v ABSTRACT
Suksmandri, Thudy Putri Rukmatea. 2009. Integrated Materials Based on Quantum Teaching for the Second Grade of Dance Department Students. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Designing English material for vocational high school is a challenge because the material has to be suitable and applicable for the students. The teacher not only gives the material but also has to make the students understand and have the ability to apply it. Vocational high schools prepare the students to work; it means that the materials should be applicable in the students’ field. The students’ motivation is also a problem. Since the vocational students focus on the primary study, they place English on the secondary. It means that the teacher has to encourage the students in studying English by raising their motivation and building a good atmosphere in the English learning activities.
This study is aimed to help the vocational high school teachers to provide the suitable material for the second grade of the dance department students based on quantum teaching. The material provides various activities and tasks to raise the students’ motivation and make them enjoy learning English. There are two questions that are discussed in this study: (1) what is the ideal design of integrated materials of English learning for second grade of dance department students based on quantum teaching? and (2) how does the design of integrated material of English learning based on quantum teaching affect the second grade of dance department students?
This study applied research and development (R&D) strategy. There are five steps adopted from R&D cycle; research and information collecting, planning and developing product, preliminary testing, revision, and field testing. This study also combines the Kemp’s and Yalden’s model in designing material. There are also some theories which are related to the study. There are theory of quantum teaching, theory of teaching listening, teaching speaking, teaching reading, and teaching writing.
There are two findings in this study. The first is the ideal design of integrated materials based on the quantum teaching for the second grade of dance department should be applicable, enjoyable, and also activate the students. There are five main activities in each unit. Those are Let’s Have Fun, Let’s Name It, Let’s Do It, Let’s Remember, and Let’s Celebrate.
The second is gained from the field testing. The result is that the students can enjoy the learning process. The activities can activate the students. The good atmosphere and the variety of the tasks also increase the students’ motivation in studying English and make them have better understanding through the material. It was shown from the reflection that 100 % students enjoyed the learning process and had better understanding. Finally, the writer hope this study enrich the learning process for vocational high school especially for dance department.
vi ABSTRAK
Suksmandri, Thudy Putri Rukmatea. 2009. Integrated Materials Based on Quantum Teaching for the Second Grade of Dance Department Students. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Membuat desain materi Bahasa Inggris untuk sekolah menengah kejuruan merupakan suatu tantangan karena harus sesuai dan bisa diterapkan oleh siswa. Guru tidak hanya mengajar tetapi harus membuat siswanya mengerti dan dapat mengaplikasikanya. Sekolah menengah kejuruan adalah sekolah yang mempersiapkan siswanya untuk bekerja, itu berarti materi yang diberikan harus bisa diterapkan sesuai bidang siswa. Motivasi siswa juga menjadi masalah. Karena siswa sekolah menengah kejuruan hanya berkonsentrasi pada bidang utamanya, maka mereka menempatkan pelajaran bahasa Inggris di tempat kedua. Ini berarti guru juga harus meningkatkan motivasi mereka dan menciptakan suasana yang menyenangkan dalam pelajaran bahasa Inggris.
Studi ini bertujuan untuk membantu guru sekolah menengah kejuruan untuk menyediakan materi yang sesuai untuk kelas dua jurusan tari berdasarkan pada quantum teching. Materi tersebut menyediakan berbagai aktivitas dan tugas untuk meningkatkan motivasi siswa dan membuat mereka menikmati proses pembelajaran. Ada dua pertanyaan yang didiskusikan dalam studi ini, (1) Seperti apa desain ideal materi bahasa Inggris untuk kelas dua jurusan tari berdasarkan quantum teaching?, (2) Bagaimana desain tersebut mempengaruhi siswa kelas dua jurusan tari?
Studi ini menggunakan strategi penelitian dan pengembangan. Ada ima langkah menurut siklus R&D, yaitu: penelitian dan pengumpulan informasi, perencanaan dan pengembangan produk, evaluasi, revisi, dan penerapan di kelas. Studi ini juga mengkombinasikan mode Kemp dan Yalden dalam pembuatan materi. Juga ada beberapa teori yang berhubungan dengan studi ini. Teori itu adalah quantum teaching, teori pengajaran mendengarkan, pengajaran berbicara, pengajaran membaca, dan pengajaran menulis.
Ada dua kesimpulan dalam studi ini. Pertama, desain ideal materi berdasarkan quantum teaching untuk siswa kelas dua Jurusan Tari harus mudah diaplikasikan, menyenangkan, dan juga dapat membuat siswa menjadi aktif. Ada lima aktivitas utama dalam setiap unit. Kegiatan tersebut adalah Let’s Have Fun, Let’s Name It, Let’s Do It, Let’s Remember, and Let’s Celebrate.
i
INTEGRATED MATERIALS BASED ON QUANTUM TEACHING
FOR THE SECOND GRADE OF DANCE DEPARTMENT STUDENTS
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
In English Language Education
By:
Thudy Putri Rukmatea S Student Number: 041214018
ENGLISH EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
ii A Thesis On
INTEGRATED MATERIALS BASED ON QUANTUM TEACHING
FOR THE SECOND GRADE OF DANCE DEPARTMENT STUDENTS
By
Thudy Putri Rukmatea S Student Number: 041214018
Approved by:
Gregorius Punto Aji, S.Pd., M.Hum. Advisor
iii
INTEGRATED MATERIALS BASED ON QUANTUM TEACHING
FOR THE SECOND GRADE OF DANCE DEPARTMENT STUDENTS
By
THUDY PUTRI RUKMATEA S Student Number: 041214018
Defended before the Board of Examiners on 3 April 2009
and Declared Acceptable
Board of Examiners
Chairperson : A. Hardi Prasetyo, S.Pd., M.A. ____________ Secretary : Made Frida Yulia, S.Pd., M.Pd. ____________ Member : Gregorius Punto Aji, S.Pd., M.Hum. ____________ Member : Yohana Veniranda, S.Pd., M.Hum ____________ Member : V. Triprihatmini, S.Pd., M.Hum, M.A. ____________
Yogyakarta, 3 April 2009
Faculty of Teachers Training and Education Sanata Dharma University
Dean,
iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, 24 March 2009
The Writer
v ABSTRACT
Suksmandri, Thudy Putri Rukmatea. 2009. Integrated Materials Based on Quantum
Teaching for the Second Grade of Dance Department Students. Yogyakarta:
English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Designing English material for vocational high school is a challenge because the material has to be suitable and applicable for the students. The teacher not only gives the material but also has to make the students understand and have the ability to apply it. Vocational high schools prepare the students to work; it means that the materials should be applicable in the students’ field. The students’ motivation is also a problem. Since the vocational students focus on the primary study, they place English on the secondary. It means that the teacher has to encourage the students in studying English by raising their motivation and building a good atmosphere in the English learning activities.
This study is aimed to help the vocational high school teachers to provide the suitable material for the second grade of the dance department students based on quantum teaching. The material provides various activities and tasks to raise the students’ motivation and make them enjoy learning English. There are two questions that are discussed in this study: (1) what is the ideal design of integrated materials of English learning for second grade of dance department students based on quantum teaching? and (2) how does the design of integrated material of English learning based on quantum teaching affect the second grade of dance department students?
This study applied research and development (R&D) strategy. There are five steps adopted from R&D cycle; research and information collecting, planning and developing product, preliminary testing, revision, and field testing. This study also combines the Kemp’s and Yalden’s model in designing material. There are also some theories which are related to the study. There are theory of quantum teaching, theory of teaching listening, teaching speaking, teaching reading, and teaching writing.
There are two findings in this study. The first is the ideal design of integrated materials based on the quantum teaching for the second grade of dance department should be applicable, enjoyable, and also activate the students. There are five main activities in each unit. Those are Let’s Have Fun, Let’s Name It, Let’s Do It, Let’s Remember, and Let’s Celebrate.
The second is gained from the field testing. The result is that the students can enjoy the learning process. The activities can activate the students. The good atmosphere and the variety of the tasks also increase the students’ motivation in studying English and make them have better understanding through the material. It was shown from the reflection that 100 % students enjoyed the learning process and had better understanding. Finally, the writer hope this study enrich the learning process for vocational high school especially for dance department.
vi
ABSTRAK
Suksmandri, Thudy Putri Rukmatea. 2009. Integrated Materials Based on Quantum
Teaching for the Second Grade of Dance Department Students. Yogyakarta:
Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Membuat desain materi Bahasa Inggris untuk sekolah menengah kejuruan merupakan suatu tantangan karena harus sesuai dan bisa diterapkan oleh siswa. Guru tidak hanya mengajar tetapi harus membuat siswanya mengerti dan dapat mengaplikasikanya. Sekolah menengah kejuruan adalah sekolah yang mempersiapkan siswanya untuk bekerja, itu berarti materi yang diberikan harus bisa diterapkan sesuai bidang siswa. Motivasi siswa juga menjadi masalah. Karena siswa sekolah menengah kejuruan hanya berkonsentrasi pada bidang utamanya, maka mereka menempatkan pelajaran bahasa Inggris di tempat kedua. Ini berarti guru juga harus meningkatkan motivasi mereka dan menciptakan suasana yang menyenangkan dalam pelajaran bahasa Inggris.
Studi ini bertujuan untuk membantu guru sekolah menengah kejuruan untuk menyediakan materi yang sesuai untuk kelas dua jurusan tari berdasarkan pada quantum teching. Materi tersebut menyediakan berbagai aktivitas dan tugas untuk meningkatkan motivasi siswa dan membuat mereka menikmati proses pembelajaran. Ada dua pertanyaan yang didiskusikan dalam studi ini, (1) Seperti apa desain ideal materi bahasa Inggris untuk kelas dua jurusan tari berdasarkan quantum teaching?, (2) Bagaimana desain tersebut mempengaruhi siswa kelas dua jurusan tari?
Studi ini menggunakan strategi penelitian dan pengembangan. Ada ima langkah menurut siklus R&D, yaitu: penelitian dan pengumpulan informasi, perencanaan dan pengembangan produk, evaluasi, revisi, dan penerapan di kelas. Studi ini juga mengkombinasikan mode Kemp dan Yalden dalam pembuatan materi. Juga ada beberapa teori yang berhubungan dengan studi ini. Teori itu adalah quantum teaching, teori pengajaran mendengarkan, pengajaran berbicara, pengajaran membaca, dan pengajaran menulis.
Ada dua kesimpulan dalam studi ini. Pertama, desain ideal materi berdasarkan quantum teaching untuk siswa kelas dua Jurusan Tari harus mudah diaplikasikan, menyenangkan, dan juga dapat membuat siswa menjadi aktif. Ada lima aktivitas utama dalam setiap unit. Kegiatan tersebut adalah Let’s Have Fun, Let’s Name It, Let’s Do It, Let’s Remember, and Let’s Celebrate.
viii
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
First of all, I will say my biggest thanks to my Lord Jesus Christ for all He has done for me. He never leaves me alone even when I stay away from Him. I can finish this thesis only because of His grace, love, patience, and kindness. His strength and guidance always cover me. His Hand always sustains and strengthens me in every part in my life.
My sincere gratitude goes to my thesis advisor, Mr. Gregorius Punto Aji, S.Pd., M.Hum for his time, guidance, advice, and patience during the process. I also thank Mr. Ag. Hardi Prasetyo, S.Pd., M.A., the head of English Language Education Study Program and Drs. Tarsisius Sarkim, M.Ed., Ph.D., the dean of Teachers Training and Education Faculty for the permission. I also thank all lecturers who have given me a lot of lessons for my provisions for the next steps. I also thank mbak Dani and mbak Tari for their help and kindness during my study in PBI.
ix
My deep gratitude goes to my beloved Caraka Kristiadhi for his love, support, smile, and patience. I also thank my new family, Bapak Arif, Ibu Tatik, Rena, and Bapak Gito Utomo’s family for their prayer and support.
I would also like to thank the English teachers in SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan: Ibu Ning, Ibu Nency, and Bapak Hadi for their help in conducting the research. I also thank the second grade students of the dance department of SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan for their participation in the research.
My gratitude goes to all of my friends and family who have colored my life and made it more wonderful. First of all, I thank Mas Gani who has helped me a lot in the material process, Tante Ismi who always helps me when I went to the workstation. I also thank all of my friends in PBI 2004, especially class A (Sita, Patrice, Rini, Lani, Christina, Cahya, Reny, and many others), Leaves, KKN Selo 2008, niners’fellowship, SD Tajem and SD Gambiranom’s teachers and students. I also thank my bestfriends Ivone, Titi, Dimas, Mbak Nana, and all of my friends in my fellowship for their hugs, supports, and prayers which always make me stronger and braver to stand still. I also thank all my friends who have sent me very wonderful messages during the time.
I also thank all people around me which I cannot mention one by one for all the encouragement, help and smile. Finally I can finish my study and it is all because of the support and prayer from everyone around me. God bless them.
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ..………. i
APPROVAL PAGES ………...………… ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ……….. iv
ABSTRACT ……… v
ABSTRAK ……….…….. vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ……… vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ……… ix
LIST OF TABLES ……….. xii
LIST OF FIGURES ……… xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES………. xiv
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ……….... 1
A. Research Background ………... 1
B. Problem Formulation ……….. 4
C. Problem Limitation ………. 4
D. Research Objectives ……….... 4
E. Research Benefits ……… 5
F. Definition of the Terms ………... 5
1. Integrated Design .………. 5
2. Integrated Material ………….……….. 6
3. Quantum Teaching ……… 6
4. Vocational School ……… 6
5. SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan ……… 7
xi
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ……… 8
A. Theoretical Description ……… 8
1. Instructional Design Model ……….. 8
a. Kemp’s Model ………. 8
b. Yalden’s Model ………... 11
2. Quantum Teaching ……….. 13
3. Second Grade of Dance Department Students ……… 17
4. Theory of Teaching Language………. 18
a. Teaching Listening ….……….. 18
b. Teaching Speaking ………... 21
c. Teaching Reading ………. 24
d. Teaching Writing ………..……… 26
B. Theoretical Framework ……… 28
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ……….. 29
A. Research Method ………. 29
B. Research Participants ………... 30
C. Research Instruments ………... 31
D. Data Gathering Technique ………... 32
E. Data Analysis Technique ………. 33
F. Research Procedures ……… 33
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION ………….. 36
A. The Ideal Design of Integrated Materials Based on Quantum Teaching for the Second Grade of Dance Department Students …… 36
1. Learners’ Characteristics and Needs ………. 37
2. Goals, General Purposes and Topics ………. 42
xii
4. Result of the Preliminary Testing……… 55
B. The Effects of the Design of Integrated Materials Based on Quantum Teaching for Second Grade of Dance Department Students………... 59
1. Description of the Participants in Field Testing ……… 60
2. Data Presentation ……….. 61
3. Discussion on the Effects ……….. 63
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS ………... 66
A. Conclusion ………... 66
B. Suggestions ……….. 67
xiii
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
4.1 Summary of Interview of Learners’ Characteristics ………. 41
4.2 Summary of Interview of Learners’ Need ……… 41
4.3 Competency Based and Basic Competences ………... 43
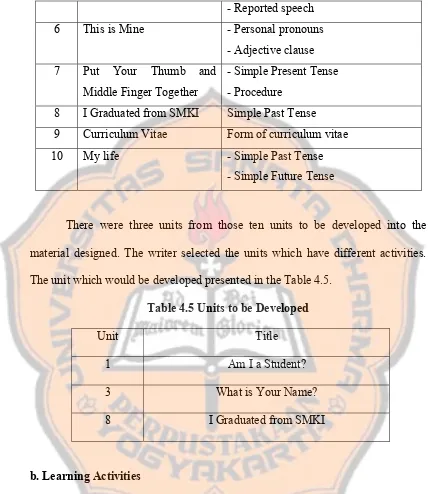
4.4 Title and Content ………. 44
4.5 Unit to be Developed ………... 45
4.6 The Variety of the Activities ……… 47
4.7 Description of the Respondent in Preliminary Testing ……… 56
4.8 Strengths and Weaknesses of the Materials Designed ……… 58
4.9 Sections Revised and the Revision ………. 59
4.10 Description of the Participant in Field Testing ………. 60
xiv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
xv
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page A. Appendix 1: Letters
1. Letter of Permission to Bappeda……… 71
2. Letter of Permission from Bappeda……….. 72
B. Appendix 2: Instruments 1. List of Questions for Interviewing the Teachers……….. 73
2. List of Questions for Interviewing the Students……….. 74
3. Raw Data of the Result of Interview………... 75
4. Open Questionnaires for Materials Evaluation……… 78
5. Questionnaires for Field Testing………. 82
C. Appendix 3: Materials’ Outline……….. 83
D. Appendix 4: Lesson Plan……… 95 E. Appendix 5: Integrated Materials Based on Quantum Teaching for
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background
In Indonesia, English is taught from the elementary until the senior high
school, including vocational high school. Indonesia has also included English for
the National Examination (Ujian Akhir Nasional), so the students have to master
it to pass the examination. In that discourse, it can be seen that English is an
important subject in Indonesia, but in the reality it does not work effectively. The
writer had an experience when the writer met a student and a teacher of vocational
high school. Based on the writer’s experience, English seemed to be not really
important in vocational high school. The teacher and the students only focus on
the main subject of the vocational high school. A student of one of vocational
high school in Sleman told the writer that English lesson at his school was not
really useful when he worked because the English lesson was not suitable and
applicable for his subject. So, when he worked, he could not use English. A
vocational high school teacher also said that the English lesson did not work much
because the students were still passive and had less motivation to learn English.
They only listened and they were afraid to speak. He told the writer that his school
is an art school and they often went abroad. The students found difficulties to
communicate with foreigners both in this country and abroad.
The writer also had an experience when did the macro teaching (PPL 2)
for the first time, they told a lot of things about their problem in learning English.
One student said that English learning activities made him bored, the others said
that they were not really interested in English because they did not like the
teacher. Actually they liked English, but because the teaching learning activity
was not interesting, they were not interested anymore in English.
This research will focus on vocational high school. A vocational high
school (SMK) is an institution for the vocational education of students to prepare
them with knowledge, skills and attitudes so that they can be productive people
who can directly work according to their field. (Vocational High School
Curriculum, 2004 edition). The writer chooses vocational high school because for
that kind of school, mastering English is not only needed to pass the examination,
but also for a foothold in life when they are working.
In this research, the object will be SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan. SMK Negeri
1 Kasihan is an art vocational high school. This school is prepared to be Sekolah
Berbasis International (SBI), and either the students or the alumni are also often
asked to go abroad. The problem is that the students are not able to speak English.
Although they got English lesson, they could not use it effectively. The students
also have less motivation to learn English. The headmaster told the writer that he
hoped the students can learn more about English language and practice it in daily
life although the time to learn is limited. It means that the English lesson’s
material should be applicable and based on the students’ need. The class activity
From those backgrounds, the writer looked for a suitable method for
those situations. The writer found about Quantum Teaching. One of the ways to
make the students understand the lesson is by giving them an experience before
they start learning a material. In the theory of this method, it increases students’
motivation and makes the students have better understanding about the material.
This method can be applied for every background of the students because it is
applied according to their abilities. The writer will apply Quantum Teaching
method to raise the students’ motivation, make them enjoy the lesson, and
improve their ability in English. Quantum Teaching has several principles. Those
are everything speaks, everything has its purpose, experience before named,
respect to every effort, and celebrate the achievement. The previous study was
about the effectiveness of quantum teaching, and in this thesis the writer designs
the materials based on quantum teaching.
There are nine intelligences for human, linguistic intelligence, logical-
mathematical intelligence, spatial intelligence, bodily-kinesthetic intelligence,
musical intelligence, interpersonal intelligence, intrapersonal intelligence,
naturalist intelligence, and existential intelligence. In Quantum Teaching, the
material covers minimum five intelligences of students. A class consists of
students who each of them have different intelligence. The teacher can not teach
using the prominent intelligence only. The material based on Quantum Teaching
B. Problem Formulation
Based on the background, the students’ motivation should be supported by
suitable materials. Based on that, the writer formulates two questions:
1. What is the ideal design of integrated material of English learning for
second grade of Dance department students based on Quantum Teaching?
2. How does the design affect the students?
C. Problem Limitation
This research will be conducted on the second grade of Dance department
students. Dance department has the most students in SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan. The
writer is going to make materials based on their needs. The materials are
integrated material, which combine Listening, Speaking, Reading and Writing
activities based on Quantum Teaching. It is included in English for Academic
Purposes. The material should be suitable and also should be applicable because
the Dance department students are often asked to present and to introduce
Javanese culture either to foreign countries or to the foreigners who come to this
country.
D. Research Objectives
The objectives of this research are:
1. To know the ideal design based on Quantum Teaching for second grade of
Dance department students.
E. Research Benefits
1. This research can be useful for the English teachers, especially the English
teachers in vocational high school, to develop the class activities as the references
to make the students enjoy learning English and motivate them to practice it
outside the class or in their daily life.
2. By conducting this research, the writer can enrich the writer’s knowledge and
experience in education. Quantum Teaching is a new method in Indonesia, so, if
the writer has experience of it, the writer can improve the ability in English
teaching.
F. Definition of Terms
1. Instructional Design
Instructional design is technologies of education and instruction. The
term technology is being used in the sense of an applied science1. When the
designers want to design, it should be based on three questions which may be
considered as the essential elements of instructional technology: (1) what must be
learnt? (objectives), (2) what procedures and resources will work best to reach the
desired learning levels? (activities and resources), (3) how will we know when the
required learning has taken place? (evaluation) (Kemp, 1977:8).
1
2. Integrated Material
Integrated material is a learning material which focuses on the mastery of
the integrated communicative skills (Richards and Rodgers, 2001:64). In this
study, integrated material combines four basic skills in English: listening,
speaking, reading, and writing. Each unit will consist of those skills, which can be
divided into several meetings.
3. Quantum Teaching
Quantum is an interaction which changes energy into light. Quantum
teaching is much interaction in a learning process. The interaction is done to make
the learning process runs effectively and change the students’ ability and talent
into light which can be useful for themselves and others. The interaction is
between the teacher-students, students-students, and also the experiences in the
process.
4. Vocational School
Based on Vocational High School Curriculum from the 2004 edition, a
vocational high school is an institution for the vocational education of students to
prepare them with knowledge, skills and attitudes so that they can be productive
people who can directly work according to their field.
According to Pedoman Model Penilaian Kelas KTSP, vocational high
school curriculum is competency-based curriculum which uses broad-based
high school apply Pendidikan Sistem Ganda (PSG). It means that the learning
activities are done both in the school and in the real working world based on the
curriculum which is arranged by the school according the field needs.
Competency-based curriculum not only focuses in improving the students’
knowledge, but also improving all competencies of reflection of the knowledge,
skills, and attitude, according to each subjects’ characteristics.
5. SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan
SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan is an art school which is located in Kasihan, Bantul. This
school has four departments; those are Dance, Karawitan, Pedalangan, and
Theater. Dance department has three classes, while Karawitan, Pedalangan,
Theater, have only one class. When there were cultural events held, this school is
often asked to participate in those events, not only in this country but also abroad.
In this school, English is taught as an adaptive lesson.
6. Second Grade of Dance Department
Dance department focuses to study about dance both practical and theory. In this
department, the students study almost all dances in Indonesia, but they study
Javanese dance in particular. Dance department has three classes in every grade.
In the second grade it also has three classes which each class consists of 12-15
students. The students of this department or the alumnus from this department are
8 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter the writer will discuss the theories which are related to the
topic. This chapter will be divided into two parts. The first part is Theoretical
Description which presents the discussion of any literature related to the topic.
The second part is Theoretical Framework which discusses the framework based
on the theory.
A. Theoretical Description
There are several theories which are used to develop the materials. Those
are instructional design model which consists of Kemp’s and Yalden’s model,
Quantum Teaching, second grade of dance department and theory of teaching
language.
1. Instructional Design Model
Teachers have to design material before teaching. To design material,
teachers need a model as the guideline. There are some models of instructional
design. The writer will take two models as the references. The first model is
according to Jerold E. Kemp and the second is according to Yalden.
a. Kemp’s Model
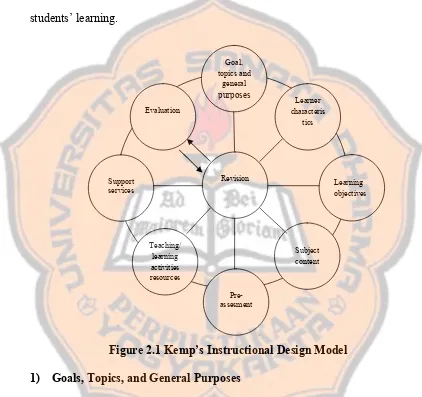
In Kemp’s model, the plan consists of eight parts (Kemp 1977: 8-9), those
each topic; enumerate the important characteristics of the learners; specify the
objectives; list the subject content that support each objectives; develop
pre-assessment to determine the students’ background; select teaching/learning
activities and instructional resources; coordinate support services; and evaluate
students’ learning.
Figure 2.1 Kemp’s Instructional Design Model
1) Goals, Topics, and General Purposes
Instructional design planning starts with a recognition of the broad goals
of the school system or institution. Within the curriculum areas, topics are chosen
for learning, in which the teacher explicitly expresses the general purposes (what
2) Learners Characteristics
There are two characteristics which are needed when designing an
instructional plan:
a. Academic factors: number of students academic background, grade-point
average, level of intelligence, study habits, background in the subject or
topic, motivation for studying the subject, expectations of the course,
vocational and cultural aspirations.
b. Social factors: age, maturity, attention span, special talents, physical and
emotional handicaps, relations among students and socioeconomic situation.
3) Learning Objectives
Objective for learning can be grouped into three major categories (Kemp,
1977: 24-26) : cognitive domain (the domain we give most attention to in
educational programs), psychomotor domain (it treats the skills requiring the use
and coordination of skeletal muscles, as in the physical activities of performing,
manipulating, and constructing) and affective domain (it concerns attitudes,
appreciations, values, and all emotion).
4) Subject Content
A student’s learning experiences must involve subject content. The
content must be closely related to the objectives and to the student’s needs.
5) Pre-assessment
The aim of this part is to determine whether students have the appropriate
background preparation for the topic through prerequisite test and to determine
6) Teaching/learning Activities and Resources
The designer should determine the most efficient and effective methods and then
select materials to provide learning experiences that will utilize the content
associated with each objective.
7) Support Services
The services include funds, facilities, equipment, and personnel whose time must
be scheduled for participation in the instructional plan. Support services must be
considered at the same time when instructional plans are being made and
materials are being selected.
8) Evaluation
The objectives indicate what the evaluation should be. When the criteria are set
and students successfully attain them, the concept mastery is realized.
b. Yalden’s Model
Yalden (1987: 88-89) describe seven stages in Language Program Development.
Figure 2.2 Yalden’s Instructional Design Model
Stage 1 : Need survey
Stage 2 : Description of purpose to be prepared in terms of
• student characteristics
• students skills on entry to and on exit from the program
Stage 3 : Selection or development of syllabus type in term of stage 4 and
physical constrains on the program
Stage 4 : The proto-syllabus: description of language and language use to be
covered in the program
Stage 5 : The pedagogical syllabus: development of teaching, learning and testing
approaches
• development of teaching materials
• development of testing sequence and decisions on testing instruments
Stage 6 :
• Development of classroom procedures
o selection of exercise types and teaching techniques
o preparation of lesson plans
o preparation of weekly schedules
• Teacher training: briefings or workshop on
o principles
o desired outcome
o exploitation/creation of teaching material
Stage 7 : Evaluation
• of students
• of program
2. Quantum Teaching
Quantum is an interaction which changes energy into light (DePotter,
2004:5). It means the students’ ability is used in the learning process to make
them have better knowledge. Quantum teaching is much interaction in a learning
process. The interaction is done to make the learning process runs effectively and
change the students’ ability and talent into light which can be useful for
themselves and others. The interaction is between the teacher-students,
students-students and also the experiences in the process. The main idea of Quantum
Teaching is bringing joy in the teaching-learning activity. This model also
integrates the learning material and life skill related to the learners’ background,
so that the students can apply the material.
The basic principle in Quantum Teaching is ‘bring the learners into our
world and bring our world to their world. The main idea is the ability to be a
bridge between the teacher and the learners (students). There are five principles in
Quantum Teaching (DePotter, 2004:7):
a. Everything speaks: everything around the learners brings important message
about learning.
b. Everything is on purpose: everything we do has its purpose.
c. Experience before label: learning is best facilitated when the learners
experience first then label the activity’s done.
d. Acknowledge every effort: every effort of each learner is important and it has
e. If it’s worth learning, it’s worth celebrating: celebration means the respectful
of the learners’ progress.
In teaching-learning activities, those five principles are represented in the
following steps (DePotter, 2004: 88-93):
a. Experience
The teacher gains the students’ attention and raises the students’ motivation in
learning the material. The strategy is by giving the students questions, short
funny story, drama, video, stories, pantomime, etceteras. Then let the students
experience the material. It can be by listening, experimentation, role play,
games, group work, etc. It can be based on the students’ experience. The
activity in this step is also to raise the students’ curiosity.
b. Learn and Label
In this step the teacher gives the concept of the material. The teacher answers
the students’ curiosity after they experience it. Learn and label can be the
information, the fact, the formula, place, etc. Experience and learn the material
before the students know the information (the name) can make the knowledge
or the material they learn to be really meaningful.
c. Demonstrate
In this step, the students have an opportunity to demonstrate or apply what
they have learned. The students can show what they have understood. The
d. Review and Reflect
The students review what they have learned on the teaching learning activity
and the teacher ask the students to make reflection on what they learned. The
format depended on the teacher’s creativity. The reflection or repetition can
strengthen the students’ memory of the material.
e. Celebration
This step aims to acknowledge the students’ effort in the teaching-learning
activity. Reinforcement can raise the students’ motivation and also students’
interest in the learning activity. This step can also give satisfaction to the
students for all their efforts in the learning process. The celebration can be
done through a compliment, sing a song, yell, clap hands, etc.
In Quantum Teaching, the material covers at least five intelligences of the
students. There are nine multiple intelligences and their characteristics (prominent
ability) by Howard Gardner:
a. Linguistic intelligence: understanding something in a sequence, understanding
word meaning, explaining, telling a story, debating, remembering,
memorizing, giving speech, making poem, linguistic analyzing, writing,
speaking, and playing a role-play.
b. Logical-mathematical intelligences: logic, reasoning, categorizing, classifying,
abstraction, symbolizing, inductive and deductive thinking, counting,
scientific thinking, problem solving, syllogism.
c. Spatial-visual: recognizing things in a space correctly, having the right
manipulating, drawing, active imagination, responsive to color, line, and
shape.
d. Bodily-kinesthetic intelligence: easy to expressing something using body,
relating main and body, having ability in facial expression, playing role-play,
sport, dancing, having high body coordination and flexibility.
e. Musical intelligence: sensitive to sound and music, knowing musical structure
well, creating melody, sensitive to intonation and rhythmic, singing, music
performing, creating music, playing music instrument.
f. Interpersonal intelligence: cooperating, having ability to recognize and
differentiate others’ feeling and personality, verbal and nonverbal
communication, responsive to friend, empathy, giving feedback.
g. Intrapersonal intelligence: having good concentration, deeply self recognizing,
empathy-ego balance, reflective, conscious thought to spiritual reality.
h. Naturalist intelligence: recognizing flora and fauna, classifying and
identifying flora and fauna, loving nature.
i. Existential intelligence: sensitivity and ability to answer human existential
problem.
In order to reach the best achievement for the students, the material covers at
least five intelligences. In Quantum Teaching, those intelligences are represented
in the previous five steps.
Teaching using Quantum Teaching forces the teacher to pay attention to
the teaching-learning process. There are three principles which have to be
It. The teacher has to know what he/she wants in the teaching-learning process. It
includes the teacher’s purpose, the students’ background, the teachers’ strategy
and also material’s mastery. It is important to prepare the learning process. The
second is Explain It. Knowing all the material well make the teacher get ready to
explain it to the students. In this second principle the teacher explains the material
using the appropriate language to the students. To make it effective, the teacher
has to have a good communication with the students. The last principle is Get It.
After the students having the explanation, they are asked to do some activities. It
is the time for the teacher to get the result and give the feedback. By listening and
paying attention to the students’ activities, the teacher is able to know whether the
students understand the material or not. That is the importance of interaction in
Quantum Teaching. After knowing the result, the teacher gives feedback to the
students. This feedback will improve the students’ ability.
3. Second Grade Students of Dance Department
The dance department is a department in SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan which
learns about dances, especially Javanese dance. The students are not only
demanded to perform their ability in dancing, but also to master the dance itself.
After the students graduate from the school, they are expected to use their skill
properly. They do not only can perform but also teach others about Javanese
dance.
The dance department has three classes in every grade. In the second
students of this department or the alumnus from this department are the most
often asked to perform either in this country or abroad.
4. Theory of Teaching Language
There are four parts in the theory of teaching language. Those are (a)
teaching listening, (2) teaching speaking, (3) teaching reading, and (4) teaching
writing. The theory is according to Nunan (2003).
a. Teaching Listening
Theory of teaching listening referred to a chapter in Nunan’s book which
is written by Marc Helgesen, Miyagi Gakuin Women’s College (Japan). He stated
that listening is an active, purposeful process of making sense of what we hear.
Listening is included in receptive skill. It means people require receiving and
understanding the information.
The principles of teaching listening are:
1) Expose students to different ways of processing information
There are two ways of processing information. Those are bottom-up and
top-down. Processing information as bottom-up means the processing information
way begins with the learners’ knowledge of vocabulary, grammar, and sounds.
The opposite is top-down. The processing information way in top-down
begins with the listener’s life knowledge. These two ways can be integrated in
2) Expose students to different types of listening
It is important to give different types of activities in listening. The students
need different types of listening activities because different activity has
different purpose. The different type of listening will enrich the students’
ability in listening. The types of listening are listening for specific
information, global or gist listening and inference. In listening for specific
information, the students are asked about the specific information from the
listening passage, such as names, time, the language form, etc. In global or
gist listening, the students’ tasks are identify the main idea and to note a
sequence of events. In inference, the students listen to the implied meaning
that is implied but not stated directly.
3) Teach a variety of tasks
The variety of tasks can be done according the students’ level. In the
beginning, they can have a simple task, such as asking the students to choose
the right choices of the listening passage’s summary. The next task level,
students are asked to make their own summary. Developing the listening task
can also increase the students’ interest.
4) Consider text, difficulty, and authenticity
Brown as quoted by Helgesen (2003:33), stated that the six factors which
can increase or decrease the ease of understanding are the number of
individuals or objects in a text; how clearly the individuals or object are
distinct from one another; simple, specific spatial relationship are easier to
needed; and the information is consistent with what the listener already
knows.
Brown and Menasche as quoted by Helgesen (2003, 34), suggested the
authenticity looking at two aspects. The first is task authenticity which
includes simulated (such as filling a form) and minimal/incidental (such as
checks understanding and numbering pictures to show the sequence). The
second is input authenticity which includes genuine (created only for the
realm of real life but used in language teaching), altered (no meaning change,
but the original is no longer as it was), adapted (words and grammatical
structures changed to simplify the text), simulated, and minimal/incidental.
5) Teach listening strategies
Rost, as quoted by Helgesen (2003:35), identified six strategies in teaching
listening. They are: (1) predicting what the effective listeners think about what
they hear; (2) inferring which is useful for learners to infer; (3) monitoring
which is the listeners notice what they do and don’t understand; (4) clarifying
which is the efficient learner’s questions and give feedback; (5) responding
which is the learners react what they hear; and (6) evaluating which the
learners check on how well they have understood.
There are two types of listening, extensive listening and intensive listening
(Harmer, 2004: 228). In extensive listening, the teacher encourages the students to
find their own listening passage to listen to for their improvement in English. In
intensive language, the teacher provides the material. Teacher can use taped
materials from radio, disk, provided listening passage, and other sources which
are recorded. For ‘live’ listening, the teacher can do the reading aloud,
story-telling, interviews, and conversations.
b. Teaching Speaking
The theory of teaching speaking is contained as one of the chapters in
Nunan’s Practical English Language Teaching (2003). The chapter of teaching
speaking is written by Kathleen M. Balley from Monterey Institute of
International Studies (USA). Balley stated that speaking is productive skill. It
consists of producing systematic verbal utterances to convey meaning (Nunan,
2003:48).
There are five principles in teaching speaking. Those are:
1) Be aware of the differences between second language and foreign language
learning context.
As stated by Balley in Nunan (2003: 54), foreign language (FL) context is
one where the target language not the language of communication in the
society, for example learning English in Japan. Second language (SL) context
is one where the target language is the language of communication in the
society, for example English in the UK. The challenges for the teacher are
determined by the target language context.
2) Give students practice with both fluency and accuracy.
Fluency is the extent to which the speakers use the language quickly and
people actually say when they use the target language (Nunan, 2003:55). The
teacher had to give big opportunities to the students to develop their fluency
and accuracy. It can be done by not correcting the students’ mistake too often.
3) Provide opportunities for students to talk by using group work or pair work,
and limiting teacher talk.
Group work or pair work give more chances to the students to speak. This
activity can also limit the teachers’ talk.
4) Plan speaking tasks that involve negotiation for meaning
Negotiation for meaning is the process which involves checking to see if
you have understood what someone said, clarifying your understanding, and
confirming that someone has understood what you mean (Nunan, 2003:55).
5) Design classroom activities that involve guidance and practice in both
transactional and interactional speaking.
Transactional speaking is the communication in social purpose. In
interactional speaking, the purpose is to make someone to do something. The
classroom activities have to be created to let the students experience both the
transactional and interactional speaking using the target language.
There are several classroom speaking activities which are explained by
Harmer (2004). The activities which are often used by the teacher are acting for
script, communication games, discussion, prepared talk, simulation and role-play.
In acting for script, the students are asked to perform based on the script provided.
Games are designed to encourage students to speak. The games can be solving a
similarities and differences between pictures (Harmer, 2004:272). The teacher can
find another games which can provoke the students to speak and have interaction
one to another. Discussion is used to avoid the students’ difficulty in public
speaking. Small group discussion can be a small simulation which allows students
to share their thoughts.
Prepared talk, simulation and role-play have the similarity that all of them
have to be prepared before. In prepared talk, it can be like a speech. The students
are given a theme or topic that they have to speak in front of the class. The teacher
gives time to the students to prepare it. Simulation and role-play are almost the
same with prepared talk. The students need time to prepare it. The difference is in
simulation and role-play, the students have to work in a group. Simulation and
role-play can be used to encourage general oral fluency or to train students for
specific situations (Harmer, 2004:274).
In teaching speaking, the teacher has three different roles to make the
students speak fluently (Harmer, 2004:275-276). The first is as a prompter. The
teacher does as a prompter without interrupting the students. The teacher can do
supportive action like offering discrete suggestion. The second is as a participant.
The teacher can be the participant in discussion or role-play to encourage the
students, but the teacher should not talk too much. The third is as feedback
provider. The feedback is given in the appropriate situation. The teacher has to
know the right situation to give the feedback, so the students can improve
c. Teaching Reading
Theory of teaching reading referred to a chapter in Nunan’s book which is
written by Neil Anderson, Brigham Young University (USA). He stated that
“Reading is a fluent process of readers combining information from a text and
their own background knowledge to build meaning. The goal of reading is
comprehension.” (Nunan, 2003:68).
There are six principles for teaching reading according to Anderson. They
are:
1) Exploit the reader’s background knowledge.
Carel and Connor as stated in Nunan’s Practical English Teaching said
that “a reader’s background can influence reading comprehension”. To
develop the student’s reading comprehension, the teacher has to activate the
student’s background. It can be done by asking questions, making prediction,
and so on.
2) Build a strong vocabulary base.
Vocabulary is an important thing in reading. The students’ comprehension
on the reading passage also depends on the vocabulary. The teacher has to pay
attention on how the students can comprehend the reading passage.
3) Teach for comprehension.
In teaching for comprehension, the teacher has to monitor the students’
comprehension process. The students are also able to discuss the reading
passage with the teacher. Anderson stated that “Students learn to engage with
(Nunan, 2003:75). That technique can be done, for example, by asking the
message from the author or the main idea rather than asking about the detail
information of the text.
4) Work on increasing reading rate.
The teacher gives the students various skills on reading such as scanning,
skimming, predicting, and identifying ides. The focus is to reduce the
students’ dependence on the dictionary.
5) Teach reading strategies.
To achieve the good result, students need to learn how to use a range of
reading strategies that match their purposes for reading. Anderson stated that
”Strategic reading means not only knowing what strategy to use, but knowing
how to use and integrate a range of strategies” (Nunan, 2003:76).
6) Strive for continuous improvement as a reading teacher.
Teacher, as facilitators, is helping students to discover what work best.
Anderson, as quoted from Andres, Hoffman, and Duffy, said “The good
reading teacher actively teaches students what to do. To succeed, teacher
needs more than classroom tips and techniques; teacher needs the nature of the
reading process.
There are two types of reading; extensive reading and intensive reading
(Harmer, 2004:210). In extensive reading, the students are allowed to find out by
themselves the reading text related to the topic and to follow the teacher’s
guidance. The task can be asking them to report what they have found. In
tasks in intensive reading are almost the same with intensive listening. They are
predicting, reading for gist and reading for detailed comprehension. Vocabulary is
an important part in the reading activity. The task can be also related to the
vocabulary learning.
d. Teaching Writing
The theory of teaching writing is written as one of the chapters in Nunan’s
Practical English Language Teaching (2003). The chapter of teaching writing is
written by Maggie Sokolik from University of California (USA). Sokolik defined
writing as a physical and a mental act, the purpose is to express and impress, and
it is a process and a product.
There are four principles for teaching writing according to Sokolik. They
are:
1) Understand your students’ reasons for writing.
The teacher has to match the teacher’s goal and the students’ work. It is
important to think about the benefit and the types of writing for the students.
2) Provide many opportunities for students to write.
Writing is like sports. It needs more practice to improve the skill. The teacher
should give opportunities to the students to write, even sometimes without
scoring it. The teacher also has to provide many types of writing to enrich the
students’ knowledge of writing.
The teacher’s comment has to be understandable to the students. It should be
in simple words. It is important to the teacher to give time for individual
consultation for the students’ improvement. The feedback has to be able to
make the students know their mistakes and correct it by themselves.
4) Clarify for yourself, and your students, how their writing will be evaluated
The scoring in writing has to be clear between the teacher and the students.
Sokolin gave advice “Take class time to ask them what they value in writing.
Ask them what features make writing enjoyable to read and what features
distract from the enjoyment.”(Nunan, 2003:96)
Ron White and Valerie Arndt as quoted by Harmer in The Practical for
English Language Teaching (2004) provided the writing process. Those are
drafting, structuring (ordering information, experimenting with arrangement, etc),
reviewing (checking context, connections, assessing impact, editing), focusing
(that is making sure you are getting the message across you want to get across),
and generating idea and evaluation. Sometimes the process seems very long. It
can be suited with the syllabus and also the task.
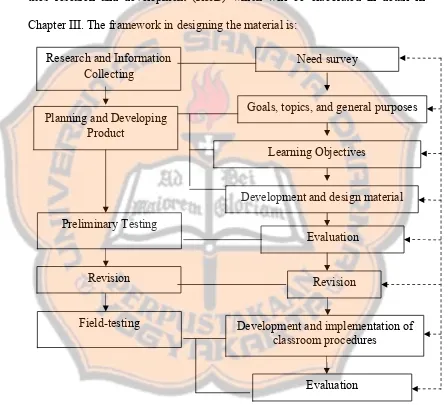
B. Theoretical Framework
The material design for second grade of department students in SMK
Negeri 1 Kasihan combines the Kemp’s and Yalden’s models. The material based
on the Quantum Teaching method. The activities in each unit are following the
five steps in quantum teaching. Since the material is integrated material, each unit
refers to the theory of teaching language in constructing the activity to make it
appropriate and suitable for the students. There is a syllabus for this school, and
the writer will develop the material from the syllabus which is also based on the
curriculum for second grade of vocational high school. In this thesis, the writer
uses research and development (R&D) which will be elaborated in detail in
Chapter III. The framework in designing the material is:
Figure 2.3 The Writer’s Theoretical Framework
continuing to consists of
feedback line
Evaluation
Revision Research and Information
Collecting
Planning and Developing Product
Preliminary Testing
Revision
Field-testing
Need survey
Development and implementation of classroom procedures
Evaluation
Goals, topics, and general purposes
Learning Objectives
29 CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
This chapter discussed the method which was used in this research. It
consisted of research method, research participants, research instruments, data
gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A. Research Method
The writer used research and development (R&D) strategy. This strategy
consists of a cycle, in which a version of the product is developed, field tested,
and revised (Borg & Gall, 1983: 771). The goal of this study was to take the
knowledge of the research and to use it as a product to the school. There were five
steps which were used by the writer according to R&D cycle (Borg & Gall, 1983:
774-775). They were Research and Information Collecting, Planning and
Developing Product, Preliminary Testing, Revision and Field Testing.
Research and information collecting was the first step in R&D cycle. In this
step, the writer looked for related literature which was stated in chapter II. Need
survey was also conducted to obtain learners’ need and characteristic. The writer
conducted interview for the need survey.
Planning and developing product was the second step. Planning included
defining skills and stating learning objectives. Developing product included
preparation of the material, and everything related to it. It also included the
Preliminary testing was the third step. In this step the writer used
questionnaire to obtain the opinion from people who were the experts in English
teaching material design. The writer would obtain feedback from them to revise
the material design.
Revision was the fourth step. In this step, the product was revised based on
the feedback and suggestion in preliminary testing. The writer also did some
improvement of the product based on the result in preliminary testing.
Field testing was the fifth step or the last step. The product which had been
revised and improved was implemented in the classroom. Through the field
testing, the writer could know the effect of the product to the students.
B. Research Participants
In this research, the writer involved the participants who were related to
this study. They were:
a. Participants for the need analysis
The writer conducted interview to gather the learners’ characteristics and
needs. There were 3 English teachers in SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan and 4 second
grade students of dance department in SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan.
b. Participants for the preliminary testing
There were three participants for the preliminary testing. Those were one
lecturer and two English teachers of second grade of dance department of
c. Participants for the field testing
Field testing was done on the students of second grade of Dance Department
students in SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan. This school has three classes of dance
department in the second grade. The writer used one class for the field testing.
The class consisted of 15 students. So, there were 15 participants for the field
testing.
C. Research Instruments
This research used interview and questionnaire as the instruments.
Interview was used in the need survey to obtain the learners’ need and
characteristics. The interview was divided into two parts. The first part was for the
English teachers of SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan. The interview was conducted to
know the condition of the English lesson, including the students’ motivation and
level, the students’ marks, and the situation in learning English. The second was
done to the second grade of the dance department students to know their opinion
about the English learning and their interest in learning English. The answers of
the interviews were analyzed to find the information about the learners’ need and
characteristic.
Questionnaire was used in the preliminary testing and field testing. There
were two types of questionnaires: structured or close and unstructured or open
questionnaires (Ary et al, 2000:175). In preliminary testing, the writer used open
questionnaire was used as the reflection of the students through the classroom
activities in field testing.
D. Data Gathering Technique
This research applied two techniques to gather the data. The first was
through interview. The writer interviewed the English teacher of SMK Negeri 1
Kasihan to know the condition of the English lesson, including the students’
motivation and level, the students’ mark, and the situation in English learning.
This interview was also conducted to know their expectation of the English
lesson. The writer also interviewed four students from the second grade of dance
department of SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan to know their opinion about English and
also the teaching learning activity. The same with the previous interview, the
writer also wanted to know their expectation in learning English. This was a part
to gather the data in the need analysis. Through the interview, the writer knew
deeper about the learner’s needs and characteristics.
The second techniques were questionnaire and observation. Questionnaire
was done in the preliminary testing to obtain the feedback of the materials from
the lecturer and the teachers. This data was used to improve the materials.
Questionnaire and observation were done in field testing to know the effect of the
material to the students. The writer observed the class activity during the learning
process to know the effect of the material and the teaching learning activity. The
writer also used questionnaire to know the students’ reflection of the activity in
E. Data Analysis Technique
The answers from the interview were listed according to the questions as
follow:
No. Questions Answers
1. Respondent 1:
Respondent 2 : etc
2 Respondent 1:
Respondent 2 : etc
etc
From the data collected, the writer concluded the participants’ answer to obtain
the students’ needs and characteristics.
In the observation, the writer observed the learning process by paying
attention to the students’ attitude during the process. In the end of the classroom
activity, the writer distributed questionnaire to obtain feedback from the students.
This data would be analyzed to know the effect of the material to the students.
E. Research Procedure
The research procedure combined the Educational Research Development
(R&D) and the instructional design based on Kemp and Yalden’s models. There
were five steps in the research procedure.
1. Research and Information Collecting
The writer looked for the literature which was related to the research. It
included the literature about instructional design, the method which would be
used, and the syllabus of the second grade of the dance department.
b. Need survey
Need survey was aimed to obtain the data of the learners’ needs and
characteristics. The writer used interview as the instrument in need survey. The
writer interviewed the English teacher of SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan and the students
of second grade of dance department in SMK Negeri 1 Kasihan. The data would
be analyzed to gain the data of learners’ needs and characteristics.
2. Planning and Developing Product
After gaining the data and knowing the learners’ needs and characteristics,
the writer went to the next step; it was planning the product. The writer had to
find out the goals, topics, and general purposes and also the learning objectives. It
was also stated in the provided syllabus for vocational high school. After
obtaining all the data, the writer started to develop and to design the integrated
material based on the Quantum Teaching.
3. Preliminary Testing
After finishing the material, the writer conducted the preliminary testing
by asking the lecturer and the English teacher to give feedback of the material
testing participants. The feedback from the participants was analyzed and used for
the revision.
4. Revision
Revision was done based on the analysis of the data in the preliminary
testing. The revision was done to make the material design more suitable to the
second grade of dance department.
5. Field Testing
The revised material was used in the field testing. The writer used one of
the three material designs the writer had developed. After the classroom activity,
the writer distributed questionnaire as the students’ reflection of the classroom
activity. The data of the feedback was used to answer the second question in the
36 CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter answers the two questions in the problem formulation. This
chapter is divided into two parts. The first is the discussion on the ideal design of
integrated material for the second grade of Dance department students based on
Quantum Teaching. The second is on the effect of the design to the students.
A. The Ideal Design of Integrated Materials for the Second Grade of Dance
Department Students Based on Quantum Teaching
This study is aimed to design the material for the second grade of dance
department students based on Quantum Teaching. Hopefully, new material can
help the students to understand English deeply and also to apply it according to
their field. To know the effect of the material, field testing was also done.
In designing the material, the writer combined the steps of Kemp and
Yalden’s model. The detail of designing integrated material of English learning
for the second grade of dance department students based on Quantum Teaching is
shown below. There were four parts, they were Learners’ Characteristics and
Needs; Goal, General Purposes, and Topics; The Integrated Materials Based on
Quantum Teaching for Second Grade of Dance Department Students and Result