Bangladesh j. crop sci. 2006, 17(1): 35-40
RESPONSE OF BRRI DHAN31 TO NITROGEN LEVEL AND SPLIT
APPLICATION OF
SESBANIA ACULEATA
AS GREEN MANURE
M.M. Rahman, M.S.U. Bhuiya1, M.A. Islam1, M.S.I. Sikdar and M.S. Islam
Department of Agronomy
Hajee Mohammad Danesh Science and Technology University Dinajpur
Abstract
An experiment was conducted at the Agronomy Field Laboratory, Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh to investigate into the effect of nitrogen level and split application of Sesbania aculeata as green manure on the performance of transplant aman rice cv. BRRI dhan31. The experiment comprised of five levels of nitrogen levels viz., 0, 25, 50, 75 and 100 kg N ha-1 and split application of Sesbania aculeata biomass viz., control, 100% as basal, 50% as basal + 50% at early tillering, 33% as basal + 33% at early tillering + 33% at panicle initiation, 100% at early tillering and 100% at panicle initiation the hight level of N i.e. (25 t ha-1). Effect of nitrogen level was found significant for most of yield contributing characters (except 1000- grain weight) grain and straw yield. The highest level of nitrogen (100 kg ha-1) produced both the highest grain (5.58 t ha-1) and straw (6.82 t ha-1) yield. On the other hand split application of Sesbania aculeata also significantly influenced most of parameters studied producing the highest grain yield (5.43 t ha-1) and straw yield (6.76 t ha-1) when applied 100% as basal. Nitrogen @ 100 kg ha-1 interacted favourably with Sesbania aculeata applied 100% as basal to produce the highest grain yield (6.22 t ha-1). On the other hand, the control combination (no nitrogen and no Sesbania aculeata) produced the lowest grain yield (4.01 t ha-1). Results suggest that BRRI dhan31 may be fertilized and 100 kg N ha-1 along with the application of 25 t ha-1 fresh biomass of Sesbania aculeata as basal for higher yield.
Key word: Nitrogen, Split application, Sesbania aculeata , Performance, Rice.
Introduction
Soil fertility and its sustainability mostly depend on the organic matter status of the soil. Sun and Hisch (1992) reported that less than 2% organic matter is generally considered to be ‘insufficient’, 2.5% ‘fair’, 3%‘good’ and more than 5% is ‘plenty’. But the organic matter status of the Bangladesh soil has been decreasing day by day, which already reached below 1% in most of the lands (Meah, 1994). It is obvious that one of the cheapest ways of maintaining and increasing the organic matter content of soil is to incorporate the green manuring crops at their vegetative stage. Green manure plays a vital role in the sustenance of soil fertility and crop productivity. In Bangladesh Sesbania aculeata, an indigenous species of Dhaincha, is considered as promising species for biomass production and nitrogen yield. Sesbania aculeata is a fast growing plant, which can be grown even on dry land with minimum cost. It has also been reported that Sesbania aculeata can supply nearly 108 kg N ha-1 when incorporated at 60 days after sowing (Beri et al., 1989). Normally green manuring is done through incorporation of green leaves or plants in the soil before transplanting rice crop. But incorporation of this crop at different stages of rice growth may reduce the nitrogen application to some extent, as it is soft and readily decomposable. Integrating nitrogen fertilizer with legume ________________________________________________________________
1
green manures (GM) can foster sustainable and environmentally sound agricultural systems in sub-tropical and semi arid soils of low organic matter content. It was found that green manuring with Sesbania aculeata could save a substantial amount of applied nitrogen. Many workers suggested that green manuring along with application of nitrogenous fertilizer helped to release nutrient elements slowly during the period of crop growth (Huang et al., 1981; Singh et al., 1990). The present study was, therefore, undertaken to find out the effect of N level and split application of Sesbania aculeata on the performance of transplant aman rice cv. BRRI dhan 31.
Materials and Methods
The experiment was carried out at the Agronomy Field Laboratory, Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh during the period from May to November 2004. The experimental area was characterized by non-calcareous dark grey floodplain soil belonging to the Old Brahmaputra floodplain; Agro-ecological Zone 9 (UNDP and FAO, 1988). The experimental field was slightly loam in texture with a pH value of 6.8 and having 0.10 % and 1.78 % total nitrogen and organic matter, respectively. The experiment consisted of five levels of nitrogen viz., 0 (N0), 25 (N1), 50 (N2), 75 (N3) and
100 (N4) kg N ha-1 and split application of Sesbania aculeata biomass viz., no application
(GM0), 100% as basal (GM1), 50% as basal + 50% at early tillering (GM2), 33% as basal
+ 33% at early tillering + 33% at panicle initiation (GM3), 100% at early tillering (GM4) and
100% at panicle initiation (GM5) stage @ 25 t ha-1. The experiment was laid out in a split
plot design with three replications. The plot size was 3m × 2m. The land was fertilized with N through Urea as per treatment specification. Urea was top dressed in three equal splits at 10, 25 and 50 days after transplanting. At the time of final land preparation each unit plot was fertilized with triple superphosphate, muriate of potash, gypsum and zinc sulphate @ 50, 60, 33 and 5 kg ha-1, respectively (BRRI, 2004). Thirty-day-old seedlings of BRRI dhan31 were transplanted in the well-prepared puddled field on 24 July 2004 at the rate of two seedlings hill-1 with 25cm × 15 cm spacing. Intercultural operations were done as and when necessary. Five hills (excluding border hill) were randomly selected at maturity and uprooted from each unit plot prior to harvest for recording data on different plant characters. The crop was harvested when 90% of the grains became golden yellow in colour. The grains were threshed, cleaned and sun dried to record grain yield plot-1. The grain yield was adjusted to 14% moisture content. Straws were sun-dried to record the straw yield plot-1. Grain and straw yields were then converted to t ha-1. The recorded data were analysed using Analysis of Variance with the help of computer package MSTAT. The mean differences among the treatments were adjudged with Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (Gomez and Gomez, 1984).
Results and Discussions
Effect of nitrogen level
RAHMAN et al 37
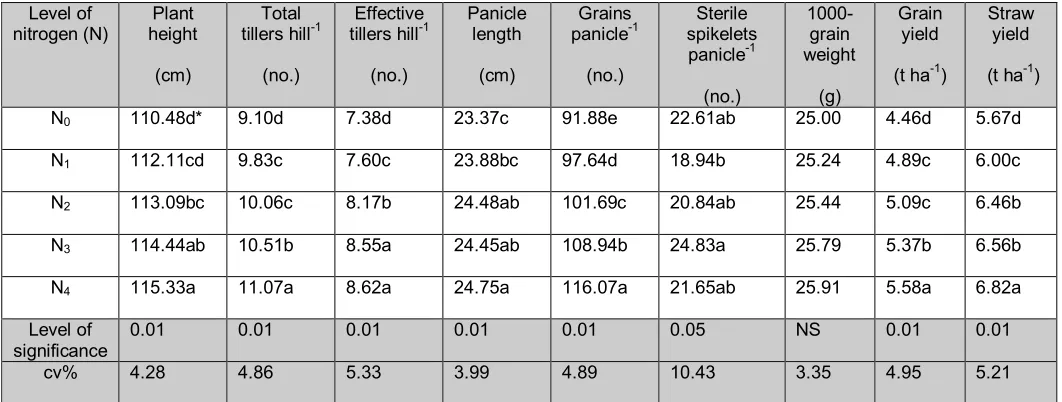
identical to those recorded with 75 kg N ha-1. The highest grain yield (5.58 t ha-1) was obtained from 100 kg N ha-1. Nitrogen level positively influenced yield contributing characters of rice, which resulted in increased the grain yield. Similar results were observed by Choudhary et al. (1998); BRRI (2000) and Singh et al. (2000). Application of nitrogen @ 100 kg ha-1 produced the highest straw yield also which was mostly the outcome of the talest plant and highest no. of total tillars hill-1. Weight of 1000-grain was not significantly influenced by N level as it mostly governed by the genetic make up of the variety. In all cases the lowest values were found in control treatment.
Table 1. Effect of nitrogen level on the yield and yield contributing characters of
BRRI dhan31
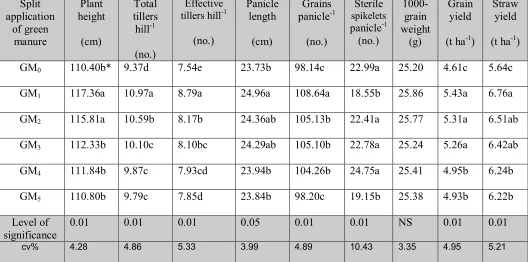
Split application of Sesbania aculeata exerted significant influence on the yield
components viz., plant height, number of total tillers hill-1, number of effective tillers hill-1,
(33% as basal + 33% at early tillering + 33% at panicle initiation stage). This result might
38 RESPONSE OF BARRI DHAN31 TO GREEN MANURE
Table 2. Effect of split application of Sesbania aculeata green manure on the yield and yield contributing characters of BRRI dhan31
* Figures in a column having common letter (s) do not differ significantly as per Duncan’s Multiple Range Test % as basal + 33% at early tillering + 33% at panicle initiation; GM4 = 100% at early tillering stage;
GM5 = 100% at panicle initiation
Effect of Interaction
Interaction of nitrogen level and split application of Sesbania aculeata significantly influenced the production of number of total tillers hill-1, number of effective
RAHMAN et al 39 % as basal + 33% at early tillering + 33% at panicle initiation; GM4 = 100% at early tillering stage;
References
Beri V, Meelu O P & Khind C S. 1989. Biomass production, N accumulation, symbiotic effectiveness and
mineralization of green manures in relation to yield of wetland rice. Trop. Agric. 66(1): 11-16.
BRRI (Bangladesh Rice Research Institute). 2000. Annual Report for July 1999-June2000. Bangladesh Rice
Res. Inst. Joydebpur, Gazipur. pp. 50-53.
BRRI (Bangladesh Rice Research Institute). 2004. Adhunik Dhaner Chash (in Bengali) 12th Edn., Pub. No. 5.
Bangladesh Rice Res. Inst. Joydebpur, Gazipur. pp. 27-28.
Chowdhary B T, Turkhede A B, Chore C N, Jiotode D J & Thoral A W. 1998. Performance of Basmati rice
varieties under various levels of nitrogen with organic manure. J. Soil Crops. 8(1): 41-43.
Gomez K A & Gomez A A. 1984. Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research. 2nd Edn. John Wiley &
Sons. New York. 680 p.
Huang D M, Hua G J & Li Z P.1981.The transformation and distribution of organic and inorganic fertilizer
nitrogen in rice soil. Systm. Acta Pedal. 18(2): 120-121.
Meah M M U. 1994. Contribution of fertilizer in national economy and sustainable environmental
development In. Proc. Workshop Environ. Issues. GTI pub. No. 99. Bangladesh Agril. Univ.
Mymensingh. pp. 24-40.
Singh Y, Singh B, Meelu O P & Miskina M S. 1990. Nitrogen equivalence of green manure for wetland rice on
coarse textural soils. Intl. Rice Res. Notes. 15 (2): 25
Singh M K, Thakur R, Verma U N, Upasani R R & Pal K. 2000. Effect of planting time and nitrogen on
production potential of Basmati rice (Oryza sativa) cultivars in Bihar Plateau. Indian J. Agron.45(2):
300-303.
Sun P M H & Hisch S C. 1992. The establishment of sustainable agricultural system in Tiwan. Sustainable
Agriculture for the Asia and Pacific Region. FFTC Book Series No. 44. p. 4.
UNDP and FAO. 1988. Land Resources Appraisal of Bangladesh for Agricultural Development. Report No.
2. Agro-ecological Regions of Bangladesh. United Nations Development Programme and Food and
Agricultural Organization. pp. 212-221.
Yadav R L. 2004. Enhancing efficiency of fertilizer N use in rice- wheat systems of Indo-Gangetic plains by
intercropping Sesbania aculeata in direct seeded upland rice for green manuring. Bio-res. Tech.