THE IMPACT OF MANAGERIAL ABILITY, TAX AVOIDANCE AND INSTITUTIONAL OWNERSHIPS TOWARD FIRM VALUE
(EMPIRICAL STUDY ON MANUFACTURING FIRM REGISTERED ON INDONESIA STOCK EXCHANGE PERIOD 2013-2015)
I Made Ngurah Iswara Mahaputra Sriada
Undergraduate Student of Accounting Study Program–Faculty of Economics and Business–Universitas Airlangga
Email: iswarams@gmail.com
Dr. Elia Mustikasari, M.Si., CA., CMA., BKP., BAK., Ak.
Department of Accountancy–Faculty of Economics and Business–Universitas Airlangga Email: lia_tito@yahoo.co.id
ABSTRACT
The purpose of this research was to obtain empirical evidence, whether managerial ability, tax avoidance and institutional ownership had an impact on frm value. The research approach was quantitative explanatory. The variables used were managerial ability, tax avoidance and institutional ownership as independent variable and frm value as dependent variable. The population were all of the manufacturing frms listed on IDt during the period of 20r13r to 20r135,, with a total of 1343r data for each year. The sample selection was purposive sampling method from the manufacturing frm during the period of 20r13r to 20r135,, with a total sample of 5,13 data for three years. The data were the frmms fnancial report, which was obtained from www.idx.co.id. The analysis model was multiple linear regression with SPSS 20r.r software. The fnding showed managerial ability had an impact on frm value, while tax avoidance and institutional ownerships did not have an impact on frm value.
Keywords: Managerial Ability, Tax Avoidance, Institutional Ownership, and Firm Value 1. INTRODUCTION
As the globalization takes place, boundaries and barriers among the countries start to diminish. As the result, the interaction among the countries start to either increase or decrease. Globalization also has an impact on every segment of life, including economic. The globalization on economic segments is, when the business and economic activities become more integrated from one country to another. This condition is shown, by frms being confdent enough to expand their products to other countries, providing opportunities to increase frmms proft. However, the globalization also provides the frm with threat. The threat is shown as the frm from another country is also confdent enough to expand their product on another country, causing an intensive business competition. The frms from home country must be able to adapt with current trend, use sufcient technology to bring new product and manage frm resources in order to gain more proft, helping the frm to compete with frm from another country. There are three strategies which aid the frm in managing frm resources managerial ability, tax avoidance and institutional ownerships.
proft increase, which is also derived from the frmms proftability ratios including ROA, ROE and EPS (Djutaningsih and Rahman, 20r1320), will attract the stakeholders including shareholders and creditors to provide additional funds on the frm, increasing the frm value (Chang and Wang, 20rr7).
Second, the frmms tax strategies especially tax avoidance strategies also play an important role in increase or decrease of frm value. It is shown as tax avoidance represents wealth transfer from the government to corporations (Chen et.al, 20r13r). Tax avoidance can maximize earnings after tax by fnding loopholes in tax regulation in order to minimize tax expense, which is done by allocating proper tax expense allowed by tax regulation (Dyreng et.al, 20rr8). Tax avoidance is also seen from how much cash tax paid. If the frm is successful implements tax cash based saving by paying small amount of tax, then the frm will restore its liquidity ability to fnance their daily business operation (Karimah and Taufq, 20r136). Maximum amount of earnings after tax followed with good tax cash based saving will attract the stakeholders to provide additional funds on frm, increasing frm value.
Third, institutional ownerships which refers to fnancial institution, including pension funds, mutual funds, money managers, insurance frms, investment banks, commercial trusts, endowment funds, hedge funds, and some hedge fund investors who buy frm outstanding shares in order to exert considerable influence to its management, can strengthen frm corporate governance through monitoring any decision made by manager, minimizing manager agency problem which can tarnish stakeholderms welfare. The higher concentrated institutional ownerships can trigger good monitoring by them to manager (Shleifer and Vishny, 13986). Institutional ownerships allow the institutional investors to monitor any manager actions, as it allow them to be involved in making strategical business decision, making it harder for the institutional investor to be easily tricked by frmms earnings manipulation (Jensen & Meckling, 13976). Institutional ownerships also encourage efciency of the frm operation by reducing the expense which is not related to frm operation and maximizing the proft (Thanatawee, 20r1343). As the institutional ownerships is successful in increasing frm proft, therefore it will attract the stakeholders to provide additional funds on frm, increasing frm value.
According to the backgrounds, author is encouraged to implement a research with a title “THE IMPACT OF MANAGERIAL ABILITY, TAX AVOIDANCE AND INSTITUTIONAL OWNERSHIPS TOWARD FIRM VALUE”.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW Agency Theory
Agency theory defnes a contractual relationship whenever the principals employ the agent to perform frmms business operation and decision making which helps to increase the principalsm beneft or frm value. However, in creating decision and running business operation, the manager may cede to the conflict of interest, causing a decrease on principalms beneft. In order to minimize this problem, the principal can hire another stakeholder who can monitor the manager actions, preventing a destruction on principalms beneft (Jensen and Meckling, 13979).
Signaling Theory
Signaling theory occurs as the manager or the sender and the stakeholders or the receiver have access to diferent information. This shows as how the manager communicate their frm condition to the stakeholders and how the stakeholders will react or give signal to that kind of information (Spence, 1397r). For example, a decrease of frm proft will give signal for investor to sell the frm shares to market.
Stakeholder Theory
influenced the frm to run the business operation in order to increase their welfare and the employees who are influenced to perform better in order to obtain more compensation and salary.
Hypotheses Development
Managerial Ability on Firm Value
Managerial ability refers to a manager who has additional knowledge about frm business, including the trend of current product and technology, the frm investing and fnancing policy that serve as additional funds for frm business operation and how the managers are able to manage their employees, which is reflected on cost of inventory, general and administrative expenses, fxed assets, operating leases, research and development, and intangible assets in order to produce more output called as revenue (Demerdjian et al, 20r1313). As the good managerial ability is successful in utilizing frm resources efciently, it can increase frm value. It is shown that good managerial ability can increase frm proftability derived from less cost and increase of output or revenue. Therefore, stakeholders including shareholders and creditors are interested to provide additional funds for the next business operation.
This statement correlates with the research conducted by Andreou et.al (20r13r), Ng Suwandi et.al (20r135,) and Djutaningsih and Rahman (20r1320) as good managerial ability can increase frm value. First, Andreou et.al (20r13r) stated that good managerial ability can reduce underinvestment through additional fnancing during crisis, which later improves the frm performance and later improves frm value as well (Ng Suwandi et.al, 20r135,). Second, Djutaningsih and Rahman (20r1320) stated that good managerial ability is able to improve frm proftability ratios including ROA, ROE and EPS, which later is used by the stakeholders to provide additional funds on the frm, increasing frm value (Sudiyatno et.al, 20r1320).
Tax Avoidance on Firm Value
Tax avoidance is one of the tax planning methods to fnd loopholes in tax regulation but still complying to them, in order to minimize tax expense. Successful tax avoidance strategies is seen from how the frm is able to maximize earnings after tax through allocating proper tax expense which is regulated by tax law and how the frm is able to maintain their liquidity ability, which is reflected on lower amount of Cash ETR, indicating the frm pays smaller amount of tax in cash compared to its pretax earnings (Karimah and Taufq, 20r136). As the frm shows a good liquidity and proftability ratios because of these strategies, the stakeholders will be interested to provide additional funds on the frm, increasing frm value.
This statement correlates with the research conducted by Chen et.al (20r13r), Desai and Dharmapala (20rr9), and Santana (20r136) as tax avoidance strategies can increase frm value followed with good corporate governance of the frm. The good corporate governance frm can be formed, when the frm employs transparent information related with frmms tax strategies and good control from family management and ownership concentration, which can prevent rent seeking opportunities implemented by manager (Chen et.al, 20r13r).
Institutional Ownerships
This statement correlates with research conducted by Thanatawee (20r1343) and Tahir et.al (20r135,) that institutional ownerships has an efect on the increase of frm value by monitoring manager actions toward an increase or decrease of frm value.
3. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Research Approach
This study is quantitative descriptive with explanatory approach. Explanatory approach gives explanations regarding causal efects among variables through hypotheses testing that aim to either strengthen or reject the theory and hypothesis of the existing research.
Variables Operational Defnitions Managerial Ability
Managerial ability is defned as their skill and characteristic in achieving good performance of the frm. This can be shown, by how efcient the manager is able to manage their resources in producing higher output. Managerial ability is measured by using DEA, which measure the efciency of Decision Making Unit (DMU) with multiple input units and output units. The input used are net property, plant and equipment, net operating leases, net research and development, purchased goodwill, other intangible assets and the output is the sales (Demerdjian et al., 20r1313). If the ratio output over input is higher, then it reflects good managerial ability, which is shown with high frm efciency score. The weight of output (i) on frm (k) is denoted as
u
i and input j on frm k asv
j. The total amount of outputs (i) and inputs (j) areTax avoidance is the way to reducing tax expense by exploiting loopholes in tax regulation in order to minimize tax expense. Tax avoidance is measured with Cash ETR developed by Dyreng et al. (20rr8), because it shows how the frm save their cash despite they do tax avoidance strategies. This show that the frm has no liquidity problem and clear prospect. Good tax avoidance strategies is shown with lower amount of tax paid in cash compared with frmms pretax earnings. Cash ETR is measured by using the following formula:
Cash ETR
=
Pretax Income
CashTax Paid
(i ,t)(i ,t)
The data of Cash Tax Paid is taken from the frmms cash flow statement, while the amount of pretax income is taken from the frmms income statement which is published during period 20r13r to 20r135,.
Institutional Ownerships
majority role in controlling managerms action in increasing their welfare or they just surrender to amount of voting power. Below are the formulas
I O
=
Outstanding SharesOwned by Institution
Outstanding Shares
(i ,t)(i ,t)
The data of outstanding shares owned by institution and outstanding shares of the frm are obtained from frmms notes disclosure on capital stock session from frmms fnancial report (i) issued during period 20r13r to 20r135, (t).
Firm Size
Firm size is defned as how big or small of the frm is. The proxy in measuring size of frm is the value of total asset. We use this proxy because it is more stable rather than capitalized market and sales value which influenced by the power of demand and supply. Because the value of total asset is high, this value needs to be simplifed, by using logarithmic natural. Below are the formulas:
S IZE
=
ln
Total Asset
(i ,t)Amount of the asset is obtained from frmms fnancial report (i) which is published during period 20r13r to 20r135, (t).
Firm Value
Firm value is defned as the welfare of the stakeholder. The increase of welfare is associated with the increase of frm performance, which is shown from frm fnancial report, increasing the stock price, which reflects an increase of shareholder welfare.
Measured with Tobinsmq by including market value of frm and internal side of frm including the total debt, inventory, current assets and total assets, showing how attractive the frm in the open market (Chang & Wang, 20rr7). Below are the formulas:
Tobi n
's Q
=
(
OS x P
)+(
TA
D
+
I
)
– CA
Where Tobinms Q is proxy to measure frm value, OS is the outstanding shares, P is stock price, D is total debt, I is total inventory, CA is current asset and TA is total asset obtained from frms fnancial report
which is published during period 20r13r to 20r135,.
Data Types and Sources
Data used in this study is quantitative data. The data collected are time series data describing historical data and cross-sectional data with an object that requires other related sub objects.
This study uses external secondary data. The data are obtained indirectly, such as from other people or documents. External secondary data are the annual report of manufacturing frms listed in Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDt) in the period 20r13r-20r135,, which was obtained from the site www.idx.co.id
and the end of year stock price which was obtained from Yahoo Finance. Population and Sample
Sample selection method uses purposive sampling method, by selecting sample from population based on fve criterions. The criterions are as follows:
13. Manufacturing frms that are go public during the period of 20r13r to 20r135,
20. Financial reports that are continuously published by manufacturing frms listed in Indonesia Stock Exchange during the period of 20r13r-20r135,.
4. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS Descriptive Statistics
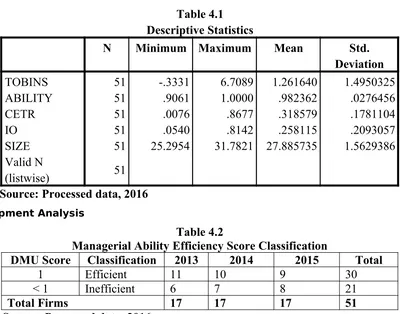
Samples used in this study are 5,13 manufacturing frms listed on Indonesia Stock Exchange during the period of 20r13r to 20r135,.
Table 4.1
Descriptive Statistics
N
Minimum Maximum
Mean
Std.
Deviation
TOBINS
51
-.3331
6.7089
1.261640
1.4950325
ABILITY
51
.9061
1.0000
.982362
.0276456
CETR
51
.0076
.8677
.318579
.1781104
IO
51
.0540
.8142
.258115
.2093057
SIZE
51
25.2954
31.7821 27.885735
1.5629386
Valid N
(listwise)
51
Source: Processed data, 2016
Data Envelopment AnalysisTable 4.2
Managerial Ability Efficiency Score Classification
DMU Score
Classification
2013
2014
2015
Total
1
Efficient
11
10
9
30
< 1
Inefficient
6
7
8
21
Total Firms
17
17
17
51
Source: Processed data, 2016.
Based on table 43.20 above, there were rr frms that could be categorized as efcient, had Managerial Ability Score equals to one or 13rr% and the remaining 2013 frms were not efcient and had MA-Score less than one or 13rr%.
Classic Assumption Test Heteroscedasticity Test
Table 4.3
Heteroscedasticity Test Result
Model
Sig.
(Constant)
,001
ABILITY
,008
CETR
,678
IO
,075
SIZE
,007
Source: Processed data, 2016.
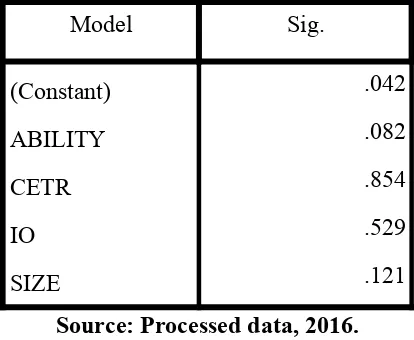
Table 43.r represents that ABILITY and SIZE has signifcance value less than r.r5,, indicating heteroscedasticity problem. Therefore, eliminating the outlier data that had the highest residual value was needed. The result of second heteroscedasticity test is shown in table 43.r
Table 4.4
Model
Sig.
(Constant)
.042
ABILITY
.082
CETR
.854
IO
.529
SIZE
.121
Source: Processed data, 2016.
Based on table 43.r each value has signifcant value more than r.r5,, indicating no heteroscedasticity problem.
Normality Test
Table 4.5
Normality Test Result
Keterangan
N
Kolmogorov-
Smirnov Z
Asymp. Sig. (2-
tailed)
Conclusion
Model 1
46
1.326
0.06
Normal
Source: Processed Data, 2016
The model consisted of managerial ability, tax avoidance, institutional ownership as independent variable, and frm value as dependent variable, with asymp. Sig more than r.r5,, showing these data were normally distributed
Multicollinearity Test
Table 4.6
Multicollinearity Test Result
Variable
Tolerance
VIF
ABILITY
.901
1.109
CETR
.943
1.061
IO
.909
1.100
SIZE
.991
1.009
Source: Processed Data, 2016
Based on table 43.6, all variables had the value of tolerance more than r.13 or VIF less than 13r, showing these variables did not have any indication of multicollinearity problem.
Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
Table 4.7
t-Statistical test result (H
1,H
2,H
3)
Model
Unstandardize
d Coefficients
t
Sig.
Conclusion
Beta
(Constant)
-16.442
-3.738
.001
ABILITY
8.212
2.061
.046 Positive significant
IO
.924
1.714
.094 Positive insignificant
SIZE
.337
4.863
.000 Positive significant
Source: Processed data, 2016
Based on table 43.7, the multiple linier regression equation is as follow:
Tobin s
'q
=−
16.442
+
8.212
DEA
−
0.920
CETR
+
0.924
INS
+
0.337
¿ ¿
Hypothesis Discussion
Managerial Ability on Firm Value
Based on table 43.7 managerial ability has signifcant value r.r436 less than r.r5,, which means H13 is accepted. This statement also means that managerial ability can increase frm value.
Good managerial ability is when the manager is successful in creating decision, frm policy and strategies in employing efcient business process. This shows that good managerial ability is able to use and process the input without producing a waste to produce optimal output. If this is achieved, the frm will be able to save the costs of processing and using the inputs with constant output or revenue so corporate profts will increase. An increase of corporate proft is also shown at the increase of proftability ratios (ROA, ROE and EPS), reflecting an increase of frm performance (Djutaningsih & Rahman, 20r1320). Stable liquidity ratios (cash ratios) and insolvency ratios also reflect better frm performance, as they reflect the frm liquidity ability in maintaining going concern ability (Weston & Copeland, 139920). These ratios later are used as the benchmark by the stakeholders including shareholders and creditors to make sure that this frm can provide good return on them and can maintain going concern of the frm (Sudiyatno et.al, 20r1320). An increase of frm value is shown as the stakeholders including shareholders and creditors are interested to provide additional funds on the frm which increase stock price and increase amount of debt as source of funds in fnancing frm resources in order to produce more output (Chang & Wang, 20rr7). The result of this research is correlated with Andreou (20r13r), Djutaningsih and Rahman (20r1320) and Ng Suwandi et.al (20r135,) that managerial ability can increase frm value.
Tax Avoidance on Firm Value
Based on table 43.7 tax avoidance has signifcant value r.13r13 more than r.r5,, meaning H20 is rejected. This statement means that tax avoidance which focuses on cash saving strategy cannot increase frm value.
According to Chen et al (20r13r) the frm who employs tax avoidance strategies followed with good corporate governance including control from family ownerships and transparent information can increase frm value. This shown as the frm who employs these strategies is successful in minimizing tax expense which also followed with good liquidity ability as the frm also pay smaller tax expense in cash, maximizing earnings after tax. Maximum amount of earnings after tax can attract stakeholders to provide additional funds on the frm, increasing frm value. However, because tax regulation grows stricter and the corporate governance also grows more intensive including the monitoring act from institutional investor, the frm will prefer to increase the frmms value in a good way in the eyes of investors or consumers by complying tax regulations (Karimah and Taufq, 20r136). The result of this research is also supported with Simarmata and Cahyowati (20r13r) that tax avoidance strategies cannot increase frm value.
Institutional Ownerships on Firm Value
The institutional investors who purchase more outstanding shares issued by the frm, can trigger good monitoring on the managersm actions. This condition is happened because of the high voting power, which can afect the managersm action to increase the efciency of frm operation by reducing the expense which is not related to frm operation and maximizing the proft. An efcient frm operation will increase welfare of the stakeholders or the frm value (Thanatawee, 20r1343). Higher concentration of institutional ownerships on frm also trigger good monitoring and exert their influence on the frm, therefore causing an increase to frm value (Shleifer & Vishny, 13986). However, since the maximum held is 20r% then the institutional ownerships cannot fully influence any manager actions, which is correlated with theory proposed by Beams et.al (20r1320). The result of this research is also supported by Sabur et al. (20r1320) and Al-Dajjar (20r135,) that institutional ownership has no efect on frm value.
5. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS Conclusions
Managerial ability has an impact on frm value, correlating with Andreou et.al (20r135,), Djutaningsih and Rahman (20r1320) and Ng Suwandi (20r135,). This shows that good managerial ability is able to create efcient business operation through utilizing the frm resources to produce optimal output or revenue which maximizes the frmms proft. Higher frmms proft will attract stakeholders including shareholders and creditors to provide additional funds on the frm, causing an increase on the frm value, which is shown on the increase of stock price, the increase amount of debt, and the increase of their total asset as there is inflow of asset from higher revenue.
Tax avoidance has no impact on frm value, correlating with Karimah and Taufq (20r136) and Simarmata and Cahyowati (20r13r) This happens, because tax regulations grow stricter, causing the manager to play safe and fnd alternative ways, which can increase the frmms proft and still acceptable by the investor, who has monitoring incentives on the frm. Therefore, manager has to focus on other strategies, which can provide value added on the frm.
Institutional Ownership has no impact on frm value, correlating with Sabur et al. (20r1320) and Al-Dajjar (20r135,). This happens when the institutional ownerships do not hold signifcant number of frm shares, causing the institutional can monitor the managersm decision making related to an increase or decrease of frm value but cannot influence their act. Therefore, the institutional investor can decide to keep invest or sell the shares to the market.
Recommendations
First for the researcher, they can use diferent proxies of tax avoidance instead of Cash ETR, and not limiting the maximum held of institutional ownerships into 20r%, but also change into more than 20r% in order to examine the major efect of institutional ownerships on frm value when they have signifcant influence on the frm.
Third for the investors, theyneed to reconsider other information about the frm. First, how the managerms ability to utilize the frm resources in order to produce more output brings beneft to the frm. Second, how concentrated institutional ownerships can exert their influence on frm decision making, in order to prevent any rent seeking opportunities which could tarnish the frmms value. Finally, how the frm tax strategies are able to minimize tax expense and amount of cash tax paid. The comparison of cash tax paid with earnings before tax shows how the frm is able to maintain their liquidity ability so the investors know the expectation of dividend they will get. If it still brings beneft, it is safe to keep the shares and the investors should sell the shares to the market if there is indication that the frm is breaking down.
Bibliography
Al-Dajjar, D. (20r135,). The Efect of Institutional Ownership on Firm Performance: Evidence From Jordanian Listed Firms. International Journals of Finance, 7(1320), 97-13r5,.
Andreou, P., Ehrlich, D., Karasamani, I., & Louca, C. (20r135,). Managerial Ability and Firm Performance: Evidence from the Global Financial Crisis. Journal of Business Research, 13-r7.
Beams, F. A., Anthony, J. H., Bettinghaus, B., & Smith, K. (20r1320). Advanced Accounting. New Jersey: Pearson.
Brigham, E. F., & Houston, J. (20rr6). Dasar-Dasar Manajemen Keuangan (A. A. Yulianto, Trans. 13r ed.). Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Chang, S.-C., & Wang, C.-F. (20rr7). The efect of product diversifcation strategies on the relationship between international diversifcation and frm performance. Journal of World Business, 4320, 613-79.
Chen, t., Hu, N., Wang, t., & Tang, t. (20r13r). Tax Avoidance and Firm Value: evidence from China, Nankai Business Review and International, 5,(13), 205,-4320.
Demerdjian, P., Lev, B., Lewis, M., & Vay, S. M. (20r13r). Managerial Ability and Earnings Quality. The Accounting Review. 88(20), 436r-4398.
Demerdjian, P., Lev, B., & Vay, S. M. (20r1313). Quantifying Managerial Ability: A New Measure and Validity Test. Management Science, 5,8(7), 1320209-1320438.
Desai, M., & Dharmapala, D. (20rr9). Corporate Tax Avoidance and Firm Value. The Review of Economics and Statistics, 913, 5,r7-5,436.
Dyreng, S. D., Hanlon, M., & Maydew, E. L. (20rr8). Long Run Corporate Tax Avoidance. The Accounting Review, 8r(13), 613-820.
Freeman, R. E. (139843). Stakeholder Theory of Modern Corporation.
Gray, R., Kouhy, R., & Lavers, S. (13995,). Corporate social and environmental reporting: A review of the literature and a longitudinal study of UK disclosure. Accounting, Auditing and Accountability Journal, 8, 437-76.
Jensen, M., & Meckling, W. (13976). Agency Cost and Ownership Structure, Journal of Finances and Economics, r(43), rr5,-r6r.
Karimah, H. N., & Taufq, E. (20r136). Pengaruh Tax Avoidance Terhadap Nilai Perusahaan. Jurnal Ekonomi dan Bisnis, 43.
Ng, Suwandi., Pahlevi, C., H & Habbe, A. H. (20r135,). Managerial Ability and Monitoring Structure as a Mechanism for Improving the Quality of Earnings and the Value of the Firms Listed in Indonesia Stock Exchange. Scientifc Research Journal, r(1313), 205,-r9.
Santana, S. L. L. (20r136). Corporate Tax Avoidance and Firm Value.
Shleifer, A., & Vishny, R. (13986). Large Shareholders and Corporate Control. The Journal of Political and Economy, 943(r), 43613-4388.
Simarmata, A. P. P., & Cahyowati, N. (20r1343). Pengaruh Tax Avoidance Jangka Panjang Terhadap Nilai Perusahaan dengan Kepemilikan Institutional Sebagai Variabel Pemoderasi. Diponegoro Journal of Accounting, r, 13-13r.
Spence, M. (1397r). Job Market Signalling. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 87, r5,5,-r743.
Sudiyatno, Bambang. Puspitasari, E., & Kartika, A. (20r1320). The Companyms Policy, Firm Performance, and Firm Value: An Empirical Research on Indonesia Stock Exchange. American International Journal of Contemporary Research, 20(1320). rr-43r.
Tahir, S. H., Saleem, M., & Arshad, H. (20r135,). Institutional Ownership and Corporate Value: Evidence From Karachi Stock Exchange (KSE) rr-Index Pakistan. Praktični menadžment, VI, 4313-439.