Management
Controlling
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 2
What is the
control process?
Controlling
– The process of measuring performance and taking action to ensure desired results.
– Has a positive and necessary role in the management process.
– Ensures that the right things happen, in the right way, at the right time.
– Organizational learning and after-action review.
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 3
Study Question 4: What is the
control process?
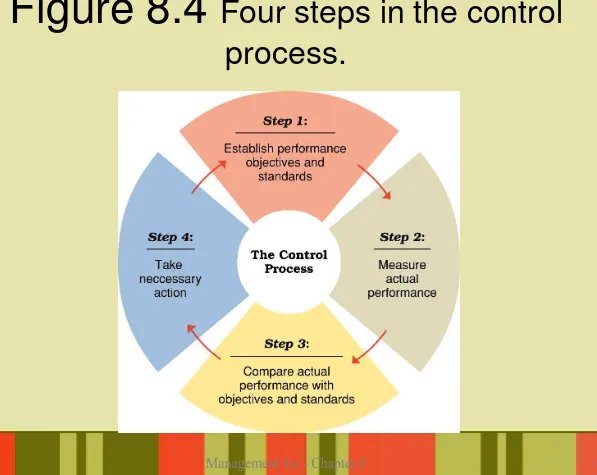
Steps in the control process:
– Step 1 — establish objectives and standards.
– Step 2 — measure actual performance.
– Step 3 — compare results with objectives and standards.
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 4
Tahap 1: Penetapan Standar
•
STANDAR
Satuan pengukuran yang digunakan sebagai patokan untuk penilain hasil.
tujuan, sasaran, kuota, target
Tahap 2: Penentuan Pengukuran
Pelaksanaan Kegiatan
Beberapa pertanyaan yang digunakan:
1. HOW OFTEN: stp jam, harian, mingguan
2. WHAT FORM: Laporan tertulis, inspeksi visual melalui telepon
3. WHO: manajer, staf departemen
Pengukuran
mudah dilakukan
tidak mahal
Tahap 2: Pengukuran Pelaksanaan
Kegiatan
Merupakan proses yang berulang-ulang,
terus-menerus
Cara:
1. Pengamatan (observasi)
2. Laporan-laporan (lisan, tertulis)
3. metode-metode otomatis
Tahap 3: Perbandingan Prestasi dengan
Standar & Analisis Penyimpangan
•
Tahap paling kritis, tetapi mudah dilakukan
•
Kompleksitas: saat menginterpretasikan adanya
deviasi
Tahap 4: pengambilan Tindakan Koreksi
Tindakan koreksi berbagai bentuk
Standar diubah
Pelaksanaan diperbaiki
Keduanya
Mengubah standar mula-mula
Mengubah pengukuran pelaksanaan - frekuensi (sering, kurang)
- mengganti sistem pengukuran
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 10
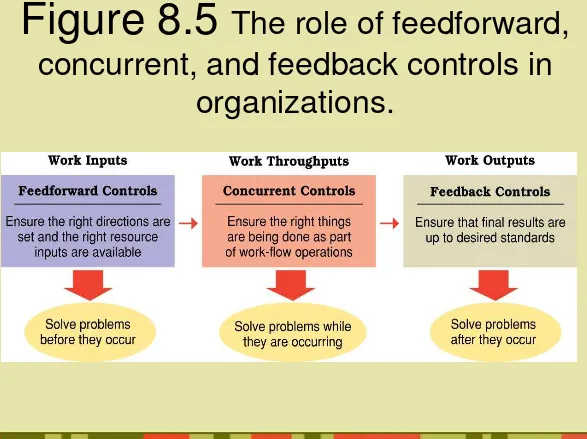
Figure 8.5
The role of feedforward,
concurrent, and feedback controls in
PENTINGNYA
Beberapa Gejala
yang memerlukan Pengawasan
• Terjadi penurunan pendapatan atau profit, namun tidak begitu jelas faktor penyebabnya
• Penurunan kualitas pelayanan (teridentifikasi dari adanya keluhan pelanggan)
• Ketidakpuasan pegawai (teridentifikasi dari adanya
keluhan pegawai, produktifitas kerja yang menurun, dan lain sebagainya)
• Berkurangnya kas perusahaan
• Banyaknya pegawai atau pekerja yang menganggur
• Tidak terorganisasinya setiap pekerjaan dengan baik
• Biaya yang melebihi anggaran
Alat Bantu Pengawasan Manajerial
• Management-by-Exception berfokus pada perhatian manajerial pada perbedaan substansi antara tampilan aktual dengan
tampilan yang diharapkan. (prinsip pengecualian)
• Management-Information System berfokus pada penyediaan informasi untuk melakukan evaluasi dari fungsi fungsi
manajemen
Management By Objective (MBO) adalah untuk memastikan bahwa setiap karyawan memiliki pemahaman yang jelas terhadap tujuan atau sasaran organisasi, seperti halnya mereka memahami peran dan
Pengendalian Manajemen
• Adalah suatu proses yang digunakan untuk mempengaruhi para anggota organisasi agar menerapkan strategi organisasi. Pengendalian manajemen merupakan:
– Aktivitas Pengendalian Manajemen
– Keselarasan Tujuan
– Salah satu alat implementasi Strategi, selain struktur organisasi, manajemen SDM, Budaya
– Menekankan aspek Keuangan dan Nonkeuangan
Konsep Pengendalian Manajemen
• Pengendalian:
adalah proses untuk menjamin agar kegiatan mengarah ke tujuan yang diinginkan
• Unsur Pengendalian:
– 1. Detektor atau sensor
– 2. Assesor atau penilai
– 3. Efektor atau pengubah
Batas Pengendalian
Manajemen
• Tiga aktivitas yang memerlukan perencanaan dan pengendalian:
– Strategy Formulation
– Management Control
Ilustrasi
•
Sopir
– Mata (sensor)
– Otak (assessor)
– Kaki (effector)
– Jaringan
komunikasi dari indera otak
Tipe-tipe Pengendalian
• (Awal) Preliminary
Kadang-kadang disebut kendali feedforward, Hal ini harus dipenuhi sebelum suatu
perkerjaan dimulai.
Tipe-tipe Pengendalian
• (Saat ini) Concurrent
Berfokus pada apa yang sedang terjadi selama proses. Kadang-kadang disebut Kendali steering, kendali ini memantau
Tipe-Tipe Pengendalian
• (Akhir) Post-action
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 21
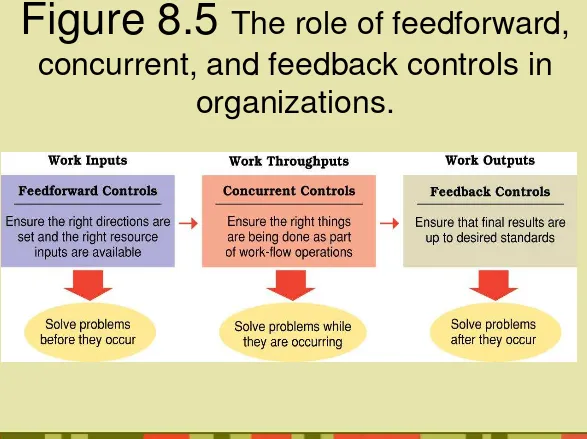
Figure 8.5
The role of feedforward,
concurrent, and feedback controls in
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 22
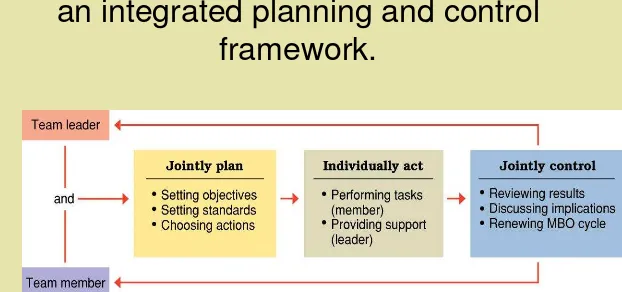
Figure 8.6
Management by objectives as
an integrated planning and control
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 23
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
MBO involves a formal agreement specifying …
– Workers’ performance objectives for a specific time
period.
– Plans through which performance objectives will be accomplished.
– Standards for measuring accomplishment of performance objectives .
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 24
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
The MBO process:
– Supervisor and workers jointly set objectives, establish standards, and choose actions.
– Workers act individually to perform tasks; supervisors act individually to provide
necessary support.
– Supervisor and workers jointly review results, discuss implications, and renew the MBO
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 25
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
Types of MBO performance objectives
– Improvement
– Personal development
– Maintenance
Criteria for effective performance objectives
– Specific
– Time defined
– Challenging
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 26
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
Types of MBO performance objectives
– Improvement
– Personal development
– Maintenance
Criteria for effective performance objectives
– Specific
– Time defined
– Challenging
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 27
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
Advantages of MBO
– Focuses workers on most important tasks and objectives.
– Focuses supervisor’s efforts on important
areas of support.
– Contributes to relationship building.
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 28
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
Employee discipline systems
– Discipline is the act of influencing behavior
through reprimand.
– Discipline that is applied fairly, consistently,
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 29
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
To be effective, reprimands should
…
– Be immediate.
– Be directed toward actions, not personality.
– Be consistently applied.
– Be informative.
– Occur in a supportive setting.
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 30
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
Employee discipline systems
– Progressive discipline ties reprimands to the
severity and frequency of the employee’s
infractions.
– Progressive discipline seeks to achieve
compliance with the least extreme reprimand
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 31
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
Important financial aspects of organizational performance …
– Liquidity
• The ability to generate cash to pay bills.
– Leverage
• The ability to earn more in returns than the cost of debt.
– Asset management
• The ability to use resources efficiently and operate at minimum cost.
– Profitability
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 32
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
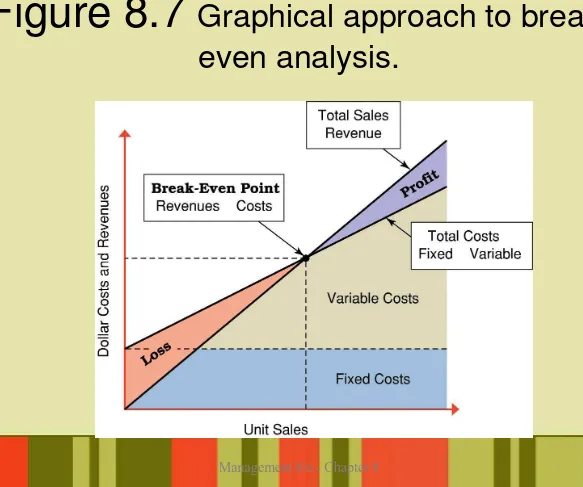
Break-even analysis
…
– Determination of the point at which sales revenues are sufficient to cover costs.
– Break-Even Point = Fixed Costs / (Price – Variable Costs)
– Used in evaluating:
• New products
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 33
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 34
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
Purchasing control
…
– A productivity tool
– Trends in purchasing control:
• Leveraging buying power
• Committing to a small number of suppliers
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 35
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
Inventory control
– Goal is to ensure that inventory is just the right size to meet performance needs, thus minimizing the cost.
– Methods of inventory control:
• Economic order quantity
Management 8/e - Chapter 8 36
Study Question 5: What are the common
organizational controls?
Statistical quality control
– Quality control involves checking processes, materials, products, and services to ensure that they meet high standards.
– Statistical quality control involves:
• Taking samples of work.
• Measuring quality in the samples.