i
DESIGNING A SET OF INSTRUCTIONAL
SPEAKING MATERIALS FOR D’COKRO HOTEL
AND HOMESTAY STAFF
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain theSarjana PendidikanDegree
in English Language Education
By
Y. Bambang. S. T Student Number: 05 1214 061
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE ARTS AND EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
vi ABSTRACT
Triyono, Yoseph Bambang Sulistyanto. 2010. Designing a Set of Instructional Speaking Material for D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay Staff. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program. Sanata Dharma University.
English mastery is a must for the hotel staff. Nowadays, many foreigners come to visit Yogyakarta and lack of English mastery will dispromote the hotel. This study is attempted to design a set of speaking material that will help hotel staff to learn English.
This research was conducted to design a set of instructional speaking materials for hotel staff. There were two problems in this research. The first is how a set of instructional speaking material for hotel staff is designed. The second is what a set of instructional speaking materials for hotel staff looks like.
To answer the research questions, the researcher applied R&D cycle (Research and development method). There were seven steps applied by the researcher. The first step was conducting need survey. The second step was deciding goals, topics and general purposes. The third step was deciding learning objectives. The fourth step was selecting syllabus type. The fifth step was deciding subject content. The sixth step was selecting activities and developing materials. And the last step was evaluation and revision.
To develop the designed materials, the researcher distributed questionnaires to 12 D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay staff and also interviewed the manager of D’Cokro hotel and Homestay staff. These were done to get the need survey and to design the materials. After the materials designed, the researcher distributed questionnaires to 4 respondents (two lecturers from Sanata Dharma University, one English instructor from ELTI and one Junior High School teacher) to obtain opinions, suggestions and comments towards the designed materials. The data from the respondents then being analyzed. The result showed mean 3,75 from the total points 4, and this means that the designed material was acceptable.
To answer the second question, the researcher presented the final version of the designed materials. This final version is presented after some revisions from opinions, suggestions and comments from the respondents. There are eight units in this designed material. They are “How do you do?”, “Good morning, I want to reserve a room…”, “Would you help me?”, “Do you need some help?”, “He has…”, “What is this?”, “How do you get to…”, “I think there is something wrong with the food…”. There are five sections in each unit,Getting started,Try this out!,Check this out!,Play the gameandShare it out. Since hotel staff have very limited time to study formally in classroom, the examples of conversations was recordeed in video so that the students can practice it at home.
vii
ABSTRAK
Triyono, Yoseph Bambang Sulistyanto. 2010. Designing a Set of Instructional Speaking Material for D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay Staff. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Penguasaan bahasa Inggris adalah sebuah keharusan bagi staf hotel. Oleh sebab itu, penelitian ini dimaksudkan untuk merancang seperangkat materi speaking yang akan memudahkan para staf hotel untuk mempelajari Bahasa Inggris.
Penelitian ini dilaksanakan untuk merancang seperangkat materi speaking untuk staf hotel. Ada dua permasalahan yang ingin dijawab melalui penelitian ini, yang pertama adalah bagaimana merancang seperangkat materi speaking untuk staf hotel. Sedangkan yang kedua adalah bagaimana bentuk dari seperangkat materi speaking untuk staf hotel?
Untuk menjawab kedua pertanyaan diatas, peneliti menerapkan langkah-langkah dalam R&D (Research and Development). Dalam penelitian ini peneliti menerapkan tujuh langkah. Langkah yang pertama adalah melakukan survey kebutuhan. Langkah kedua adalah menentukan tujuan, topik dan tujuan umum. Langkah ketiga adalah menentukan tujuan khusus. Langkah keempat adalah menentukan jenis silabus. Langkah kelima adalah menentukan subject content. Langkah keenam adalah menentukan aktivitas dan mengembangkan materi. Langkah terakhir adalah mengevaluasi dan merevisi.
Dalam rangka mengembangkan rancangan materi, peneliti membagikan kuisoner kepada 12 staf hotel D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay dan juga mewawancarai manager D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay. Hal ini dilakukan untuk mengetahui kebutuhan dan untuk merancang materi. Setelah materi dirancang, peneliti kemudian membagikan kuisoner kepada 4 responden (dua orang dosen Universitas Sanata Dharma, seorang pengajar di ELTI dan seorang guru Sekolah Menengah Pertama) dan meminta mereka untuk memberikan pendapat, masukan dan komentar terhadap rancangan materi. Data dari para responden kemudian dianalisa. Hasilnya menunjukkan mean sebesar 3,75 dari total 4 poin dan ini menunjukkan bahwa rancangan materi ini diterima oleh para responden.
viii
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to give my biggest and deepest gratitude for the Almighty God in Jesus Christ. Because of His blessing I can finally finish this thesis. I will always belong to Jesus and I will always believe that everything will be beautiful in His time. I would also like to give my gratitude to Caecilia Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd. who patiently has helped me finish my thesis. I would also to give my appreciation to Fauzi Ardian and D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay, Agustinus Hardi Prasetyo, S.Pd., M.A., Chrisoggonus Sidda Maillilang, S.Pd., Nicholaus Eling Lukman Wijaya, and Josephine Sri Purwaningsih, S.Pd. who helped me in designing and evaluating the designed material.
My best gratitude also to my beloved father Yoseph Triyono and my beloved mother Maria Magdalena Alina Rosni who always support me in every condition, give me never ending prayers, love, affection, motivation and sacrifice everything to make S.Pd. finally attached to my name.
I would also thank my dearest Pipit Ardiani Adhi Atmaja S.Farm., Apt. with whom I share the love, joy, happiness, sadness and failure, and for always being my motivator when I am hopeless, my direction when I am lost, my shoulder to cry on when I fail.
x
Ignatius Soewardjo who have been waiting patiently for me to finish “the job” and let me be their future member of the family.
I would also thank my “Mawoet gank” (Iwan, Indra, Aan), “Arimbi 2 gank (Singgih, Apin, mas Yanto, Hiroshi) for the friendship and the laughter we shared together, may the friendship be eternal no matter what happen.
Last but not least I would like to thank Intifo crew, the actors and actress (Iwan, Bangkit, Indra, Eddi, Dida, Lusi) for the video (nice results guys!), HAWKEYE ENGLISH COURSE family,ibuSoewarno, JAGIK family, PPL SMAN 1 (Ella, Mega, Dea, Nita, Dida), my 1997 Honda Grand AA 5423 EK, my guitar, Juventus, Italy, Del Piero, Buffon, pito, and everyone who have made me as I am now. May God be with us now and forever.
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE………. i
PAGES OF APPROVAL………... ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY………..….. iv
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI…………..….……..… v
ABSTRACT……….. vi
ABSTRAK………..… vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS……...……….….. ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS………... xi
LIST OF FIGURES………. . xv
LIST OF TABLES……… xvi
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Research Background………... 1
B. Problem Formulation……… 4
C. Problem Limitation………... 4
D. Research Objectives……….. 5
E. Research Benefits……….. 5
xii
CHAPTER II: REVIEW ON RELATED LITERATURE
A. Review On Related Theories……...……….. 8
1. Model of Instructional Design……… 8
a. Kemp’s Model………. 8
b. Yalden’s Model……….. 11
2. Communicative Language Teaching………. 14
3. Task Based Language Teaching……… 17
4. Syllabus………. 19
B. Theoretical Framework………. 21
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY A. Research Method…….……… 24
1. Conducting Research and Information Collecting……….. 25
2. Planning……… 25
3. Developing Preliminary Form of Product....……… 26
4. Conducting Preliminary Field Test……….. 26
5. Conducting Main Revisions………. 26
B. Research Participants……… 27
C. Research Instruments……… 28
D. Data Gathering Technique..……….. 30
E. Data Analysis Technique……….. 31
xiii
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
A. Research Results…….………. 35
1. Conducting Research and Information Collecting……… 35
2. Planning……… 37
3. Developing Preliminary Form of Product....………... 39
4. Conducting Preliminary Field Test………... 43
5. Conducting Main Revisions……….... 46
B. Discussions……….. 47
C. Presentation of the Instructional Material Design………...…….. 48
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS A. Conclusions….……….. 51
B. Suggestions....……… 52
REFERENCES…..…..……….. 54
APPENDICES……….. 55
Appendix A: Letter of Permission………....56
Appendix B:Transkrip wawancara………....58
Appendix C:Kuisioner untuk Karyawan Hotel……….61
Appendix D: Lesson Plan……….64
xiv
xv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2.1 Kemp’s Model of Instructional Development………11 Figure 2.2 Yalden’s Model……….14 Figure 2.3 Dave and Willis TBT Framework……….17 Figure 2.4 Adapted Procedures on Designing
A Set of Instructional Speaking Materials for Hotel Staff……..23 Figure 3.1 the Relation between R&D and
xvi
LIST OF TABLES
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the writer would like to present the background of the study, problem formulation, problem limitation, research objectives, the benefits of the study, and the definition of terms.
A. Research Background
Nowadays, people are accustomed to English. English is not only a supplementary subject, but has become a major subject, even in elementary school. This phenomena is not strange because English now has become an international language and everybody should master it. It means that English not only deals with general use, but also for specific needs. Hutchinson and Waters (1987) state that “as English becomes the accepted international language of technology and commerce, it creates a new generation of learners who wants to study English specifically based on their needs of learning English.” This new generation of English learners is the person who has no need of learning general English, but they only need specific English. This new generation of English learners realizes that they need English as their ability to help them in their job. One of the fields which need specific English is tourism.
Yogyakarta is one of the tourist destinations in Indonesia. Many foreigners spend their time in Indonesia to study, have holiday or even conduct cultural research. Foreigners have their own reasons to be in Yogyakarta, but they will always need a place to stay. Hotel is a common place for the foreigners to stay while they are in Yogyakarta.
Because of this reason, it will be very important for hotel staff to master English conversation. English will not be matters for five stars hotel but for three stars hotel it will be matter because many of the staff hotel know English very little. In order to understand English well, the hotel staff need to learn specific English that will only give them examples of common conversation in hotel situation. For the reason above, the writer needs to analyze the needs of English in order to provide English speaking materials for staff hotel.
skill. Sometimes the staff knew what the guest asked them, but they did not know how to reply it. But mostly, they did not know what the guest asked them. This would be a major obstacle for the staff because they could not give the best service to the foreign guest.
The situation mentioned previously makes the foreign guests unsatisfied and this could dispromote the hotel. In order to minimize the situation, the hotel staff needs to improve their English, especially their speaking ability. Considering the situation, the writer conducted a study in designing a set of Instructional speaking materials for Hotel staff.
In designing a set of Instructional Speaking material for hotel staff, the writer applied an approach called English for Specific Purposes (ESP). The writer decided to use the approach because the situation was the same as what Hutchinson and Waters (1994:19) proposed that is “English for Specific Purpose is an approach to language teaching in which all decisions, as to content and method, are based on the learners’ reason for learning.” The writer also apply Task based language teaching to accomodate the learning materials.
From the fact in the last paragraph of page 2, it is clear that Hotel staff really need to master English language. There were two problems that can be identified from the situation.
hospitality, front officer, etc. This is why they have different abilities to speak in English. The front officers, who have to face the guest, are better in speaking, but the rest of the staff is difficult to communicate in English.
The second problem that occurs is the difficulties to find the time to learn English. Hotel staff are busy with their responsibility, so it will be difficult for them have time to learn English formally. So, what they need is an instructional speaking material to help them practice anytime and anywhere. In order to make the hotel staff easier in the learning process, the writer offers a new way in learning English through video. The staff are asked to watch a certain video that illustrates daily situation in hotel which deals with foreigners. The purpose is to give the staff example of English conversation and situation that would help the staff easier in the learning. Video is chosen because it is very useful and enjoyable.
B. Problem Formulation
In this study, the two problems are formulated as follows:
1. How a set of Instructional Speaking Materials for Hotel Staff is designed? 2. What the designed set of materials looks like?
C. Problem Limitation
D. Research Objectives
There are two objectives of this study:
1. to describe the process of designing a set of Instructional speaking materials for Hotel Staff,
2. to present a set of Instructional speaking materials for Hotel staff.
E. The Benefits of the Study
This study may contribute some benefits for the teaching learning process. It is expected to give benefits to:
1. D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay staff
The result of this study may function as a source of learning for D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay Staff to develop their speaking ability and help them to become better in serving their guest, especially foreigners.
2. English Teachers and instructors
The result of this study may help the English teachers or instructor as the source of learning.
F. Definition of Terms
1. Designing
According to Hutchinson and Waters (1994) designing is “creating a new set of materials that fit the learning objectives and specific subject area of particular learners.” In this study, the materials are designed to be fit to three stars Hotel staff.
2. Instructional Materials
“Instructional materials are materials planned by the teacher for instruction” (Dick and Reiser, 1989:3). In this study, the instructional materials are designed by the designer to help the teacher or instructor focus on the learning objectives.
3. Speaking
Widdowson (1979: 58) says that “speaking is a kind of active and productive interaction that makes us use aural mediums”. Aural mediums are mouth, lips, tongue, and the other oral cavities. Widdowson also emphasizes face-to-face interaction including dialogue or other forms of verbal exchange as an act of communication. If people use non-verbal language in face-to-face interaction, then it is not speaking. In this study, speaking refers to active interaction using aural mediums.
4. D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay
D'Cokro Hotel is a boutique hotel which is located in the Yogyakarta downtown. It is located in Jl. Taman Siswa 56 Yogyakarta 51151.
Yudhistira Rooms, and 2 Kresna Rooms. Every room is facilitated with AC, Satellite TV, and IDD Phone, and in certain rooms. There are also comfortable balconies and terrace. In certain rooms there is also a lobby lounge that can be used to relax with the family or to serve business colleagues.
5. D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay Staff
CHAPTER II
REVIEW ON RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter deals with some theories that become the basis for the discussion. The purpose of this chapter is to obtain the understanding of what the basic principles of the study are, so that the problems stated in the previous chapter can be answered.
In this chapter, there are two major points are discussed. First, the review of related theories that discusses the relevant theories underlying the study. Second is theoretical framework that focuses on the steps in developing a set of English listening materials.
A. Review on Related Theories
1. Models of Instructional Design
In this study, there are two models of instructional design which are presented. The first is Kemp’s model and the second is Yalden’s model.
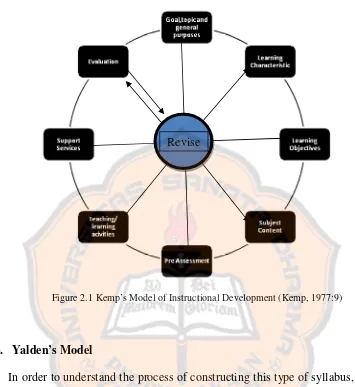
a. Kemp’s Model
The first model of the instructional materials design is proposed by Kemp. Kemp offers a flexible model. This is the strength of Kemp’s model. It lies on the existence of the concept that design and development process may start from any step and then move back and forth to the other steps whenever the designer is ready.
There are three important questions which are needed in instructional design as stated by Kemp (1977: 68), namely:
1. What must be learned? (the objectives)
2. What procedures and resources will work best to reach the desired learning levels? (activities and resources)
3. How will we know the required learning has taken place? (evaluation)
The designer should consider those three elements as the basic of creating an instructional design. If one of them is missed, then the designer fails to make a good design. In Kemp’s model (1977), there are eight interdependent elements that must be considered in designing instructional materials:
1. Determining the Goals, Topics, and General Purposes for Teaching Each Topic In determining the instructional design, a designer should decide the goals of the system, select the topic to be taught, and then specify the general purposes of each topic. The selection of each topic should consider the items from the simple to complex level, the correlation with subject content, and the students’ characteristics. The general purposes are derived from the topics and explicitly express students’ expectation and teachers’ accomplishment.
2. Mentioning the Learners’ Characteristics
3. Specifying the Learning Objectives
The designer determines the learning objectives in order to achieve certain students’ performances. The objectives should be measurable and ambiguous so that the students are able to do the objectives.
4. Listing the Subject Content
The designer lists the subject content such as selecting and organizing the specific knowledge and skill to support each objective.
5. Developing Pre-Assessment
The aim of developing pre-assessment is to determine the learners’ background and to present level of knowledge about topic. The pre-assessment may be done in the form of a formal test and questionnaires.
6. Selecting the Teaching/ learning Activities and Instructional Resources
The designer selects the teaching or learning activities and instructional resources that will treat to the subject content, so learners will accomplish the objectives.
7. Coordinating Support Services
The support services include budget, personnel, facilities, equipment, and schedules to carry out the instructional plan. If one of the elements is missed, it will affect the other elements. This shows that those elements have to be prepared to prevent any possible constraints in designing the plan.
8. Evaluating the Students’ Learning
Figure 2.1 Kemp’s Model of Instructional Development (Kemp, 1977:9)
b. Yalden’s Model
In order to understand the process of constructing this type of syllabus, the writer should examine the overall process of planning a second language program. Yalden stages of instructional plan can be divided into seven stages.
1. Need Survey
Yalden (1987 :101) gives a brief description that relates to the needs survey. When a needs survey is being undertaken, there is potentially a great deal of information to be gathered. The information includes communication, requirements, personal needs and motivation, and relevant characteristic of learners as well as those of their
“partners of learning.” The reason of this information gathering is to understand as much information about the learner as possible prior of the beginning of the program. in order to establish realistic and acceptable objectives (Yalden, 1987 : 101). The needs survey can be applied in “survival course”. It can be given to individuals who need a basic command of the language of immediate, everyday requirements. The teacher may make decision on behalf of the learners concerning what interests are general enough for them all, or in which situation the learners will have to survive (Yalden, 1987: 92).
2. Description of purpose
After the information of needs survey is collected, the next step is to get expected and specific purpose of the learners. By identifying the purpose of their needs, a writer could form the appropriate language content from simplest case to the wider scope. Robinson (1980) divides general purposes into two kinds of purposes namely educational and occupational purposes (Yalden, 1987:107). Understanding the learners’ purpose will guide the teacher to design the instructional materials that is suitable for the learners’ field.
3. Selection or development of syllabus type
and structural-functional syllabus that involves combination between grammar and skill development (Yalden, 1987 :108).
4. Production of a proto syllabus
In the communicative syllabus type, there would be a lot of elements to be considered. Those elements are general notions and specific topics, communicate functions, discourse and rhetorical skills, variety of language, role sets and communicative events as well as grammar and lexis. The work which involved in selecting and combining items in each category is somewhat complicated. It is suggested for the teacher to start mapping up the syllabus content which is usually inventing a list of topics or functions (Yalden, 1987:139). The result of mapping up will serve as the guidelines for the teacher in preparing and compiling the syllabus for the learners easier.
5. Production of a pedagogical syllabus
The pedagogical syllabus provides a repertoire of words and phrases which were chosen as exponent of function and suitable to the topics identified as important to the learners (Yalden, 1987:144). Such syllabus combines the knowledge and appropriate content and teaching techniques, the learners’ actual purposes and needs in the classroom.
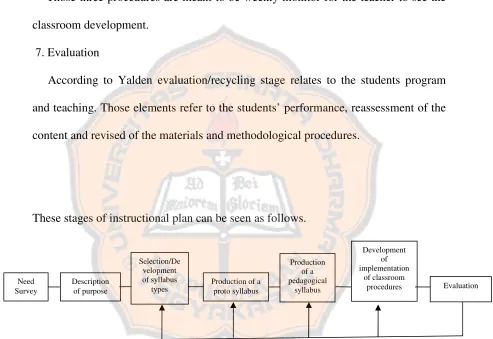
6. Development and implementation of classroom procedures
a. Selection of exercise types and teaching techniques b. Preparing of lesson plans
c. Preparation of weekly schedules.
Those three procedures are meant to be weekly monitor for the teacher to see the classroom development.
7. Evaluation
According to Yalden evaluation/recycling stage relates to the students program and teaching. Those elements refer to the students’ performance, reassessment of the content and revised of the materials and methodological procedures.
These stages of instructional plan can be seen as follows.
Figure 2.2 The Yalden’s Model (Yalden, 1987:88)
2. COMMUNICATIVE LANGUAGE TEACHING (CLT)
A communicative approach is an approach that is based on the view that language is “a vehicle for the expression of functional meaning, it is emphasizes the semantics Need
types Production of aproto syllabus
and communicative dimension rather than merely grammatical characteristics of language.” (Richard and Rodgers, 1986: 17)
Communicative approach aims to make communicative competence the goal of language teaching and develop procedures for teaching the four language skills that acknowledge the interdependence of language and communication (Richard and Rodgers, 1986: 66). Littlewood (1981 : 1) as cited in Richard and Rodgers (1986 : 66) states that “One of the most characteristic features of communicative approach is that it pays systematic attention to functional as well as structural aspect of language.” It means that language teaching should include not only elements of grammar, but also elements of communicative function.
a. The Role of the Learner
Breen and Candlin (1980 : 77) as quoted by Richard and Rodgers (1986 : 77) describe the learners’ role in communicative Language Teaching are as negotiators between the self, the learning process and the learning objectives. The implication of the learners is that they should contribute as much as they gain, and thereby learn in an interdependent way. To promote successful communication, the learner should have an active, negotiative role, and contribute as well as receive as much as possible.
b. The Role of the Teacher
role and arose from it. This role implies a set of secondary roles for the teacher; as an organizer of resources and a guide within the classroom procedures and activities (Richard and Rodgers, 1986 : 77-78)
c. The Role of Instructional Materials
The instructional materials should help the learners in achieving the objectives of the program. The materials should encourage the learners to be creative and inventive. Materials have the primary roles in promoting communicative language use. There are three kind of materials considered in communicative language teaching according to Richard and Rodgers (1986 : 79), namely:
1. Text-based Materials
Text-based Materials are materials that based on the text. The examples of these materials are pictures, visual cues and sentence fragment. These materials help the teacher to initiate conversation. Other examples that employ pair work such as role play and discussion based on texts promote the process of learners’ language learning.
2. Task-based Material
3. Realia
Realia is authentic materials taken from the real life. The realia might include language-based realia such as signs, magazines, advertisements, newspapers, graphics and tables. It is also suggested that the teacher use visual sources around which communicative activities can be built such as maps, pictures, graphs, charts, and symbols.
3. TASK BASED LANGUAGE LEARNING
Task-based language learning (TBLL), also known as task-based language teaching (TBLT) or task-based instruction (TBI) focuses on the use of authentic language and on asking students to do meaningful tasks using the target language (Dave and Jane Willis, 2007). Example of the tasks include visiting a doctor, conducting an interview, or calling customer service for help. Assessment is primarily based on task outcome rather than on accuracy of language forms. This makes TBLL especially popular for developing target language fluency and student confidence.
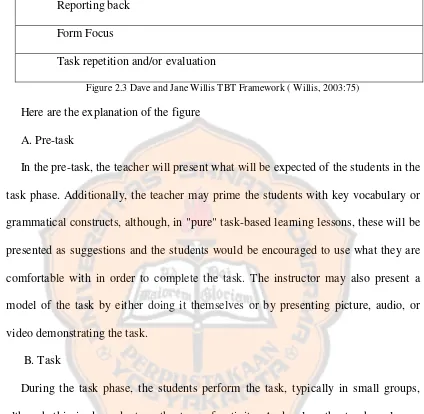
There may be several effective frameworks for creating a task-based learning lesson according to Dave and Jane Willis (2007). They can be seen as follows:
Pre-task priming activities/ mini-task Task
Reporting back Form Focus
Task repetition and/or evaluation
Figure 2.3 Dave and Jane Willis TBT Framework ( Willis, 2003:75) Here are the explanation of the figure
A. Pre-task
In the pre-task, the teacher will present what will be expected of the students in the task phase. Additionally, the teacher may prime the students with key vocabulary or grammatical constructs, although, in "pure" task-based learning lessons, these will be presented as suggestions and the students would be encouraged to use what they are comfortable with in order to complete the task. The instructor may also present a model of the task by either doing it themselves or by presenting picture, audio, or video demonstrating the task.
B. Task
C. Planning
Having completed the task, the students prepare either a written or oral report to present to the class. The instructor takes questions and otherwise simply monitors the students.
D. Report
The students then present this information to the rest of the class. Here the teacher may provide written or oral feedback, as appropriate, and the students observing may do the same.
E. Analysis (Form Focus)
Here the focus returns to the teacher who reviews what happened in the task, in regards to language. It may include language forms that the students were using, problems that students had, and perhaps forms that need to be covered more or were not used enough.
F. Task repetition/evaluation
This stage stage may be used to cover material mentioned by the teacher in the analysis stage. It is an opportunity for the teacher to emphasize key language.
4. SYLLABUS
guideline for teaching content (Robinson, 1991 : 34). Besides, a syllabus the teacher ideas of what the course will be and to what direction it should be brought and done.
There are three types of syllabus stated by Robinson (1991 : 35): 1. Content-based syllabus
Content-based syllabus has a purpose to teach some content using the language that the learners are also learning. This syllabus consists of:
a. Structure syllabus, consisting of an ordered set of language items graded by supposing difficulty of learning.
b. Notional or functional syllabus, syllabus in which the content of the language teaching is a collection of functions that are performed when language is used.
c. Situational and contextual focus syllabus, syllabus in which situation become the basis of activities.
d. Topic or informational syllabus is syllabus which consists of some topics relevant to the learners or the learners’ content of work.
2. Skill-based syllabus
It is syllabus in which the content of the language teaching was a collection of specific abilities that may play a part in using language. There are two kind of skill-based syllabus:
b. Based on the learning skills. It is looking at the constituents of the language skills that are sub-skills and micro skills.
3. Method-Based syllabus
Method-based syllabus is divided into sub categories as clarified below: a. Process syllabus. This syllabus refers to produce or method of language
learning.
b. Task syllabus. This type of syllabus consists of a set of task which is ordered according to cognitive difficulty.
Since the writer use Task-Based language learning as the approach and the subject is to perform English for Specific Purposes, so the writer choose content based syllabus or functional/notional syllabus in specific because it is fit with Task-Based language learning and accomodate the writer’s material design.
B. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
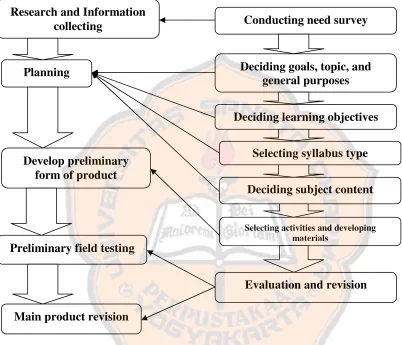
In designing a set of instructional speaking materials for Hotel staff, the writer combined materials designed by Kemp and Yalden. They are combined because the writer feels that some steps in both model are unneccesary for the writer’s model. So, the framework of designed model consist of seven steps, they are:
1. Conducting need survey (Taken from 1ststep of Yalden’s model)
requirements, personal needs and motivation, and relevant characteristic of learners.
2. Deciding goals, topic and general purposes (Taken from 1st step of Kemp’s model)
In determining the instructional design, the writer decide the goals of the system, select the topic to be taught and specify the general purpose of each topic.
3. Deciding learning objectives (Taken from 3rdstep of Kemp’s model)
The writer determines the learning objectives in order to achieve certain students’ performances. The objectives should be measurable an ambigous so that the students are able to do the objectives.
4. Selecting syllabus type (Taken from 3rdstep of Yalden’s model)
The writer choose a syllabus that will able to help in achieving the goals and purposes. In this model the writer choose functional/notional syllabus (Robinson 1991:35). It is chosen because in this syllabus, the content of language teaching is a collection of functions that are performed when language is used. So, it will be beneficial for the staff because they only learn what they need to.
5. Listing the subject content (Taken from 4thstep from Kemp’s model)
6. Selecting activities (Taken from 6thsteps of Kemp’s Model)
The writer selects the teaching learning activities and develop the materials using CLT as the principles. The activities are involving the learners, the teacher and the materials. The learner should be active, negotiative and contribute as well as receive as much as possible. The teacher is participated in learning as the facilitator and as interdependent participant in group learning. The media is to help the learners in achieving the objectives.
7. Evaluation (Taken from 7thstep of Yalden’s model)
The writer evaluate the whole material with help from some experienced participants and revise it for the better and effective material.
The theoretical framework of this design model can be seen in Figure 2.3.
Figure 2.3 Adapted procedures on designing a set of Instructional
Figure 2.4 Adapted procedures on designing a set of instructional speaking materials
for D’Cokro Hotel and Homestat Staff Conducting need survey
Deciding goals, topics, and general purposes
Deciding subject content Deciding learning objectives
Selecting syllabus type
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
In this chapter, the writer would like to present the clarified methodology of this study. This chapter discusses the research method, the participants of this study, the research instruments, gathering data techniques, data analysis techniques, and the procedure of the research.
A. Research Method
In this part, the writer explains the method of the study. The method employed in this research is Research and Development. “Educational Research and Development is a process used to develop and validate educational products, it is known as Research and Development cycle” (Borg, 196:772).
The first step in R & D is research and information collecting, which includes the literature review, classroom observation, and preparation of report of state of the art. The second step in R & D is the planning. The third step of R & D is developing preliminary form of product. The next steps are preliminary field testing, and the last one is main product revision.
Some steps in educational research and development (R&D) theory were as follows:
1. Conducting research and information collecting
According to R & D (Borg and Gal, 1983: 775), “this step included review of literature, classroom observations, and preparation of report of state of the art.” In this step, the researcher collected information for two things as the following:
a. The theories
The first was information about the theories related to this research or review of literature. The researcher gathered the information related to this research by doing library study. It was done to find theories and any information related to speaking, the teaching of speaking and material development.
b. The learners
The second was information about the learners. It was done by conducting a needs survey. In needs survey, questionnaire were distributed to the D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay staff and interviews were conducted to the manager of D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay. By doing the needs survey, the researcher could find the learners characteristics, motivation, needs, and interest towards English especially speaking skill as the basis to design the appropriate materials.
2. Planning
specifying objectives and listing and deciding subject contents and its activities. In this step, the researcher focused on determining what should be achieved by the learners and how to achieve it.
3. Developing Preliminary Form of Product
Continuing the previous step, according to R & D, this step included preparation of instructional materials, handbooks, and evaluation devices. In this step, the researcher selected the teaching-learning activities and the instructional resources. 4. Conducting Preliminary Field Test
According to R & D, the product was field tested by doing interview, observation and distributing questionnaire. In this research, the researcher conducted evaluation towards the designed materials by distributing questionnaire to four respondents; they were 2 English lectures of Sanata Dharma University, one English instructor in ELTI and one Junior High School students that have experienced more than 20 years in teaching English.
5. Conducting Main Product Revision
Figure 5 presents the relation between Instructional Design model used in the research and Reseach and Development.
applied in this research.
Figure 3.1 The relation between R&D and instructional design model
B. Research Participants
In order to fulfill research and information collecting, the writer needed some participants. The participants of this study were divided into two groups. The first group were participated in reseach and information collecting, and the second group were participated in preliminary field testing.
Planning
Deciding learning objectives
Deciding subject content Research and Information
collecting
Main product revision
Selecting syllabus type
Preliminary field testing Develop preliminary
form of product
Deciding goals, topic, and general purposes Conducting need survey
Selecting activities and developing materials
1. Participants for research and information collecting
The first group was chosen to contribute the data for reseach and information collecting. They were manager and the hotel staff of D’Cokro Hotel. It was done to find out the characteristics, motivation and need in learning English.
2. Participants for preliminary field testing
The second group was chosen for the preliminary field testing. The writer expected that the respondents could evaluate the instructional materials and gave comments and suggestions on the instructional material. By getting comments, the writer could make necessary changes in the instructional material.
C. Research Instruments
This study conducted using two instruments, they were interview and questionnaire. In reseach and information collecting, both instrument were used to fulfill it, while in preliminary field testing only questionnaire used.
1. Instrument for Reseach and information collecting a. Interview
“An interview is conducted to obtain information by actually talking to the subject” (Seliger and Shohamy, 1989 : 166). There are two types of interview (Ary,
The writer conducted the second type of interview that is unstructured interview. It was conducted informally to the manager of D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay. The interview was conducted in Bahasa Indonesia so that the information clearer. The interview was conducted in the very beginning of the research. The writer asked the manager of D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay about what kind of English education that his staff needed. He mentioned that his staff came from different educational background but they had the same problem that is difficulties in mastering English. He wanted to have specific English training that the materials were fit to the staff daily activities. He also wanted a new way of learning, because sometimes it was difficult to have extra time to have formal training. We then agreed that the teaching would be easier with video as the media.
b. Questionnaire
Generally, there are two types of questionnaires according to Ary et, al.,
(1979:175) open form or unstructured and close form or structured. The open form (unstructured) does not provide the options; the respondents are free to answer the question in their own words. On the other hand, the close form (structured) questionnaire provide the options that were chosen by the writers.
The form used to gather information is close form questionnaire. The hotel staff were asked to answer 9 questions with yes no answer. The questions were used to know the hotel staff’s background and their opinion about the designed material.
2. Instrument for preliminary field testing
In this preliminary field testing, the writer conducted only the questionnairre. The questionnaire (including the designed materials) is given to four respondents. It was conducted to get the information on material that had been designed by the writer, so that the writer could make necessary changes in the instructional material. The research was conducted to evaluate the product. It contains 15 closed questions and 4 open questions.
D. Data Gathering Technique
The data gathering technique was by distributing the questionnaire sheets to the participants and also by an interviewing the manager of D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay. The writer distributed 9 closed questions to the Hotel staff and asked the manager about what materials that his staff need to master.
E. Data Analysis Techniques
Data analysis is process of organizing and ordering the data into pattern and categories in a certain way to find the theme (Moleong, 1998 :88). The data were analyzed to know what the learner’s need and how to design the material. The data from interview were organized, interpreted and then developed as the basis of designing
the materials. To analyze the data from the questionnaires, descriptive analysis was
chosen.At the end, the writer made some revisions on the designed materials..
In the first questionnaire (given to the hotel staff), the students were to answer yes/no question with a space for suggestion about what materials to be taught. The analysis was simple, it was by counting how many students answer yes and no for each number.
In questionnaire B (given to four respondents), the judgment of the participants’ statements on the questionnaires used five points of agreement. They are:
Points of agreement Meaning
1 If the respondents strongly disagree with the statements. 2 If the respondents disagree with the statements.
3 If the respondents feel uncertain about the statements. 4 If the respondents agree with the statements.
5 If the respondents strongly agree with the statements. Table 3.1 Points of Agreement
No Statements Central tendency
N Mean Median Mode
Table 3.2 The Descriptive Statistic of Respondents’ Opinions (Blank)
Mean is the average point that is counted by adding all the points and divided them by the number of questions. The median is the middle point of the odd ordered data from the smallest point into the biggest one. The mode is the points that frequently appear in the data.
The formulation of mean is presented as below:
X
N X
Where
X = the mean
= the sumX = each values in the distribution
N = number of respondents
The formulation was used to analyze the answer in each number. For instance, there were eight respondents and the first question asked was whether the designed materials were suitable for students in that level or not. The answers might be like this 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 3, 3, 3.
the rest of the data were analyzed similarly from the data above. The standard point used to measure whether the designed materials appropriate or not were as follows.
Very good : 3.5 – 4.0
Good : 3.0 – 3.4
Average : 2.5 – 2.9
Poor : 2.0 – 2.4
Very Poor : 0 – 1.9
Therefore, the researcher concluded that most of the respondents agreed that the
designed materials were suitable for D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay staff Yogyakarta.
The result of the second questionnaire will be the tool for measuring the materials designed. The suggestion and the critics from the respondents will be useful for some revisions and make the designed material better.
F. Research Procedures
There were several procedures that should be done to finish this research. They are:
1. Asking for permission to conduct the research and the video taking in D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay. The letter was given by Sanata Dharma University and addressed to the manager of D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay. 2. Conducting review of related literature in Sanata Dharma University
3. Conducting the needs analysis by interviewing the manager of D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay and distributing questionnaire to the Hotel staff. 4. Designing set of instructional speaking material for Hotel staff based on the
result of need analysis.
5. Recording the materials for the video
6. Giving the raw materials to the respondents (2 lectures, 1 teacher, 1 English instructor) for opinion and feedback.
7. Analyzing the opinion and feedback from the respondents.
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH AND DESIGN RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this chapter, the researcher would like to present the result of the study, the discussion and the presentation of the designed material. The writer discussed the result of the study in order to answer the first question (i.e. how is a set of instructional speaking materials for Hotel staff designed). The presentation of the designed materials is aimed to answer the second question (i.e. what does the designed set of materials look like). The detail information is presented as follows.
A. RESEARCH RESULTS
In order to answer the first question in problem formulation, the writer applying R&D method which supported the designing of a set of instructional speaking materials for Hotel staff. They can be seen as follows:
1. Conducting research and information collecting
The respondents for this research and information collecting were the manager of D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay and the 12 staff of the hotel. First of all, the writer conducted an informal interview with the manager of D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay about what kind of English materials that needed by hotel staff in general. The result was that staff hotel needed to master speaking because there were many foreign guests in hotels in Yogjakarta, but they had very limited time to learn formally and no place for them to practice to speak. The writer then, distributed questionnaires to the
hotel staff to gain more information about their educational background, what materials they wanted to learn and how the teaching activities would be. From the result, the writer offered an instructional speaking material. The writer then distributed 12 questionnaire containing respondents’ identity, positions, their last education and their opinion about the suggested topics for the speaking material.
From the questionnaire it was found that the hotel staff had different background of education, but already had English lesson before. The result of the staff hotel opinion about the suggested topic was done like this. The staff hotel was given a list of those materials and they are to give tick (v) in the column of the materials they like. From the result, it was found that 12 persons gave tick on greetings, check in, request, offering, describing place, describing location, describing person, direction and handling complains. 8 persons gave check on check out, 5 persons for compliment and 2 persons for describing things. There were 9 materials chosen by the entire respondent. Since describing place and location are similar and connected to each other, they were considered as 1 unit. From the result, 8 materials found, they are:
1. Greetings
2. In the reservation
3. Make, accept, and refuse a request 4. Make, accept, and refuse an offering 5. Describing person
7. Direction
8. Handling complains
2. Planning
Based on the informal interview with the manager of D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay, it was found that the staff needed to master English speaking skills, because of the demand of the globalization. The goal of the study would be mastering English speaking skills in order to communicate actively with foreign guests. The topic would be around hotel activities that showed the hotel staff interacted with foreign guest.
Considering also the time limitation to study English, the writer and the hotel managers agreed to give real example of conversation between foreign guest and the staff in the hotel it self. The materials are using the real price of the hotel, real location and real property. The purpose is that the staff would deal with the situation they faced daily, so the learning process would be easier and effective.
choose. The result was 9 materials chosen by the entire respondent. Since describing place and location are connected to each other, they were considered as 1 unit. From the result, 8 materials found, they are: Greetings, in the reservation, make, accept, and refuse a request, make, accept, and refuse an offering, describing person, describing things, direction and handling complains.
The topics then were converted to be more specific in language focus. For example the first unit was greetings. The language focus was to greet someone and the unit’s name changed into how do you do. The second unit was in the reservation and the unit’s name changed into Good morning, I want to reserve a room, etc.
Syllabus is designed as the guideline for the materials designed. The syllabus contain major item that will be discussed in each unit. There were eight topics presented in this syllabus. These eight topics were based on the hotel staff’s need in their daily work. The writer also applied the Content based syllabus or in specific functional or notional syllabus.
3. Developing preliminary form of product
Since the syllabus have been chosen, the next step was deciding the activities used in the materials. The writer applied task-based language learning (TBLL) for the material. Examples of the tasks include visiting a doctor, conducting an interview, or calling customer service for help. There are frameworks to follow in TBLL. In this design, the writer used the framework below.
A. Pre-task
In the pre-task, the teacher will present what will be expected of the students in the task phase. The instructor may also present a model of the task by either doing it themselves or by presenting picture, audio, or video demonstrating the task. In the designed material, the writer used video to demonstrate the task
B. Task
During the task phase, the students perform the task, typically in small groups, although this is dependent on the type of activity. In the designed material, the students were asked to perform the example themselves in a group.
C. Planning
Having completed the task, the students prepare either a written or oral report to present to the class. In the designed material, the students were to create a role play to perform or to play pantomime in a group.
D. Report
do the same. In the designed material, the students are to share their experience by shared it in front of the classroom. It was done in the end of the meeting.
E. Analysis (Form Focus)
Here the focus returns to the teacher who reviews what happened in the task, in regards to language. It may include language forms that the students were using, problems that students had, and perhaps forms that need to be covered more or were not used enough. In the designed material, the analysis was done in the sharing time.
F. Task repetition/evaluation
This stage may be used to cover material mentioned by the teacher in the analysis stage. It is an opportunity for the teacher to emphasize key language.
The activities also applied cooperative learning. The activities were done in groups. The clarification of the activity for each section was stated below.
a. Sharing
b. Drilling vocabulary and expressions
Drilling vocabulary and expressions were in the first part of main activity. The purpose of this activity was to provide the students pronunciation practice about the word or expressions used in daily conversation. The teacher showed the students how to pronounce the word or expressions correctly and the students were to repeat and then tried to pronounce it themselves and if there are some mistakes, the teacher can correct them directly. The vocabulary and the expressions were written in a list, so the students can learn it themselves in their free time.
c. Conversation practice
Conversation practice was the most important thing in this designed material. This second part of the main activity was to provide the students (hotel staff) real conversation example. The conversation (which is recorded in D’Cokro Hotel and Homestay) was using the real property of D’Cokro hotel. The real price, the real place, the real gestures were provided for the students so the can imitate the examples and in some examples, they can correct the example if there were some fake mistake in the example (like in unit 5).
d. Role play
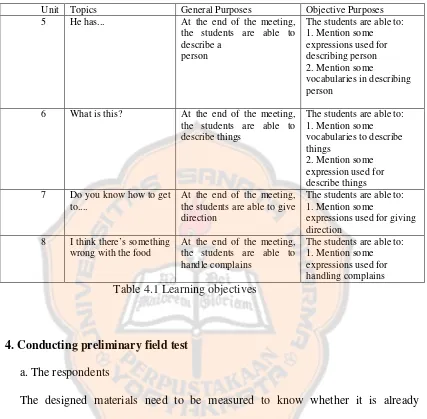
Further more, the general purposes and specific purposes were made in order to lead the teaching learning process. The topics chosen by the hotel staff were still broad. The general purposes and specific purposes can be seen in the table 3.
Unit Topics General Purposes Objective
Purposes 1 How do you do? At the end of the meeting,
the students are able to greet people and express their feelings appropriately
The students are able to: 1. use the appropriate greeting based on the time 2. greet people both in formal and non formal 3. Ask someone’s feelings and express their feelings 4. give farewells
2 Good morning, I want to reserve a room
At the end of the meeting, the students are able to handle reservation
The students are able to: 1. Mention some
vocabularies in reservation desk
2. Mention and read the numbers
3 Would you help me? At the end of the meeting, the students are able to make, accept and refuse request
The students are able to: 1. Mention some
expressions used for make a request
2. Mention some
expressions used for accept a request
3. Mention some
expressions used for refuse a request
4 Do you need some help? At the end of the meeting, the students are able to make, accept and refuse offering
The students are able to: 1. Mention some
expressions used for make an offering
2. Mention some
expressions used for accept an offering
3. Mention some
Unit Topics General Purposes Objective Purposes 5 He has... At the end of the meeting,
the students are able to describe a
person
The students are able to: 1. Mention some
6 What is this? At the end of the meeting, the students are able to describe things
The students are able to: 1. Mention some
At the end of the meeting, the students are able to give direction
The students are able to: 1. Mention some
expressions used for giving direction
8 I think there’s something wrong with the food
At the end of the meeting, the students are able to handle complains
The students are able to: 1. Mention some expressions used for handling complains Table 4.1 Learning objectives
4. Conducting preliminary field test
a. The respondents
degree, teaching in Sanata Dharma University) and the last one represents fresh graduate lecturer (two years teaching experience in Sanata Dharma University).
Group of respondents
Educational Background Teaching Experiences in Years Bachelor
Table. 4.2 The respondents’ data b. Data presentation
The writer obtained the data from open and closed questionnaires. From the questionnaires, the writer obtained the respondent’s evaluation on the designed materials. The results of the closed questionnaire were arranged in the following table.
No Statement N Mean Median Modus
1 The competence standard
are well formulated 4 3 3 3
2 The indicators are well
formulated 4 3,5 3 3
3
The indicators are able to support the attainment of basic competencies
4 3,75 4 4
4 The topics are well selected
and well developed 4 4 4 4
5
The videos are suitable with the competencies and indicators
No Statement N Mean Median Modus
The materials are interesting, suitable and relevant for the hotel staff
4 3,75 3 3
8
The materials are able to help the students to develop their ability in speaking
4 4 4 4
9
The content is relevant with the context and the situation where the language is used
4 3,5 3 4
10 The main and detailed
materials are well elaborated 4 3,25 3 3 11 The vocabuary bank is useful
for the students 4 4,25 4 4
12 The recording materials are
clear 4 3,25 4 4
13
The recording materials are useful for the student's exercises
4 3,5 4 5
14 Generally, the materials are
well elaborated 4 3,75 4 4
Table 4.3 The respondents’ opinion on the designed materials
The results of open questionnaire are as follows
1. What are the strengths of the instructional speaking materials?
2. What are the weaknesses of the instructional speaking materials?
Two of the respondents found there are some grammatical mistakes. The respondents agreed that the materials had not enough models and the activities were repeated too often (the same activities in every unit).
3. What are your suggestions in order to improve the sets of instructional speaking materials?
Two respondents said that the indicators should be revised. The grammatical mistakes should be avoided and give more exercises and variation of activities. If it is possible, the videos will be better if added with subtitle. The formatting and the lay out of the instructional materials should be more interesting.
4. What are your comments about the overall materials?
The respondents agreed that the instructional materials are nice and fine and with some revisions are ready to use.
5. Main product revision
B. DISCUSSION
The result of the second process was the respondents’ opinion and evaluations on the designed material. They were presented in data and used to make revisions and improvement on the designed materials. The results can be seen in the table 4.3. The points of agreement ranged 1 to 5. 1 represented strongly disagree, whereas 5 represented strongly agree. In descriptive statistic of respondents’ opinion on the set of instructional speaking material for hotel staff it was found that the mean was 3,75 from the maximum point 4. It can be concluded that the set of instructional speaking material for hotel staff was appropriate.
Based on the recommendation and suggestions, the writer conducted some revisions on the designed materials. The revisions and improvements are as follows.
1. Changing the lay out to be more interesting.
The previous design was very plain. In order to make it more interesting the writer changed the lay out by adding more pictures and changing the arrangement to make it more interesting.
2. Revising the indicators and grammatical mistakes
3. Giving varied activities and exercises and adding games
The activities and the exercises were varied to avoid the students’ boredom. Games also added in order to refresh the students in studying.
C. PRESENTATION OF THE INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIAL DESIGN
This part aimed to answer the second problem in problem formulation. After making the revisions and improvements on the designed materials, the writer presented the final version of set of instructional speaking materials for hotel staff. Each unit consists of three major part. The complete final version can be seen in appendix C. The overall presentation can be seen in the following table:
Unit Title What to learn Sections
1 How do you do? 1. Greetings 1. Getting started
2. Expressing feelings 2. Try this out 3. Farewells 3. Check this out
4. Play the game 5. Share it out 2 Good morning, I want to
reserve a room
1. Vocab in reservation 1. Getting started
2. Numbers 2. Try this out
3. Check this out 4. Play the game 5. Share it out 3 Would you help me? Expressions in making and
accepting request
1. Getting started 2. Try this out 3. Check this out 4. Play the game 5. Share it out 4 Do you need some help? Expressions in offering,
accepting and refusing help
Unit Title What to learn Sections 5 Describing person
Vocabulary in describing
person 1. Getting started
2. Try this out 3. Check this out 4. Play the game 5. Share it out 6 Describing things 1. Vocab in describing things 1. Getting started
2. Expressions in describing
something 2. Try this out
3. Check this out 4. Play the game 5. Share it out 7 How do you get to... Expressions in asking and
giving direction
1. Getting started 2. Try this out 3. Check this out 4. Play the game 5. Share it out 8 I think there is something
wrong with the food
1. Expressions in handing
complains 1. Getting started
2. Tips for handling complains 2. Try this out 3. Check this out 4. Play the game 5. Share it out Table 4.4 The overall Presentation of the Designed Material
Each unit lesson is divided into five major sections as can be seen in the table 5. They are:
A. Getting started
B. Try this out
The students are given short conversation and the example. They are to watch the example videos then try it themselves.
C. Check this out
After experiencing the conversation and get the information about the materials by experience it themselves, the students were given vocabulary and/or expressions fit to the materials given.
D. Play the game
The students were given games to refresh their mind and after that dome exercises to apply what they have learned in section 3
E. Share it out
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
The last chapter presents the conclusions which can be drawn from the study and the suggestion which are proposed to the English teacher and/or whoever concerned in the teaching of English for hotel staff and also the writer himself.
A. CONCLUSIONS
This study was intended to answer two questions, (1) How is a set of English Instructional Speaking Materials Hotel Staff designed?, (2) What does the designed set of materials look like?
In order to answer the first question, the writer combines Kemp and Yalden’s models with R&D. The result of adaptation was five stages in designing materials. The first step was research and information collecting. The second was planning. Planning consists of 4 sub steps, they are deciding goals, topics and general purposes, deciding learning objectives, selecting syllabus type, and deciding subject content. The third step was developing preliminary field of product. The next step was preliminary field testing and the last one was main product revision.
The statistical computation showed that the overall mean was 3,75 from the maximum scale 5. It means that most of the respondents agreed that this designed set
of instructional speaking materials had been generally well designed and believed to be helpful for the hotel staff to develop their speaking ability.
The second answer was answered by the presentation of the designed materials. The designed materials were presented in eight units. Each unit consists of five parts, getting started, try this out, check this out, play the game and share it out.
B. SUGGESTIONS
1. For English teachers
a. The teacher should first understand the nature and the routines of the hotel staff in order to create good learning atmosphere. Most of the staff is busy with their jobs and when they have to learn in class after it, it will be better if the class atmosphere is fun.
b. The teacher may use the video to gain fun atmosphere with the learners. Ask the students to catch the funny expressions of the actors and also their awkward acting. Ask the learners to find what gestures are wrong, what expressions are wrong so they can feel that the learning is not only about English but also to review their gestures while doing their jobs.
d. The teacher are suggested to give more feedback, especially on the learner’s performance because in speaking students learning by doing and by learn from the mistakes it will make the students more aware in the future.
2. For the future researchers
54
REFERENCES
Ary, D., L. C. Jacobs, A. Razavieh. 1979.Introduction to Research and Education
(Second Edition). New York: Reinhart and Winston, Inc.
Borg, W. R. and Gall, M. D. 1983.Educational Research. New York: Longman, Inc. Dick, Walter and Reiser, R. A. 1989.Planning Effective Instruction. Boston: Allyn
and Bacon.
Hutchinson, T, and Waters, A. 1995.English for A Specific Purposes. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Kemp, J. E. 1977.Instructional Design: A Plan for Unit and Course Development. Belmont, CA: Fearon-Pitman Publisher, Inc.
Richard, J. C. and Rodgers, T. S. 2001.Approaches and Methods in Language Teaching.Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Robinson, P. C. 1991.ESP Today: A Pracitioner’s Guide. New York: Prentice Hall. Widdowson, H. 1990.Aspects of Language Teaching. Oxford: Oxford University
Press.
55
56
58
APPENDIX B
59
TRANSKRIP WAWANCARA
DENGAN MANAGER D’COKRO HOTEL AND HOMESTAY - Selamat pagi pak!
- Selamat pagi mas Itok
- Seperti janji yang saya buat kemarin pak, saya ingin mewawancarai bapak untuk materi skripsi yang sedang saya siapkan
- Iya mas, saya akan bantu semua yang diperlukan - Trima kasih pak, nama lengkap bapak?
- Fauzi Ardian, General manager Hotel D’Cokro
- Bagaimanakah kemampuan bahasa Inggris karyawan hotel bapak?
- Sangat kurang, selama ini setiap ada tamu dari luar selalu saya yang turun langsung menghadapi karena karyawan tidak mampu dan tidak berani berinteraksi
- Apakah bapak merasa perlu diberikan pelatihan bahasa inggris kepada karyawan bapak?
- Sangat perlu sekali, karena saat ini hotel kami sudah berbintang tiga dan seharusnya setiap karyawan kami sudah bisa berbahasa inggris
- Pelatihan bahasa inggris seperti apa yang bapak inginkan untuk karyawan bapak?
- Pelatihan yang efektif. Jadi langsung ke latihan percakapan sehingga bisa langsung diaplikasikan
- Materi apa saja yang bapak rasa perlu untuk dipelajari oleh karyawan bapak? - Ya kalo materi ya seputar Greetings, reservation, describing itu kayaknya juga
perlu
- Describing people sama things ya pak?
- Iya mas, lalu mungkin memberi dan merespon permintaan, bantuan, direction.. gitu..
60
- Ya perlu sekali mas, justru itu yang sangat penting. Saya kelupaan.
- Jika ada pelatihan bahasa inggris yang contoh percakapannya dibuat dalam bentuk video, percakapan tersebut dilakukan di hotel bapak, dan segala macam percakannya disesuaikan dengan kebutuhan hotel bapak, bagaimana tanggapan bapak?
- Saya sangat setuju sekali dan mendukung. Jika langsung contohnya dari hotel saya maka karyawan akan sangat familiar dan memudahkan mereka dalam memahami bahasa inggris. Selain itu, dengan adanya video memudahkan para karyawan untuk dapat berlatih sendiri di rumah dengan fasilitas video yang disiapkan
- Saya akan mendesain materi berdasarkan masukan yang tadi bapak berikan... Apakah nantinya saya diperkenankan untuk mengambil adegan-adegan di hotel ini?
- Boleh sekali mas, nanti akan saya lihat kira-kira hari apa mas bisa shooting di hotel kami
- Sebelum pengambilan shooting nanti saya akan datang lagi dengan materinya pak, nanti bisa bapak lihat dan revisi sebelum kita shooting
- Ya mas
- Ya mungkin sekian saja pak, terima kasih sekali atas kesediaan waktu wawancaranya dan masukan-masukannya.