THE EFFECTIVENESS OF GRAPHIC ORGANIZER TO TEACH READING
VIEWED FROM STUDENTS’ MOTIVATION
Fitri Nurdianingsih
Dosen Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro Email: [email protected]
Abstract:
The objective of the research is to identify whether or not: (1) Graphic Organizer is more effective than Lecture to teach reading; (2) students who have high motivation have better reading skill than those who have low motivation; and (3) there is an interaction effect
between teaching methods and the students’ motivation on the students’ reading skill. The
research was conducted in IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro, East Java. The research was conducted from March to May 2014. The method used for the research was experimental study. The population of the research was the fourth semester students of IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro. The sampling used was cluster random sampling. The sample of the research was two classes, they were experimental class taught using Graphic Organizer and control class taught using
Lecture. The instruments used to collect the data were students’ motivation questionnaire in
the form of likert scale and reading test in the form of multiple choice. Meanwhile, to analyze the data, Multifactor Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) test 2 x 2 and Tukey test were used. The data analysis shows the following findings: (1) Graphic Organizer is more effective than Lecture to teach reading for the fourth semester students of IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro; (2) the students who have high motivation have better reading skill than those who have low
motivation; and (3) there is an interaction between teaching methods and students’
motivation to teach reading at the fourth semester students of IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro. Based on the research findings, it can be concluded that Graphic Organizer is an effective technique to teach reading for the fourth semester students of English Education Department, IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro, in the academic year 2013/2014. The effectiveness of this technique
is affected by students’ motivation level.
Keyword: Graphic Organizer, Reading, Motivation
English is very useful for people to improve themselves in all aspects, especially for the university students. English is learnt from primary school to the university level in Indonesia and it is a hard work not only for the government, but also for the teachers, parents and the students.
Spolsky (1999: 653) states that reading is the process of perceiving and deriving meaning from what has been written. However, reading comprehension has become the problems among students. English teacher should create a better technique in teaching reading. In order to achieve the objective of teaching reading, the teacher should be careful in designing and selecting the instructional materials used. Good materials also provide models
for teachers to follow developing their own materials (Nunan, 1988: 98). Coopersmith in Brown (2000: 103) states that motivation is the evaluation which the individual makes and customarily maintains with regard to himself; it expresses an attitude of approval or disapproval, and indicates the extent to which an individual believes himself to be capable, significant, successful, and worthy. Motivation is considered as one of the important affective factors because success or failure of a person depends mostly on the degree of one’s motivation.
Considering to that background, the writer formulates the problems of this study as follows:
reading for the fourth semester students of IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro in the academic year 2013/2014? Do the students who have high motivation have better reading skill than those who have low motivation?
Is there any interaction between teaching methods and students’ motivation on the students’ reading skill for the fourth semester students of IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro in the academic year 2013/2014?
This research is aimed at finding out the influences of teaching methods and students’ motivation on the students’ reading skill. In detail, this research has the objective too find out whether:
Graphic Organizer is more effective than Lecture to teach reading for the fourth semester students of IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro in the academic year 2013/2014.
The students who have high motivation have better reading skill than those who have low motivation. There is an interaction between teaching methods and students’ motivation in teaching reading for the fourth semester students of IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro in the academic year 2013/2014.
The discussion of the nature of reading, in general, cannot be separated from different ways of defining the term of reading. Moats in Westwood (2008: 2) states that reading is the fundamental skill upon which all formal education depends. Another definition from Patel and Jain (2006: 114) state that reading is an active process which consists of recognition and comprehension skill. Reading is the process of perceiving and deriving meaning from what has been written (Spolsky, 1999: 653). Further, reading is the process of combining textual information with the information a reader brings to a text. In this view, the reading process is not simply a matter of extracting information from the text (Widdowson in
Carell, et al., 1996: 56). Moreover, reading comprehension can be defined as an active thinking process through which a reader intentionally constructs meaning to form a deeper understanding of concepts and information presented in a text (Westwood, 2008: 31). To comprehend, readers must use information they already process to filter, interpret, organize, and reflect upon the incoming information from the page. Efficient interpretation of text involves a combination of word recognition skills, linking of new information to prior knowledge, and application of appropriate strategies such as locating the main idea, making connections, questioning, inferring, and predicting. In line with the theories and elaboration of reading, it can be stated that reading skill is a mental process which involves a readers to understand the text. It includes understanding the main idea, understanding explicit and implicit information, understanding reference, and understanding meaning of words or phrases based on the context. According to Grabe and Stoller (2002: 12-15) there are several purposes of reading, such as, reading to search for simple information, reading to skim quickly, reading to learn from texts, reading to integrate information, reading to write, and reading for general comprehension.
newly acquired information. By using Graphic Organizer, educators hope to facilitate the readers’ understanding of the text through visual depictions of key terms, concepts and the relationships among them (Simmons, Griffin, &Kame’enui, 1988).
Besides, Lecture is the one of the oldest and overused teaching methods. McIntosh (1996: 96) points out that lecture is frequently a one-way verbal communication unaccompanied by discussion, questioning or immediate practice. The lecturer or instructor will be the center of an activity. Lecture in teaching reading will make the students as passive hearers and have no chance to critically give their arguments or responses. The teacher as a learning center does not pay attention on the students comprehension so that the learning objectives less emphasized.
The concept of student’s motivation is used to explain the degree to which students invest attention and effort in various pursuits which may or may not the ones desired by their teachers. The term motivation is defined by Gardner (1995) as referring to combination of effort plus desire to achieve the goal of learning the language plus favorable attitudes toward learning the language. Student’s motivation is an internal and external drives which energize and activate student’s learning attitude to do efforts in order to achieve the goal. The indicator of internal drives are such as interest, curiosity, concentration, need for achievement, participation in learning activity, cooperation in doing the assignment, and persistence with the learning task, while those for external drives are such as a hope to get praise, ridicule, reward, punishment, good mark, and exam. Students having high motivation have high aspiration, great effort, believe themselves to be capable, successful, and worthy. Based on its source, student’s motivation can be categorized as intrinsic and extrinsic
motivation. Intrinsic motivation is motivation which appears without needing internal stimulus, because it has been internal to the person that is suitable with his or her need. Intrinsic motivations are inherent in learning situation and meet pupil needs and purposes. This motivation is often called pure motivation, real motivation, which emerges from internal. Intrinsic motivation is motivation which is alive internally to the person and it is useful in functional learning situation.
Extrinsic motivation appears because there is stimulus/incentive from outside the individual. Extrinsic motivation is a kind of motivation in which learning activities started and continued based on external drives which are not absolutely related to learning activities. Extrinsic motivation is motivation which is caused by external factors of learning situation, such as, reward, certificate, levels, medal, competition, etc. (in positive response) and the other forms, such as, teasing allusion, sarcasms, and punishment (in negative response).
Based on the rationale, the writer proposes the hypothesis of this study as the following: (1) Graphic Organizer is more effective than the lecture to teach reading at the fourth semester of IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro; (2) The students who have high motivation have better reading skill than those who have low motivation at the fourth semester of IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro; (3) There is an interaction effect between teaching strategy and the students’ motivation on the reading skill of the fourth semester of IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro.
METHODOLOGY
dependent variable in this study is reading skill. The fourth variable is a secondary independent variable or attributive variable. It is motivation.
The population of this study is the fourth semester students of IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro in the academic year 2013/2014. It consists of 3 classes, divided into class 3A, 3B, and 3C.
In this study, the writer only took two classes were 3A and 3B. 3A was the experimental class and 3B was the control class.
The sample in this study was chosen randomly from the population of cluster which is usually called cluster random sampling. It means that all the members of cluster must be included in the sample.
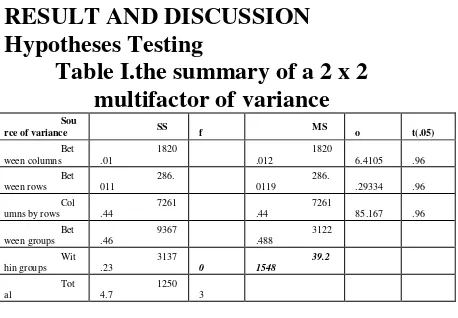
RESULT AND DISCUSSION Hypotheses Testing
Table I.the summary of a 2 x 2 multifactor of variance
Sou
rce of variance SS f MS o t(.05)
Bet ween columns
1820 .01
1820
.012 6.4105 .96 Bet
ween rows
286. 011
286.
0119 .29334 .96 Col
umns by rows
7261 .44
7261
.44 85.167 .96 Bet ween groups 9367 .46 3122 .488 Wit hin groups 3137 .23 0
39.2 1548 Tot
al
1250
4.7 3
Based on the table above, it can be concluded that: (1) because Fo between
columns (46.41055) is higher than Ft at the
level of significance α = 0.05 (3.96), Ho is
rejected and the difference between columns is significant. It can be concluded that the teaching methods differ significantly from one another in their effect on reading skill. Based on the computation result, the mean score of the students who are taught using Graphic Organizer (72.095) is higher than that of those who are taught using Lecture (62.786). Thus, it can be concluded that the students who are taught using Graphic Organizer have better reading skill than that of those who are taught using Lecture; (2) because Fo between rows (7.293343) is
higher than Ftat the level of significance α
= 0.05 (3.96), Ho is rejected and the
difference between rows is significant. It can be concluded that students having high motivation and those having low motivation are significantly different in their reading skill. Based on the computation result, the mean score of the students who have high motivation (69.286) is higher than that of those who have low motivation (65.595). Thus, it can be concluded that the students who have high motivation have better reading skill than that of those who have low motivation; (3) because Fo interaction
(185.1677) is higher than Ft at the level of
significance α = 0.05 (3.96), Ho is rejected
and there is an interaction effect between teaching techniques and motivation toward students’ reading skill. It means that the effect of teaching methods depends on the degree of motivation.
Table II. The Summary of Tukey Test
etwe en grou ps 0 t (.0 5) t (.0 1) eanin g C ategor y
1 - A2 .634
.8 6
.8
2 o>qt
S ignific ant
1 - B2 .820
.8 6
.8
2 o>qt
S ignific ant
1B1 -
A2B1
0.42 0
.9 5
.0
2 o>qt
S ignific ant
1B2 -
A2B2 .795
.9 5
.0
2 o>qt
S ignific ant
(1) Comparing two means between columns (A1 – A2). Because qo
between A1 and A2 (9.634) is higher than
qt at the level of significance α = 0.05
(2.86), Graphic Organizers differs significantly from the lecture for teaching reading. The mean score of the students who are taught by using Graphic Organizers (72.095) is higher than that of those who are taught by using Lecture (62.786). Thus, it can be concluded that the students who are taught using Graphic Organizer have better reading skill than that of those who are taught using Lecture.
between B1 and B2 (3.820) is higher than qt
at the level of significance α = 0.05 (2.86), students having high motivation differ significantly from those having low motivation in their reading skill. The mean score of students having high motivation (69.286) is higher than that of those having low motivation (65.595). Thus, it can be concluded that the students who have high motivation have better reading skill than that of those who have low motivation.
(3) Comparing two means between cells (A1B1 - A2B1). Because qo
between A1B1 and A2B1 (20.420) is higher
than qtat the level of significance α = 0.05
(2.95), Graphic Organizers differs significantly from the Lecture to teach reading for students having high motivation. The mean score of students having high motivation who are taught by using Graphic Organizers (83.238) is higher than that of those who are taught by using Lecture (55.333), so Graphic Organizer is more effective than Lecture method to teach reading for students having high motivation.
(4) Comparing two means between cells (A1B2 - A2B2). Because qo
between A1B2 and A2B2 (6.795) is lower
than qtat the level of significance α = 0.05
(2.95), Lecture method differs significantly from Graphic Organizer to teach reading for students having low motivation. The mean score of students having low motivation who are taught by using Lecture (70.238) is higher than that of those who are taught by using Graphic Organizer (60.952). Thus, it can be concluded that Lecture is more effective than Graphic Organizer to teach reading for students having low motivation.
(5) Based on the point c and d, Graphic Organizer is more effective than Lecture method to teach reading for students having high motivation and Lecture method is more effective than Graphic Organizer to teach reading for students having low motivation, so it can be concluded that there is an interaction
between teaching methods and motivation to teach reading.
By considering the data analysis above, there are some conclusions that can be drawn.
(1) Graphic Organizer is more effective than lecture to teach reading.
Graphic Organizer is a technique of teaching and learning process where the activities in the classroom are focused on the students as a center of the teaching and learning process. Because Graphic Organizer present material through the visual and spatial modalities, the use of Graphic Organizer helps the students internalize what they are learning.
Gregory and Carolyn (2007: 101) state that Graphic Organizer is useful thinking tools that allow students to organize information and allow students to see their thinking. They are visual/spatial, logical/mathematical tools that appeal to many learners for managing and organizing information.
On the other hand, Lecture is less effective to improve students’ reading skill since Lecture less motivates students to involve in the teaching-learning process. In Lecture, teaching reading will make the students as passive hearers and have no chance to critically give their arguments or responses. The teacher as a learning center does not pay attention to the students’ comprehension so that the learning objectives are less emphasized. Lecture fosters passive learning with very low students’ involvement (Moore, 1994: 182). Students just become the followers and depend on the teacher during the teaching-learning process.
unimportant. The lecturer or instructor will be the center of an activity.
Therefore, Graphic Organizer is more effective than Lecture to teach reading.
(2) The students who have high motivation have better reading skill than those who have low motivation.
Student’ motivation is one important aspect of reading process. The aspect affects how hard the students will work at the reading task. For example, the students who are highly motivated in the reading materials presented to them will put for much more efforts in the reading process than students who have no motivation in the available reading materials.
However, to arouse the student’s motivation to actively participate in learning process is not an easy work in learning reading because, basically, reading itself is a complex activity which needs a thinking process in order to construct an interpret the message conveyed in a text. Every student has different level of motivation. The level of low or high motivation in learning reading will, of course, determine how far the student attempts to comprehend the texts. The honest attempts and real desires which are based on high motivation will, of course help students to achieve a good result. Therefore, teacher should help them in arousing their motivation to be active in learning process. If students have high motivation, of course, they will be easier to understand the reading materials. And if they understand the reading material well, there is a good chance to obtain a good result.
On the other hand, if students do not have motivation in learning process, then, their duties and responsibilities will be gradually ignored. They do not feel responsible if their scores decrease. Also, they do not have ambition to achieve good proficiency. Therefore, the students who have high motivation have better reading skill than those who have low motivation.
(3) There is an interaction effect between teaching method and students motivation on the reading skill.
Graphic Organizers are teaching and learning tools. When they are integrated into classroom activities, students are better able to understand new material. Graphic Organizers support students by enabling them to literally see connections and relationships between facts, information, and terms. Hyerle in Zwiers (2006: 17) states that one of the most important features of Graphic Organizers is their ability to help the reader create a mental picture of text’s information.
Students with high motivation believe in their abilities and feel that they are capable of achieving their goals and succeed. Students with high motivation have high aspiration, great persistence, positive judgment about themselves, and good moral. They are loved by others and it is easy for them to get friends. Atwater (1990: 155) states that the students having high level of motivation expect to do well in their accomplishments, try hard and try to be successful. People who have high motivation feel they are more capable, appreciative, and contributive. They also practice self-responsibility. Therefore, Graphic Organizer is more effective for students having high motivation.
Meanwhile, Lecture is the one of the oldest and overused teaching strategy. Teacher is more active and students are passive during teaching-learning process. Lecture is one way instructional strategy to convey the ideas or information but ignoring the students’ active involvement in form of discussion, questioning or immediate practices. In Lecture, students usually get knowledge from their teacher. They are not demanded to elaborate their ideas, thoughts, and feelings. Atwater (1990: 155) states that in Lecture, teacher is more active and students are passive.
focusing on your weaknesses instead of paying attention to your strengths. Passer and Smith (2004: 442) state that students with low motivation are less likely to try to make them feel better when they experience negative moods in response to perceived failures in their lives. They are more prone to psychological problems, such as anxiety and depression, to physical illness, and to poor social relationships. In fact, students having low motivation exert less effort on their tasks, especially challenging and demanding ones. In other words, they prefer being passive in the teaching-learning process. That is why, lecture is more effective for students having low motivation.
Therefore, there is an interaction effect between teaching methods and motivation toward students’ reading skill. Graphic Organizer is more effective than Lecture method to teach reading for students having high motivation. Meanwhile, Lecture is more effective than Graphic Organizer to teach reading for students having low motivation.
CONCLUSION, IMPLICATION, AND SUGGESTION
Conclusion
One, graphic Organizer is more effective than Lecture to teach reading to the fourth semester students of English Education Department, IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro, in the academic year of 2013/2014.
Two, the students having high motivation have better reading skill than those having low motivation of the fourth semester students of English Education Department, IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro, in the academic year of 2013/2014. Three,
There is interaction between teaching methods (Graphic Organizers and Lecture Methods) and motivation to teach reading to the fourth semester students of English Education Department, IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro, in the academic year of 2013/2014.
Based on the research findings, it can be concluded that Graphic Organizer is an effective technique to teach reading for the fourth semester students of English Education Department, IKIP PGRI Bojonegoro, in the academic year of 2013/2014. The effectiveness of this technique is affected bt students’ motivation level.
Implication
The research findings imply that the use of Graphic Organizers can affect the students’ reading skill. It is proved from the research findings showing that students who are taught using Graphic Organizers have better reading skill than those who are taught using lecture. In applying the Graphic Organizers, teacher should really use it optimally.
Hopefully, by applying the suitable teaching technique, that is Graphic Organizers, the students are able to obtain an optimum result in reading achievement. Suggestion
For the lecturers
Teachers can use Graphic Organizers to teach reading to improve students’ reading skill and teachers have to consider that motivation plays a crucial role in learning
For students
Students must be more active in the teaching and learning process in order to improve their reading skill, and students having low motivation should encourage themselves and realize the importance of active involvement in the teaching learning process
For other researchers
The result of this study, hopefully, can urge other researchers to conduct further study concerning with the method and the role of the learning motivation to improve the students’ reading skill.`
REFERENCES
Alderson, J.C & Urquhart, A.H. (1984).
Reading in Foreign Language.
Atwater, Eastwood. (1990). Psychology of Adjustment: Personal Growth in a
Changing World. New Jersey:
Prentice Hall.
Barkley, Elizabeth F., Cross, K. Patricia., Major, Claire Howell. (2005).
Collaborative Learning Techniques: a Handbook for College Faculty.
California: Jossey-Bass A Willey Imprint.
Brown, H.Douglas. (2001). Teaching by Principles: An Interactive Approach
to Language Pedagogy. New York:
Longman.
Brown, James Dean. (1995). The Element
of Language Curriculum: A
Systematic Approach to Program
Development. Boston:
Heinle&Heinle Publishers.
Cloninger, Susan C. (2009). Theories of Personality: Understanding Persons. 5thed. New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hill.
Destari, Dina. (2010). The Effectiveness of Internet-Based Material to Teach
Reading Comprehension Viewed
from Learning Motivation. (An Experimental Research at the First Semester of Pesantren Kampus STAIN Samarinda in the Academic
Year of 2009/2010). Surakarta
Finnegan, Nicholas. (2007). Higher
Motivation and More….: Growing to
Become More of where You
Currently are in Your Life. Victoria:
Trafford Publishing.
Gregory, Gayle H., and Carolyn Chapman. (2007). Differentiated Instructional
Strategies. California: Corwin Press,
Sage Publications Ltd.
Gunning, Thomas G. (2010). Reading
Comprehension.Boosters. California:
john Wiley and Sons Inc.
Harmer, Jeremy. (1998). How to Teach English: An Introduction to the
Practice of English Language
Teaching. Essex: Longman.
Harris, David P. (1969). Testing English as
a Second Language. United States of
America: McGraw-Hill Inc.
Huang, Patricia. (2002). The Effects of Graphic Organizer Use on Reading
Comprehension. Southeastern
LousianaUniversity.Available at http://pangea.
Tec.selu.edu/~phuang/600/readorgan .pdf
Hughes, Arthur. (2003). Testing for
Language Teachers. 2nd ed.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Kim, Ae-Hwa., Vaughn, Sharon.,Wanzek, Jeanne., & Wei, Shangjin. (2004).
Graphic Organizers and Their
Effects on the Reading
Comprehension of Students with LD:
A Synthesis of Research.Journal of
Learning Disabilities. Vol.37.
Available at
http://proquest.umi.com/pqdweb?did =580845071&sid=3&Fmt=3&clientI d=44698&RQT=309&VName=PQD
Merkley, Donna M. and Debra Jeffries. (2001). Guidelines for Implementing a Graphic Organizer.
McIntosh, N. (1996). Why Do The
teachers Lecture? Baltimore, USA:
JHPIEGO Corp.
McKnight, Katherine S. (2010). The
Teacher’s Big book of Graphic
Organizers: 100 Reproducible
Reading, Writing, and the Content
Areas. California: Jossey-Bass A
Wiley Imprint.
Moreillon, Judi. (2007). Collaborative Strategies for Teaching Reading
Comprehension. Chicago: American
library Association.
Nation, I.S.P. (2009). Teaching ESL/EFL
Reading and Writing. New Yok:
Routledge.
Ngadiso. (2006). Statistics. Surakarta: English Education Department, Teacher Training and Education Faculty.
Nunan, David. (1991). Language Teaching
Methodology: a Textbook for
Teachers. Prentice Hall.
Patel, Dr. M.F. & Jain, Praveen M. (2006).
English Language Teaching. Jaipur:
Sunrise Publishers & Distributors.
Pearson, P. David. (2000). Handbook of
Reading Research: Volume III. New
Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publisher.
Snow, Catherine E. (2002). Reading for Understanding: toward a Research
and Development Program in
Reading Comprehension. California:
RAND Education.
Spolsky, Bernard. (1999). Concise
Encyclopedia of Educational
Linguistics. Oxford: Elsevier.
Ur, Penny. 1996. A Course in Language Teaching. Practice and Theory.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Westwood, Peter. 2008. What Teachers
Need to Know about. Australia:
ACER Press.
William, Marion and Burden, Robert L. 1997. Psychology for Language Teachers: A Social Constructivist
Approach. New York: Cambridge
University Press.
Woolfolk, Anita. 2007. Educational
Psychology. 10th ed. New York: