IDENTITY-BUILDING STRATEGY IN THE ENGLISH ADVERTISEMENTS IN KOMPAS NEWSPAPER
A THESIS
Presented as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Magister Humaniora (M.Hum.) Degree
in English Language Studies
by
Lelly Sepniwati 106332014
THE GRADUATE PROGRAM OF ENGLISH LANGUAGE STUDIES SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
iv
DEDICATION PAGE
My brethren, have not the faith
of our Lord Jesus Christ, the Lord of glory,
with respect of persons.
For if there come unto your assembly
a man with a gold ring, in goodly apparel,
and there come in also a poor man in vile raiment;
And ye have respect to him that weareth the gay clothing,
and say unto him, Sit thou here in a good place;
and say to the poor, Stand thou there, or sit here under my footstool:
Are ye not then partial in yourselves,
and are become judges of evil thoughts?
James 2:1-4 (KJV)
v
STATEMENT OF WORK ORIGINALITY
This is to certify that all ideas, phrases, sentences, unless otherwise stated, are the ideas, phrases, and sentences of the thesis writer. The writer understands the full
consequences including degree cancellation if she took somebody else’s ideas,
vi
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma :
Nama : Lelly Sepniwati NIM : 106332014
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul :
Identity-Building Strategy in the English Advertisements in Kompas Newspaper
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Dibuat di Yogyakarta
vii support and encourage me in the completion of my thesis. My special gratitude goes to Dr. B. B. Dwijatmoko, MA, my thesis advisor, for his patience and kindness in giving me invaluable guidance and suggestion in the completion of this thesis. I would also like to thank the distinguished lecturers: Prof. Dr. Soepomo Poedjosoedarmo, Dr. Novita Dewi, M.S., M.A. (Hons), Dr. Fr. B. Alip, M. Pd., M. A., Drs. Barli Bram, M.Ed., Ph.D., Dr. J. Bismoko, Dr. Alb. Budi Susanto, S.J., Prof. Dr. Ch. Bakdi Sumanto, S.U., and Drs. F.X. Mukarto, M.S., Ph.D., for their guidance and willingness to share their valuable thoughts and experiences during my educational journey in Sanata Dharma University. I also express my sincere gratitude to Mbak Lely, Pak Mul, and all staff of Sanata Dharma University for their assistance in my study.
viii
also like to thank my dearest friends, Susva, Frisma, Desy, Nora, Kristian, Andre, Nisa, Yentli, and Muamar, for supporting and accompanying me in the precious moments of my life.
My deepest gratitude goes to my late father, Pdt. Drs. Yaphie Gaman, my beloved mother, Pdt. Awina Gaman, my elder sisters Leni, Yana, and Ani, my elder brother, Adi, and my big family. I am sincerely grateful for their pray, patience, love, encouragement, support, and admonition given to me to complete my study. Without their irreplaceable presence, I would not have the strength to follow this path.
ix
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH…… vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ……… vii
CHAPTER II. LITERATURE REVIEW ………... 10
2.1 Advertisements .……….. 10
2.2 Printed Advertisements ……… 12
2.3 Language in Advertisements ………... 16
2.4 Identity-Building Strategy ………... 18
2.5 Discourse Analysis ……….. 20
2.6 Transitivity Processes ……….. 24
2.6.1 The Process and Participants ………. 25
2.6.1.1 Material clauses: processes of doing-and-happening………. 26
2.6.1.2 Mental clauses: processes of sensing ………. 29
2.6.1.3 Relational clauses: processes of being and having…………. 31
2.6.1.4 Behavioural clauses………. 36
1.6.1.5Verbal clauses………. 36
2.6.1.6 Existential clauses………... 37
2.6.2 Circumstances……….………... 37
x
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ………. 51
3.1 Type of the Study ..……….. 51
3.2 Source of the Data ....………... 52
3.3 Data Collection ………... 54
3.4 Data Presentation Technique ……….. 56
3.5 Data Analysis of the Study ……….. 57
3.6 Substantiation ….……… 59
CHAPTER IV. ANALYSIS RESULTS AND DISCUSSION …………... 63
4.1 The Transitivity Processes Analysis………. .……. 63
4.1.1 The Relational Process Analysis……… 65
4.1.2 The Material Process Analysis…………..……… 80
4.2 The Social Actor Representation Analysis..………. 90
4.2.1 The Exclusion/Inclusion Representations……... 90
4.2.2 The Active/Passive Representations………..……. 97
4.2.3 The Personalization/Impersonalization Representations..………….. 103
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS ………… 109
5.1 Conclusions ………... 109
5.2 Recommendations ………. 111
BIBLIOGRAPHY ………... 114
xi
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1 The characteristics of process types ………. 26
Table 2.2 The principal categories of ‗relational’ clause... 31
Table 2.3 Examples of process in behavioural clause………... 36
xii
LIST OF CHARTS
Chart 4.1. The transitivity processes in the data ……….………….. 64
Chart 4.2. The relational processes in the data ………... 66
Chart 4.3. The material processes in the data ……….. 81
Chart 4.4. Inclusion/exclusion representations in the data ……… 91
Chart 4.5. Active/passive representations in the data ... 98
xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1 The Selected Display Advertisements Taken from Kompas
Newspaper……… ………. 117
Appendix 2 The Domain of the Commodity in the Selected Data………. 176
Appendix 3 The Transitivity Clauses in the Data ………..……… 178
Appendix 4 The Relational Clauses in the Data ……….……… 186
Appendix 5 The Material Clauses in the Data ……… 191
xiv ABSTRACT
Lelly Sepniwati. 2014. Identity-Building Strategy in the English Advertisements in
Kompas Newspaper. Yogyakarta: The Graduate Program in English Language Studies, Sanata Darma University.
Advertisements have become an integral part in the contemporary community. Their significance in asserting a certain idea is widely acknowledged, especially the consumerism ideology. In spreading this ideology, the commercial advertisements have implemented various strategies to increase the capital advantage aimed by the advertisers. Concerning the calculated framework of consumerism, there is a tendency from the producers to imply an influential effect of the brands and the products on the social value toward the community. This tendency is recognized as the identity-building strategy. In this identity representation, the common technique found and analyzed by many researches is the English utilization in the non-English speaking countries. The advertisers are prone to strengthen the English implication as the international language with the manner in which it is configured, both in the grammatical and lexical choices, in the identity-building strategy. For that matter, the problems of the study are formulated into two consisting of what types of transitivity process are typically exploited in the English clauses and what representations of social actor are applied in constructing the identity-building strategy in the
Based on the indications, this study emphasized the commercial advertisement attempts to persuade the customers to buy the product by promoting additional social and psychological benefits of the merchandise, namely identity. The data were taken from a prominent newspaper which contains many commercial advertisements, namely Kompas newspaper. There were 188 English clauses contained in 59 display advertisements from the first to fourteenth June in 2012. In analyzing these clauses, there were two methods applied in the research. The transitivity process as the initial step was conducted to examine the exploitation of the grammatical and lexical choices in proposing the appealing value of social identity in the discourse. Consecutively, the social actor representation analysis was implemented to give better understanding on how the commodities and the social community are generally depicted considering the effect they have toward each other in the identity assigning strategy.
xv
participant strong influences toward the other. When the action refers to the consuming act, the influence of the customers is significant in the realization. However, the focus is shifted when the depicted processes denote the providers for this improvement attitude. It shows that the ones that have greater influence in realizing the transformation attitude are the brands and the products.
xvi ABSTRAK
Lelly Sepniwati. 2014. Identity-Building Strategy in the English Advertisement in
Kompas Newspaper. Yogyakarta: Program Paskasarjana Kajian Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Iklan telah menjadi bagian integral dalam masyarakat kontemporer. Peranan penting iklan dalam menegaskan sebuah ide khususnya ideologi konsumerisme telah diakui secara luas. Dalam menyebarkan ideologi ini, iklan komersial telah menerapkan berbagai macam strategi untuk meningkatkan keuntungan finansial yang ditargetkan oleh para pengiklan. Berkenaan dengan kerangka pemikiran konsumerisme, ada kecenderungan dari produsen untuk mengimplikasikan pentingnya pengaruh merek dan produk terhadap nilai sosial masyarakat. Kecenderungan ini dikenal sebagai strategi pembentukan identitas. Dalam penggambaran identitas ini, teknik yang umum ditemukan dan dianalisis oleh banyak penelitian adalah pemanfaatan Bahasa Inggris di negara-negara yang bahasa nasionalnya bukanlah Bahasa Inggris. Para pengiklan seringkali menguatkan implikasi dari posisi Bahasa Inggris sebagai bahasa internasional di dalam strategi pembentukan identitas dengan pemilihan tata bahasa dan kosakata yang digunakan di dalam teks. Dengan bertumpu pada wacana ini, penelitian ini memiliki dua pokok permasalahan yang terdiri dari proses transitivitas apa yang biasanya digunakan di dalam klausa Bahasa Inggris dan representasi aktor sosial apa yang digunakan dalam strategi pembentukan identitas pada iklan tertulis berbahasa Inggris.
Berdasarkan indikasi tersebut, penelitian ini memfokuskan pada bagaimana iklan komersial membujuk para konsumer untuk membeli barang yang dipromosikan dengan menawarkan keuntungan sosial dan psikologis barang tersebut, yaitu identitas. Data diambil dari sebuah surat kabar terkenal yang berisikan banyak iklan komersial, yaitu harian Kompas. Ada 188 klausa Bahasa Inggris yang terdapat dalam 59 iklan display terhitung dari tanggal satu sampai empat belas Juni 2012. Dalam menganalisis klausa-klausa ini, ada dua metode yang diterapkan di dalam penelitian. Proses transitivitas adalah metode pertama untuk menelurusi eksploitasi pemilihan tata bahasa dan kosakata dalam menyiratkan nilai menarik identitas sosial di dalam wacana. Selanjutnya, analisis representasi aktor sosial dilakukan untuk memberikan pemahaman yang lebih mendalam mengenai bagaimana komoditi dan masyarakat sosial secara umumnya digambarkan di dalam strategi pembentukan identitas dengan mempertimbangkan pengaruh yang mereka miliki terhadap satu sama lain.
xvii
biro iklan sering menekankan sisi peningkatan diri dan aksi yang berkesinambungan ini sebagai hasil dari pengaruh kuat seorang aktor terhadap aktor lainnya. Ketika proses merujuk pada kegiatan pembelanjaan, pengaruh pelanggan sangatlah penting dalam mewujudkannya. Namun, hal ini berubah ketika proses tersebut menunjukkan penyedia jasa dalam sikap peningkatan diri. Ini menunjukkan bahwa keberadaan yang memiliki pengaruh lebih kuat dalam mewujudkan sikap transformasi diri ini adalah merek dan produk.
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In the beginning chapter of this study, the introduction of this thesis is presented. In the background of the study, as the opening part, it elaborates the importance of advertisements and its relation with society, a glance of the elements in advertisements, the types of analysis which are implemented and the classification of the study. This part is followed by the problem formulations comprised of the research questions which are explained further in the research objectives part. Eventually, this chapter ends with the significance of this research in some fields of study framed in the benefits of the study.
1.1 Background of the Study
For the past few years, many countries had been affected by the global monetary crisis which was also referred to as the Great Recession. Indonesia was one of several countries which managed to avoid the impact of the Great Recession. In spite of its status as a developing country, Indonesia was able to maintain its stable economic growth compared with many European countries which had been affected by the recession in a great extent.
Indonesia managed to decrease the impact of the global economic crisis due to several reasons. The main contributor was consumption. Nasution in Kompas
having the most stable economic growth in the world. He explained that the main factor behind this positive condition was brought by the enormous consumption rate from both the household and the government sectors followed by the export and foreign investment sectors. This positive economic condition makes Indonesia one of the prominent marketing industries in the world.
In line with the marketing notion, it has been widely known that in order to make the product purchased by the consumers in a great quantity and continuously, there must be a well-developed marketing strategy to realize it. One of the most common applications is the usage of advertising. With creative words and layouts suitable with the context, advertisements have an ability to penetrate the mind of society in accepting certain kind of messages which are implied in them. Hence, it is not an understatement that advertisements are considered as one of the most powerful devices in manipulating the subconscious realm of the audience. Simultaneously, advertisements grow considerably in intense amount recently in Indonesia.
Due to its main purpose, advertisements, namely commercial advertisement, ooze with the ideology of consumerism. This ideology is imbued in advertisements by exploiting the desires, feelings, and needs possessed by an individual (Goatly, 2000). The copywriters utilize this exploitation by offering positive values of the products or services toward the readerships. In other words, they sell them by entrancing the readerships of the significant benefits they can gain in their daily life.
In offering these benefits, advertisement uses different strategies deemed to be appropriate in the respectable context of the target market. Those strategies can be in the form of informative content, influencing approaches, emotive appeal, and brand exposure (Armstrong, 2010). Thus, to fully grasp the situation and condition of the prospective buyers, the advertisers from transnational and international companies usually employ some market researchers to recognise or create fresh methods of consumption (Goatly, 2000). Afterwards, the findings of the researches will be utilized to segment the market according to numerous specialised niches which are fragmented based on the income level, age, household type and locality. This strategy is able to guide the change of culture rapidly and enable the development of modern consumer capitalism encouraged by the powerful economic groups in the society.
even literate in English. Such techniques should not be applied by the advertisers as it is very ineffective for the financial purpose. Nevertheless, the reality speaks otherwise.
There is an underlying motive which drives the robust of the English exploitation in the domestic country. Bhatia (2006) argues that this seemingly counter-intuitive and counter-productive advertisement actually relies on unconscious planning by the national or international advertisers who assume that their readerships are bilingual in English. This assumption foregrounds a conceptualization of the global citizen reinforcing English as a prerequisite to be acknowledged as a global citizen.
This particular phenomenon suggests that English enhances the values of the advertised products or services. The advertisers consider English as a ―cool‖ language which has miraculous power to render the audience identity to become
―international, modern, rational, objective, ethno-cultural stereotypes, etc.,‖ (Bhatia, 2006). This identity-building propaganda is a formidable appeal of the product for it is typically inclined by the contemporary society nowadays.
advertisement is viewed as a discourse in this study as it expresses identity representation by means of specific sets of linguistic, visual and other semiotic resources (Machin and van Leeuwen, 2007).
The view is grounded by the concept of discourse in the way it perceives text as a tool that functions above the grammatical and lexical construction applications. Fairclough (1995) argues that texts comprise of two fundamental social practices, specifically cognition and representation of the reality, and social interaction. The linguistic configurations are constructed by the producers to present and describe the world based on their perspective to the others. This communication is motivated by certain idea or principle which is designed to penetrate the mind of society. This
‗conversion’ can also be used to strengthen their domination in the community. It is in line with the purpose of advertisement in this study which is to assert identity- building propaganda in the context of Indonesia intended by the large industries incorporated in the persuasive element for the benefit of monetary income.
To figure out the pattern in this social practice, there are two types of method employed in this study. The first method is the application of Systemic Functional Grammar proposed by Halliday (2004). This method is considered appropriate because it sees the meaning mirrored by the functions of the structures and the constituents of linguistic elements in a particular context as the primary concern (Lock, 1996). The communicative aspect of the text is emphasized simultaneously with the rules implemented in the formation of linguistic element.
in representing the world and how they act and relate to each other (Thompson, 2004). In other words, it analyses the grammatical and lexical features contained in a text and correlates them to reflect the idea, belief, opinion, notion, etc. in certain context which is in line with the purpose of this study. Therefore, the manner in which the English linguistic features configure the positive identity-building message can be traced in the persuasive element of the advertisements.
The second method is closely related to the initial type. However, the major interest is dedicated to the participants involved in the social activity. It is embodied in the social actor representation introduced by van Leeuwen (2008). This method is regarded as an important enclosure in the analysis for it uncovers the systematic consideration on the way the main social actors are represented in relation with the identity construction by the powerful economic groups in Indonesia.
Meanwhile, the source of data in this study is the English advertisement in
advertisement to persuade the readerships to buy the product or use the service presented in the newspaper advertisements in relation to the identity-building strategy.
1.2 Problem Formulation
Based on the explanation above, the problems were formulated as follows. 1. What transitivity processes are typically exploited in the English clauses to
construct the identity-building strategy in the English printed advertisements? 2. What are the representations of social actors in constructing the identity-building
strategy in the English printed advertisements? 1.3 Research Objectives
As it has been mentioned earlier, the producers of advertisement attempt to hypnotize the market to consume the product or service by applying identity-building strategy in the discourse. Therefore, the objectives of this study are to find the traces of this identity-building pattern employed in the grammatical and lexical features of English contained in the print advertising and to reveal the social actor representations in the aforementioned social practice. For that purpose, this study utilizes transitivity processes and social actor analysis as the main tools which are integrated in the context of the advertisements.
general transitivity processes in motivating inherent image or personality fabrication integrated in the commercial discourse in Indonesia.
Afterwards, it is deemed necessary to find how the cluster of people is represented in realizing this identity transformation activity. Thus, the second objective of this study is to uncover the social actor representational choices in the referred social practice. It is congruent with the purpose of social actor representational analysis for it assesses the categorization of people ingrained in the discourse in terms of their roles and social strata in the society (Machin and van Leeuwen, 2007). Through the incorporation between these two methods, there is an expectation that the results of the analysis can reflect the manner in which an aspirational identity is constructed through the spectacles of corporate institutions, so that it can intensify the appeals of the brand toward the target market.
1.4 Research Benefits
Theoretically, this study can give contribution to the discourse analysis, especially in the field of advertisement. It is intended to enrich the discussion of the language of advertisements concerning the notion of identity reconstruction strategy which is eloquently designed by the producers of advertisements.
In addition, the practical benefit of this study is to present better understanding on the system of language use in advertisement. In this case, the way English is used by the copywriters integrated with the context of the discourse for the purpose to persuade the readers to consume the advertised products or promoted
10
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
In this chapter, the review of theories applied in this study and their applications are presented. There are several theories which become the foundation of this study. They are the theory of advertisement, language in advertisement, discourse analysis, transitivity, and social actor representation. The way these theories implemented is summarized in the theoretical framework in the following part. In addition, the related studies are also presented to show several similar studies conducted in this field.
2.1 Advertisements
product or service, this type of advertisement pays more attention on the effort of increasing the good image of an institution or company or suggesting an idea toward the audience. words, it is a text to sell goods or services of the producers for monetary purpose.
To reach the monetary benefit aim, advertisement cannot be separated from the power of persuasion. In fact, this power is the integral part of advertisement. It is unquestionable because advertising is a mean of a company designated to sell certain commodities and services, propose an idea and enhance the image of an institution or company (Danesi, 2002; Goddard, 1998). Mostly for the commercial advertisements, it is a massive industry involving a great amount of capital in the business focused on
stimulating the ‗consumption of the goods and services advertised’ (Paxson, 2010) toward the audience. Therefore, without the persuasive essence, any kind of form of advertisement is meaningless resulting in a significant financial loss.
from the merchants without asking what the manufacturer was because everything was created and crafted in a limited production manually. Most people directly offered their services to the customers with the absence of organization or company. This tradition drastically changed when machine was introduced in the Industrial Revolution. Small scale production was abandoned gradually and converted into mass production. Consequently, the manufacturers met new problem of how they needed to sell their large quantities of product in a rapid way which occurred before the birth of automatic devices. Thus, advertisements were the needed solution for this matter.
Early advertisements were not as complicated as the current situation though. They were usually created by the manufacturers of the advertised products with the
consequences of ‗little selling’ (Paxson, 2010) because they did not possess the ability of selling charmingly though they knew their products thoroughly. The competitors started to act aggressively in the early 1900s by seeking the help of advertisement agencies which had been evolved from placing the advertisements to be published into firms that exploits creative strategy and technique in the promoting media.
2.2 Printed Advertisements
advertisements (Belch & Belch, 2003). They need to consider the effectiveness of the advertisements through the use of certain media.
Nowadays, the types of media have been developed from the printed ones, such as newspapers, brochures, etc., into the digital ones, such as internet. Hence, these variations of media have affected the form of advertisements. It is hardly possible to generalize the components or structures of advertisements in every media because of different characteristics possessed by each type of media. Despite the complexity, there is one type of advertisement which can reach the largest market, namely the printed advertising (Danesi, 2002).
This advertisement employs static components thus it tries to compensate the immobile elements by using various techniques for the readers to catch their interest at least for a short period of time at the advertisement (Paxson, 2010). It tends to get the attention by relying on the visual elements in which the photographs and illustrations work carefully to cause the image transmits information as much as it can without putting a heavy burden for the customers in gathering the meaning (Paxson, 2010).
photo or drawing, caption, copy, paragraph headings, logo, price, response device and overall layout.
The first classification focuses on the organization of the execution of the headline, pictures, and text. In other words, the main focus is the layout. Thus, the structures of the headlines and text are not described in a satisfactory way which is crucial in analyzing the third aspect of strategy—linguistics—in an advertisement (Myers, 2010). The latter classification is more detailed related to the ‗missing’ elements. Unfortunately, many advertisements do not apply the whole elements in the organization and the tendency of overlapping can be found in a high frequency. This flaw may cause unnecessary complexity in the research.
Aside of the above organization, there is a classification which divides the basic elements of the printed advertisements. These fundamental elements are comprised of headlines, body copy, visual elements, and layout (Belch & Belch, 2003). By using this classification, the tendency of overlapping can be decreased significantly because the rest of the elements can be part of those basic elements. Furthermore, most of the printed advertisements apply these basic elements in their structural domains.
larger than the body copy which is recognized as the subheads. The following element is the main text which describes the product or service advertised referred as the body copy. The main selling message for the product or service is the content of this part. Hence, this element is usually known as the ―heart of the advertising
message‖ (Belch & Belch, 2003). Those linguistic aspects are usually accompanied by illustrations which are the third major component. Its function is to attract major component in the structural domains of a printed advertisement.
These structural domains are configured cleverly based on the creativity of the producers. Though creativity does not have any boundary, the producers need to consider the type of printed advertisement they intend to use. There are several types of printed advertisement. Despite these varieties, display printed advertisement is the most favourable marketing tool chosen by many corporations.
‗domain’, they can be found throughout the newspaper and generally apply visual and
verbal device configurations (Belch and Belch, 2003).
The second consideration is related to the marketing region of the products or services merchandised in this type. The marketers of branded products or services in this advertisement are usually sold their merchandise or commercial act on a national or regional level (Belch and Belch, 2003). They are designed for the purpose of
creating and maintaining demand for a company’s product or service. Moreover, they
act as a promoting device for the local retailers that stock and market the advertiser’s
products.
Based on the indication presented above, an advertisement is constructed of
multiple layers of creative symbols in such a way in order to ‗mystify’ the customers
to consume the products. However, these ‗unrestricted’ attempts to enthral the
prospective buyers actually need to take some salient considerations in creating this money maker device. Therefore, the following discussion present the restrictions of the communicative aspect that envelope the implied meaning camouflaged by the creators of the advertisements.
2.3 Language in Advertisements
Due to the strategy and technique, advertisement is quite different with other types of text, especially in the language aspect. An advertisement uses creative or innovative language in order to catch the attention of the target audience (Myers, 2009). This cogitation is extremely crucial because every competitor compete with
each other to achieve the potential customers’ attention which is the initial stage of
various attention getter elements, mostly humour, sex and emotion (Sutherland, 2008).
It should be taken into account that getting attention is merely one component of effective advertisements. The advertisements are not considered fully effective if the audience fails to direct their attentions toward the brands and the contained messages (Sutherland, 2008). Furthermore, the various elements, such as verbal and visual, in the advertisements should blend together in a perfect harmony. Therefore, these diversities should be seen as a mosaic in which the uniqueness of each element is presented together in an artistic way. For the audience to understand the content of the advertisements, the elements should project coherence which can be captured from the network of creativity by the advertising agencies (Matheson, 2005).
However, there is an additional crucial information about the elements in the advertisements regarding with the language is the focus. Sugarman (2007: 29) states
that ―All the elements in an advertisement are primarily designed to do one thing and
one thing only: get you read the first sentence of the copy.‖ Every element is
important because they constitute a single purpose in making the readers read the copy. This statement leads to a conclusion that the copy of an advertisement is the main selling point in the promotional text.
the context (Myers, 2009). The copywriters should discuss the linguistic elements contain in the advertisements with their production teams whether they are appropriate or not with the other elements in advertisements. They also need to gain agreement from the clients whether their advertisements can bring the intended image of the product or services. The language must not cross the boundary of legal regulatory constraints in particular domains. In brief, these skilled professionals should create an advertisement under the supervision of bureaucrats and combine those regulations in their works (Myers 2009).
Leaving aside the regulation constriction, this type of text offers a unique characteristic of language differs from others. Myers (2009) argues that advertisements do not have special register of their own because they usually adopt various kinds of grammatical features or lexis contained in other genres. He explains that, in the environment saturated with advertising, they need to make clever use of language to stand out, to engage the reader/viewer, to be talked about and recycled in popular culture. In turns, innovative use of language is constantly foregrounded for the purpose and audience of advertising.
2.4 Identity-Building Strategy
Nowadays, the linguistic choices of many advertisements are prone to convey a particular message to promote the brand or product toward the audience. The accompanying persuasive aspect is the identity-building implication. Regarding the
commercialization of identity, it is very important to understand the term ―identity‖.
is. It relates to the perspective on the way someone defines his or herself in the community. The markers of identity are varied, from age, nationality, job and income to social class and psychological aspects, such as free, fun, independent and loving individual. These traits are salient to prove and acknowledge the existence of someone in the world.
The global media, in this case is advertisements, have included identity notion in their marketing strategies. They typically orient the additional prominent benefits of the products toward various enticing modern lifestyles and identity indicating identity crisis phenomenon in contemporary society (Goatly, 2000). In response, the consumers are being led to chase the temporary perfect identity provoked by the advertisements by purchasing and using the products. Thus, identity has become accompanying merchandise promoted in the commercial discourse.
Intriguingly, the identity promoted in the advertisements can be categorized as superficial identity. Machin and van Leeuwen (2007) remark the uniqueness by
stating that the consumers’ identity is defined based on the lifestyle they indulge in, namely clusters of behaviours, attitudes, and consumption patterns of the prospective buyers. They include this type of identity as ‗lifestyle’ identity in which it relies heavily on the reflection of the attitudes, values and preferences in appearances, namely dress, accessories, gadgets, and so on. Therefore, the promoted products are becoming the markers of identity in contemporary society.
domain, but it is also acknowledged as a powerful tool to provoke certain images of the products (Bhatia, 2006). Bhatia (2006) remarks this identity implication by emphasizing that English possesses influencing psycholinguistics behemoth in the non-Anglophone countries. This essential role is proven from its immense employment in product and brand information message contained in the advertisement.
2.5 Discourse Analysis
From the above explanations, it is noticeable that the psychological benefits of the products are regarded as an important persuasive tool. Hence, it needs to be conveyed rhetorically in the advertising message. It leads to an assumption that communication is the central point in the creative construction of advertising strategy. Fiske (1990) gives a general definition of communication by stating that it is a social interaction through messages. By assuming that people transmit and receive the message, it is considered as a social practice within particular set of social value in a community.
communication as the transmission of messages. The salient matter is on how the senders and receivers encode and decode the messages through the channels and media of communication. It suggests that intention is a crucial factor in deciding what constitutes a message to affect the behaviour or state of mind of another.
Based on the above explanation, this study follows the second school which is
referred as the ‗process’ school by Fiske. It is in line with the focus of the study
because it views advertisement as a persuasive tool to promote products by evoking certain feelings associated with the brands to the mind of the consumers in the identity fabrication act. Therefore, it uses discourse analysis as the approach in investigating the process of communication in print advertising.
Discourse analysis gives the linguistic construction of a text a prominent position in its focus of study. It views texts as devices that can influence and contribute the changes of society (beliefs, attitudes, etc.), actions, social relations, and the representation of the physical realm (Fairclough, 2003). Pertaining to this angle, language is a site of ideology that shapes what speakers feel and think to the extent
that it is able to direct public’s opinion to support the interest of certain powerful
groups (Matheson, 2005). It proposes that texts play a role on social change through the meaning of language.
include the participants and the purpose of this communicative discourse, the social conditions of the target society, the medium of the discourse, and the way the communication is conducted. These elements are encapsulated into eight types of context presented as follow.
The first one is the concrete material which carries or relays text, namely the substance or media. The second element is the non-grammatical features of the text, such as music and pictures. The third element is the accompaniment of meaningful behaviour of language referring to voice quality, gestures, facial expressions and touch, and choice of typeface and letter sizes. The situation represented in the text is also included in the context for it builds a relation between the surrounding objects and people realized in the text as perceived by the participants. The text which precedes or follows the analyzed text – co-text – is also considered as a part of the context if it is perceived as belonging to the same discourse. Intertext — mentioned by Myers (2009) in the preceding section – is included as a factor to be investigated in relation with context because, usually, there is a certain text associated with the text under consideration that affects the interpretation though it belongs to other discourse.
text. However, they can also be the outsiders of the discourse because the interpretation of the meaning making process is devoted to them. Thus, they are assigned double roles in the advertising discourse, as a part of the context and an observer of it.
These aforementioned elements are organized in a clever way to communicate the messages of advertisement. This act of communication is guided by the final
element of the context, the function. Based on Fiske’s (1990) argumentation, the
function can be defined into the intention of the producer or the interpretation by the consumers of the discourse. Either way, the analysis on advertisement discourse needs to correlate the text and context implications utilized by the advertisers.
Regarding the function of the context, this study focuses greatly on the intention of the producers, especially on their attempts to persuade and influence the behaviour and mind of the targeted consumers. Hence, the participants as the ones who play an integral part of the context as well as the receiver of the messages are the main features in the analysis.
2.6 Transitivity Processes
As it has been mentioned previously, the language of advertisement is creative which is established on the ground of consumerism ideology. Ergo, the analysis focuses on the rules of the linguistic device solely cannot grip the stimulating idea behind the English linguistic system constructed by the copywriters through the Indonesia advertisements. Indeed, the grammatical and lexical configurations are the fundamental requirements in enacting the social practice. However, if the analysis implements the approach focusing on the linguistic construction forms without taking into account the context of the unfolding activity, it may cause a misrepresentation of the human communication complexity (Cook, 1992). On the other hand, by conducting systemic functional grammar as the analysis tool, the functions of each element can be investigated thoroughly in the respective contexts.
2.6.1 The Processes and Participants
In this system, meaning is established toward the process involved in a clause. The focal point is that a clause consists of process or a flow of events (Halliday, 2004). The continuous flow of event with its variation experienced and intended by the writers is captured and transferred into a clause. Simultaneously, the process affects the choice of grammar and vocabulary in a clause by determining the way it encodes an experience of the real world into the realm of language system (Thompson, 2004).
related to existence. The components of each process type are summarized in Table 2.1 below.
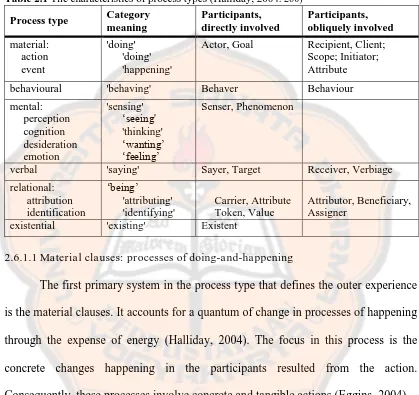
Table 2.1 The characteristics of process types (Halliday, 2004: 260) Process type Category
behavioural 'behaving' Behaver Behaviour
mental:
verbal 'saying' Sayer, Target Receiver, Verbiage relational:
The first primary system in the process type that defines the outer experience is the material clauses. It accounts for a quantum of change in processes of happening through the expense of energy (Halliday, 2004). The focus in this process is the concrete changes happening in the participants resulted from the action. Consequently, these processes involve concrete and tangible actions (Eggins, 2004).
action can be extended is the Goal (Halliday, 2004). Therefore, the Goal does not always appear in this process type which makes it an oblique participant.
Related to the two participants, there are two types of clauses which address the issue of the one in which the outcome is registered to. The process which indicates the confinement of the outcome of the process to the Actor is intransitive
clause which represents a ―happening‖ process (Halliday, 2004). It stresses that ‗an
entity does something’, thus, it does not require the existence of the Goal. It is usually
proven by asking what did x do? probe. The type of process which includes the Goal
participant is called transitive clause which represents a ―doing‖ which can be probed
by a question, ―what did x do to y?‖ (Halliday, 2004). Hence, the outcome is
registered on the Goal. For instance, ―the lion sprang (Halliday, 2004)‖ indicates a happening or intransitive clause in which it implies that the Actor or the lion did the action of sprang. The outcome of the action is confined to the Actor itself which is the inherent participant. On the other hand, in ―the lion caught the tourist‖ (Halliday, 2004), the Actor did something to the other participant which is the Goal or the tourist. Hence, the Goal undergoes the outcome of the process which indicates a doing or transitive clause.
Regarding the final phase of the unfolding process in one of the participants in the clause, there are additional subtypes which are deemed important to be discussed. Halliday (2004) presents two subtypes to distinguish the nature of the outcome. The first one is creative clause which implies that the Actor or the Goal comes into existence as the result of the process conducted. Ergo, the outcome of the process is
(Thompson, 2004).‖ The Goal or the Christmas pudding is brought into existence through the process conducted by the Actor. The second subtype is transformative clause which brings the notion of different final phase condition of the initial one of the participant. Instead of coming into existence, the participant undergoes changing which is the effect of the process. It should be noted that the participant has already existed before the action is conducted. However, Halliday (2004) argues that it can also suggest maintaining the condition of initial phase of the participant because it
still has a connection with the condition of the existing participant. For example, ―My
mum never eats Christmas pudding (Thompson, 2004).‖ The sentence implies that
my mum or Christmas pudding has already existed before the action. Consequently, it indicates that the outcome of the process is to maintain the condition of the participant of never consuming the dessert.
Scope does not receive any effect performed by the process, (ii) the Scope can act as the actual process in the clause, (iii) it cannot be probed by do to or do with question, (iv) it cannot be followed by a resultative Attribute (a resultant qualitative state of the Actor or the Goal of a completed process), (v) it is regulated to the participant of non-personal pronoun, and (vi) possessive modification cannot be implemented in this element.
2.6.1.2 Mental clauses: processes of sensing
In contrast with the previous clause, the Mental processes possess a focal point toward the inner experience as the term itself refer to. Its major concern is the quantum of change in the experience or process in the realm of consciousness (Halliday, 2004). The focus is on the working of the inner self of a conscious being on the surrounding event, belief, entity, and so on. Hence, the effect is mainly directed at the participant who conducts the process himself rather than other participant mentioned in the clause or something triggers the working of consciousness of someone which marks the contrast with the material process.
In this process, there are usually two inherent participants involved. The first participant is the Senser which is always recognized as human-like entity that bears the consciousness characteristic (Halliday, 2004). It is a highly isolated role which is occupied by an entity that is acknowledged to possess abilities of feeling, thinking, wanting or perceiving. This role is followed by the Phenomenon as the element that the process of consciousness is being reflected (Halliday, 2004). It denotes the participant which is being projected to be felt, thought, wanted or perceived. These
(Thompson, 2004).‖ The participant she is considered as the Senser who is able to perceive the process of hearing whereas his voice – the things which are perceived as being heard by the Senser – is put under the Phenomenon category.
Regarding the Phenomenon characteristics, its similarity with the Goal in the material processes is quite high. However, Halliday (2004) argues that the Phenomenon, in fact, has a far greater range of elements than the Goal. Instead of regarding the participant as a tangible thing, the mental workings can project it further into abstract entity, such as action and cognition. Hence, he has proposed two types of embedded Phenomena: Acts and Facts. The Act is usually projected into the mental processes of perception and realized by a non-finite clause which is
considered as a noun phrase. For instance, ―I saw the operation taking pla ce (Eggins,
2004).‖ The second type of embedded Phenomenon, the Fact Phenomenon, is often found in the form of a finite embedded clause introduced by that (explicitly or
implicitly) and treated as a noun phrase. For example, ―She didn’t realize that it was a bomb (Eggins, 2004).‖ Furthermore, it can be examined by adding the word fact
before that. For instance, ―She didn’t realize the fact that it was a bomb (Eggins
2004).‖
related to senses, for example see and hear, are put under the perception subcategory. Meanwhile, the final mental workings which describe the processes of desiring something are classified into desideration subcategory, e.g., want and need.
2.6.1.3 Relational clauses: processes of being and having
This type of process is considered as the third category of the main processes accompanies the previous process types, the Material and Mental processes. It features the characterization and identification processes of an existence resulting from the relation of one aspect with the others (Halliday, 2004; Eggins, 2004). This tenet suggests that in a relational clause two inherent participants construe an abstract relationship that share the same domain or being. This abstract relationship is configured into two distinct mode of being, namely the processes of characterization and identification, which are labelled as attributive and identifying clauses, along with three main types of relational processes: intensive, possessive, and circumstantial.
class (Halliday, 2004). From table 2.2, Sarah as the participant who has the characteristic of wisdom is the Carrier whereas the Attribute is the assigned characteristic, wise.
This type of clause typically uses a Predicator (be) to signify the relationship between the Carrier and the Attribute (Thompson, 2004). However, other verbs, such as seem, are commonly found in this type as long as they keep the essence of assigning an evaluative Attribute to the Carrier. It should be noted that this mode of being is usually irreversible and the article assigned to the nominal group is typically indefinite. Furthermore, it can be probed by what?, how? or what... like? questions (Halliday, 2004; Thompson, 2004).
Halliday (2004) divides the intensive attribution further based on the membership specification, whether it is entity or quality. When the Attribute refers to the entity that constitutes the class by realizing the nominal group with Thing as Head, it is the entity Attribute, for example He was an architect (Halliday, 2004). On the other hand, when the class of the Attribute is constituted by referring to a quality or qualities, as in Sarah is wise, it is identified as the quality attribution. An Epithet is used as the Head instead of the Thing in the nominal groups in which the Thing in nominal group can be considered as general and inferred from the context. The Epithet is realized by an adjective or participial verbal form, which is frequently accompanied by adverbs of degree.
certain identity to an entity, ―x is identified by a‖, (Halliday, 2004). The function of this type of clause is to establish certain uniqueness, define (technical) names, and assess evidence (Halliday, 2004).
In determining the Token and Value in an intensive clause, the crucial factor is in distinguishing whether it is a specific realization or the general one (Thompson, 2004). From Table 2.2, Sarah in ―Sarah is the leader‖ can be considered as the specific entity realizes or embodies the general category of the leader. Hence, Sarah
is labeled as the Token whereas the leader fills the role of Value. In order to
strengthen the assessment, the clause can be paraphrased into ―Sarah fills the role
of/represents the leader.‖ Halliday (2004) elaborates it further by stating that the
Token is the member whereas the Value is the exclusive status or role assigned to it. This mode of being is reversible in which the Predicator or lexical verb acts as an equivalent sign of the two participants. In addition, the nominal group in this type of clause is usually realized by a definite article as well as a proper noun or pronoun
which can be probed by ―What/Who/Which is x(the Identified)?‖ (Thompson, 2004). Aside of Carrier/Attribute and Token/Value participants, there may be an
additional ―third‖ participant in the equation. This third role represents the entity that assigns the relationship of these two modes (Halliday, 2004). In the case of identifying, it is labelled as the Assigner; in the case of attributing, it is labelled as the Attributor.
the name indicates – relates an entity with circumstance elements, such as time, place, manner, cause, accompaniment, role, matter or angle (Halliday, 2004). The salient feature is the utilization of background information to point out the relational aspects in the clause.
The possessive clause of the attributive mode can be expressed in two ways, the role of the Attribute and the process. In the first type, the Carrier is the thing
owned by the possessor or the Attribute, e.g.: ―This [Carrier] is yours [Attribute] (Eggins, 2004).‖ In the latter type, the possessing is encoded through the process, the possessor is the Carrier, and likewise the Attribute is the possessor. Halliday (2004) suggests assessing the ascribing of the Attribute to mark out the differences using this
example, ―Peter [Carrier] has a piano [Attribute].‖ The Carrier is labelled to Peter
because it conveys the meaning that the piano-ownership is the ascribing Attribute. It
differs with: ―The piano [Carrier] belongs to Peter [Attribute].‖ Here, the Carrier serves as the possessed one which underlines the attribution of Peter.
by stating that the difference is in a very delicate level which is on the shifting of the point of view. If it signifies a membership of certain class, in this case the group of Peter’s possession, it is the attributive one. On the other hand, if it embodies the issue of the owner-owned relationship, the identifying one is more appropriate. The second embodiment, which is the process, is encoded in the verbs of possessing which is typically realized by the verb own. The owner participant is the Token whereas the possessed participant is the Value.
In further discussion, the ownership construing is not limited to tangible participants only. Halliday (2004) argues that in construing the sense of ‗owning’, the relationship can be extended to an abstract level. Therefore, some verbs, such as
include and involve, are included in the possessive clause.
In the attributive mode of circumstantial type, the possible occurrences are similar to the possessive one, the Attribute and the Process. The first circumstantial process construes the Attribute by utilizing a circumstantial element which is usually
expressed by a prepositional phrase: ―my story is about a poor shepherd boy‖
(Halliday, 2004) or an adverbial group: ―she was there with three Zen master‖
(Halliday, 2004). In the latter one, on the other hand, the circumstance is construed as
the process, thus it is realized by a lexical verb: ―My story concerns a poor shepherd
boy‖ (Halliday, 2004).
circumstantial element, for instance a (circ: time) = x (circ: time), as in tomorrow is the 10th. On the contrary, the circumstantial processes are featured in the verbs to construct the relation between the participants (Halliday, 2004), for example, ―this situation is apparently caused by anomalous low temperatures (Halliday, 2004).‖ Simultaneously, it follows the nature of identifying clause which is reversible.
2.6.1.4 Behavioural clauses
These clauses are considered as the first ancillary clauses in process type which are situated on the borderline between the material and the mental clauses. These human-like processes are characterized as physiological and psychological behaviour (Halliday, 2004). The conscious being who is conducting the behaviour is bracketed into the Behaver accompanied by the Behaviour as the action which appears as a participant rather than a process.
Table 2.3 Examples of Process in behavioural clauses (Halliday, 2004: 251) [near
verbal processes as forms of behaviour chatter, grumble, talk, gossip, argue, murmur, mouth
physiological processes manifesting states of consciousness
cry, laugh, smile, frown, sigh, sob, snarl, hiss, whine, nod
attitudes (Halliday, 2004). Such clauses are usually detected in the creation of narrative in the dialogic passages.
Analogously, these clauses contain several participants: the Sayer, the Receiver, the Verbiage and the Target. As the name indicated, the Sayer is the participant who initiates the verbal processes. Along with the Verbiage, the Receiver is clustered as oblique participants in which to whom the saying is addressed. The Verbiage functions as a class of thing which marks the content or nature of the verbal processes. The last participant is the Target which is typically constituted in sub-type clauses of verbal that forms the targeted entity in the verbal processes.
2.6.1.6 Existential clauses
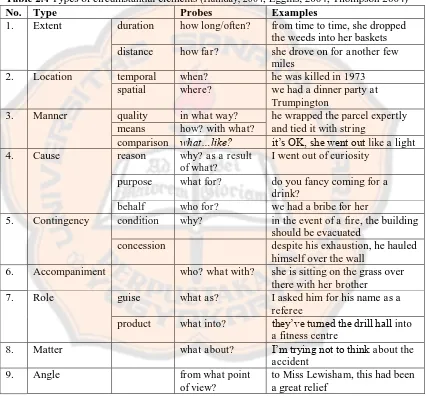
There are several types of circumstances. Thompson (2004) mentions nine circumstantial types: extent, location, manner, cause, contingency, accompaniment, matter, role, and angle. The list of circumstantial elements along with the examples is presented below.
Table 2.4 Types of circumstantial elements (Halliday, 2004; Eggins, 2004; Thompson 2004)
No. Type Probes Examples
1. Extent duration how long/often? from time to time, she dropped the weeds into her baskets distance how far? she drove on for another few
miles
2. Location temporal when? he was killed in 1973 spatial where? we had a dinner party at
Trumpington
3. Manner quality in what way? he wrapped the parcel expertly and tied it with string
means how? with what?
comparison what…like? it’s OK, she went out like a light 4. Cause reason why? as a result
5. Contingency condition why? in the event of a fire, the building should be evacuated
concession despite his exhaustion, he hauled himself over the wall
6. Accompaniment who? what with? she is sitting on the grass over there with her brother
7. Role guise what as? I asked him for his name as a referee
product what into? they’ve turned the drill hall into a fitness centre
participants, processes, and circumstances (Halliday, 2004). Though these important elements have their own significant contribution to the meaning making configuration, there is only one that partakes the role of players in this systematic linguistic realm. Without any doubt, it is the participants. Hence, van Leeuwen pays a considerable amount of attention to this particular element or context ((suggested by Cook (1992), see 2.4 for further discussion)).
In a grammatical process, the participants are the key part in realizing the activity. Van Leeuwen (2008) refers this activity as the social practice which is conducted by the participants or the social actors. By applying these social terms, he assigns sociological roles to these actors. However, he argues that sociological and linguistic categories cannot be specified into precise relations. If the theory and method are organized in a neat fit, they can be poor organized semantically, for example, the dictionary which has one form but many meanings. On the other hand, they are well organized semantically, but quite messy in formal construction, such as the thesaurus that have one concept with amplitude possible realizations. This problem may lead to overgeneralization of the social actors in the discourse because
certain relevant instances of agency might be overlooked because of their ―absence‖
in the linguistic system. To minimize the problem, he takes a different approach to investigate the social actors that partake in the social practices in the world of language.
the social practices might change the flow of the discourse. Therefore, the writers tend to express the relevant social actors in a rather peculiar manner concerning the social practices in the clause. They can be represented directly or indirectly based on the linguistic choice considered by the writers for intended purposes.
To assess these social actor representations, he delivers several categories of social actor representations. In analyzing the social actor representation in the advertisement discourse, this study takes three categories of them: exclusion and inclusion, activation and passivation, and personalization and impersonalization. The aforementioned categories are presented in the subsequent sections.
2.7.1 Exclusion/Inclusion
In the social practices, some social actors are represented directly whereas the others are not mentioned explicitly. The former set of social actors falls under the category of inclusion and the other is under the category of exclusion. These types of representation include or exclude the actors to suit their interests and purposes that affect the readers for whom they are intended (van Leeuwen, 2008).
The suppression and backgrounding representations can be realized in the same configuration for they exclude the actors who do the activity, but include the
traces of their involvement in the clause. For instance, ―To maintain this policy is hard (van Leeuwen, 2008).‖ The non-finite clause to maintain this policy is considered as an act of suppression because the writer does not state implicitly who is responsible for the policy maintenance both in the clause and in the text. However, it can also be realized as a backgrounding attempt if the social actor is mentioned elsewhere in the text. Hence, it can be noticed that, through the suppression, the trace of the actor becomes less accessible rather than the backgrounding strategy. The possible implication behind the suppression can be caused by the shared knowledge the writer and the readers are assumed to have related to the statement leading to comprehensible deletion agreement. Another implication maybe caused by the hidden intention of the writer to prevent possible objection on the excluded actor regarding the action.
2.7.2 Activation/Passivation
In this category, the social actors are deemed to have a significant role in the
grammatical realization. They can be represented as ―agent‖ or ―patient‖ with respect
to a given action (van Leeuwen, 2008). In other words, the social actors bear either active or passive roles in the realization of the social activity.
process (van Leeuwen, 2008). Furthermore, van Leeuwen (2008) presents and exemplifies alternative grammatical configurations in the process of activation which
are ‗circumstantialization’ with by or from (e.g., ―...a cold shoulder from neighbours and co-workers‖), premodification (e.g., ―public support‖) or postmodification (e.g.,
―the influx of Asians‖) of nominalization, and ‗possessivation’ (e.g., ―our intake‖).
Passivation occurs when they are represented as the ones who are
―undergoing‖ the activity. Contrasted with the activation, it is often realized as the Goal in material process, the Phenomenon in mental process, and the Carrier in relational process. Despite the contrastive grammatical participants, van Leeuwen (2008) includes similar additional manners and examples of passivation which
consist of ‗circumstantialization’ (e.g., ―A racist backlash against ethnic Asians...)
and ‗possessivation’ (e.g., ―my teacher‖). This strategy of role allocation is important
to reallocate roles or rearrange the social relations between the participants which can be different from the actual reality.
A further distinction is necessary in the passivated role allocation. The social actors can passivated into two roles: subjected or beneficialized. When they are treated as objects in the representation, they are being subjected. When there is a third party which gains benefit from the action, either positively or negatively, they are treated as beneficiary.
2.7.3 Personalization/Impersonalization
include the sense of ―human‖ feature. Hence, the typical manifestations of
personalization are realized by personal or possessive pronouns, proper names, or nouns (van Leeuwen, 2008).
On the contrary, impersonalization represents the social actors as inhuman actors in a given action. It can be divided into two types of representation. If there is a certain quality that represents the actors, they are included into abstraction, e.g.,
―Many Australians...were ‗bewildered’ by the changing face of Australia (van Leeuwen, 2008).‖ If there are references to a place or thing closely associated either with their person or with the action to represent them, they are included into objectivation.
In particular, objectivation realizes four types of metonymical reference. The first one is spatialization in which the reference is the place with which they are
closely associated in the given context, e.g., ―Australia was bringing in about 70.000 migrants a year (van Leeuwen, 2008).‖ The utterances can also be a mean of reference in the representation which is put under utterance autonomization type, e.g.,
―This concern, the report noted, was reflected in surveys... (van Leeuwen, 2008).‖ The third instalment occurs when the social actors are referred by means of the instrument with which they carry out the action. It is specified under the category of
instrumentalization, e.g., ―A 120mm mortar shell slammed into Sarajevo’s
marketplace (van Leeuwen, 2008).‖ The final instalment is somatization which
represents the social actors by means of reference to a part of their body, e.g., ―She