Please bring this handbook with you every time you come in for services
at the government and private hospitals.
Recommendation for practice
The birth certificate form (T.r. 1/1) in this handbook signed
by health personnel to certify the birth of the child is neither
an official birth certificate nor birth registration. Parents should
contact the district or local registration officer at district/
sub-district office, municipality office, or Bangkok
Metropolitan Administration Office to register the birth of the
child in order to get an official Birth Certificate and to add the
childûs name into the household record within 15 days after
birth. Parents should bring with them this handbook, a copy of
household record, and the identification card of the childûs
mother or father when registering for the official Birth
Certificate. If you register later than 15 days, you as the
parents, will be fined for 1,000 baht by the law.
For your childûs well-being:
1. A copy of household record.
2. Identification card of the childûs mother or father.
3. Marriage license of the parents (if any).
Name-Surname of Child
Please do not lose
this handbook
Documents required for official birth registration :
If the mother is physically and mentally
healthy, then the child will be healthy and happy.
Good physical and mental health of mother has resulted from the
good care of the husband.
This handbook can be used as a reference for obtaining your babyûs Birth Registration Certificate, This handbook can be used as a reference for obtaining your babyûs Birth Registration Certificate,This handbook can be used as a reference for obtaining your babyûs Birth Registration Certificate, This handbook can be used as a reference for obtaining your babyûs Birth Registration Certificate,This handbook can be used as a reference for obtaining your babyûs Birth Registration Certificate,
and adding your childûs name into the household record and adding your childûs name into the household record and adding your childûs name into the household record and adding your childûs name into the household record and adding your childûs name into the household record
1.
Having children at the ages between 20-35 years2.
Spacing between each child for at least 2 years.3.
Together with the husband, having ANC visit soonest before 12 weeks of gesta-tional age, following every appointment of ANC visits, and having the delivery by medical and health personnel.4.
Receiving complete doses of T.T.vaccine. Having self-practice during the pregnancy5.
delivery, and postpartum periods as rec-ommended in MCH handbook.6.
The childûs birth-weight is 2,500 grams or more.7.
Having the baby suck breastmilk instantly after birth with exclusive breastfeeding for at least 6 months, continuing breastfeeding for at least 24 months along with other food for ages.8.
Bringing up a healthy child without malnutrition and obesity.9.
Promoting the childûs age appropriate development as recommended in MCH handbook.10.
Bringing the child to receive vaccina-tions on appointments.Chaiman of Advisory group Chaiman of Advisory group Chaiman of Advisory group Chaiman of Advisory group Chaiman of Advisory group
Dr.Vichai Tienthavorn Former Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Health Consultants
Consultants Consultants Consultants Consultants
Dr.Somyos Deerasamee Director-General, Department of Health Dr.Somsak Pattarakulwanich Deputy Director-General, Department of Health Dr.Sompong Sakulisariyaporn Director of Bureau of Health Promotion,
Department of Health Editors
Editors Editors Editors Editors
Dr.Nipunporn Woramongkol Bureau of Technical Advisors Department of Health Dr.Sirikul Issaranurak Professor Emeritus, Mahidol University
Dr.Sarawut Boonsuk Chief of Maternal and Child Health Group
Mrs.Nareeluck Kullurk Public Health Technical Officer, Senior Professional Level Mrs.Chailai Leartvanangkul Public Health Technical Officer, Senior Professional Level Ms.Sukjing Worngdechakul Nutritionist, Senior Professional Level
Mrs.Jintana Pattanapongthorn Public Health Technical Officer, Senior Professional Level Mrs.Nongluk Roongsubsin Dissemination Technical Officer, Senior Professional Level Mrs.Prapaporn Jungpanich Public Health Technical Officer, Professional Level Mrs.Isaree Jedprayuk Public Health Technical Officer, Professional Level Ms.Chaweewan Tonputsa Public Health Technical Officer, Professional Level
Mother and Child Health Handbook
Published Published Published Published
Published bybybybyby Bureau of Health Promotion, Department of Health, Ministry of Pubic Health, Thailand Total
Total Total Total
Total 102 pages 1st
Printing: 1400 copies Printing Office
Printing Office Printing Office Printing Office
General Identification Number ...
(Pregnant woman)
General Identification Number (Child)...
Firstly Issued at...
Name-surname of pregnant woman...
Identification Number
Occupation... Religion...
Education (Highest educational attainment)...
Telephone number...
Name-surname of the husband...
Identification Number
Occupation... Religion...
Education (Highest educational attainment)...
Telephone number...
Current address No... Moo...Name of village...
Soi...Street...Sub-district...
District... Province...Zip Code
Name-surname of the child... Blood group...
Date of birth...Month... Year 20... time of delivery... hrs.
Identification Number
Child's
Photograph
ID
1
Introduction to the Use of MCH Handbook
This MCH handbook is a personal health record for the mother
during pregnancy, intra-partum, and post-partum periods, and for the
child since birth up until 6 years of age.
Advantages
Advantages
Advantages
Advantages
Advantages
™
A source of knowledge and record for the health of mother and
child from pregnancy up until the child is 6 years old.
™
Helping the father and mother to take appropriate care for their
child from birth up until 6 years olds.
™
Providing an evidence for notification of birth and obtaining a
birth certificate using the form T.R.1/1 signed by the birth
at-tendant presented in this handbook.
Instruction
Instruction
Instruction
Instruction
Instruction
™
Read through and follow all the contents in this handbook.
™
Bring along this book whenever you receive services at any
health facilities.
™
Record the data all by yourself and have your husband record
the data on the pages as identified.
™
When your child attends school, hand over this book to the
teacher for continuous care of the childûs health.
™
If the book is torn or lost, obtain the new one from health
personnel.
CONTENTS
Page Page Page Page Pagewoman to give birth to a newborn > 2,500 g.
■Advantage of nutritional graph 63 ■Nutritional graph for pregnant woman 64
[image:5.420.216.392.58.566.2]■Nutrition for pregnancy women: 65-66 Table for comparison of percentage
of standard BMI values (BMI 21 = 100) ■Illustration of sets of food exchange 67-68
for pregnant woman
■Fetal development 69
■Thalassemia 70-71
■What is hypothyroidism? 72
■Prevention of mother-to-child 73 transmission of HIV
■Family planning 74
■Self assessment and analysis 75-76 of stress
Part 4 Child related knowledge to bring 77
up a healthy, brilliant, good, happy child
■Breast-milk is the first drop of family 78 love bond
■Food for infant at birth › 12 months 79-80
■Adequate amount of daily food intake 81 for a child 1 › 5 years
■Caring for your child 82
■Caring for your child suffering from 83 respiratory tract infection
■Caring for your childûs teeth 84
■Vaccinations guide 85
■Miracle of reading 86
■Guide to bringing up a brilliant, good, 87 happy child
■Suggestion for parents and guardian in 88 recording the childûs development
■Child development promotion 89-97
■Risks and guide to prevention of 98-100 injuries in early childhood
■Childûs vaccination record 101
■Next appointment date for health exam 102
Page Page Page Page Page
General I.D. number (pregnant woman) 1 Introduction to the use of MCH handbook 2
Part 1 Pregnancy 4
■Health history of pregnant woman 4 and family
■Risk assessment criteria for pregnant 5 woman at the 1st ANC visit
■History of current pregnancy 6
■Pregnancy examination record 7 ■Checklists of care for quality pregnant 9
woman
■Checklists of service inclusion by 10 gestational age
■Uterine heigh graph 11
■Fetal movement count 12 ■Maternal delivery record 15
■Record of the newborn 16
Part 2 Child Care 17
■Risks assessment in mother and 17-18 newborn (prior to hospital discharge)
■Oral health for children aged 6 19 months › 5 years
■Child Development and service 20-39 activities for children aged 1 month›4 years
■Head circumference graph 40-41 (separated for male and female)
■Guide to the use of child nutritional graph42
■Child nutritional graph 43-54
Part 3 Essential Knowledge for Safe 55
and Quality Pregnancy
■Discomforts during pregnancy 56
■Maternal practice during pregnancy 57
■Table of minimum weight for pregnant
58
woman to give birth to a newborn of 2,500 g.
■Self care during pregnancy using 59-60 pregnancy pathway chart
PART 1: PREGNANCY
Having been married for
...
yrs. Use...
as a contraceptive method forÇ.years/Ç.months. Most recently stop using contraception before pregnancy forÇÇ.yrs./Ç.months.Pregnancy History
Pregnancy PregnancyPregnancy PregnancyPregnancy D/M/YD/M/YD/M/YD/M/YD/M/Y
delivery/ delivery/ delivery/ delivery/ delivery/ abortion abortionabortion abortionabortion Gesta-tional tionaltional tionaltional age(wks) age(wks)age(wks) age(wks)age(wks) Delivery/ Delivery/ Delivery/ Delivery/ Delivery/ abortion abortion abortion abortion abortion Method Method Method Method Method of ofof of of delivery/ delivery/ delivery/ delivery/ delivery/ abortion abortionabortion abortion abortion Birth-Birth- Birth-weight weightweight weight weight Sex Sex Sex Sex
Sex PlacePlacePlacePlacePlace of of of of of delivery/ delivery/delivery/ delivery/delivery/ abortion abortion abortion abortion abortion Complica-tions tionstions tions tions Current Current Current Current Current Status of Status ofStatus of Status ofStatus of infant infant infant infant infant
1
2
3
4
5
6
Diabetes Hypertension Heart Disease Thyroid
Anemia Thalassemia Others...
...
History of surgeries
...
in the year...
at...
Hospital...
in the year...
at...
HospitalHistory of drug allergy Name of the drug
...
Symptom...
Name of the drug
...
Symptom...
History of illnesses and pregnancies of family membersSeizure Diabetes Hypertension Congenital anomaly
Multiple pregnancy Mental retardation Others
...
History of menstruation cycle Regular/irregular menstruationÇÇÇand at everyÇ..daysHistory of Illnesses
(recorded by pregnant woman)
Past History
1.
Stillbirth or neonatal death (first 1 month)2.
3 consecutive abortions3.
Having baby with birth wieight < 2,500 g.4.
Having baby with birth wieight > 4,000 g.5.
Hospitalized for hypertension treatment during pregnancy or toxemia of pregnancy6.
Undergone surgery of reproductive system organ such as myoma, mypmecomy, cervical cerclage, etc.Current History
7.
Multifetal pregnancy8.
Age < 17 years (up to EDC)9.
Age > 35 years (up to EDC)10.
Rh Negative11.
Vaginal bleeding12.
Pelvic myoma13.
Diastolic pressure≥
90 mmHg14.
Diabetes15.
Kidney disease16.
Heart disease17.
Drug addiction, alcohol addiction18.
Other diseases of internal medicine such as anemia, thyroid, SLE, tc. (please specify)...
Item ItemItem Item
Item Criteria for AssessmentCriteria for AssessmentCriteria for AssessmentCriteria for AssessmentCriteria for Assessment NoNoNoNoNo YesYesYesYesYes
If any of the responses fall into çYesé, the new approach of pregnancy care is not If any of the responses fall into çYesé, the new approach of pregnancy care is not If any of the responses fall into çYesé, the new approach of pregnancy care is not If any of the responses fall into çYesé, the new approach of pregnancy care is not If any of the responses fall into çYesé, the new approach of pregnancy care is not applicable to the pregnant woman and special care and/or additional assessment applicable to the pregnant woman and special care and/or additional assessmentapplicable to the pregnant woman and special care and/or additional assessment applicable to the pregnant woman and special care and/or additional assessmentapplicable to the pregnant woman and special care and/or additional assessment should be employed.
should be employed.should be employed. should be employed.should be employed.
AssessorÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇ.ÇÇÇ.DateÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇ
5
PART 1: PREGNANCY
Risk Assessment Criteria for
Pregnant Woman at the 1
stANC Visit
History of Current Pregnancy
Pregnancy #...Last menstrual period...Expected due date... Weight before pregnancy...kg. Height...cms. BMI before pregnancy... Number of C/S...Number of living children...Age of the last child...yrs...months
Laboratory Test
■ STIs (VDRL)
1
sttime
Date... Result...2
ndtime
Date... Result...■ Blood test for HBsAg
1
sttime
Date... Result...■ Blood test for Hematocrit
1
sttime
Date... Result...2
ndtime
Date... Result...■ Screening for Thalassemia (Wife) Date...
Result OF...DCIP...MCV... (Husband) Date...
Result OF...DCIP...MCV...
■ Blood group and (Wife) Blood group...Rh...Hemoglobin type.... Hemoglobin type (Husband) Blood group...Rh...Hemoglobin type....
■ Other examination results...
■ Couple counseling Pre-blood test Date... Pre-blood test Date...
■ Participation in parental school activities 1st
time at gestational age...months 2nd
time at gestational age...months
(recorded by health personnel)
Tetanus Toxoid Vaccination
(Recorded by health personnel)
Received vaccination before pregnancy...times.
Date of most recent vaccination... Vaccination is not given for this pregnancy as the 3rd
dose was given no more than 10 years or with previous tetanus vaccinations for 5 times.
1st
Dose, date... 2nd
Dose, date... Booster Dose, date...
Diabetes screening
...
Record of Pregnancy Examination
Result of U/S exam, day
...
BPD
...
FL
...
Fetal position
...
Gestational age
...
Corrected EDC...
By
LMP
PV U/S Ut Size
GA...wks Sign...Date...
Date
of
Exam
Weight
Kg.
Blood
Pressure
mm.Hg.
Size of
Uterure
(cm.)
Fetal
position/
presentation
Fetal
heart
sound
Fetal
movement
Gestational
age (wks.)
General physical
exam and risks
assessment
Diagnosis and
Treatment
Appointment
Officer
Place
Urine Exam
Bacteria/
Protein/Sugar
(recorded by health personnel)
Other special exam
...
8
7
...
1. Check classifying form, no high risks
2. Check weight, height, blood pressure
3. General physical examination
4. Urine exam (Multiple dipstick) for protein, sugar,
asymptomatic bacteria
5. Transfer to the doctor for lung and heart
sounds exam
6. Pelvic exam (may postpone to the 2nd visit)
7. Test for Hb/Hct/OF/DCIP (every gestational age)
and test for VDRL, Anti HIV, blood gr, Rhtyping,
HbsAgr
8. Give the 1st
dose of tetanus toxoid vaccine
9. Give iron and/or folic, and iodine supplementation
10. Give advice in case of emergency with
abnormal signs, with telephone number for
emergency contact
2 2 2 2 2ndndndndnd
Visit, Date...(20 weeks) Visit, Date...(20 weeks) Visit, Date...(20 weeks) Visit, Date...(20 weeks) Visit, Date...(20 weeks)
1. Check weight, blood pressure
2. Pelvic exam (in case not performed at the 1st
visit)
3. Ultrasound exam (if applicable)
4. Give iron, iodine, calcium supplementation
5. Give the 2nd
dose of tetanus toxoid vaccine
(at least 1 month interval of the 1st dose)
6. Give post-test counseling for the blood result
and abnormal signs, with telephone number for
emergency contact
Checklists of Service Inclusion by Gestational Age
<
12
20
26
32
38
1. Check weight, blood pressure
2. Test urine for protein, sugar
3. General physical examination, check for anemia,
edema
4. Pregnancy exam, estimate gestational age,
measure uterine height, Listen to fetal heart
sound
5. Give iron, iodine, calcium supplementation
through the pregnancy period
6. Advice mother to observe fetal movement
7. Give advice in case of emergency with
abnormal signs, with telephone number for
emergency contact
4 44 44ththththth
Visit, Date...(32 weeks) Visit, Date...(32 weeks) Visit, Date...(32 weeks) Visit, Date...(32 weeks) Visit, Date...(32 weeks)
1. Test for Hb/Hct, VDRL. Anti HIV
2. Give advice about delivery, breastfeeding plan,
contraception
5 55 55ththththth
Visit, Date...(38 weeks) Visit, Date...(38 weeks) Visit, Date...(38 weeks) Visit, Date...(38 weeks) Visit, Date...(38 weeks)
1. Check fetal position, if breech presentation,
refer to ECV or CS
2. Record in ANC booklet, remind of bringing it
along when coming for delivery
3. If delivery does not occur at 41 weeks of
gestation, give advice to come to the hospital
Checklists of Service Inclusion by Gestational Age
Weeks WeeksWeeks Weeks Weeks 1 1 1 1 1ststststst
Visit, Date Visit, Date Visit, Date Visit, Date
Visit, DateÇÇÇÇ...(should be before 12 weeks)(should be before 12 weeks)(should be before 12 weeks)(should be before 12 weeks)(should be before 12 weeks)
<
12
20
26
32
38
Weeks Weeks Weeks Weeks Weeks 3 33 3 3ndndndndndVisit, Date Visit, Date Visit, Date Visit, Date
Visit, DateÇÇÇÇ...(should be before 26 weeks)(should be before 26 weeks)(should be before 26 weeks)(should be before 26 weeks)(should be before 26 weeks)
(recorded by health personnel)
(recorded by health personnel)
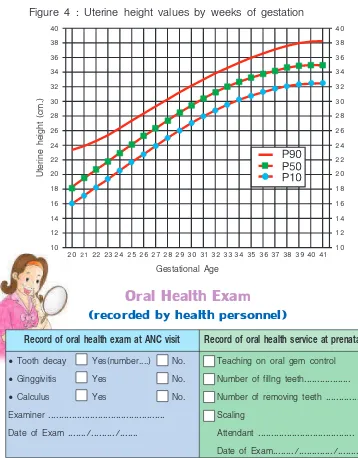
Uterine Height Graph
Figure 4 : Uterine height values by weeks of gestation
(recorded by health personnel)
Gestational Age
11
PART 1: PREGNANCY
20 21 2223 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 10
12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40
10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40
Uterine height (cm.)
Record of oral health exam at ANC visit
Record of oral health service at prenatal
ë
Tooth decay Yes(number....) No.ë
Ginggivitis Yes No.ë
Calculus Yes No.Examiner
...
Date of Exam.../.../...
Teaching on oral gem control
Number of fillng teeth
...
Number of removing teeth...
ScalingAttendant
...
Date of Exam.../.../...
Oral Health Exam
Talk to the baby in your womb everyday to create your baby.
Date Morning (time) Daytime (time) Before bedtime (time) Date Morning (time) Daytime (time) Before bedtime (time)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
1. Counting fetal movement is to prevent fetal death possibly occurs especially in the mothers with complications such as diabetes, hypertension, toxemia of pregnancy, approaching or beyond the due date of delivery.
2. Begin to observe and count the frequencies of fetal movement from 6 months of gestational age up until delivery.
3. Observe fetal movement everyday and record at least 3 times a day. 4. Observe fetal movement when you are free from work such as after a meal,
before bedtime, or getting up in the morning, etc.
5. Fetal movement is when you feel your baby moves in your abdomen, if you only feel abdominal tense or your baby stretches up, it is not considered a fetal movement.
6. If you are doubtful, not understand or unable to do so, consult your doctor or nurse immediately.
7. During 1 hour of observation, you should feel fetal movement at least 3 times, if not or less than 3 times in 1 hour, see your doctor or nurse promptly for additional exam such as to check fetal heart rate with modern device.
MonthÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇ
Fetal Movement Count
13
Date Morning (time) Daytime (time) Before bedtime (time) Date Morning (time) Daytime (time) Before bedtime (time)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
MonthÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇ Date Morning (time) Daytime (time) Before bedtime (time) Date Morning (time) Daytime (time) Before bedtime (time)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
MonthÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇWhen your baby moves 1 time, mark / in the grid
more then 3 /// should be marked in 1 hour of observation
Record of Fetal Movement Count(continued)
MonthÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇ Date Morning (time) Daytime (time) Before bedtime (time) Date Morning (time) Daytime (time) Before bedtime (time)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
Abnormal signs during pregnancy to be promptly seen
Abnormal signs during pregnancy to be promptly seen
Abnormal signs during pregnancy to be promptly seen
Abnormal signs during pregnancy to be promptly seen
Abnormal signs during pregnancy to be promptly seen
by the doctor or health personnel
by the doctor or health personnel
by the doctor or health personnel
by the doctor or health personnel
by the doctor or health personnel
■ Headache, blurred vision ■ Vaginal bleeding
■ Stomachache, abdominal pain ■ Fluid from vagina
■ Vaginal discharge ■ Less fetal movement
■ Irritable bowel Syndrome ■ convulsions and coma
Maternal Delivery Record
(record by health personnel
Abnormal signs during postpartum period to be promptly seen
Abnormal signs during postpartum period to be promptly seen
Abnormal signs during postpartum period to be promptly seen
Abnormal signs during postpartum period to be promptly seen
Abnormal signs during postpartum period to be promptly seen
by the doctor or health personnel
by the doctor or health personnel
by the doctor or health personnel
by the doctor or health personnel
by the doctor or health personnel
■ Postpartum hemorrhage, blood clot ■ Uretritis, obstructed urine, retention
■ High fever for 2 days of urine
■ Lochia with foul smell, turbid, or ■ Perineum pain, edema, or broken red color for more than 2 weeks wound
■ Sore nipples or mastitis Place of delivery
Place of deliveryPlace of delivery
Place of deliveryPlace of delivery
...
bybybybyby( )
Doctor( )
Nurse( )
Others (specify)...
Gestational ageGestational ageGestational age
Gestational ageGestational age
...
weeksweeksweeksweeksweeks Mode of deliveryMode of deliveryMode of deliveryMode of deliveryMode of delivery...
Intrapartum complicationIntrapartum complicationIntrapartum complication Intrapartum complicationIntrapartum complication
Yes (specify) No
...
Postpartum complicationPostpartum complicationPostpartum complication Postpartum complicationPostpartum complication
Yes (specify) No
...
Record of Postpartum Check-up
Date of exam
Blood Pressure
Level of Uterus
Lochia Breast and Nipple
Flow of Breast-milk
Hygiene of Umbilical
cord
Name of examiner
Postpartum Check-up: Week 1 › 2, at least 1 time
Week 6, at least 1 time
15
Postpartum check-up, safe motherhood
Record of the Newborn
(recorded by health personnel)
Date/month/year of birth
...
Sex...
Birth-weight...
grams Length...
cms.Head circumference
...
cms. Apgar Score (1 minute)...
(5 minutes)...
Congenital anomaly Yes (specify)...
No
Health condition at birth Healthy Abnormal (specify)
...
Date of hospital discharge...
Weight at the date of discharge...
Vitamin K injection Yes No
Newborn screening Date...
...
-
Thyroid deficiency Normal Abnormal-
PKU Normal Abnormal■ Jaundice ■ Refuse suckling
■ Raised body temperature, fever, ■ No urination within 24 hrs. drowsiness
■ Rapid breathing over 60 breaths/minute or difficult breasting
■ Swelling, redness, leaking pus at the umbilicus, eyes or skin
■ Diarrhea and/or vomiting
The newborn should be promptly seen by the doctor or
The newborn should be promptly seen by the doctor or
The newborn should be promptly seen by the doctor or
The newborn should be promptly seen by the doctor or
The newborn should be promptly seen by the doctor or
health personnel if displays the following abnormal signs
health personnel if displays the following abnormal signs
health personnel if displays the following abnormal signs
health personnel if displays the following abnormal signs
health personnel if displays the following abnormal signs
Yellow stool is normal in a child.
If your child had white or pale yellow stool as in the picture below, bring your child to the doctor promptly as he or she may have liver or
PART 2: CHILD CARE
Assessment of Risks in Mother and Newborn
(prior to hospital discharge) (recorded by health personnel)
Maternal History Maternal HistoryMaternal History
Maternal HistoryMaternal History YesYesYesYesYes NoNoNoNoNo UncertainUncertainUncertainUncertainUncertain UnknownUnknownUnknownUnknownUnknown 1. Risk group for 6-month exclusive
breastfeeding
2. History of illness effecting child raising
3. Less than 17 years of age 4. Father or mother or relative
raising the child alone. 5. Blood test
- HBsAg+
6. History of a genetic disease about hearing
7. BMI < 18.5 before pregnancy 8. Malnutrition from 20 weeks of
gestation and beyond 9. Other risk conditions
Additional details
Additional details
Additional details
Additional details
Additional details
Item 1 Item 1Item 1
Item 1Item 1. Risk group for 6 ›month exclusive breastfeeding refers to the mothers with abnormal nipples/working outside the home.
Item 2 Item 2Item 2
Item 2Item 2. History of illness effecting child raising refers to requirement of regular medication or mental illness.
Item 9 Item 9Item 9
Item 9Item 9. Other risk conditions such as undesirable pregnancy, tobacco, alcohol, and substance uses, etc.
17
Child History Child HistoryChild History
Child HistoryChild History YesYesYesYesYes NoNoNoNoNo UncertainUncertainUncertainUncertainUncertain UnknownUnknownUnknownUnknownUnknown 1. Premature birth (gestational age
< 37 weeks)
2. Birth-weigh < 2,500 grams. 3. Hypoglycemia
4. Hyperbilirubinemia
5. Birth Asphyxia at 5 mins ≤ 4 and with complication
6. Sepsis
7. Convulsion, Meningitis
8. Difficulties in suckling-swallowing, poor suckling
9. Down Syndrome
10. Congenital Anomaly (as determined by the doctor)
11. Anemia Central Hct < 40% (at < 7 days of age)
12. Others (specify)...
Family history
Family history
Family history
Family history
Family history
- History of genetic diseases, hearing,
mental retardation in the family
Remarks
Remarks
Remarks
Remarks
Remarks
If with more than 1 risk, indicating the high risk case, make an appointment to see the doctor at 1 month old.19
PART 2: CHILD CARE
Oral Health Record for Children Aged 6 Months-5 Years
(recorded by health personnel)
Age
D/M/Y of Check up
Having sweeten milk
Using Bottle feeding
Having sweet Time/day
Brushing teeth everyday by parents
Using fluoride toothpaste
Having plaque
Initial stage of tooth aecay
Having tooth cavities(number) Advice tooth Treatment
6
months
9
months
1
year
1
1/2
year
2
year
2
1/2
year
3
year
4
year
5
year
Attendant
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
No
■ Child development Stares at faces
Follows objects with eyes along the body midline
Makes sound (ask)
Lifts head (ask)
■ Food and nutrition Exclusive breast-milk
■ Record of parents about the child and problems that require counseling
...
...
...
...
...
...
Consult the doctor or health personnel if Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if
Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if the child tends to exhibit poor development or any of the following signs.
■ At 3 months, no eye contact, no smiling back, no head lifting when lying on stomach
■ Red or inflamed umbilicus
■ Self rolling over before 3 months, may due to tight muscle
Strat having your breastmilk pressed and kept in the fridge, when your child is 1 month old.
Child Development at 1 Month Old (
±
7 Days)
21
Service Activities for Children at 1 Month Old (
±
7 Days)
(Recorded by health personnel)
Date of examination
...
Weight...
kg.Length
...
cm.Head circumference
...
cm. Nutritional status...
...
Check physical appearance, eyes, ears, mouth, heart, abdomen, sexual organ, legs, arms, anterior fontanelle, posterior fontanelle (check
thoroughly), if not possible to complete all, check for the heart sound.
Additional check with the childûs development in case with doubts.
...
...
Problems with child raising and health (ask from the caregiver) include:
...
Parental school arrangement Yes No
Advices given:
How to use MCH handbook
Exclusive breastfeeding
Food for mothers
Promoting child development in subsequent ages
Accident prevention
...
Refrain the child from wearing gloves, sucking finger, using pacifier,traditional medicine, throat paint.
Others
...
Referral in case of abnormalities and for care and treatment
No Yes, specify
...
PART 2: CHILD CARE
Do not use bottle milk supplementation with an idea that you have less
breastmilk because our body can produce sufficient milk supply for the baby.
Child Development at 2 Months Old (
±
7 Days)
(recorded by parents or caregiver)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
No
■ Child development Social smile (ask)
Follows through with eyes along the body midline
Babbles (ask)
Lifts the head 45
■ Food and nutrition Exclusive breast-milk
■ Record of parents about the child and problems that require counseling
...
...
...
...
...
...
Consult the doctor or health personnel if Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if
Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if the child tends to exhibit poor
development or any of the following signs.
■ At 3 months, no eye contact, no smiling back, no head lifting in prone position
■ Red or inflamed umbilicus
23
Service Activities for Children at 2 Months Old (
±
7 Days)
(Recorded by health personnel)
Date of examination
...
Weight...
kg.Length
...
cm.Head circumference
...
cm. Nutritional status...
...
Check physical appearance, eyes, ears, mouth, heart, abdomen, sexual organ, legs, arms, anterior fontanelle, posterior fontanelle (check thor-oughly), if not possible to complete all, check for the heart sound.
...
Additional check with the childûs development in case with doubts.
...
...
Problems with child raising and health (ask from the caregiver) include:
...
...
Parental school arrangement Yes No
Advices given:
How to use MCH handbook
Exclusive breastfeeding
Food for mothers
Promoting child development in subsequent ages
Accident prevention suckling as drowning, scald.
Refrain the child from wearing mittens, sucking finger, using pacifier,
traditional medicine, throat paint.
Others
...
Referral in case of abnormalities and for care and treatment
No Yes, specify
...
PART 2: CHILD CARE
Child Development at 4 Months Old (
±
15 Days)
(recorded by parents or caregiver)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
No
■ Child development
Looks at his/her own hands (ask)
Follows objects with eyes at 180
Makes cooing sound (ask)
Lifts upper chest when lying on stomach
■ Food and nutrition Exclusive breast-milk
■ Record of parents about the child and problems that require counseling
...
...
...
...
...
...
Consult the doctor or health personnel if Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if
Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if the child tends to exhibits poor
development or any of the following signs.
■ At 4-5 months, does not lit the head, unable to grasp things.
25
Service Activities for Children at 4 Months Old (
±
15 Days)
(Recorded by health personnel)
Date of examination
...
Weight...
kg.Length
...
cm.Head circumference
...
cm. Nutritional status...
...
Physical check-up (If with doubts, check thoroughly)
...
...
Additional check with the childûs development in case with doubts.
...
...
Problems with child raising and health.
...
...
Advices given:
How to use MCH handbook
Breast-milk and food at ≥ 6 months
Promoting child development in subsequent ages
Reading pictorial books with the child
No use of baby walker
Accident prevention such as drowning and scald.
Refrain the child from wearing gloves, sucking finger,
using pacifier, and baby walker.
Referral in case of abnormalities and for care and treatment
No Yes, specify
...
PART 2: CHILD CARE
Child Development at 6 Months Old (
±
15 Days)
(recorded by parents or caregiver)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
No
■ Child development
Gets things to feed him/herself (ask)
Follows falling objects with eyes
Turns toward the calling voice
Holds head steady not flop
■ Food and nutrition Breast-milk
Other food include
...
■ Record of parents about the child and problems that require counseling
...
...
...
...
...
...
Consult the doctor or health personnel if Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if
Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if the child tends to exhibits poor development or the child displays any of the following signs.
■ At 6 months, does not follow objects with eyes, does not turn towardAt 6 months, does not follow objects with eyes, does not turn towardAt 6 months, does not follow objects with eyes, does not turn towardAt 6 months, does not follow objects with eyes, does not turn towardAt 6 months, does not follow objects with eyes, does not turn toward voice, does not pay attention to the one who plays with, does not roll voice, does not pay attention to the one who plays with, does not roll voice, does not pay attention to the one who plays with, does not roll voice, does not pay attention to the one who plays with, does not roll voice, does not pay attention to the one who plays with, does not roll over in either front to back or back to front
over in either front to back or back to front over in either front to back or back to front over in either front to back or back to front over in either front to back or back to front.
27
Service Activities for Children at 6 Months Old (
±
15 Days)
(Recorded by health personnel)
Date of examination
...
Weight...
kg.Length
...
cm.Head circumference
...
cm. Nutritional status...
The values of Hematocrit or Hemoglobin
...
(Test performed when the child wasÇÇ.Çmonths)Check physical appearance, eyes, ears, mouth, heart, lung, abdomen, sexual organ, legs, arms, skin.
If time is not allowed, check for cross-eyes, tight muscles, and hearing.
...
Additional check with the childûs development in case with doubts.
...
Problems with child raising and health (ask from the caregiver) include:
...
Giving iron supplementation Yes No
Parental school arrangement Yes No
Advices given:
How to use MCH handbook
Breast-milk and age appropriate food
Promoting child development in subsequent ages
Reading pictorial books with the child, playing with the child
Accident prevention such as drowning, electric shock, scald, aspiration No use of baby-walker
Oral health care
Try to avoid feeding the baby after bedtime during 8.00 pm.-6.00 am and never put the baby to bed with breastfeeding
Referral in case of abnormalities and for care and treatment No Yes, specify
...
PART 2: CHILD CARE
Child Development at 9 Months Old (
±
15 Days)
(recorded by parents or caregiver)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
No
■ Child development
Waives hands to bye bye (ask)
Holds a cube in each hand
Copies talking voices (ask)
Sits up (ask)
■ Food and nutrition Breast-milk
Other food include
...
Number of meals per day...
meals■ Record of parents about the child and problems that require counseling
...
...
...
...
...
...
Do not use baby walker as it frequently cause accidents
and the child may walk on tiptoe.
Consult the doctor or health personnel if Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if
Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if the child tends to exhibit poor development or the child displays any of the following signs.
■ Stretched and tense legs when creeping and crawling or sitting in
W
position.Service Activities for Children at 9 Months Old (
±
15 Days)
(Recorded by health personnel)
Date of examination
...
Weight...
kg.Length
...
cm.Head circumference
...
cm. Nutritional status...
Physical check-up (If with doubts, check thoroughly)
...
Dental check-up
...
Additional check with the childûs development in case with doubts.
...
Problems with child raising and health (ask from the caregiver) include:
...
...
Giving iron supplementation Yes No
Advices given:
How to use MCH handbook
Breast-milk and 2 meals of food for ages
Promoting child development in subsequent ages
Reading pictorial books with the child, and plying with the child Accident prevention such as drowning, electric shock, scald, aspiration Dental health care
No milk feeding after bedtime
No use of baby-walker
No watching T.V., CD, DVD until 2 years old
Referral in case of abnormalities and for care and treatment
No Yes, specify
...
29
Never let the child play with small toy less then 2 cm. as the child may put
it into the month and be choked by it.
Child Development at 12 Month Old (
±
15 Days)
(recorded by parents or caregiver)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
No
■ Child development Expresses the need (ask)
Puts a cube in a container
Says meaningful words Pa-Ma (ask)
Says 1 meaningful word (ask)
■ Food and nutrition Breast-milk
Other food include
...
Eat snack food Yes No
■ Record of parents about the child and problems that require counseling
...
...
...
...
...
...
Consult the doctor or health personnel if Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if
Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if the child tends to exhibit poor
developmentany or the child displays any of the following signs.
■ At 1 year, unable to walk holding on to something, unable to feed him/ herself with fingers, unable to imitate posture or voice, unable to say a single word.
Service Activities for Children at 12 Month Old (
±
15 Days)
(Recorded by health personnel)
Date of examination
...
Weight...
kg.Length
...
cm.Head circumference
...
cm. Nutritional status...
Check physical appearance, eyes, ears, mouth, heart, lung, abdomen,
legs, arms, skin, if not possible to complete all, check the heart, abdomen,
interior fontanelle.
...
Oral and dental check-up (advice given by dental officer)
...
Additional check with the childûs development in case with doubts.
...
Autism screening Normal Suspicious
Problems with child raising and health (ask form the caregiver) include:
...
Giving iron supplementation Yes No
Parental school arrangement Yes No
Advices given:
How to use MCH handbook
Giving the child 3 meals, continuing breastfeeding, no milk feeding
after going to bed.
Promoting child development in subsequent ages
Reading pictorial books with the child, and playing with the child
Accident prevention such as drowning, electric shock, scald, aspiration
No watching T.V., CD, DVD until 2 years old
Effects of television on the child
Referral in case of abnormalities and for care and treatment
No Yes, specify
...
31
PART 2: CHILD CARE
Child Development at 18 Months Old (±1 Month)
(recorded by parents or caregiver)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
No
■ Child development
Uses spoon to feed him/herself
Follows objects with eyes along the body midline
Makes sound (ask)
Lifts the head (ask)
■ Food and nutrition Exclusive breast-milk
■ Record of parents about the child and problems that require counseling
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
Consult the doctor or health personnel if Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if
Consult the doctor or health personnel ifConsult the doctor or health personnel if your 18-month-old child tends to exhibits poor developmentany or cannot follow simple instructions such as sayingor cannot follow simple instructions such as sayingor cannot follow simple instructions such as sayingor cannot follow simple instructions such as sayingor cannot follow simple instructions such as saying hello, walking toward the mother.
hello, walking toward the mother.hello, walking toward the mother. hello, walking toward the mother.hello, walking toward the mother.
Service Activities for Children at 18 Month Old (±1 Month)
(Recorded by health personnel)
Date of examination
...
Weight...
kg.Length
...
cm.Head circumference
...
cm. Nutritional status...
Physical check-up especially the anterior fontanelle (if with doubts, check
thoroughly)
...
Additional check with the childûs development in case with doubts.
...
Problems with child raising and health problems (ask from the caregiver) include:
Giving iron supplementation Yes No Advices given:
How to use MCH handbook
Giving the child 3 meals, continuing breastfeeding, no milk feeding after going to bed, allowing the child for food self-feeding. Promoting child development in subsequent ages
Reading pictorial books with the child, and playing with the child Accident prevention such as drowning, electric shock, scald, aspiration, falling over the high.
Caring for the childûs teeth twice a day in the morning and before
bedtime
Toilet training, give up disposable diapers.
No watching T.V./CD/DVD until the child is 2 years old Effects of television on the child
Referral in case of abnormalities and for care and treatment
No Yes, specify
...
33
Train the child to help with easy household chores such as collecting toys,
sweeping the floor.
Child Development at 2 Years Old (
±
1 Month)
(recorded by parents or caregiver)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
No
■ Child development Removes clothes (ask)
Stacks 4 cubes
Points at 6 parts of body organs
Says 2 words together (ask)
Throws a ball
■ Food and nutrition
Food intake
...
Number of meal per day...
mealsEating crunchy/crispy snacks Yes No
Having soft drinks Yes No
■ Record of parents about the child and problems that require counseling
...
...
...
...
Consult the doctor or health personnel if your 2-year-old child tends to exhibit poor development or cannot speak 2 meaningful words together.
Teach the child about morality such as thoughtfulness, making merit,
giving alms to monks, praying to the Lord Buddha,
Service Activities for Children at 2 Years Old (
±
1 Month)
(Recorded by health personnel)
Date of examination
...
Weight...
kg.Length
...
cm.Head circumference
...
cm. Nutritional status...
Physical check-up (if with doubts, check thoroughly)
...
Additional check with the childûs development in case with doubts.
...
Problems with child raising and health, and behavioral problems
...
Giving iron supplementation Yes No
Parental school arrangement Yes No
Advices given:
How to use MCH handbook
Giving the child 3 meals, allowing the child for food self feeding, and
drinking milk from the glass or box about 2-3 times/day.
Promoting child development in subsequent ages
Reading pictorial books with the child, and playing with the child
Accident prevention such as electric shock, scald, aspiration by food particles, falling from the stairs.
Allowing the child to watch T.V. no more than 1 hour/day Toilet training, give up disposable diapers.
Participation in religious activities.
Referral in case of abnormalities and for care and treatment
No Yes, specify
...
35
Do not allow your child to play computer games,
and parents do not play them in presence of the child.
Child Development at 3 Years Old (
±
1 Mounth)
(record by parents or caregiver)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
No
■ Child development
Puts on T-shirt by him/herself (ask)
Stacks 8 cubes
Knows at least 2 adjectives
Stands on one leg for 1 second
Imitates in drawing a vertical line
■ Food and nutrition
Food intake
...
Number of meal per day...
mealsEating crunchy/crispy snacks Yes No
Having soft drinks Yes No
■ Record of parents about the child and problems that require counseling
...
...
...
...
...
Consult the doctor or health personnel if your child tends to exhibit poor
development or delayed development for age.
■ Cannot follow simple instruction.
Service Activities for Children at 3 Years Old (±1 Month)
(Recorded by health personnel)
Date of examination
...
Weight...
kg.Length
...
cm.Head circumference
...
cm. Nutritional status...
Physical check-up (if with doubts, check thoroughly)
...
Additional check with the childûs development in case with doubts.
...
Autism screening result
...
Emotional intelligence screening result
...
Problems with child raising and health, and behavioral problems
Parental school arrangement Yes No
Advices given:
How to use MCH handbook
Giving the child 3 meals, no crispy and crunchy snacks and soda drinks.
Promoting child development in subsequent ages
Reading pictorial books with the child, and playing with the child Teaching the child to help him/herself.
Teaching the child to collect the toys every time after playing them. Participation in religious activities.
Accident prevention such as electric shock, scald, aspiration by food particles, falling from the stairs.
Allowing the child to watch T.V. no more than 1 hour/day. Referral in case of abnormalities and for care and treatment
No Yes, specify
...
37
PART 2: CHILD CARE
Child Development at 4 Years Old (
±
1 Month)
(recorded by parents or caregiver)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
No
■ Child development
Dresses by him/herself (ask)
Copies a picture
Tells 4 colors
Stands on one leg for 3 seconds
Copies a circle
■ Food and nutrition
Food intake
...
Number of meal per day...
mealsEating crunchy/crispy snacks Yes No
Having soft drinks Yes No
■ Record of parents about the child and problems that require counseling
...
...
...
...
Consult the doctor or health personnel if your child exhibits delayed development or nutritional disorder or tends to have poor development.
Train your child to do more things every by him/herself such as putting on
clothes, scooping rice, putting the dish into the basin, washing his/her dish,
Service Activities for Children at 4 Years Old (
±
1 Month)
(Recorded by health personnel)
Date of examination
...
Weight...
kg.Length
...
cm.Head circumference
...
cm. Nutritional status...
Physical check-up (if with doubts, check thoroughly)
...
Urine exam Eye exam Hearing exam Check blood pressure
Emotional intelligence screening
...
Additional check with the childûs development in case with doubts...
Problems with child raising and health, behavioral problems
...
Parental school arrangement Yes No Advices given:
How to use MCH handbook
Giving the child 3 meals and 2 boxes of milk per day, no soda drinks and crispy and crunchy snacks.
Promoting child development in subsequent ages
Reading pictorial books with the child, and playing with the child Accident prevention such as drowning, electric shock, scald, falling from the high, domestic toxicants.
Allowing the child to watch T.V. no more than 1 › 2 hours per day. Effects of television on the child
Referral in case of abnormalities and for care and treatment
No Yes, specif
...
39
Teach Your child about disciplines such as eating on regular time,
reading and doing homework on regular time everyday.
40
55
50
45
40
35
30
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
3
10
25
50
75
90
97
41
HEAD CIRCUMFERENCE GRAPH (male and female separated)
Reference graph for head circumference, female 0-6 years
55
50
45
40
35
30
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
3
10
25
50
75
90
97
cm.
Age (year)
Guide to the Use of Child Nutritional Graph
(can be recorded by parents or guardian)
Child nutritional graph is used to continuously monitor the change of childûs weight and height whether the trends of childûs growth follow the standard criteria. The graphs are presented in 3 types:
1.Weight for age graph 1.Weight for age graph 1.Weight for age graph 1.Weight for age graph
1.Weight for age graph presents 5 levels of growth status: 1)
1)1) 1)
1) Under standard weight refers to having malnutritionUnder standard weight refers to having malnutritionUnder standard weight refers to having malnutritionUnder standard weight refers to having malnutritionUnder standard weight refers to having malnutrition. 2)
2)2) 2)
2) Relatively low weight refers to risk of having malnutritionRelatively low weight refers to risk of having malnutritionRelatively low weight refers to risk of having malnutritionRelatively low weight refers to risk of having malnutritionRelatively low weight refers to risk of having malnutrition, a warning sign, if without appropriate care, overweight for age is likely.
3) 3)3) 3)
3) Standard weight refers to well growthStandard weight refers to well growthStandard weight refers to well growthStandard weight refers to well growthStandard weight refers to well growth. It should be promoted to maintain the weight at this level.
4) 4)4) 4)
4) Relatively high weight: refers to risk of having over standard weightRelatively high weight: refers to risk of having over standard weightRelatively high weight: refers to risk of having over standard weightRelatively high weight: refers to risk of having over standard weightRelatively high weight: refers to risk of having over standard weight. It should be check against the weight for height graph.
5) 5)5) 5)
5) Over standard weight does not identify whether the child is obeseOver standard weight does not identify whether the child is obeseOver standard weight does not identify whether the child is obeseOver standard weight does not identify whether the child is obeseOver standard weight does not identify whether the child is obese. It needs to check for obesity against the weight for height graph.
2. Height for age graph presents 5 levels of growth status 2. Height for age graph presents 5 levels of growth status 2. Height for age graph presents 5 levels of growth status 2. Height for age graph presents 5 levels of growth status 2. Height for age graph presents 5 levels of growth status:
1) 1)1) 1)
1) Short refers to having chronic malnutritionShort refers to having chronic malnutritionShort refers to having chronic malnutritionShort refers to having chronic malnutritionShort refers to having chronic malnutrition, reflecting inadequate food in-take for a prolonged period or frequent illnesses, with minor or no increase of height, affecting low intelligence, more frequent illnesses. It requires immediate improvement.
2) 2)2) 2)
2) Relatively short refers to risk of having chronic malnutritionRelatively short refers to risk of having chronic malnutritionRelatively short refers to risk of having chronic malnutritionRelatively short refers to risk of having chronic malnutritionRelatively short refers to risk of having chronic malnutrition, a warning sign, if without appropriate care, the height discontinues and the child is likely to become short.
3) 3)3) 3)
3) Standard height refers to well growthStandard height refers to well growthStandard height refers to well growthStandard height refers to well growthStandard height refers to well growth, reflecting adequate food intake, so it should be promoted to contiue at this level.
4) 4)4) 4)
4) Relatively tall refers to very well growthRelatively tall refers to very well growthRelatively tall refers to very well growthRelatively tall refers to very well growthRelatively tall refers to very well growth. It should be promoted to maintain at this level.
5) 5)5) 5)
5) Over standard age refers to excellent growthOver standard age refers to excellent growthOver standard age refers to excellent growthOver standard age refers to excellent growthOver standard age refers to excellent growth. It should be promoted to continue at this level.
3. 3. 3. 3.
3. Weight for height graphWeight for height graphWeight for height graphWeight for height graphWeight for height graph represents 6 levels of growth status: 1)
1)1) 1)
1) Thin refers to having short term malnutritionThin refers to having short term malnutritionThin refers to having short term malnutritionThin refers to having short term malnutritionThin refers to having short term malnutrition 2)
2)2) 2)
2) Relatively thin refers to risk of having malnutritionRelatively thin refers to risk of having malnutritionRelatively thin refers to risk of having malnutritionRelatively thin refers to risk of having malnutritionRelatively thin refers to risk of having malnutrition, a warning sign, if without appropriate care, the weight will not increase or decrease to the thin level.
3) 3)3) 3)
3) Proportionate refers to well growthProportionate refers to well growthProportionate refers to well growthProportionate refers to well growthProportionate refers to well growth, reflecting appropriate weight for height. The child should be promoted to continue at this level of growth.
4) 4)4) 4)
4) Moderate refers to risk of having obesityModerate refers to risk of having obesityModerate refers to risk of having obesityModerate refers to risk of having obesityModerate refers to risk of having obesity, a warning sign, if without appropriate care, the weight will increase to the level of initiating fat.
5) 5)5) 5)
5) Initiating fat refers to the first degree of obesityInitiating fat refers to the first degree of obesityInitiating fat refers to the first degree of obesityInitiating fat refers to the first degree of obesityInitiating fat refers to the first degree of obesity. The child is likely to become a fat adult in the future if without weight control.
6) 6)6) 6)
44
43
48
47
52
51
PART 3
ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE
FOR SAFE AND QUALITY PREGNANCY
■
Discomforts during pregnancy
■
Maternal practices during pregnancy
■
Minimum weight for pregnant women to give birth to a newborn of
2,500 grams. (VALLOP WEIGHT LOG)
■
Self care during pregnancy through pregnancy pathway
■
Minimum weight for pregnant women to give birth to a newborn of
>2,500 gram.
■
Advantage of the nutritional graph
■
Nutritional graph for pregnant woman
■
Nutrition for pregnant woman: Table for comparison of percentage
of standard BMI values (BMI 21 = 100)
■
Illustration of sets of food exchange for pregnant woman
■
Fetal development
■
Thalassemia
■
Risk opportunity to have a child with thalassemia
■
What is congenital hypothyroidism?
■
Prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV
■
Family planning
■
Self assessment and analysis of stress
55
Morning sickness Morning sickness Morning sickness Morning sickness
Morning sickness is commonly experienced in early period of pregnancy, with nausea and vomiting in the morning. The symptoms can be improved by mental adjustment, avoiding unfavorable food, eating small meal each time but several times, or having soft food and warm drinks. The symptoms will disappear at 4 months of gestation.
Vaginal discharge Vaginal discharge Vaginal discharge Vaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge will commonly increase during pregnancy. Take a usual bath, except if accompanied with itching and smelling, see the doctor.
Constipation Constipation Constipation Constipation
Constipation is found in some pregnant women and can be lessen by drinking more water and eating more vegetables and fruits, if not improved, see the doctor.
Frequent urination Frequent urination Frequent urination Frequent urination
Frequent urination is caused by the expansion of uterus which places more pressure on the bladder. If experiencing burning pain or obstructed urinating, see the doctor.
Fatigue and drowsiness Fatigue and drowsiness Fatigue and drowsiness Fatigue and drowsiness
Fatigue and drowsiness is common early in pregnancy with feeling tired and sleepy.
Varicose veins Varicose veins Varicose veins Varicose veins
Varicose veins usually disappear after delivery. Always change your gesture properly, avoid long period of walking or standing, sit with your feet elevated for 15 › 20 minutes every day after walking or working, use legs support hose to provide compression.
Stretch Masks Stretch Masks Stretch Masks Stretch Masks
Stretch Masks should be applied gently with cream, avoid scratching.
Pigmentation Pigmentation Pigmentation Pigmentation
Pigmentation or darken skin is due to the change of hormone. Try to avoid sunlight. It will be faded after delivery.
Heartburn Heartburn Heartburn Heartburn
Heartburn is caused by the stomach acid refluxing into the esophagus, and delayed functioning of digestive system. Consult the doctor for the use of antacid.