i
ABSTRACT
CAHYA, KARANA LINTANG. Analysis of Requesting Speech Act in the Movie FROZEN by Walt Disney. Yogyakarta: Department of English Letters, Faculty of Letters, Sanata Dharma University, 2016.
Requesting speech act sometimes is used directly or indirectly in daily life. When someone request something to another, she or he can express it by uttering requesting, asking, greeting, giving information, complaining, offering, and criticizing. Based on this case, the researcher tries to analyze and classify request speech act and its politeness strategy in Frozen.
In order to understand that background, the researcher provides two problem formulations. The first problem, the researcher describes and analyzes the strategies of request speech act of speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition employed in character in Frozen. The second problem, the researcher describes and analyzes the types of politeness strategy used to make a request employed character in Frozen.
This research belongs to descriptive qualitative study. The data of this research are all utterances in Frozen which indicates both kinds of requests to make a limitation of all the data showing request speech act. There are some steps to analyze the data in this research. First, the researcher determined all utterances which were categorized as request speech act using Searle’s theory. Next, the data of request were then classified based on speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition using Trosborg’s theory. To answer the problem of the research, the researcher analyzed the types of request using speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition. The researcher then determined the politeness strategy of each datum of speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition based on Brown and Levinson’s theory.
ii
ABSTRAK
CAHYA, KARANA LINTANG. Analysis of Requesting Speech Act in the Movie FROZEN by Walt Disney. Yogyakarta: Sastra Inggris, Fakultas Sastra, Universitas Sanata Dharma, 2016.
Tuturan permintaan sering diterapkan secara langsung maupun tidak langsung dalam komunikasi sehari-hari. Ketika seseorang meminta sesuatu kepada orang lain, dia akan mengucapkannya secara langsung, bertanya, memberikan informasi, mengeluh, menawarkan, mengkritik. Berdasarkan hal tersebut, peneliti mencoba untuk menganalisis dan mengklasifkasi tindak tutur dan kesantunan di Frozen. Melalui analisis tersebut dapat ditemukan bentuk, tipe, dan pola dari tuturan permintaan berdasarkan kondisi penuturnya dan mitra tuturnya, serta strategi kesantunannya dalam film tersebut.
Untuk memahami latar belakang penelitian, peneliti menyertakan dua permasalahan. Pertama, peneliti mendeskripsikan dan menganalisis strategi tuturan permintaan berdasarkan kondisi penuturnya dan berdasarkan kondisi mitra tuturnya yang terdapat dalam Frozen. Kedua, peneliti mendeskripsikan dan menganalisis jenis strategi kesantunan tuturan permintaan yang digunakan oleh para tokoh dalam Frozen.
Penelitian ini merupakan penelitian deskripsi kualitatif. Data penelitian ini adalah semua permintaan dalam Frozen yang mengindikasikan kedua jenis tuturan permintaan tersebut untuk membuat batasan dalam penelitian ini. Terdapat beberapa langkah untuk menganalisis data di penelitian ini. Pertama, peneliti mengkategorikan semua permintaan berdasarkan teori dari Searle. Kemudian, data tersebut dikategorikan dalam tuturan permintaan berdasarkan kondisi penuturnya dan kondisi mitra tuturnya. Peneliti kemudian menentukan jenis strategi kesantunan dari data tersebut berdasarkan teori Brown dan Levinson.
i
ANALYSIS OF REQUESTING SPEECH ACT
IN THE MOVIE FROZEN BY WALT DISNEY
AN UNDERGRADUATE THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
for the Degree of Sarjana Sastra in English Letters
By KARANA LINTANG CAHYA
Student Number : 104214080
ENGLISH LETTERS STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH LETTERS
FACULTY OF LETTERS SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
ii
ANALYSIS OF REQUESTING SPEECH ACT
IN THE MOVIE FROZEN BY WALT DISNEY
AN UNDERGRADUATE THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
for the Degree of Sarjana Sastra in English Letters
By KARANA LINTANG CAHYA
Student Number : 104214080
ENGLISH LETTERS STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH LETTERS
FACULTY OF LETTERS SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
vii
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Alhamdulillahi Rabbil ‘Aalamiin. All gratitude for Allah SWT the almighty
for all the blessing given to me in completing my undergraduate thesis. During the process of thesis completion, I met people who gave me support and help. I owe them so much due to the fact that without their contribution, this undergraduate thesis could not be completed. Therefore, I would like to express my gratitude to those who have supported and helped me in finishing my undergraduate thesis.
I would like to deliver thanks to my advisor, Adventina Putranti, S.S., M.Hum., for all her concern, advice, time and patience in guiding me to complete my undergraduate thesis. I would like also thank my co- advisor, Wedhowerti, S.Pd., M.Hum., for the detailed correction and valuable input.
From the bottom of my heart, I want to thank my Dad, Drs. Widdi Srihanto, M.M., my Mom, Dra. Sulianti, and my Sisters, Imas and Sari, for their endless love and support that keep me motivated to complete this undergraduate thesis. I love them.
For all of my friends in English Department ’10, I thank them so much for
all the storms and rainbows we have been through and of course the never ending friendship. I treasure every moment we spend together.
viii
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF LITERATURE………..….. 6
A. Review of Related Studies……… 6
ix
Frozen Movie……… 24
1. The Strategy of Speaker-Based Condition in Request Speech Act……….. 24
a. Wishes or desires ……… 25
b. Needs or demands ……… 29
2. The Strategy of Hearer-Based Condition in Request Speect Act……….. 31
a. Ability or willingness ……….. 32
b. Suggestory formulae ……… 37
B. Type of Politeness Strategy Used to Make A Request Employed by Character in Frozen Movie…….…….………..… 41
1. Bald-on Record………. 43
2. Positive Politeness……….…… 46
3. Negative politeness………... 55
C. Discussion……….……….. 59
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION..……….. 64
BIBLIOGRAPHY…………..………..………….…… 67
APPENDICES...……….………..…. 69
APPENDIX 1: Synopsis of Frozen ……..……...…….……….… 70
x
ABSTRACT
CAHYA, KARANA LINTANG. Analysis of Requesting Speech Act in the Movie FROZEN by Walt Disney. Yogyakarta: Department of English Letters, Faculty of Letters, Sanata Dharma University, 2016.
Requesting speech act sometimes is used directly or indirectly in daily life. When someone request something to another, she or he can express it by uttering requesting, asking, greeting, giving information, complaining, offering, and criticizing. Based on this case, the researcher tries to analyze and classify request speech act and its politeness strategy in Frozen.
In order to understand that background, the researcher provides two problem formulations. The first problem, the researcher describes and analyzes the strategies of request speech act of speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition employed in character in Frozen. The second problem, the researcher describes and analyzes the types of politeness strategy used to make a request employed character in Frozen.
This research belongs to descriptive qualitative study. The data of this research are all utterances in Frozen which indicates both kinds of requests to make a limitation of all the data showing request speech act. There are some steps to analyze the data in this research. First, the researcher determined all utterances which were categorized as request speech act using Searle’s theory. Next, the data of request were then classified based on speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition using Trosborg’s theory. To answer the problem of the research, the researcher analyzed the types of request using speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition. The researcher then determined the politeness strategy of each datum of speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition based on Brown and Levinson’s theory.
xi
ABSTRAK
CAHYA, KARANA LINTANG. Analysis of Requesting Speech Act in the Movie FROZEN by Walt Disney. Yogyakarta: Sastra Inggris, Fakultas Sastra, Universitas Sanata Dharma, 2016.
Tuturan permintaan sering diterapkan secara langsung maupun tidak langsung dalam komunikasi sehari-hari. Ketika seseorang meminta sesuatu kepada orang lain, dia akan mengucapkannya secara langsung, bertanya, memberikan informasi, mengeluh, menawarkan, mengkritik. Berdasarkan hal tersebut, peneliti mencoba untuk menganalisis dan mengklasifkasi tindak tutur dan kesantunan di Frozen. Melalui analisis tersebut dapat ditemukan bentuk, tipe, dan pola dari tuturan permintaan berdasarkan kondisi penuturnya dan mitra tuturnya, serta strategi kesantunannya dalam film tersebut.
Untuk memahami latar belakang penelitian, peneliti menyertakan dua permasalahan. Pertama, peneliti mendeskripsikan dan menganalisis strategi tuturan permintaan berdasarkan kondisi penuturnya dan berdasarkan kondisi mitra tuturnya yang terdapat dalam Frozen. Kedua, peneliti mendeskripsikan dan menganalisis jenis strategi kesantunan tuturan permintaan yang digunakan oleh para tokoh dalam Frozen.
Penelitian ini merupakan penelitian deskripsi kualitatif. Data penelitian ini adalah semua permintaan dalam Frozen yang mengindikasikan kedua jenis tuturan permintaan tersebut untuk membuat batasan dalam penelitian ini. Terdapat beberapa langkah untuk menganalisis data di penelitian ini. Pertama, peneliti mengkategorikan semua permintaan berdasarkan teori dari Searle. Kemudian, data tersebut dikategorikan dalam tuturan permintaan berdasarkan kondisi penuturnya dan kondisi mitra tuturnya. Peneliti kemudian menentukan jenis strategi kesantunan dari data tersebut berdasarkan teori Brown dan Levinson.
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A.Background of the Study
Language is one of important things in the world. If there is no language, there will be no communication from one people to another. Without communication, we do not know what happens around our environment. Communication is also one way to us to deliver or express our ideas and feelings.
Speech acts play an important role in daily communication, for example requesting. Requesting speech act sometimes is used directly or indirectly in the daily life. When someone requests something to someone, she or he can express it by uttering requesting, asking, greeting, giving information, complaining, offering, and criticizing. Besides, there are many factors influencing the relationships among the participants' request behaviors, such as social status, familiarity, and etc. The following is the example of requesting speech act which the researcher finds in Frozen (2013) .
The King : Please... Help!My daughter! Grand Pabbie : Cuties. I'm gonna keep you.
The conversation above takes place in Grand Pabbie’s village, the valley of the living rock. The participants are between the King of Arendelle and Grand Pabbie, a wise and elderly ruler of the trolls (a group of ancient creatures there). The King of Arendelle has two little daughters, Elsa and Anna. One day, Anna asks Elsa to play magic by making snowman but
accidentally Elsa’s magic hits and almost kills her sister (Anna). Then, the
King and Queen come to Elsa to know what happens with Anna. Anna is getting hurt and the King has to save her quickly by carrying her to Grand Pabbie. When he comes there, the King asks Grand Pabbie to save her by requesting.
In the dialogue above, the King requests to Grand Pabbie by saying “Please... Help!My daughter!”. It means that the King uses speech act of
his daughter. In this case, Grand Pabbie complies the King request by comforting his daughter by saying “Cuties. I'm gonna keep you.”
The King also applies politeness strategy called negative politeness strategy in delivering his request. It is shown by the use of the word “Please” at the beginning of his utterance. Hence, the factor influencing the relationships
between the King’s request behaviors towards Grand Pabbie is because of
familiarity of each other and the king is one who needs a help from Grand Pabbie.
Based on the example above, I am interested in analyzing the requesting speech act in Frozen by Walt Disney. Therefore, I conduct a research entitled Analysis Of Requesting Speech Act In The Movie Frozen By Walt Disney.
B.Problem Formulation
The problem formulation in this research is:
1. What strategies of request expression of speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition are employed by characters in Frozen?
2. What types of politeness strategy are used to make a request employed by characters in Frozen?
C.Objectives of the Study
The objectives of studying this research are:
2. To describe the types of politeness strategy used to make a request employed by characters in Frozen.
D. Definition of Terms
The analysis in this research provides some definitions of “Speech
act”, “Request”, and “Politeness” to make it clear and to avoid ambiguity.
Searle (1969: 16) state that the unit of linguistics communication is not the symbol, word or sentence, but rather the production or issuance of the symbol or word or sentence in the performence of the speech acts. It means that the basic minimal unit of linguistic comunication are speech acts. Meanwhile, Yule (1996: 47) says that speech act is action pearformed via utterence.
Request speech act subsumes utterances which have been referred to, in the speech act literature as request, invite, ask for permission, and offer (Tsui, 1994: 91). Meanwhile, Trosborg (1995: 187) gives definition that
“Request is an illocutionary act whereby a speaker convise a hearer to peform
an act which is for the benefiit of the speaker.”
6 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
In this chapter, the writer provides three parts that will be discussed. The first part is review of related studies, including other related studies previously. Second part is review of related theories which provides some theories in doing this research. Third part is theoretical framework which explains the contribution between the theories and the reviews to solve the problem formulation.
A. Review of Related Studies
This research consists of only one previous study. That research tells about discussing the analysis of directive speech act.
The first undergraduate thesis entitled Politeness Strategies Applied in Directive Speech Acts According to The Interpersonal Relationships in “The
Related to the Ciptaningrum’s research which analyzes about directive
speech ach, politeness strategy, and interpersonal relation among the characters, the writer uses different ways in conducting the result through linguistics. However, Ciptaningrum only focuses on those matters without analyzing the factors influencing the character to apply politeness strategy in directive speech act.
B.Review of Related Theories
1. Pragmatics
Pragmatics refers to speaker’s meaning or utterance interpretation.
The first definition of pragmatics is quoted from Steven C. Levinson, followed by Jenny Thomas and the last is George Yule.
Levinson (1983: 21) states that pragmatics is the study of the ability of language users to pair sentences with the contexts in which they would be appropriate. It means that pragmatics cannot be separated from context and principles of language usage. Then, Thomas (1995: 23) defines pragmatics as meaning in interaction.
contextual meaning. Context here includes to whom the speaker talking, where, when, and under what circumstances. Context has important role in communication between the speaker and the hearer. Third, Pragmatics is the study of how more gets communicated than what is said. By understanding pragmatics, people can explore what is unsaid be recognized as part of what is communicated. Fourth, Pragmatics is the study of the expression of relative distance. Relative distances means how close between the speaker and the hearer are communicating each other including physical, social or conceptual closeness.
From the definitions above, it can be concluded that Pragmatics is a significant field to study in communication that is about language, context, and the meaning of the utterances between the speaker and the hearer. 2. Speech Act
Pragmatics studies how people understand and produce a speech act in a social situation, usually in conversation. Speech act is a part of pragmatics that studies about utterances. According to Searle (in Levinson, 1983: 240), speech act can be classified into five categories, they are representative, directive, commisive, expressive and declaration.
a. Representative
speakers’s intention in uttering his/her belief. Example: The earth is flat.
(Yule, 1996: 53) b. Directive
Directive is a kind of speech act that is intended to make someone do something. In this case, the speaker utters directive in order to get the prospective action. Acts of requesting, commanding and persuading can be classified into directive.
Example: Could you lend me a pen, please? (Yule, 1996: 54) c. Commisive
Commisive is kind of speech act that commits the speaker to some future action. Acts of promising, refusing, threatening and pledging can be classified into commisive.
Example: We will not do that. (Yule, 1996: 54) d. Expressive
Expressive is a kind of speech act that is used by the speaker to express their feeling that are either pain or pleasure. Acts of apologizing, congratulating and thanking can be classified into expressive.
Example: Congratulations! (Yule, 1996: 53) e. Declarative
Example: I now pronounce you husband and wife. (Yule, 1996: 53)
3. Requesting speech act
Requesting speech act is commonly used in daily communication which focuses on asking someone (the addressee/ hearer) to do something by giving him or her an option for complying and not complying the request. It is a part of directive speech act in pragmatics as stated by Searle because request action has an illocutionary purpose to get the hearer to do something. Trosborg (1995: 192) has divided the requesting speech act according to what the benefit to the speaker and the hearer when they are having conversation. This strategy classifies requesting speech act into four catagories and involves them eight-sub strategies, namely indirect request, hearer-oriented condition, speaker-based condition and direct request. a) Indirect request
Indirect request is a request without explicit requestive illocutionary force. Consequently, the speaker omits to mention (or specify) the desired act and avoids mentioning the hearer as the intended agent (Trosborg, 1995:192). There is only one strategy of indirect request called hinting strategy. Hinting strategy is used by the speaker by making a request which does not explicitly state that the
speaker’s request for the desired action. There are two kinds of hinting
desired action altogether, and (2) strong hint, used by the speaker by mentioning his/her wish.
For example: I have to be at the airport in half an hour. (Trosborg, 1995: 205)
The request above employs indirect request expression with mild hint strategy. The speaker does not explictly mention that the speaker asks the taxi driver to speed up the taxi since he is in hurry. The speaker leaves out the request, he lets the hearer to figure out by himself whether the speaker wants to speed up the taxi.
b) Hearer-oriented condition
This request conveys that hearer is in a position of control to decide whether or not to perform the request. This request uses two strategies, that strategies are ability (willingness) and suggestory formula. 1. Ability (willingness)
The condition of ability refers to hearer’s capacity to perform the
desired act. Two different conditions are relevant: 1) the inherent capacities of the hearer both physical and mental, 2) the external circumstances relates to time and place of the action.
2. Suggestory formulae
By using suggestory formulae, the speaker makes his/her request more tentative and plays down his/her own interest as a beneficinary of the action.
For example : How about lending me your car? (Trosborg, 1995: 205) c) Speaker-based condition
By placing the speaker interest above the hearer’s, this request becomes more direct in its demand. There are two strategies in speaker-based condition. They are by using whises/desires and needs/demands.
1. Wishes or desires
The speaker’s statement of his/her intention maybe expressed
politely as a wish.
For example : I would like to borrow your car. (Trosborg, 1995: 205)
2. Needs or demands
Its a request strategy which expresses the speaker’s request
more blindly as demand.
For example : I needs to borrow your car. (Trosborg, 1995: 205) d) Direct Request
request uses three strategies namely obligation, performative, and imperative.
1. Obligation
This strategy is used by employing a statement of obligation. When employing this strategy, the speaker exerts either his/her authority, or he/she refers to some authority outside the speaker.
For example : You have to lend me your car. (Trosborg, 1995: 205) 2. Performative
The inclusion of performative verb conveys requestive intent, e.g. asking, requesting, demanding, commanding, and explicitly marking the utterence as an order.
For example : I would like to ask you to borrow your car. (Trosborg, 1995: 205)
3. Imperative
Imperative is the grammatical form directly signaling that the utterance is an order. An order issued by authority figures must be obeyed, such as the older’s to the younger’s.
For example : Lend me your car! (Trosborg, 1995: 205) 4. Politeness
politeness is strategic conflic avoidance which can be measured in terms of the degree of effort put into the avoidance of a conflict situation. In short, politeness is defined as using communicative strategies to create and maintain social harmony as stated by Culpeper (1996: 349). Politeness can be done in many various ways, they are being contextually appropriate, following social and cultural norms, and being socially positive by addresing face needs.
There are many experts discussing about politeness strategy. This research only uses politeness strategy proposed by Brown and Lenvinson as an approach to analyze the data. This theory is choosen to explain about politeness strategy in detail. Brown and Levinson (1987: 92) have divided the politeness strategies according to how much the speakers and the hearers minimize the threat when they are having conversation. The strategies range from doing the FTA directly without minimizing the threat at all to not doing FTA. They are bald-on record, positive politeness, negative politeness, and off-record strategy.
a. Bald-on Record
Bald-on record strategy does not attempt to minimize the threat to
hearer’s face. Brown and Levinson state that speaker mostly uses
bald-on record strategy when she wants to do FTA (Face
Threatening Acts) with maximum efficiency toward the hearer’s
hearer feels uncomfortable. This strategy is a direct way of saying things, without any minimization to the imposition, in a direct, clear, unambiguous, and concise way. This strategy is usually employed in some occasion, such as in emergency situation, unequal power relationship, and task oriented activities.
For example: Give me a pen! (Yule, 1996: 63) b. Positive Politiness
Positive politeness provides an attempt to minimize the damage to
the hearer’s face (Brown and Levinson, 1987: 101). This strategy is
intended to avoid the conflict and to minimize the social distance between the speaker and the hearer. There are some indication of positive politeness strategy, such as using in-group indetity makers, offering solidarity through friendship, seeking agreement, avoiding disagreement, presupposition/ raise/ assert common ground, joking,
asserting or presuppose speaker’s knowledge, concerning for
hearer’s wants, offering and promising, being optimistic, including
both speaker and hearer in the actvity, giving (or asking) reasons, assuming or asserting recipocity, giving gifts to hearer (goods, sympathy, understanding, cooperation), etc (1987: 102).
c. Negative Politeness
Brown and Levinson (1987: 129) state that negative politeness
attends to a person’s negative face needs, which appeals to the
hearer’s desire not to be impeded or put upon and to be left free to
act as they want. This strategy is to express respect and consideration. There are some indication of negative politeness strategy, such as being conventionally indirect, questioning, hedge, being pesimistic, minimizing the imposition or friction, formality in language use, apoligizing, giving deference and respect (1987: 130).
For example: Could you lend me your pen? (Yule, 1996: 64) d. Off-record Strategy
A communicative act is done by using off record strategy if it is not possible to attribute only one clear intention act (Brown and Levinson, 1987). When the speaker uses this strategy, she/ he wants to avoid the responsibility for doing FTA. As stated by Brown and Levinson, 1987: 211, this strategy is used when the speaker wants to
damage another’s face without any responsibility of doing it, by
leaving it up to the hearers to be interpreted by themselves.
C.Theoretical Framework
The aim of this study is to know the strategy of requesting speech act in the Frozen and the types of politeness strategy applied in that movie. Some applicable theories are used in this research to support the process of the data analysis.
First, researcher uses Searle’s theory about classification speech act especially directive requesting speech act. And then, researcher uses Trosborg’s theory in Searle’s statement about speaker based-condition and hearer oriented-condition to solve the problem one. From that theory, researcher can classify the strategies is applied in Frozen.
18 CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
Research methodology is important to know how research is done scientifically to solve the research problem (Kothari, 1990: 8). This research belongs to descriptive qualitative study. It means that this research uses descriptive method which emphasis on describing the data used in the research. In conducting the research, the researcher only examines the data and it is not propose any hypothesis as it started from a phenomenon. In qualitative research, the data can be in the form of words, sentences, and terminology. Milles and Huberman (1984: 21) state that the qualitative research is essentially an investigating process: someone investigates a kind of social phenomenon by contrasting, comparing, replicating, cataloging, or classifying the object. This research does not include any calculation or enumeration, since the data produced are in the form of word. It is like what is stated by Bogdan and Taylor (in Moleong, 2000: 3) that qualitative research is a research that produces descriptive data consisting of written and spoken words and also behavior.
A.Object of the Study
The object of this research is Frozen. Frozen is a 2013 American 3D computer-animated musical fantasy film produced by Walt Disney Animation
Studios and released by Walt Disney Pictures. It is the 53rd animated feature in
the Walt Disney Animated Classics series. Inspired by Hans Christian Andersen's fairy tale The Snow Queen, the film tells the story of a fearless princess who sets off on an epic journey alongside a rugged iceman, his loyal pet reindeer, and a naïve snowman to find her estranged sister, whose icy powers have inadvertently trapped the kingdom in eternal winter. This movie is directed by Chris Buck and Jennifer Lee. This movie became the best-selling film of the year in the United States. By January 2015, Frozen became the all-time best-selling Blu-ray Disc in the United States. It won two Academy Awards for Best Animated Feature and the Golden Globe Award for Best Animated Feature Film.
This research is conducted to find out the types of request speech act using speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition, as well as the politeness strategy used in the request. By focusing on request speech act in that movie, the researcher collected the data using speech act theory under pragmatics study. The data were classified based on its types and forms of request. They were then analyzed speaker-based condition, hearer-oriented condition and the politeness strategy in order to understand how request is
B.Approach of the Study
In conducting this research, the researcher analyzed all utterances from Frozen which indicate request speech act. The researcher uses pragmatics theory about request which is included in directive speech act as proposed by Searle (in Levinson, 1983: 240). Then, the researcher only focuses on request of speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition to make a limitation of all the data showing request speech act. In speaker-based condition, the request is focused on the speaker as the one who places the interest above the hearer. So, the request becomes more direct as wishes or desires and needs or demands. Meanwhile, in hearer-oriented condition the request is focused on the
hearer’s position of control to decide whether or not to perform the request.
Both of us these types of request are also more polite than direct request. Consequently, the researcher prefers to analyze the politeness strategy in speaker-based condition of request based on Brown and Levinson’ theory.
C.Method of Study
1.Data Collection
The object of this study is the application of request of speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition, also politeness strategy used by the character in Frozen. It means that the researcher collected the data purposively. The data is limited only speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition in request.
The first step to get the data, the researcher watches Frozen for several times in order to understand the whole story. Then, the researcher searched the transcript of Frozen on the internet and compared it to the movie. The researcher also underlined the dialogues employed by the characters which indicated a request speech act of speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition using Searle and Trosborg’s theory.
The next step in collecting the data is by giving code on each type of datum. The coding of the datum in this research is as follows:
a. The number of the datum
b. The title of the movie. This research uses a movie entitled Frozen
c. The types of request speech act employed by the characters based on Searle’s theory the researcher used speaker-based condition type and hearer-oriented condition.
d. The type of condition of request speech act based on Searle’s theory. e. The type of politeness strategies on Brown and Levinson’s theory
08/ F/ SBC/ W/ N
The coding above means that the datum is number eight (8). F means Frozen. Meanwhile SBC is the type of request speech act that is
speaker-based condition. Then, W is the condition of speaker-speaker-based condition that is Wishes. Last, N is one of the politeness strategies is applied in that datum, that is Negatives.
2.Data Analysis
There are some steps to analyze the data in this research. First, the researcher determined all utterances which were categorized as request
speech act using Searle’s theory. Next, the data of request were than
classified based on speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition
using Trosborg’s theory. After that, the researcher labeled the data in the
form of code based on the number of datum, the title of the movie, and the type of request speech act (speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition).
24 CHAPTER IV
ANALYSIS RESULT AND DISCUSSION
This chapter consists of two parts. The first part is analysis result. Based on the objectives of the result, the analysis result in this research focuses on analyzing the strategies of speaker-based condition and hearer-oriented condition
in request speech act using Trosborg’s theory and analyzing types of politeness
strategy used to make a request employed by characters in Frozen using Brown’s
and Levinson’s theory. The second part of this chapter is discussion. It provides
the discussion of some finding from the analysis results that are relevant to the research objectives. In this research, the total data are 17 data of request speech act to analyze.
A. The Strategies of Request Speech Act Employed by Character in Frozen
Movie
In this part, there are two strategies of request speech act are used to analyze the character in Frozen, namely Speaker-Based Condition and Hearer-Oriented Condition by Trosborg’s theory.
1. The Strategy of Speaker-Based Conditions in Request Speech Act
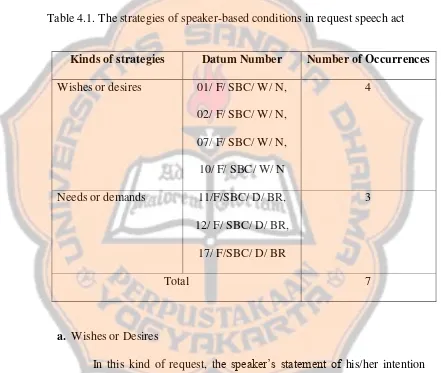
speaker finds both kinds of those strategies. Therefore, the total data using this strategy are 7 data. There are 4 data that show the strategy of wishes or desires and 3 data that show the strategy of needs or demands. The description of each strategy of speaker-based conditions in request speech act can be shown in the following table.
Table 4.1. The strategies of speaker-based conditions in request speech act
a. Wishes or Desires
In this kind of request, the speaker’s statement of his/her intention maybe expressed politely as a wish. There are 8 data of request using wishes or desires in this research. The following is the description of each datum showing request by wishes or desires.
1) Datum number : 01/ F/ SBC/ W/ N
Duration : 00:08:39,886 00:08:45,252
Kinds of strategies Datum Number Number of Occurrences
Wishes or desires 01/ F/ SBC/ W/ N, 02/ F/ SBC/ W/ N,
07/ F/ SBC/ W/ N, 10/ F/ SBC/ W/ N
4
Needs or demands 11/F/SBC/ D/ BR, 12/ F/ SBC/ D/ BR, 17/ F/SBC/ D/ BR
3
Context of situation : Elsa wants to invite Anna to play together
by building a snowman with Anna’s magic. However, Anna does not
want to do it because she is afraid that her magic can hurt Elsa. Elsa
asks Anna by making a request from the outside of Anna’s room.
Because Anna does not want to come out from her room, Elsa than becomes curious about what happens to her sister. She wishes her sister can tell her the reason.
Elsa : I wish you would tell me why Anna : - (not answering)
The datum above shows that Elsa, as the speaker, is in a position of control of Anna, as the hearer. Then it is marked by the
use of subject “I” as the person who needs something from the hearer.
In this context, Elsa wishes Anna to tell her about why Anna always locks herself in her room and does not want to play with her like before. Elsa makes a request by using the word “wish” to make it polite. Therefore, it can be said that Elsa makes a request to Anna by showing her wish.
2) Datum number : 02/ F/ SBC/ W/ N
Duration : 00:17:46,437 00:17:47,720
She almost falls down but a horse ridden by Hans, the Prince of Southern Island, helps her. Next, Hans gets off from the horse and helps her to stand up. But the horse bothers them by stamping on the boat, so that both of them fall down. Hans feels guilty toward Elsa and makes a request to forgive him and his horse.
Hans : I'd like to formally apologize for hitting the Princess of Arendelle. With my horse.
Anna : No. No-no. It's fine.
The datum above shows that Hans as the speaker places her interest above Anna as the hearer. Hans is in a position of control of Anna. It is marked by the use of subject “I” as the person who needs something from the hearer. In this context, Hans makes request by showing his desire. Hans wants Anna to forgive him about the mistake caused by his horse. Hans makes a request by using the words “Would like to” to make it acceptable for hearer. From the datum above, it can be said that Hans makes a request to Anna by showing his desire.
3) Datum number : 07/ F/ SBC/ W/ N
Duration : 00:25:57,498 00:26:00,421
Context of situation : Because Anna has agreed Hans’ request to
marry him, Anna and Hans go into the dance’s floor to meet Elsa.
Anna and Hans : We would like... your blessing of... our marriage!
Elsa : Marriage? I'm sorry, I'm confused.
The datum above, the request of speaker-based condition is expressed by both Anna and Hans. Anna and Hans make a request to Elsa by showing their wish. It means that Anna and Hans as the speaker places their interest above Elsa as the hearer. Then it is
marked by the use of subject “We” as the persons who need
something from the hearer. In this context, Anna and Hans want to tell something to Elsa that is to get blessing for marrying Anna as her little sister. Anna and Hans make a request by using the words “We
would like…” to make it polite and acceptable. It can be said that the
speakers use the request rather indirectly by showing their desire. 4) Datum number :10/ F/ SBC/ W/ N
Duration : 00:27:04,101 00:27:08,024
Context of situation : Elsa does not agree with Anna and Hans
marriage. Elsa then wants to leave the party because of Anna’s
stubbornness. However, Anna still wants to get Elsa’s blessing for her
marriage before Elsa leaves the party.
Anna : Elsa, please. Please. I can’t live like this anymore. Elsa : Then leave.
the person who needs something from the hearer. The word “I” has in a position of control in this request. In this context, Anna wants to get
Elsa’s blessing for her marriage. Anna makes a request by using the
words “Please. Please. I…” to show her wish or desire. It can be said
that Anna makes a request to Elsa rather indirectly by showing her wish.
b. Needs or Demands
In this request strategy, the speaker expresses his or her request more blindly as a demand or need. There are 3 data of request using needs or demands in this research. The following is the description of each datum showing request by needs or demands. 1) Datum number : 11/ F/ SBC/ D/ BR
Duration : 00:30:24,108 00:30:27,210
Context of situation : Elsa leaves her palace after she did magic with her hands. All people in palace have known her secret so she must run away. Anna then chases after her to bring her back to the palace. Elsa chooses Hans to replace her sister to handle Arendelle for a moment.
Anna : I need you here to take care of Arendelle. Hans : On my honor.
of subject “I” has in a position of control in the request. In this
context, Anna wants to hand her palace over to Hans for a moment.
Anna makes a request by using the words “I need you here to…” to
make Hans do her request without rejecting it. It can be said that Anna makes a request to Hans directly by showing her need.
2) Datum number :12/ F/ SBC/ D/ BR
Duration : 00:39:29,319 00:39:32,081
Context of situation : After Kristoff sings a song at her room, Anna comes and she makes request to Kristoff that she wants to go to North Mountain to find her sister, Elsa. At first, Kristoff rejects
Anna’s request, after that he agrees with Anna’s plan and they will go
in the morning before sun rises.
Anna : I want you to take me up the North Mountain. Kristoff : I don't take people places.
From the datum above, Anna as the speaker places her interest more blindly above Kristoff as the hearer. Anna has in position of control in this request. Then it is marked by the use of subject “I” as the person who needs something from the hearer. In this context, Anna wants to him to take her to North Mountain. She wants to find her sister, Elsa. Anna makes a request by using the words “I
want you to…” to make Kristoff do her request immediately. It can be
3) Datum number :17/ F/ SBC/ D/ BR
Duration : 01:30:03,000 01:30:04,999
Context of situation : After Anna backs to home, she makes many new rules. One of the rules is to stops make a business with Weselton because Duke of Weselton has bad motive toward her and her palace and he has aligned with Hans. Soldiers of Arendelle catch Duke of Weselton and they will give Duke of Weselton back to his hometown, but Duke of Weselton does not accept the reality because he feels as the victim of Hans’ deed. However the effort of Duke of Weselton does not succeed, the soldiers then take him back to the ship.
Duke of Weselton : I demand to see the Queen! Soldiers of Arendelle : - (not answering)
Chief Minister of Arendelle : Oh I have a message from the
Queen.
From the datum above, Duke of Weselton as the speaker places her interest more blindly above the soldiers as the hearer. Then it is marked by the use of subject “I” as the person who needs something from the hearer. In this context, Duke of Weselton demands his soldier of Arendelle to do his request. Duke of Weselton
makes a request by using the words “I demand…” to make the
that Duke of Weselton makes a request to soldiers directly by showing his demand.
2. The Strategy of Hearer-Oriented Conditions in Request Speech Act
In this kind of request speech act, the hearer is in a position of control to decide whether or not to perform the request. In this research, there are 10 data showing request of hearer-oriented condition. The data use ability (willingness) and suggestory formula. There are 5 datum that show the strategy of willingness or ability and 5 data that show the strategy of suggestory formulae. The description of each strategy of hearer-oriented conditions in request speech act can be shown in the following table
Table 4.2. The strategies of hearer-oriented conditions in request speech act
Kinds of strategies in Datum Number Number of
Occurrences
Willingness or ability 03/ F/ SBC/ A/ P, 04/ F/ SBC/ A/ P, 05/ F/ SBC/ A/ P, 06/ F/ HBC/ A/ P, 08/ F/ SBC/ A/ P
5
Suggestory formulae 09/ F/ HBC/ S/ P, 13/ F/ HBC/ S/ P, 14/ F/ HBC/ S/ N,
a) Ability or Willingness
The condition of ability refers to hearer’s capacity to perform the
desired act. In this research, there is only 5 datum using this kind of
request strategy and it is related to hearer’s capacity of both physical and
mental.
1) Datum number : 03/ F/ SBC/ A/ P
Duration : 00:23:43,753 00:23:46,650
Context of situation : Anna meets Hans in the dance’s floor. Hans helps Anna because Anna almost falls down after Anna and Elsa have a little trouble. Hans asks Anna to dance with him. After
that, Anna asks Hans to get out from the dance’s floor. They then get
exciting conversation in the balcony of dance’s floor.
Anna : Okay, Can I just say something crazy? Hans : I love crazy.
The datum above shows Anna becomes the speaker and Hans becomes the hearer, then it is marked by the expression “Can I” as a kind of request using hearer-oriented condition which focuses on the
hearer’s willingness. It means that Hans as the hearer is the person
who will do or refuse the Anna’s request. In this context, Anna asks for Hans’ permission to say something crazy that is to marry him. It
15/ F/ HBC/ S/ P, 16/ F/ HBC/ S/ P
can be said that Anna makes a request to Hans by asking for Hans’ willingness.
2) Datum number : 04/ F/ SBC/ A/ P
Duration : 00:25:28,732 00:25:30,933
Context of situation : Hans and Anna talk each other in the balcony. Anna tells Hans why Elsa shuts her out. And then Hans says that he will not shut her out because Hans has falling in love with her. Anna also loves him and then Hans asks Anna to marry him.
Hans : Can I say something crazy? Will you marry me? Anna : Can I just say something even crazier? Yes!
The datum above shows, Hans becomes the speaker and Anna becomes the hearer, then it is marked by the expression “Can I” is a kind of request using hearer-oriented condition which focuses on
the hearer’s willingness. It means that Anna as the hearer is the
person who will do or refuse Hans’ request. In this context, Hans asks
for Anna’s permission to say something crazy that is to marry him. It
can be said that Hans makes a request to Anna by asking for Anna’s willingness.
3) Datum number : 05/ F/ HBC/ A/ P
Duration : 00:25:32,976 00:25:35,196
that he will not shut her out because Hans has falling in love with her. Anna also loves him and then Hans asks Anna to marry him.
Hans : Can I say something crazy? Will you marry me? Anna : Can I just say something even crazier? Yes!
From the datum above, it can be said that Hans makes a request to Anna by asking for Anna’s willingness. It means that Hans becomes the speaker and Anna becomes the hearer, then it is marked by use of object “you” as the person who will do or refuse the
speaker’s request, to emphasize the request towards the hearer. In
this context, Hans asks something crazy to Anna that is to marry him. Hans makes a request to by using the word “Will you....” to ask
Anna’s willingness that is hearer’s condition both physical and
mental.
4) Datum number : 06/ F/ SBC/ A/ P
Duration : 00:25:53,134 00:25:55,631
Context of situation : Because Anna has agreed Hans’ request to
marry him, Anna and Hans go into the dance’s floor to meet Elsa.
They ask Elsa for her blessing to their marriage. They ask for it by using request.
Anna: May I present, Prince Hans of the Southern Isles. Hans : Your Majesty.
The datum shows that Anna becomes the speaker and Elsa becomes the hearer, then it is marked by the expression “May I” as a kind of request using hearer-oriented condition which focuses on the
hearer’s willingness. It means that Elsa as the hearer is the person
who will do or refuse the Anna’s request. In this context, Anna asks for Elsa’s permission to present Hans and to give her blessing to their marriage. It can be said that Anna makes a request to Elsa rather directly by asking for Elsa’s willingness.
5) Datum number : 08/ F/ SBC/ A/ P
Duration : 00:26:28,606 00:26:31,991
Context of situation : Elsa does not agree with Anna’s plan to marry Hans. Anna thinks that their marriage is to sudden because they know each other not too long ago. Elsa then wants to talk with Anna without Hans about Anna and Hans’s plan by using a request.
Elsa : May I talk to you, please? Alone.
Anna : No. Whatever you have to say, you... you can say to both of us.
From the datum above, it can be said that Elsa makes a request to Anna by asking for Anna’s willingness. It means that Elsa becomes the speaker and Anna becomes the hearer, then it is marked
by the expression “May I” as a kind of request using hearer-oriented
condition which focuses on the hearer’s willingness. It means that
request. In this context, Elsa asks for Anna’s permission to talk with
her alone without Hans that is to discuss about Anna’s plan to marry
Hans.
b) Suggestory formulae
By using suggestory formulae, the speaker makes his/her request more tentative and plays down his/her own interest as a beneficinary of the action. The followings are 5 data using this kind of request strategy. 1. Datum number : 09/ F/ HBC/ S/ P
Duration : 00:26:36,434 00:26:39,511
Context of situation : Elsa does not agree with Anna’s plan to marry Hans. Anna thinks that their marriage is too sudden because they know each other not too long ago. She makes a request to Anna by giving suggestion about her plan of marrying with Hans.
Anna : Fine. You can't marry a man you just met…You Can if it's true love.
Elsa : Anna, what do you know about true love?
someone who just met. It is shown by the utterance “you can’t ... you can if ... “.
2. Datum number : 13/ F/ HBC/ S/ P
Duration : 00:53:31,708 00:53:33,507
Context of situation : Anna finds where her sister, Elsa, is hiding. It is an ice palace in the top of mountain. Anna then opens the door and makes request to her two companions, Krisstof and Olaf by suggesting them to wait in front of the door.
Anna : It opened. That's a first. You should probably wait out here.
Krisstof : What ?
From the datum above, it can be said that Anna makes a request to Krisstof in the form of suggestion. It means that Anna becomes the speaker and Krisstof becomes the hearer, then it is marked by use of object “you” in the utterance as the person who will
do or refuse the speaker’s request, to emphasize the request towards
the hearer. In this context, Anna makes a request by giving suggestion to Krisstof that is to wait in front of the door because Anna wants to say something privately with her sister meanwhile Krisstof is just a stranger who wants to help her. The request using suggestory formulae
is marked with the use of modal ‘should’ in the utterance “You should
probably wait out here”.
Duration : 00:54:38,650 00:54:41,693
Context of situation : Anna apologizes to Elsa for her mistake about what happened in Arendelle. But, Elsa does not want to blame Anna and she just wants her to leave. Elsa does not want to cause
Anna’s condition worse with hermagic.
Elsa : No, it's okay… You don't have to apologize. But you should probably go, please.
Anna : But I just got here.
From the datum above, it can be said that Elsa makes a request to Anna in the form of suggestion. It means that Elsa becomes the speaker and Anna becomes the hearer, then it is marked by use of object “you” in the utterance as the person who will do or refuse the
speaker’s request, to emphasize the request towards the hearer. In this
context, Elsa makes a request by giving suggestion to Anna that isto leaver her alone so that nothing bad will happen again because of her uncontrolled magic power. The request using suggestory formulae is
marked with the use of modal ‘should’ in the utterance “But you
should probably go, please.”
4. Datum number : 15/ F/ HBC/ S/ P
Duration : 00:58:09,749 00:58:11,099
request by suggesting her to go home. Anna refuses to go home without bringing Elsa back to Arendelle.
Krisstof : Anna, I think we should go.
Anna : No. I'm not leaving without you, Elsa.
From the datum above, it can be said that Krisstof makes a request to Anna in the form of suggestion. It means that Krisstof becomes the speaker and Anna becomes the hearer, then it is marked by use of object “we” in the utterance that refers to both speaker and
hearer. However, the speaker rather uses ‘we’ than ‘you’ so that the
hearer will do what he asked though he is also do it too. In this context, Krisstof makes a request by giving suggestion to Anna that is to go back to Arrendele so nothing bad happened again to her. The request
using suggestory formulae is marked with the use of modal ‘should’ in
the utterance “Anna, I think we should go.”
5.Datum number : 16/ F/ HBC/ S/ P
Duration : 01:01:59,602 01:02:01,573
Context of situation : Krisstof wonders why Anna’s hair
becomes white. It may be caused by Elsa’s magic that makes her
“Frozen”. Anna thinks that her white hair is caused by the snow when
saying that her hair is turning white. It means that Anna’s conditon
worsen.
Anna : Just fell off a cliff. You should see your hair. Krisstof : No, yours is turning white.
From the datum above, it can be said that Anna makes a request to Krisstof in the form of suggestion. It means that Anna becomes the speaker and Krisstof becomes the hearer, then it is marked by use of object “you” in the utterance as the person who will do or refuse the
speaker’s request, to emphasize the request towards the hearer. In this
context, Anna makes a request by giving suggestion to Krisstof that is
to see his hair turning white. On the other hand, Anna’s hair is actually
turning white naturally not because of the snow like Krisstof’s but she does not believe it. The request using suggestory formulae is marked
with the use of modal ‘should’ in the utterance “You should see your
hair.”
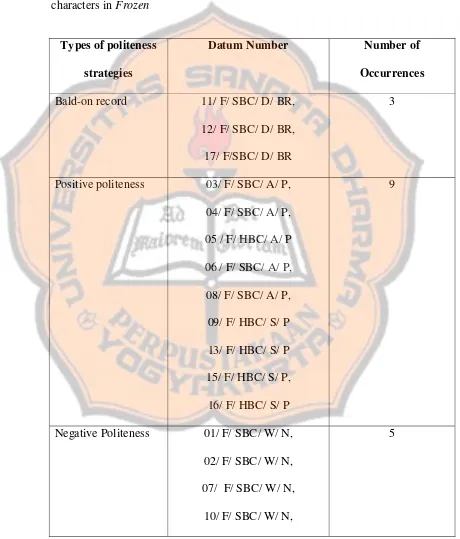
B. Types of Politeness Strategy Used to Make a Request Employed by
Characters in Frozen
1. Bald-on Record
In this research, there are only 3 data of request of speaker-based condition using bald on record strategy. Bald-on record strategy does not
attempt to minimize the threat to hearer’s face. Brown and Levinson state
that speaker mostly uses bald-on record strategy when he wants to do FTA (Face Threatening Acts) with maximum efficiency toward the hearer’s face. This strategy will make the hearer feels uncomfortable. This strategy is a direct way of saying things, without any minimization to the imposition, in a direct, clear, unambiguous, and concise way. This strategy is employed by the characters in some occasion, they are emergency situation and unequal power relationship.
1)Datum number : 11/ F/ SBC/ D/ BR
Duration : 00:30:24,108 00:30:27,210
Context of situation : Elsa leaves her palace after she did magic with her hands. All people in palace have known her secret so she must run away. Anna then chases after her to bring her back to the palace. Elsa chooses Hans to replace her sister to handle Arendelle for a moment.
14/ F/ HBC/ S/ N,
Off record - -
Anna : I need you here to take care of Arendelle. Hans : On my honor.
From the datum above, it can be said that Anna makes a request to Hans by using politeness of bald-on record strategy. Anna as the speaker does not try to minimize the threat to Hans’ face as the hearer. When making a request, Anna wants to do FTA (Face Threatening Acts) with maximum efficiency toward Hans’ face.
Bald-on record strategy is marked by using the expressiBald-on ‘I need you here
to …. ‘ so that this strategy will make Hans feels uncomfortable and
cannot reject Anna’s request. Anna makes request directly, without
any minimization to the imposition because the conversation happens in an emergency situation.
2) Datum number : 12/ F/ SBC/ D/ BR
Duration : 00:39:29,319 00:39:32,081
Context of situation : After Kristoff sings a song at her room, Anna comes and makes request to Kristoff that she wants to go to North Mountain to find her sister, Elsa. At first, Kristoff rejects
Anna’s request, after that he agrees with Anna’s plan and they will go
in the morning before sun rises.
Anna : I want you to take me up the North Mountain. Kristoff : I don't take people places.
Anna as the speaker does not try to minimize the threat to Kristoffs’ face as the hearer. When making a request, Anna wants to do FTA (Face Threatening Acts) with maximum efficiency toward Kristoffs’ face. Bald-on record strategy is marked by using the expression ‘I want you to…. ‘ so that this strategy will make Kristoff feels uncomfortable and cannot reject Anna’s request. Anna makes request directly, without any minimization to the imposition because of unequal power between Anna and Kristoff. Anna has a power as the Princess of Arendelle while Kristoff is just a true outdoorsman. He lives high up in the mountains where he harvests ice and sells it to the kingdom of Arendelle.
3) Datum number : 17/ F/ SBC/ D/ BR
Duration : 01:30:03,000 01:30:04,999
Context of situation : After Anna goes back home, she makes many new rules. One of the rules is to stop making a business with a Duke of Weselton because he has bad motive toward her and her palace and he has aligned with Hans. Soldiers of Arendelle catch Duke of Weselton and they will give Duke of Weselton back to his hometown, but Duke of Weselton does not accept the reality because he feels as the victim of Hans’ doing. However the effort of Duke of Weselton does not succeed, the soldiers then take him back to the ship.
Soldiers of Arendelle : - (not answering)
Chief Minister of Arendelle : Oh I have a message from the
Queen.
From the datum above, it can be said that Duke of Weselton makes a request to the soldiers of Arendelle by using politeness of bald-on record strategy. Duke of Weselton as the speaker does not try to minimize the threat to soldiers’ face as the hearer. When making a request, Duke of Weselton wants to do FTA (Face Threatening Acts) with maximum efficiency toward the soldiers’ face. Bald-on record
strategy is marked by using the expression ‘I demand you…. ‘ so that
this strategy will make the soldiers feel uncomfortable and cannot
reject Duke of Weselton’s request. Duke of Weselton makes request
directly and briefly, without any minimization to the imposition because of unequal power between Duke of Weselton and the soldiers. Duke of Weselton has higher position than the soldier.
2. Positive Politeness
such as requesting through friendship or family, seeking agreement, and avoiding disagreement.
1) Datum number : 03/ F/ SBC/ A/ P
Duration : 00:23:43,753 --> 00:23:46,650
Context of situation : Anna meets Hans in the dance floor. Hans helps Anna because Anna almost falls down after Anna and Elsa have a little trouble. Hans asks Anna to dance with him. After that, Anna
asks Hans to get out from the dance’s floor. They then get exciting
conversation in the balcony of dance’s floor.
Anna : Okay, Can I just say something crazy? Hans : I love crazy.
From the datum above, it can be said that Anna makes a request to Hans by using politeness of positive strategy. Positive politeness applied by Anna as the speaker provides an attempt to minimize the damage to Hans’ face as the hearer. This strategy is intended to avoid the conflict and to minimize the social distance between the speaker and the hearer. Anna is the princess of Arendelle while Hans is the prince of Northern Island. Both of them have not known each other yet but they fall in love. Hans wants to express his love first by requesting permission to Anna. This strategy is marked
by the expression ‘…Can I …?” in order to make the request more
that is a permission to say something crazy. As a result, Hans accepts
Anna’s request.
2)Datum number : 04/ F/ SBC/ A/P
Duration : 00:25:28,732 00:25:30,933
Context of situation : Hans and Anna talk to each other in the balcony. Anna tells Hans why Elsa chases her away. And then Hans says that he will not chase her away because Hans has falling in love with her. Anna also loves him and then Hans asks Anna to marry him. Hans : Can I say something crazy? Will you marry me?
Anna : Can I just say something even crazier? Yes!
permission to say something crazy about proposing her. As a result, Anna accepts Hans’s request to marry him.
3)Datum number : 05/ F/ HBC/ A/ P
Duration : 00:25:32,976 00:25:35,196
Context of situation : Hans and Anna talk each other in the balcony. Anna tells Hans why Elsa shuts her out. And then Hans says that he will not shut her out because Hans has falling in love with her. Anna also loves him and then Hans asks Anna to marry him.
Hans : Can I say something crazy? Will you marry me? Anna : Can I just say something even crazier? Yes!
that is a permission to say something crazy about proposing her. As a result, Anna accepts Hans’s request to marry him.
4) Datum number : 06/ F/ SBC/ A/ P
Duration : 00:25:57,498 00:26:00,421
Context of situation : Because Anna has agreed Hans’ request to
marry him, Anna and Hans go into the dance’s floor to meet Elsa.
They ask Elsa for her blessing to their marriage. They ask for it by using request.
Anna : May I present, Prince Hans of the Southern Isles. Hans : Your Majesty.
Elsa : - (surprised)
From the datum above, it can be said that Anna makes a request to Elsa by using politeness of positive strategy. Positive politeness applied by Anna as the speaker provides an attempt to minimize the damage to Elsa’ face as the hearer. This strategy is intended to avoid the conflict and to minimize the social distance between the speaker and the hearer. Anna is Elsa’s little sister and also Elsa is the queen of Arrendele. This strategy is marked by the
expression “May I present…?” in order to make the request more
him not too long ago and then she wants to introduce him as her future husband.
5) Datum number : 08/ F/ SBC/ A/ P
Duration : 00:26:28,606 00:26:31,991
Context of situation : Elsa does not agree with Anna’s plan to marry Hans. Anna thinks that their marriage is to sudden because they know each other not too long ago. Elsa than wants to talk with Anna without Hans about Anna and Hans’s plan by using a request.
Elsa : May I talk to you, please? Alone.
Anna : No. Whatever you have to say, you... you can say to both of us.
From the datum above, it can be said that Elsa makes a request to Anna by using politeness of positive strategy. Positive politeness applied by Elsa as the speaker provides an attempt to minimize the damage to Anna’ face as the hearer. This strategy is intended to avoid the conflict and to minimize the social distance between the speaker and the hearer. Anna is Elsa’s little sister and also Elsa is the queen of Arendelle. This strategy is marked by the
expression “May I talk…?” in order to make the request more polite
to hear than it is said directly. Elsa wants to talk to Anna alone. As a
result, Anna accepts Elsa’s request.
6) Datum number : 09/ F/ HBC/ S/ P
Context of situation : Elsa does not agree with Anna’s plan to marry Hans. Anna thinks that their marriage is too sudden because they know each other not too long ago. She makes a request to Anna by giving suggestion about her plan of marrying with Hans.
Anna : Fine. You can't marry a man you just met…You can if it's true love.
Elsa : Anna, what do you know about true love?
From the datum above, it can be said that Anna makes a request to Elsa by showing her suggestion using positive politeness. In this case, Anna has position as the speaker and Elsa is as the hearer. Then, positive politeness is marked by the use of modal “can/
can’t” in the utterance ‘You can't marry a man you just met…You can
if it's true love’ as a form of suggestion so the hearer is willing to do
what the speaker said. In this context, Anna wants Elsa not to marry Hans by giving suggestion.
7) Datum number : 13/ F/ HBC/ S/ P
Duration : 00:53:31,708 00:53:33,507
Context of situation : Anna finds where her sister, Elsa, is hiding. It is an ice palace in the top of mountain. Anna then opens the door and makes request to her two companions, Krisstof and Olaf by suggesting them to wait in front of the door.