vi ABSTRACT
Sukesti, Petra Sri. 2011. A Set of Integrated English Materials for Grade XI Students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
The eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department need to improve their ability in learning the four English skills since it will really help them to use English properly as a hotel staff candidate. In order to respond to the problem, a study was conducted. The study was intended to design a set of integrated English materials for grade XI students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. The designed materials were based on Communicative Language Teaching approach. The task-based materials were chosen which hopefully could improve the students’ ability to communicate in English properly. The study focused on the integrated skills based on consideration that it is the only plausible approach within a communicative and interactive framework. Two problems are discussed in this study. Those problems are (1) How are integrated English materials for the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan designed? (2) What will the designed materials look like?
To conduct this study, the writer employed Research and Development Method (R&D) which consisted of ten steps. In the study, the writer only employed the first five steps of R&D Method. Those steps were (1) Research and Information Collecting, (2) Planning, (3) Developing Preliminary Form of Product, (4) Preliminary Field-testing, and (5) Main Product Revision. In order to answer the first question, the writer applied seven stages of instructional design model, which were adapted from Kemp’s and Yalden’s models. The stages were (1) conducting needs survey, (2) formulating goals, topics, and general purposes, (3) formulating learning objectives, (4) selecting teaching learning activities and materials, (5) designing the instructional materials, (6) evaluation, (7) revision. In order to answer the second question, the writer presented the integrated English materials based on Communicative Language Teaching approach for the grade XI students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. The materials consist of seven units.
vii
viii ABSTRAK
Sukesti, Petra Sri. 2011. A Set of Integrated English Materials for Grade XI Students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. Yogyakarta: Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Para siswa kelas sebelas jurusan Akomodasi Perhotelan mempunyai kebutuhan untuk meningkatkan kemampuan mereka dalam keempat ketrampilan berbahasa Inggris karena hal ini akan membantu siswa untuk menggunakan bahasa Inggris dengan tepat sebagai calon staff hotel. Maka untuk menanggapi masalah tersebut sebuah penelitian dilaksanakan. Penelitian tersebut bertujuan untuk merancang materi pembelajaran bahasa Inggris terpadu berdasarkan pendekatan Communicative Language Teaching bagi siswa kelas sebelas jurusan Akomodasi Perhotelan SMK N I Kalasan. Materi berbasis tugas yang dipilih diharapkan mampu meningkatkan kemampuan siswa berkomunikasi dalam bahasa Inggris dengan tepat. Penelitian ini difokuskan pada keterampilan terpadu berdasarkan pertimbangan bahwa itu merupakan pendekatan yang masuk akal dalam kerangka komunikatif dan interaktif. Penelitian ini membahas dua masalah. Masalah-masalah tersebut adalah (1) bagaimana satu set materi bahasa Inggris terpadu untuk siswa kelas sebelas jurusan Akomodasi Perhotelan SMK N I Kalasan dirancang? dan (2) akan seperti apakah penyajian materi tersebut?
Guna melakukan penelitian ini, penulis mengimplementasikan Research and Development Method (R&D) yang terdiri dari sepuluh langkah. Akan teapi dalam penelitian ini , penulis hanya mengimplementasikan lima langkah pertama dari R&D Method. Langkah-langkah tersebut adalah (1) Research and Information Collecting, (2) Planning, (3) Developing Preliminary Form of Product, (4) Preliminary Field-testing, dan (5) Main Product Revision. Untuk menjawab pertanyaan pertama, penulis menerapkan tujuh langkah dari model instruksional yang diadaptasi dari model Kemp dan Yalden. Langkah-langkah tersebut adalah (1) melakukan survei kebutuhan, (2) merumuskan tujuan, topik dan tujuan umum, (3) merumuskan indikator pembelajaran, (4) memilih kegiatan belajar mengajar dan bahan, (5) merancang materi pembelajaran, (6) evaluasi, dan (7) revisi. Untuk menjawab pertanyaan kedua, penulis menyajikan materi pembelajaran bahasa Inggris terpadu untuk siswa kelas sebelas jurusan Akomodasi Perhotelan SMK N I Kalasan yang terdiri dari tujuh unit.
ix
pengulangan dari materi yang telah dipelajari untuk memperdalam pemahaman siswa.
E
DE
FA
A SET O
OF HOT Present to ENGLISH L EPARTME ACULTY O S OF INTEGR FOR GR TEL ACCO
OF SM
ted as Partia o Obtain the in Englis
P Student
LANGUAGE
ENT OF LA
OF TEACH
SANATA D
Y
RATED EN
RADE XI ST
OMMODAT
SMK N I KAL
A THESIS
l Fulfillment Sarjana Pen sh Language
By Petra Sri Suk
t Number: 03
E EDUCAT ANGUAGE A ERS TRAIN DHARMA U OGYAKAR 2011 GLISH MA TUDENTS TION DEPA LASAN S
E
DE
FA
A SET O
OF HOT Present to ENGLISH L EPARTME ACULTY O S OF INTEGR FOR GR TEL ACCO
OF SM
ted as Partia o Obtain the in Englis
P Student
LANGUAGE
ENT OF LA
OF TEACH
SANATA D
Y
i RATED EN
RADE XI ST
OMMODAT
SMK N I KAL
A THESIS
l Fulfillment Sarjana Pen sh Language
By Petra Sri Suk
t Number: 03
E EDUCAT ANGUAGE A ERS TRAIN DHARMA U OGYAKAR 2011 GLISH MA TUDENTS TION DEPA LASAN S
Dedicated
My be
My si
My de
Th
N
No
Ther
N
Noth
to:
eloved pare
isters and b
earest one,
here's noth
Nothing
othing you
re's nothin
No one y
thing you
ents
brothers
Didik
iv
hing you c
you can s
u can say
play t
ng you can
you can sa
can do bu
you
B
can do tha
sing that
but you c
the game
n make th
ave that c
ut you can
in time
By The B
at can't be
can't be s
can learn
hat can't b
can't be sa
n learn ho
Beatles
e done
sung
how to
be made
aved
v
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, June 9, 2011
The Writer
vi ABSTRACT
Sukesti, Petra Sri. 2011. A Set of Integrated English Materials for Grade XI Students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
The eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department need to improve their ability in learning the four English skills since it will really help them to use English properly as a hotel staff candidate. In order to respond to the problem, a study was conducted. The study was intended to design a set of integrated English materials for grade XI students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. The designed materials were based on Communicative Language Teaching approach. The task-based materials were chosen which hopefully could improve the students’ ability to communicate in English properly. The study focused on the integrated skills based on consideration that it is the only plausible approach within a communicative and interactive framework. Two problems are discussed in this study. Those problems are (1) How are integrated English materials for the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan designed? (2) What will the designed materials look like?
To conduct this study, the writer employed Research and Development Method (R&D) which consisted of ten steps. In the study, the writer only employed the first five steps of R&D Method. Those steps were (1) Research and Information Collecting, (2) Planning, (3) Developing Preliminary Form of Product, (4) Preliminary Field-testing, and (5) Main Product Revision. In order to answer the first question, the writer applied seven stages of instructional design model, which were adapted from Kemp’s and Yalden’s models. The stages were (1) conducting needs survey, (2) formulating goals, topics, and general purposes, (3) formulating learning objectives, (4) selecting teaching learning activities and materials, (5) designing the instructional materials, (6) evaluation, (7) revision. In order to answer the second question, the writer presented the integrated English materials based on Communicative Language Teaching approach for the grade XI students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. The materials consist of seven units.
vii
viii ABSTRAK
Sukesti, Petra Sri. 2011. A Set of Integrated English Materials for Grade XI Students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. Yogyakarta: Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Para siswa kelas sebelas jurusan Akomodasi Perhotelan mempunyai kebutuhan untuk meningkatkan kemampuan mereka dalam keempat ketrampilan berbahasa Inggris karena hal ini akan membantu siswa untuk menggunakan bahasa Inggris dengan tepat sebagai calon staff hotel. Maka untuk menanggapi masalah tersebut sebuah penelitian dilaksanakan. Penelitian tersebut bertujuan untuk merancang materi pembelajaran bahasa Inggris terpadu berdasarkan pendekatan Communicative Language Teaching bagi siswa kelas sebelas jurusan Akomodasi Perhotelan SMK N I Kalasan. Materi berbasis tugas yang dipilih diharapkan mampu meningkatkan kemampuan siswa berkomunikasi dalam bahasa Inggris dengan tepat. Penelitian ini difokuskan pada keterampilan terpadu berdasarkan pertimbangan bahwa itu merupakan pendekatan yang masuk akal dalam kerangka komunikatif dan interaktif. Penelitian ini membahas dua masalah. Masalah-masalah tersebut adalah (1) bagaimana satu set materi bahasa Inggris terpadu untuk siswa kelas sebelas jurusan Akomodasi Perhotelan SMK N I Kalasan dirancang? dan (2) akan seperti apakah penyajian materi tersebut?
Guna melakukan penelitian ini, penulis mengimplementasikan Research and Development Method (R&D) yang terdiri dari sepuluh langkah. Akan teapi dalam penelitian ini , penulis hanya mengimplementasikan lima langkah pertama dari R&D Method. Langkah-langkah tersebut adalah (1) Research and Information Collecting, (2) Planning, (3) Developing Preliminary Form of Product, (4) Preliminary Field-testing, dan (5) Main Product Revision. Untuk menjawab pertanyaan pertama, penulis menerapkan tujuh langkah dari model instruksional yang diadaptasi dari model Kemp dan Yalden. Langkah-langkah tersebut adalah (1) melakukan survei kebutuhan, (2) merumuskan tujuan, topik dan tujuan umum, (3) merumuskan indikator pembelajaran, (4) memilih kegiatan belajar mengajar dan bahan, (5) merancang materi pembelajaran, (6) evaluasi, dan (7) revisi. Untuk menjawab pertanyaan kedua, penulis menyajikan materi pembelajaran bahasa Inggris terpadu untuk siswa kelas sebelas jurusan Akomodasi Perhotelan SMK N I Kalasan yang terdiri dari tujuh unit.
ix
pengulangan dari materi yang telah dipelajari untuk memperdalam pemahaman siswa.
x
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First and foremost, my greatest gratitude is addressed to Jesus Christ My Savior for His guidance and blessings so that I can finish my study.
I would like to address my deepest gratitude to my sponsor, Carla Sih Prabandari, S.Pd., M.Hum., for her guidance and support to my thesis. My sincere appreciation goes to Drs. Y. B. Gunawan, M.A., Henny Herawati, S.Pd., M.Hum., Sutama, S.Pd., M.Hum., and Florentina Sri Wartini, S.Pd., for willingly spending time evaluating my designed materials.
My greatest appreciation goes to all lecturers and secretariat staff of PBI for their kindness and support during my study and to all thelibrarians for their assistance and dedication they have shared.
I would also like to express my never-ending thanks to my beloved parents, Babe and Ibu for their everlasting love, care, support, encouragement, and prayer. I thank my sisters and brothers, Anung, Anton, Nina and Thomas, for their advice, understanding, prayer, and abundance affection.
Many thanks are addressed to all of my wonderful friends, Nina ‘Bebeb’, Febri ‘Jopai’, Jony, Santi ‘Mami’, Mia, Lala, Linda, Mayora, Panda Uri, Pipin, Sari 04, Wiwin 05, and all Happy Holly Kid’s students and staff for the sharing and positive encouragement. I also warmly thank Dion for his help on giving ideas of the layout of the designed materials.
xi
process of doing my thesis. I also thank him for patiently convincing me that everything is going to be alright in the end.
Last but not least, I would like to thank all people whose names I could not mention one by one for help and support that have been given during my study.
Jesus Christ blesses them all.
xii
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama : Petra Sri Sukesti Nomor mahasiswa : 031214086
Demi perkembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
“A SET OF INTEGRATED ENGLISH MATERIALS FOR GRADE XI STUDENTS
OF HOTEL ACCOMMODATION DEPARTMENT
OF SMK N I KALASAN”
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di internet atau di media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalty kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya, Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal: 9 Juni 2011 Yang menyatakan,
xiii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
DEDICATION PAGE ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ABSTRAK ... viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... x
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PUBLIKASI ... xii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... xiii
LIST OF TABLES ... xvi
LIST OF FIGURES ... xvii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xviii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Problem Identification ... 4
C. Problem Limitation ... 5
D. Problem Formulation ... 6
E. Objectives of the Study ... 6
xiv
G. Definition of Terms ... 7
CHAPTER II. LITERATURE REVIEW A. Theoretical Description ... 9
1. Instructional Design Models ... 9
2. Communicative Language Teaching... 17
3. Integrated Materials ... 22
B. Theoretical Framework ... 23
CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY A. Research Method ... 28
B. Research Participants... 36
C. Research Instruments... 36
D. Data Gathering Techniques ... 39
E. Data Analysis Techniques ... 39
F. Research Procedure ... 41
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION A. The Designing Process of the Integrated English Materials for Grade XI Students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan . 43 1. Research and Information Collecting... 44
2. Planning ... 50
xv
4. Preliminary Field Testing ... 59
5. Main Product Revision ... 65
B. Presentation of the Designed Materials ... 66
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS A. Conclusions ... 71
B. Suggestions ... 73
REFERENCES ... 75
xvi
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page 3.1. The Description of the Respondents of the Preliminary Field Testing
(Blank) ... 36
3.2. The Format of Descriptive Statistic of the Respondents’ Opinion (Blank) ... 41
4.1. The List of 8 Top Topics ... 50
4.2. The Goals and General Purposes of the Designed Materials ... 51
4.3. The Topics ... 51
4.4. The Indicators of the Students’ Performance in Each Skill ... 52
xvii
LIST OF FIGURES
xviii
LIST OF APPENDICES
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents the introduction of the study. There are seven important parts in this chapter; they are background, problem identification, problem limitation, problem formulation, objectives of the study, research benefits, and definition of terms.
A. Background
English proficiency has central contribution to the emergence of intellectual, social, and to the student’s success in studies, business, careers, and personal relationship. In order to achieve the students’ success in studies and careers, there must be chances for the teacher to be more creative in developing the teaching-learning activities. Hence, in 2006 the Indonesian National Department has made revisions in previous curriculum named School-Based Curriculum or Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) for the better language teaching. KTSP gives a great chance for teachers to develop their teaching-learning activities.
professional attitudes, to be able to choose their careers, to be middle class workers, and to meet the needs of business fields and industries for the present and future times. The goal of English language teaching and learning in vocational secondary school, as stated on KTSP Curriculum, is to enable the students to do simple English communication both in oral or written form in order to prepare the students to be able to compete in the real work.
In vocational secondary schools, English becomes a major subject taught especially for Hotel Accommodation Department classes. As students of Hotel Accommodation Department, they are expected to be able to master English including the four skills that are listening, speaking, reading, and writing because it can support the students’ career in the future. Moreover, as Hotel Accommodation Department students, who later on will be the hotel personnel, they have to be able to speak English fluently in order to communicate and give best service for the foreign guests who may come from many different countries.
the English materials which enable the students to do simple English communication both in oral or written form in order to prepare the students to be able to apply it in the real working world as a hotel staff. In order to design the English materials which are suitable for the Hotel Accommodation Department students, the writer should provide and create more interesting English texts and also interesting activities.
As stated by Brown (2001: 235) that research and practice in English language teaching has identified the “four skills” – listening, speaking, reading, and writing – as of paramount importance. By integrating the language skills, it provides the teacher with flexibility in creating interesting and motivating lessons. Through the interesting materials, it is hoped that the students will be motivated in learning English. Therefore, the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department have to master all four skills; listening, speaking, reading, and writing because it can support the students’ career in the future.
Therefore, the writer’s purpose in designing a set of integrated English materials is to motivate and help the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan to prepare the students for the industrial practice. The writer hopes through the material design the students will be able to develop their English competence. The writer also expected that the materials design will give the students enough preparation for the industrial practice.
B. Problem Identification
It is considered that the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan have lack of English performance. It is shown by the students’ English exam score which is under seven in their tenth grade. The teaching-learning activities are also limited in time because they are only six contact hours in a week. Because the time is limited, the teaching-learning become less effective and often there is not enough time for practising listening skill. The English book that is used also needs more improvement. There are lot of unnecessary English text that being used and need more activities that can support the students to improve their English.
English fluently in their working places as the hotel personnel. It is expected that at least the students are able to use simple English to communicate with the hotel guest while they go on the Industrial Practice.
Therefore, the writer will try to design a set of integrated English materials for the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. The designed materials were intended to help the students to improve their performance in the Industrial Practice.
C. Problem Limitation
The design was presented for the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department because they must develop the English competence from the very beginning before using their English in the Industrial Practice. By doing this study, it is hoped that the English materials designed will help the students to practice and develop their English skills in order to prepare the students to face the Industrial Practice. It is expected that they will be ready to practice their English and have strong basic knowledge of English when they are going on Industrial Practice in the second semester.
D. Problem Formulation
The problems of the study are formulated as follows based on the Background, Probem Identification, and Problem Limitation above.
1. How are English materials for the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan designed?
2. What will the designed materials look like?
E. Objectives of the Study
There are two main objectives of the study by considering the problems that are stated in the problem formulation. The objectives are presented as follows.
1. Designing a set of English materials for the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan.
2. Presenting a set of English materials for the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan.
F. Research Benefits
They will get appropriate materials based on their needs and interests so that they will have sufficient knowledge in using English in certain situation.
2. For the teachers
They can apply the instructional materials for Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan students. The instructional materials can be their model in creating their own materials in a more creative and interesting way.
3. For the researcher
The researcher can develop her creativity in designing an instructional program concerning English materials for the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan.
G. Definition of Terms
In order to avoid the different perceptions to these key words, here are discussed some related terms.
1. Hotel Accommodation Department
It is one of the departments in vocational secondary school. This department is for the students who are interested in being the hotel staff.
2. SMK Negeri I Kalasan
Negeri I Kalasan is a school in which students are taught the skills needed to perform a particular job. This school includes three departments namely art, craft, and tourism. In this study, the writer focuses on Hotel Accommodation Department.
3. Integrated Materials
Integrated materials refer to a set of instructional materials that covers all four skills of language (Richards & Rodgers, 1988:64). In this study, integrated materials refer to a set of English materials that focuses on more than one language skill.
4. Communicative Language Teaching
9
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter discusses some theories used as the basis to design a set of English materials for the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. There are two sections in this chapter, namely: Theoretical Description and Theoretical Framework. The theoretical description discusses some related literature that is needed as the basic concepts to design the materials. The theoretical framework presents the designer’s framework and the steps in designing the materials.
A. Theoretical Description
The writer discusses some theories that support the designed materials in this section. They are instructional design model, communicative language teaching, and integrated skills. In the instructional design model, the writer gives a general view of the methods of instructional material design. The communicative language teaching is discussed as the basic theory in designing materials in this study. Integrated skills are also discussed because it provides the teacher with flexibility in creating interesting and motivating lessons in this study.
1. Instructional Design Model
a. Kemp’s Model
As stated by Kemp (1977: 8) the instructional design plan is designed to supply answers to three questions, they are:
1) What must be learned? (objectives)
2) What procedures and resources will work best to reach the desired learning levels? (activities and resources)
3) How will we know when the required learning has taken place? (evaluation) Kemp’s instructional design plan consists of nine parts, they are:
1) Consider goals, and then topics, stating the general purposes for teaching each topic.
Instructional design planning starts with a recognition of the broad goals of the school system or institution. Those goals may be derived from the society, students, and subject area. Statements of goals should recognize changes in learners’ needs and interest, as well as changes in the needs of society and its institution. Then, a planning team should list the major topics to be treated within the content area. Those topics, or unit headings, would become the scope of the course or program, the basis for the instruction. General purposes are important as an initial expression, signifying broadly what the teacher wants to accomplish in the topic. They usually express the planners’ own aims or purposes for the topic or unit.
To best assure an individual’s success in his or her educational program, we should recognize and respect the student as an individual learner. Ideally, each person should be assisted in pursuing learning at his or her own pace, on his or her own schedule, and with his or her own selection of learning experiences and materials. To serve both group and individual means that we must obtain information about the learners’ capabilities, needs, and interest. In designing an instructional plan, there are four factors to be considered. They are academic, social, learning conditions, and learning styles.
3) Specify the learning objectives to be achieved in terms of measurable student behavioural outcomes.
Objectives must be stated in terms of activities that will best promote learning. It can be grouped into cognitive, psychomotor, and affective domain. A learning objective is a precise statement that answers the questions, “What does the student have to do in order to show that he or she has learned what you want the student to learn?” Each objective – to the degree possible – should be unambiguous. Objective must mean exactly the same thing to all other teachers, and it must also clearly communicate to all students who will use it.
4) List the subject content that supports each objective.
5) Develop pre-assessment to determine the student’s background and present level of knowledge about the topic.
It is important to find out specifically (1) to what extent each student has acquired the necessary prerequisites for studying the topic and (2) what the student may have already mastered about the subject to be studied, in order to plan learning activities for which students are prepared and at the same time to ensure that learners do not waste their time on things they already know.
6) Select teaching/learning activities and instructional resources that will treat the subject content so students will accomplish the objectives.
The designer must determine the most efficient and effective methods and then select materials to provide learning experiences that will utilize the content associated with each objective. The selection of instructional materials is closely associated with the planning of teaching and learning activities, both of which should be considered together. Closely associated with the selection of teacher and student activities is the selection of supporting materials that can motivate students and can effectively explain and illustrate subject content, these resources include printed materials of many kinds, audiovisual media, and other items for group and individual uses.
7) Coordinate such support services as budget, personnel, facilities, equipment, and schedules to carry out the instructional plan.
planned program with other operational aspects of the institution (student’s schedules, guidance services, and so forth).
8) Evaluate student’s learning in terms of their accomplishment of objectives, with a view to revising and re-evaluating any phases of the plan that needs improvement.
In this step, the teacher is ready to measure the learning outcomes relating to the objectives. In order to measure students’ achievement, the teacher should determine standards of achievement. The measurement can be in the form of evaluation. There are two kinds of evaluation, namely formative and summative evaluation. Formative evaluation takes place during developments and tryouts, while summative evaluation takes place at the end of the course. Evaluation also refers to the evaluation of the program to know how well the program serves the objectives.
9) Revision
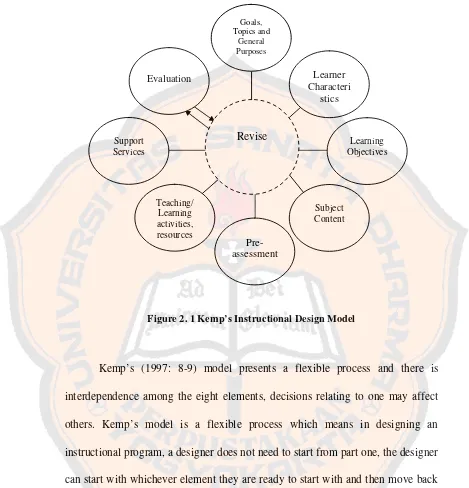
Figure 2. 1 Kemp’s Instructional Design Model
Kemp’s (1997: 8-9) model presents a flexible process and there is interdependence among the eight elements, decisions relating to one may affect others. Kemp’s model is a flexible process which means in designing an instructional program, a designer does not need to start from part one, the designer can start with whichever element they are ready to start with and then move back and forth to the other steps in the eight parts of Kemp’s model. The circular shape of the model gives a sense that the design and the development process is a continuous cycle that requires constant planning, design, evaluation and assessment, to insure effective instruction.
Revise
Pre-assessment
Subject Content
Learning Objectives Support
Services
Teaching/ Learning activities, resources Evaluation
Goals, Topics and
General Purposes
Learner Characteri
In this study, there are some steps chosen by the writer, they are formulating goals, topics and general purposes, formulating learning objectives, selecting teaching or learning activities and resources, evaluating, and revising. Those chosen steps are not a complete model yet because the writer also has to know the needs of the subjects of this study. The step of the needs survey can be found in Yalden’s model. That step will be combined with Kemp’s model. Before combining the step, the writer will explain the procedure of Yalden’s model. b. Yalden’s Model
The writer also adopts Yalden’s model. Yalden (1987: 88) presents eight stages in designing materials as follows:
1) Needs Survey
Needs survey is conducted in order to analyse the learners’ needs of learning the target language and to understand students’ characteristics which enable the designer to make acceptable objectives that complete the students’ needs.
2) Description of purpose
3) Selection or development of syllabus type
This stage is to select or develop the appropriate syllabus type. It is the time for the designer to decide what kind of syllabus type will be used. It should be based on the students’ needs and the purpose of the program.
4) Production of a proto-syllabus
The proto-syllabus describes the language itself and language use to be covered in the program. The designer should consider the purpose of the program that the specification of the syllabus contents will be taken accordingly.
5) Production of a pedagogical syllabus
The pedagogical production develops the teaching materials, learning and teaching approaches which consists of testing sequence and decisions on testing instruments. The specification of every single word and phrase will be conducted in this stage. Therefore, the production of proto-syllabus will be completely developed.
6) Development and implementation of classroom procedures
Selection of exercise types and teaching techniques, preparation of lesson plan, and preparation of weekly schedules, those three procedures in this stage should be weekly monitored by the teacher to see the classroom development. 7) Evaluation
8) Recycling
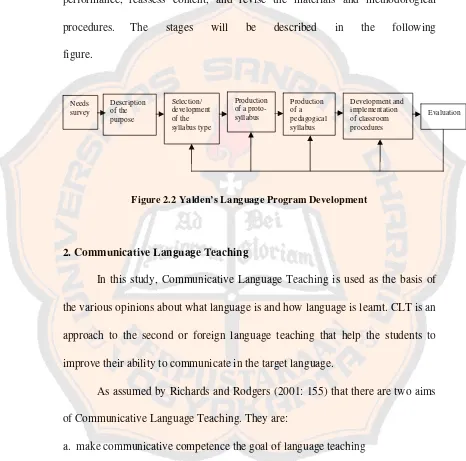
[image:40.612.70.536.170.631.2]In this last stage, the designer has to fit the goal set and students’ performance, reassess content, and revise the materials and methodological procedures. The stages will be described in the following figure.
Figure 2.2 Yalden’s Language Program Development
2. Communicative Language Teaching
In this study, Communicative Language Teaching is used as the basis of the various opinions about what language is and how language is learnt. CLT is an approach to the second or foreign language teaching that help the students to improve their ability to communicate in the target language.
As assumed by Richards and Rodgers (2001: 155) that there are two aims of Communicative Language Teaching. They are:
a. make communicative competence the goal of language teaching
b. develop procedures for the teaching of the four language skills that acknowledge the interdependence of language and communication
Needs survey Description of the purpose Selection/ development of the syllabus type Production of a pedagogical syllabus Development and implementation of classroom procedures Evaluation Production
Communicative language teaching makes use of real life situations that need communication. CLT emphasizes the process of communication rather than the mastery of language form. Therefore, the writer considered CLT as the most appropriate approach for the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan.
a. The Characteristics of CLT
Brown (2000: 266) offers the four interconnected characteristics of CLT. First, classroom goals are focused on all of the components of the communicative competence and not restricted to grammatical or linguistic competence. Second, language techniques are designed to engage learners in the pragmatic, authentic, functional use of language for meaningful purposes. Organizational language forms are not the central focus but other aspects of language that enable the learner to accomplish those purposes.Third, fluency and accuracy are seen as competency principles underlying communicative techniques. At times fluency may have to take on more importance than accuracy in order to keep learners meaningfully engaged in language use. Fourth, in the communicative classroom, students ultimately have to use the language, productively and receptively, in unrehearsed contexts.
b. Types of Classroom Activities in Communicative Language Teaching
Littlewood (1981: 85) offers two kinds of activities in the CLT classroom. They are:
1. Pre-communicative activities
In these activities, the teacher isolates specific elements of knowledge or skill which compose communicative ability, and provides the learners with opportunities to practice them separately. The learners are being trained in the part-skills of communication rather than practising the total skill to be acquired. The pre-communicative activities aim is to provide the learners with a fluent command of the linguistic system, without actually requiring them to use this system for communicative purposes. The learners aim is to produce language which is acceptable rather than to communicate meanings effectively. These activities can be distinguished as quasi-communicative and structural activities. It is quasi-communicative when they take account of communicative as well as structural facts about language. Structural activities is performing mechanical drills or learning verb paradigms.
2. Communicative activities
perform a task by communicating as best as he can, with whatever resources are available for the learner. Functional communication activities include tasks in comparing similarities and differences things, arranging sequence of events, discovering missing features, giving instructions, following directions, and solving problems. In social interaction activities, the learner is encouraged to take account of the social context in which communication takes place. Social interaction activities include conversation and discussion sessions, dialogues and role plays, simulations, skits, improvisations, and debates.
c. The Role of Teachers and Learners in Communicative Activities
According to Breen and Candlin in Richards and Rogers (2001: 167) the teacher has two main roles in communicative classroom. They are as a facilitator and as an independent participant. Other teacher roles are:
1. Needs analysis
Teacher has a responsibility for determining and responding to learner language needs. It can be done informally and formally. Informally by one-to-one sessions with the students to get the students’ perception of his or her learning style, learning assets, and learning goals. Formally is by administering a needs assessments instrument.
2. Counselor
3. Group process manager
CLT requires teachers to acquire less teacher-centered classroom management skills. Teachers should organize the classroom as a setting for communication and communicative activities.
The learner should contribute as much as he gains and learns in an interdependent way. The learners are expected to be actively interacting among learners and to be active in the classroom activities.
d. The Role of Instructional Materials
Materials have important role in promoting communicative language use. There are three kinds of materials currently used in CLT discussed by Richards and Rogers (2001: 169). They are:
1. Text-based materials
Text-based materials are materials that are based on text and it uses visual cues, taped cues, pictures, and sentence fragments in order to initiate conversations.
2. Task-based materials
3. Realia
Realia are authentic materials taken from the real life. It is including signs, magazines, advertisements, newspaper, maps, pictures, symbols, graphs, and charts.
3. Integrated Skills
This study does not focus only on one language skill, but focuses on four language skills. It is based on the consideration that the integration of the four skills is the only plausible approach within a communicative and interactive framework. Brown (2001: 234) stated that most of the interactive techniques involve the integration of skills. Through integrated skills, it provides the teacher with flexibility in creating interesting and motivating lessons.
There are two types of integrated skills instruction that will be explained as follows.
a. Content-Based Instruction
According to Brown (2001: 235) content-based teaching presents some challenges to language teacher. The teacher can view the teaching way from an entirely different perspective by allowing the subject matter to control the selection and sequence of language items.
Completing integration of language skills are allowed in content-based instruction. It would be hard not to involve at least three of the skills of the four skills because the students should read, discuss, solve problem, analyse data, and write the answer or their opinions.
b. Task-Based Instruction
As explained in Oxford (2001) that in task-based insruction basic pair work and group work are often used to increase students interaction and collaboration.
B. Theoretical Framework
In this design, the communicative activities such as role play and simulation will be the major tasks for the learners. It is to prepare the students with many chances to improve their English through role play and simulation. By giving the students a lot of communicative activities it is expected the students will be ready for the industrial practice.
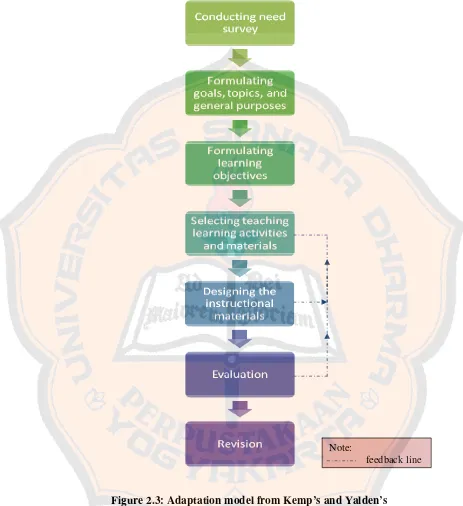
modifies and combines the Instructional Materials as proposed by Kemp and Yalden.
The writer combined these two models to design the materials because the combination indicates a clear and complete step in designing the materials. Kemp provides the flexibility to where the teacher will begin. Kemp offers to revise in each step to obtain better performance in the next chances. Yalden’s instructional model will also give contribution in arranging the framework by combining a step with some of Kemp’s steps. Those two models are modified to produce a framework to conduct the study. The instructional model implemented in this study is determined based on the consideration that it should be applicable, simple, effective, efficient, also fit with the real condition to achieve the goals.
The steps are explained as follow:
1. Conducting needs survey (Yalden’s model)
The writer distributes a questionnaire to the eleventh grade students of SMK N I Kalasan. The writer also conducts an interview with the English teachers of SMK N I Kalasan in order to obtain the supporting needs. The results of questionnaire and interview are considered the materials development.
2. Formulating goals, topics, and general purposes (Kemp’s model)
3. Formulating learning objectives (Kemp’s model)
In this step, the writer specifies the objectives which are important since it is the outcome that should be achieved by students. The writer performs the objectives for each topic. At the end of each topic, the students are expected to achieve those objectives.
4. Selecting teaching learning activities and materials (Kemp’s model)
In this step, the writer decides the most efficient and effective activities then select the appropriate materials for the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department in SMK N I Kalasan. The activities and tasks will be based on the needs analysis. Task-based materials, one of the kinds of materials currently used in Communicative Language Teaching discussed by Richards and Rodgers are applied in these designed materials. The communicative activities such as role play and simulation will be the major tasks for the learners.
5. Designing the instructional materials
prepare them for the industrial practice. The materials designed are also based on the competence standard and basic competence.
6. Evaluation and revision (Kemp’s model)
In order to obtain feedback, the writer distributed the design materials to two English teachers of SMK N I Kalasan and two English lecturers of Sanata Dharma University. The feedback determines whether or not the design materials have fulfilled the requirements. The writer uses the feedback given, as an evaluation, to make improvement and revision on the designed materials.
Figure 2.3: Adaptation model from Kemp’s and Yalden’s Note:
28
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
This chapter discusses the methodology used in this research in detail. This methodology is used in order to answer the two major questions. First is to find out how a set of integrated English materials for the eleventh grade of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan is designed. Second is to present a set of English materials for the eleventh grade of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. Those problems will be answered in five sections, namely: research methods, research participants, research instruments, data gathering techniques, data analysis, and research procedures.
A. Research Method
In order to obtain the objectives of this study, the writer used Research and Development (R & D) method. According to Borg and Gall (1983: 772), Educational Research and Development (R & D) is a process used to develop and validate educational products. The writer chose Research and Development method because it takes the findings generated by basic and applied research and uses them to build tested products that are ready for operational use in schools.
1. Research and information collecting
This step includes review of literature, classroom observations, and preparation of report of state of the art. The purposes of doing review of literature are to determine the state of knowledge in designing materials and to identify several instructional techniques that improve learning.
2. Planning
Planning includes defining skills, stating objectives determining course sequence, and small scale feasibility testing.
After the writer has completed her review of the literature and collected some important information for her study, she began to start the planning step of the R & D cycle. In this step, the writer formulated the statement of the specific objectives to be achieved by the materials. The statement of the specific objectives is to be achieved by the materials which is the most important aspect of planning a research-based educational product.
3. Develop preliminary form of product
4. Preliminary field test
The preliminary field test is conducted in order to obtain an initial qualitative evaluation of the new educational product. Interview, observational, and questionnaire data collected and analyzed.
5. Main product revision
The data which was gathered through preliminary field test was compiled and analyzed to re-plan the course and make the revision.
6. Main field testing
The aim of this stage is to determine whether the educational product which has been developed meets its performance objectives and to collect necessary information that can be used to improve the course. In this step, the writer obtained the questionnaires data from all the participants in the main field test to collect information that can be used to improve the course in the next revision.
7. Operational product revision
The revision of product as suggested by main field-test results is conducted if the educational product still cannot achieve the objective.
8. Operational field testing
distributing questionnaires or interview to some teachers or lecturers to get their feedback on the product in order to do the final revision.
9. Final product revision
The final revision of product is conducted as suggested by operational field-test results. The revision includes both all scripts and printed materials. 10. Dissemination and implementation
Dissemination refers to the process of helping potential users become aware of R & D products. It is necessary to demonstrate that the R & D product is implemented according to the developers’ specifications so that it produces the intended effects. Implementation refers to the process of helping the adopter of an R & D product to use it in the way intended by the developers. In this step, the writer reported on product at professional meetings and in journals.
In this study, the writer only adopted the first five steps of R&D due to the limitation of time and resources. They are research and information collecting, planning, develop preliminary of product, preliminary field testing, and main product revision. They are explained as follow.
1. Research and information collecting.
very essential to be used as a basis of designing the English materials for the eleventh grade of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMKN I Kalasan.
2. Planning
The second steps of the writer’s model are formulating goals, topics, and general purposes were conducted. Formulating learning objectives were then stated. The next step was selecting teaching learning activities and materials. Those three steps of the writer’s model are presented in this R&D cycle.
3. Develop preliminary form of product.
This step in designer’s model is called constructing a set of integrated English materials for eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department in SMK N I Kalasan. In this step, the writer developed the questioners and interview guides which are used in this study.
4. Preliminary field testing.
In order to get feedback necessary for improving designed a set of English materials, evaluating the set of English materials was carried out. In R&D cycle, it is known as preliminary field testing.
5. Main product revision.
In writer’s model, this step is called evaluating a set of English materials. Evaluation of a set of integrated English materials was conducted by distributing questionnaire to some respondents.
According to Sprinthall (1991: 93), survey is designed to gather information from samples (occasionally, even some populations) by using questionnaire or sometimes interview.
Survey research was used for two purposes in this study. The first purpose was for the need analysis (pre-design survey) which was closely related to research and information collecting, planning, and developing preliminary form of product in R & D cycle. The second purpose was for evaluation on the design materials (post-design survey) this was important in preliminary field-testing and main product revision in R & D cycle.
1. Pre-design Survey
The very beginning survey was conducted to obtain data about what the students` needs and expectations in learning English. The survey was done by conducting an informal interview and distributing questionnaires. The informal interview was conducted with an English teacher of SMK N I Kalasan. Meanwhile, the questionnaire distributed to eleventh graders of SMK N I Kalasan. The data collected in this survey research became the core of designing appropriate instructional materials.
2. Post-design Survey
participant. The survey was conducted by distributing and gathering questionnaires to two English teachers of SMK N I Kalasan and two English lecturers of Sanata Dharma University. The data was used as guidance to revise and improve the designed materials.
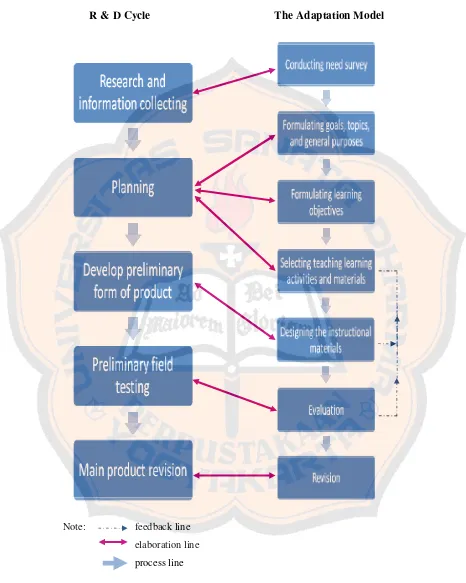
By emphasizing on the steps of R & D cycle, the writer found out that there were some similar purposes between the steps of the writer’s model and the steps of R & D cycle in designing the materials. Moreover, those steps could support each other to design materials for eleventh grade students of Accommodation Hotel Department of SMK N I Kalasan. It could be concluded that between the writer’s framework and R & D framework were match.
R & D Cycle
Note: feedback line
elaboration line
process line
The Adaptation Model
[image:58.612.70.536.98.681.2]
B. Research Participants
This study was conducted in September 2008. This study took place in SMK N I Kalasan which is located in Randugunting, Tamanmartani, Kalasan, Sleman.
[image:59.612.71.533.237.632.2]The writer chose the students of SMK N I Kalasan as the population and the eleventh grade of Hotel Accommodation students as the sample of this study. The writer chose the English teachers of SMK N I Kalasan and some English lecturers of Sanata Dharma University to be the second respondents in order to find whether the suggestive materials were effective or not. The writer believed that their experiences in teaching English would give valuable input to construct better materials.
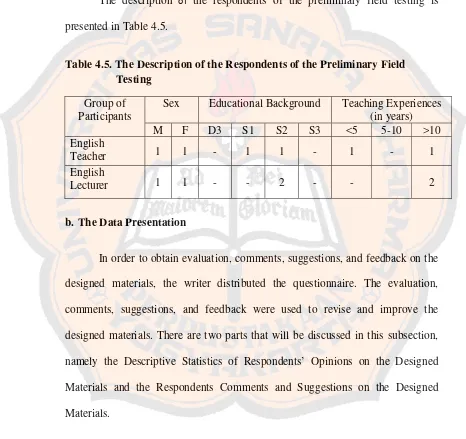
Table 3.2 The Description of the Respondents of the Preliminary Field Testing Groups of
respondents
Sex Educational background
Teaching experiences in years
F M S1 S2 S3 1-5 6-10 10-15 >15
English teachers
English lecturers
C. Research Instruments
1. Questionnaires
The purpose of distributing the questionnaires was to figure out the learners’ real need related to their needs, aims, and difficulties in learning English. The questionnaire used was both in closed and open form. The purpose of the closed form was to help the respondents with the question given by using the alternative for them. It had advantages in providing the respondents with the answers; therefore the respondents’ task was only to choose the appropriate answers that were really significant to the actual facts. This type was combined with the open form was to give freedom for the respondents to answer and fill the question given.
The writer made the questions in Indonesian to avoid the misinterpretation both for the writer and for the respondents. It was hoped that the respondents would get the points of the questions and could answer easily.
The writer distributed two questionnaires in this study. The first, as the pre-design survey, the questionnaire was distributed to eleventh graders of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan in order to find the students’ needs and interests. The second, as the post-design survey, the questionnaire was conducted to English teachers of SMK N I Kalasan and two English lecturers of Sanata Dharma University to get the feedback on the designed materials.
2. Interview
to obtain additional information and evaluation of the designed materials. Ary et al. (1976: 174) stated that there are also two types of interviews: “structured interview” and “unstructured interview”. In structured interview, the researcher has made the questions and alternative answers which have to be followed rigidly by all respondents. In contrast, the unstructured interview permits the respondents to give answers freely regarding their views, attitudes, beliefs, and other information. While the structured interview can be considered formal, the unstructured one is more informal. In this study, the writer conducted the unstructured interview since the answers needed were in form of information. Moreover, the writer did not use tape recorder in order to eliminate the respondents’ awkwardness of being interviewed.
In this study, the interview was held as the pre-design survey in order to gather the information about the teaching learning process as the guidance in designing the materials. The interview was done to an English teacher of SMK N I Kalasan informally by using Indonesian to make the questions understood. The questioned asked in the interview were:
a. the teaching technique b. the teaching media
c. the starting point activities d. the opening activities e. the main activities f. the evaluation method
D. Data Gathering Technique
The methods used to collect the data are by filling the questionnaire for the students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan and interviewing the English teachers of SMK N I Kalasan and some English lecturers in English Education Program of Sanata Dharma University to get the meaningful feedback on the material design.
There were two types of data gathering in this study. The first was gathering data for needs survey. The writer collected the data interview from two English teachers of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. The interview was held in September 2008 in the Hotel Accommodation Department office. The writer distributed the questionnaire to the eleventh grade students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. The second type was data gathering for conducting revision and improvement of the designed set materials. The writer distributed the questionnaire to two English lecturers in English Language Education Study Program and two English teachers in SMK N I Kalasan. The post-design survey questionnaires were distributed in order to obtain the opinions,
comments, and suggestions on the designed materials. The feedback from the English
lecturers and teachers is gained to revise the designed materials. The type of
questionnaire is the combination of both open- and closed- form.
E. Data Analysis
them in the form of table. The results of the survey functioned as one of the considerations in designing the materials. The data collected in the pre-design survey questionnaire would be calculated using percentage as follows.
%
100
×
∑
n
N
Note:
N = the total number of students who choose certain topic
∑
n = the total number of studentsIn order to compute the data from the materials evaluation questionnaire, three indexes were used as proposed by Ary, Jacob, and Razavieh (1976: 103). They were “mean, median, and mode”. Since the data have been arranged into a frequency distribution, the sum of the scores can be computed by multiplying each score by its frequency and summing these products, which simplifies the computation of the mean. The assessment of the participants’ opinion was based on five points of agreement:
5 = strongly agree with the statement 4 = agree with the statement
3 = doubt with the statement 2 = disagree with the statement
1 = strongly disagree with the statement
[image:64.612.68.533.152.676.2]
respondents’ opinion on the designed set of English materials is like the following one:
Table 3.3. The Format of Descriptive Statistic of the Respondents’ Opinion (Blank)
No Respondents’ Opinions
Statements N Central
Tendency
1 2 3 4 5 Mn
1.
N = number of the participants Mn = mean
F. Research Procedure
The writer applied some steps in her study. They were:
1. Asking permission letter from Sanata Dharma University to conduct the research in SMK N I Kalasan.
2. Asking permission from the head master of SMK N I Kalasan.
3. Distributing the questionnaire to the students in order to obtain the information needed for designing materials.
4. Conducting interview toSMK N I KalasanEnglish teacher. 5. Reading and analyzing the respondents’ answers.
8. Distributing questionnaires to four respondents (two SMK N I Kalasan English teachers and two Sanata Dharma University English lecturers) in order to obtain feedback of materials designed.
9. Analyzing the results of the questionnaires.
10.Revising the designed materials based on the results of the questionnaires in order to obtain the final version.
43
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter is divided into three main parts to answer two questions as stated in the Problem Formulation in chapter one. The first is the designing process of the integrated English materials for grade XI students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. The second part is the findings and discussion on the designed materials evaluation. The third part is the presentation of the integrated English materials for grade XI students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan.
A. The Designing Process of the Integrated English Materials for Grade XI
Students of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan
Development (R&D) cycle in designing the materials. They were (1) research and information collecting; (2) planning; (3) developing preliminary form of product; (4) preliminary field testing and (5) main product revision.
1. Research and Information Collecting
In this first step, the writer conducted needs survey by distributing questionnaire and conducted interview. In order to obtain the data of the students’ needs, the writer conducted interview and distributed the questionnaire. The interview was for the eleventh grade English teacher of SMK N I Kalasan and the questionnaire was for the eleventh grade students of SMK N I Kalasan. The detail information of these two results is presented below.
a. Students’ Needs Based on the Interview with the Teacher
gave them instructions. She also said that the students were familiar with greeting and instruction in English. They could also use simple sentences for certain topics in the dialogue such as greeting and personal identity.
The writer found out that the teaching learning activities usually used in the classroom are games, conversation, group discussion, presentation, role play, listening, and written exercises. As the starting point, the teacher usually began the class by sharing the experiences, giving new vocabularies, pictures, and texts. The teacher said that she evaluated the students by giving written test, group work, presentation, and students being active in the class activities.
b. Students’ Needs Based on the Questionnaires for the Students
In order to obtain a clear description of students’ needs, the writer distributed questionnaires to the eleventh grade students of SMK N I Kalasan on September 18, 2008. The writer only distributed the questionnaire in one class eleventh grade of Hotel Accommodation Department because of the limited time. The eleventh grade of Hotel Accommodation Department consisted of 12 male students and 23 female students, so the total number of the participants was 35. The writer gathered the data of the respondents’ opinion in the form of open-closed questionnaire, the respondents would choose the answer based on their opinions but still they have a chance to provide their own opinion. In each question the respondents might choose more than one answer. The writer presented the questionnaire on the needs survey on Appendix D and the result of the questionnaire on the needs survey on Appendix E. The writer analyzed the result of the questionnaire on the needs survey as following.
Related to the type of method using in teaching learning process from 35 students (77%) liked games. It means that more than half of the students liked games in the teaching learning process. Less than half of the students chose group discussion, sharing experience, role play, presentation, and only a few of the students chose question and answer, and lecturing. From this result, the designed materials will include those activities such as games, group discussion, sharing experience, role playing, and presentation.
Furthermore the question number 3 was aimed at knowing what kinds of techniques were preferred by the students to help them learn English well. From 35 students, 69% of them preferred learning by doing and more than a half of the students preferred lecturing. Less than a half of the students preferred pair work, indoor activities, individual learning, using media, outdoor activities, and group work as techniques which can help the students to learn English well. Based on the result above, the designed materials will apply such techniques as learning by doing, lecturing, and pair work in the designed materials.
The question number 4 was aimed to know the English skills which should be learned by the students. As the result, more than half of the students chose speaking and some students chose listening, reading, and writing. Based on the result above, the designed materials will cover four English skills. They are speaking, listening, reading, and writing.
internet because it could broaden their knowledge, interesting, and not boring. The rest, 14% of the students did not like using internet because they had difficulty in operating the internet. The materials designed will provide some activities for the students to use the internet as a media in learning English.
Based on question number 6.80% of the students considered using song in the listening activities was interesting, challenging, and could help them understand English more easily. Only few of the students found difficulty in using song in the listening activities because they did not understand the words in the English song. This means that the designed materials will include listening to the songs as one of the activities.
The question number 7 was aimed to know whether the English book used in the classroom was interesting or not. 70% of the students considered it was not interesting because the layout was not interesting (no picture and not colorful) and the reading text is not suitable for Hotel Accommodation. Only few of the students considered the book used in the classroom was interesting because the materials are easy to understand. This means that the designed materials will be colorful, has some picture, and provide the reading text which is suitable for Hotel Accommodation Department.
Accommodation and interesting pictures and colorful. The designed materials will include those criteria.
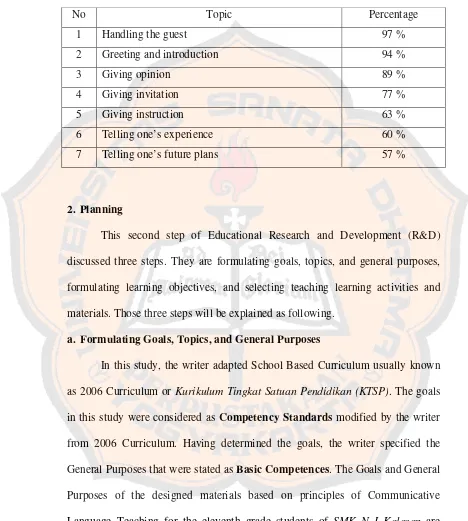
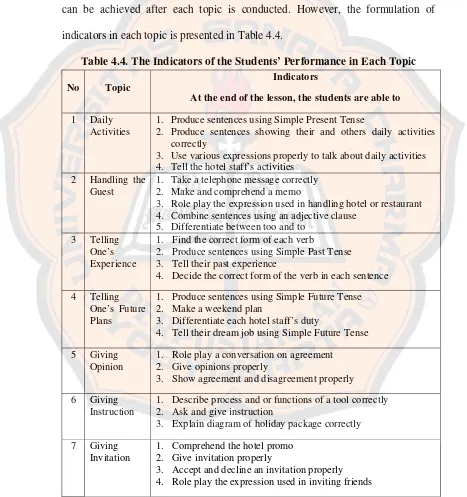
The last question of the questionnaire, number 9, was aimed to find out the suitable topics for Hotel Accommodation based on the students’ opinions. The writer provided nine options of topics on the questionnaire based on the syllabus used by eleventh grade of Hotel Accommodation Department of SMK N I Kalasan. The result showed that 97% of the students chose handling the guest. More than half of the students also chose daily activities, giving opinion, giving invitation, giving instruction, telling one’s experience, and telling one’s future plans. The rest of the students, less than 10%, chose bargaining and weather forecast as an appropriate topic for Hotel Accommodation. Based on the result above, the topic of the designed materials will be handling the guest, daily activities, giving opinion, giving invitation, giving instruction, telling one’s experience, and telling one’s future plan.
Table 4.1 The List of 7 Top Topics
No Topic Percentage
1 Handling the guest 97 %
2 Greeting and introduction 94 %
3 Giving opinion 89 %
4 Giving invitation 77 %
5 Giving instruction 63 %
6 Telling one’s experience 60 %
7 Telling one’s future plans 57 %
2. Planning
This second step of Educational Research and Development (R&D) discussed three steps. They are formulating goals, topics, and general purposes, formulating learning objectives, and selecting teaching learning activities and materials. Those three steps will be explained as following.
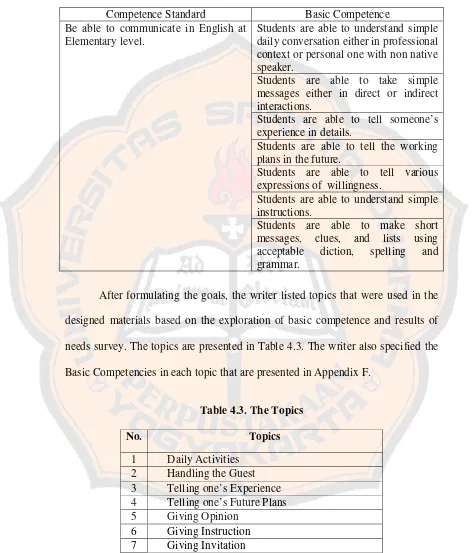
a. Formulating Goals, Topics, and General Purposes
Table 4.2. The Goals and General Purposes of the Designed Materials
Competence Standard Basic Competence
Be able to communicate in English at Elementary level.
Students are able to understand simple daily conversation either in professional context or personal one with non native speaker.
Students are able to take simple messages either in direct or indirect interactions.
Students are able to tell someone’s experience in details.
Students are able to tell the working plans in the future.
Students are able to tell various expressions of willingness.
Students are able to understand simple ins