Health Research Expo I
Buku Abstrak
Discover, Learn, Share
Fakultas Kedokteran
Universitas Gadjah Mada
Daftar Isi
1. Pengantar
2. Peta Jalan Penelitian
3. Featured research
4. Abstrak Fokus 1 : Kebugaran, Penuaan Dan Gaya Hidup Sehat
5. Abstrak Fokus 2 : Teknologi Intervensi Medik dan Kesehatan Masyarakat 6. Daftar Publikasi Jurnal International
TIM PENYUSUN
Penanggung jawab : Prof. dr. Adi Utarini, M. Sc, MPH, Ph.D Ketua Tim Penyusun Buku : Harry Freitag LM, S.Gz, M.Sc
Ketua Tim Pameran Poster : Eri Yanuar Akhmad BS, S.Kep., Ns Ketua Seminar : dr. M. Ary Zucha, Ph.D
Asisten : dr. Renata Uli Aviola
Editor Buku Abstrak : dr. Dian Kesumapramudya Nurputra, Ph.D dr. Junaedy Yunus, M.Sc, Ph.D
Melyza Perdana, S.Kep, MN
Harry Freitag Luglio M, S.Gz, M.Sc, RD
Layouter : Ceria Ciptanurani, S.Gz
Muhammad Cahyono Tito Handoyo Rasyid Herlambang Wicaksono Dimas Septian Eko Wahyu Sumunar Sekretariat dan Panitia : Glory Hapsara Suryandari, S.Pd
Rahma Hanggia Iswandi, S.I.Kom
PENGANTAR
Assalaamu’alaikum Wr Wb,
Penelitian merupakan salah satu pilar Tridharma Perguruan Tinggi yang memberikan kontribusi nilai yang kompetitif dalam kinerja, baik di tingkat Fakultas maupun Universitas. Dalam hal ini, fungsi utama Fakultas adalah menciptakan atmosfer penelitian yang kuat sebagai sistem pendukung bagi para dosen dan peneliti (termasuk mahasiswa di berbagai tingkatan pendidikan).
Agar kegiatan penelitian dapat berkembang, minimal diperlukan tiga pilar sistem pendukung, yaitu:
1. Tata kelola penelitian (research governance); 2. Pelaksanaan penelitian (research production); dan
3. Diseminasi hasil-hasil penelitian (research dissemination).
Kegiatan ini digagas bermula dari pertanyaan sederhana dari mahasiswa tingkat sarjana: “Bagaimana kami dapat mengetahui penelitian-penelitian yang sedang dikerjakan oleh para dosen di FK UGM?”. Pertanyaan sederhana ini ternyata jauh dari sederhana untuk menjawabnya. Mahasiswa miskin informasi sekalipun berada di institusi Fakultas Kedokteran yang kaya akan kegiatan penelitian dan publikasi di jurnal internasional. Bahkan Fakultas Kedokteran menempati posisi tertinggi di UGM dalam hal jumlah kegiatan penelitian yang dilakukan, dana penelitian yang dikelola serta jurnal internasional. Kondisi ini tentu tidak dapat dibiarkan.
Dengan kegiatan ini, kami berharap minat kegiatan penelitian mahasiswa baik di tingkat sarjana maupun pascasarjana serta dosen-peneliti menjadi semakin berkembang. Kami percaya bahwa diantara sekian banyak mahasiswa, akan bermunculan peneliti-peneliti handal yang dibutuhkan oleh bangsa Indonesia di masa mendatang. Selain itu, kami berharap pula bahwa kegiatan Health Research Expo seterusnya akan menjadi bagian dari budaya Fakultas dalam memperingati puncak acara Dies Fakultas Kedokteran UGM.
Kami mengucapkan terima kasih atas partisipasi seluruh dosen-peneliti dalam kegiatan ini, serta atas kerja keras para dosen dan staf kependidikan di tim buku abstrak, tim pameran poster serta tim seminar. Segala kekurangan mohon dapat disampaikan kepada kami melalui email [email protected], untuk dapat diperbaiki di masa mendatang. Semoga kegiatan ini memberikan manfaat bagi kita semua. Amin.
Wassalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb.
Prof. dr. Adi Utarini M.Sc, MPH, Ph.D
PETA JALAN PENELITIAN DI FK UGM
Dokumen peta jalan (road map) penelitian disusun dengan beberapa pemikiran yang melandasi relevansinya. Secara umum, relevansinya adalah sebagai berikut:
1. Untuk mengukur pemahaman internal mengenai penelitian-penelitian yang dilakukan oleh institusi serta menggali pemikiran tentang prioritas penelitian;
2. Mengidentifikasi peluang perbaikan dan memberikan rekomendasi sistem dan proses penelitian kedepan;
3. Memetakan dan merencanakan pendekatan implementasi peta jalan penelitian dengan serangkaian inisiatif dan pencapaian kinerja; 4. Meningkatkan komunikasi dengan para peneliti, institusi penelitian
dan pendidikan, serta para pemangku kepentingan;
5. Mendeskripsikan manfaat yang diharapkan dan mengidentifikasi ukuran keberhasilan dari investasi untuk penelitian.
Tujuan penyusunan peta jalan penelitian ini adalah untuk menetapkan strategi penelitian FK UGM yang terukur dan mengkomunikasikannya kepada para peneliti, pemangku kepentingan di Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta, nasional, internasional serta kepada lembaga-lembaga yang memberikan dana penelitian. Dengan tersedianya dokumen ini, diharapkan pula akan memudahkan para peneliti untuk meningkatkan daya saing di tingkatnasional dan internasional.
Kedokteran UGM. Uji publik ketiga dan keempat menghadirkan para pemangku kepentingan eksternal, yaitu dari Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta (RSUP dr. Sardjito, RS UGM, DinasKesehatan Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta, Kagama Kedokteran, Dewan Riset Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta) dan nasional (Kementerian Riset Teknologi dan Pendidikan Tinggi serta Kementerian Kesehatan).
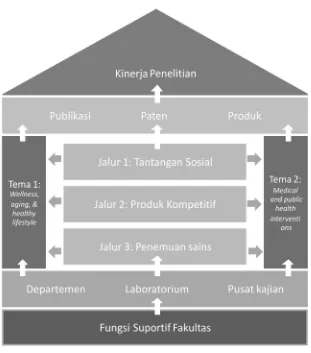
Melalui serangkaian proses tersebut, maka prioritas riset FK-UGM terdiri dari dua fokus, yaitu kebugaran, penuaan, dan gaya hidup sehat serta teknologi intervensi medik dan kesehatan masyarakat. Fokus pertama terkait kebugaran, penuaan dan gaya hidup sehat merupakan riset yang berfokus pada pemahaman mekanisme yang mendasari masalah kebugaran, penuaan dan gaya hidup, dan mencakup topik mengenai genetika dan penyakit, gaya hidup yang mempengaruhi kesehatan, lingkungan dan gizi, perawatan rehabilitatif dan paliatif, dan problem kesehatan mental. Sementara fokus kedua terkait teknologi intervensi medik dan kesehatan masyarakat merupakan riset yang berfokus pada pasien untuk mengidentifikasi teknologi-cara baru untuk pembelajaran, pencegahan, diagnosis, pengobatan penyakit, dan intervensi untuk meningkatkan kesehatan masyarakat. Pada setiap fokus penelitian, dapat dikembangkan tiga jalur ruang penelitian, yaitu penelitian yang memiliki orientasi untuk memecahkan masalah kesehatan yang menjadi tantangan sosial, penelitian yang menghasilkan produk kompetitif, serta penelitian yang menghasilkan temuan sains baru (Gambar 1).
Knowledge and Attitudes Towards Rotavirus Diarrhea And The Vaccine Amongst Healthcare Providers In Yogyakarta Indonesia
Holly Seale1*, Mei Neni Sitaresmi2, Jarir Atthobari2, Anita E. Heywood1, Rajneesh Kaur1, Raina C. MacIntyre1, Yati Soenarto2 and Retna Siwi Padmawati2
1School of Public Health & Community Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of New
South Wales, Australia; 2Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), Yogyakarta, Indonesia
* Correspondence: [email protected]
Background
Rotavirus has been identified as the most common pathogen associated with severe diarrhoea. Two effective vaccines against the pathogen have been licensed. However, many countries including Indonesia have yet to introduce the vaccine into their national immunisation programs. This study aimed to examine the attitudes of healthcare providers (HCPs) and other health stakeholders towards the pathogen and the vaccine.
Methods
Semi-structured in-depth interviews were undertaken in two districts of Yogyakarta Province, Indonesia with nurses, midwives, primary care providers, pediatricians and other health stakeholders. Thematic analysis was undertaken.
Results
Fourteen interviews were conducted between August and October 2013. We identified that while participants do not consider diarrhea to be an important problem in Indonesia, they do acknowledge that it can be serious if not properly treated. While the majority had some level of knowledge about rotavirus, not all participants knew that a vaccine was available. There were mixed feelings towards the need for the vaccine. Some felt that the vaccine is not ranked as a priority as it is not listed on the national program. However, others agreed there is a rationale for its use in Indonesia. The cost of the vaccine (when sold in the private sector) was perceived to be the primary barrier impacting on its use.
Conclusions
The Importance of Molecular Genetic Analysis for Diagnosis of Disease
Gunadi1, Rochadi1, Akhmad Makhmudi1, Kristy Iskandar2, Hisahide Nishio3, Aravinda Chakravarti4
1Pediatric Surgery Division, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, UGM/Dr. Sardjito Hospital; 2Faculty of Medicine, UGM/UGM Hospital; 3Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Kobe, Japan; 4Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA.
Contact: [email protected]
Background
Molecular diagnosis of genetic disease is detection of various changes in DNA, RNA, chromosome, or protein related to an inheritable disorder.We have performed molecular analysis of the following genetic disorders: 1) Hirschsprung disease; 2) Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia; and 3) Spinal Muscular Atrophy.
Method
Three genetic markers (RET rs2435357, NRG1 rs16879552 and rs7835688) were examined using TaqMan assays for association with Hirschsprung disease. To screen an ED1 mutation, DHPLC and direct sequencing were performed in genomic DNA of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia patients. To investigate p.G381R could alter EDA overall structure, electrostatic surface and molecular structure were analyzed. The adenine number in SMN intron 3 in spinal muscular atrophy patients were determined by GeneScan.
Result
Hirschsprung disease (HSCR): RET rs2435357 showed strongest association with HSCR both by case-control analysis (p=2.5x10-8) and transmission disequillibrium test (p=4.2x10-6). NRG1 rs7835688 was modestly associated with HSCR only by case-control analysis (p=4.3x10-3), whereas rs16879552 demonstrated no association (p>0.097).
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (HED): We identified two novel mutations, p.L40fsX100 and p.G381R, in ED1 of HED patients. Simulation analysis suggested that the p.G381R mutation hampers binding of EDA to its receptor via alteration of overall EDA structure.
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA): Almost all individuals, including healthy individuals, SMA patients and SMA-like patients, carried only alleles with a normal polyadenine tract. Hypomutability of the polyadenine tract in SMN intron 3 suggests the existence of transcriptional mechanisms preventing alterations to open reading frame of axonal SMN and not allowing variability in the protein structure of a-SMN.
Multiple Markers for Early Identification of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Susanna Hilda Hutajulu,1 Luh Putu Lusy Indrawati,2 Camelia Herdini,2 Jajah Fachiroh,3 Sagung Rai Indrasari,2 Bambang Hariwiyanto,2 Harijadi,4 Hesti Gunarti,5 Retno Dwi Danarti,5 Sofia Mubarika Haryana,3 Astrid E. Greijer,6 I. Bing Tan,2,7 Jaap M. Middeldorp6
1Department of Internal Medicine, 2Department of Ear, Nose and Throat, 3Department of Histology and Cell Biology, 4Department of Pathology, and 5Department of Radiodiagnostic and Radiotherapy, Faculty of Medicine/Dr Sardjito Hospital, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 6Department of Pathology, VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 7Department of Ear, Nose and Throat, The Netherlands Cancer Institute/Antoni van Leeuwenhoek Hospital, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Background
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is the most prevalent head and neck cancer in Indonesia and closely linked to active Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. EBV-based markers are proposed for identifying early stage of NPC allowing aberrant antibodies against EBV and viral DNA load as screening tools. We performed a clinical, serological and viral load study in subjects presenting with chronic symptoms in head and neck to define the serologic response to EBV antigens and EBV DNA load and find early onset NPC. Besides those markers, methylation analysis in the promoter of tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) may serve as a complementary marker for identifying early cases. This study also determined methylation status of multiple TSGs and evaluated whether it may improve early detection.
Methods
A total of 217 individuals were recruited and underwent clinical examination. Blood samples were taken from all subjects and nasopharyngeal brushing was collected from the majority of individuals. Initial serology analysis was done by peptide-based EBV IgA ELISA and confirmed with IgG immunoblot. Furthermore, nasopharyngeal brushings from 53 NPC patients, 22 high risk subjects and 25 healthy EBV carrierswere tested for analysis of methylation-specific PCR (MSP) using primers targeting ten TSGs.
Results
methylation markers (RASSF1A, p16, WIF1, CHFR and RIZ1) gave best result to discriminate NPC from healthy individuals with detection rate of 98%.
Conclusions
The incremental cost-effectiveness of engaging private practitioners to refer tuberculosis suspects to DOTS services in Jogjakarta, Indonesia
Yodi Mahendradhata, Ari Probandari, Riris A. Ahmad, Adi Utarini, Laksono Trisnantoro, Lars Lindholm, Marieke J. van der Werf, Michael Kimerling, Marleen Boelaert, Benjamin Johns, Patrick Van der Stuyft
Department of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, Gadjah Mada University, Jogjakarta, Indonesia; Centre for Health Service Management, Faculty of Medicine, Gadjah Mada University, Jogjakarta, Indonesia; Epidemiology and Disease Control Unit, Public Health Department, Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp, Belgium; Department of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, Sebelas Maret University, Surakarta, Indonesia; Epidemiology and Public Health Sciences, Public Health and Clinical Medicine, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden; KNCV Tuberculosis Foundation, The Hague, The Netherlands; Department of Infectious Diseases, Tropical Medicine & AIDS, Center for Infection and Immunity Amsterdam (CINIMA), Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Gorgas TB Initiative, UAB School of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Birmingham, Alabama; WHO Country Office for Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
Background
We aimed to evaluate the incremental cost-effectiveness of engaging private practitioners (PPs) to refer tuberculosis (TB) suspects to public health centers in Jogjakarta, Indonesia. Effectiveness was assessed for TB suspects notified between May 2004 and April 2005. Private practitioners referred 1,064 TB suspects, of which 57.5% failed to reach a health center. The smear-positive rate among patients reaching a health center was 61.8%. Two hundred eighty (280) out of a total of 1,306 (21.4%) new smear-positive cases were enrolled through the PPs strategy. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio per smear-positive case successfully treated for the PPs strategy was US$351.66 (95% CI 322.84–601.33). On the basis of an acceptability curve using the National TB control program's willingness-to-pay threshold (US$448.61), we estimate the probability that the PPs strategy is cost-effective at 66.8%. The strategy of engaging PPs was incrementally cost-cost-effective, although under specific conditions, most importantly a well-functioning public directly observed treatment, short-course (DOTS) program.
Methods
positive case successfully treated.We set a hypothetical willingness-to-pay threshold based on the National TB control program's estimated marginal cost. We further analyzed the sensitivity of total costs to input values that are likely to be under the control of program managers. To do this, we assessed possible scenarios to the CEACs:
Results
Eventually, only 410 PPs referred suspects during the study intake period. The number of suspects (1,064) notified by the 410 PPs was much lower than the number of suspects (10,878) notified through the HCs (Figure 1). Most of the suspects (57.5%) notified and referred by PPs never reached a health center. The PPs strategy allowed registering an additional 280 new smear-positive cases over 12 months.
• Sensitivity analysis on the total patient cost ratio between the two strategies indicates that our estimate is robust to changes across a number of key variables (Figure 2). Only when the cost for laboratory and consultation before DOT in patients referred by PPs is at the lower bound of the 95% CI, costs to patients notified by PPs are not substantially higher than to those notified by HCs.
• Average Cost-Effectiveness Ratio per smear-positive case successfully treated for the HCs strategy was US$321.66 (95% CI 190.71–342.99), whereas Incremental Cost-Effectiveness Ratio per smear-positive case successfully treated for the PPs strategy was US$351.66 (95% CI 322.84–601.33)
• At a willingness-to-pay threshold for a smear-positive case successfully treated of US$448.61 (the estimated National TB control program's marginal cost in 2004– 2005), the PPs strategy was incrementally cost-effective in 66.8% of simulation iterations (Figure 3). Adjusting the DOT consultation cost in HCs to the most efficient observed value (US$1.04) increased this percentage to 83.1%, whereas lowering the smear-positive rate to 20% and increasing the proportion of suspects who reached the HCs to 62% reduced the percentage to 63.1%. Lowering the willingness-to-pay threshold obviously reduces all the above percentages and at, for instance, US$400 the PPs strategy is less than 50% likely to be cost-effective in most scenarios.
Conclusions
Frequent Deregulation Of Rb1 Expression By Loss Of Imprinting In Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Sumadi Lukman Anwar1,3, Till Krech1, Britta Hasemeier1, Elisa Schipper1, Nora Schweitzer2, Arndt Vogel2, Hans Kreipe1, Ulrich Lehmann1
1Institute of Pathology, Medizinische Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany; 2Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Endocrinology, Medizinische Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany; 3Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia,
Contact: [email protected]
Background
The tumour suppressor gene RB1 is frequently silenced in many different types of human cancer including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, mutations of the RB1 gene are relatively rare in HCC.
Method
A systematic screen for the identification of imprinted genes deregulated in human HCC revealed that RB1 shows imprint abnormalities in a high proportion of primary patient samples. Quantitative DNA methylation analysis and allele specific methylation were performed as well as expression of main RB1 and alternative transcript were performed in HCC cell lines and primary HCC tissues.
Results
Altogether 40% of the HCC specimens (16/40) showed hyper -or hypomethylation at the CpG island in intron 2 of the RB1 gene. Demethylation at the intron 2 CpG island by DNMT1 knockdown or aza-deoxycytidine (DAC) treatment stimulated expression of RB1-E2B transcript accompanied by diminished RB1 main transcript expression. No aberrant DNA methylation was found at the RB1 locus in hepatocellular adenoma (HCA, n=10), focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH, n=5) and their corresponding adjacent liver tissue specimens. Deregulated RB1 expression due to hyper- or hypomethylation in intron 2 of the RB1 gene is found in tumours without loss of heterozygosity and is associated with a decrease in overall survival (p = 0.032) if caused by hypermethylation of CpG85.
Conclusion
Fokus #1
Kebugaran, Penuaan Dan Gaya Hidup Sehat
A. Genetika dan penyakit
B. Gaya hidup yang mempengaruhi kesehatan
C. Lingkungan dan gizi
A. Genetika dan penyakit
1. Discrepancy of acetylation status prediction using genetic polymorphism in the NAT-2 Coding region examination with acetylsulphadimidine measurement.
2. Mammograohic density thresholding method, estradiol, and estrogen receptor a gen polymorphism (ESR 1) as breast cancer predictor.
3. Clinical characteristics and gene mutation of tuberculosis sclerosis patients in Indonesia.
4. Neurofibromatosis tipe 1: karakteristik gambaran klinis dan indentifikasi mutasi gen.
5. Hubungan polimorfisme gen ACE dengan keparahan dan luaran stroke iskemik.
6. Association of ondansetron serum concentration and polimorphisms of
CYP2D6, ABCB1 and 5-HT3B receptor genes in the treatment of chemoterapy induced nausea and vomiting.
7. Hubungan antara interaksi polimorfisme gen UCP2, KCNJ11 dan TCF7L2 dengan asupan tinggi lemak dan karbohidrat sederhana dalam kaitannya dengan kejadian obesitas.
8. Polymorphism of the DATI and DRD4 genes are not associated with ADHD in Indonesia children.
9. Hubungan polimorfisme alel CYP2A6*4 dan CYP2A6*9 dengan kadar dihydroartemisinin-piperakuin pada penderita malaria falciparum.
10. Pengaruh polimorfisme reseptor Fc gamma IIIA (FcJRIIIA) dan jumlah sel efektor terhadap respon kemoterapi trastuzumab pada pasien kanker payudara lokal lanjut dan metastasis dengan HER2/NEU positif.
11. Polimorfisme gen p53Arg72Pro, MDM2SNP309, HER2Ile655Val, ER594 A>G, p21 Ser31Arg dan FGFR2 rs2981582; studi risiko kanker payudara onset dini di Yogyakarta.
12. Hubungan antara mutasi gen filaggrin dengan dermatiti atopik. Kajian mutasi gena filaggrin tipe asia di suku Jawa.
13. Distribusi dan dinamika genotype serta analisis gen vp4, vp7, nsp2, nsp4 dan nsp5 rotavirus penyebab diare anak balita di indonesia.
14. Korelasi Polimorfisme Genetik Sitokrom P450 2A6 dan 2B6 dengan Kuantitas Merokok di Kota Yogyakarta
15. Cytoarchitecture of the olfactory bulb in the laggard mutant mouse. 16. Prognostic Impact Of Metastatic Status In Patients With
19. Case report on pediatric nasopharyngeal carcinoma at Dr. Sardjito Hospital, Yogyakarta
20. Results of Treatment With Neoadjuvant Cisplatin-5fu In Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Local Experience 21. Geriatrics with Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Discrepancy of acetylation status prediction using genetic polymorphisms in the NAT-2 coding region examination with acetylsulphadimidine measurement
Erna Kristin, Dwi Aris Agung Nugrahaningsih, Mustofa
Department of Pharmacology and Therapy, Faculty of Medicine, UGM Contact: [email protected]
Background
N-acetyltransferase2 (NAT2) gene polymorphism is known to be associated with the isoniazid hepatotoxicity. NAT2 polymorphism results in slow and fast acetylator phenotype. Using NAT2 polymorphism to predict acetylator status is a future project to individualized isoniazid therapy.
Methods
The aim of our study is to investigate the NAT2 genotype in Javanese, one of dominant ethnics in Indonesia, to predict hepatotoxicity in tuberculosis (TB) patients receiving isoniazid in combination with other TB drugs. We examined NAT2 polymorphisms on coding region using PCR direct sequencing. We also determined the acetylation status by measuring acetyl sulphadimidine.
Results
Nineteen subjects were enrolled in this study. Most of them were male. The age average was 43.58 ± 15.43 years old. Their average body mass index and serum transaminase were within normal range. In this study, we identified 11 different NAT2 genotypes. We found that the major NAT2 genotypes were NAT2*4/*4 (31.58%) and NAT2*6A/*6A (21.05%). Based on the genotype prediction, most of the subjects were slow acetylator (63.16%). Meanwhile based on acetylation status determination using acetylsulphadimidine measurement in the urine, 52.63% were fast acetylator and 47.37% were slow acetylator. The serum transaminase increase also tended to be higher on slow acetylator group compared with those on fast acetylator group, even though the different was not statistically significant. Interestingly, we found discrepancy between acetylation status prediction using NAT2 genotype and acetylsulphadimidine examination.
Conclusions
Mammographic density thresholding method, estradiol level and estrogen receptorɲ gene polymorphism (ESR1) as breast cancer predictor
Lina Choridah1, Teguh Aryandono2, Arif Faisal1, Ahmad Hamim Sadewa3
1Department of Radiology. 2Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada. 3Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada.
Contact:[email protected]
Background
Estrogen is believed to play an important role in the development and progression of breast cancer. Mammographic densities equivalent to the cell proliferation, estradiol and ESR 1 Gene Polymorfism allegedly acted as a predictor of breast cancer.
Methods
We performed an observational study, data were collected prospectively using a cohort study design. Subjects were women who came to oncologic clinic for mammographic screening, with either high or low breast density. Subjects were then grouped into two, with and without breast cancer. The data were analyzed using relative risk and multivariate logistic regression.
Results
Women with PMD 25-34% , 35-49%, 50-64% and >65% had relative risk of 1.67 (95% CI, 0.47 to 5.89), 3.4 (95% CI, 1.16 to 9.97), 3.43 (95% CI, 31.19 to 9.88) and 3.45 (95% CI, 1.174 to 10.14%) times, respectively, compared to PMD <25%. The highest quartile of estradiol's level did not have significant association compare with the lowest. CT and TT genotypes of ESR1 PvuII had a relative risk 1.9104 (95% CI, 0.9594 to 3.803) and 3.36 (95% CI, 1.729 to 6.526) times, respectively, compared to CC genotype. AG genotypes of ESR1 XbaI had relative risk 2.6800 (95% CI, 0.7273 to 9.88151) times than the GG genotype, whereas AA had relative risk 3.6393 (95% CI 1.01667 to 13.1050) times.
Conclusions
Clinical characteristics and gene mutation of tuberous sclerosis patientsin Indonesia
Retno Danarti1, Hardyanto Soebono1, Sunartini2, Elisabeth Siti Herini2,Zamh Zabidi-Hussin3,4, Nur Farrah Dila Ismail4,5, Teguh Haryo Sasongko4,5
1Department of Dermatology and Venereology Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada/ Dr. Sardjito Hospital.2Department of Pediatrics Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada/ Dr. Sardjito Hospital.3Department of Pediatrics School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia.4Center for Neuroscience Services and Research, Universiti Sains Malaysia.5Human Genome Center, School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia.
Contact:[email protected]
Background
Tuberous sclerosis is an autosomal dominant neurocutaneous disorder characterized by the growth of benign tumors in multiple organs as well as neuropsychological manifestations. To date, many TSC1 and TSC2 mutations have been reported all over the world. However, no TSC clinical and mutation studies have been performed in Indonesian population. The aim of this study is to identify the clinical characteristics and mutation of TSC lociin tuberous sclerosis patients from Indonesia.
Methods
Fifteen patients were enrolled from the out-patients clinic Department of Dermatology and Venereology Sardjito Hospital, Yogyakarta Indonesia from the period of January 2009-June 2015. We performed clinical examination and genetic mutation. Genomic DNA was extracted from whole-blood obtained from only eight patients. Mutation analysis employed Amplicon Sequencing using Illumina MiSeq for detecting mutations in TSC1 and TSC2 genes.
Results
Seven patients were females and 8 males. The mean age at first diagnosis was 3.9 years. All patients presented dermatological and neurological manifestations. CTscan showed cortical tuber in 33.33% of the patients. Psychiatric manifestations were present in 50% of the patients. No cardiac, renal, pulmonary, ophthalmological and skeletal disorders were found. Nonsense mutations were found in 2 patients i.e. c.3094C>T;p.R1032X and c.3937G>T;p.E1313X. Both mutations were found in TSC2
gene exons 26 and 32, respectively. Conclusions
Neurofibromatosis tipe 1: karakterisasi gambaran klinis dan identifikasi mutasi gen
Retno Danarti1, Dewi Kartikasari Paramita2, Elisabeth Siti Herini3,Tetra Rianawati1,Hardyanto Soebono1
1Departemen Dermatologi dan Venereologi Fakultas Kedokteran UGM/ KSM Kulit dan Kelamin RSUP Dr Sardjito. 2Departemen Histologi, Fakultas Kedokteran UGM.
3Departemen Ilmu Kesehatan Anak Fakultas Kedokteran UGM/ KSM Kesehatan Anak RSUP Dr Sardjito.
Kontak: [email protected]
Latar Belakang
Neurofibromatosis tipe 1 (NF1) merupakan penyakit neurokutan yang paling sering ditemukan. NF1 disebabkan oleh mutasi pada gen neurofibromin yang terletak pada kromosom 17q11.2. Meskipun NF1 merupakan kelainan genetik yang paling sering ditemukankarakterisasi gambaran klinis NF1 dan identifikasi mutasi gen NF1 belum diketahui di Indonesia. Penelitian bertujuan untuk: 1) mengetahui prevalensi neurofibromatosis tipe-1, 2) mengetahui karakteristik gambaran klinis pasien NF1 baik yang sporadik maupun familial, dan 3) mengidentifikasi mutasi pada gen NF1. Metode
Penelitian ini dibagi dalam beberapa tahap, yaitu: 1) melacak rekam medis dan memanggil kembali pasien yang didiagnosis NF1 yang pernah berobat di RSUP Dr. Sardjito Yogyakarta pada periode 2010-2015, 2) pemeriksaan kelainan kulit, saraf, dan psikologis pada pasien yang didiagnosis NF1, dan 3) skrining mutasi gen.Dilakukan pemeriksaan klinis, neurologis, dan oftalmologis lengkap pada seluruh pasien NF1 sporadik maupun familial, sedangkan untuk anggota keluarga NF1 familial pemeriksaan lengkap hanya dilakukan apabila dari pemeriksaan fisik ditemukan tanda dan gejala NF1. Analisis genetik molekular dilakukan pada semua pasien NF1 yang terlibat pada penelitian ini. Seluruh ekson NF1 diamplifikasi dengan polymerase chain reaction, dilakukan sekuensing, dan sekuen basa nitrogen gen NF1 ekson 19-20, ekson 25, dan ekson 28-29 dari masing-masing pasien dengan sekuen yang ada di
genbank.
Hasil
Hubungan polimorfisme gen ACE dengan keparahan dan luaran stroke iskemik
Rusdy Ghazali Malueka, Sri Sutarni, Ismail Setyopranoto, Abdul Gofir Departemen Ilmu Penyakit Saraf, Fakultas Kedokteran, UGM
Kontak: [email protected]
Latar Belakang
Polimorfisme insersi/delesi gen ACE (ACE I/D) diketahui berhubungan dengan kejadian stroke iskemik melalui efeknya pada patognesis aterosklerosis dan hipertensi. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk melihat hubungan antara polimorfisme gen ACE dengan keparahan dan luaran stroke iskemik.
Metode
Penelitian ini menggunakan desain penelitian belah lintang pada populasi pasien stroke iskemik di Unit Stroke RS Sardjito, Yogyakarta. Data demografis, faktor risiko stroke, komorbiditas, serta keparahan stroke (NIHSS) dinilai pada saat admisi. Luaran klinis (NIHSS) dan luaran fungsional (Indeks Barthel) dinilai saat pasien keluar rumah sakit. Genotipe ACE I/D pasien diidentifikasi dengan PCR.
Hasil
Hingga akhir April 2016 telah terkumpul sampel sebanyak 34 pasien dari target besar sampel 70 pasien. Analisis DNA sudah diselesaikan pada 29 pasien. Dari jumlah ini sebanyak 10 pasien (34,5 %) memiliki polimorfisme II dan 19 pasien (65,5 %) memiliki polimorfisme ID pada gen ACE. Rerata NIHSS saat admisi adalah 8±8,2. Tidak terdapat perbedaan bermakna pada keparahan stroke yang dinilai dengan NIHSS admisi antara pasien dengan polimorfisme II dan pasien dengan polimorfisme ID (rerata NIHSS admisi berturut-turut 14,28 dan 13,44; p=0,796). Tidak terdapat perbedaan bermakna dalam luaran klinis pasien dengan polimorfisme II dan ID (rerata NIHSS akhir berturut-turut 13,47 dan 13,56; p=0,978). Tidak ditemukan pula perbedaan bermakna antara luaran fungsional pasien dengan polimorfisme II dan ID (rerata indeks Barthel akhir berturut-turut 15,05 dan 10,56; p=0,149).
Kesimpulan
Association of ondansetron serum concentration and polimorphisms of CYP2D6, ABCB1 and 5-HT3B receptor genes in the treatment of chemoterapy induced nausea and
vomiting
DA Perwitasari 1, Mustofa2
1
Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Ahmad Dahlan. 2Department of Pharmacology and Therapy, UGM
Contact :[email protected]
Background
Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) is still become the most distressing side effect of chemotherapy in cancer patients. Only 70% patients who had good response of antiemetic. Some pharmacogenetic markers are supposed to be involved in the antiemetic response. This study was aimed to understand the association between ondansetron serum concentration and the antiemetic responses, polymorphisms of 5HT3B receptor, CYP2D6 and ABCB1 genes in Indonesian cancer patients treated with high emetogenic cytostatics.
Methods
We recruited cancer patients in Dr Sardjito Hospital treated with cisplatin ( 50 mg/m2) as monotherapy or combination therapy. Patients were treated with ondansetron 8 mg intravenously and dexamethasone 8 mg intravenously and metoclopramide (10 mg orally) after cytostatic administration until 5 days after chemotherapy. The inclusion criteria were patients with age 18 years old and they have a Karnofsky Performance Scale (KPS) of 50%. We assesed the nausea using 0-100 of Nausea Visual Analog Scale (NVAS) for 5 days after chemotherapy, the vomiting was assesed by quantifying the number of vomiting that was separated at least 1 minute betweeen each of vomiting episode and ondansetron serum concentration was determined using HPLC. We cathegorize the nausea and vomiting according to the National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria v.3 (NCI CTC v.3). We determined some SNPs of ABCB1, 5HT3Band
CYP2D6 genes. We recruited 191 cancer patients in this study with the average of ondansetron serum concentration reached 33.48 ng/ml (SD: 18.54).
Results
According to the patients’ response to the antiemetic, during the acute phase, 21.8% patients experienced acute nausea and 30.2% patients experienced acute vomiting. Only the haplotype of CTG-CTG of ABCB1 which have significant association with ondansetron serum concentration. EM patients of CYP2D6 and patients with haplotype of delAG of
5HT3B had lower ondansetron serum concentration. However, IM patients of CYP2D6
showed higher ondansetron serum concentration and lower grade of nausea and vomiting.
Conclusions
Hubungan antara interaksi polimorfisme gen UCP2, KCNJ11 dan TCF7L2 dengan asupan tinggi lemak dan karbohidrat sederhana dalam kaitannya dengan kejadian
obesitas
Emy Huriyati
Departemen Gizi Kesehatan, Fakultas Kedokteran, Universitas Gadjah Mada Kontak: [email protected]
Latar Belakang
Prevalensi obesitas pada remaja semakin meningkat, hal ini berkaitan dengan kejadian penyakit kardiovaskuler di masa datang.Penyebab obesitas bersifat multifaktorial, genetik dan lingkungan.Pola makan, aktivitas, ditambah dengan sifat genetik individu tentu semakin menyumbang terhadap kejadian obesitas.
Metode
Penelitian ini menggunakan jenis penelitian observasional dengan rancangan
unmatched case control (n kasus=106 dan n kontrol=155). Seluruh subjek penelitian dilakukan penilaian pola makan, aktivitas fisik, pemeriksaan antropometri (tinggi badan dan berat badan), gula darah puasa dan insulin puasa. Resistensi insulin ditentukan berdasarkan pengukuran HOMA-IR (>3,16), penurunan fungsi sel beta ditunjukkan dengan HOMA Beta (>150%). Substitusi UCP2, KCNJ11 dan TCF7L2 dideteksi dengan metode PCR-RFLP pada DNA subjek yang sebelumnya telah diisolasi.
Hasil
Tidak ada hubungan antara polimorfisme rs659366 gen UCP2, rs5219 gen KCNJ11, dan rs12255372 gen TCF7L2 dengan kejadian obesitas dengan nilai p masing-masing 0,175; 0,081; 0,794. Polimorfisme -866G/A gen UCP2 setelah dikontrol dengan asupan lemak menunjukkan perbedaan yang bermakna pada kelompok dengan polimorfisme dan asupan lemak tinggi dengan nilai OR= 0,19 dan p=0,065. Peningkatan HOMA-IR lebih rendah pada polimorfisme -866G/A gen UCP dibanding yang tidak polimorfisme tetapi secara statistik tidak bermakna. Polimorfisme E23K gen KCNJ11 lebih berisiko terhadap kejadian obesitas dengan OR=2,35; p=0,036; dalam keadaan asupan karbohidrat sederhana yang tinggi. Sementara peningkatan HOMA Beta menunjukkan kecenderungan meningkat pada kelompok polimorfisme walaupun secara statistik tidak bermakna. Hubungan interaksi polimorfisme rs12255372 gen TCF7L2 dengan asupan tinggi karbohidrat sederhana tidak ada hubungan yang bermakna.
Kesimpulan
Polymorphisms of the DAT1 and DRD4 genes are not associated with ADHD in Indonesian children
Cempaka Thursina1, Rusdy Ghazali Malueka1, Indra Sari Kusuma Harahap1, Samekto Wibowo1, Sri Sutarni1, Ahmad Hamim Sadewa2
1
Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah
Mada.2Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada. Contact: [email protected]
Background
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is one of the most common neurobehavioural disorders in children. Genetics are known to be one of the contributing factors in ADHD. In this study, we examined the association of ADHD with the VNTR polymorphism on DAT1 and DRD4 genes in Indonesian children. Methods
Sixty-five ADHD children and 70 normal children (aged 6-13 years) were included in the study. Controls were matched by age and gender. ADHD was diagnosed using the DSM-IV. We performed a case-control study to find the association between ADHD and the VNTR polymorphism on the DAT1 and DRD4 genes.
Results
The 10-repeat allele of DAT1 and 2-repeat allele of DRD4 were higher in Indonesian children. However, the distribution was similar in ADHD and control groups. Neither the DAT1 nor DRD4 gene exhibited significant differences in genotype distribution or allele frequency between the two groups (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
Hubungan polimorfisme alel CYP2A6*4 dan CYP2A6*9 dengan kadar dihydroartemisinin-piperakuin pada penderita malaria falciparum
Eti Nurwening Sholikhah, Mahardika Agus Wijayanti, Mustofa
Department of Pharmacology and Therapy, Faculty of Medicine, UGM Kontak: [email protected]
Latar Belakang
Respon terapi penderita malaria falciparum sangat beragam tergantung beberapa faktor, misalnya resistensi parasit, imunitas penderita, kualitas obat, dan farmakokinetika obat yang diberikan. Adanya polimorfisme gen yang mengkode enzim yang memetabolisme obat berperanan dalam variasi profil farmakokinetika obat yang diberikan yang berakibat pada perbedaan respon individu terhadap suatu obat. Oleh karena itu perlu diketahui polimorfisme gen yang mengkode enzim sitokrom P450 yang memetabolism obat terutama yang memetabolisme derivat artemisinin yaitu gen alel CYP2A6*4 dan CYP2A6*9 kaitannya dengan kadar obatnya. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui hubungan antara alel CYP2A6*4 dan CYP2A6*9 dengan kadar dihydroartemisinin-piperaquin pada penderita malaria falciparum. Penelitian ini juga akan mengevaluasi terapi malaria falciparum dan mengetahui resistensi terhadap dihidroartemisinin-piperakuin sehingga dapat menjadi pertimbangan dalam membuat kebijakan terapi malaria.
Metode
Pengaruh polimorfisme reseptor Fc gamma IIIA (FcJRIIIA) dan jumlah sel efektor terhadap respon kemoterapi trastuzumab pada pasien kanker payudara lokal lanjut
dan metastasis dengan HER2/NEU positif
Yolanda Dyah Kartika1, Ira Puspitwati2, Susanna Hilda Hutajulu3, Kartika Widayati3, Benny4 Issakh, Herniah Asti W5
1Departemen Farmakologi & Terapi, Fakultas Kedokteran, UGM. 2Departemen Patologi Klinik, Fakultas Kedokteran UGM-RSUP dr Sardjito. 3Departemen Penyakit Dalam, Fakultas Kedokteran UGM-RSUP dr Sardjito. 4Departemen Ilmu Bedah, RSUP dr Kariadi. 5Departemen Patologi Klinik, RSUP dr Kariadi
Kontak : [email protected]
Latar Belakang
Penderita kanker payudara di Indonesia meningkat cukup pesat. Sebanyak 20-30% dari total penderita kanker payudara mengalami overekspresi HER2/neu. Salah satu terapi untuk pasien HER2/neu positif adalah dengan memberikan humanized
monoklonal IgG1 antibodi trastuzumab. Mayoritas pasien kanker payudara yang telah metastasis merespon terapi inisial trastuzumab dengan baik, namun menjadi resisten dalam jangka waktu 1 tahun setelah pemberian terapi inisial.Mekanisme penghambatan sel kanker oleh trastuzumab adalah dengan mengaktivasi proses
Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC). Sisi fragmen konstan (Fc) dari Trastuzumab akan berikatan dengan activating Fc Reseptor sel efektor [sel
Natural Killer (NK), monosit, dan sel dendritik tipe myeloid]. Sel NK adalah tipe sel yang paling efisien dalam ADCC dan paling banyak mengekspresikan FcJRIIIa. Polimorfisme FcJRIIIa (CD16) sangat mempengaruhi afinitas IgG1 terhadap FcJR. Subjek dengan fenotip valin, memediasi proses ADCC anti HER2/neu IgG1 lebih baik daripada subjek dengan fenotip fenilalanin. Pada proses ADCC diperlukan pula jumlah sel efektor (sel NK, monosit dan sel dendritik] di sirkulasi yang seimbang. Hingga saat ini belum ada penelitian di Indonesia yang menghubungkan antara polimorfisme FcJRIIIa dan jumlah sel efektor dalam darah dengan respon terapi trastuzumab.
Metode
Penelitian ini merupakan studi kohort prospektif.Subyek penelitian adalah pasien penderita kanker HER2/neu positif stadium lokal lanjut dan metastasis. Sampel DNA diekstraksi dari sample darah tepi. Polimorfisme gen FcJRIIIa dideteksi dengan metode nested PCR-RFLP menggunakan enzim restriksi NIa III. Jumlah sel efektor dianalisa dengan flowcytometry.Respon klinik terhadap trastuzumab dinilai menggunakan Progression Free Survival.
Polimorfisme gen p53 Arg72Pro, MDM2SNP309, HER2Ile655Val, ER594 A>G, p21Ser31Arg dan FGFR2rs2981582; studi risiko kanker payudara onset dini di
Yogyakarta
Dewajani Purnomosari, Clarista Ardelia Raharjo, Alvin Santoso Kalim, Rangga Athallah Fajar, Karina Kazia Harris, Markus Yushan Nandiwardhana, Rahma Herviastuti, Sri Fatmawati, Artanto Wahyono
Departemen Histologi dan Biologi Sel. Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Gadjah Mada Kontak:[email protected].
Latar Belakang
Kanker payudara onset dini bersifat progresif dan mempunyai prognosis buruk. Apakah terdapat hubungan variasi p53Arg72Pro, MDM2SNP309, HER2Ile655Val, ER594A>G, p21Ser31Arg, FGFR2rs2981582 dengan usia penderita kanker payudara di Yogyakarta mengingat studi genetik di beberapa negara menunjukkan hasil berbeda. Metode
DNA genomik dua ratus enam penderita kanker payudara yang dirawat di RS dr. Sardjito pada tahun 2006-2012 berusia <40 tahun (kasus) dan >55 tahun (kontrol) dianalisis dengan PCR-RFLP. Analisis chi-square dilakukan untuk melihat hubungan persebaran genotip antara usia <40 tahun dan usia >55 tahun dan membandingkan dengan populasi Hapmap. Perbandingan proporsi setiap genotip dalam kelompok umur digunakan analisis z-score. Hubungan peningkatan risiko kanker payudara onset dini dianalisis menggunakan odds ratio.
Hasil
Seratus empat dan seratus enam DNA penderita kanker payudara usia <40 tahun dan >55 tahun diperiksa variasi genetiknya. Terdapat kedekatan genetik etnik penderita kanker payudara di Yogyakarta dengan etnik Han Cina yang ditunjukkan dengan kemiripan proporsi genotip pada 4 gen yang diperiksa, kecuali gen HER2 yang mirip dengan etnik Jepang dan FGFR2 yang mirip dengan etnik di Meksiko. Dari ke enam polimorfisme gen yang dianalisis, hanya polimorfisme FGFR2 rs2981582 yang menunjukkan hubungan antara variasi genotip dengan usia penderita kanker payudara, dimana pasien dengan genotip TT mempunyai risiko 2.63 kali lebih tinggi (P= 0.016, 95% CI = 1.187 – 5.839) menderita kanker payudara onset dini daripada genotip CC. Mengingat hingga saat ini baru diketahui hubungan asosiasi antara polimorfisme FGFR2 dengan usia penderita kanker payudara, maka diperlukan studi fungsional untuk mengetahui pengaruh variasi genotip terhadap fungsi protein yang dihasilkan oleh gen FGFR2.
Kesimpulan
Hubungan antara mutasi gena filaggrin dengan dermatitis atopik. Kajian mutasi gena filaggrin Tipe Asia di Suku Jawa.
Niken Trisnowati, Flandiana Yogianti, Hamim Sadewa, Hardyanto Soebono Departemen Dermatologi dan Venereologi FK UGM
Kontak: [email protected]
Latar Belakang
Tujuan penelitian untuk mengetahui hubungan mutasi gena filaggrin (FLG) dengan dermatitis atopik (DA), khususnya skrining mutasi FLG tipe Asia (3321delA, S2554X, 441delA, 1249insG, Q2417X, E2422X, 7945delA, R4307X) dan hubungan mutasi FLG
tersebut dengan parameter sawar kulit dan derajat keparahan penyakit. Metode
Penelitian dilakukan Januari 2012-Mei 2014 di RSUP Dr Sardjito. Disain penelitian kasus kontrol, jumlah sampel 160 orang. Diagnosis DA ditegakkan dengan kriteria Hanifin-Rajka, derajat keparahan dinilai dengan SCORAD (Scoring Atopic Dermatitis) obyektif. Skrining mutasi FLG menggunakan sekuensing. Ekspresi filaggrin diperiksa dengan imunohistokimia menggunakan anti-human profilaggrin monoclonal antibody. Parameter sawar kulit diperiksa dengan Tewameter dan Corneometer. Hasil
Mutasi FLG tipe Asia yang diskrining tidak didapatkan pada kelompok subyek DA dan kelompok kontrol, tetapi ditemukan 2 mutasi FLG baru yaitu 7487delC dan 7979ins3 masing-masing pada seorang subyek DA. Pemeriksaan imunohistokimia subyek dengan mutasi 7487delC menunjukkan penurunan ekspresi profilaggrin/filaggrin dibandingkan dengan kontrol normal. Terdapat perbedaan rerata TEWL yang bermakna antara DA ringan dengan DA berat (p<0,05) dan DA sedang dengan DA berat (p<0,05) serta korelasi positif sedang ( =0,41, p<0,01) antara TEWL dengan SCORAD obyektif. Terdapat perbedaan hidrasi stratum korneum yang bermakna antara DA sedang dengan DA berat (p<0,05) serta korelasi negatif lemah ( =-0,29, p<0,05) antara hidrasi stratum korneum dengan SCORAD obyektif.
Kesimpulan
Distribusi dan dinamika genotype serta analisis gen VP4, VP7, NSP2, NSP4 DAN NSP5 rotavirus penyebab diare anak balita di Indonesia
Hera Nirwati1, Tri Wibawa1, Abu Tholib Aman1, Yati Soenarto2
1
Departemen Mikrobiologi, Fakultas Kedokteran UGM
2Departemen Ilmu Kesehatan Anak, Fakultas Kedokteran UGM
Kontak: Latar Belakang
Rotavirus merupakan penyebab diare berat pada anak balita di negara maju dan negara berkembang serta banyak menyerang anak berusia 3-24 bulan. Di daerah tropis, rotavirus terjadi sepanjang musim dengan hanya ada sedikit variasi. Usaha pencegahan dengan perbaikan hygine dan sanitasi tidak banyak mengurangi morbiditasnya, sehingga penggunaan vaksin merupakan salah satu pilihan terbaik. Agar memberikan proteksi maksimal, maka sebelum penerapan vaksin perlu dilakukan penelitian untuk mengetahui beban sakit akibat rotavirus, jenis genotype rotavirus yang bersirkulasi di populasi serta karakteristik rotavirus penyebab infeksi. Oleh karena itu, penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menganalisis (1) distribusi genotype rotavirus yang beredar di Indonesia, (2) dinamika perubahan genotype rotavirus di Indonesia, (3) electropherotype rotavirus isolat Indonesia, (4) filogenetik gen VP4, VP7, NSP2, NSP4 dan NSP5 rotavirus isolat Indonesia, (5) variasi asam amino penyusun gen VP4, VP7, NSP2, NSP4, dan NSP5 rotavirus isolat Indonesia dibanding isolat negara lain yang sekuennya disimpan di GenBank , dan (6) variasi asam amino penyusun gen VP4 dan VP7 rotavirus isolat Indonesia dibanding isolat penyusun vaksin.
Metode
Penelitian ini merupakan repeated cross sectional study yang dilakukan di 7 rumah sakit di 6 kota berbeda di Indonesia. Anak balita penderita diare akut yang dirawat di rumah sakit tersebut diambil sampel feses dan data epidemiologisnya. Deteksi rotavirus dilakukan dengan enzyme immunoaasay dan deteksi genotype dengan RT-PCR. Pola migrasi RNA rotavirus diketahui dengan elektroforesis pada PAGE. Sekuensing dilakukan untuk mengetahui nukleotida penyusun gen VP4, VP7, NSP2, NSP4, dan NSP5. Analisis filogenetik dan analisis perbandingan asam amino penyusun gen dilakukan dengan menggunakan program MEGA 5.1.
Hasil
Korelasi Polimorfisme Genetik Sitokrom P450 2A6 dan 2B6 dengan Kuantitas Merokok di Kota Yogyakarta
Ratika Marchelaona1; Arta Farmawati1; Indwiani Astuti2 Departemen Biokimia FK UGM1; Farmakologi FK UGM2 Contact: [email protected]
Latar Belakang
Gen sitokrom P450 (CYP) 2A6 dan 2B6 bersifat sangat polimorfik. Enzim sitokrom yang dihasilkan terlibat utama dalam metabolisme oksidatif nikotin. Masalah utama mengenai rokok di Indonesia adalah tingginya jumlah individu perokok dan jumlah rerata konsumsi batang rokok harian individu perokok.
Metode
Penelitian ini merupakan penelitian metode observasional jenis analitis kategorik berpasangan, dengan rancangan case-control study prosedur matching terhadap subjek perokok dan nonperokok. Subjek perokok dibedakan dalam kategori perokok ringan, perokok sedang, dan perokok berat serta sudah menjadi perokok minimal selama 6 bulan. Studi ini menggunakan subjek tampak sehat suku Jawa berjumlah 94 diklasifikasikan sebagai perokok (n=47) dan nonperokok (n=47). Informasi mengenai kebiasaan merokok didapatkan melalui kuesioner. Genotyping genotip dan alel CYP2A6*1A, CYP2A6*1B, CYP2B6*1, dan CYP2B6*4 dilakukan dengan metode PCR-RFLP.
Hasil
Penelitian ini menunjukkan adanya korelasi positif bermakna tetapi lemah antara genotip CYP2A6 dengan kuantitas merokok (p=0,027), sebaliknya berkorelasi negatif tidak bermakna dan sangat lemah untuk genotip CYP2B6 (p=0,562). Analisis genotip dan alel CYP2A6 menunjukkan adanya perbedaan signifikan (p<0,05) antara subjek perokok dan nonperokok. Hal ini menjadi salah satu penjelasan atas peningkatan jumlah individu perokok dari tahun ke tahun di Indonesia. Fujieda et al. (2004) melaporkan polimorfisme genetik CYP2A6 merupakan salah satu faktor genetik yang menentukan kebiasaan merokok. Analisis genotip dan alel pada gen CYP2B6 tidak menunjukkan perbedaan bermakna (p>0,05) antara subjek perokok dan nonperokok. Hal tersebut dapat dipengaruhi oleh adanya interaksi alel polimorfik. Subjek perokok memiliki OR=2,016 untuk mendapatkan alel CYP2A6*1B dan OR=0,760 untuk mendapatkan alel CYP2B6*4 daripada subjek nonperokok.
Kesimpulan
Cytoarchitecture of the olfactory bulb in the laggard mutant mouse
Junaedy Yunus1, Tomiyoshi Setsu2, Satoshi Kikkawa2, Toshiaki Sakisaka3, and Toshio Terashima2
1Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada.2Division of Developmental Neurobiology, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Kobe, Japan.3Division of Membrane Dynamics, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Kobe, Japan
Contact: [email protected]
Background
The laggard (lag) mutant mouse, characterized by hypomyelination and cerebellar ataxia, is a spontaneously occurring mutant mouse caused by mutation in the Kif14
gene. In this mutant mouse, the laminated structures such as the cerebral and cerebellar cortices and the dentate gyrus are cytoarchitecturally abnormal.
Methods
We studied the cytoarchitecture of the lag mutant olfactory bulb on the basis of hematoxylin-eosin staining and immunohistochemistry in the mouse pups at various pre- and postnatal ages.
Results
Macroscopically, the olfactory bulb of the lag mutant mouse was smaller in size and more transparent than the normal counterpart. Hematoxylin-eosin staining revealed that the mutant olfactory bulb had normal lamination in general, but detailed analysis had demonstrated that olfactory periglomerular cells and granule cells were reduced in number. In the mutant, olfactory glomeruli were cytoarchitecturally disorganized and mitral cells were arranged in multiple cell layers instead of being arranged in a single layer. The rostral migratory stream in the mutant became gradually thinner or obliterated during early postnatal days. Some of mitral cells and periglomerular cells were multinucleated, suggesting that Kif14 mutation led to an abnormal cell division. In the mutant, TUNEL-positive cells in the subventricular zone of the lateral ventricle were increased in number, especially at perinatal age, suggesting that the decreased population of granule cells in the lag mutant mouse was caused by the increased apoptotic cell death. The olfactory input appeared to be intact, as indicated by anterograde labeling of olfactory nerves with an injection of WGA-HRP into the olfactory mucosa.
Conclusions
Prognostic Impact Of Metastatic Status In Patients With Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Susanna Hilda Hutajulu1, Guntara Khuzairi2, Camelia Herdini3, Henry Kusumo4, Mardiah Suci Hardianti1, Kartika Widayati Taroeno-Hariadi1, Ibnu Purwanto1, Johan Kurnianda1
1
Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, UGM 2Study Program of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine,UGM
3Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, UGM 4Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, UGM
Contact: [email protected]
Background
The M1 stage of TNM classification in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) does not discriminate patients based on metastatic site and number of metastatic lesions. The role of metastatic status in predicting survival has not been analyzed in the local setting. This study aimed to determine the prognostic impact of metastatic status of NPC patients.
Methods
Data of 81 metastatic NPC patients diagnosed between January 2007 and December 2011 were retrospectively reviewed. Diagnosis of metastasis was based on imaging results. Patients were grouped according to various prognostic variables, including age (<50 versus 50 years), sex, histology grading, T and N classification, the time order of metastasis (synchronous versus metachronous), and number of metastatic sites (single versus multiple). Rates of overall survival (OS) were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method. The log rank test was performed to analyze the difference between survival curves. Cox regression was used to calculate the hazard ratio (HR) and 95 % confidence interval (CI).
Results
The median OS was 24.4 months (ranged from 12.4-36.4 months). The 1 year-, 2 year-, and 3 year-survival rate were 64.4 %, 49.5 %, and 39.0 %, respectively. Involved single metastatic sites included the bone (39, 48.1 %), lung (18, 22 %), liver (11, 13.6 %) and brain (1, 1.2 %), whereas the involvement of multiple organs occurred in 12 (14.8 %) patients. In univariate analysis, patients with lung-only metastasis had favourable survival compared with other single- (HR = 0.698, 95 % CI 0.236-2.065) and multiple-distant metastases (HR = 0.195; 95 % CI0.653-0.058). T4 and N1-N3 were insignificant negative predictors for survival (HR = 1.937, 95 % CI 0.887-4.229 and HR = 3.712, 95 % CI 0.502-27.472, respectively). Interestingly, cases with metachronous lesion had worse survival than those with synchronous disease (HR = 2.312, 95 % CI 1.090-4.900). However, when tested in multivariate analysis, metastatic site was the only significant independent prognostic factor for patients’ survival (95 % CI 0.912-0.449), while metastatic time lost its prognostic influence (95 % CI 0.224-1.018).
Factors Influencing Treatment Adherence Of Nasopharyngeal Cancer And The Clinical Outcomes: A Hospital-Based Study
Mardiah Suci Hardianti1, Sindhu Wisesa2, Kartika Widayati Taroeno-Harijadi1, Ibnu Purwanto1, Bambang Hariwiyanto3, Wigati Dhamiyati4, Johan Kurnianda1
1Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine,
Faculty of Medicine UGM; 2Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Jenderal Soedirman University; 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, UGM; 4Division of Radiotherapy, Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, UGM Contact: [email protected]
Background
Adherence to treatment regimens offers both a better survival rate and lower recurrence in nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC) patients. Various factors influencing the adherence to long term therapy include socio economic and medical factors. Understanding those factors is essential to improve the patients’ outcome. This study aims to define factors influencing adherence of NPC patients to their treatment regimens and the correlations between those factors and clinical outcomes.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study was conducted in Dr. Sardjito Hospital based on medical record from 2007-2011. Factors examined were socio-demography, baseline characteristics, and survival. Adherence was defined as completion of the entire course of therapy and clinical follow-up. Data were described and analyzed with Kruskall-Wallis analysis. Kaplan-Maier survival analysis was done to observe its clinical outcome.
Results
Differential expression of microRNA-21 on nasopharyngeal carcinoma plasma patient
SY Bintoro1,R Oktriani1, C Herawati2, A Surono3, Sofia M Haryana1
1Department of Molecular Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada,
Yogyakarta, Indonesia; 2Depatment of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Dharmais Cancer Hospital, Jakarta, Indonesia; 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada/Dr Sardjito Hospital, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Contact: [email protected]
Background
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a common malignancy of the head and neck in South-East Asia, including Indonesia. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) has been considered as the most active miRNA and play important role in several cancers, including NPC. In this research, we analyzed the expression of miR-21 on NPC patients and compared it to healthy people. We also determined its correlation to the stage of NPC.
Methods
A total of 63 samples from 53 NPC patients and 10 healthy controls were used in this study. In the patient group, there were seven individuals with early stage and 46 with advanced stage. Total RNA were isolated from plasma, cDNA was synthesized, and quantified by means of qPCR.
Results
Case report on pediatric nasopharyngeal carcinoma at Dr. Sardjito Hospital, Yogyakarta
Camelia Herdini1, Sagung Rai Indrasari1, Jajah Fachiroh2,3, Dwi Hartati3, T Baning Rahayudjati4
1Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine,
Universitas Gadjah Mada/Dr Sardjito General Hospital;2Department of Histology and Cell Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada; 3Molecular Biology Laboratory, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada; 4Department of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada
Contact: [email protected]
Background
NPC is rare, accounting for only 1-3 % of all pediatric malignancies. Its incidence varies widely in different regions, reflecting interactions between genetic and environmental factors.To describe clinical characteristic and environmental exposures of two pediatric NPC cases.
Methods Case report. Results
We reported two cases from Dr. Sardjito Hospital Yogyakarta, Indonesia recruited in 2014. A 10-year-old boy and a 12-year-old girl have already visited general practitioners several times with flu-like complaints. After several unsuccessful attempts at medication, visible lumps in the neck then appeared and they were referred to Dr. Sardjito Hospital. Flexible nasal endoscopy for both patients showed soft tissue masses in the nasopharynx. Histopathology examination revealed undifferentiated carcinoma. The stages were T3N3aM0 and T3N2M0. From the questionnaire given to the parents, it was shown that both patients had high consumption of instant noodles, grilled food, preserved meat, and soy sauce. Additionally, on a daily basis, the boy was exposed to burning firewood and was a passive smoker, while the girl was exposed to wood dust and the use of insecticide spray at home on a daily basis. IgA-EBV ELISA showed that results of both childrens’ parents and the boy were below cut off (< 0.41), but not the girl (0.84).
Conclusion
Results of Treatment With Neoadjuvant Cisplatin-5fu In Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Local Experience
Diah Ari Safitri1, Susanna Hilda Hutajulu1, Camelia Herdini2, Sri Retna Dwi Danarti3, Ibnu Purwanto1, Kartika Widayati Taroeno-Hariadi1, Johan Kurnianda1
1Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine,
Faculty of Medicine, UGM;2Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, UGM; 3Division of Radiotherapy, Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, UGM Contact: [email protected]
Background
The significance of the problem of radiotherapy waiting lists in local patients has been documented. Delays in initiating radiation treatment may result in poorer treatment outcomes. Even though neoadjuvant chemotherapy had not been considered a standard approach for locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), it may be given while waiting for the radiotherapy schedule. The platinum-based chemotherapy combined with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) was the most frequently used for NPC. Data on NPC patients receiving neoadjuvant cisplatin 5-FU chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy at our cancer clinic had not been comprehensively analyzed. To analyze the survival rate of NPC patients who received neoadjuvant cisplatin-5-FU chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy.
Methods
An observational study was conducted on data of NPC patients diagnosed at Dr Sardjito Hospital Yogyakarta between January 2007 and December 2011. Patients with stage IIB-IVB disease who received cisplatin IV infusion 100 mg/m2 on day 1 and 5-FU IV infusion 1000 mg/m2/24 hours on days 1 to 4, or 1 to 5 as neoadjuvant therapy were analyzed.
Results
Fourty-three (n = 43) stage IIB-IVB NPC were analyzed. The age of subjects ranged from 17 to 76 years (median 48 years), with male predominant (67.40 %). Stage III, IVA, and IVB were 17 (39.54 %), 6 (13.95 %) and 20 (46.51 %) subjects, respecively. WHO type III was predominant (95.35 % cases). The radiation dose ranged from 18 to 70 Gy (median 66 Gy). A total of 37 (86.05 %) subjects received 3 cycles of cisplatin-5FU, while 4 (9.31 %) received 4-6 cycles and 2 (4.64 %) received 1 cycle only. The median survival was 34.63 months. The 3 year- and 5 year-survival rates were 45.30 % and 37.80 %, respectively. The median follow up period was 23.27 months. When compared, stage III and IV subjects had similar median survival (36.50 months versus 33.93 months, p = 0.295).
Geriatrics with Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Suryo A. Taroeno1, Sindhu Wisesa2, Kartika Widayati Taroeno-Hariadi1, Ibnu Purwanto1, Bambang Hariwiyanto3, Wigati Dhamiyati4, Johan Kurnianda1
1Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine,
Faculty of Medicine, UGM;2Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Jenderal Soedirman University; 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, UGM; 4Division of Radiotherapy, Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, UGM
Contact: [email protected]
Background
Aging patients with cancer commonly pose special problems. As a special population of cancer patients, they may have specific clinical features and treatment outcomes. Aims to explore the database of nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC) geriatric patients in the local centre, regarding the specific clinical features and the treatment outcomes. Methods
Retrospective analysis was done on data of NPC patients diagnosed between 2007-2011 at Dr Sardjito Hospital, Yogyakarta Indonesia (organ-specific cancer registry). Geriatric patients were defined as cases of 60 years old at first visits. The effect of age and treatment on patients’ survival were analyzed.
Results
The Expression of miR-141 in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Widyandani Sasikirana1, Tirta Wardana1, Muhammad Radifar1, Cita Herawati2, Agus Surono3, Sofia Mubarika Haryana4
1
Department of Biotechnology, UGM; 2Dharmais National Cancer Hospital, Jakarta, Indonesia; 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, UGM;2Department of Histology and Cell Biology, Faculty of Medicine, UGM Contact: [email protected]
Background
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is the fourth highest malignancy in Indonesia. MicroRNA is a potential biomarker for NPC early diagnosis. Previous studies indicated that miR-141 was oncomir, that target PTEN mRNA. Both acted on cisplatin resistance. Aims to determine the expression profile of miR-141 and mRNA PTEN in blood plasma of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients compared to healthy controls. Additionally, we wanted to determine the expression profile of miR-141 and PTEN mRNA in NPC patient prior and post theraphy.
Methods
The study was conducted by in silico prediction to analyze the interaction of miR-141 with PTEN mRNA. Further laboratory research analyzed the expression level of miR-141 and PTEN mRNA compared to healthy controls. Expression analysis was performed using qRT-PCR with miR-16 and beta-actin as reference genes. The analysis of the relationship between miR-141 and PTEN mRNA was done through the chi square test.
Results
B. Gaya hidup yang mempengaruhi kesehatan
1. The Role of Lesser Yam (Discorea Esculenta) Based Cookies on Fasting Glucagon Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1), Appetite and Lipid Profile in
Overweight/Obese Adults
2. Leptin, Metabolic Indices, Appetite and Weight Rebound in Obese Individuals Undertook Weight Loss Program Using A Low Calorie Diet with/without Exercise
3. Gambaran Perilaku Merokok Setelah Kebijakan Peringatan Bergambar Pada Kemasan Rokok
4. Peningkatan Risiko Penyakit Kardiovaskular Pada Laki-Laki Dewasa Perokok Di Kota Yogyakarta
5. Tobacco Smoking, Chronic Reactive Protein (CRP), TNF , and risk of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
6. Sexual network of young MSM in Jogjakarta, Indonesia
7. Describing sexual histories of young HIV seropositive MSMs and MSMs with unknown serostatus in Jogjakarta, Indonesia
8. Rasio Ldl/Hdl-Kolesterol, Total/Hdl-Kolesterol, Dan High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Pada Laki-Laki Dewasa Perokok Dan Non-Perokok Di Kota Yogyakarta