iv
THESIS
Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
UIN SUNAN AMPEL
S U R A B A Y A
By:
Maimunasih
NIM. D55211106
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SURABAYA
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id x
ABSTRACT
Maimunasih. 2015. The Effect of Simulation Technique in Improve Students’ Speaking Ability of Procedure Text of SMP Patriot Jombang. A Thesis. English Education Department, Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher Training, SunanAmpel State Islamic University, Surabaya. Advisor: Dr. Phil. KhoirunNiam,S.Ag
Key words: Students’ Speaking Ability, Procedure Text, Simulation Technique In mastering English, speaking is the most used skill by people rather than three other skills. However most of students were low motivation and passive in learning English. The teacher has to be creative and innovative to create good atmosphere in the classroom. In this study the researcher intended to know the effect of improving speaking abilityof procedure text by implementing simulation technique. Therefore this study was aimed to know the significance difference between the students who wereusing simulation technique and who were using non simulation technique. The design that the researcher used was quasi-experimental design, especially in nonequivalent (pre-test post-test) exactly control group design. In collecting the data, the instrument used by the researcher was a test and observation. There were two kinds of test there are pre-test and post-test in which both of the test were administered to both control and experimental classes. In analyzing the data, the researcher used t-test formula with significant degree of 5% and df 56.
After doing the research, the researcher could conclude that simulation was an effective technique in improvingspeaking ability of procedure text. There
was progress in students’ pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, and fluency.
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id iv
ABSTRAK
Maimunasih. 2015. Pengaruh Simulasi Teknik di Meningkatkan Kemampuan Berbicara Siswa dari Prosedur Teks SMP Patriot Jombang. Sebuah Tesis. Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, SunanAmpel Universitas Islam Negeri, Surabaya. Advisor: Dr. Phil. KhoirunNiam, S.Ag
Kata kunci: Kemampuan Berbicara Siswa, Prosedur Teks, Teknik Simulasi
Dalam menguasai bahasa Inggris, berbicara adalah yang paling sering digunakan keterampilan oleh orang-orang bukan tiga keterampilan lainnya. Namun sebagian besar siswa motivasi rendah dan pasif dalam belajar bahasa Inggris. guru harus kreatif dan inovatif untuk menciptakan suasana yang baik di dalam kelas. Dalam studi ini peneliti bertujuan untuk mengetahui efek meningkatkan berbicara abilityof teks prosedur dengan menerapkan teknik simulasi. Oleh karena itu penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui perbedaan yang signifikan antara siswa yang wereusing teknik simulasi dan yang menggunakan teknik simulasi non. Desain yang peneliti digunakan adalah desain kuasi-eksperimental, terutama di nonequivalent (pre-test post-test) persis rancangan. Dalam pengumpulan data, instrumen yang digunakan oleh peneliti adalah tes dan observasi. Ada dua jenis tes ada pre-test dan post-test di mana kedua dari tes diberikan untuk kedua kontrol dan kelas eksperimen. Dalam menganalisis data, peneliti menggunakan rumus t-test dengan tingkat signifikan 5% dan df 56.
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id xiv
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Title Sheet ... i
Advisor Approval Sheet ... ii
Approval Sheet ... iii
Motto ... iv
Acknowledgement ... v
Dedication Sheet ... vi
Abstract ... vii
Pernyataan Keaslian Tulisan ... viii
List of Tables ... ix
List of Appendices ... x
CHAPTER I :INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Research Question ... 5
C. Objective of the Study ... 5
D. Reseach Hypothesis ... 6
E. Significance of the Study ... 6
F. Scope and Limitation of the Research ... 6
G. Definition of Key Terms ... 7
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Speaking ... 10
B. Teaching Speaking ... 12
C. Procedure Text ... 15
D. Simulation Technique ... 17
E. The Advantage of Simulation Technique ... 19
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id xv
G. The Role of Teacher in Speaking Simulation ... 23
H. Previous Study ... 24
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Research Design ... 28
B. Population and Sample ... 29
C. Research Instrument ... 31
D. Data Collection Technique... 33
E. Research Procedure ... 38
F. Data Analysis Technique ... 46
CHAPTER IV : FINDING AND DISCUSSION
A. Finding 53
B. Discussion 64
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A.Conclusions 68
B.Suggestions 69
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id 1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter discusses the background of the study, research question,
objectives of the study, hypothesis, significance of the study, scope and limit of
the study, and definition of the key term.
A.Background of the study.
According to Nunan “Speaking is the process of producing utterances
or articulate sounds in comprehensible manner thus he can reach
communicative competence as the objective of speaking Being able to speak
well and fluently is the key of a successful interaction.”1 By speaking well, the
listener would understand the message we are talking about. It is supported by
Halley and Austin who stated that “Being able to communicate orally in
another language means that we have opportunities to express our ideas and
support for making our intentions clearer.”2
Richardson also stated that learners consequently often evaluate their
success in language learning as well as the effectiveness of their English course
on the basis of how well they feel they have improved in their spoken
proficiency3. As a skill, speaking is the most used skill by people rather than
1
David Nunan, Second Language Teaching and Learning.(Canada:Heinle&Heinle Publisher, 1999), 225
2
Heley M.J, Austin T.Y, Content-Based Second Language Teaching and Learning, An Interactive Approach,(USA: Pearson2004,), 191
3
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id the three other skills. It can be said that most language learners learn English in
order to develop proficiency in speaking. Besides, many language learners
regard speaking ability as the measure of knowing a language.Nunan said that
the learners define fluency as the ability toconverse with others, much more
than the ability to read, write, or comprehend oral language4. They regard
speaking as the most important skill they can acquire, and they assess their
progress in terms of their accomplishments in spoken communication.
Better achievement of students’ speaking skill depends on some factors
that teacher brings during teaching and learning process. According to Bailey
in Nunan, teaching speaking should be done communicatively5. The teacher
has to maintain interactions with the students as well as the interaction between
each student in the classroom. The teacher has to be creative and innovative to
create a good atmosphere in the classroom. Teacher is demanded to make
English lesson more exiting, easy and joyful, so students will not feel afraid of
making mistake and burdening. Thus, the teacher has to be able to package
English lesson as an interesting lesson. The teacher has to find an appropriate
and interesting method in teaching process because language teaching can be
an interesting process when the teacher makes an effort to explore a variety of
methods which can motivate students to speak. This is in line withBrown who
4
David Nunan, Practical English Language Teaching,(New York: McGrow-Hill Education, 2003), 51
5
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id explained that teaching is guiding and facilitating learning, enabling the learner
to learn, setting the conditions for learning6.
English lesson is one of compulsory subject which is taught in Junior
High School. The students of Junior High School have to master four skills in
English. According to the English Standard Competence, there are four
language skills that have to be mastered by the students, one of them is
speaking skill and there are two types of text that have to be mastered by the
students. One of those texts is procedure text7. Procedure text is a kind of text
type or genre that has to be mastered by the students. The students are
supposed to express what they have understood of a particular procedure text
both in oral and written. But, the students often find difficulties to express the
meaning of it in spoken language because accorder to Brown, they are
supposed to express its meaning in a simple short monolog by using variety
oral language, accurately, orderly, and acceptably to communicate with the
surroundings8. It proves that mastering procedure text in speaking skill is very
important.
There are many techniques of language teaching that may be selected
for teaching speaking skill. One of them is simulation technique. As stated by
Harmer, simulation technique can increase the self-confidence of the students,
in which the students pretend that they are in a real life contexts and have a
6
H. Douglas Brown,Principles of Language Learning and Teaching, Fifth Edition. ( New York: Pearson Longman,2001),8
7
Depdiknas, StandartKompetensidanKompetensiDasar,(Jakarta:Depdiknas,2006), 279 8
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id variety of social roles9. However, simulations are more elaborate than role
plays10. This is supported by Kayi thatin simulations students can bring items
to the class to create a realistic environment11. This technique can motivate
the students because it is entertaining. Furthermore, the students can speak
easily when they actively participate in activities.
Based on the description above, the researcher is interested in using
simulation to teach speaking of procedure text. The researcher wants to know
whether simulation technique is effective in improving students speaking
ability of procedure text. The researcher chooses procedure text because
procedure text consists of series of actions and the material does not have to
depend on the text book only. By using simulation technique the students are
given chance to speak English freely. As stated by Dewey one learns best by
doing an active experimentation.12The students will enhance their speaking
ability because they are not only doing an oral presentation but also relating
themselves with the authentic materials.
In this research, researcher focuses on the students on seventh grades
at SMP Patriot Jombang. Based on preliminary study at seventh grade of
Patriot Jombang Junior High School there was a low motivation in study
English, the students were passive in learning English. They did not have self
confidence in speaking English because of many factors. One of them is the
9
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching: Fourth Edition, (England: Pearson Longman, 2007), 353
10
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice………, 352 11
HyriyeKayi, open international education (http://unr.edu//homepage/hyriek. accessed at June 24, 2015)
12
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id conventional method used by English teachers, the teacher only translate the
words and ask their students to remember the dialog on the book. The
researcher thought that the teachers need a new creative method to assist the
student in improving their speaking ability in order they can be motivated to
speak effectively too. Therefore the researcherchose one of the techniques to
teach speaking that is simulation technique.
B.Research Question
Based on the background of the study above the research question can
be formulated as follow:
”Is simulation technique more effective to teach speaking of procedure
text than using non simulation technique (conventional method) in SMP Patriot
Jombang?”
C.Objective of the Study
Related to the research question, this study attempts to know the
effective of simulation technique in improving speaking ability of procedure
text than students’ speaking ability of procedure text by using non simulation
technique.
D. Research Hypothesis
The working hypothesis (Ha) for this study is: there are some
differences between students speaking ability of procedure text taught by using
simulation technique and the students speaking ability of procedure text taught
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id
E. Significance of the study.
The research aims to found out the alternative way of teaching speaking
to improve the students speaking ability. The result is significant for:
a. Teacher:
1) This research can give information about new creative teaching method.
2) To give information that speaking ability can improve by using
simulation technique.
b. Students:
1)To improve students’ motivation and interest.
2)To build students’ confidence in communicating
c. Future researcher:
This research can be used for reference of their knowledge.
F. Scope and Limit
1. Scope
Seventh grade of SMP Patriot Jombang which used procedural text
and simulation technique.
2. Limit
This study only focuses on the seventh grade of SMP Patriot
Jombang in academic year 2014-2015 and procedure text. This study only
focuses on simulation technique in teaching speaking procedure text.
G. Definition of Key Term
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id The effect is a change produced by an action or a cause a result or
outcomes.13 A result caused by something or an action. The improvement
ofstudents’speaking of procedure text score as a result that caused by the
implementation simulation technique to teach speaking of procedure
text.The effect of this research was the degree of improvement in the
students' speaking ability of procedure text as a result of using simulation
technique, and measured statistically by T-test paired sample using SPSS
16 for windows of the effect size.
Effective is defined as the capability of producing a desired
result14. When something is effective, it means it has an expected outcome
or a deep produce. In this research, effective was indicated by
improvement of speaking ability of procedure text that measured by
comparing the mean score of posttest both experimental and control group.
The technique is effective if the score of test in experimental group is
better than the result of control group.
2. Simulation Technique.
Simulation is a technique to teach speakingin whichthe students
simulate a real- life encounter as if they were doing so in the real world15.
In this research, simulation technique is used to teach in speaking of
procedure text. The implementations of this technique are: setting up,
getting going, managing the activity, winding down, and assessing
13
AS Hornby, Oxford Advance Learner’s Dictionary,(New York: Oxford University Press,1987), 369
14
AS Hornby, Oxford Advance……..,369 15
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id students.The teacher also asked the students to bring some materials they
needed to make simulations about how to make drinks and food.
3. Speaking Ability
Speaking ability is the competence of the students to convey
information, express ideas, thoughts, feeling and reaction in appropriate
structure, speech sounds, appropriate vocabulary according to the situation
and subject matter, and used the language fluently16
In this research, speaking ability is the competence of the students
to convey information, to express the ideas to the audience about how to
make something in procedure text.
16
digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id digilib.uinsby.ac.id
4. Procedure Text
A procedure text is a piece of text that tells the readers or listeners
how to do something. According to Andersonits purpose is to provide
instructions for making something, doing something or getting
somewhere17.
In this research procedure text is a text that shows a process in
order about how to make something completely18. Procedure text is
dominantlystructured with imperative sentence since it actually an
instruction. Procedure textusually explains the ingredient or material
which is need though sometime it is omitted, after that procedure text will
explain step by step how to make drink and food.
17
Mark Anderson and Kathy Anderson, Text Type in English(Australia: Macmillan Education Australia Pty. Ltd,1997 ), 28
18
10
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter presents some literatures which are related of the study,
specifically it covers speaking, teaching speaking, procedure text, simulation
technique, the advantage of simulation technique, the procedure of simulation
technique for speaking skill, the role of teacher in speaking simulation technique and
previous studies.
A.Speaking.
Speaking is a part of learning besides listening, reading, and writing.
According to Brown, speaking is “The ability to accomplish pragmatic goals
through interactive discourse with other speakers of the language”19. According to
Harmer speaking is “To convey message to the listeners effectively, the speaker
should understand who the listeners are such us he should give articulate in
comprehensible manner thus he can reach communicative competence as the
objective”20.
Speaking is very important in our daily lives because it is a mean of
communication. According to Brown and Yule as quoted by Jack C. Richards,
speaking has been classified into three functions in human interaction. Those
19
H. Douglas Brown, Teaching by Principle: An Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy, Second Edition. (Longman,2001), 267
20
classifications are interactional function of speaking (talk as interaction), the
transactional functions of speaking (talk as transaction), and talk as performance21.
1. Interactional function is a function that serves to establish and maintain social
relations. It is usually called as conversation. The focus is more on the
speakers and how they wish to present themselves to each other than on the
message.
2. Transactional function is a function of speech which focuses on the exchange
of information. This type of talk refers to situations where the focus is on what
is said or done. The central focus is on the message and the way to make the
speaker himself is understood clearly and accurately, rather than participants
an how he interacts socially with each other. The main features of talk as
transactions are; it has a primarily information focus, the main focus is the
message and not the participants, participants employ communication
strategies to make themselves understood, there may be frequent questions,
repetitions, and comprehension checks, there may be negotiation and
digression, linguistic accuracy is not always important.
3. Talk as performance. This kind of function includes public talk which
transmits information to the audiences, public announcements, and speeches.
Most of these talks are in the form of monolog rather than dialog and are closer
to written language rather than conversational language. The main features of
21
talk as performance are; there is a focus on both message and audience, it
reflects organization and sequencing, form and accuracy is important, language
is more like written language, it is often monologue.
Procedure text includes transactional function because the student as the
speaker which is explaining about some steps procedurally. The focus is on the
message. By explaining those steps, the students can deliver some messages or
some information of procedure text. Simulation technique can increase the
students to learn the material of procedure text and practice speaking.
B. Teaching Speaking.
In the teaching of English, the students are expected master four
language skills, and speaking is one of the skills that must be learned by all
students when they are learning English. Richard, Platt and Weber stated that
communicative competence as an important part of teaching speaking includes
(a) knowledge of the grammar and vocabulary of the language; (b) knowledge of
rules of speaking; (c) knowing of how to use language appropriately22
Teaching speaking is a challenging responsibility as there are many
problems related to every day practice. Some fundamental problems that appear
in the speaking class include inhibition, complete silence, and low participation23.
Learners often feel afraid to say things in a foreign language classroom. They are
22
David Nunan, Second Language Teaching and Learning, (Canada: Heinle&Heinle Publisher, 1999), 226
23
usually worried in making mistakes, fearful of criticism or loosing face. In
addition, learners often complain that they can’t think of anything to say; they
have no motive to express themselves beyond the guilty of feeling that they
should speak. Commonly, in the speaking class, most of the students still confuse
with the teacher’s speak, so that they are decided to keep silence. According to
Penny Ur the problem is compounded by the tendency that some learners are
dominant, while others speak very little or not at all24.
The teacher is demanded to design an activity that will be able to
overcome those problem. Penny Ur suggests four characteristic of successful
speaking in the class25. First, much of the time should be used for the activity
involving the learners to talk. Second, classroom activity should not be
dominated by talkative participants. Third, learners are eager to speak because
they are interested in the topic. Last, learners express themselves in utterances
that are relevant, easily comprehensible to each other, and of an acceptable level
of language accuracy.
Effective is defined as the capability of producing a desired result26. When
something is effective, it means it has an expected outcome or a deep produce.
Effective to improve means the students who were using simulation
technique got higher score in speaking ability of procedure text than those who
24
Penny Ur. A Course in Language Teaching: Practice and Theory(United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, 1999), 122
25
Penny Ur. A Course………., 120 26
were not.27Moreover, the effectiveness of simulation technique in improving the
speaking of procedure textdetermined from the speaking score gotten by
experimental group.
An effective speaking class can be seen when the post-test score is of
experimental group shows significant score improvement, it means that simulation
technique is effective to improve the speaking ability of procedure text. The
effectiveness simulation technique was calculated by using T-test paired
sampleusing SPSS 16 for windows of the effect size.
If Tvalue is lower than T table, it means that the students who were teach
using simulation technique does not get significant score improvement and it
indicates that simulation technique is not effective. But if Tvalue is higher than
Ttable, it means that the students who were teach using simulation technique get
significance score improvement and it indicate that simulation technique is
effective28
Simulation technique help the students to act out behave based on the
material that they have to deliver. The students have to simulate the real activity
as they were doing so in the real world. By simulation technique, the students can
improve their speaking skills. They can practice English while simulate the real
activity as they were doing in real life. So, simulation technique can solve the
speaking problem in the classroom.
27
Sugiyono. Statistika untuk Penelitian.(Bandung: Alfabeta, 2010), 125 28
C. Procedure Text.
One ofstandard competences that have to be mastered by seventh
graders is able to respond and express the meaning in a monologue of procedure
text and also get the idea of the text29. According to Mark Anderson a procedure
text is a piece of text that tells the readers or listeners how to do something. Its
purpose is to provide instructions for making something, doing something or
getting somewhere.30
A procedure text usually has three sections. These sections are also
called generic structure. There are:
1. An introductory statement or title that gives the aim or goal
a. This may be the title of the text
b. This may be an introductory paragraph
2. Materials needed for completing the procedure
a. This may be list
b. This may be paragraph
c. This step may be left out in some procedure
3. A sequence of steps in the correct order
a. Numbers can be used to show first, second, third and so on.
b. The order is usually important.
29
Depdiknas, StandarKompetensidanKompetensiDasar, (Jakarta: Depdiknas,2006), 4 30
c. Words such as now, next, and after this can be used.
d. The steps usually begin with a command such as add, stir, or push.
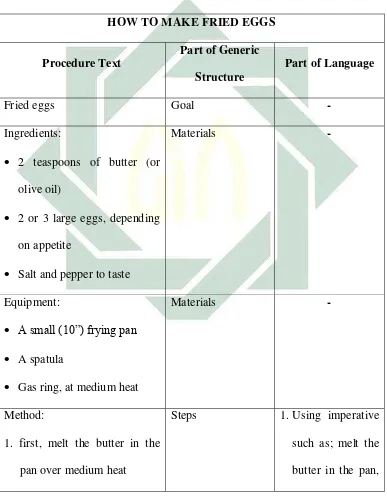
Table 2.1
Example of procedure text
HOW TO MAKE FRIED EGGS
Procedure Text
Part of Generic
Structure
Part of Language
Fried eggs Goal -
Ingredients:
2 teaspoons of butter (or
olive oil)
2 or 3 large eggs, depending
on appetite
Salt and pepper to taste
Materials -
Equipment:
A small (10”) frying pan
A spatula
Gas ring, at medium heat
Materials -
Method:
1. first, melt the butter in the
pan over medium heat
Steps 1.Using imperative
such as; melt the
2. then, crack open the eggs into
the pan and let fry until the
yolks begin to harden at the
edges (indicated by a
lightening in the yolk color)
3. using the spatula, flip the
eggs over and allow to cook
ten seconds for over-easy, or
up to one minute for
over-Simulation is a technique to teach speaking which are students simulates a
real- life encounter as if they were doing so in the real world32. Simulations are
31
Ken Hyland, Language Learning Simulation: A Practical Guide.(online serial) 31 (4) (http://eca.state.goy/forum/vols/vol31/no4/p16.htm accessed on June 21, 2015) 32
very similar to role-play both are interactive learning events, but generally role
play involves learners taking on characters that are not their own, while
participants in simulation they can act out behave as they. However, simulations
are more elaborate than role-play. In simulations, the students can bring items to
the class to create a realistic environment.
Accorder toJones the activities which involve simulation such as;
performing memorized dialogues, contextualized drills, cued dialogues,
role-playing, and improvisation33. Those activities are parts of simulation, but differ in
terms of teacher-control and learner-creativity. They can be viewed as part of
single continuum which links pre-communicative and communicative activities. In
dialogue-performance, the teacher’s control is at a maximum and the learner’s
creativity is at a minimum. In contextualized drills, the learner creates sentences
that may be new to him, but they have been predetermined by the teacher. Cued
dialogues are the borderline between pre-communicative and communicative
simulation. In cued dialogues, the teacher exercises direct control over the
meanings that are expressed, but not over the language that is used for expressing
them. In role-playing, the teacher controls only the situation and the learners’ roles
in it, but leaves the learners themselves to create the interaction. Improvisation is
the least controlled activity. The starting point for an improvisation may be a
simple everyday situation into which the learners are asked to project themselves.
33
E. The Advantage of Simulation Technique.
Hyland stated that there are five advantages of simulation34:
1. Motivation. Simulations encourage motivation because they ensure that
communication is purposeful rather than artificial. Participants are involved
as they identify with their roles and have the freedom to choose the
meanings they want to express. Because students can bring their background
experiences into class and make their own decisions, more interest and
excitement is created in learning.
2. Fluency development. A tenet of communicative teaching is that people
learn by doing. This statement is also supported by Richards and Lockhart,
there is some learners who learn best when they are physically involved in
the experience. They remember new information when they actively
participate in activities, field trips, and role play or simulation. Fluency is
encouraged in simulations because learners are immersed in a language-rich
environment where language use is centered on immediate communicative
needs.
3. Integrated of skills. Simulations provide the opportunity to learn the
pragmatic skills of using language appropriately, to develop the nonverbal
components of language, and to acquire intercultural and interpersonal
competence in a second language. Participants learn that successful
34
communication is a jointly achieved accomplishment involving a range of
skills. Simulations can also help develop cognitive abilities such as
analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information.
4. Active participant. Simulations provide a unique means of encouraging
learners to respond actively and to participate with their fellows. Absorbing
students’ in interaction encourages attention to input, an essential
requirement for language acquisition. Learning is more effective the more it
engages the learner, and simulations seek to achieve this.
5. Reduced anxiety. Simulations reduce the stress associated with learning and
using new language. This is due partly to the shift in classroom roles and
partly to the low cost of making errors compared with error consequences in
the real world. Not only do simulations offer a relatively safe environment
for making mistakes, but they also promote an egalitarian atmosphere
because there is no error correction to undermine confidence and divert
attention to utterance form. Students are not judged, corrected, or evaluated,
and this reduces their anxieties about linguistic performance, with a
consequent improvement in achievement. Moreover, there is less stress
F. The Procedure of Simulation Technique for Speaking Skill
Hyland said that the most important point of running a simulation is to
believe that is going to work35. He also has out lined some preparations and
procedures of implementing this technique as follow:
1. Setting up. The simulation should be carefully planned and chosen on the
basis of issues that are likely to maximize motivation and language use. The
emphasis is on creating believable situations that emphasize reality of context
over language, and this may mean using resources not specifically designed
for language work.
2. Getting going. Once the simulation has been selected or written, the students
can be introduced to the central ideas of the activity and encouraged to discuss
them. Participants must understand the nature of the task, their roles, and the
constraints of the environment. Information should be kept as brief and simple
as possible to avoid confusion, but can be given as homework texts or in the
native language to help speed understanding of what is involved. A variety of
listening and reading exercises will reinforce the transfer of information and
generate motivation, particularly if learners recognize they are developing
useful skills. Any specialist vocabulary and expressions should be introduced
at this stage.
35
3. Managing the activity. Fluency work demands that the teacher disengage from
the governing role and allow learners to produce and interpret language on
their own. Once the simulation is underway, the teacher becomes an activity
manager, advising and monitoring the learning environment. The management
of time and the activity during the simulation should be handled by the
students themselves. During the simulation the teacher becomes the observer
and collecting the data to share in the debriefing. Overt error correction should
be avoided and mistakes noted for discussion later.
4. Winding down. This is another communicative language opportunity for
students and should be approached positively rather than critically. During the
language debriefing the teacher takes a more directive and teaching role, as
this explores what was said and what was not said because the students did not
have appropriate language skills. It is a good idea to focus on the
communicative effectiveness of the language used and have a number of
general issues in mind to discuss. The content of the language debriefing may
be determined by the next stage of the syllabus or remedial urgency, but its
relationship to student needs is certain to be more apparent to the learners than
if it is simply based on a textbook course.
5. Assessing students. Students can be assessed in a variety of ways, depending
on the purpose of the activity. Generally, however, assessment will be based
on how students have performed on individual tasks and on their participation
such as a diary, report, oral presentation, news bulletin, etc., students can be
allocated marks for this. If this product is a joint effort, a group mark can be
allocated to each member, or the group itself can be asked to fairly share an
allocated mark among its members.
G.The Role of Teacher in Speaking Simulation.
According to Harmer the teachers need to play a number of roles during
speaking activities. However three have particular relevance to get students to
speak fluently36:
1. Prompter: students sometimes get lost, can’t think of what to say next or in
some other way lose the fluency we expect of them. Teacher can leave the
students to struggle out of such situations on their own, and indeed sometimes
this may be the best option. However, teacher may be able to help them and
the activity to progress by offering discrete suggestions.
2. Participant: teachers should be good animators when asking student to
produce language. Sometimes this can be achieved by setting up an activity
clearly and with enthusiasm.
3. Feedback provider: When the students have completed an activity, the teacher
just give the respond to the content of the activity as well as the language
used.When the students are in the middle of speaking task, the teacher must
36
give them helpful and gentle correction to get students out of difficult
misunderstanding and hesitations.
H.Previous Study
1. The Technique to Teach Speaking Viewed from Students’ Creativity. An Experimental Study on Informatics Students’ of STT RRI Malang in the
Academic Year of 2012/2013, by AfiNormawati
AfiNormawati described that the research method applied in this
research was an experimental research. The samples were taken by using cluster
random sampling technique. The experimental class was taught by using
simulation technique, while the control class was taught using cooperative
script technique.
The research findings are: (1) Simulation technique is more effective
than Cooperative Script technique to teach speaking for Informatics students of
STT RRI Malang; (2) the speaking skill of the students having high creativity is
better than that of the students having low creativity; (3) there is an interaction
between teaching techniques and students’ creativity in teaching speaking. For
the students who have high creativity, Simulation technique is more effective
than Cooperative Script technique.
2. Improving Students’ Speaking Skill through Simulation of Eleventh Grade
Students in SMK PGRI I Bojonegoro in Academic Year 2010/2011 by
The writer employs a classroom action research. This research was
conducted in five meetings. The data sources of this research are the scores of
students pre-test and post-test. Methods of the collecting data are observation
format, field note, test and documentation.
Based on the analysis the writer draws some conclusions. First, the
implementation of simulation technique in class action research is effective
because the students can enrich the vocabulary more, not afraid and shy to
perform in front of the class and they are active in speaking activities. The
processes of improving speaking skill using simulation are asking the students
to act as other person in different situation. Second, the result of teaching action
using simulation technique shows that the students’ score of post-test is higher
than students’ score of post-test. So, the writer can conclude that the students
are able to achieve a good result. Third, the students’ response of teaching
speaking using simulation technique in speaking class is good.
3. The Effectiveness of Using Simulation in Improving Students’ Speaking
Skill for Vocational High School. ( An Experimental Study at The Eleventh
Grade Students of SMKN 2 Jepara in The Academic Year of 2010/2011 )
This final project aims at examining the effectiveness of simulation
technique in improving students’ speaking skill for Vocation High School. This
study was conducted because teaching speaking for vocational school students
The post-test only quasi experimental design was used in conducting
the research. The experimental group was taught by using simulation technique
for speaking whereas the control group was taught without using simulation
technique. After giving treatment, the post test, mini role play- open instruction,
was conducted both in classes.
Based on the result of the study it showed that the level in speaking
skill for experimental group got better than the control group. There was
significant difference between the students who were taught by using
simulation technique and the students who were taught without using
simulation technique.
The writer concluded that simulation technique could be one of the
appropriate techniques in teaching speaking to improve the students speaking
skill because it gives authentic model and builds contextual situation in group
activities that enhances students social and personal development.
4. An Investigation of Effectiveness of Simulation in Developing Oral Skills:
A Case Study, by Dr.ChoudharyZahitJavidTaif University, Taif, Saudy
Arabia.
The rationale and purpose behind this research study was to implement
this modern technique of simulation in English language teaching to freshman
students of pharmacy. The sample of this study comprised of the whole
group was taught by using integrated simulation activities in their English
language classes. The control group was taught without this technique. The
pre-test and post-pre-test scores have been analyzed that have clearly reported that the
experimental group out-performed the control group in their oral
communication.
But the results of both the groups in their listening skills quizzes have
not showed significant differences. The research suggests that ELT faculty
members should use this innovative teaching technique especially in their oral
communication classes.
Finally, according to those findings, the researcher is interested in
conducting this study. By using simulation technique, the researcher hopefully
that solve the teaching and learning problem in the classroom. The researcher
interested in applying the simulation technique to teach speaking of procedure
text.
The difference between the previous study and this study is to find out
the effect of simulation technique in teaching speaking of procedure text at
seventh grade of Patriot Junior High School Jombang in academic year
2014-2015. The researcher only focuses on improving speaking ability of procedure
text by using simulation technique.
28
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter describes the steps taken to conduct the study. The description
involves the research design, population and sample, research instruments, data
collection technique, and data analysis technique.
A.Research Design
The research design which is used in this study is an experimental
research. In conducting the experiment, the researcher devotes great care to the
manipulation and the control of the variables and to the observation and
measurement of the result37.
In this experimental design, the researcher used quasi-experimental
design, especially in nonequivalent (pre-test and post-test) control group design. In
this design, there are two groups: experimental group and control group. Both of
the groups are given pre-test and post-test. First, both groups are given a pre-test.
Then the treatment is administered to the experimental group only. Both groups
then are given a post-test to examine the difference between the two groups as the
effect of treatment. In this research there are two variables of the study.
37
1. Independent variable:
According to Sugiono independent variable is a variable that affects or
is the cause of the change or the emergence of the dependent variable38.
Independent variable is the mayor variable that is selected, manipulated, and
measured to investigation. In this study, the used of simulation technique in
teaching speaking of procedure text was the independent variable, which
given symbol X.
2. Dependent variable:
According to Sugiono, dependent variable is a variable that is affected
or which become result, because of the independent variable39. Dependent
variable is the variable that observed and measured for determines the effect
of independent variable. In this study the scores of speaking ability of
procedure text at seventh graders of SMP Patriot Jombang was dependent
variable, that given symbol Y.
B. Population and Sample
The importantpart of a research is population and sample. Population is
all subject have certain quality or characteristic which is determined by the
38
Sugiyono, MetodePenelitianKuantitatif, Kualitatifdan R&D, (Bandung: Alfabeta, 2013), 39 39
researcher. Meanwhile, sample is a part of the number of characteristics owned
by the population40.
1. Population
According to Sugiyono, population is a generalization region
consisting of the object or subject that have certain qualities and
characteristics defined by the researcher to learn and then drawn
conclusions41.
The populations on this study are all the students of seventh graders at
SMP Patriot Jombang in the academic year 2014-2015. There are three classes
and all of the classes had similar average in score.
2. Sample
According to Sugiyono, sample is part of the number and
characteristics possessed by this population. What is learned from the sample,
the conclusion will be applied to the population42. In this research, the
researcher took A and B classes by lottery in which A class was experimental
class which got a treatment while B class was the control class. Each class
consisted of 29 students, where A class consisted of 24 male and 5 female,
while B class consisted of 23 male and 6 female.
Schematically, the experimental research is described below:
40
Sugiyono, MetodePenelitianKuantitatif, Kualitatifdan R&D, (Bandung: Alfabeta, 2013), 80-81. 41
Sugiyono, MetodePenelitian……., 80 42
Group Pretest Independent variable Post test
A
B
Y1
Y1
X
-Y2
Y2
(Non- randomized control group. Pretest post-test design. Ary, 2012: 307)
A : The experimental group that will be taught speaking of procedure text
by using simulation technique.
B : The control group that will be taught speaking of procedure text by
using non-simulation technique.
X : The treatment (simulation technique).
Y1 : The pre-test before the experimental treatment.
Y2 : The post-test after the experimental treatment.
C. Research Instrument.
As an experimental research, the instrument used in this research was test.
By the test, the researcher differentiates the result of pre-test and post-test.
According to Bachman and Palmer the test rubric defines the structure of an
assessment and provides instructions to participants about what they should do.43
The use of instrument is very important in the research, because its
function as the device used to collect the data. According to Arikunto, research
43
instrument are tools or facilities that are using by the researcher in order to collect
data. So that makes the job easier, complete and systematic44
1. Paper based Test.
The teacher will use Test to answer the research question about whether
simulation technique is more effective to improve students’ speaking ability of
procedure text or not. It was divided into two, pretest and post-test:
a. Pretest: pretest it is preliminary test administered to determine a students’
baseline knowledge for an educational experience or course of study45
It wasa administered to both experimental and control group. This test was
purposed to obtain the data of the students, basic speaking skill. Speaking
test was the instrument for the study. The students were asked to present a
speaking of procedure text orally. Four criteria are assessed in this test, they
are grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation and fluency. (Appendix 3and
Appendix 4)
b. Posttest: it is a test given to students after completion of experimental that
used to measure the students’ ability after getting treatments.
The last instrument used was posttest. It was conducted at the end of the
study. It was used to measure the students’ speaking ability after the
treatment. It was also intended to know the differences between the
students’ score of both groups.
44
Suharsimi Arikunto,Procedure Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan Praktek, (Jakarta: PT Adi Mahasatya,2006),149
45
D. Data Collection Technique.
Data collection technique used in this study was in the form of test. The
tests consisted of pre-test and post-test administered consecutively in both the
experimental and control group.
Test is used to know the students’ achievement in speaking of procedure
text. The data in this study collected through the perform students speaking
procedure text by using simulation technique, and also using scores, scores
obtained by using scoring rubric.
1. Pre- Test.
Pre-test was a test which was given before the students get a treatment.
Pre-test to measure the students’ speaking ability in the beginning related to
the material will be used. The pre-test is used in both experimental and
control groups. The purpose of pre-test is to measure the equivalence scores
between experimental and control class.
The researcher gives a performance test for the experimental group and
control group about how to make omelet in procedure text. In giving the test
the students have to retell the procedure text after they make a procedure text
by their group. The teacher divided the class into some group, one group
contains of 4-5 students, and then the teacher shows one picture about
omelet in the slide.
In this test the students are scored based on some speaking
vocabulary. In each aspects there are score in level one until four, the
students would get maximum score four when he or she masters in that
aspect, they would get score three when there is one item that they cannot
master it. They would lack one score when there is one item again that they
cannot master and so on. After the test end, determine the score by
calculation the total score.
2. Post-test
Post-test was given after teaching learning process done. Post-test is
giving to both experimental group and control group. The aim is to know the
different result between experimental and control group. In the post-test, the
control groups will be create a procedure text with free topics and the topic
must be different from the text which used for pre-test.
The experimental groups are asked to create a procedure text, first, the
students prepare the thing they need to do simulation technique and present
their procedure text in front of the class. Theresearcher examines the
students’ performance and gives score about their pronunciation, fluency,
structure, and vocabulary. The last stage was assessing the students that had
been done during their performance.
1. Standard Competence
Express the meaning in simple functional oral text and short functional
text to communicate with the surroundings.
2. Basic Competence
Express the meaning in simple and short monolog by using variety oral
language, accurately, orderly, and acceptably to communicate with the
surroundings in the form of descriptive and procedure.
3. Sub Basic Competence
Express the meaning in simple and short monolog by using variety oral
language, accurately, orderly, and acceptably to communicate with the
surroundings in the form of descriptive.
4. Indicators
1) The students are able to understand the procedure text well.
2) The students are able to tell the goal of their procedure text.
3) The students are able to mentions the ingredients and the materials of
their procedure text.
4) The students are able to mentions the steps of their procedure text.
5) The students are able to present their procedure text based on its
generic features; use of imperative, use of simple present tense, use of
appropriate conjunctions.
Based on the topic, please compose a procedure text with your group then
present it in front of the class!
Choose one of the topics below!
a. How to make a cup of coffee
b. How to make a cup of energen
c. How to make a cup of sweet lemon tea
d. How to make a cup of milk
d. How to make a bowl of instant noodle
e. How to make a plate of instant fried noodle
f. how to make fried egg.
In this scoring there are four aspects which scored, there are grammar,
pronunciation, fluency, and accuracy. The rubric of scoring as follow:
Accent may be
research. In conducting this research some step which the researcher will do are:
2. Asking permission to the headmaster of SMP Patriot Jombang, where the
research was done.
3. Determining the class as the subject of the study. The researcher took A and B
classes by lottery, which A class was the experimental and B class was the
control class.
4. Giving pre-test to both experimental and control group.
5. Teaching the experimental group (A class) about procedure text material by
using simulation technique. Simulation technique was a kind of treatment
which the researcher gives.
6. Teaching the control group (B class) about procedure text material without
using simulation technique.
7. Conducting a post test for both experimental (A class) and control group (B
class). For A class, the students were asked to make a procedure text in a group
and present it in front of the class by using simulation. For control group, the
researcher will be asked the students to make a procedure text in group and
present it in front of the class without using simulation technique.
8. Analyzing the result of comparation between pre-test and post-test from both
groups.
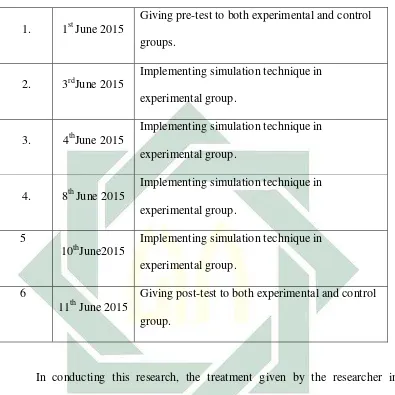
Table 3.3
The schedule of treatment
1. 1st June 2015
Giving pre-test to both experimental and control
groups.
2. 3rdJune 2015
Implementing simulation technique in
experimental group.
3. 4thJune 2015
Implementing simulation technique in
experimental group.
4. 8th June 2015
Implementing simulation technique in
experimental group.
5
10thJune2015
Implementing simulation technique in
experimental group.
6
11th June 2015
Giving post-test to both experimental and control
group.
In conducting this research, the treatment given by the researcher in
experimental group is simulation technique. This technique is the independent
variable which could affect the dependent variable in which the dependent variable
of this research is the students’ speaking ability. The steps in giving treatment to
experimental group can be seen as follow:
Table 3.4
Process of Doing Treatment in Experimental and Control Group
Experimental Group Control Group
1. Greeting.
2. Checking students’ presence.
3. Delivering the instructional
objectives.
Whilst- activity
Exploration
1. The researcher sets up the class by
dividing the class into some
groups which consists of 4-5
students.
2. The researcher explains about
procedure text.
3. The researcher explains about
simulation technique as the way in
giving the example of procedure
text.*
4. The researcher gives the example
of procedure text while doing
simulation.*
5. The researcher gives some topics
and ask each group to choose one
1. Greeting.
2. Checking students’ presence.
3. Delivering the instructional
objectives.
Whilst- activity
Exploration
1. The researcher explains about
procedure text.
2. The researcher gives the
example of procedure text
without doing simulation.*
3. The researcher divides the
students into some groups.
4. The researcher gives some
topics and asks the students to
choose one of the topics by
lottery.
5. The researcher asks the students
to compose a procedure text
of the topic by lottery.
6. The researcher explained the
students’ task and what should do
with their task.
7. The researcher asks the students to
compose a procedure text with
their group based on the topic they
get.
Elaboration
1. The researcher asks the students to
present their procedure text in turn
with their group while doing
simulation in front of the class.*
2. The researcher observes the
students’ performance.
Confirmation
1. The researcher gives questions
related to the procedure text that
has been presented.
2. The researcher asks the students
whether they get difficulty during
Elaboration
1. The researcher asks each group
to present the procedure text in
turn in front of the class without
doing simulation.*
2. The researcher observes the
students’ performance.
Confirmation
1. The researcher gives some
questions related to the
procedure text that has been
presented.
2. The researcher gives feedback
and correct the students’
mistakes.
Post- activity
1. Conclusion.
simulation.*
3. The researcher does debriefing. In
this case, the researcher discusses
the students’ performance and the
students’ mistakes and also gives
some exploration presented.
Post- activity
1. Conclusion.
2. Closing.
Based on the table above, it could be seen that the teaching and
learning process in both of the groups will do in many steps. But there are
some differences in the way of teaching and the differences activities which
the researcher do is show by asterisks. The difference is the technique that
the researcher used. In control group the researcher will not use simulation
as a technique in teaching learning process. Meanwhile, in experimental
group the researcher use simulation technique in teaching procedure text and
this technique is a kind of treatment that is given to the students.
1. The process conducted the treatment in experimental group.
The activity was divided into five parts; they were setting up, getting
setting up, the teacher prepared the topic and the materials which would be
needed. The teacher also asked the students to bring some materials by
themselves.
The teacher chose some topics that were familiar to the students to
make the lesson became meaningful. Then, the teacher moved on the
second stage that was getting going. In getting going, the teacher introduced
the students to their roles in the simulation by giving an example of making
a glass of lemon tea. The teacher tried to make the students understood
about their task.
After that, the teacher moved on to the third stage that was managing
the activity. In this stage, the teacher asked the students to do the simulation
in front of the class according to the topic that had been prepared by the
teacher. The simulations were done depended on the topics. If the topics
were easy and did not need much preparation, then the simulation would be
done spontaneously. The students manage their activity and control the time,
while the teacher only observed their performance and also assessed them.
The fourth stage was winding down. In winding down, the teacher did
debriefing with the students. The teacher reviewed and discussed the
students’ mistake. The last stage was assessing the students that had been
done during their performance.
The students were going to make simulations about making drinks and
simulation spontaneously. The teacher had prepared some ingredients to
make some kind of drinks. The captain of each group was asked to pick
some of the ingredients that they would need to make a drink. After that, the
teacher commanded the students to not make their drink yet. The teacher
asked them to imagine what they were going to do with those ingredients.
She gave 5 minutes for the students to prepare. After the time for discussion
and preparation was up, the teacher asked the students to come forward and
do the simulation of making a drink. Before they did the simulation of
making a drink, the teacher explained the criteria that would be assessed.
Those criteria were grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation and fluency.
After getting treatment in four meetings, the post-test was conducted.
They were given the speaking test of procedure text. The students are asked
to create a procedure text, first, the students prepare the thing they need to do
simulation technique and present their procedure text in front of the class.
Theresearcher examines the students’ performance and gives score about
their pronunciation, fluency, structure, and vocabulary. The researcher was
assessing the students that had been done during their performance.
2. The process of teaching in control group.
In teaching learning process, the students of seventh B class, as control
class, were taught in four meetings using conventional method (lecturing
First, the teacher was informed about the topic would be going to
discuss.Then the teacher explained about procedure text, generic structure,
and language feature.The teacher also explained some related vocabulary.
The teacher was explanation about how to make a glass of lemon tea.The
students read a text about the related topic, they practice orally in
groups.Then the teacher gave some correction of their mistaken.
After the time for discussion and preparation was up, the teacher asked
the students to come forward and performed about their speaking of
procedure text.Before they did the speaking of procedure text, the teacher
explained the criteria that would be assessed. Those criteria were grammar,
vocabulary, pronunciation and fluency.
In the next meeting, the teacher gave the other topic about speaking of
procedure text. Then they try to discuss in groups and performed in front of
class.
After four meetings, the post test was conducted. They were given the
speaking test of procedure text. The students are asked to create a procedure
text, first, the students prepare about their speaking and present their
procedure text in front of the class. The researcher examines the students’
performance and gives score about their pronunciation, fluency, structure,
and vocabulary.