i
SAINS
KURIKULUM STANDARD SEKOLAH RENDAH
DOKUMEN STANDARD KURIKULUM DAN PENTAKSIRAN
TAHUN LIMA
iii
KURIKULUM STANDARD SEKOLAH RENDAH
DOKUMEN STANDARD KURIKULUM DAN PENTAKSIRAN
SAINS
TAHUN 5
(Edisi Bahasa Inggeris)
Cetakan Pertama 2016
Kementerian Pelajaran Malaysia 2016
Hak Cipta Terpelihara. Tidak dibenarkan mengeluar ulang mana-mana bahagian artikel, ilustrasi, dan isi kandungan buku ini dalam
apa-apa juga bentuk dengan apa cara pun sama ada secara elektronik, fotokopi, mekanik, rakaman, atau cara lain sebelum
mendapat kebenaran bertulis daripada Pengarah Bahagian Pembangunan Kurikulum, Kementerian Pelajaran Malaysia, Aras 4-8,
Blok E9, Kompleks Kerajaan Parcel E, Pusat Pentadbiran Kerajaan Persekutuan , 62604 Putrajaya.
33
CONTENT
NATIONAL PRINCIPLES
v
NATIONAL EDUCATION PHILOSOPHY
vi
NATIONAL SCIENCE EDUCATION PHILOSOPHY
vii
INTRODUCTION
1
DESIGN OF THE STANDARD-BASED CURRICULUM FOR PRIMARY SCHOOL
1
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES
4
FOCUS
5
ELEMENTS ACROSS THE CURRICULUM
12
SKILLS FOR 21
STCENTURY
15
SKILLS AND VALUE FOR THE 21
STCENTURY
16
STUDENT PROFILE
17
TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES
18
METHODS OF TEACHING AND LEARNING SCIENCE
20
ASSESSMENT OF TEACHING AND LEARNING
23
34
THEME : INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE
1.0 Scientific Skills
2.0 Science Room Rules
30
46
THEME : LIFE SCIENCE
3.0 Life Processes In Animals
4.0 Life Processes In Plants
48
56
THEME : PHYSICAL SCIENCE
5.0 Energy
6.0 Properties of Light
7.0 Electricity
8.0 Heat
60
64
68
72
THEME : MATERIAL SCIENCE
9.0 Matter
10.0 Acid and Alkali
74
78
THEME : EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE
11.0 Earth, Moon and Sun
80
THEME : TECHNOLOGY AND SUSTAINABILITY OF LIFE
v
RUKUN NEGARA
BAHAWASANYA negara kita Malaysia mendukung cita-cita untuk mencapai perpaduan yang lebih erat dalam kalangan seluruh masyarakatnya; memelihara satu cara hidup demokratik; mencipta masyarakat yang adil bagi kemakmuran negara yang akan dapat dinikmati bersama secara adil dan saksama; menjamin satu cara yang liberal terhadap tradisi-tradisi kebudayaannya yang kaya dan berbagai-bagai corak; membina satu masyarakat progresif yang akan menggunakan sains dan teknologi moden; MAKA KAMI, rakyat Malaysia, berikrar akan menumpukan seluruh tenaga dan usaha kami untuk mencapai cita-cita tersebut berdasarkan atas prinsip-prinsip yang berikut:
•
KEPERCAYAAN KEPADA TUHAN•
KESETIAAN KEPADA RAJA DAN NEGARA•
KELUHURAN PERLEMBAGAAN•
KEDAULATAN UNDANG-UNDANGvi vi
Pendidikan di Malaysia adalah suatu usaha
berterusan ke arah memperkembangkan lagi
potensi individu secara menyeluruh dan
bersepadu untuk mewujudkan insan yang
seimbang dan harmonis dari segi intelek,
rohani, emosi dan jasmani berdasarkan
kepercayaan dan kepatuhan kepada Tuhan.
Usaha ini adalah bagi melahirkan rakyat
Malaysia yang berilmu pengetahuan,
berketerampilan, berakhlak mulia,
bertanggungjawab dan berkeupayaan
mencapai kesejahteraan diri serta memberikan
sumbangan terhadap keharmonian dan
kemakmuran keluarga, masyarakat dan negara.
vii
FALSAFAH PENDIDIKAN SAINS NEGARA
FALSAFAH PENDIDIKAN SAINS KEBANGSAAN
Selaras dengan Falsafah Pendidikan Kebangsaan,
pendidikan sains di Malaysia memupuk budaya Sains dan
Teknologi
dengan
memberi
tumpuan
kepada
perkembangan individu yang kompetitif, dinamik, tangkas
dan berdaya tahan serta dapat menguasai ilmu sains dan
keterampilan teknologi.
1
INTRODUCTION PREFACE
As articulated in the National Education Philosophy, education
in Malaysia is an on-going effort towards developing the
potential of individuals in a holistic and integrated manner to
produce individuals who are intellectually, spiritually,
emotionally and physically balanced. The primary and
secondary school science curriculum standard is developed
with the aim of producing such individuals.
The overall Science Standard Curriculum encompasses three core science subjects and four elective science subjects. The Core Science Subjects are Primary School Science, Lower Secondary Science, and Upper Secondary Science. The Elective Science subjects offered in upper secondary are Biology, Chemistry, Physics, and Additional Science.
The Core Science Subjects for primary and lower
secondary school are designed with emphasis on the
knowledge and understanding of science to produce science
literate pupils so as to prepare them for science at higher
levels. The Core Science subjects in upper secondary school
aim to develop pupils’ science literacy, innovative skills and to
equip them to enter fields of science. The Elective Science
Subjects offer options to pupils based on their inclinations,
interests and abilities in the science field to venture into
careers specifically in science and technology fields. This
group of pupils will continually contribute to the development
of the nation.
This group of pupils will become the human resources
in the field of science and technology that will contribute to the
continuity in the development of the country.
DESIGN
OF
THE
STANDARD-BASED
CURRICULUM FOR PRIMARY SCHOOL
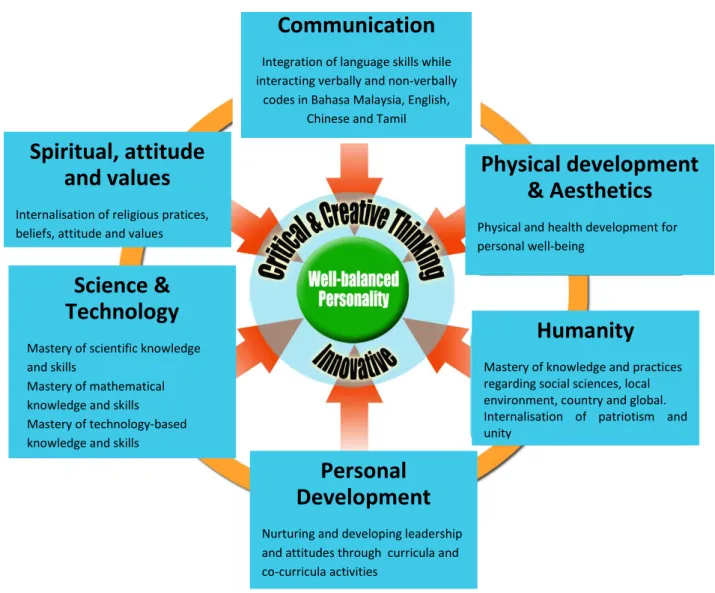
The concept of strands introduced in KSSR, is a form of classification of knowledge, skills and values. This concept focuses on the development of a physically, emotionally, spiritually and intellectually balanced human capital. Six strands are identified to represent the fields of knowledge, skills and values that form the
2 basis of development of creative and critical thinking, and innovative individuals (Diagram 1). The strands reflect explicit structuring of discipline of knowledge, skills and values that pupils need to acquire.Each strand is interconnected and integrated.
Communication
The communication strand emphasises the integration process of the language skills in the form of verbal and non-verbal during interaction. This strand focuses on language skills such as listening and speaking, reading and writing, as well as the added value of reasoning. Pupils need to master these skills to assist them in the process of acquisition of knowledge, skills and values in the other strands. Language proficiency prepares pupils to select accurate and systematic language used in social interaction.
The knowledge disciplines within the communication strand include Bahasa Melayu, English Language, Bahasa Cina, Bahasa Tamil, Bahasa Arab, Bahasa Iban, Bahasa Kadazandusun and Bahasa Semai.
Physical and Aesthetic Development
The Physical Development and Aesthetic strand emphasises on physical and health development for personal well-being and nurturing of imagination, creativity, talent and appreciation. Knowledge disciplines that develop the physical aspects are Physical Education and Health Education. Creativity, talent and appreciation are nurtured through Visual Art Education and Music Education.
Humanity
The Humanity strand emphasises on the mastery and practice of knowledge about community and the environment locally, nationally and globally as well as the appreciation of the spirit of patriotism and unity. History is the knowledge discipline in the Humanity strand introduced at Level II of the primary school.
3
Figure 1: Framework for Curriculum KSPK and KSSR
Communication
Integration of language skills while interacting verbally and non-verbally
codes in Bahasa Malaysia, English, Chinese and Tamil
Physical development
& Aesthetics
Physical and health development for personal well-being
Fostering imagination, creativity, talent
Humanity
Mastery of knowledge and practices regarding social sciences, local environment, country and global. Internalisation of patriotism and unity
Personal
Development
Nurturing and developing leadership and attitudes through curricula and co-curricula activities
Science &
Technology
Mastery of scientific knowledge and skills
Mastery of mathematical knowledge and skills Mastery of technology-based knowledge and skills
Spiritual, attitude
and values
Internalisation of religious pratices, beliefs, attitude and values
4 The Personal Development strand emphasises the nurturing of leadership and character building through curricular and co-curricular activities. Pupils are given the opportunity to integrate knowledge, skills and values learned in the classroom and practise them in co-curricular activities. Participation in co-co-curricular activities such as societies, uniformed bodies and sports provide opportunities for pupils to lighten their potential as leaders to themselves, friends, family and the community.
Science and Technology
The Science and Technology strand emphasises the mastery of:
scientific knowledge, skills and scientific attitude
knowledge, skills and values in mathematics
knowledge and technology-based skills
Knowledge discipline in Science and Technology Strand are Science, Mathematics, Design and Technology (DT) and Information and Communication Technology (ICT).
The Spiritual, Attitude and Value strand emphasises the learning areas that focus on religious practices, beliefs, attitudes and values. Knowledge disciplines in this strand are Islamic Studies for Muslim pupils and Moral Education for non-Muslim pupils.
AIMS
The aim of Science Standard Curriculum for primary is to instil interest and develop creativity amongst pupils through experience and investigation so as to master knowledge in science, scientific skills, thinking skills and, scientific attitudes and values.
OBJECTIVES
The Level Two Primary School Science Curriculum aims to: 1. Stimulate pupils’ curiosity and develop their interest about
the world around them.
2. Provide pupils with opportunities to develop scientific skills as well as critical and creative thinking skills.
5 4. Provide pupils with an understanding on scientific facts and
concepts.
5. Enables pupils to apply knowledge and skills in a critical, creative and analytical manner for problem solving and decision making.
6. Instil scientific attitudes and noble values amongst pupils, thus putting these into practice.
7. Be aware of the need to care for the environment.
FOCUS
Science Curriculum focuses on thoughtful learning. Thoughtful learning is a process of acquisition and mastery of knowledge and skills that can develop pupils’ minds to the optimum level. Thoughtful learning does not just focus on the content to be taught, but also encompasses pedagogy and assessment. Thoughtful learning occurs when the inquiry approach that emphasises scientific skills and thinking skills are integrated.
SCIENTIFIC SKILLS
Science emphasizes inquiry method and problem solving. In inquiry and problem solving processes, scientific and thinking skills need to
be utilised. Scientific skills are vital in any activities involving scientific investigation.
Scientific skills encompass science process skills and manipulative skills.
Science Process Skills
Science Process Skills enable pupils to formulate questions and find out the answers systematically.
Descriptions of the science process skills are as the following:
Observing Using the sense of sight, hearing, touch,
taste or smell to gather information about objects and phenomena.
Classifying Using observations to group objects or
phenomena according to similar characteristics
Measuring and Using Numbers
Making quantitative observations using numbers or tools with standard units or tools standardised with reference units.
Making Inferences
\Making initial conclusions that are reasonable, that may be true or false to
6 explain events or observations.
Predicting Making forecast about events based on
observations and previous experiences or collected data.
Communicating Accepting, choosing, arranging, and
presenting information or ideas in the form of writing, verbal, tables, graphs, figures or models.
Using Space- Time
Relationship
Describing changes in parameters such as location, direction, shape, size, volume, weight and mass with time.
Interpreting Data Giving rational explanations about an
object, event or pattern derived from collected data.
Defining Operationally
Defining concepts by describing what must be done and what should be observed.
Controlling Variables
Identifying manipulated variables, responding variables and fixed variables. In an investigation, a variable is manipulated to observe its relationship with the responding variable. At the same time, the other variables are kept the same.
Making Hypothesis
Making a general statement about the relationship between the voo]
ariables that is assumed to be true to explain an observation or event. The statement can be tested to determine its validity.
Experimenting Planning and conducting an investigation to
test a hypothesis, collecting and interpreting data until a conclusion can be obtained.
Manipulative Skills
In a scientific investigation, manipulative skills are psychomotor skills that enable pupils to:
Use and handle science apparatus and substances correctly.
Store science apparatus and substances correctly and safely.
Clean science apparatus correctly
Handle specimens correctly and carefully.
7
SCIENTIFIC ATTITUDES AND NOBLE VALUES
Learning experiences science can foster positive attitudes and values in pupils. Positive attitudes and values fostered in the teaching of science in schools include scientific attitudes and noble values as the following:
Having an interest and curiosity towards the environment.
Being honest and accurate in recording and validating data.
Being diligent and persevere when carrying out a task.
Being responsible about the safety of oneself, others and the environment.
Realising that science is a means to understand nature.
Appreciating and practising clean and healthy living.
Appreciating the balance of nature.
Being respectful and well-mannered.
Appreciating the contribution of science and technology.
Being thankful to God.
Having critical and analytical thinking.
Being flexible and open-minded.
Being kind-hearted and caring.
Being objective
Being systematic
Being cooperative
Being fair and just.
Dare to try
Thinking rationally
Being confident and independent
The inculcation of scientific attitudes and noble values generally occurs through the following stages:
Be aware and understand the importance and the need of scientific attitudes and noble values.
Giving attention and response.
Internalising and practising.
Inculcate scientific attitudes and noble values in life.
In this curriculum standard, learning standard for the affective domain is written explicitly where appropriate. However, scientific attitudes and noble values in teaching and learning need to be integrated continuously. For example, during science practical work, the teacher should remind pupils the importance of being careful, thorough, cooperative, honest and persevere when carrying out experiments.
Proper planning is required to optimize the inculcation of scientific attitudes and noble values. Teachers are encouraged to go through all learning standards related to the content standard including the learning standard about the inculcation of scientific attitudes and noble values before starting a lesson in the particular learning area.
8
Critical Thinking Skills
A brief description of each critical thinking skill is as the following:
Attributing Identifying characteristics, features,
qualities and elements of a concept or an object.
Comparing and Contrasting
Finding similarities and differences based on criteria such as characteristics, features, qualities and elements of objects or events.
Grouping and Classifying
Separating and grouping objects or phenomena into groups based on certain criteria such as common characteristics or features.
Sequencing Arranging objects and information in order
based on the quality or quantity of common characteristics or features such as size, time, shape or number.
Prioritising Arranging objects or information in order
based on their importance or urgency.
Analysing Processing information in detail by
breaking it down into smaller parts to understand concepts or events as well as to find the implicit meanings.
Detecting Bias Detecting views or opinions that have the tendency to support or oppose something.
Evaluating Making consideration on the good and bad
qualities of something based on valid evidences or propositions.
Making Conclusions
Making a statement about the outcome of an investigation based on a hypothesis or strengthening something based on an investigation.
Creative Thinking Skills
A brief description of each creative thinking skill is as the following:
Generating Ideas Producing ideas related to something. Relating Making connections in certain situations
or events to find a structure or pattern of relationship.
9
Making Inferences
Making initial conclusions that are reasonable, that may be true or false to explain events or observations.
Predicting Making forecast about events based on observations and previous experiences or collected data.
Making
Generalisations
Making a general statement about certain matter from a group of observations on samples or some information from that group.
Visualising Forming perception or making mental
images about a particular idea, concept, situation or vision.
Synthesising Combining separate elements to produce
an overall picture in the form of writing, drawing or artefact.
Making Hypotheses
Making a general statement about the relationship between the variables that is assumed to be true to explain an observation or event. The statement can
be tested to determine its validity.
Making Analogies Forming an understanding about a
complex or abstract concept by relating it to simple or concrete concepts with similar characteristics.
Inventing Producing something new or modifying
something already in existence to overcome problems in a systematic manner.
Thinking Strategies
Description of each thinking strategy is as the following:
Conceptualising Making generalisations towards building of meaning, concept or model based on inter-related specific common characteristics.
Making Decisions
Selecting the best solution from several alternatives based on specific criteria to achieve the intended aims.
10
Problem Solving Finding the right solutions in a
systematic manner for situations that are uncertain or challenging or unanticipated difficulties.
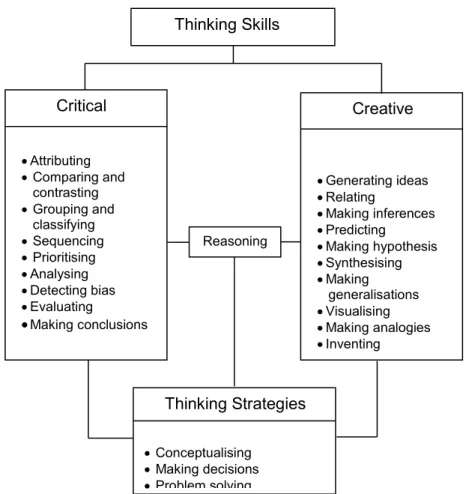
Besides thinking skills and thinking strategies, another skill emphasised is reasoning. Reasoning is a skill used in making logical, rational, fair and just consideration. Mastery of critical and creative thinking skills and thinking strategies is made easier if an individual is able to provide reasoning in inductive and deductive manner. Figure 2 gives an overall picture of the thinking skills and thinking strategies (TSTS).
Figure 2: TSTS Model in Science
Thinking Skills
Critical
Attributing Comparing and contrasting Grouping and classifying Sequencing Prioritising Analysing Detecting bias Evaluating Making conclusionsCreative
Generating ideas Relating Making inferences Predicting Making hypothesis Synthesising Making generalisations Visualising Making analogies InventingThinking Strategies
Conceptualising Making decisions Problem solving Reasoning11 Mastery of TSTS through the teaching and learning of science can be developed through the following stages:
1. Introducing TSTS.
2. Practising TSTS with teacher’s guidance. 3. Practising TSTS without teacher’s guidance.
4. Applying TSTS in new situations and developed with teacher’s guidance.
5. Applying TSTS together with other skills to accomplish thinking tasks.
Further information about the stages on the implementation of TSTS can be referred to the guidebook “Buku Panduan Penerapan
Kemahiran Berfikir dan Strategi Berfikir dalam Pengajaran dan Pembelajaran Sains (Curriculum Development Centre, 1999)”.
Relationship between Thinking Skills and Science
Process Skills
Science Process Skills are skills that are required in the process of finding solutions to a problem or making decisions in a systematic manner. It is a mental process that promotes critical, creative, analytical and systematic thinking. Mastery of Science Process Skills
together with knowledge and suitable attitudes ensure pupils to think effectively.
The mastery of Science Process Skills requires pupils to master the relevant thinking skills. The main thinking skills that are related to each science process skill are as the following:
Science Process Skills
Thinking Skills
Observing
Attributing
Comparing and contrasting
Relating
Classifying
Attributing
Comparing and contrasting
Grouping and classifying
Measuring and Using
Numbers
Relating
Comparing and contrasting
Making Inferences
Relating
Comparing and contrasting
Analysing
Making Inferences
Predicting
Relating
Visualising
Using Space-Time
Relationship
Sequencing
Prioritising
12
Science Process Skills
Thinking Skills
Interpreting data
Comparing and contrasting
Analysing
Detecting bias
Making conclusions
Making Generalisations
Evaluating
Defining operationally
Relating
Making analogies
Visualising
Analysing
Controlling variables
Attributing
Comparing and contrasting
Relating
Analysing
Making hypothesis
Attributing
Relating
Comparing and contrasting
Generating ideas
Making hypothesis
Predicting
Synthesising
Experimenting
All thinking skills
Communicating
All thinking skills
Teaching and Learning Based on Thinking Skills
and Scientific Skills
This Science Curriculum Standard emphasises thoughtful learning based on thinking skills and scientific skills. In this curriculum, the intended learning standard is written by integrating acquisition of knowledge with mastery of thinking skills and scientific skills. Thus in teaching and learning, teachers need to integrate mastery of skills together with acquisition of knowledge and the inculcation of scientific attitudes and noble values.
ELEMENTS ACROSS THE CURRICULUM
The Elements across the Curriculum (EMK) is a value-added element applied in the teaching and learning process other than those specified in the Content Standard. The integration of these elements is aimed at strengthening the human capital skills and competency as well as intended to prepare pupils for the challenges of the present and the future. The elements across the curriculum in KBSR i.e. language, science and technology, environmental
13 sustainability, values and patriotism are still relevant to be used in KSSR.
The new elements of EMK, namely creativity and innovation, entrepreneurship, as well as ICT are identified as a complementary effort to enhance the quality of KSSR implementation. The following is a description about the new elements of EMK in KSSR:
Creativity and Innovation
Creativity and Innovation are two related items.
Generally, creativity refers to the act of generating new ideas, approaches and new actions. Innovation on the other hand, is the process of generating new ideas and applying creative ideas in certain contexts.
The element of creativity and innovation is an element that is stressed upon in KSSR to prepare students to handle 21st century
challenges. Creativity and innovation in students need to be inculcated and developed to optimum levels so that they are capable of generating ideas and inventions that are of quality, that become practices and cultures in the lives of Malaysian citizens in the future.
To reach this aim, the writing of the learning standard for the subject of Science that is related to inculcating creativity and innovation is stated clearly. However, teachers are also encouraged to instil elements of creativity and innovation in any topic deemed suitable if these elements are not stated clearly. Teachers should prepare activities that increase interest and creativity and students should be equipped with knowledge, skills and tools that will enable them to develop creativity and inculcate attitudes and personalities of creative individuals.
Entrepreneurship
In the New Economic Model, among the characteristics of Malaysia in 2020 is innovation and entrepreneurship. The instilling of the element of entrepreneurship in KSSR is aimed at forming the characteristics and practices of entrepreneurship until it becomes a culture among students. Entrepreneurship characteristics can be formed by:
Practicing entrepreneurship
Applying entrepreneurship thinking
Applying knowledge and business management skills
Formulating concepts, processes or products of entrepreneurship
14 All characteristics and practices are implemented according to
primary school children’s abilities.
Information and Communication Technology
Technology is an effective method to strengthen the learning of science. The use of technology like television, radio, computer, computer internet software, course software, and computer interface makes the learning of science more interesting and effective.
Animation and computer simulations are a useful method to learn a difficult and abstract concept and can be presented in the form of course software or website.
The element of Information and Communication Technology is one of the elements added to KSSR. There are three approaches in using Information and Communication Technology in KSSR:
Learning about ICT
Learning through ICT
Learning with ICT
Teachers must ensure that EMK are integrated effectively in the teaching and learning process in order to produce individuals as intended in the National Education Philosophy.
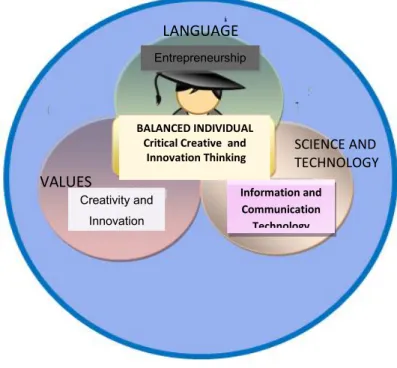
The relationship between EMK and the development of a balanced individual is illustrated in Diagram 3.
Diagram 3: EMK in the development of a Balanced individual
LANGUAGE
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
VALUES
Information and Communication Technology
Creativity and Innovation
Entrepreneurship
BALANCED INDIVIDUAL Critical Creative and Innovation Thinking
15
SKILLS FOR 21
STCENTURY
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
The national curriculum aims to produce pupils who are well balanced, resilient, curious, principled, well informed, and patriotic and possess thinking and communication skills and able to work in teams. The 21st century skills are in line with the six aspirations as outlined in the Malaysia Education Blueprint. The six aspirations are leadership skills, bilingual proficiency, ethics and spirituality, social identity, knowledge and thinking skills intended to be acquired by every pupil to enable them to compete globally.
Thinking skills have been emphasized in the curriculum since 1994 to introduce Creative and Critical Thinking Skills (KBKK). KBKK emphasises on thinking from the low to the higher level. Starting from 2011, the Primary School Curriculum Standard (KSSR) has placed emphasis on Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS).
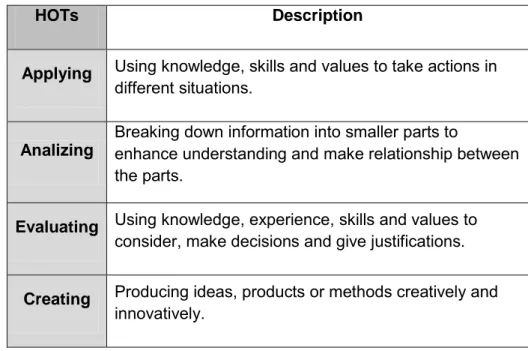
Higher order thinking skills is the ability to apply knowledge, skills and values for reasoning and reflecting in solving problems, making decisions, to innovate and to create. HOTs refer to the skills of applying, analizing, evaluating and creating as shown in Table 1.
HOTs Description
Applying Using knowledge, skills and values to take actions in
different situations.
Analizing
Breaking down information into smaller parts to
enhance understanding and make relationship between the parts.
Evaluating Using knowledge, experience, skills and values to
consider, make decisions and give justifications.
Creating Producing ideas, products or methods creatively and
innovatively.
Table 1: Description of HOTs
HOTS can be applied in the classroom through activities in the form of inquiry, solving problems and projects. Teachers and pupils need to use the thinking tools such as thinking maps, mind maps, and Thinking Hats and high level questioning, inside and outside the classroom to encourage pupils to think. Pupils are accountable to their own learning.
16
SKILLS AND VALUE FOR THE 21
stCENTURY
A student must be equipped with skills, knowledge and values to excel in life and career in the 21st century. The Ministry of Education
Malaysia (MOE) has identified skills and values that each pupil needs to have to face the 21st century. Skills and values consist of 3
aspects:
Thinking skills: Prepares pupils to face life and current working
environment which is becoming more challenging. The skills are:
Creative
Critical
Reasoning
Innovative
Problem solving
Decision making
Career and Life Skills: Crucial than thinking skills and knowledge.
Pupils develop career and life skills to face a complex life and current working environment which is becoming more challenging. These are:
Communication Skills
Information and Communication Technology
Cooperation Entrepreneurship Leadership Lifelong learning Flexibility Ability to Adapt
Initiative and Self-direction
Values: Guideline for pupils to become individuals with noble
character, capable of making decisions and act responsibly towards family, society and country which encompass:
Spirituality
Humanity
Patriotism
Integrity
Responsibility
Unity
17
STUDENT PROFILE
The critical factor that contributes towards social growth, culture and economy of a country is the development of innovative and highly skilled human capitals. Hence each pupil must be physically, emotionally, spiritually and intellectually balanced as stated in the National Education Philosophy.
To compete at a global stage, MOE has outlined 10 Student Profiles which are characterised as below:
Balanced: Physically, emotionally, spiritually and
intellectually balanced to achieve personal satisfaction, show empathy, compassion, and respect for others. Able to contribute towards a harmonious family, community and country
Resilient: Able to face and overcome difficulties,
overcome challenges with wisdom, confidence, tolerance and empathy.
Thinker: Able to think critically, creatively and
innovatively; handle complex problems and make ethical decisions. Think about learning and themselves as pupils. Generate questions and are open to perspective, values and individual and societal traditions. Confident
and creative in handling new learning fields.
Skilled in
communication:
Able to voice out and express their thoughts, ideas and information with confidence and creatively in verbal form and in writing, using various media and technology
Teamwork: Work effectively and harmoniously with others.
Take on responsibility while respecting and appreciating the contributions given by team members. Become better leader and team mate by obtaining interpersonal skills through collaborative activities
Curious: Develop natural curiosity to explore strategies
and new ideas. Learn skills that are needed to carry out inquiry and research, as well as practice independent learning. Enjoy continuous lifelong learning experiences.
Principled: Honest and have integrity, equality, fair and
respect the dignity of individuals, group and community. Responsible for their actions, consequences and decisions.
18
Informative: Knowledgeable and form wide understanding
which is balanced across various disciplines. Explore knowledge on local and global issues effectively and efficiently. Understand ethical issues/laws related to the information gained.
Caring/ Concern Show empathy, compassion and respect
towards needs and feelings of others. Committed to serve the society and ensure sustainability of nature.
Patriotism Portray love, support and respect towards the
country.
TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES
Teaching and learning strategies in the science curriculum emphasise on thoughtful learning. Thoughtful learning is a process that helps pupils acquire knowledge and master skills that will help them develop their minds to the optimum level. Learning activities should therefore be geared towards activating pupils’ critical and creative thinking skills and not be confined to routine method. Pupils
should be made aware of the thinking skills and thinking strategies that are being used in their learning. They should be challenged with higher order questions and problems and be required to solve problems creatively and critically. Pupils should be actively involved in the teaching and learning that integrate the acquisition of knowledge, mastery of skills and inculcation of scientific attitudes and noble values. Thoughtful learning can take place through various learning approaches such as inquiry, constructivism, science, technology and society, contextual learning and mastery learning.
Approaches to Teaching and Learning Science
Inquiry-Discovery Approach
Inquiry-discovery approach emphasises learning through experiences. Inquiry generally means to find information, to question and to investigate a phenomenon. Discovery is the main characteristic of inquiry. Learning through discovery occurs when the main concepts and principles of science are investigated and discovered by pupils themselves. Through activities such as experiments, pupils investigate a phenomenon and draw conclusions by themselves. Teachers then lead pupils to understand the science concepts through the results of the inquiry. Thinking skills and
19 scientific skills are thus developed further during the inquiry process. However, the inquiry-discovery approach may not be suitable for all teaching and learning situations. Sometimes, it may be more appropriate for teachers to present concepts and principles directly or through guided inquiry-discovery to pupils.
Constructivism
Constructivism is an ideology that suggests pupils learn by building their own understanding that is meaningful to them. The important attributes of constructivism are:
Teachers considered pupils prior knowledge.
Learning is the result from pupil’s own effort.
Learning occurs when pupils restructure their existing ideas by relating new ideas to old ones.
Pupils have the opportunities to cooperate, share ideas and experiences and reflect on their learning.
Science, Technology and Society approach
Meaningful learning occurs if pupils can relate what they have learnt with their daily life. Meaningful learning happens to various
approaches such as contextual learning and the science, technology and society (STS) approach. The theme and objective of learning that is based on STS is reflected in this standard curriculum. The STS approach recommends that the learning of science is done through investigation and discussions based on science, technology and society issues. Science and technology knowledge can be learnt together with the application of science and technology and their implications on the society.
Meaningful learning occurs if pupils can relate their learning with their everyday experiences. Meaningful learning can take place in learning approaches such as contextual learning and Science, Technology and Society (STS). Learning themes and learning objectives that carry elements of STS are incorporated into the curriculum. STS approach suggests that science learning takes place through investigation and discussion based on science, technology and society issues. Knowledge of science and technology can be learnt with the application of science and technology and their impact on society.
Contextual Learning
Contextual learning is an approach that associates learning with pupil’s everyday life. This approach involves investigative learning as
20 in the inquiry-discovery approach. In contextual learning, the relationship between knowledge taught and everyday life is explicitly demonstrated. In this context, pupils not only learn in theory but learn to appreciate the relevance of science in their lives.
Mastery learning
Mastery learning is an approach that ensures all pupils to acquire and master the intended learning objectives. This approach is based on the principle that pupils are able to learn if given the opportunities. Pupils should be allowed to learn at their own pace, with the incorporation of remedial and enrichment activities as part of the teaching-learning process.
METHODS
OF
TEACHING
AND
LEARNING
SCIENCE
Teaching and learning approaches can be implemented through various methods such as experiments, discussions, simulations, projects, the usage of external resources, future research and problem solving. In this curriculum standard, suggestions for these
teaching and learning methods are not explicitly stated. This is to enable teachers to use their own creativity in teaching and pupils to acquire the intended knowledge, skills, attitudes and values.
The teaching and learning method determined should be based on the contents of the curriculum standard, pupils’ abilities and pupils’ repertoire of intelligences and the availability of resources and infrastructure. Besides the role of presenting information and subject matter expert, teachers also act as facilitators in teaching and learning. Teachers should be attentive to the various repertoire of intelligences among pupils. Different methods and activities should be planned to cater to pupils with multiple intelligences.
The following are brief descriptions of some teaching and learning methods.
Experiment
An experiment is a method commonly used in science lessons. Pupils test hypotheses through investigations to discover specific science concepts and principles. Scientific methods are used when conducting an experiment involving thinking skills, science process skills, and manipulative skills.
In general, procedures to follow when conducting an experiment are:
21
Making a hypotheses
Planning the experiment - Controlling variables
- Determining equipment and materials needed - Determining the procedures of the experiment - Determining the method of data collection - Determining the method of data analysis
Conducting the experiment
Collecting data
Analysing data
Interpreting data
Making a conclusion
Writing the report
In this standard curriculum, it is suggested that, besides guiding pupils to carry out experiments, pupils are given the opportunity to design experiments, which involves drafting their own experimental method, the data that can be measured, how to analyse data and how to present the results of their experiments. These activities can be done individually or in small groups.
Discussion
A discussion is an activity in which pupils question and present their opinions based on arguments or valid reasons. During discussions, pupils must have an open mind to accept others’ opinions. The teacher should play the role of a facilitator by asking questions that
lead pupils towards the topic discussed. Discussions can be conducted during and after experiments, projects, data collection and interpretation activities, simulations using external resources, problem solving etc.
Simulation
Simulation is an activity that resembles the actual situation. Simulations can be carried out through role-play, games or use of model. In role-play, pupils act out a particular role spontaneously based on a certain pre-determined conditions. Games require procedures that need to be followed. Pupils play games in order to learn a particular principle or to understand the process of decision-making. Models are used to represent objects or real situations. Pupils will be able to visualise the real situation, thus understanding the concepts and principles learned.
Project
A project is an activity carried out individually or in groups to achieve a certain goal that takes a long time and exceeds formal teaching hours. Pupils are required to identify methods to solve the problem given and thus plan the entire project.The outcome of the project either in the form of a report, an artefact or in other forms needs to be presented.
22 Visits and Use of External Resources
Learning science through visits to zoos, museums, science centres, research institutes, mangroves swamps and factories can make learning more effective, enjoyable and meaningful. Learning through visits can be optimised by careful planning whereby pupils have to carry out or perform tasks during the visit. Discussion after the visit should be held to conclude the activities carried out.
Future Research
Pupils use critical and creative thinking to explore changes from the past to the future. This pedagogy is pupils-centered and integrates various fields. Noble values such as responsibility and cooperation are cultivated through this method.
Problem Solving
Problem solving is a method that involves pupils actively participating in decision making or to achieve a particular aim. During problem solving, activities such as simulations, discussions and experiments can be carried out. Generally, problem solving involves these steps:
Identify and understand a problem
Explain the problem
Finding alternative solutions
Carry out operations to solve the problem
Evaluate solutions
Use of Technology
Technology is an effective tool for enhancing the learning of science. Through the use of technology such as the television, radio, video, computer, internet, computer software, courseware and computer interfaces make the teaching and learning of science more interesting and effective. Animation and computer simulation is an effective tool for learning of difficult and abstract science concepts and can be presented in the form of courseware or website.
23
ASSESSMENT OF TEACHING AND LEARNING
Assessment is an element in the learning process that encompasses describing, collecting, recording, scoring, and interpreting information about pupils’ learning for a particular purpose. Therefore assessment is a process of getting information and making evaluation of pupils’ achievement.
Assessment is a yardstick to assess pupils’ achievement in obtaining knowledge, skills and ethics besides assessing the activities carried out during T&L.
Assessment supports pupils’ learning and provides valuable feedback to stakeholders such as administrators, teachers, pupils and parents/guardians about pupils’ progress and achievement.
The feedback is used to enhance the quality of T&L.
T&L assessment is more inclined to be formative and prioritises the progress of each pupil from one level to another. A teacher is able to diagnose and detect the development of pupils. This provides an opportunity for teachers to rectify mistakes and weaknesses of pupils immediately so that it is not accumulated. The teachers will be able to identify pupils’ weaknesses and do follow up. The type and needs of T&L assessment is illustrated in Figure 4 below.
Achievement Level is arranged in a hierarchy to be used as a benchmark in the individual report.
STANDARD TERMS OF PERFORMANCE
PERFORMANCE
LEVEL STANDARD
1 Know
2 Know and Understand
3 Know, Understand and Can Do
4 Know, Understand and Can Do with Good Attitude
5 Know, Understand and Can Do with Good Attitude and Laudable
6 Know, Understand and Can Do with Excellent Attitude, Laudable and Exemplary
Who should conduct the assessment?
The task of assessing is not only limited to teachers. Assessment can also be carried out by peers, pupils themselves and their
24 parents/ guardians. Parents/guardians may assess the achievement of their children, guided by assignment instructions or checklists. Therefore parents/guardians are directly involved in monitoring the learning progress of their children.
How is the assessment done?
T&L assessment can be carried out according to the proposed steps as shown in Figure 5.
Performance Standard
Performance Standard is a statement of pupils’ learning development level measured based on the standard and it indicates the position of pupils’ progress in their learning development. Developments in the Standard are divided into two; i.e. horizontal development (construct) and vertical development (level of achievement). Pupils’ developments are explained with one or more qualifiers using correct words or phrases to describe the Standard in the form of learning outcomes. Performance Standard is developed as a guide for the teachers to improve School Assessment (SA) in line with Standard Reference of Assessment.
General Interpretation of Achievement Level PERFORMANCE
LEVEL INTERPRETATION
1 Pupil knows the basics or can perform basic skills or can respond to the basics.
2 Pupil shows their understanding by changing type of communication or translates and can explain what they have learned.
3 Pupil uses knowledge to perform a skill in a particular situation.
4 Pupil performs a particular skill with proper attitude by following procedure or being systematic.
5 Pupil performs a particular skill in a new situation by following procedure or being systematic, persistent with positive attitude.
6
Pupil can express their creative and innovative ideas, has the ability to make decisions to adapt to requirements and challenges of everyday life, communicate to obtain and convey information using proper and polite sentences and be an exemplary pupil.
25
Interpretation of Achievement Level for Primary
Science
Assessment conducted comprises of knowledge, skills, scientific attitudes and moral values. Assessment of knowledge and skills are stated in the Performance Standard related to Content Standard.
PERFORMANCE
LEVEL INTERPRETATION
1 Know the basic knowledge and skills in science
2 Understand the science knowledge and skills and can explain the understanding in any way.
3 Apply knowledge and scientific skills in completing the task in a situation
4
Analyzing knowledge and scientific skills to be applied in completing the task in a situation systematically
5
Analyze and synthesize knowledge and scientific skills to be applied in completing the task or in a new situation persistently, systematically and with positive attitude
6 Analyze and synthesize knowledge and scientific skills to be applied creatively and innovatively in creating, evaluating or conceptualising
something new in completing a task
2. VALUE
Value Interpretation of Achievement Level for Primary Science
PERFORMANCE
LEVEL INTERPRETATION
1 Interest
2 Interest and curious
3 Interests, curious, honest and accurate in recording data.
4 Interest, curious, honest and accurate in recording data, brave and systematic.
5
Interest, curious, honest and accurate in recording data, brave and systematic, cooperates, diligent and perseverance in completing task.
6
Interest, curious, honest and accurate in recording data, brave and systematic, cooperates, diligent and perseverance in
completing task, responsible for oneself, friends, environment and courteous.
26
ORGANISATION OF THE SCIENCE STANDARD
CURRICULUM
The Science Standard Curriculum for Year 1 to Year 6 has six themes; Introduction to Science, Life Science, Physical Science, Science of Matter, Science of the Earth and The Universe as well as Technology and Sustainability. However, these themes are not present in every year of study.
Introduction to Science, Life Science, Physical Science, Material Science, The Earth and The Universe and Technology and Sustainability are elaborated according to the Content Standard and Learning Standard. The Content Standard has at least one or more Learning Standards that are conceptualised based on determined fields of study. The Content Standards are written according to hierarchy in cognitive and affective domains. The Content Standard is a general statement that contains elements of knowledge, scientific skills, thinking skills, scientific attitudes and noble values in line with the desired Learning Standard.
The Learning Standard is a tangible learning objective. It comprises the scope of learning with scientific skills and thinking skills that
require the students to master the intended science concepts. Generally, the Learning Standard is ordered according to level of difficulty. However, the Learning Standard can be modified accordingly. The Content Standard for the affective domain is written at the end of the relevant cognitive domain. However not all cognitive domains are followed by affective domains.
Performance Standard is a statement of the level of pupils’ learning development measured with Standard Content and Learning Standard as well as to indicate the position of pupils’ progress in their learning development.
Pupils’ developments are explained with one or more qualifiers using correct words or phrases to describe the Standards in the form of learning outcomes. Performance Standard is developed as a guide for the teachers to implement School Assessment (SA) in line with Standard Reference of Assessment.
The teaching and learning process should be planned holistically and integrally to allow several Learning Standards to be achieved. Teachers should analyse all the Learning Standards and Content Standards before planning teaching and learning activities. The
27 activities can be varied to achieve the Content Standard to fulfil leaning objectives. Teachers are encouraged to shape activities that require the active participation of students to generate analytical, critical, innovative and creative thinking while using technology as a means to achieve the Content Standard affectively.
The teaching and learning process involves activities, investigations and experiments which are deemed appropriate to achieve learning standard should be carried out to strengthen students' understanding.
The Thematic Core Modules of World of Science and Technology is introduced to Level One pupils. This module is a combination of Science elements, Design & Technology and Information & Communication Technology. The time allocated for the subject is 60 minutes per week.
For Level Two, Science is a single subject and the time allocated is 120 minutes per week.
30
INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE
1.0 SCIENTIFIC SKILLS
CONTENT
STANDARD
LEARNING STANDARD
PERFORMANCE STANDARD
PERFORMANCE LEVELDESCRIPTOR
1.1
Science
process skills.
1.1.1
Pupils are able to:
Observe
1
2
3
4
State all the senses involved in making
observations about the phenomena that
occurs.
Describe the utilization/use of the senses
involved when making observations about
the phenomena or changes that occur.
Use all the senses involved to make
observations about the phenomena or
changes that occur.
* Use all the senses involved to make
qualitative observations to describe the
phenomena or changes that occur
* Use appropriate tools where necessary to
assist in making observations.
31
CONTENT
STANDARD
LEARNING STANDARD
PERFORMANCE STANDARD
PERFORMANCE LEVELDESCRIPTOR
5
6
* Use all the senses involved to make
qualitative and quantitative observations to
describe the phenomena or changes that
occur
* Use appropriate tools where necessary to
assist in making observations.
* Use all the senses involved systematically
to make qualitative and quantitative
observations to describe the phenomena or
changes that occur.
* Use appropriate tools where necessary to
assist in making observations.
32
CONTENT
STANDARD
LEARNING STANDARD
PERFORMANCE STANDARD
PERFORMANCE LEVELDESCRIPTOR
1.1.2
Classify.
1
2
3
4
State the characteristics of objects by
observing
the/its
similarities
and
differences
Describe the characteristics of objects by
observing
the/its
similarities
and
differences.
Sort and group the objects based on its
common characteristics and differences.
Sort and group the objects based on its
common characteristics and differences
and state the common characteristics
used.
33
CONTENT
STANDARD
LEARNING STANDARD
PERFORMANCE STANDARD
PERFORMANCE LEVELDESCRIPTOR
5
6
Sort and group the objects based on its
common characteristics and differences
and state the common characteristics used
and are able to use another characteristic
to sort and group these objects.
Sort and group the objects based on its
common characteristics and different until
to the final stage by stating the
characteristic used
34
CONTENT
STANDARD
LEARNING STANDARD
PERFORMANCE STANDARD
PERFORMANCE LEVEL
DESCRIPTOR
1.1.3
Measure and use numbers.
1
2
3
4
5
6
State more than one appropriate tool to
measure a quantity.
Describe the tools and correct methods to
measure the quantity.
Measure using tools and standard units
correctly.
Measure using tools and standard units
with correct techniques.
Measure using tools and standard units
with correct techniques and record
systematically and completely in a table
Demonstrate how to measure using tools
and
standard
units
with
correct
techniques and record systematically and
completely in a table
35
CONTENT
STANDARD
LEARNING STANDARD
PERFORMANCE STANDARD
PERFORMANCE LEVELDESCRIPTOR
1.1.4
Make inference.
1
2
3
4
5
6
State a reasonable interpretation of an
event or observation.
Describe more than one reasonable
interpretation of an event or observation.
Draw a reasonable initial conclusion
based on interpretations of an event or
observation.
Draw a reasonable initial conclusion of an
event or observation by using gathered
information.
Draw more than one reasonable initial
conclusion of an event or observation by
using gathered information.
Draw more than one reasonable initial
conclusion of an event or observation by
using gathered information and able to
explain the conclusion drawn.
36
CONTENT
STANDARD
LEARNING STANDARD
PERFORMANCE STANDARD
PERFORMANCE LEVELDESCRIPTOR
1.1.5
Predict.
1
2
3
4
5
6
State a possibility of an event or data.
Describe a possibility or event.
Make a prediction of an event based on
observations, past experience or data.
Justify the most suitable and reasonable
prediction of an event or data.
Make predictions of an event based on
observations, past experience or data.
Make predictions of an event based on
0bservations, past experience or data.
Predict using interpolation or
37
CONTENT
STANDARD
LEARNING STANDARD
PERFORMANCE STANDARD
PERFORMANCE LEVELDESCRIPTOR
1.1.6
Communicate.
1
2
3
4
5
6
Arrange information obtained in a
suitable form.
Record information or ideas in a suitable
form.
Record information or ideas in more than
one suitable form.
Record information or ideas in a suitable
form and present it systematically.
Record information or ideas in a suitable
form, present it systematically and have
a positive attitude towards information
collected.
Record information or ideas in a suitable
form, present it systematically, creatively
and innovatively in various forms and
able to provide feedback.
38
CONTENT
STANDARD
LEARNING STANDARD
PERFORMANCE STANDARD
PERFORMANCE LEVEL
DESCRIPTOR
1.1.7
Use space and time
relationship.
1
2
3
4
5
6
State a parameter that varies with time
based on a situation.
Describe a parameter that varies with time
based on a situation.
Arrange
the
occurrences
of
a
phenomenon or event chronologically with
time
Provide reasoning on changes in
parameter
of
a
chronological
phenomenon or event with time
Arrange graphically the occurrences of a
phenomenon or event chronologically with
time.
Present and explain the chronological
changes of a phenomenon or events with
time.
39
CONTENT
STANDARD
LEARNING STANDARD
PERFORMANCE STANDARD
PERFORMANCE LEVELDESCRIPTOR
1.1.8
Interpret data.
1
2
3
4
5
6
Provide an explanation based on data.
Provide a description of more than one
explanation based on data.
Choose relevant ideas to make an
explanation about objects, events or
patterns of data
Correlate between the parameters in the
data based on the relationship between the
parameters or science concepts.
Provide a rational explanation using
interpolation of objects, events or patterns
of data collected.
Provide a rational explanation using
interpolation or extrapolation of data
collected.
40
CONTENT
STANDARD
LEARNING STANDARD
PERFORMANCE STANDARD
PERFORMANCE LEVELDESCRIPTOR
1.1.9
Define operationally
1
2
3
4
5
6
State what is done and what is observed
in a situation.
Describe what is done and what is
observed in a situation
Interpret what is done and what is
observed
in
a
situation
for
the
predetermined aspects
Make more than one interpretation of what
is done and what is observed in a situation
for the predetermined aspects
Select the most appropriate interpretation
of a concept by stating what is done and
what is observed in a situation.
Describe
the
most
appropriate
interpretation of a concept by stating what
is done and what is observed in a
situation.
41
CONTENT
STANDARD
LEARNING STANDARD
PERFORMANCE STANDARD
PERFORMANCE LEVELDESCRIPTOR
1.1.10
Control variables
1
2
3
4
5
6
Identify the variables that affect an
investigation.
Describe the variables that affect an
investigation
Determine the manipulated variable in an
investigation.
Determine the responding and constant
variables
after
determining
the
manipulated variable in an investigation
Explain the relationship between the
manipulated and responding variable in an
investigation.
Change the constant variable in an
investigation to manipulated variable and
state the new responding variable
42