xv ABSTRACT
Widyasarastri, Bernadia Hastiwi. 2010. Designing Multimedia for Teaching Vocabulary to the First Grade Students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
The most of children at Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta are unmotivated in learning, hopeless, pessimistic, and poor. The tutors need special strategy to teach them, especially teach English. However, the students have to learn English because Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta wants to prepare them to guide their own life in globalization era. Nowdays, the technology influences English learning. computer can be used as a medium in teaching. Considering that, this study aimed at developing multimedia for teaching vocabulary for the first grade of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta.
There were two questions formulated in the problem formulation i. e. (1) how is multimedia for teaching vocabulary for the first grade of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta designed? (2) what does the designed multimedia look like?. To answer the first question, the writer employed the adaptation of Kemp and CALL instructional design which related with Reasearch and Development (R&D) steps. There were five instructional design steps employed in this study, namely, (1) analyzing learner characteristics, (2) formulating goals, topics, and general purposes, (3) formulating learning objectives, (4) developing instructional multimedia, and (5) conducting evaluation and revision.
In this study, the data obatined through the research and information collecting step served as the basis to develop the multimedia. After designing the multimedia, the writer conducted expert validation to gain evaluation on the designed multimedia from two tutors of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta and two English lecturers of Sanata Dharma University. Besides, the designed multimedia were tried out to the students of the first grade of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta and were evaluated by the students. The data from the expert validation and materials try out were analyzed using qualitative data analysis. The evaluation was then employed as the basis for revisions. The revisions included the pronunciation, pictures, text, game, song, and the instructions of the designed multimedia.
xvi ABSTRAK
Widyasarastri, Bernadia Hastiwi. 2010. Designing Multimedia for Teaching Vocabulary to the First Grade Students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Anak-anak Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta adalah anak-anak yang kurang motivasi dalam belajar, tidak berpengharapan, mudah putus asa, dan miskin. Para pengajar Domby Kid’s Hope 2 membutuhkan strategi khusus untuk mengajar anak-anak Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta, khususnya dalam mengajar Bahasa Inggris. Bagaimanapun juga, siswa-siswi harus belajar Bahasa Inggris karena Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta ingin mempersiapkan mereka untuk menghadapi globalisasi. Dan sekarang ini, teknologi mempengaruhi pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris. Komputer dapat digunakan sebagai media pengajaran. Mempertimbangkan hal itu, penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengembangkan multimedia untuk pengajaran vocabulary pada kelas satu Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta.
Dalam penelitian ini, ada dua pertanyaan dalam perumusan masalah yaitu (1) bagaimanakah multimedia untuk penganjaran vocabulary pada kelas satu dari Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta dirancang? (2) bagaimanakah penyajian multimedia yang telah disusun tersebut? Untuk menjawab pertanyaan pertama, penulis mengadaptasi model perancangan instruksional yang dikembangkan oleh Kemp and CALL yang sama dengan langkah-langkah Reasearch and Development (R&D). Terdapat lima langkah perancangan instruksional dalam penelitian ini, yakni (1) pengidentifikasian karakter siswa, (2) perumusan tujuan besar, topik, dan tujuan umum, (3) perumusan tujuan pembelajaran, (4) pengembangan multimedia, dan (5) pengadaan evaluasi dan revisi multimedia.
Dalam penelitian ini, data yang diperoleh melalui penelitian dan pengumpulan informasi digunakan sebagai dasar pengembangan multimedia. Setelah selesai merancang multimedia, penulis mengadakan expert validation untuk mendapatkan evaluasi multimedia dari dua tutor Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta dan dua dosen Bahasa Inggris Universitas Sanata Dharma. Selain itu, multimedia yang telah selesai dirancang diujikan pada siswa kelas 1 Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta dan dievaluasi oleh mereka sendiri. Data yang telah diperoleh dari expert validation dan pengujian multimedia kemudian dianalisis menggunakan kualitatif data. Evaluasi kemudian digunakan sebagai acuan untuk perevision multimedia. Perevisian meliputi pelafalan, gambar, teks, permainan, lagu, dan petunjuk dari multimedia.
DESIGNING MULTIMEDIA FOR TEACHING VOCABULARY
TO THE FIRST GRADE STUDENTS
OF DOMBYKID’S HOPE 2 YOGYAKARTA
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain theSarjana PendidikanDegree
in English Language Education
By
Bernadia Hastiwi Widyasarastri Student Number: 041214060
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
i
DESIGNING MULTIMEDIA FOR TEACHING VOCABULARY
TO THE FIRST GRADE STUDENTS
OF DOMBYKID’S HOPE 2 YOGYAKARTA
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain theSarjana PendidikanDegree
in English Language Education
By
Bernadia Hastiwi Widyasarastri Student Number: 041214060
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
ii A Thesis on
DESIGNING MULTIMEDIA FOR TEACHING VOCABULARY TO THE FIRST GRADE SUDENTS OF DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2
YOGYAKARTA
By:
Bernadia Hastiwi Widyasarastri Student Number: 041214060
Approved by:
Date
Dr. Retno Muljani, M.Pd. May 21, 2010
iii A Thesis on
DESIGNING MULTIMEDIA FOR TEACHING VOCABULARY TO THE FIRST GRADE SUDENTS OF DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2
YOGYAKARTA
By:
Bernadia Hastiwi Widyasarastri Student Number: 041214060
Defended before the Board of examiners on June 14, 2010
and Declared Acceptable
Board of Examiners
Chairperson : C. Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd. ____________ Secretary : Made Frida Yulia, S.Pd., M.Pd. ____________ Member : Dr. Retno Muljani, M.Pd. ____________ Member : Drs. Y.B. Gunawan, M.A. ____________ Member : C. Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd. ____________
Yogyakarta, June 14, 2010
Faculty of Teachers Training and Education Sanata Dharma University
Dean,
iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and reference, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, 14 June 2010 The Writer
v
DEDICATION
Mintalah maka akan Kuberi,
Ketuklah maka pintu akan dibukakan.
A Deep dedication to: my lovely heavenly mother, my lovely tough father, mb Enta, dek Wowo, my Michael, all family, and all friends. JanjiMu Seperti Fajar Pagi Hari
Ketika kuhadapi kehidupan ini Jalan mana yang harus kupilih
Kutahu kutak mampu, Kutahu kutak sanggup Hanya Kau Tuhan tempat
jawabanku
Akupun Tahu kutak pernah sendiri Sebab Engkau Allah yang
menggendongku tanganMu membelaiku, cintaMu memuaskanku
Kau mengangkatku ke tempat yang tinggi
JanjiMu sperti fajar pagi hari Dan tiada pernah terlambat
bersinar
CintaMu sperti sungai yang mengalir
vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I believe, I can finish my “masterpiece”, and I would like to say my gratitude to everyone behind me in finishing this thesis.
The first is Jesus Christ for his blessing, forgiving me and always giving chance. He always reminds me to do this thesis and always gives the best to me. I believe that I also glorify Him by writing this thesis.
I thank very much Dr. Retno Muljani, M.Pd. as my sponsor and my everything who helps me a lot during the process of writing this thesis. I thank for guidance, patience, and support. I also would like to thank Agustinus Hardi Prasetyo, S.Pd., M.A., Gregorius Punto, S.Pd., M.Hum., Made Frida Yulia, S.Pd., M.Pd., Drs. Concilianus Laos Mbato, M.A., and all of PBI lectures and alsombakDani andMbakTari.
My sincere and deepest gratitude are addressed toibu,bapak,MbakEnta, and Dek Wowo for their irreplaceable love, patience, support, care, guidance, money, and everything. They have been waiting for me to finish my thesis for about two years. I love them.
vii
I would like to thank Marc Reid and Charlie who read and checked my grammar. I am deeply grateful to My Michaelwho wants to share his holy spirit, always asks how far my thesis is, always mocks me, and always loves me.
This is my honor to thankMasEric and Felixwho helped me to make my multimedia comes true. I thankErang and Destafor their music.
I would also express my gratitude to the big family ofDomby Kids Hope 2 Yogyakarta for allowing me to conduct this research and helping me. I thank
Mas Yusak,Mbak Indri, and all of mentors and tutors, and especially for the students there. They are my inspiration.
My gratitude also goes to my best friends; Nita, Mbak Tina, Empi, and Liafor their support, their advice, and their time when I need someone to talk.
Finally, I would like to show my gratitude to all those who have helped me and supported me and could not be mentioned by names. Thank you so much, without them this thesis might not have been finished.
viii
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswi Universitas Sanata Dharma Nama : Bernadia Hastiwi Widya Sarastri
Nomor Mahasiswa : 041214060
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
DESIGNING MULTIMEDIA FOR TEACHING VOCABULARY TO THE FIRST GRADE STUDENTS OF DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2
YOGYAKARTA
Beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin saya maupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal: 14 Juni 2010
Yang menyatakan
ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE……… i
APPROVAL PAGES……… ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY……….. iv
DEDICATION PAGE………. v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS……… vi
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN………. viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS……… ix
LIST OF TABLES... xiii
LIST OF FIGURES……….. xiv
ABSTRACT... xv
ABSTRAK... xvi
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Research Background……….. 1
B. Problem Formulation………... 4
C. Problem Limitation………. 4
D. Objectives of The Study………. 5
E. Benefits of The Study………. 5
F. Definition of Terms………. 6
CHAPTER II: LITERATURE REVIEW A. Theoretical Description……… 8
1. Instructional Designs……….. 8
x
b. CALL Design……… 11
2. Instructional method for designing the multimedia……… 15
3. Computer in Learning………. 17
4. Macromedia Flash 8……… 18
a. Artwork………. 18
b. Symbol and instance………. 18
c. Component……… 19
d. Asset……….. 19
e. Animation……….. 19
f. Movie and scene……… 20
g. Movie clip……….. 20
h. Document……… 20
5. Teaching English in the Elementary School………... 23
a. Children’s ability to grasp meaning………. 21
b. Children’s creative use of limited language resources… 22 c. Children’s capacity for indirect learning……… 23
d. Children’s instinct for play and fun……… 24
e. The role of imagination……….. 24
f. The instinct for interaction and talk………... 25
6. The nature of vocabulary learning…….……….. 25
a. Learning from meaning-focused input……….. 26
b. Deliberate learning……… 27
c. Learning from meaning-focused output……… 27
d. Fluency development……… 27
7. Holistic Learning……… 29
8. Description of the general curriculum and the goal of the English teaching-learning activities at Domby Kid’s Hope 2…… 30
B. Theoretical Framework 1. Analyzing learner characteristic……… 31
2. Formulating goals, topics, and general purposes………….. 31
xi
4. Developing multimedia……… 31
5. Conducting evaluation and revision………. 32
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY A. Research Method………. . 35
1. Research and information collecting……… 36
2. Planning……… 36
3. Developing a preliminary form of product……….. 37
4. Preliminary field testing……… 37
5. Main product revision……….. 38
B. Research Participants………... . 39
C. Research Setting……… 40
D. Research Instruments……… 40
1. Interview……….. 40
2. Observation……….. 41
3. Questionnaire……… 41
E. Data Collection………. 41
F. Data Analysis Techniques………. 44
G. Research Procedures………. 46
1. Finding theories……… 46
2. Interviewing the tutors and observation……… 46
3. Designing the multimedia……… 46
4. Evaluating Multimedia……… 46
5. Designing the final multimedia……… 46
CHAPTER IV: ANALYSIS RESULT A. The steps of designing the multimedia for teaching vocabulary to the first grade students of Domby Kid’s Hope2 Yogyakarta... 47
1. Analyzing learners’ characteristics……….. 47
2. Formulating goals, topics, and general purposes…………. 51
3. Formulating learning objectives………. . 52
xii
a. Activity types……… 53
b. Presentation scheme………. 56
c. Multimedia production………. 57
5. Conducting evaluation and revision………. 59
a. Evaluation... 59
1) Expert validation... 60
2) Material try out... 63
b. Revisions... 64
B. The presentation of the design set of instructional media... 65
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS A. Conclusions……… 67
B. Suggestions………. 68
REFERENCES... 69
xiii
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
Table 3.1: Product Specification……….. 38
Table 3.2: The overall process of data collection………. 43
Table 3.3: The research result calculation form……….. 44
Table 4.1: The result of the interview………. 48
Table 4.2: Class observation note……….. 50
Table 4.3: Topics and titles of the designed multimedia……... 51
Table 4.4: List of general purposes……… 52
Table 4.5: List of learning objectives………. 52
Table 4.6: Data Calculation of the participants’ opinion toward the designed multimedia………... 61
Table 4.7: The result of the interview in the materials try out……. 63
xiv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
Figure 2.1: Kemp’s Instructional Design Model……… 11
Figure 2.2: CALL Methodology Framework……… 12
Figure 2.3: Development Module………. 15
Figure 2.4: The writer’s Synchronization Instructional Design……. 34
Figure 3.1: Research Development Study combined with Kemp and CALL steps instructional design……… 39
Figure 4.1: Unit 1: Greeting ……….. 54
Figure 4.2: Drilling in unit 1 ………. 55
Figure 4.3: Game in Unit 1 ……… 56
Figure 4.4: Domby Picture ……… 57
Figure 4.5: Jane Picture ………. 57
Figure 4.6: Ben Picture ………. 57
xv ABSTRACT
Widyasarastri, Bernadia Hastiwi. 2010. Designing Multimedia for Teaching Vocabulary to the First Grade Students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
The most of children at Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta are unmotivated in learning, hopeless, pessimistic, and poor. The tutors need special strategy to teach them, especially teach English. However, the students have to learn English because Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta wants to prepare them to guide their own life in globalization era. Nowdays, the technology influences English learning. computer can be used as a medium in teaching. Considering that, this study aimed at developing multimedia for teaching vocabulary for the first grade of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta.
There were two questions formulated in the problem formulation i. e. (1) how is multimedia for teaching vocabulary for the first grade of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta designed? (2) what does the designed multimedia look like?. To answer the first question, the writer employed the adaptation of Kemp and CALL instructional design which related with Reasearch and Development (R&D) steps. There were five instructional design steps employed in this study, namely, (1) analyzing learner characteristics, (2) formulating goals, topics, and general purposes, (3) formulating learning objectives, (4) developing instructional multimedia, and (5) conducting evaluation and revision.
In this study, the data obatined through the research and information collecting step served as the basis to develop the multimedia. After designing the multimedia, the writer conducted expert validation to gain evaluation on the designed multimedia from two tutors of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta and two English lecturers of Sanata Dharma University. Besides, the designed multimedia were tried out to the students of the first grade of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta and were evaluated by the students. The data from the expert validation and materials try out were analyzed using qualitative data analysis. The evaluation was then employed as the basis for revisions. The revisions included the pronunciation, pictures, text, game, song, and the instructions of the designed multimedia.
xvi ABSTRAK
Widyasarastri, Bernadia Hastiwi. 2010. Designing Multimedia for Teaching Vocabulary to the First Grade Students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Anak-anak Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta adalah anak-anak yang kurang motivasi dalam belajar, tidak berpengharapan, mudah putus asa, dan miskin. Para pengajar Domby Kid’s Hope 2 membutuhkan strategi khusus untuk mengajar anak-anak Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta, khususnya dalam mengajar Bahasa Inggris. Bagaimanapun juga, siswa-siswi harus belajar Bahasa Inggris karena Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta ingin mempersiapkan mereka untuk menghadapi globalisasi. Dan sekarang ini, teknologi mempengaruhi pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris. Komputer dapat digunakan sebagai media pengajaran. Mempertimbangkan hal itu, penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengembangkan multimedia untuk pengajaran vocabulary pada kelas satu Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta.
Dalam penelitian ini, ada dua pertanyaan dalam perumusan masalah yaitu (1) bagaimanakah multimedia untuk penganjaran vocabulary pada kelas satu dari Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta dirancang? (2) bagaimanakah penyajian multimedia yang telah disusun tersebut? Untuk menjawab pertanyaan pertama, penulis mengadaptasi model perancangan instruksional yang dikembangkan oleh Kemp and CALL yang sama dengan langkah-langkah Reasearch and Development (R&D). Terdapat lima langkah perancangan instruksional dalam penelitian ini, yakni (1) pengidentifikasian karakter siswa, (2) perumusan tujuan besar, topik, dan tujuan umum, (3) perumusan tujuan pembelajaran, (4) pengembangan multimedia, dan (5) pengadaan evaluasi dan revisi multimedia.
Dalam penelitian ini, data yang diperoleh melalui penelitian dan pengumpulan informasi digunakan sebagai dasar pengembangan multimedia. Setelah selesai merancang multimedia, penulis mengadakan expert validation untuk mendapatkan evaluasi multimedia dari dua tutor Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta dan dua dosen Bahasa Inggris Universitas Sanata Dharma. Selain itu, multimedia yang telah selesai dirancang diujikan pada siswa kelas 1 Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta dan dievaluasi oleh mereka sendiri. Data yang telah diperoleh dari expert validation dan pengujian multimedia kemudian dianalisis menggunakan kualitatif data. Evaluasi kemudian digunakan sebagai acuan untuk perevision multimedia. Perevisian meliputi pelafalan, gambar, teks, permainan, lagu, dan petunjuk dari multimedia.
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter is divided into seven parts. They are the background of the study, problem identification, problem limitation, problem formulation, objectives of the study, benefit of the study, and definition of terms.
A.
Research Background
Nowadays, English is very important. English is a global language. According to Crystal (2000), “global language” is a means of communication that is recognized in every country. According to him, there are the closest links between language dominance and economic, technological, and cultural power. Technology, primarily in the form of movies and records, fuelling new mass entertainment industries which expand by using English. The use of English offers an international intellectual and research environment in which scholarship and further education are pursued, thus, it is through transfers of knowledge in English that scientific and technological progress is enabled (Crystal, 2000). The scientific and technological dominance of English speaking nations means that international students must learn English if they wish to benefit from this knowledge.
learn. In Yogyakarta, there are many Non Governmental Organisations (NGO) working in social and education field. Many NGOs offers free education. One of these NGOs is Domby Kid’s Hope. It serves children who are poor. Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta is an informal school for children who are living on poverty line nearbyKali Code. This informal school has about 201 students who are 3-19 years old. Domby Kid’s Hope is similar to formal school and it teaches some subjects. The environment where Domby Kid’s Hope 2 children live does not support them in learning. They are unmotivated, hopeless, and pessimistic (Paduan Pembina DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2, 2008).
English is the one of subjects which Domby Kid’s Hope 2 teaches to the children. The following are two reasons why English is taught starting from the first grade. Firstly, the children are prepared to guide their own life in globalization era. The second reason is the children are good language learners. According to Halliwell (1992), children have a well-established set of instincts, skills, and characteristics which will help them to learn another language. At this age, children are capable of learning many new words.
Moreover, the students’ mind set is English difficult to learn because it is foreign language. as a result, they are affraid of learning English.
On the other hand, the development of technology influences English learning to be a modern language learning process. Recently, the teacher has used a computer as medium for teaching. Computer software can offer language learning in effective ways by using videos, sounds, or many pictures. These can help students to learn the language (Philips, 1992). These developments have influenced some researchers to develop software that utilizes computers in the language learning. The most famous example is CALL or Computer-Assisted Language Learning. In Hubbard’s research (1992), many teachers have big questions about how personal computers can assist Language learning.
Some researchers develop multimedia to assist language learning. Multimedia is the form of software that combinates some media, they are pictures, flash cards, videos, and sounds. The effect of teaching by using multimedia is very great. The students can have meaningful experiences in learning because the students can see, hear, and practice through media(Heinich er al., 1993:5).
Therefore, there is an oppurtunity to integrate multimedia tools into the teaching activities at Domby Kid’s Hope 2 in order to create a more fullfilling of richer learning experience. The coordinator interviewed said the aim of teaching English in Domby Kid’s Hope 2 is to make the students like learning English. He thinks that multimedia will be a good solution of students’ fearness of English.
technology in learning, the writer has tried to design a set of multimedia for teaching vocabulary by using software for the first grade students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2. Since the design involves animation, pictures, and sounds that can give meaningful experience in learning English, it is hoped that the students who have special characteristics can enjoy learning English.
B.
Problem Formulation
From the background, the researcher can formulate the problem formulation, they are:
1.
How is a set of multimedia for teaching vocabulary to the first grade students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 designed?2.
What does the designed set of multimedia for teaching vocabulary to the first grade of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 look like?C.
Problem Limitation
This research tries to design a set of multimedia for teaching vocabulary English in Domby Kid’s Hope 2 by using software. The set of multimedia can help students and the tutors to make the teaching learning activities interesting and effective. By using characters of animation, picture, and sound, this design offers meaningful learning experience for children.
vocabulary (Slaterry and Willis, 2001). However, the basic vocabulary will provide an important foundation for future learning, including advanced vocabulary.
D.
Objectives of the Study
The objectives of this study are as follows:
1. To describe the steps in designing multimedia for teaching vocabulary to the first grade students of DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2.
2. To present the designed multimedia for teaching vocabulary to the first grade students of DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2.
E.
Benefit of the Study
The benefits of this research are:
1. For the first grade of DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2
The multimedia designed by using software provides fun in learning teaching activities so it can help the first grade of DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2 students enjoy learning English and contribute to improving their lives. Hopefully, they can master the language.
2. For English tutors of DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2
3. For DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2 children
By using the multimedia, children can learn with fun and they can then feel more confident in learning English in their formal school.
4. For other Social Organisations
This study can provide information to other social organizations providing suggestions in teaching children with special characteristics. By using interesting media it helps make the student’s learning more enjoyable.
5. For the researcher
This study can be used as one of the references in the design of multimedia. So it can be inspiration to other researchers who may build on the conclusions with their own investigations.
F.
Definition of Terms
This study presents six importance terms which are used in this research. They are:
1. Vocabulary
Vocabulary is a number of words that is found in daily life. The vocabulary is the foundation of learning English to the higher level.
2. Multimedia
which have different variations (sounds, pictures, and animation) especially with computers, one example is Encarta. In this study, the multimedia combines sounds, pictures, and animation. The second example is Barney. This uses a funny dynosour named Barnney as the main character. Barrney guides the students in learning English by using songs to attract the students. In this study, the writer uses a lamb, named Domby, to guide the students in learning.
3. DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2 Yogyakarta
DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2 Yogyakarta is an informal school managed by Yayasan Pelita Bangsa. It is located at Terban nearby Kali Code. This
organisation serves marginalized people. It concentrates activities on children’s education start from 3 to 19 years old. The goal of this organisation is to reduce the numbers of people living in poverty.
4. First grade students of DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2 Yogyakarta
35
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
This chapter discusses the research method, research participants, research setting, research instruments, data gathering, instruments, data analysis techniques, and research procedures.
A. Research Method
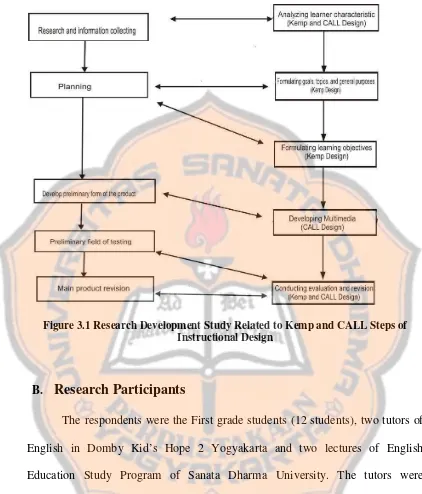
The method of study used research and development study (R&D Study). According to Brog and Gall (1985:772), educational research and development (R&D) is “a process used to develop and validate educational products”. The term “products” in Brog and Gall’s definition referred to instructional materials. In this study, the product is multimedia for teaching vocabulary. The writer applied R&D methodology since this research type matched the steps in designing multimedia as described in the theoretical framework in chapter two.
which consisted of five steps. The five steps of the modified R & D study employed in this study are;
1. Research and Information Collecting
There were two parts in the research and information collecting step. They were review of literature and learners’ need analysis. Each was described further as follows.
a. Review of literature provided some references and information as the basis of the study. From the literature review the writer used theories to support the design of multimedia for teaching vocabulary, namely, the theories of instructional designs, vocabulary, the nature of computer assisted learning, teaching English for Elementary School, and multimedia design.
b. Learners’ need analysis was done by conducting observation and interviewing the tutors in Domby Kid’s Hope 2. The needs analysis focused on measuring the students’ interest, motivation, and needs in learning English.
2. Planning
3. Developing a Preliminary Form of Product
In this step, the writer prepared the media, handbooks, pictures, and songs to make attractive multimedia by using Flash 8 software. The selection of materials and activities was based on the analysis of the data obtained from the research and information collecting with the stated objectives as guides and also goals to achieve. Since the design needed to be evaluated, the instrument of the evaluation was also developed. This step was similar to step 4 which was adapted from the CALL Design.
4. Preliminary Field Testing
This step contains expert validation and materials validation. The term expert validation means that the writer needed to gain feedback, comments, and suggestions from some respondents who were considered as expert on designing materials. The respondents were tutors of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta and English lectures of Sanata Dharma University. They were chosen because they had experiences in designing and teaching learning process.
Another term was materials validation. In this study, the materials changed, it became multimedia. The writer tried out the media designed to the first grade of Domby Kid’s hope 2 Yogyakarta. After that, the writer distributed questionnaire to the tutors and the lectures.
5. Main Product Revision
In this step, the writer revised the multimedia based on the result of the evaluation obtained in the fourth step. That is the main product revision. This step was similar to step 5 in designing materials adapted from Kemp’s and CALL Design. The specification of product in this study is explained as follows.
3.1 Table Product Specification
Aspects Specification
Name Multimedia for teaching vocabulary for the first grade students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta Purpose To enable the students to be able to understands and
use the vocabulary about daily life.
Target The first grader of Domby Kid’s Hope 2
Yogyakarta Language skill Listening
Sources Text book and CD Room,
Time allocation 3 meetings x (2x30’) Type of product Software (CD Room)
The use of materials As media used in class with teacher’s guide
Activities Singing songs about the materials, watching the simultion of the use of vocabulary, and playing games.
Strategies Class discussion
Evaluation tools Quiz
Figure 3.1 Research Development Study Related to Kemp and CALL Steps of Instructional Design
B.
Research Participants
In the preliminary field testing step, the lectures of Sanata Dharma Unversity and the tutors were asked to fill in the questionnaires to get their feedbacks and suggestions the media designed. It was very useful to get the final revision of the media so that the media were appropriate for the First grade students.
C.
Research Setting
This research was done in Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta. This study was conducted on May 2009-May 2010.
D.
Research Instruments
In this Study, the writer uses observation, interview, and questionnaires session for the instrument.
1. Interview
2. Observation
Observation was to find data that is needed for the researcher. In order to understand the English teaching-learning activities carried out at Domby Kid’s Hope 2, the researcher conducted two observations. The researcher observed the learners’ responses during the English teaching-learning activities to understand their real behaviors and activities in class. The observations were done in class, outside of class, the facility, and English teaching-learning activity in Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta.
3. Questionnaire
Questionnaire is a list of questions asking about people’s opinion (Elliot, 1991:82). The questionnaires were distributed to the tutors and lectures of English Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. There are two types of questionnaires (Ary et al, 2002), one is structured or closed form and the other one is unstructured or open form. The questionnaires used both closed-ended questions and open-ended questions. It was used to get their suggestions on the materials. The suggestions were important to make final revisions of the design so that the software would be most beneficial to First grade students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta.
E. Data Collection
1. Models of Instructional Material Design
2. Books and articles concerning the theory of CALL
3. Books and articles concerning the theory of teaching and learning vocabulary
4. Books and article concerning the theory of teaching children 5. Books and articles concerning the theory of multimedia
The second was the data from interviews and observations, included for designing the Multimedia. The observation was conducted after the writer interviewed the tutors. The observation data was to find out characteristic of the students, the tutor, and the facilitation in Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta that could enhance teaching learning activities. After the data from the research and information collecting were gathered, the writer analyzed them, and then designed the media.
In the preliminary field testing step, the data were gathered by distributing questionnaires to lectures of Sanata Dharma University and the tutors of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta. The questionnaires used both opened and closed questions.
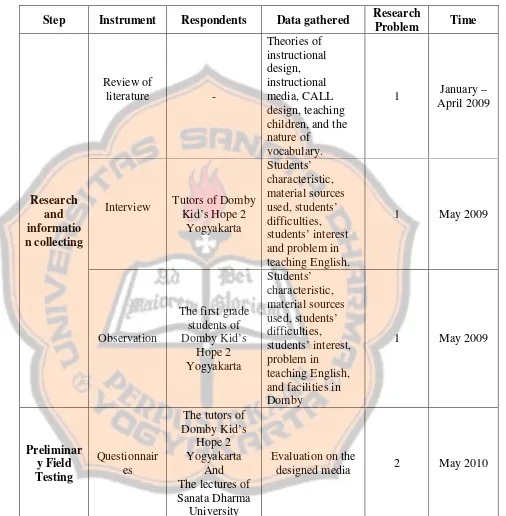
Table 3.2 The Overall Process of Data Collection
Step Instrument Respondents Data gathered Research
Problem Time Research and informatio n collecting Review of literature -Theories of instructional design, instructional media, CALL design, teaching children, and the nature of
vocabulary.
1 January –
April 2009
Interview Tutors of Domby Kid’s Hope 2
Yogyakarta Students’ characteristic, material sources used, students’ difficulties, students’ interest and problem in teaching English.
1 May 2009
Observation
The first grade students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta Students’ characteristic, material sources used, students’ difficulties, students’ interest, problem in teaching English, and facilities in Domby
1 May 2009
Preliminar y Field Testing
Questionnair es
The tutors of Domby Kid’s
Hope 2 Yogyakarta
And The lectures of Sanata Dharma
University
Evaluation on the
F.
Data Analysis
First, the researcher was doing observation of the learners’ characteristic, the facilitation, and the students’ needs by using check list.
Second, questions in interview session were to get the data that would be useful in making the appropriate instructional media for them. The data from these interviews were analyzed. Then, all the data from observations and interviews was gathered together to inform the design of the material in addition to information taken from some books and internet sources.
Fourth, the measurement of the lectures’ opinions uses to make final revision. The assessments of the lectures’ opinion on the design used five points of agreements:
1= if they strongly disagree with the statement 2=if they disagree with the statement
3=if they neither agree nor disagree, or they do not know or doubt. 4= if they agree with the statement
5= if they strongly agree with the statement
[image:36.595.85.515.218.629.2]The descriptive statistics uses the central tendency (mean, median, and mode) of the respondents’ opinion on the multimedia design. They are presented in the following table.
Table 3.3 The Research Result Calculation Form
No Respondent’s opinion on
Central Tendency
There are three ways to obtain a measure of central tendency. They are: a. The mean, it is symbolized as M, is the arithmetic average of all
the scores.
The formula to get Mean is:
= Mean
The sum of the scores Raw score
Number of respondents
b. The median is symbolized as Mdn. The median is the exact midpoint of any distribution, or the point that separates the upper half from the lower half.
c. The Mode is symbolized as Mo. The mode is the most frequently occurring, score in the distribution.
The assessment of central tendency of every statement was categorized as in the following page:
1-2 : BAD. It means that the writer had to change the nature of the designed multimedia.
3 : FAIR. It means that the writer had to revise or improve the designed multimedia.
G.
Research Procedure
The research is separated into two stages first is pre-design, the second is post-design, conducted as follows:
1. Finding theories
The writer read some books to find theories to support this research and browse the Internet to find some information.
2. Interviewing the tutors and doing observation.
In this phase, the writer interviewed the two English tutors and observed the teaching-learning class of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta. The results are used to propose the instructional materials for them.
3. Designing the multimedia
By using the results and based on the literary review, the writer designed the materials.
4. Evaluating the designed multimedia
Once the multimedia was done, and then the writer distributed 4 questionnaires for 2 lectures of English Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University and to 2 tutors to get opinions and suggestions about the designed multimedia. Then, the multimedia was tried out to the first graders of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta. To get feed back or the multimedia try out, the writer interviewed all the students.
5. Designing the final multimedia
47
CHAPTER IV
ANALYSIS RESULTS
This chapter presents the results of the research to answer the questions stated in the Problem Formulation in Chapter I. The questions are how is multimedia for teaching English to first grade students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 designed? And what does the designed set of multimedia for teaching vocabulary to the first grade students of DOMBY KID’S HOPE 2 look like? To analyze them, this chapter is divided into four topics. Those are the results of the multimedia, results of the survey research, discussion, and the presentation of the multimedia.
A. The steps of designing the multimedia for teaching vocabulary to the first grade students of Domby Kid’s Hope2 Yogyakarta
The writer conducted five steps of designing multimedia adapted from Kemp’s (1977) and CALL design by Hubbard (Penningthon, 1996). These steps were analyzing learners’ characteristics, formulating goals, topics, and general purpose, formulating objectives, developing multimedia, conducting evaluation and revision. The deeper findings of each step are explained below.
1. Analyzing learners’ characteristics
Hope 2 Yogyakarta by employing an unstructured interview. The interview was conducted on June 3rd, 2009. The results of the interview are presented as follows.
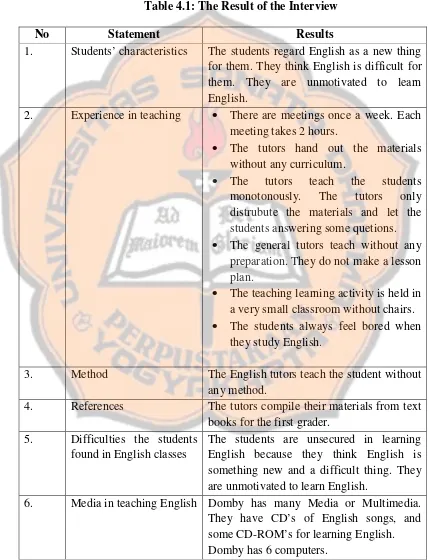
Table 4.1: The Result of the Interview
No Statement Results
1. Students’ characteristics The students regard English as a new thing for them. They think English is difficult for them. They are unmotivated to learn English.
2. Experience in teaching There are meetings once a week. Each meeting takes 2 hours.
The tutors hand out the materials without any curriculum.
The tutors teach the students monotonously. The tutors only distrubute the materials and let the students answering some quetions. The general tutors teach without any
preparation. They do not make a lesson plan.
The teaching learning activity is held in a very small classroom without chairs. The students always feel bored when
they study English.
3. Method The English tutors teach the student without any method.
4. References The tutors compile their materials from text books for the first grader.
5. Difficulties the students found in English classes
The students are unsecured in learning English because they think English is something new and a difficult thing. They are unmotivated to learn English.
7. Material Domby does not have recent material 8. Suggestion for teaching
multimedia
The multimedia can help to create an informal situation so the students do not realize if they are actually studying English.
The teaching learning activities are not monotone. They can play a game or sing a song
From the interview, there were some points to note as a consideration to design the material:
1) The topics and material should be appropriate for the first graders of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta.
2) The teaching learning activities should be not monotone in order to motivate the students in learning English.
3) The multimedia should encourage the students to enjoy and like learning English.
4) The multimedia provides such fun activities.
Table 4.2: Class Observation Note Day/date :Thursday/ June 10th, 2009
Tutor : Ms. B
Learners : 6-8 class students (first grade) Location : Domby classroom
Time : 12.00p.m-02.00p.m Description
The tutor greeted the students in English and the students responded it.
The tutor asked for a volunteer student to lead the prayer but none wanted to lead it. Then the tutor asked one student to lead the prayer in English with the tutor’s help.
The tutor reviewed the previous materials.
The tutor started to give a task to the students by writing some questions on the whiteboard.
The tutor gave some time for the students to do the task. The tutor asked the students to submit the task.
Break
The tutor discussed the answers of the task. The tutor made a quiz to review the material Closing
The second observation was to investigate the facilities that Domby has. The writer found out:
1) Domby has six computers that are used for learning activities. 2) Domby has internet connection that is used for learning activities. 3) Domby has one television set, one DVD player, and one VCD
player that are used for learning activities. Because of ill-prepared teaching, the tutor does not have time to prepare the media.
2. Formulating goals, topics, and general purposes
Based on the gathered information from the observation and interviews, the writer subsequently formulated the goals. The goals of the design show what the students will be able to do after finishing doing all of the instructions. The goals of the designed multimedia are as follows:
1) Motivating the students in learning English.
2) Give the students the ability to understand simple and basic English.
3) Give the students the ability to identify the names of certain objects around them in English.
4) Give the students the ability to mention the names of certain objects around them in English.
[image:43.595.85.516.240.625.2]After formulating the goals, the writer established the topics to be presented in the designed multimedia. The topics were formulated based on the goals of the developed multimedia. In formulating the topics, the writer considered two points. First, the writer reviewed some text books for English for first graders, whether these topics were appropriate or not to be given to the first grade students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2. Second, the writer chose to the topics that were interesting for the students by considering the results of the research and information collecting. As a result, there were three topics selected in this study. The writer also put a title on each unit. The topics were as follows:
Table 4.3: Topics and Titles of the Designed Multimedia
No Topics Title
1. Introducing people and greeting Greeting
2. Parts of body My Body
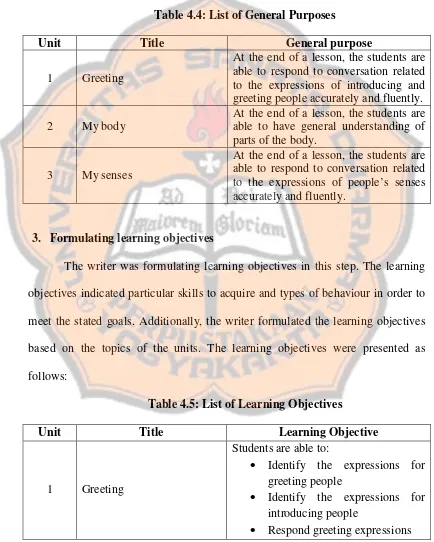
After the goals and topics were formulated, the next step was formulating the general purposes of materials in designed multimedia. The general purposes are what the learner is expected to be able to do after finishing the multimedia. The general purposes were formulated as follows:
Table 4.4: List of General Purposes
Unit Title General purpose
1 Greeting
At the end of a lesson, the students are able to respond to conversation related to the expressions of introducing and greeting people accurately and fluently.
2 My body
At the end of a lesson, the students are able to have general understanding of parts of the body.
3 My senses
At the end of a lesson, the students are able to respond to conversation related to the expressions of people’s senses accurately and fluently.
3. Formulating learning objectives
The writer was formulating learning objectives in this step. The learning objectives indicated particular skills to acquire and types of behaviour in order to meet the stated goals. Additionally, the writer formulated the learning objectives based on the topics of the units. The learning objectives were presented as follows:
Table 4.5: List of Learning Objectives
Unit Title Learning Objective
1 Greeting
Students are able to:
Identify the expressions for greeting people
Identify the expressions for introducing people
Respond expressions of introducing people
2 My body
Students are able to:
Identify parts of the body Mention parts of the body
3 My senses
Students are able to:
Identify the expressions for people’s senses
Respond the expressions of people’s senses
4. Developing multimedia
After goals and objectives had been formulated, the next step was developing the multimedia. In CALL steps that the writer adopted, there were four steps that were presented as follows:
a. Activity types
In Unit 2, Dom saying “these are my act and say what the cream!”
[image:46.595.86.511.117.643.2]Second was dr done by the teacher multimedia was easy played. The first thing repeat the word or phr presented in the next
Figure 4.1 Unit 1: Greeting
Domby and friends showed the students parts my knees”. In Unit 3, the simulation was Dom
they were doing. For example says Domby:
drilling the vocabulary. The control of the her, so the teacher can repeat the vocabula
sy to operate, by just clicking the words the hing that the students had to do was to listen phrase, and finally saying the word. The drill t page
ts of their body by omby and friends’ y: “I taste an ice
Third was sing this multimedia. Each song. They were “hel in unit 2, “have you sunshine”. The last w the students had to gu multimedia will pay ‘try again’. In unit 3, that they can taste, sm page is an example of
Figure 4.1: Drilling in Unit 1
singing a song. There were four songs that w ach unit had one song and the closing for all ello how are you” in unit 1, “head, shoulders, ou ever smelled?” in unit 3, and for closing st was game. In unit 1 and 2, there were some pi
guess the vocabulary or expression. If the answ y a compliment; ‘excellent!’. But if it was wr 3, the students were asked to choose the items , smell, hear, touch, or see. The following pic
of the game.
b. Presentation schem The presentati including the modalit control option, the for input. Nevertheless, teacher, the students onl
For the screen sound, music, and pic can move. ‘Frame by different frame and moving. However, the background of the ani
Figure 4.2: Game in Unit 1
heme
ation scheme determines how the language w lities (text, audio, graphics, and video), screen form of input judging, and the feed back in ss, all the control of this program was in the s only watch and do what the program asks for. een layout of this multimedia the writer used
pictures. By using ‘frame by frame animation’ by frame animation’ means every animated pi nd every frame is played together so the anim
the writer still used the ‘tween animation’ met animation. Here, the writer only put the animat
will be presented, n layout, help and in response to the the hands of the or.
first and the last fram Domby, Jane, and Be
Figure 4.3 Dom
Figure 4.5 Ben
c. Multimedia Produc The main sof However, the writer design the multimedi specifications used:
1. Intel Dual Cor 2. 120G SATA 3. 12.1” WXGA
ame. There were three characters in this multi en. The pictures of them are presented as follow
omby picture Figure4.4 Jane pictur
en Picture
oduction
software to create this multimedia was Macrom ter needed additional hardware and supporti
dia. The following page showed the details of
ore T5550 CPU
A wide screen display
ultimedia, they are ollows.
ure
4. Wireless LAN Additional hardware:
1. Microphone 2. Stereo headphones 3. Scanner
There are some supporting software: 1. Cool Editor
2. Corel Draw
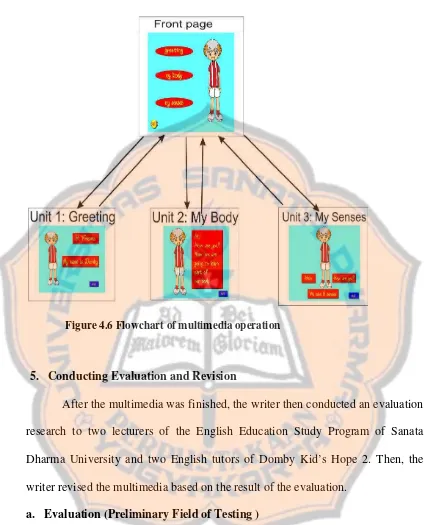
The form of the multimedia was software in VCD. In one class there was only one computer that would be played the multimedia. All the control of the multimedia was under the teacher’s control.
Figure 4.6 Flowchart of multimedia operation
5. Conducting Evaluation and Revision
After the multimedia was finished, the writer then conducted an evaluation research to two lecturers of the English Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University and two English tutors of Domby Kid’s Hope 2. Then, the writer revised the multimedia based on the result of the evaluation.
a. Evaluation (Preliminary Field of Testing )
techniques were conducted in separated time, since the respondents were also different.
1) Expert Validation
In this step, the writer distributed the designed multimedia to two lectures of English Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma and two English tutors of Domby Kid’s Hope 2, and asked them to fill the questionnaire. The evaluation questionnaires were employed to know the respondents’ general opinion towards the designed materials. The writer determined a scale ranging from 1 to 5 as degree of agreements toward the statements in the questionnaires. The scale describes as follows:
1= if they strongly disagree with the statement
2=if they disagree with the statement
3=if they neither agree nor disagree, or they do not know or doubt.
4= if they agree with the statement
5= if they strongly agree with the statement
Table 4.6 Data calculations of the participants’ opinion toward the designed multimedia
No Respondent’s opinion on
Central Tendency
N Mn Md
1 Topics in each unit are interesting and relevant for the children aged 6-8 years old (first grader).
4 4 4
2 The types of exercises and activities are good and can facilitate the students to understand the materials.
4 3.75 4
3 The contents of the material are easy to fit curriculum 4 3.75 4 4 The contents of the material are well organized. 4 3.75 4 5 The contents of the material are interesting 4 4.25 4 6 The contents provide effective practice learning. 4 2.75 3 7 The contents provide meaningful interaction
between multimedia and learner.
4 4 4
8 The contents provide communicative interaction between students.
4 2.25 2
9 The instructions of the multimedia are clear. 4 2.25 1 10 The layout of the designed is interesting for students and
teacher.
4 4.5 5
11 The program operation is easy to follow. 4 3 4 12 The multimedia is suitable for teaching the students with
special educational needs.
4 2.75 3
13 This multimedia contributes to the learning
scenario in ways that cannot be achieved equally well by other resources (non-multimedia based).
4 3.5
-14 Generally the multimedia are well developed 4 3.5 4 Total mean score 3.43
could be concluded that the writer had to revise or improve the designed multimedia. There were four respodents’ opinions that were categorized as bad. First, the contents of the designed multimedia did not provide effective practice learning. Second, the contents of the multimedia did not provide communicative interaction between students. The third was about the instructions of the multimedia which were not clear. The last opinion was about the multimedia which was not suitable for teaching the students with special educational needs. However, not all of the respondets knew about Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta so their expectation might be different. In order to improve whether the respondents’ opinions were suitable to Domby Kids Hope 2 children or not, the writer applied the multimedia to the first graders at Domby Kids Hope 2. The result showed that the expert validation respondents’ opinion were not suitable to the first graders of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta.
The writer also asked the respondents to provide comments and suggestion in the questionnaire sheets. The suggestions are presented as follows:
a) Some participants suggested that the writer had to pay attention to the pronunciation of some words and the intonation of the sentences that mostly raising which was sometimes incorrect.
b) Some participants suggested that the instruction of the multimedia should be clear.
d) Some participants suggested that the writer had to pay attention to the pictures which were not clear and confusing.
e) Some participants suggested that the writer had to add more activities. 2) Materials Try Out
[image:55.595.87.518.235.612.2]The writer tried out the designed multimedia in first grade class of DOMBY Kid’s Hope 2. Because of the time limitation, the materials that were tried out were two, they were Unit 1: Greeting and Unit 2: My Body. After trying out each unit, the writer interviewed to the all students. There were 6 students in class.
Table 4.7 The Result of the Interview in the Materials Try Out
No Statement Results
1. Students’ experience in learning by using multimedia
The students enjoyed the learning. They were interested in the Domby character. 2. The difficulty of the
multimedia
The students were confused of the pictures.
3. The topics of the
multimedia
The students enjoyed the topics. 4. The contents of the
multimedia
The contents of the multimedia were interesting.
5. The exercises of the multimedia
The students enjoyed the exercises because the exercises were easy
confused about the pictures. The pictures were not clear whether it was morning or evening. In unit 2, the pictures of the songs and the song itself were too fast. They cannot repeat the songs.
In summary, there were two weaknesses of the multimedia based on the students’ opinion. First, there were some pictures which were not clear. Second, the songs were too fast for them.
b. Revision
In this step, the writer adapted some suggestions given by respondents of expert validation and materials try out to improve and revise the designed multimedia related to the designed multimedia. It consisted of some aspect below. 1) The pronunciation
The writer changed the pronunciation of some words and some sentences. There were some words which pronounced incorrectly. They are toe, rabbit, and parts. There were some sentences which were incorrect intonation. Mostly the sentences of the multimedia pronounced with raising intonation, which is sometimes incorrect.
2) The pictures
3) The text
The writer changed some written text in the multimedia. There were some texts which were missed typed. The writer rechecked the grammar and revised them.
4) The games
The writer changed the pictures of the game in unit 3. Considering the suggestions of one lecturer that the topic of unit 3 could be a bit confusing since the examples were limited, he suggested to give different pictures in the game. 5) The songs
The writer rechecked and revised the song in unit 2, namely, Head, Shoulders, Knees, and Toes. The song was too fast to follow, so the writer revised the song to be slower.
6) The instruction
The writer added the instruction of the multimedia since the instruction of the multimedia was not clear.
B. The presentation of the designed multimedia
Table 4.8. The Presentation of the Designed Multimedia Unit Main Material Learning Objectives Activities
1 Greeting Students are able to: Identify the
expressions for greeting people Identify the
expressions for introducing people Respond greeting
expressions Respond
expressions of introducing people
Opening: simulating the material.
Main activity: Drilling the
expressions; good morning, good afternoon, and good evening. Singing: “hello
how are you” Games: “choose
the correct answer!” 2 My Body Students are able to:
Identify parts of the body
Mention parts of the body
Opening: simulating the material.
Main activities: Drilling the
vocabulary; head, shoulders, knees and toes.
Singing: “head, shoulders, knees and toes”
Games: “choose the correct answer!” 3 My Senses Students are able to:
Identify the expressions for people’s senses Respond the
expressions of people’s senses
Opening: simulating the material.
Main activities: Drilling the
expressions: “I smell a flower...”. Singing: “have
you ever smelled?” Games: “choose
67
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
This chapter consists of two parts. The first part is conclusions of the study, while the second part is suggestions for the English tutors or teachers, especially the English tutors of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta.
A. Conclusions
This study is aimed to provide multimedia the first grade students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta. As stated in the problem formulation on Chapter I, this study is aimed to dicover how multimedia for teaching vocabulary for the first grade students of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta was designed and the presentation of the developed multimedia.
To answer the first questions, the instructional model that is being used in this study was stated from the sychronization of two instructional designs developed by Kemp and Hubbard. Some steps of both instructional designs related to fit R&D cycle. The steps of the designing the multimedia are follows: 1. Analyzing learner’s characteristic
2. Formulating goals, topics, and general purposes 3. Formulating learning objectives
4. Developing the multimedia
In the first step, the writer conducted a need analysis by interviewing the two English tutors and the coordinator of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta, and doing observations. In the second step, the writer formulated goals, topics, and general purposes, after analyzing learner characteristics. In third step, the writer formulated measurablelearning objectives that were to be achieved by the first graders of Domby Kid’s Hope Yogyakarta. The objectives are conducted from the results of interview with the coodinator and the tutor of Domby Kid’s Hope 2. Then, the writer developed the multimedia which is divided into four parts of exercises, they are simulation of the material, singing a song, drilling the material, and playing game. After the designed materials were complete, the writer distributed questionnaires for two lectures of English Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. Then, the multimedia was tried out, and then two English tutor of Domby Kid’s Hope 2 Yogyakarta were requested to evaluate by filling the quetionnaires. All the responses were analyzed.
In addition, the writer presented the final version of the multimedia. It was aimed to answer the second question in the problem formulation. There were three topics in the designed multimedia. The topic were Greeting, My Body, and My Senses.
B. Suggestions
In this part, the writer gave some suggestions to the English teachers, especially the English teacher in Domby Kid’s Hope 2 and other researchers who are interested in conducting research.
1. English teachers, especially the English teacher in Domby Kid’s Hope 2 a. The writer suggests that it is important to conduct creative teaching
The interesting activity of learning will attract the students attention. The fun activities are important to create good enviroment of learning.
b. The writer suggests that is important to conduct the materils of learning based on the school curriculum. It can support the students achievements at school.
2. Other researchers
70
REFERENCES
Ary, D.; Jacobs L.C.; Razavieh, A. 2002. Introduction to Research in Education, 6thEdition. New York: Wodsworth Thomson Learning.
Boyle, T. 1997.Design for Multimedia Learning. Harlow: Prentice-Hall Europe. Brog, W. R. and Gall, M.D. 1983. Educational Research: an Introduction. New
York: Longman Inc.
Crystal, D. 1997. English as a Global Language. New York: Cambridge University press.
Halliwell, S. 1992.Teaching English in the Primary Classroom. Harlow: Pearson Education Limited
Hamalik, O. 1994.Media Pendidikan. Bandung: PT. Citra Aditiya Bakti.
Kemp, J. 1977. Instructional Design: A Plan for Specific Purposes: A Learning Centered Approach. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Kurniawan, Y, S.T. 2006. Belajar Sendiri: Macromedia Flash 8. Jakarta: PT Elex Media Komputindo.
Levy, M. 1997. Computer-Assisted Language Learning: Context and Conceptualization. Oxford: Claredon Press.
Newby, T, et al. 2000. Instructional Technology for Teaching and Learning, Designing Instruction, Integrating computers, and Using media. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall Inc.
Nunan, D. 2003. Practical English Language Teaching. New York: Mc Graw-Hill.
Pennington, M. 1996.The Power of CALL. Athelstan: Athelstan Publications. Read, J. 2000.Assessing Vocabulary. New York: Cambridge University Press. Slattery, M and Jane W. 2001. English for Primary Teachers: A Handbook of
Activities and Classroom language. New York: Oxford University Press.
Internet Source:
71
APPENDIX
A
73
APPENDIX
B
INTERVIEW GUIDLINE
74
Interview Guideline
1. Bagaimana minat belajar siswa kelas satu dalam belajar Bahasa inggris? 2. Apa mereka menyukai kelas Bahasa Inggris?
3. Materi seperti apa yang mereka sukai?
4. Berapa jam pelajaran yang tersedia untuk mata pelajaran Bahasa Inggris setiap minggu?
5. Kegiatan seperti apa yang biasa anda gunakan untuk mengajar Bahasa Inggris?
6. Metode pembelajaran seperti apa yang anda pakai dalam mengajarkan Bahasa Inggris? Apa metode tersebut efektif?
7. Apakah sering mengalami kesulitan dalam kelas Bahasa Inggris? Kesulitan apa yang sering mereka hadapi?
8. Apa yang anda dan atau siswa lakukan saat mengalami kesulitan tersebut? 9. Media apa sering anda gunakan dalam belajar Bahasa Inggris? Bagaimana
respon anak terhadap media yang anda pakai?
10. Bagaimana pendapat anda tentang media pembelajaran bahasa Inggris menggunakan software?
75
APPENDIX
C
76
Name :……….
Age :……….
Education : S1 S2 S3 others
Teaching experience :……..years
This questionnaire is aimed to obtain the data from the respondents to get the feedback as an evaluation for the designed multimedia.
This respondent of this research is expected to:
1. Give his/her evaluation towards the designed multimedia by putting a tick (V) to the number which represents his/her agreement. The number indicating point of agreement can be categorized as follows:
1= strongly disagree with the statement 2= disagree with the statement
3= neither agree nor disagree or doubt. 4= agree with the statement
5= strongly agree with the statement
2. Write the suggestion, opinion, comments on the strength and the weakness of the designed multimedia in the provided space.
Points of agreement
No Respondent’s opinion on
1 2 3 4 5
1. Topics in each unit are interesting and relevant for the children aged 6-8 years old (first grader). 2. The types of exercises and activities are good
and can facilitate the students to understand the materials.
3. The contents of the material are easy to fit curriculum
4. The contents of the material are well organized. 5. The contents of the material are interesting 6. The contents provide effective practice learning. 7. The contents provide meaningful interaction
between multimedia and learner.
8. The contents provide communicative interaction between students.
9. The instructions of the multimedia are clear. 10. The layout of the designed is interesting for
students and teacher.
11. The program operation is easy to follow.
scenario in ways that cannot be achieved equally well by other resources (non-multimedia based). 14. Generally the multimedia are well developed
15. The weaknesses of the multimedia:
……… ……… ……… ……… 16. The strengths of the multimedia:
……… ……… ……… ……… 17. Sugestions to develop multimedia:
……… ……… ……… ………
78
APPENDIX
D
79
1. Apa yang kamu pelajari hari ini?
2. Apakah pelajaran bahasa Inggris hari ini menyenangkan?
3. Bagian manakah yang kamu sukai?
4. Bagian manakah yang sulit bagimu?
80
APPENDI