LEVEL AND
THEIR TECHNIQUES FOR INCORPORATING TARGET
CULTURAL CONTENT INTO ENGLISH LANGUAGE
TEACHING IN ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT UIN SUNAN AMPEL SURABAYA
THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement for The Degree of Sarjana
Pendidikan (S.Pd) In Teaching English
By
NIM D05211041
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND TEACHER TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SURABAYA
LEVEL AND
THEIR TECHNIQUES FOR INCORPORATING TARGET
CULTURAL CONTENT INTO ENGLISH LANGUAGE
TEACHING IN ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT UIN SUNAN AMPEL SURABAYA
THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement for The Degree of Sarjana
Pendidikan (S.Pd) In Teaching English
By
NIM D05211041
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND TEACHER TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SURABAYA
. Level and Their
Techniques for Incorporating Target Cultural Content into English Language Teaching in English Teacher Education Department of UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya. A Thesis. English Teacher Education Department, Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, Sunan Ampel State Islamic University Surabaya. Advisors: Afida Safriani, MA, Diah Karmila Sari Putri, M.Pd.
Keywords: Cultural awareness, Level of cultural awareness, The techniques to incorporate culture into English language teaching, Micro-teaching class, Factual Knowledge, Intercultural Competence
interaction and to communicate appropriately. The level of cultural awareness, however, will show how good the ability of someone to recognize and even to behave towards a cultural practice and believe. Having good cultural awareness in this case is critical for students taking micro-teaching class of ETED UIN Surabaya as English teacher candidates. As foreign language teachers, ETED students need to provide meaningful learning process in order for their students can save the language learned in their long term memory. To gain meaningful English teaching, ETED students need to highlight that language learning without involving any cultural contents means nothing. Considering those facts, this study aims to examine the questions: (1) What is micro teaching class of English Teacher Education Department?, (2) What strategies are used by students of micro teaching class to incorporate cultural aspect into their English language teaching?. To conduct this study, mixed method especially Explanatory sequential design was employed. The first question was answered by quantitative descriptive using a test, and the second question was answered by qualitative approach using observation. The result of this
level 3 became the most achieved level by students. Furthermore, the second question which only 35 students coming from different levels became the sample was answered by the fact that
was the technique most used. Then,
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN TULISAN ... xi
LIST OF CONTENT ... x
C. Research Instrument ... 33
D. Data collection technique ... 35
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 38
F. Data Source ... 40
CHAPTER IV : RESEARCH FINDING A. Findings ... 42
1. ... 42
Factual Knowledge Level ... 45
... 58
... 71
2. The Techniques for Incorporating Target Cultural Competence Used by the Students of Micro Teaching Class ... 73
2.1 The techniques of level 1 student for incorporating target language culture into English language teaching ... 75
2.2 The techniques of level 2 student for incorporating target language culture into English language teaching ... 76
2.3 The techniques of level 3 student for incorporating target language culture into English language teaching ... 84
2.4 The techniques of level 4 student for incorporating target language culture into English language teaching ... 89
B. Discussion ... 88
1. ... 92
2. into English language teaching ... 97
3. The relations between students level of cultural awareness and the techniques they use for incorporating target language content into EFL teaching ... 100
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ... 105
B. Suggestion ... 107
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter discusses the area of the study that will be covered in some
headings (1) The Background of this Study, (2) Statements of the Problem, (3)
Objectives of this study, (4) Significance of this Study, (5) Scope and Limitation, (6)
Definition of Key Terms.
A. Background of The Study
After the implementation of Asian Free Trade Area (AFTA) in
December 31, 2015,1 having cultural awareness becomes something critical
for every people. The logic is that the implementation of AFTA will bring
people to easily come, live, and possibly work in other countries. There will
be a lot of people from other countries having different cultures coming,
trading, and interacting in Indonesia. Facing this fact, cultural awareness is
extremely needed to build a good communication in which people can tolerate
diversity and commend others appropriately.
The irony is that the use of foreign languages is something less in
Indonesia. It is confirmed by the data of World Bank stating that the
discrepancy of foreign language ability of using among man power in
1
2
Indonesia is about 44 %.2 This might be caused by the fact that the language is
learned without giving meaning. Then, cultural awareness here is also needed
in order that ones can use English appropriately. AFTA will open the chance
for all people in South of Asia speaking different languages and not using
English as the first language to interact each other. This case becomes
possibility to make English as lingua franca as its function as an international
language. Indeed, it is important to learn English contextually.
In learning a foreign language, teachers or lecturers should transfer not
only the linguistic items but also the cultural evidence that is adhered in the
target language itself.3 It is positively a must in order that the students can
comprehensively master the target language since the items in every language
cannot be separated from the cultural context. This is synchronic with the
purpose of language learning in 2013 curriculum.
The 2013 curriculum highlights that classroom teaching-learning
interact with the society. Integrating culture and language together in a
teaching becomes a solution to make English learning more practical. This
2
Ekonomi Asean (MEA Academia.edu, (http://www.academia.edu/9069749/PELUANG_DAN_TANTANGAN_PEKERJA_PARIWISATA_ DALAM_MENGHADAPI_ERA_MASYARAKAT_EKONOMI_ASEAN_MEA_2015, accessed on April 24, 2015)
3
3
demand stated in the regulation of Indonesian Minister of Education and
Culture No. 70 Year 2013 about the basic outline and structure of Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan or Madrasah Aliyah Kejuruan. He said that school should be media for students to learn everything they can use in their society.
Thus, what is learned in school needs to be applicable and meaningful. 4
Meanwhile, the second main competence of 2013 curriculum of
English lesson also states that the purpose of teaching English is to make
students aware on the way how to behave in global interaction. Hence,
cultural awareness is needed in this case, since as expected by the regulation
of Indonesian Minister of Education and Culture No. 70 Year 2013 about the
basic outline and structure of Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan or Madrasah
Aliyah Kejuruan, students learning foreign language will realize their role as a
representation of nation in the international relations.
English is one of the languages that are commonly learned by people
from the entire world because of its role as an international language. English
learned as a communication medium between people to people in
international relationship. Considering this reason, it is clear that in studying
English, students are not only expected to understand the structure of English
4
4
itself, but also to have intercultural competence or to understand the concept
of language use in real life context.5
The ability to gain intercultural competence is called as cultural
awareness. Cultural awareness is very important to bridge students in
understanding the target culture that may be very different from their own
culture.6
culture. This knowledge ideally can be used to strengthen their own culture
and identity, because the interaction between cultures ideally should create a
reinvention of local tradition and identity.7 In addition, students also will be
able to use their understanding about a language appropriately looking from
the behavior, value, faith, and cultural background of the target language
studied.
In this matter of fact, it is important to know to what techniques used
by the students of English Education Department because they will be
teachers in the future who are demanded to not only transfer linguistic
competence to the students but also to transfer cultural content as a bridge for
students to understand about cultural diversity and the way to respect and face
it. In assumption, it will be difficult to awareness about the
5
The Challenge of Assessing Cultural Understanding in the Context of Foreign Language Instruction Foreign Language Annals. Vol. 40 No. 1; Education Module, 200, 9
6
Renate
7
5
culture if the teachers themselves do not know exactly what the culture of the
target language is.
As an initiation, it is believed that the
teacher. As the consequence, the result of this research can be made as a
reflection for the department to know whether the students of English Teacher
Education Department are ready or not to face the demand to incorporate any
cultural knowledge they can transfer into their English teaching. Another
benefit is that this research finding will give information to the world dealing
with the relationship between levels of cultural awareness and the
techniques they use to incorporate cultural knowledge in foreign language
teaching, especially English.
The students of Micro teaching class of English Education Department
(PPL 1) is chosen as the subjects since they have taken Cross Culture
Understanding Class to learn about the way ho
and how to face the differences. Then, they are also regarded having better
understanding of English since they are equipped by knowledge and skills to
be an English techer for five semesters in the university. They have taken all
courses enriching their pedagogical needs, such as TEFL, Curriculum
Development, IMALT, and vice versa. Moreover, in micro-teaching class,
6
As candidate, the students should have a good cultural
awareness. Later, after graduating from State Islamic University of Sunan
Ampel Surabaya, they should be able to teach their student, transfer the
information not only from the linguistic rule but also from the culture. The
ability to incorporate culture in language teaching will benefit for both teacher
and students to strengthen and improve their English proficiency. As the
result, it is important to assess their readiness to face that demand.
In order to use English that is culturally appropriate, English teacher
candidates need to know the way how to incorporate cultural context in their
teaching, and they would practice doing it in PPL 1 class. As well, it gives
lecturers guidelines about what to do in their teaching. The lecturers will
benefit a view dealing with how to teach their students in order that they can
be good teachers in the future who can incorporate cultural context in their
teaching.
B. Research Questions
This study intended to examine the following questions:
1. micro teaching class
of English Teacher Education Department?
2. What techniques are used by students of micro teaching class to
7
C. Objectives of The Study
Considering the research questions stated, this study aimed to find the
following case:
a. The level of students cultural awareness in Micro-teaching class of
English Education Department
b. The techniques used by students of micro-teaching class for
incorporating any target cultural content into their English Language
Teaching.
D. Significance of The Research
This study is expected to raise students knowledge about their cultural
awareness level. After the students know their ablity, it is believed that they
will get motivated to improve it. Then, it is also useful for the Department to
reflect the success of applied curriculum, especially cross culture
understanding that had been learned. In addition, it can be a reference for the
lectures of English Education Department UIN Sunan Ampel dealing with
how they should teach and direct their students.
It is also important for the Department
8
students are ready or not to face the demand in which the teachers should be
able to transfer not only the linguistic items but also cultural items to the
students. If the level is already known, the Department absolutely can design a
strategy on how to make the students as teachers in the future have that
requirement.
E. Scope and Limitation
Culture and language cannot be separated, so it is better to teach
language and culture integrated in language teaching. Culture also plays
significant role in the success of someone English learning. The ability to
This research has two scopes to examine. The first scope is the level of
cultural awareness. A theory of World languages SAC will be used as the
cultural awareness. World
languages SAC states that there are some aspects that should be analyzed to
.8
They are: factual knowledge,
intercultural skills, understanding of values and perspectives, and personal
engagement. But in this research, there are only two aspects that will be
examined ; they are factual knowledge
and intercultural competence. Each aspect that will be examined has four
8
9
levels; description and identification, comparison/contrast, analysis, and
evaluation and reflection.
The second scope is about the techniques to incorporate cultural
knowledge in English language teaching. Here, some points summed up by
Rodliyah and Muniroh in their research will be taken as the examined
techniques.
knowledge in English language teaching are also employed. The techniques
are:9
a. Providing more authentic materials involving target cultural and social
elements
b. Giving lectures or having discussion on culturally-related linguistic
aspects
c. Using pictures, maps, realia, posters, etc. to help students develop a
mental image
d. Comparing and contrasting home and target cultures
e. Role plays, where students can learn the difference of attitudes/values
of different characters associated with the culture
f. Design a project where students can have an exchange with people
from different culture
9
Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa UPI, (
10
g. Providing students with culture based activities, such as singing,
reading, film, simulation, and so on10
h. Providing students with any topic talking about culture whether the
surface or the depth one.11
The limitation of this study is the students of micro teaching class (PPL 1).
F. The Definition of Key Terms
Here are the definitions of the key terms based on the perspective of this
study or in other words the terms below are defined operationally.
a. Cultural awareness
Moran states that cultural awareness is a kind of intercultural competence
enabling learners to have appropriate behavior, perspectives, and attitudes
towards another culture.12 It is defined as a general understanding of
learner to world cultures, emphasizing on how they can recognize the
difference and similarities among those cultures. There are 2 aspects of
Cultural Awareness will be measured here: 1. Factual Kowledge, 2.
Intercultural Skill.
b. Level of cultural awareness
The level of cultural awareness deals with the degree of students ability
in having cultural awareness. In term of cultural awareness, there are 4
10
. Turkey: Krikkale University, 4
11
12
11
levels that are possible to reach;13 1.Description and Identification, 2.
Comparison/Contrast, 3. Analysis, 4. Evaluation and Reflection.
c. The techniques to incorporate culture into English language teaching
The ways used by teachers to engage cultural knowledge into English
language teaching.14 There can be several ways to teach culture and
language integrative. The details can be seen in scope of the study.
d. Micro-teaching class
A class in English Teacher Education Department of UIN Sunan Ampel
Surabaya in where the students can do English teaching practice.
e. Factual Knowledge
Factual knowledge deals with the knowledge of someone about any
cultural practices, attitudes, or beliefs.15 Thus, Factual knowledge can be
defined as any knowledge of students about target cultural competence.
f. Intercultural Competence
Intercultural competence defined as the ability of someone to show any
appropriate behavior toward the different culture and it also refers to how
people give the views to the differences.16 Confirming this definition,
intercultural competence in this study is defined as the view, attitudes, and
13
World Languages SAC, Outcome Assessement for Cultural Awareness (Japan, 2011)
14
15
Chantal Crozet, .Australian Government: Research Centers for Languages and Cultures Education, 2007, 1
16
12
or perspectives of students toward target cultural content which differs to
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter, the researcher explicates several theories through
reviewing some literatures related to this study. This theoretical construct
deals with some main areas: the definition of culture, cultural awareness, and
culture in language learning. Furthermore, some previous studies related to
this current study are also discussed here.
A. Review of Related Literature
1. The Definition of Culture
Empirically, culture is one of the components that cannot be separated
s life. It is already glued into any interaction among people
around the world. The world culture is easy to find, to hear, to say, but
hard to define. When it is defined, there will be many interpretations
through any field of science; anthropology, sociology, linguistic, and
many others. Each field will define culture differently. It is synchrony
with what Barker says that culture does not have any exact and definitive
meaning.1
However, as cited by Hofsted, Kluckhohn quotes a definition of
culture as the way how people think, feel, and react in particular way
1
14
which then internalized and transmitted through symbols, work, opus, and
so on. The essence of culture is developed the traditional ideas and
values.2 Furthermore, Hofsted cites the definition of culture according to
culture as the concept of
values, meaning, and ideas which is transmitted and developed generation
to generation as something to shape human behavior and artifacts.3 From
is resulted from the interaction among them. It can be the way how the
people socialize, how they pour their ideas into such kind of art, how their
belief is, how they run their life, and others.
Culture itself is divided into two categories. The first is material
culture or what is called by people as surface culture, and the second is
immaterial culture or deep culture.4 It is synchrony with what Moran
states in his book that the categorization of culture is manifested in an
iceberg model which a half of its part is under the water.5 The top part of
the iceberg is surface culture in analogy, and the hidden part is the deep
culture.
2
International Studies of Management & Organization. Vol. 10 No. 4, Organizations and Societies, Winter 1980/1981, 23
3
4
Taken from Cliff Notez; Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. Material and Non Material Culture.
http://www.cliffsnotes.com/sciences/sociology/culture-and-societies/material-and-nonmaterial-culture. Accessed on 12, 23, 2013 at 13.15
5
15
Surface or material culture is defined as any kind of culture that is
obvious to observe. It is primarily in awareness. The examples of this kind
of culture are: fine arts, food, clothing, and others. Meanwhile, immaterial
or deep culture is defined as any kinds of culture that is less obvious and
unclear. The production of this culture is out of awareness, for instance:
attitudes, beliefs, religion, and so on.
2. Cultural Awareness
One of intercultural competence is cultural awareness.6 It is defined as
a general understanding of learner to world cultures, emphasizing on how
they can recognize the differences and similarities among those cultures.
In terms of English as foreign language (EFL) learning, cultural awareness
will enable the learners to find the difference and similarity between the
culture of native English countries; UK and USA, and then compare it
with their own culture. In this case, learners also will have any
competence to judge a cultural situation resulting from the condition of
each country.
The awareness of culture is extremely important because the
awareness itself will be a basic knowledge that will deal with the way how
6
16
learners use their target language in context.7 For example: it will be less
appropriate if learners use a term, a word, or an expression of target
language without knowing the use; how it is used in the native English
country. As the reason, it is important for learners to acquire any target
cultural knowledge through language learning to train their discourse
sensitivity.
There are several uses of cultural awareness in language teaching.8
Firstly, it is to build the knowledge of other societies and cultures. It is
important to help learners having a good behavior when they face cultural
diversity. Secondly, it is to build empathy. Empathy here functions as the
bridge that connects the feeling of learners into the condition of target
language culture they learn. Thirdly, it is to build approval. Approval is
important to help the learners avoiding ethnocentrism, or racism; how they
can see any culture from several dimensions.9 Fourthly, it is to enable
learners in passing task performance. It deals with the preparation of them
to be able to use the target language as a foreigner in several needed
context.
7
The Relationship between Awareness Raising Activities and - Bound Materials
Pubhlishing. Mediteranian Journal of Social Sciences. Vol. 4 No. 3, 2013, 516
8
Striving for the Third Place: Intercultural Competence through Language Education The National Languages and Literacy of Australia, 1999, 66
9
17
Considering the importance of the transmission of cultural knowledge
through language learning, it is also important to assess how success it is
acquired by students. Assessing is a part of teaching and it is a must to
conduct.10 By assessing, teachers will know in what level their students
are, what to be improved, and so on. So does in language teaching; both
communicative and intercultural competence should be well assessed.
3. The Level of Cultural Awareness
Four things can be tested dealing with cultural awareness, they are:11
Factual knowledge (the way how they interact with cross cultural
knowledge), Intercultural skill (how they interpret any cultural
information that seems abstract and contradictive for them), understanding
values and perspectives (how they can catch the value, ideology and
morality) and the last is personal engagement (how well they can present
their cultural knowledge, and how well those information effects the
belief, attitudes, and others).
But here this current study is only focused on two aspects; factual knowledge and intercultural skills. The reason was because the two aspects (understanding values and perspectives) are already covered by the second
aspects, intercultural skill. For the reason, intercultural skill deals with the
10
H. Douglas Brown, Language Assessment Principles and Classroom Practices (UK: Longman press, 2003), 5.
11
18
way how people set their view and attitudes toward other culture outside
them, including how people interpret the values and how they see the
differences through their own perspective.
World Language SAC employs 4 levels of cultural awareness in which
cultural content.12 In other
words, the following levels of cultural awareness describe what people
actually able to do facing target cultural content:
a. Level 1 or description and identification, here ones are only able
to do description and identification. The ability of them in term of
factual knowledge is only mentioning, discovering, or identifying
target cultural practices without being able to do further step.
Then, dealing with intercultural competence, someone achieving
this level is only able to discover their own cultural practices
relating to target cultural content they know.
b. Level 2 or compare and contrast, someone achieving this level is
one step further than the one achieving level 1. Inside of being able
to describe and identify cultural knowledge, achieving this level
means that someone is also able to do such kind of comparison and
contrast. In factual knowledge aspect, they are able to compare or
to contrast target cultural content they know with their own
19
perspectives. Then, dealing with intercultural competence, being in
this level means that someone able to give an opinion towards
target cultural practices.
c. Level 3 or analysis, being in this level means that someone instead
able to discover and identify, compare and contrast, is also able to
present further analysis towards target cultural content. In term of
factual knowledge, someone being here is able to analyze target
cultural knowledge which differs to theirs. In term of intercultural
competence, they are able to analyze and give opinions without
underestimating on how cultural practices and assumptions impact
individuals in the specific context.
d. Level 4 or evaluation and reflection, being here means that
someone already achieves the highest level of cultural awareness.
Someone achieving this level is able to evaluate and reflect any
target cultural aspects they know. In term of factual knowledge,
someone being here is able to connect target cultural practices or
believes to the historical background or issues existing in place
where the cultural contents come from. In term of intercultural
competence, being here means that someone is able to give points
20
4. Culture and Language Learning
Language is a symbol of a culture; it can show the cultural reality
around its user.13 Considering this fact, it is no doubt that language and
culture cannot be separated. Both language and culture are integrated. It is
synchrony as what Lambert says in his book is that the nature of cultural
knowledge is acquired through the variants level of language
competence.14 It goes further when Lambert says in his book that most
language has any way to relate with culture, and that most cultural aspect
can be reached through the use of language.15
Basically, in language learning, there are two kinds of competence in
general that should be more emphasized. The first is communicative competence. It is a kind of fundamental competence that deals with the social competence, linguistic competence, and communication
competence; the way in which people interact each other, transact any
messages, and so on. Spietzberg states that communicative competence
makes people easily address the links between communication processes
and functional outcomes.16 The second is intercultural competence. It
13
, 515
14
, 149
15
Josep , 66
16 Spietzberg and Cupach, Interpersonal Communication Competence (London: Sage, 1984), 70-71 as
deals with the ability of learners to be aware, understand, accept,
appreciate, respect, value, and develop anything included in other
culture.17
Figure 2.1 Kind of Language competences
Many experts have dealt with the belief that it is imprecise and
imperfect to conduct foreign language teaching without incorporating
culture inside it.18 It means that the demand for teachers to engage the
target language culture in their teaching becomes something important to
fulfill. If it is not, there will be such kind of disconnection in the language
teaching itself. Furthermore, Genc and Bada state that the
teaching-learning process inside the classroom will not be meaningful if the
students have no knowledge about the people using the target language or
17
Darla K Dardoff, The Identification and Assessment of Intercultural Competence as A Student Outcome of Internalization at Institution of Higher Education in the United States (Reigh: North Carolina State University, 2004), 43.
18
The Reading Matrix, Vol. 5 No.1, April 2005, 73
Kind of Language competences
Communicative Competence
22
the country where it is spoken.19 This fact stimulate a new phenomenon in
which culture becomes the main additional topic engaged which is
emphasized in L2 curriculum designs and textbooks.20
Actually, the demand to integrate culture in language teaching is still
debatable. The contrary side to this belief is represented by Sapir. Sapir, as
21
However, believing that integrating culture in
language teaching is extremely needed, for the reason that it will be
difficult for the students to use the language appropriately if they have no
background on how to use the language practically. To strengthen this
22
First, Kitao states that studying the target culture besides target
language will provide students with strong willingness to learn the target
culture in depth. 23 This means that without involving cultural aspect, the
study of target language will only pass and leave no effect or trace on
fe. In analogy, it is regarded that target language and the study of
linguistic items as body. In other side, the study of culture integrated will
be like the soul that will give a power to the body to feel the life.
23
Second, the incorporation of culture in language teaching will provide
knowledge to students that will help them in shaping their perspective
about target language.24 This fact will lose the distance between the
foreign languages that are studied by students with the real condition
where the languages are used. There are many cases in which English is
learned by people in the very long time, but has no function when they are
demanded to use it. The reason why it happened is just because they do
not learn English through the way to use it.
motivation to learn the language itself.25 Culturally based activities such as
singing, dancing, role playing, and soon will attract students much better
than the way how the language taught traditionally. It is already proven by
the experience in teaching in which the students feel better in studying
when they were provided not only by the linguistic and grammatical
transfer, but also the integration of any information about culture.
Lafayette and Schulz maintained that actually there are three broad
goals which are realistic for foreign language learners:26
a. Students should acquire the knowledge dealing with any
cultural information about the target culture
24
b. Students need to develop understanding; it deals with the ability
of students to develop more understanding about the cultural
information they get. In other words, the students are able to
redefine the culture they learn through their own point of view
c. The third goal discusses merely on the way how the students
develop behavior toward the target culture, moreover in broader
intercultural relationship
Dealing with incorporating culture in English language teaching,
Rodliyah and Muniroh sum up the theories stated by some experts about
the way to incorporate culture in language teaching, later the following
techniques will be made as a checklist used to examine whether the
students of micro teaching class are able or not to engage culture in their
teaching. The techniques are:27
a) Providing more authentic materials involving target cultural and
social elements28
27
e of Incorporating the Target Culture Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa UPI,
( http://file.upi.edu/Direktori/FPBS/JUR._PEND._BAHASA_INGGRIS/197308062002122-ROJAB_SITI_RODLIYAH/The_Importance_of_Incorporating_the_Target_Culture_in_Englis.pdf
28
Language Universitas Kristen Indonesia,
25
b) Introducing or using native idioms, proverbs, or sayings in
teaching-learning process29
c) Using pictures, maps, realia, posters, etc. to help students
develop a mental image
d) Comparing and contrasting home and target cultures30
e) Role plays, where students can learn the difference of
attitudes/values of different characters associated with the
culture31
f) Design a project where students can have an exchange with
people from different culture32
Cakir on his research also states some techniques that can be used to
incorporate cultural competence in English language teaching, they are:
a) Providing students with culture based activities, such as singing,
reading, film, simulation, and so on.33 It is also further asserted
29
, accesed on August 10, 2015)
30
Programs, (http://www.afs.org/blog/icl/?p=3533, accessed on August 10, 2015)
31
Jerrold Frank, Raising Cultural Awareness in The English Language Classroom . English Teaching Forum, No. 4, 2013, 10
32
Jerrold Frank, Raising Cultural Awareness in The English Language Classroom . English Teaching Forum, No. 4, 2013, 8
26
by Choudhory that film and so on can be one of techniques for
incorporating target cultural content into ELT.34
b) Providing students with any topic talking about culture whether
the surface or the depth one.35 Liu explored kind of topics can be
used to incorporate culture into ELT, such as Holidays,
Christmas, Lunar New Year, and vice versa.36
Dai also contributes a technique that can be used by the teacher to help
them incorporating culture into their teaching, that is positive classroom
interaction.37
B. Previous Study
There are some studies related with the current study:
1. A study conducted by World Languages SAC entitled Outcome
Assessement for Cultural Awareness
cultural awareness in Japan. The level of
was assessed here and the result was that the students were already
moderate in term of having cultural awareness.
34
Murshed Haider
IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS, Vol. 13 No. 1, July August 2013, 22
35
36
Yi- -Langua Department of
Applied Foreign Languages, Chia Nan University of Pharmacy & Science: International Journal of Humanities and Social Science, Vol. 4, No. 6, April 2014, 244-245
37
27
2. A study conducted by Darla K. Deardo
Identification and Assessment of Intercultural Competence as a
Student Outcome of Internationalization at Institutions of Higher
This research told the reader about the
intercultural competence, what to use as
the instrument, and why it was regarded as something important.
3. A study conducted by
Competency and Multicultural Teacher Education .
4. A study conducted by Bilal Culture
in Language Learning and Teaching xamined What Students Think
about The Effects of The Culture Class They Attended in The Fall
Semester Of
2003-Furthermore, dealing with incorporating cultural knowledge in English
language teaching, there was a study that had examined this topic. The study
was conducted by
Incorporating the Target Culture in Englis which
examined English towards the use of culture in English
Language Teaching.
The previous studies and this current study are the same in term of
measuring, checking, or assesing the cultural awareness of students. But,
28
a. This study was conducted using two designs; qualitative and
quantitative designs, so that, it is expected that this research will
be more comprehensive than others.
b. The excessiveness of this study is that this study examined
follow up on the way how
they teach. In other word, this study examined how culture
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter discusses the area of the study that will be covered in some
headings (1) Research Design, (2) Research Subject, (3) Data, (4) Research
Instrument, (5) Data Collection Technique, (6) Data Analysis Technique, (7) Data
Source.
A. Research Design
This research used mixed method design since it used mixed method approach. Creswell defines mixed method as the following: procedures for collecting, analyzing, and mixing both quantitative and
qualitative data in a single study or 1 In
this research, both quantitative and qualitative in term of collecting,
analyzing, and concluding the data were conducted. Then, the type of
mixed method taken in this study was explanatory sequential design. Explanatory sequential design is the design that was used when the
problems are unraveled using both quantitative and qualitative in
separated studies. The sequence was that the quantitative conducted first,
1
30
then qualitative conducted as the follow up and finally the data was
interpreted.2 Here is the diagram of explanatory sequential study:3
Figure 3.1 Explanatory Sequential Design
From the diagram above, it is clear that to answer the research
questions, this research used two research approaches. They were:
1. Quantitative study. To answer the first question, quantitative
method, specifically quantitative descriptive, was used. The reason
was that because in the first question, this study aimed to examine
d
attitudes toward multiculturalism to then describe it. Another reason
was that because the used instrument was test. To collect the data, a
set of questions was given after the participants read an article.
Furthermore, the result would be described through percentage and
numeric description.
2. Qualitative study. As the follow up, the second question was
answered by using qualitative method specifically descriptive
2
John W. Creswell, Educational 542
3
31
method. For the reason, this study observed a behavioral teaching
process of students for incorporating target cultural content into
language teaching. Observation was chosen in this current study. In
this case, structured-observation was used for what to examine was
known exactly. Knowing what to examine is classified into structured observation.4
B. Research subject
As mentioned that there would be two studies in this research, the
subjects taken for each study were the same but in the different number.
The subjects of this study were all students taken micro teaching class of
English Teacher Education Department in UIN Surabaya.
1. Quantitative study
The subject of the quantitative study in this current research was the
students of micro-teaching class of English education department UIN
Sunan Ampel Surabaya. The number of students taking micro teaching
class (PPL 1) was about 83 students.
2. Qualitative Study
The same as the quantitative study, the subject of the qualitative
research in this study was the students of micro teaching class of
4
32
English education department UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya. The
numbers of taking microteaching class were 83. But here, this study
employed some students taking microteaching (35) which came from
each level of cultural awareness as the representative. The sampling
technique used in this study was purposeful sampling, especially
maximal variation sampling. The reason why maximal variation
sampling was used was because this current research selected students
from each level of cultural awareness. For the reason, the participants
at first were classified into groups and taking some of them which
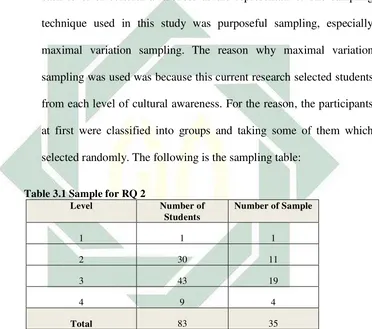
selected randomly. The following is the sampling table:
Table 3.1 Sample for RQ 2
Level Number of
Students
Number of Sample
1 1 1
2 30 11
3 43 19
4 9 4
Total 83 35
The location where this research conducted was in UIN Sunan
Ampel, which located in Surabaya, Jalan Ahmad Yani no. 117, Jawa
Timur. UIN Sunan Ampel is the only state Islamic university in
Surabaya and a university that has an English Teacher Education
33
C. Research Instrument
In conducting this research, some instruments were used. Because both
quantitative and qualitative were employed in this current study, the
research instruments were also divided into two parts:
a. First part; Quantitative Data
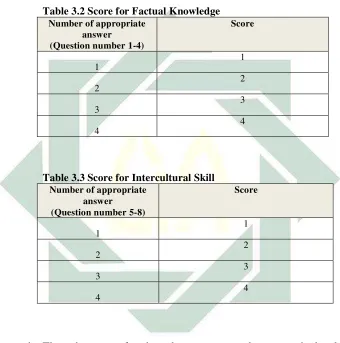
What was used in this study were test and grading rubric.
1) Comprehension Test was level of cultural
awareness. It consisted of an article entitled
(See appendix, page xvii). Then, 8 comprehensive
questions which examining two aspects of cultural awareness;
factual knowledge, and intercultural skills were given. Questions number
1-knowledge. Then, questions number 5-8 aimed to test
intercultural competence of students. Each number was scored.
The score of question number 1 was 1, number 2 was 2, number 3
was 3, number 4 was 4, number 5 was 1, number 6 was 2, number
7 was 3, and the score of number 8 was 4. (see appendix, page
xvi)
2) Grading rubric was used to give some criteria in measuring the
34
rubric benefited as the
cultural awareness classified into levels. The grading rubric was
attached in the appendix.
of test whether it was correct or not. By having this grading
level of cultural awareness precisely. The rubric contained of the
list of levels for each aspect of cultural awareness (factual
knowledge and intercultural competence), description and identification, compare and contrast, analysis, and evaluation and reflection. (see appendix, page xiv)
b. Second part; Qualitative Data
The instruments that were used in conducting the study were
video recorder and checklist.
1) Video recorder was supporting instrument that was used to record
the teaching-performance of students in micro teaching class.
Actually, the process of teaching was observed directly, but here
the recording of teaching was needed to get deeper result. the
recorder benefited to record all the teaching performance of the
observed students. Later on, the recorded performance could be
re-watched if further data was needed.
2) Checklist was used to measure whether the students were able or
35
Teaching. At first, the checklist consisted of the
identity. Then, it was also written there the techniques that
possibly used by the students to incorporate cultural knowledge in
their English teaching. There are 9 techniques provided. Then, yes
and no column were also provided to record whether students
employed the techniques. Furthermore, explanation column was
also provided to provide more spaces for noting in what ways
students employed the techniques. (see appendix, page xv)
D. Data collection technique
The data collection technique that was used in this method was
explanatory technique. Furthermore, Creswell in his book gives a brief
overview about explanatory techniques, he assumes that one of the reason
why explanatory model is taken as the data collection technique is that the
researcher wants to examine multilevel behavior characteristic.1
In collecting the data, this study was divided into two parts. The
first part was conducted to answer the first question as it used quantitative
descriptive. Then, the second part was conducted to answer the second
question as it used descriptive qualitative design. For the first part, an
article and set of questions were given to the students. Ten, they were
1
36
asked to bring it back in the next meeting. In the second part, such kind of
observation was conducted to know whether the students could
incorporate culture in their mini-teaching. Both collection techniques were
conducted after the middle test or in the second cycle of teaching turn with
an assumption that students already had bckground knowledge dealing
with the way how to teach correctly.This is the detail of how this research
was conducted:
1. Quantitative Data
a. In a meeting, a test consisting of questions to examine their level
of cultural awareness was given to the participants.
b. After conducting the test, the answer was
interpreted using grading rubric. And finally, any information
To
visualize what had been done, see the following diagram:
37
2. Qualitative Data
In collecting the data for the second question, the sample was
decided first. Some videos of chosen
-teaching class were taken to than observed and described. The whole
performances gave a brief overview dealing with how the students
incorporate cultural aspect in their teaching. And checklist was
employed to notice the techniques for incorporating target cultural
content into English language teaching of students.
E. Data Analysis Technique
Data analysis technique plays an important role in conducting a
research, since analysis can help the researcher to get a valuable meaning
to solve the problem.2 In order to get a good understanding related to the
data, there were some steps that should be done first:
a. The data was collected. This
collection was conducted through quantitative descriptive design by
giving test.
b. The first data got from the test were analyzed to get the level of
each student. Here, the data were classified into two groups; factual
knowledge and intercultural skills.
2
38
c. answers for the test were scored. It was done by giving
score for each question answered by the students. Here are the
scoring details:
Table 3.2 Score for Factual Knowledge
Number of appropriate
Table 3.3 Score for Intercultural Skill
Number of appropriate
d. Then, the mean of each student score was taken to get the level of their
cultural awareness.
The
awareness:
Level of CA: N1+N2 / 2
39
N1 : Score for Factual Knowledge N2 : Score for Intercultural Competence
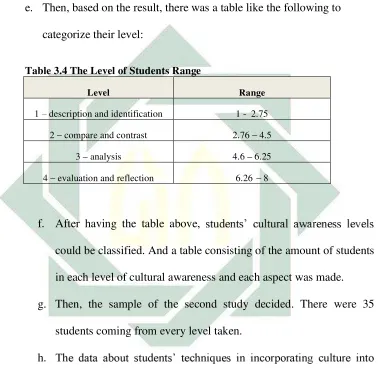
e. Then, based on the result, there was a table like the following to
categorize their level:
Table 3.4 The Level of Students Range
Level Range
1 description and identification 1 - 2.75 2 compare and contrast 2.76 4.5
3 analysis 4.6 6.25 4 evaluation and reflection 6.26 8
f. After having the table above,
could be classified. And a table consisting of the amount of students
in each level of cultural awareness and each aspect was made.
g. Then, the sample of the second study decided. There were 35
students coming from every level taken.
h.
language teaching was collected in a kind of observation.
i. Then, dealing with the second question, the videos were observed to
then noticed whether the students can incorporate the target
40
j. was
concluded
k. The data gotten were described.
l. After describing the cultural awareness of students and the way how
they teach, the analysis on how the students in each level
incorporate culture into teaching was conducted
m. The finding whether the level of cultural awareness could influence
teaching was achieved
n. The findings were discussed.
o. The result, whether the students have good cultural awareness or
not and know how to apply it in English language teaching, was
concluded.
F. Data Source a. Primer source
The primer data of this research was the data got from
performance. The result of interpreting the data became the answer of
the questions raised. The data then would be analysis using the
procedures written in data analysis technique to arrive into the
41
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING
This chapter presents the research findings and discussions of the study. It
describes
techniques for incorporating target cultural content. While, the discussion of this
study deduces the findings to then concludes it.
A.
Findings
In this subtitle, something that will be presented is the research findings.
As an init
cultural awareness will be presented first. Then, the second finding dealing with
the techniques that were used by students for incorporating target language
culture in English language teaching will be presented as the following.
1. Level
Examining the level of studen ame the first focus
of this research. As mentioned in the previous chapter, to answer this question,
it was used There were
eight questions in the test. Questions 1 4 ar
knowledge dealing with target culture. Then, questions 5-8 aimed to test
82. 3 3 3
83. 3 2 3
From the table
described by the following diagram:
1.1
Factual knowledge was the first aspect examined to
areness level. In the conducted test,
heir
Figure 4.
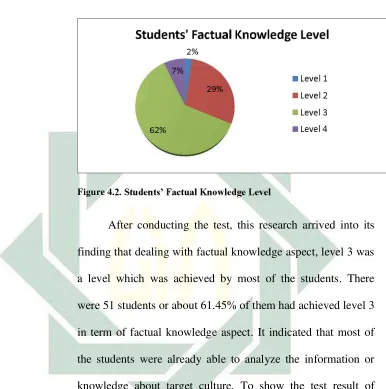
After conducting the test, this research arrived into its
finding that dealing with factual knowledge aspect, level 3 was
a level which was achieved by most of the students. There
were 51 students or about 61.45% of them had achieved level 3
in term of factual knowledge aspect. It indicated that most of
the students were already able to analyze the information or
knowledge about target culture. To show the test result of
students achieving level 3, the following table is presented:
Table 4.2 The Factual Knowledge of Students in Level 3 Level 1
Rubric Students are able
to discover, their own culture in the
47
practices of others
very appropriate manner demographical or historical each individual pays half. How about in while in her custom boy pays everything when
48
this question was benefit to fulfill the requirements of
achieving level 1 based on the rubric provided.
Continuing to the next question, those 51 students were
demanded to answer what cultural behavior they have in
Indonesia relating to splitting bill so met with
the criteria that should have been achieved by students based
on the rubric.
Actually, there were two various answers of students
facing this second question. First, some students answered that
the boys in Indonesia pay everything for the girls if they asked
the girls to go out. Second, some other students said that some
couples in Indonesia sometime pay each other but it is not as
must as splitting bill. They just apply sharing principle, the one
having money is the one needs to pay the cost. And both of the
answers are exist in Indonesia .
Question number 3, to arrive into level 3, was also a
must to answer by the students correctly. This question aimed
to check whether the students can do further than only
49
this question, students were challenged to do an analysis on
Fifty one students achieving level 3 could give an
appropriate answer towards the question mentioned previously.
For
students were able to answer questions number 1 and number 2
and unable to answer questions number 3 and 4. The following
table is presented to give detail information about students
achieving level 2 of factual knowledge:
Table 4.3 The Factual Knowledge of Students in Level 2 Level 1
Rubric Students are able
50 their own culture in the very appropriate manner each individual pays half. How about in
high prestige to pay all
- Mostly, boy pays all the bill. But sometimes, the woman if they have money will pay for the
51
those 24 students were able to put a thick on true column
which automatically showed that they have achieved level 1.
Then, in the second question, students were demanded
to compare and contrast splitting bill with their own habit
dealing with it . This demand was reflected in the question
number 2.
As the previous level, the answers of students were also
divided into two categories. First, some of them stated that
some boys pay the entire bill when they ask a girl to gout.
Second, they wrote that some of couples are mixed up in an
unwritten agreement that the one having money can treat
another.
The third and fourth questions could not be answered
well by the students, some of them left the questions and some
others answered it without having connection to the topic, as an
example: students only answered
to the question number 3. In contrast, the question
asked the reason why Jennifer surprised that she had to pay the
52
All of this became an exact sign that the factual
knowledge level of 24 students was only stuck in level 2,
where they only could contrast and compare. In details, being
in level 2 meant that the students were able to compare and
contrast the cultural beliefs or perspectives of others with their
own culture in an appropriate manner (without
underestimating).
The second latest level which had been achieved by
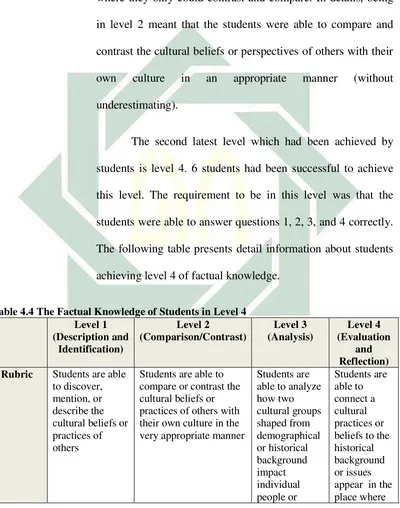
students is level 4. 6 students had been successful to achieve
this level. The requirement to be in this level was that the
students were able to answer questions 1, 2, 3, and 4 correctly.
The following table presents detail information about students
achieving level 4 of factual knowledge.
Table 4.4 The Factual Knowledge of Students in Level 4 Level 1 Rubric Students are able
53
personal view the culture
comes from each individual pays half. How about in the boy should pay for their dating. For me, it shows that boy is other. If the boy having money, he pays the bill. If the girl having money, she pays the boy. But
answer true-false question ents are
54
students could put a thick on true column which became the
right choice. Actually, this question aimed to achieve the
criteria of level 1 based on the rubric provided.
Then, stepping to question 2, those 6 students were also
able to answer it. In this question, they were demanded to
compare splitting the bill custom which is common in
America with the habit of Indonesian relating to it . This
question was answered by students without having significant
differences with other students coming from level 3 and 2. And
their answers met them with the criteria that shall be achieved
in the rubric
Then, question number 3 was also answered precisely
by those 6 students. This question challenged the students to
do an analysis toward splitting bill custom as stated in the
question number 3. The question was
perspective on the reasons why Jennifer surprised that she had
to pay some of the bill. This question needed students to do
analysis rather than only mention or comparing something to
55
This third question was answered by those 6 students
without having significant differences with the students coming
from other levels.
Being in level 4 indicated that those 6 students were
already able to connect a cultural practice or belief to the
historical background or issues appear in the place where the
culture comes from. In this test, gender issue which was
booming in America was taken to connect it with splitting bill
culture.
Most students answered that splitting bill was
connected to gender issue, as the reason that both gender issue
and splitting bill offer equality between men and women in
term of acquiring right and fulfilling obligation. Most students
thought that splitting bill was an impact of gender issue. By
splitting bill, the position of women would be equal with men
and there would be no discrimination. And it had been matched
with the rubric.
Level 1 was the level which only 2 students achieved it.
This fact described that the students who were in this level
56
practices and beliefs of others. In details, students who were in
this level only could discover that splitting bill is a common
American habit through true-false question. The detail is as the
following:
Table 4.5 The Factual Knowledge of Students in Level 1 Level 1 Rubric Students are able
57
by her
All those students could put a thick on true column
which became the right choice. Actually, this question aimed to
achieve the criteria of level 1 based on the rubric provided.
The rest of questions were left blank and answered
inappropriately. The evidence could
answer. One of them, when answering questions number 2
asking about Indonesian custom closed to splitting bill, only
wrote
Then, the answer of the third question was
Another one left the second and fourth questions, and only
From those answers, it was clear that both students
were in the first level which they only able to describe and
58
1.2
level, here
questions numbers 5-8 were used. All of the questions were
developed based on the rubric provided and the article red by
the students. Question number 5 aimed to indicate that the
students were able to, dealing with intercultural competence,
do a kind of description and identification. Question number 6
aimed to examine whether students were arrived into
comparison and contrast. Question number 7 aimed to check
whether students having ability to analyze an intercultural
knowledge. Question number 8 examined students whether
they were already able to do evaluation and reflection.
Figure 4.
21%
34% 44%
1%
St udent's Factual Know ledge Level
59
Level 3 became the level which was achieved by most
students. 35 students or about 42.2% from the test takers had
achieved this level. As mentioned above, being in level three
automatically indicated that the students could answer
questions number 5 and 6 and even number 7 rightly. To give a
brief overview dealing with students factual knowledge in
level 3, the following table is presented:
Table 4.6 The Intercultural Competence of Students in Level 3 Level 1
appropriately to give their own opinions on
Question If American
have splitting
bill, how about Indonesian?
Do you think that
60
reason first. Or at least, she find it by her own the reason why Eddie do
-competence as stated in the rubric.
Stepping further, those 35 students were also able to
61
students ability in doing analysis . The question above aimed
to check or examine whether students could give a statement
on how their belief and perspective influence their view to
this
question asked students to give reasons on their view whether
Jennifer should have been angry facing splitting bill or not.
Dealing with the question stated above, the answers of
those 35 students indicate two categories, agree and disagree.
Some students in this level stated that Jennifer should have
been so angry with Eddy. It was because the cultural shock she
faced and it was common to happen in the very first contact
with a new strange culture. Then, some others disagreed that
Jennifer should have been angry. They thought that Jennifer
should clarify Eddy the reason why he did it. Students also
thought that Jennifer also needs to be aware on the cultural
differences possibility.
The seventh question asked students about their opinion
whether it was reasonable to expect high school students to