CHAPTER 6:
DESIGN & REDESIGN
OF
Exhibit 6-1 Exhibit 6-1
Model for Design of Work Systems
Model for Design of Work Systems
Exhibit 6-1
Exhibit 6-1
Model for Design of Work Systems
Design of Work Systems
Design of Work Systems
Design of Work Systems
Design of Work Systems
• Job SpecializationJob Specialization
– Creates jobs with very narrow task (activity) assignmentsCreates jobs with very narrow task (activity) assignments
– Resulted in high efficiency, quickly achieved job competency, low Resulted in high efficiency, quickly achieved job competency, low
training costs, but created monotonous jobs
training costs, but created monotonous jobs
• Job EnlargementJob Enlargement
– An increase in task variety to relieve boredomAn increase in task variety to relieve boredom
• Job RotationJob Rotation
– Employees moved across different specialized positionsEmployees moved across different specialized positions
– Enlargement and rotation add variety, but not necessarily responsibilityEnlargement and rotation add variety, but not necessarily responsibility
• Job SpecializationJob Specialization
– Creates jobs with very narrow task (activity) assignmentsCreates jobs with very narrow task (activity) assignments
– Resulted in high efficiency, quickly achieved job competency, low Resulted in high efficiency, quickly achieved job competency, low
training costs, but created monotonous jobs
training costs, but created monotonous jobs • Job EnlargementJob Enlargement
– An increase in task variety to relieve boredomAn increase in task variety to relieve boredom • Job RotationJob Rotation
– Employees moved across different specialized positionsEmployees moved across different specialized positions
Design of Work Systems
Design of Work Systems
Design of Work Systems
Design of Work Systems
• Job EnrichmentJob Enrichment
– Increasing amount of responsibility for quality and productivity Increasing amount of responsibility for quality and productivity
that employees have for their own work
that employees have for their own work
• Vertical LoadingVertical Loading
– Reassignment of job responsibility formerly delegated to Reassignment of job responsibility formerly delegated to
supervisor to the employee
supervisor to the employee
• Job EnrichmentJob Enrichment
– Increasing amount of responsibility for quality and productivity Increasing amount of responsibility for quality and productivity that employees have for their own work
that employees have for their own work • Vertical LoadingVertical Loading
– Reassignment of job responsibility formerly delegated to Reassignment of job responsibility formerly delegated to supervisor to the employee
Five Core Job Characteristics
Five Core Job Characteristics
Five Core Job Characteristics
Five Core Job Characteristics
• Skill varietySkill variety
–Extent to which work allows Extent to which work allows
employee to use variety of skills
employee to use variety of skills
• Task identityTask identity
–Extent to which work allows Extent to which work allows
employee to complete whole or
employee to complete whole or
identifiable piece of work
identifiable piece of work
• Task significanceTask significance
–Extent to which employee Extent to which employee
perceives that work is important
perceives that work is important
and meaningful to those inside or
and meaningful to those inside or
outside organization
outside organization
• Skill varietySkill variety
–Extent to which work allows Extent to which work allows
employee to use variety of skills
employee to use variety of skills • Task identityTask identity
–Extent to which work allows Extent to which work allows
employee to complete whole or
employee to complete whole or
identifiable piece of work
identifiable piece of work • Task significanceTask significance
–Extent to which employee Extent to which employee
perceives that work is important
perceives that work is important
and meaningful to those inside or
and meaningful to those inside or
outside organization
outside organization
• AutonomyAutonomy
–Extent to which employee is able Extent to which employee is able
to work and determine work
to work and determine work
procedure at own discretion
procedure at own discretion
• FeedbackFeedback
–Extent to which work allows Extent to which work allows
employee to gain sense of how
employee to gain sense of how
well job responsibilities are met
well job responsibilities are met
• AutonomyAutonomy
–Extent to which employee is able Extent to which employee is able
to work and determine work
to work and determine work
procedure at own discretion
procedure at own discretion • FeedbackFeedback
–Extent to which work allows Extent to which work allows
employee to gain sense of how
employee to gain sense of how
well job responsibilities are met
Exhibit 6-2 Exhibit 6-2
Job Characteristics Model
Job Characteristics Model
Exhibit 6-2
Exhibit 6-2
Job Characteristics Model
What Workers Need
What Workers Need
What Workers Need
What Workers Need
• Changing demographics Changing demographics
& life styles
& life styles
– Worker needs vary by age, Worker needs vary by age,
gender, race, religion,
gender, race, religion,
physical abilities, sexual
physical abilities, sexual
orientation, and marital and
orientation, and marital and
family status
family status
• Employee needs for work/Employee needs for work/
life balance
life balance
– Workers less committed to Workers less committed to organizations today
organizations today
– Also suffer from burnout and Also suffer from burnout and
lower performance
lower performance
• Changing demographics Changing demographics
& life styles
& life styles
– Worker needs vary by age, Worker needs vary by age,
gender, race, religion,
gender, race, religion,
physical abilities, sexual
physical abilities, sexual
orientation, and marital and
orientation, and marital and
family status
family status
• Employee needs for work/Employee needs for work/
life balance
life balance
– Workers less committed to Workers less committed to organizations today
organizations today
– Also suffer from burnout and Also suffer from burnout and
lower performance
lower performance
• Employee needs Employee needs
representation (“voice”)
representation (“voice”)
– Workers want to be involved Workers want to be involved
in work-related issues, and
in work-related issues, and
expect organization to listen
expect organization to listen
to concerns
to concerns
• Employee concerns about Employee concerns about
safety in workplace
safety in workplace
– Workers want safe, hazard-Workers want safe,
hazard-free working environment
free working environment
• Employee needs Employee needs
representation (“voice”)
representation (“voice”) – Workers want to be involved Workers want to be involved
in work-related issues, and
in work-related issues, and
expect organization to listen
expect organization to listen
to concerns
to concerns
• Employee concerns about Employee concerns about
safety in workplace
safety in workplace
– Workers want safe, hazard-Workers want safe,
hazard-free working environment
Types of Task Interdependence
Types of Task Interdependence
Types of Task Interdependence
Types of Task Interdependence
• Pooled interdependencePooled interdependence
– Individual employees work Individual employees work
independently of each other in
independently of each other in
performing tasks but utilize
performing tasks but utilize
coordination of activities
coordination of activities
• Sequential Sequential
interdependence
interdependence
– Work in process flow is linear, Work in process flow is linear, from one individual to another
from one individual to another – One individual depends on One individual depends on
timely completion of quality
timely completion of quality
work from another coworker
work from another coworker
• Pooled interdependencePooled interdependence – Individual employees work Individual employees work
independently of each other in
independently of each other in
performing tasks but utilize
performing tasks but utilize
coordination of activities
coordination of activities • Sequential Sequential
interdependence
interdependence
– Work in process flow is linear, Work in process flow is linear, from one individual to another
from one individual to another – One individual depends on One individual depends on
timely completion of quality
timely completion of quality
work from another coworker
work from another coworker
• Reciprocal Reciprocal
interdependence
interdependence
– Workflow is randomWorkflow is random – Responds to immediate Responds to immediate
situation
situation
– Employees have joint and Employees have joint and
shared responsibilities for
shared responsibilities for
work
work
• Higher levels of Higher levels of
interdependence require
interdependence require
higher levels of
higher levels of
coordination and attention
coordination and attention
• Reciprocal Reciprocal
interdependence
interdependence – Workflow is randomWorkflow is random – Responds to immediate Responds to immediate
situation
situation
– Employees have joint and Employees have joint and
shared responsibilities for
shared responsibilities for
work
work
• Higher levels of Higher levels of
interdependence require
interdependence require
higher levels of
higher levels of
coordination and attention
Redesign of Work Systems
Redesign of Work Systems
Redesign of Work Systems
Redesign of Work Systems
• Current and future work systems more broadly Current and future work systems more broadly defined, and more closely related to strategic defined, and more closely related to strategic
choices choices
• Workers becoming more involved in design and Workers becoming more involved in design and reengineering of jobs
reengineering of jobs
• Cross-function teams strategically beneficialCross-function teams strategically beneficial
– Also create challenges in effectively managing themselvesAlso create challenges in effectively managing themselves
• Employees raised in individualistic cultures need Employees raised in individualistic cultures need training to be effective team members
training to be effective team members
• Current and future work systems more broadly Current and future work systems more broadly defined, and more closely related to strategic defined, and more closely related to strategic
choices choices
• Workers becoming more involved in design and Workers becoming more involved in design and reengineering of jobs
reengineering of jobs
• Cross-function teams strategically beneficialCross-function teams strategically beneficial
– Also create challenges in effectively managing themselvesAlso create challenges in effectively managing themselves • Employees raised in individualistic cultures need Employees raised in individualistic cultures need
Outsourcing
Outsourcing
Outsourcing
Outsourcing
• Involves contracting out some of organization’s Involves contracting out some of organization’s noncore work activities to outside specialists
noncore work activities to outside specialists
– Can do work more effectivelyCan do work more effectively
– Often for less than cost of doing work in-houseOften for less than cost of doing work in-house
• Areas frequently outsourced:Areas frequently outsourced:
– PayrollPayroll – BenefitsBenefits
– Technological supportTechnological support
• More than 75% of organizations outsource at least More than 75% of organizations outsource at least one HR function
one HR function
• Involves contracting out some of organization’s Involves contracting out some of organization’s noncore work activities to outside specialists
noncore work activities to outside specialists – Can do work more effectivelyCan do work more effectively
– Often for less than cost of doing work in-houseOften for less than cost of doing work in-house • Areas frequently outsourced:Areas frequently outsourced:
– PayrollPayroll – BenefitsBenefits
– Technological supportTechnological support
• More than 75% of organizations outsource at least More than 75% of organizations outsource at least one HR function
Outsourcing
Outsourcing
Outsourcing
Outsourcing
•
Can free up HR staff to focus on more
Can free up HR staff to focus on more
strategic issues
strategic issues
•
Considerations:
Considerations:
– Cost savingsCost savings
– Whether contractor can deliverWhether contractor can deliver – Compliance with lawsCompliance with laws
– Impacts on employees whose jobs might be lostImpacts on employees whose jobs might be lost – Impacts on morale of remaining employeesImpacts on morale of remaining employees
•
Can free up HR staff to focus on more
Can free up HR staff to focus on more
strategic issues
strategic issues
•
Considerations:
Considerations:
– Cost savingsCost savings
– Whether contractor can deliverWhether contractor can deliver – Compliance with lawsCompliance with laws
Offshoring
Offshoring
Offshoring
Offshoring
• Involves exporting tasks and jobs to countries Involves exporting tasks and jobs to countries
where labor costs are significantly less than in the where labor costs are significantly less than in the
U.S. U.S.
• India remains largest marketIndia remains largest market
• Wages approximately 10% of those paid in U.S.Wages approximately 10% of those paid in U.S.
– Often considered good by local standardsOften considered good by local standards
• Challenge of managing virtual global teamsChallenge of managing virtual global teams • Need for tight organizational and operational Need for tight organizational and operational
control to ensure coordination and communication control to ensure coordination and communication • Involves exporting tasks and jobs to countries Involves exporting tasks and jobs to countries
where labor costs are significantly less than in the where labor costs are significantly less than in the
U.S. U.S.
• India remains largest marketIndia remains largest market
• Wages approximately 10% of those paid in U.S.Wages approximately 10% of those paid in U.S. – Often considered good by local standardsOften considered good by local standards
• Challenge of managing virtual global teamsChallenge of managing virtual global teams • Need for tight organizational and operational Need for tight organizational and operational
Offshoring
Offshoring
Offshoring
Offshoring
•
Advantages
Advantages
– Cost savingsCost savings
– Extend work day to Extend work day to
24 hours
24 hours
•
Advantages
Advantages
– Cost savingsCost savings– Extend work day to Extend work day to
24 hours
24 hours
•
Disadvantages
Disadvantages
– Loss of domestic Loss of domestic
jobs
jobs
– Transfer of technical Transfer of technical
knowledge
knowledge
– Public image/loyalty Public image/loyalty
concerns
concerns
•
Disadvantages
Disadvantages
– Loss of domestic Loss of domesticjobs
jobs
– Transfer of technical Transfer of technical
knowledge
knowledge
– Public image/loyalty Public image/loyalty
concerns
Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and Acquisitions
•
Mergers pursued for a variety of reasons:
Mergers pursued for a variety of reasons:
– Economies of scale in operationsEconomies of scale in operations – Consolidation in saturated marketsConsolidation in saturated markets
– Improving competitive position through larger asset Improving competitive position through larger asset
base
base
•
Two thirds of mergers fail
Two thirds of mergers fail
– Largely because of inability to merge cultural and Largely because of inability to merge cultural and
other human factors
other human factors
•
Mergers pursued for a variety of reasons:
Mergers pursued for a variety of reasons:
– Economies of scale in operationsEconomies of scale in operations– Consolidation in saturated marketsConsolidation in saturated markets
– Improving competitive position through larger asset Improving competitive position through larger asset
base
base
•
Two thirds of mergers fail
Two thirds of mergers fail
– Largely because of inability to merge cultural and Largely because of inability to merge cultural and
other human factors
Barriers to Change
Barriers to Change
Barriers to Change
Barriers to Change
• Disrupting status quo may be met with Disrupting status quo may be met with resistanceresistance by both employees and managers
by both employees and managers • Costs and reallocation of resourcesCosts and reallocation of resources
• Employees will resist change unless theyEmployees will resist change unless they
– Perceive need to changePerceive need to change – See benefits from changeSee benefits from change
• Risk and uncertainty; no guarantee of Risk and uncertainty; no guarantee of improvements
improvements
• Poor coordination and communication can Poor coordination and communication can undermine change initiatives
undermine change initiatives
• Disrupting status quo may be met with Disrupting status quo may be met with resistanceresistance by both employees and managers
by both employees and managers • Costs and reallocation of resourcesCosts and reallocation of resources
• Employees will resist change unless theyEmployees will resist change unless they – Perceive need to changePerceive need to change
– See benefits from changeSee benefits from change
• Risk and uncertainty; no guarantee of Risk and uncertainty; no guarantee of improvements
improvements
• Poor coordination and communication can Poor coordination and communication can undermine change initiatives
To Overcome Resistance to Change
To Overcome Resistance to Change
To Overcome Resistance to Change
To Overcome Resistance to Change
• Promote and implement change so it provides Promote and implement change so it provides benefits to those impacted
benefits to those impacted
• Involve employees in change process to increase Involve employees in change process to increase their commitment to change
their commitment to change
• Open, two-way communicationOpen, two-way communication
– Early, before change decisions are made Early, before change decisions are made – Dispel rumorsDispel rumors
– Increase trust and acceptance of change by keeping Increase trust and acceptance of change by keeping
employees informed and asking for input
employees informed and asking for input
• Promote and implement change so it provides Promote and implement change so it provides benefits to those impacted
benefits to those impacted
• Involve employees in change process to increase Involve employees in change process to increase their commitment to change
their commitment to change
• Open, two-way communicationOpen, two-way communication
– Early, before change decisions are made Early, before change decisions are made – Dispel rumorsDispel rumors
– Increase trust and acceptance of change by keeping Increase trust and acceptance of change by keeping employees informed and asking for input
Reading 6.1 (Nahavandi & Aranda) Reading 6.1 (Nahavandi & Aranda)
Restructuring Teams for Re-engineered Organizations
Restructuring Teams for Re-engineered Organizations Reading 6.1 (Nahavandi & Aranda)
Reading 6.1 (Nahavandi & Aranda)
Restructuring Teams for Re-engineered Organizations
Restructuring Teams for Re-engineered Organizations
•
Reasons for using teams in organizations:
Reasons for using teams in organizations:
– Unlikely one individual will have all of the knowledge Unlikely one individual will have all of the knowledge
and information needed to make complex decisions
and information needed to make complex decisions – Teams provide more “buy-in” to decisionsTeams provide more “buy-in” to decisions
– Managers believe teams enhance motivation and Managers believe teams enhance motivation and
productivity
productivity
– Facilitate acquisition and sharing of information vital Facilitate acquisition and sharing of information vital
to organizational growth and flexibility
to organizational growth and flexibility
– Facilitate variety of internal quality control initiativesFacilitate variety of internal quality control initiatives
•
Reasons for using teams in organizations:
Reasons for using teams in organizations:
– Unlikely one individual will have all of the knowledge Unlikely one individual will have all of the knowledge
and information needed to make complex decisions
and information needed to make complex decisions – Teams provide more “buy-in” to decisionsTeams provide more “buy-in” to decisions
– Managers believe teams enhance motivation and Managers believe teams enhance motivation and
productivity
productivity
– Facilitate acquisition and sharing of information vital Facilitate acquisition and sharing of information vital
to organizational growth and flexibility
to organizational growth and flexibility
Reading 6.1 Reading 6.1
Restructuring Teams for Re-engineered Organizations
Restructuring Teams for Re-engineered Organizations Reading 6.1
Reading 6.1
Restructuring Teams for Re-engineered Organizations
Restructuring Teams for Re-engineered Organizations
•
Problems with teams
Problems with teams
– May fail without proper training and supportMay fail without proper training and support
– Often poorly integrated into organization’s hierarchyOften poorly integrated into organization’s hierarchy – Individuals often feel their team contributions dilute Individuals often feel their team contributions dilute
personal success
personal success
– Few teams have found effective means to deal with Few teams have found effective means to deal with
“freeloaders”
“freeloaders”
– Usually not represented at top levels of organizations, Usually not represented at top levels of organizations,
sending a mixed message about their importance
sending a mixed message about their importance
•
Problems with teams
Problems with teams
– May fail without proper training and supportMay fail without proper training and support
– Often poorly integrated into organization’s hierarchyOften poorly integrated into organization’s hierarchy – Individuals often feel their team contributions dilute Individuals often feel their team contributions dilute
personal success
personal success
– Few teams have found effective means to deal with Few teams have found effective means to deal with
“freeloaders”
“freeloaders”
– Usually not represented at top levels of organizations, Usually not represented at top levels of organizations,
sending a mixed message about their importance
Reading 6.1 Reading 6.1
Restructuring Teams for Re-engineered Organizations
Restructuring Teams for Re-engineered Organizations Reading 6.1
Reading 6.1
Restructuring Teams for Re-engineered Organizations
Restructuring Teams for Re-engineered Organizations
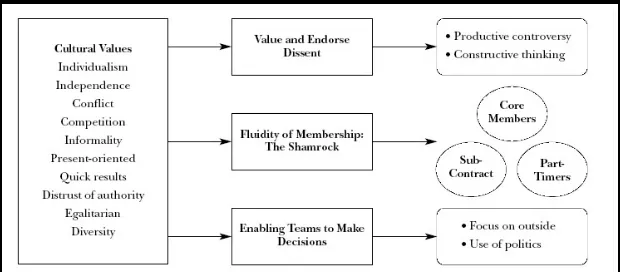
•
Three keys to successful teams
Three keys to successful teams
– Value and endorse dissentValue and endorse dissent
– Encourage fluidity of membershipEncourage fluidity of membership – Enable teams to make decisionsEnable teams to make decisions
•
Three keys to successful teams
Three keys to successful teams
– Value and endorse dissentValue and endorse dissentFigure 1
Figure 1
Three Key Elements for Success of US Teams
Three Key Elements for Success of US Teams
Figure 1
Figure 1
Three Key Elements for Success of US Teams
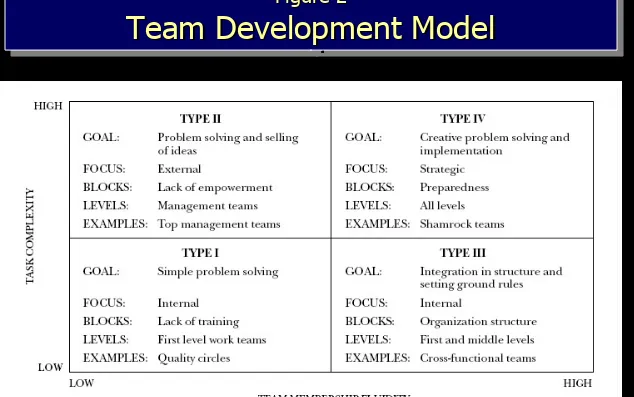
Figure 2 Figure 2
Team Development Model
Team Development Model
Figure 2
Figure 2
Team Development Model
Supplement to Reading 6.1 (Werner & Lester, 2001) Supplement to Reading 6.1 (Werner & Lester, 2001)
Research on Student Case Teams
Research on Student Case Teams Supplement to Reading 6.1 (Werner & Lester, 2001)
Supplement to Reading 6.1 (Werner & Lester, 2001)
Research on Student Case Teams
Research on Student Case Teams
What predicts the performance of student teams?
What predicts the performance of student teams?
SatisfactionSatisfaction GradeGrade
– Team structureTeam structure positive positive strong positive strong positive – Team spiritTeam spirit strong positive strong positive strong positive strong positive – Social supportSocial support strong positive strong positive negative negative
– Workload sharingWorkload sharing positive positive not significant not significant – CommunicationCommunication not significant not significant not significant not significant
What predicts the performance of student teams?
What predicts the performance of student teams?
SatisfactionSatisfaction GradeGrade
– Team structureTeam structure positive positive strong positive strong positive – Team spiritTeam spirit strong positive strong positive strong positive strong positive – Social supportSocial support strong positive strong positive negative negative
Reading 6.2 (Greer et al.)
Reading 6.2 (Greer et al.)
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
Reading 6.2 (Greer et al.)Reading 6.2 (Greer et al.)
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
•
Five competitive forces driving
Five competitive forces driving
organizations to outsource HR activities:
organizations to outsource HR activities:
– DownsizingDownsizing
– Rapid growth or declineRapid growth or decline – GlobalizationGlobalization
– Increased competitionIncreased competition – RestructuringRestructuring
•
Five competitive forces driving
Five competitive forces driving
organizations to outsource HR activities:
organizations to outsource HR activities:
– DownsizingDownsizing– Rapid growth or declineRapid growth or decline – GlobalizationGlobalization
Reading 6.2
Reading 6.2
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
Reading 6.2Reading 6.2
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
•
Operational rationales for outsourcing
Operational rationales for outsourcing
– Small firms lack resources; large firms gain Small firms lack resources; large firms gain
economies of scale
economies of scale
– Specialized HR expertise and objectivitySpecialized HR expertise and objectivity
• Reduced liability and risk in legally sensitive HR Reduced liability and risk in legally sensitive HR
areas
areas
– Innovations and economies of scale in HRIS Innovations and economies of scale in HRIS
technology used by outside vendors
technology used by outside vendors • Simplify transactions Simplify transactions
•
Operational rationales for outsourcing
Operational rationales for outsourcing
– Small firms lack resources; large firms gain Small firms lack resources; large firms gaineconomies of scale
economies of scale
– Specialized HR expertise and objectivitySpecialized HR expertise and objectivity
• Reduced liability and risk in legally sensitive HR Reduced liability and risk in legally sensitive HR
areas
areas
– Innovations and economies of scale in HRIS Innovations and economies of scale in HRIS
technology used by outside vendors
technology used by outside vendors
Reading 6.2 Reading 6.2
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
Reading 6.2
Reading 6.2
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
•
Operational rationales for outsourcing
Operational rationales for outsourcing
(continued):
(continued):
– Time-sensitive issues better handled by outsourcingTime-sensitive issues better handled by outsourcing – Temporary or cyclical increases in HR needsTemporary or cyclical increases in HR needs
– Efficient vendor management practices drive costs Efficient vendor management practices drive costs
down more than economies of scale
down more than economies of scale
– Specialized vendors offer activities as their core Specialized vendors offer activities as their core
business and strategic focus
business and strategic focus
•
Operational rationales for outsourcing
Operational rationales for outsourcing
(continued):
(continued):
– Time-sensitive issues better handled by outsourcingTime-sensitive issues better handled by outsourcing – Temporary or cyclical increases in HR needsTemporary or cyclical increases in HR needs
– Efficient vendor management practices drive costs Efficient vendor management practices drive costs
down more than economies of scale
down more than economies of scale
– Specialized vendors offer activities as their core Specialized vendors offer activities as their core
business and strategic focus
Reading 6.2 Reading 6.2
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
Reading 6.2
Reading 6.2
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
•
Strategic rationales for outsourcing:
Strategic rationales for outsourcing:
– Outsourcing nonstrategic activities permits HR to Outsourcing nonstrategic activities permits HR to
move away from administration toward strategic role
move away from administration toward strategic role – Decentralization of HR function through Decentralization of HR function through
redeployment of some of assets to operating units
redeployment of some of assets to operating units – Develop less bureaucratic HR departmentsDevelop less bureaucratic HR departments
– Downsizing may require HR to reduce staff, Downsizing may require HR to reduce staff,
eliminating specialized in-house expertise
eliminating specialized in-house expertise
– Outsourcing provides “big picture” perspectiveOutsourcing provides “big picture” perspective
•
Strategic rationales for outsourcing:
Strategic rationales for outsourcing:
– Outsourcing nonstrategic activities permits HR to Outsourcing nonstrategic activities permits HR to
move away from administration toward strategic role
move away from administration toward strategic role – Decentralization of HR function through Decentralization of HR function through
redeployment of some of assets to operating units
redeployment of some of assets to operating units – Develop less bureaucratic HR departmentsDevelop less bureaucratic HR departments
– Downsizing may require HR to reduce staff, Downsizing may require HR to reduce staff,
eliminating specialized in-house expertise
eliminating specialized in-house expertise
Reading 6.2 Reading 6.2
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
Reading 6.2
Reading 6.2
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
•
Positive outcomes
Positive outcomes
– Lower HR costsLower HR costs
– Higher service qualityHigher service quality
– Realignment or redeployment of internal HR Realignment or redeployment of internal HR
expertise
expertise
– Development of negotiation and broker skillsDevelopment of negotiation and broker skills – Enhanced credibility of HR functionEnhanced credibility of HR function
– Risk and uncertainty absorption by HR vendorRisk and uncertainty absorption by HR vendor
•
Positive outcomes
Positive outcomes
– Lower HR costsLower HR costs– Higher service qualityHigher service quality
– Realignment or redeployment of internal HR Realignment or redeployment of internal HR
expertise
expertise
– Development of negotiation and broker skillsDevelopment of negotiation and broker skills – Enhanced credibility of HR functionEnhanced credibility of HR function
Reading 6.2 Reading 6.2
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
Reading 6.2
Reading 6.2
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
HRM Outsourcing: Make or Buy Decision
•
Negative outcomes
Negative outcomes
–
Significant cost savings not always
Significant cost savings not always
experienced
experienced
–
Vendor switching costs
Vendor switching costs
–
Long-term vendor contracts
Long-term vendor contracts
–
Disruption of firm’s culture
Disruption of firm’s culture
–
Removal or distancing of HR function from
Removal or distancing of HR function from
employees
employees
•
Negative outcomes
Negative outcomes
–
Significant cost savings not always
Significant cost savings not always
experienced
experienced
–
Vendor switching costs
Vendor switching costs
–
Long-term vendor contracts
Long-term vendor contracts
–
Disruption of firm’s culture
Disruption of firm’s culture
–
Removal or distancing of HR function from
Removal or distancing of HR function from
employees
Reading 6.3 (Evangelista & Burke) Reading 6.3 (Evangelista & Burke)
Productivity in Downsizing
Productivity in Downsizing
Reading 6.3 (Evangelista & Burke)
Reading 6.3 (Evangelista & Burke)
Productivity in Downsizing
Productivity in Downsizing
•
Many downsizing firms face immediate
Many downsizing firms face immediate
challenge of keeping operations going with
challenge of keeping operations going with
minimal staff
minimal staff
•
Productivity often declines
Productivity often declines
•
Survivors
Survivors
– Working more hours Working more hours
– Receive with bigger workloadReceive with bigger workload
•
Morale often plummets
Morale often plummets
•
Many downsizing firms face immediate
Many downsizing firms face immediate
challenge of keeping operations going with
challenge of keeping operations going with
minimal staff
minimal staff
•
Productivity often declines
Productivity often declines
•
Survivors
Survivors
– Working more hours Working more hours
Reading 6.3 Reading 6.3
Work Redesign
Work Redesign
Reading 6.3
Reading 6.3
Work Redesign
Work Redesign
•
Typical problems
Typical problems
–
Failure or inability to identify and categorize
Failure or inability to identify and categorize
duties and assignments
duties and assignments
–
Failure to identify when employee is over-
Failure to identify when employee is
over-tasked
tasked
–
Failure to see when business unit’s demands
Failure to see when business unit’s demands
exceed its capacity
exceed its capacity
•
Typical problems
Typical problems
–
Failure or inability to identify and categorize
Failure or inability to identify and categorize
duties and assignments
duties and assignments
–
Failure to identify when employee is over-
Failure to identify when employee is
over-tasked
tasked
–
Failure to see when business unit’s demands
Failure to see when business unit’s demands
exceed its capacity
Reading 6.3 Reading 6.3
Work Redesign: Task Categories
Work Redesign: Task Categories
Reading 6.3
Reading 6.3
Work Redesign: Task Categories
Work Redesign: Task Categories
• Critical tasks Critical tasks
– Enable company to Enable company to
accomplish primary
accomplish primary
objectives
objectives
• Sub-critical tasks Sub-critical tasks
– Need to be Need to be
performed, but
performed, but
average standard of
average standard of
quality will suffice
quality will suffice
• Critical tasks Critical tasks
– Enable company to Enable company to
accomplish primary
accomplish primary
objectives
objectives
• Sub-critical tasks Sub-critical tasks – Need to be Need to be
performed, but
performed, but
average standard of
average standard of
quality will suffice
quality will suffice
• Minor tasks Minor tasks
– Add value to firm, but Add value to firm, but
will not hinder
will not hinder
operations or goals if
operations or goals if
left undone
left undone
• Unnecessary tasks Unnecessary tasks
– Can be discarded Can be discarded
because they drain
because they drain
resources
resources
• Minor tasks Minor tasks
– Add value to firm, but Add value to firm, but
will not hinder
will not hinder
operations or goals if
operations or goals if
left undone
left undone
• Unnecessary tasks Unnecessary tasks – Can be discarded Can be discarded
because they drain
because they drain
resources
Reading 6.3 Reading 6.3
Work Redesign
Work Redesign
Reading 6.3
Reading 6.3