehension. The specificlty explanation in each number was in the chapter IV. Then, in Advanced level, Yn was given test from the book of Irvine (2002: ), in the book explained that contained critical Reading Comprehension encourages student to use prior knowledge, experiences, careful thought, and evaluation. Advance level of this book, contained critical, inferential, and literal Reading Comprehension, which the explanation each number was in the chapter IV.
C. Autism 1. Autism
In 1943, Leo Kanner made the first attempt to describe a particular
type of childhood psychosis when he published a paper entitled “Autistic
Disturbances of Affecting Contact”. His original description of early
characteristic of the condition: (1) severe withdrawal of contact with other people, (2) an intense need to preserve sameness, (3) an inability to deal with people, (4) particular skills in motor functioning, (5) apparently good intellectual potential as reflected by average or better performance in some tasks and by an intelligent facial expression, and (6) severe disturbance of language functioning (Erickson, 1992: 176).
Darland (1996) in Sastra (2011: 134) stated that Autism is from Greece language auto, means own self. The condition of autism is held by the thought or behavior leaning to own self and subjective. Beside, autism has communication disorder and behavior seriously. In addition, the clinical term Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is used to classify the broad range of developmental disorders characterized by deficits in communication, social interaction and rigid, repetitive thinking and behavior (ICD-10, 1993 World Health Organisation; DSM-IV, 2000 American Psychiatric Association). From statements above, we can conclude that autism is brain developmental disorder since born which has some specific characters, communication disorder, interact with their own world, and also has many more complex disorder which repetitive thinking.
2. Criteria of Autism
a. A total of six (or more) items from (1), (2), and (3), with at least two from (1), and one each from (2) and (3):
1) Qualitative impairment in social interaction, as manifested by at least two of the following:
a) Market impairment in the use of multiple nonverbal behaviors such as eye-to-eye gaze, facial expression, body postures, and gestures to regulate social interaction
b) Failure to develop peer relationships appropriate to developmental level
c) A lack of spontaneous seeking to share enjoyment, interest, or achievements with other people (e.g., by a lack of showing, bringing, or pointing out objects of interest)
d) Lack of social or emotional reciprocity.
2) Qualitative impairments in communication as manifested by at least one of the following:
a) Delay in, or total lack of, the development of spoken language (not accompanied by an attempt to compensate through alternative modes of communication such as gesture or mime) b) In individuals with adequate speech, marked impairment in the
ability to initiate or sustain a conversation with others
d) Lack of varied, spontaneous make-believe play or social imitative play appropriate to developmental level.
3) Restricted repetitive and stereotype patterns of behavior, interest, and activities, as manifested by at least one of the following: a) Encompassing preoccupation with one or more stereotyped
and restricted patterns of interest that is abnormal either in intensity or focus
b) Apparently inflexible adherence to specific, nonfunctional routines or rituals
c) Stereotyped an repetitive motor mannerisms (e.g., hand or finger flapping or twisting, or complex whole-body movements)
d) Persistent preoccupation with parts of objects
From some characteristics cited above, the researcher observes that the subject YN has some characteristics as Autism diagnosed, as follow; from point of 1), YN includes the characteristic in point a) and d), for point of 2), YN concludes in characteristic in point c), for the last session 3), YN has characteristic written in point d).
From this point, according interview with her therapist, this autism student has language as used in social communication decrease since two years old. Actually, she can be bubbling like the others baby usually, but since in the two years old she has decrease in language and also effects in the next step, language as social communication. In line with YN mother said that YN can be bubbling in two words (mama and tempe) in 2,5 years old, but after that she didn‟t continue her bubbling like the others baby. She was just to be silent baby, if her
mother and others tried to make her laugh she didn‟t ever laugh even
just smile. But, she was active baby, her foot and hands always ranged.
c. The disturbance is not better accounted for by Rett‟s Disorder or Childhood Disintegrative Disorder.
From this point, the autism student is not better in making chaos than CDD (Childhood Disintegrative Disorder).
In addition, Baihaqi (2008) in Sastra (2011: 137) stated generally autistic disorder has three main difficulties as follows:
a. Communication
The difficulties language passes through all way to communicate, such as talks, intonation of hand movement, face gaze.
b. Imagination
c. Socialization
Difficulties with social relationship, timeless social, emphatyless, refuse normal body contact, and lack of eye contact.
From three difficulties are explained above, based on the researchers‟
observation, for communication, she is rarely to use the face gaze, such as when she is happy but she not using smile face gaze. For imagination, based on her classmate explained, YN usually refuse towards the changing of schedule class immediately. For the last, socialization difficulty,YN often timeless social, she rarely has friends outsides on the campus. She always interacts with herself when in the campuss, such as she likes to search in google or youtube when spare time.
3. Factors of Autism
Sastra (2011: 135) stated six factors cause of autism generally as follows:
a. Neuroanatomy Disorder
1) Head Size
The autism almost shows the circle of head is bigger. The investigation with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) shows the brain volume is bigger. But, the small or big brain is not a specific symptom in autism courchesne.
2) Cerebellum
Disorder in small brain (cerebellum) effects presence disorder in sensories process, IQ, thinking, study language, and attention. Besides, there is less of Purkinye Cell in the brain that effects happening of disorder or confusion of impulse pass-move in the brain. According to MRI investigation by Eric Courchesne defined
that the autisms‟ cerebellum is smaller than normal children.
3) Limbic System
Limbic system disorder (hippocampus or amygdala) effects happening function control disorder towards emotion and aggression. So, children have less control and almost aggressive or passively. Amygdala has responsible towards some sensoris stimulant, such as hearing, eyesight, smelling, and sense.
4) Parentialis Lobus
b. Genetic Factor
Generic factor has assumption to be the main factor of autism, although the concrete proof still difficult found. Chromosome disorder of autism indeed is discovered, but these disorder not always as same as.
c. Mother Parenting
The first theory which explains autism from psychological is Refrigerator Theory and this theory developed by Bruno Battelheim. He argues that the autism is caused not be warm mother parenting, so that they are interest with their own world. Then, Margaret argues that autism children has serious damage on their ego because of unableness since born and interest create mother or others as friend. (Ginanjar: 2007).
d. Lot of Peptide Opioid
Peptide comes from splitting-up of Gluten protein which discovered in wheat and casein protein. Gluten protein comes from milk protein needed just a little for brain activity. Abnormal condition can improve the amount of opioid peptide, as follows:
2) The amount of peptide in intestine is normal, but there is leakage in buttress of intestine. It is above effects a lot of absorption into blood.
3) The amount of normal protein, but leakage in intestine buttress and brain-blood limitation.
e. Food Allergy
Allergy in children can be aggressive with all part of body. Food allergy indeed can disturb the brain function so that very obstructs the children development. Food allergy can make appear of autism.
f. Prenatal Factor
Some obstacle in pregnant phase can make appear autism. In the first trimester, 0-4 month, it can be from infection (toksoplasmosis, rubella, and candida), heavy tin (PB, A, Hg, Cd), chemical substance (MSG, preservatives, and dye), drug, laxative meal, heavy vomit (hiperemesis), heavy bled (Handojo, 2003).
D. Learning Style of Autism
There are some learning styles dominantly of Autism in Fern Sussman
cited in Dwi Suryani‟s Thesis (2018: 16):
1. Rote Learner
can spell letter correctly and well organized, but unknown if these letter are clustered into meaning word).
2. Gestalt Learner
Children is inclining learn to see something globally. Example: they are commanded to put toys in rack, they confused because not yet understand how to put, and just learn from habitual.
3. Visual Learner
This kind of children, they like to watch drawing book, TV, and easy to catch information what they see than what they listen globally. Example: like watching advertisement in TV.
4. Hands of Learner
These children like to try and get knowledge from their experiences
usually. Example: they didn‟t know the meaning of „open‟, but after we
put their hands in hand-grip of door and help their hands to open the door (open), they as soon as know the meaning of „open‟ word.
5. Autiditory Learner
These children like to speak and listen the other‟s speak and getting
information from their listening.
E. WCC (Weak Central Coherence)
In thesis of Robert (unyear: 39) mentioned that the term „central
“… an information processing style, specifically the tendency to process incoming information in its context: that is, pulling information together for higher-level meaning” (Hill & Frith, 2003: 284).
In other words, it is the tendency for typically developing individuals to process information to establish a global sense of meaning or to see the
„big picture‟, at the expense of paying attention to or remembering specific
details. However, for the autistic individual, it is proposed that they demonstrate “weak central coherence”, is a processing bias for local and featural aspects and details, at the expense of extracting the „gist‟ and contextual meaning. Thus, this theory is closely aligned with the original observations by Kanner (1948), who noted that autistic individuals tended to focus on the details, exhibiting an, “inability to experience wholes without
full attention to the constituent parts” (Kanner in Robert, unyear : 37).
Reading comprehension is critically dependent upon intergrating information not only from within the same text, but from prior or external knowledge, to ultimately establish meaning (Nation & Norbury, in Robert:
37). Therefore, the notion of „weak central coherence‟ presents a rational
monitoring). Put simply, it is possible to have an understanding at the word or sentence level, without establishing the message conveyed in the text in
its entirely, a process referred to as „word-to-text‟ integration (Perfetti, Yang
& Schmalhofer, 2008).
A study by Wahlberg & Magliano (2004) cited in Robert‟s thesis
assessed whether high functioning readers with autism are able to draw upon background knowledge, and to integrate the knowledge to facilitate their understanding of ambiguous text. Their findings supported the suggestion
that individuals with ASC‟s have particular difficulties making use of
relevant background knowledge compared to typically developing individuals. Considering the component skill of comprehension monitoring, Perfetti, Landi & Oakhill (2005) highlight that readers who endeavour to establish a thorough understanding of the reading material, i.e. their goal and
purpose is to derive meaning, are described as having a „high standard for
text coherence‟ and thus, are more likely to self-monitor than those readers
who have a „low standard for text coherence‟. In light of the weak coherence
theory, it is plausible to suggest that individuals with ASC‟s, due to their
bias for local processing, may have particular difficulties in monitoring their comprehension as they are reading, however this metacognitive skill has yet to be thoroughly investigated in individuals with an ASC.
Although not widely accepted within the field due to a lack of empirical evidence, a construct that holds a close position to weak central
41). Fundamentally, the theory is based upon the „restricted range of
interests‟ outlined in the diagnostic criteria for ASC‟s (DSM-IV; American
Psychiatric Association, 2000; ICD-10: World Health Organisation, 1993),
together with „patterns of subject experiences‟ as reported by individuals
with ASC‟s. Individual with ASC‟s are described as having a „monotropic
tendency‟ (few interests, less highly aroused) and this differs from a
„polytropic tendency‟ (many interest, less highly aroused) in typically
developing individuals (Robert, unyear: 41).
F. Testing of Reading Comprehension
In Madsen (1983: 79) stated, there are some tests for sentence comprehension and passage comprehension:
1. Testing Sentence Comprehension
Sentence comprehension must precede essay comprehension. Some sentence level comprehension items are good for beginning students. Some elementary questions simply ask for a one-word response. In such questions, it will check vocabulary, grammar, and sometimes even social appropriateness at the same time.
Elicitation Techniques a. Picture Cues
The children are playing on their new toy.
In the form we give some pictures, one as appropriate (right) picture with the sentence, and up to others picture. So, the children circles the best answer based on the appropriate pictures with sentence. b. Phrase and Sentence Cues
One of the simplest forms of sentence comprehension is the true-false sentence. It is used with beginners. The student looks for truths, untruths, or impossibilities:
1) The sun sets in the east. T F 2) She is my brother. T F 2. Testing Passage Comprehension
This kind of test is the most integrative and challenging kind of test type.
Here, „context selection‟ is interesting to notice how many unusual
“passages” or “contexts” that students are introduced. Besides, the usual
articles and stories, these may include advertisements, want ads, business
and social letters, driver‟s license and loan applications, bank statements,
rental, and sales agreements, and mail order catalogs. For example: a. 75 Gremlin. 6 cyl 2 dr 4 spd A-1 cond. 20 MPG city 8 trk AM/FM
P.S. P.B., auto/cruise bucket seats Terms 379-1892 after 5.
This automobile has…
D. Air conditioning
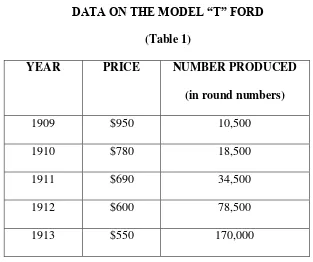
DATA ON THE MODEL “T” FORD
(Table 1)
YEAR PRICE NUMBER PRODUCED
(in round numbers)
1909 $950 10,500
1910 $780 18,500
1911 $690 34,500
1912 $600 78,500
1913 $550 170,000
This requires the student to be able to make inferences. They need to recognize that there is a probable relationship between the increased number of cars produced.
This below is rubric in assessing:
Score Criteria
91-100 Excellent
81-90 Very good
71-80 Good
61-70 Average
51-60 Bad
41-50 Very bad
G. Biography of Subject
The subject is YN who was born in Klaten, June 1st, 1994. She is 24 years old now. She is third child. She has 1 elder brother, 1 elder sister ad 1 younger sister. Her hobby is cooking. She likes cooking nasi goreng in the home and also sing song. Her father job is businessman and her mother is housewife.
YN was not like the others baby, she cannot be laugh if the parents
„ngliling‟ (ngliling: effort makes a baby to be laugh) her, her eye-contact
was zonk, but her parents didn‟t suspicious about her, because they think that every baby has their own characteristics. The first time she can walk in the 1 year old. As like the others babies, she can be babbling in 1, 5 years
old, but she just can “ibu” and “tempe”. She stuck can be continue in
babbling until 4 years old. She was just to be silent baby with hyperactive (a lot of moving in her hands and feet, like to „ginjal-ginjal‟ (ginjal-ginjal: a lot of movement in hands and feet) and also likes to cry often.When she was
0-30 days old, she always cried loudly after „maghrib‟ till 12 o‟clock, the
parent rarely slept tight. Then in 4 years old, the parents knew that the she is Autism Children from news in TV. The parents think the characteristics of their baby were as seen as in news TV, Autism Children. She likes with
5 years old too, till she had been wish not to drink „ASI‟ again. Then she
ever had fallen too, for about 2 years old. Her mother said, “bocah iki kaet cilik ketulo-tulo” (this child was very sad).
Starting from followed the National Seminar about difable children, the parents carried YN in some doctors. It started from dr. HS (children special doctor) who mistake in diagnosed her, he diagnosed that she just
„hyperactive children‟ not more. He gave „Retalin‟ medicine, but she was
sleepy directly like „mabuk‟ person. So, her parents stop this medicine. Then
they moved to others doctor while they followed National Seminars. When they got National Seminar in Riyadi Hotel, they asked for dr. DP who has Autism Children too, about Autism. Dr. DP said that this kind of children
must avoid “Gluten and Kasein, additive¸ preservatives). She must do full
diet.
For her education histories, she graduated from SLB N Surakarta (8-14 years old), SMP Galuh Handayani Surabaya ((8-14-17 years old), SMA Galuh Handayani (17-20 years old), IAIN Surakarta (20-now). She has teacher shadow (Miss DW) started from she was in Elementary School until now. She got therapy in Thorison Polokarto (when children). She also got therapy in therapy clinic of SLBN Surakarta (with Miss DW till now). In Thorison Polokato, she got therapy such as; Okupasi, terapi wicara, and ABA (Applied Behaviour Analysis). The therapy (Thorison and therapy clinic
School (she cannot sit down calmly), hyperactive, but now she more can be calmly if there is not something can make her emotionally.
H. Inclusive Education
1. Meaning of Inclusive Education
According to Echols in Facmiansyah thesis (2012: 31), inclusive term is form English Language “Inclusive” means included, take. Inclusive education means included difable student in regular class with the others students. In widely, inclusive education is involving all students without exception in regular education. In International Journal of Instruction Vol. 6 No. 1, January 2013 cited in Nastiti (2015: 29) declared that:
“In an inclusive school, children are given equitable support so that every
child can be able to participate physically, socially, and academically with their peers. This means that in an IE setting the environment, curriculum,
teaching methods, assessment and reporting to be adjusted or differentialed”.
From this statement above, Nastiti (2015: 29) argues that in learning process, inclusive education will serve environment, curriculum, learning method, assessment, and learning report which appropriate with students.
environment, curriculum, learning method, assessment, and learning report which appropriate with students.
2. The Goals of Inclusive Education
In Nastiti (2015: 30) stated the goals of inclusive education, cited from Pedoman Umum Penyelenggaraan Pendidikan Inklusi (2007: 10) as follow:
a. Giving occasion widely for all children (involve difable children) get suitable education and also appropriate for them,
b. Helping advancing the basis education for obligatory study program, c. Helping increasing elementary and high school education quality
with compress the number of class leave and school break,
d. Creating education system which appreciate diversity, not discrimination, and also friendly toward environment,
e. To fulfill Undang-Undang Dasar 1945 especially in Pasal 32 ayat 1
which stated „every citizen has obligation to get education‟, and in
ayat 2 stated „every citizen has obligation to follow basis education
and government has obligation for financing‟. UU Number 20/2003 about National Education System, especially Pasal 5 ayat 1 which
stated „every citizen has same authority to get quality education‟. UU
Number 23/2002 about Children Protection,especially in Pasal 51
same occasion and accessibility for getting common education and uncommon education.
IAIN Surakarta has a unit special for disability student, it names PSLD (Pusat Studi dan Layanan Disabilitas) which is Mr. HS as the
chairman. This unit is for giving facilities for disable student in the campus.
I. Previous Study Related to The Topic
1. The thesis of Elizabeth (Libby) Roberts, the title is “Autism and Reading Comprehension: Bridging theory, Research and Practice”.
This research is divided into two sessions; first the researcher researched 24 children ASC (Autism Spectrum Condition) of their reading, cognitive, and receptive language ability. The findings are the heterogeneity of reading and cognitive profiles and receptive language abilty of them. To make easier in learning process, the researcher gave intervention in each level. Study Two involved the development of a reading comprehension intervention involving three children from Study One, in their first term of secondary education. Findings are discussed with reference to the theories of autism and implications for parents, teachers and Educational Psychologists supporting the learning of
2. Thesis of Melissa L. Ball-Erickson with the title “Effective Reading Comprehension Strategies For Students With Autism Spectrum
Disorders In The Elementary General Education Classroom”.
For second research in the same topic is from Melissa L. Ball-Erickson with the title “Effective Reading Comprehension Strategies For
Students With Autism Spectrum Disorders In The Elementary General
Education Classroom”. This study focuss on the research centered on effective reading comprehension strategies for students with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) in the elementary general education classroom. The result and conclusion of this study indicated all of the discussed strategies (Direct Instruction, assistive technology and computer assisted instruction, classwide peer tutoring, activating prior knowledge, think aloud, and retelling) proved to be effective to the various small groupings of participants. Recommendations for improving effectiveness of reading comprehension strategies for students with ASD in the elementary general education classroom include the concept that no single isolated reading diagnosis can be given to all children with ASD.
3. “Reading Comprehension Interventions for Students with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A SYnthesis of Research” by Farah El Zein et. al.
For next same research is about “Reading Comprehension Interventions
for Students with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A SYnthesis of Research”
intervention studies conducted between 1980 and 2012 with K-12 students identified with autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Nine subject design studies, one quasi-experimental study, and two single-group design studies met the criteria for inclusion. Findings from the studies indicate that modifying instructional interventions associated with improved comprehension for students with reading difficulties may improve reading comprehension in students with ASD.
4. The last is from ThereseAnne Carberry “Teaching Reading Comprehension to Students with High Functioning Autism Spectrum
Disorder: A Review of the Literature”.
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter deals with research design, subject of the research, setting of the research, the research instrument, source of the data and technique of collecting data, technique of analyzing data, and trustworthiness of the data.
A. Research Design
Research design is very important to know and to use the right method during the research to get deep understanding about the problem being discussed, valid, and reliable data. This research used case study which a study of a single individual for the purpose of obtaining a description of the individual. The description is typically prepared as a report, usually containing a detailed of observations and experiences during diagnosis and treatment of a specific clinical client, including a detailed description of the unique characteristics and responses of the individual (Gravetter and Forzano, 2016: 393). Qualitative research is an approach in research which is oriented in phenomenon or symptom naturally (Mohammad Ali and Muhammad Asrori, 2014: 121). Fraenkel and Wallen (1990:50) stated that qualitative research is the research study that investigates the relationship, the activity, the situation, or the material. In addition, Geoffrey (2006:399) said that qualitative research is the collection, analysis, and interpretation of comprehensive narrative and visual (non-numerical) data in order to gain insight into a particular
phenomenon of interest. Here, the product of the research is a narrative report with rich description (Johnson and Cristenson, 2000: 312).
Based on the definition above, we can conclude that the descriptive qualitative research is a research which put forward the data collecting based on the thing investigated and explored by the researcher and occurs naturally from the situation without manipulating the data and the data collected are descriptive words not numeric or score.
B. Subject of the Study
The subjects of the study was an autism student in sixth fifth semester English Education Department IAIN Surakarta. This student is the only one autism student of English Education Department IAIN Surakarta. It was actually the background of this student was from SLB (Sekolah Luar Biasa) since Elementary School until Senior High School.
C. Setting of the Research
The researcher choosed IAIN Surakarta as the setting of the research. It is located at Pandawa street, Pucangan, Kartasura, Sukoharjo Regency. This research was conducted from the time the researcher proposed the tittle on November 2017 up to propose the proposal and it will be continued up to the time the researcher collected the result of how the Reading Comprehension of Autism student English Education Department in IAIN Surakarta.
D. The Research Instrument
as the main role in looking for the data in how the reading comprehension of autism student that the researcher focuses on. The researcher also used some additional instruments such as recording equipment, camera, and field note book.
E. Data and Source of the Data 1. Data
The main data of this research are result of score Reading Comprehension and also the result of observation of the researcher herself during Reading Comprehension test.
2. Source of the Data
In this research, the data were the result of Reading Comprehension and field note which taken from observations during Reading Comprehension test. The data were information about the reading of the object. Sutopo (2002:23) stated that data sources of the qualitative research can be taken from man and his behavior, phenomena, documents, archives, and others. The sources of the data in this research was:
a. Events
F. Technique of Collecting Data
Based on the source of the data, the techniques of collecting data that will be used in this research to find the data about reading comprehension of Autism English Education Department student at IAIN Surakarta were as follows: 1. Testing
The researcher gave the subject with testing for getting the score and also the behaviour of Yn while she did the testing. The testing gave in sixth (and also did in 6 meeting too), with time and place in different. The testing included the reading for Beginner, Intermediate, and Advance level, with each level there were the level of Reading Comprehension (Literal, Interpretative and Critical). For testing 1 and 2 were for Beginner level of reading, testing 2 and 3 were for Intermediate level of reading, and testing 4 and 5 were for Advance level of reading. The first testing there were 4 questions, second testing with 5 questions, third testing with 5 questions, fourth testing with 4 questions, fifth testing with 9 questions, and sixth testing with 7 questions. 2. Observation