PROCEEDING
The 2
ndInternational Conference on
Electrical Engineering, Computer Science and Informatics (EECSI 2015)
Copyright and Reprint Permission: Abstracting is permitted with credit to the source.
Libraries are permitted to photocopy beyond the limit of copyright law.
Copyright ©2015 by IAES.
Editors :
DR. Deris Stiawan
Pacu Putra, B.CS., M.Comp. Sc.
Munawar A.Riyadi, Ph.D
Imam Much. Ibnu Subroto, Ph.D
Publisher :
Universitas Sriwijaya Press (UNSRI PRESS)
In collaboration with
Institute Advanced and Engineering and Science (IAES)
ISBN : 979-587-553-1 (PRINT)
ISBN : 979-587-554-X (CD-ROM)
Additional copies may be ordered to:
Griya Ngoto Asri D2, Bangun harjo, Sewon Bantul 55187, Yogyakarta
vi
ORGANIZING COMMITTEE OF EECSI 2015 CONFERENCE
Steering Committee
Adam Skorek, IEEE Fellow, University of Quebec at Trois-Rivières, QC, Canada
Mohd.Ruddin Abd Ghani, Universiti Teknologi Malaka, Malaysia
Ary Setijadi Prihatmanto, IEEE Indonesia Chapter Chair (Computer Society)
Fitri Yuli Zulkifli, IEEE Indonesia Section (Technical Activity)
John E. Batubara, IEEE Indonesia Section (Conference Coordination)
Pekik Argo Dahono, IEEE Indonesia Chapters Chair (EdSoc/EDS/PELS/SPS)
Soegijardjo Soegijoko, IEEE Indonesia Chapters Chair (CAS/EMBS)
Wahidin Wahab, IEEE Indonesia Section (Advisory Committee)
Zainudin Nawawi, IEEE Indonesia Section (Advisory Committee)
Badia Perizade, Universitas Sriwijaya, Palembang, Indonesia
Anis Saggaff, Universitas Sriwijaya, Palembang, Indonesia
Darmawijoyo, Universitas Sriwijaya, Palembang, Indonesia
Siti Nurmaini, Universitas Sriwijaya, Palembang, Indonesia
Hermawan, Universitas Diponegoro, Semarang, Indonesia
Ida Ayu Dwi Giriantari, Universitas Udayana, Bali, Indonesia
Rahmat Budiarto, Surya University, Indonesia
Tumiran, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
General Chair
Deris Stiawan, Universitas Sriwijaya,
Indonesia
General Co-Chair
Tole Sutikno, Universitas Ahmad Dahlan,
Indonesia
Finance Chair and Treasurer
Wiwiek Fatmawati, Universitas Islam
Sultan Agung, Indonesia
Lina Handayani, Universitas Ahmad
Dahlan, Indonesia
Publication Chair
Mochammad Facta, Universitas,
Diponegoro, Indonesia
Publicity Chair
Imam Much Ibnu Subroto, Universitas
Islam Sultan Agung, Semarang,
Indonesia
Balza Achmad, Universitas Gadjah
Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Technical Program Chairs
Munawar A. Riyadi, Universitas
Diponegoro, Indonesia
Mudrik Alaydrus (Senior Member of
IEEE), Universitas Mercu Buana Jakarta,
Indonesia
Teddy Mantoro (Senior Member of IEEE),
Universitas Siswa Bangsa Internasional,
Jakarta, Indonesia
Local Arrangement Committee
Hadi Purnawan Satria, Universitas
Sriwijaya, Palembang, Indonesia
Ahmad Heriyanto, Universitas Sriwijaya,
Palembang, Indonesia
Pacu Putra, Universitas Sriwijaya,
Palembang, Indonesia
Angina Primanita, Universitas Sriwijaya,
Palembang, Indonesia
Technical Program Members
Ali Kattan, Ishik University, Iraq
Adya Pramudita, UnikaAtma Jaya,
Indonesia
Angela Amphawan, Universiti Utara
Malaysia, Malaysia
Arianna Mencattini, University of Rome
“Tor Vergata”, Italy
vii
International Advisory Committee
Lech M. Grzesiak, Warsaw University of
Technology, Poland
Leo P. Ligthart, Delft University of
Technology, Netherlands
Hamid A. Toliyat, Texas A&M
University, USA
Patricia Melin, Tijuana Institute of
Technology, Mexico
Tae Jin Park, Samsung Heavy
Industries, Korea
Abdul Hanan Abdullah, Universiti
Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia
Ahmad Ashari, Universitas Gadjah
Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
AtifIqbal, Qatar University, Qatar
Cheng-Wu Chen, National Kaohsiung
Marine University, Taiwan
Dimitrios Lekkas, University of the
Aegean, Greece
Djamel H Sadok, Federal University of
Pernambuco, Brazil
Frédéric Cuppens, Sciences Sociales et
de l’Information, France
Jefri bin Din, Universiti Teknologi
Malaysia
Jaime Lloret Mauri, Polytechnic
University of Valencia, Spain
Juan Jose Martinez Castillo, “Gran
Mariscalde
Ayacucho” University,
Venezuela
Lei Zhang, East China Normal
University, China
Muhammad Nadzir Marsono, Universiti
Teknologi Malaysia
Nabil Sultan, University Campus
Suffolk, United Kingdom
Qiang Li, Bielefeld University, Germany
Sotirios G. Ziavras, University Heights,
United States
Surinder Singh, Sant Longowal Inst of
Eng& Tech, India
Takashi Obi, Tokyo Institute of
Technology, Japan
Tarek Bouktir, University of Setif 1,
Algeria
Vicente Garcia Diaz, University of
Oviedo, Spain
Yudong Zhang, Columbia University,
United States
Melaka, Melaka, Malaysia
Dwi H. Widyantoro, Institut Teknologi
Bandung, Indonesia
Farzin Piltan, Sanatkadehe Sabze
Pasargad Company, Iran
Faycal Djeffal, University of Batna, Batna,
Algeria
Florentinus Budi Setiawan,
Soegijapranata Catholic University,
Indonesia
Han Yang, University of Electronic
Science and Technology, China
Irfan Syamsuddin, Politeknik Negeri
Ujung Pandang, Indonesia
Heroe Wijanto, Telkom University,
Bandung, Indonesia
Kartika Firdausy, Universitas Ahmad
Dahlan, Yogyakarta
Kridanto Surendro, Institut Teknologi
Bandung, Indonesia
Kristin Y. Pettersen, Norwegian
University of Science and Technology,
Norway
M. Sukrisno Mardiyanto, Institut
Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia
Marcin Kowalczyk, Warsaw University of
Technology, Warszawa, Poland
Media Anugerah Ayu, Universitas Siswa
Bangsa Internasional, Indonesia
Mokhtar Beldjehem, University of Ottawa,
Canada
Mohammad Hossein Anisi, University of
Malaya, Malaysia
Muhammad Abu Bakar Sidik, Universiti
Teknologi Malaysia
Nidhal Bouaynaya, University of
Arkansas at Little Rock, United States
Rudi Kurianto, Universitas Tanjungpura,
Indonesia
Shahrin Md. Ayob, Universiti Teknologi
Malaysia, Johor, Malaysia
Supavadee Aramvith, Chulalongkorn
University, Thailand
Wudhichai Assawinchaichote, King
Mongkut’s University of Technology
Thonburi, Thailand
xiii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Foreword from General Chair
Foreword from Rector Universitas Sriwijaya
Foreword From IAES Indonesia Chapter
Organizing Committee of EECSI 2015 Conference
International Advisory Committee
EECSI 2015 Agenda / Programs
Table of Contents
INVITED SPEAKERS
iii
iv
v
vi
vii
viii
xiii
INV-1
QUANTUM NANOENGINEERING
NONEQUILIBRIUM HIGH-ELECTRIC-FIELD
TRANSPORT FOR SIGNAL PROPAGATION
Vijay K. Arora
Wilkes University
,
U. S. A.
1
INV-2
POWER ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT CONTROL
USING HYBRID APPROCH
Tri Desmana Rachmilda, Yanuarsyah Haroen
Institut Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia
TRACK: COMPUTER SCIENCE AND INFORMATICS
2
CS-03
NOVICE ASSISTANCE TOOL AND
METHODOLOGY: DESIGN DECISION AND
TASK-PATTERN MAPPING
Meei Hao Hoo, Azizah Jaafar
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Malaysia
xiv
CS-05
THE APPLICATION OF FUZZY TIME SERIES
SINGH FOR FORECASTING BANDWIDTH
NETWORK DEMAND
Aryanti, Ikhthison Mekongga
State Polytechnic of Sriwijaya, Indonesia
7
CS-06
NUMERICAL SOLUTION FOR SOLVING
SPACE-FRACTIONAL DIFFUSION EQUATIONS USING
HALF-SWEEP GAUSS-SEIDEL ITERATIVE
MMETHOD
A. Sunarto, J. Sulaiman, A. Saudi
Universiti Malaysia Sabah, Malaysia
8
CS-08
GENERALIZED MINLP OF INTERNET PRICING
SCHEME UNDER MULTI LINK QOS NETWORKS
Fitri Maya Puspita, Irmeilyana, Indrawati
Sriwijaya University, Indonesia
10
CS-09
NET.OS: NETWORK SERVER OPERATING
SYSTEMS BASED ON OPEN SOURCE
Evan Enza Rizqi, Idhawati Hestingsih, Mardiyono
Politeknik Negeri Semarang, Indonesia
11
CS-10
THE OPTIMIZED K-MEANS CLUSTERING
ALGORITHMS TO ANALYZED THE BUDGET
REVENUE EXPENDITURE IN PADANG
Dony Novaliendry
1, Yeka Hendriyani
2, Cheng-Hong
Yang
1, Hafilah Hamimi
21
National Kaohsiung University of Applied Sciences
Kaohsiung, Taiwan,
2State University of Padang, Indonesia
xv
CS-11
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS ON TEXT
STEGANALYSIS METHOD USING A
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE APPROACH
Roshidi Din
1, Shafiz Affendi Mohd Yusof
1, Angela
Amphawan
1, Hanizan Shaker Hussain
2, Hanafizah
Yaacob
2, Nazuha Jamaludin
2, Azman Samsudin
31
University Utara Malaysia, Malaysia,
2Kolej Poly-Tech
MARA, Malaysia,
3University Sains Malaysia, Malaysia
13
CS-12
PATTERN RECOGNITION ON PAPER
CURRENCY'S FEATURE USING LVQ
ALGORITHM
Dewanto Harjunowibowo
Sebelas Maret University, Indonesia
14
CS-13
ENHANCED RIDGE DIRECTION FOR THE
ESTIMATION OF FINGERPRINT ORIENTATION
FIELDS
Saparudin
Sriwijaya University, Indonesia
15
CS-14
VIRTUALIZATION TECHNOLOGY FOR
OPTIMIZING SERVER RESOURCE USAGE
Edwar Ali
STMIK-AMIK RIAU, Indonesia
16
CS-15
NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING APPROACH OF
WIRELESS PRICING MODELS
Irmeilyana, Fitri Maya Puspita, Indrawati
Sriwijaya University, Indonesi
xvi
CS-16
SEGMENTATION OF URDU NASTALIQ SCRIPT
USING STRUCTURAL FEATURES
Aliya Khan
National University of Science and Technology, Pakistan
18
CS-18
IMPLEMENTATION OF AUDIO WATERMARKING
USING FAST FOURIER TRANSFORM FOR AUDIO
DIGITAL COPYRIGHT PROTECTION
Megah Mulya, Yogha Saputra Utama
Sriwijaya University, Indonesia
19
CS-19
APPLICATION OF NFC TECHNOLOGY FOR
CASHLESS PAYMENT SYSTEM IN CANTEEN
Evizal Abdul Kadir
1, Sri Listia Rosa
21
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia,
2Universitas
Islam Riau, Indonesia
20
CS-20
THE BIG DATA MANAGEMENT PROTOTYPE
DEVELOPMENT FOR ANALYSIS VARIOUS OF
DATA
S Heri Pracoyo
Bina Nusantara University, Indonesia
21
CS-21
OPTIMIZATION OF SALIENT OBJECT
SEGMENTATION BY USING THE INFLUENCE OF
COLOR IN DIGITAL IMAGE
Edvin Ramadhan, Iping Supriana Suwardi, Bambang
Riyanto Trilaksono
Institut Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia
xvii
CS-22
OBJECT DETECTION AND TRACKING
–
A
SURVEY
Rasool Reddy kamireddy
1, Hari Priya K
1, Mohan Lakshmi
21
Malla Reddy Institute of Technology & Science, India,
2
CMR Technical Campus, India
23
CS-23
IDENTIFICATION OF SPEED AND UNIQUE
LETTER OF HANDWRITING USING WAVELET
AND NEURAL NETWORKS
Esmeralda C. Djamal, Febriyanti
Universitas Jenderal Achmad Yani, Indonesia
24
CS-24
DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM FOR HEART
DISEASE DIAGNOSING USING K-NN
ALGORITHM
Tito Yuwono
1,Ipin Prasojo
1, Sri Kusuma Dewi
1, Ridho
Rahmadi
1, Noor Akhmad Setiawan
2, Hanung Adi
Nugroho
2, Anugrah Galang Persada
21
Islamic University of Indonesia Yogyakarta, Indonesia,
2
Gadjah Mada University, Indonesia
25
CS-25
EAR IMAGE RECOGNITION USING HYPER
SAUSAGE NEURON
Samsuryadi, Anggina Primanita
Sriwijaya University, Indonesia
xviii
TRACK: ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION
EL-01
REAL TIME ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING IN
PALM OIL PLANTATION USING WIRELESS
SENSOR NETWORK
Reza Firsandaya Malik
Sriwijaya University, Indonesia
27
EL-02
REALIZATION OF ZIGBEE WIRELESS SENSOR
NETWORKS FOR TEMPERATURE AND
HUMIDITY MONITORING
Helmy Fitriawan, Danny Mausa, Ahmad Surya Arifin,
Agus Trisanto
University of Lampung, Indonesia
28
EL-03
WIRELESS FIRE ALARM SYSTEM IN POWER
PLANT
Andri Suryabrata, Tatang Mulyana, Deden Witarsyah
Telkom Unversity, Indonesia
29
EL-04
IN SITU SOLAR PANEL OUTPUT POWER
MEASUREMENT RELATED TO CLIMATE
PARAMETERS USING DIGITAL RECORDING
Mardiyono, Endro Wasito, Sugeng Ariyono
Politeknik Negeri Semarang, Indonesia
xix
EL-05
GPS AND GSM MODEM APPLICATION AS CAR
POSITION AND FUEL MONITORING SYSTEM
Ahmad Taqwa, Masayu Anisah, Evelina, Sabilal Rasyad
and Amperawan
State Polytechnic of Sriwijaya, Indonesia
31
EL-06
GAS LEAK LOCALIZATION USING MOBILE
SENSOR NETWORKS
Siti Nurmaini
Sriwijaya University, Indonesia
32
EL-07
ELECTRONIC IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM OF
HAZARDOUS VOLATILE ORGANIC COMPOUND
GASES USING ROSELLE-CHITOSAN BLEND
Ahmed M. S. Eljali
1, Irwana Nainggolan
2, Shahrir
Hashim
1, Tulus Ikhsan Nasution
31
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia,
2University
Malaysia Perlis, Malaysia,
3Universitas Sumatera Utara,
Indonesia
33
EL-08
AN ULTRASONIC SYSTEM FOR DETERMINING
MANGO PHYSIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
Sallehuddin Ibrahim
1, Mohd Amri Md Yunus
1, Mohd
Taufiq Md Khairi
1, Aini Hazwani Mohd Zelan
21
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia,
2German
Malaysia Institute, Malaysia
xx
EL-09
CONTROL SYSTEM SEMI-AUTOMATIC
PALEMBANG SONGKET SHAWL USING SPLAY
TREE ALGORITHM BASED ATMEGA 8 SECTION
Sholihin
Polytechnic of Sriwijaya, Indonesia
35
EL-10
DESIGN OF UBIQUITOUS PULSE OXIMETRY
Reza Firsandaya Malik, Rifky Primartha, Adit Rubinurwan
Sriwijaya University, Indonesia
36
EL-11
DESIGN OF REAL TIME ANEMOMETER BASED
ON WIND SPEED AND DIRECTION
Triwahju Hardianto, Bambang Supeno, Dedy Kurnia
Setiawan, Syamsul Arifin, Gunawan, Ekky Wahyu
University of Jember, Indonesia
37
EL-12
SUB-TRESHOLD PERFORMANCE COMPARISON
OF JUNCTIONLESS FET AND SOI-BASED MOSFET
Munawar A Riyadi, Irawan Dharma Sukawati, Teguh
Prakoso and Darjat
Universitas Diponegoro, Indonesia
TRACK: INFORMATION SYSTEM
38
IS-01
COMPUTER ANXIETY AND COMPUTER
ATTITUDE TOWARDS CSE POLSRI STUDENT ON
WRITING THE FINAL
Irma Salamah, M. Aris Ganiardi, RD. Kusumanto
Politeknik Negeri Sriwijaya, Indonesia
xxi
IS-02
BUILDING STUDENT’S STUDY PATH USING
MARKOV CHAIN PROCESS WITH APRIORI
CROSS JOIN PEARSON CORRELATION
Tekad Matulatan, Martaleli Bettiza
Universitas Maritim Raja Ali Haji, Indonesia
40
IS-03
ANALYSIS AND IDENTIFICATION OF LANDUSE
ON THE EAST COAST OF SOUTH SUMATERA
USING GIS
Yuanita Windusari, Laila Hanum, and Margareta Sri
Lestari
Sriwijaya University, Indonesia
41
IS-04
EVALUATION OF MATURITY LEVEL OF
E-PROCUREMENT APPLICATION SYSTEMS
Irfan Sandy Kosasi
1, I Dewa Ayu Eka Yuliani
1, Vedyanto
21
STMIK Pontianak,
2Tanjungpura University Pontianak
42
IS-05
END-USER ACCEPTANCE OF E-GOVERNMENT
SERVICES IN AN INDONESIA REGENCY
Deden Witarsyah
1, Mohd Farhan Md Fudzee
2, Mohamad
Aizi Salamat
21
Telkom University, Indonesia,
2Universiti Tun Hussein
Onn, Malaysia
43
IS-06
USING Q-LEARNING FOR RECOMMEND
LEARNING OBJECT ON E-LEARNING SYSTEM
Hasibuan S Muhammad
Information System Institute Business and Informatics
Darmajaya, Indonesia
xxii
IS-07
THE INFLUENCE OF STEMMING ON INDONESIAN
TWEET SENTIMENT ANALYSIS
Ahmad Hidayatullah
Universitas Islam Indonesia, Indonesia
45
IS-08
AUTOMATED BALANCED DIET PLANNING
ALGORITHM FOR CHILDREN
Ashivini Kale
1, Nisha Auti
21
Symbiosis International University, India,
2Research Guide,
Symbiosis International University, India
46
IS-11
THE USE OF KPI IN GROUP DECISION SUPPORT
MODEL OF ICT PROJECTS PERFORMANCE
EVALUATION
Herri Setiawan, Jazi Eko Istiyanto, Retantyo Wardoyo,
Purwo Santoso
Gadjah Mada University, Indonesia
49
IS-12
DEVELOPMENT OF ECG FEATURE EXTRACTION
SOFTWARE
Pratondo Busono
Center for Information and Communication Technology
(BPPT) Kawasan PUSPIPTEK Serpong, Indonesia
xxiii
TRACK: ELECTRICAL & POWER ENGINEERING
PE-01
POTENTIAL OF RESIDENTIAL
GRID-CONNECTED PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM AS THE
FUTURE ENERGY SOURCE IN MALAYSIA
S. S. Abd Wahid
1, Z. Nawawi
2, M. I. Jambak
2, M. A. B.
Sidik
2, Y. Z. Arief
3, M. W. Mustafa
3, Z. Adzis
31
Universiti Teknologi MARA, Malaysia,
2Sriwijaya
University, Indonesia,
3Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
Malaysia
52
PE-03
GENERATING ELECTRICITY USING PV/FC
HYBRID SYSTEM
Z. Nawawi
1, M. A.B. Sidik
1, M.I. Jambak
1, R.F. Kurnia
1,
A. S. Aziz
2, H. J. Kareem
2, A. Z. Abdulameer
2, M. A. A.
Aziz
2, Z. Buntat
2, Y. Z. Arief
21
Sriwijaya University, Indonesia,
2Universiti Teknologi
Malaysia, Malaysia
54
PE-04
TRANSFORMER FAULT EARLY WARNING
SYSTEM MODEL USING GSM NETWORK
M. A. M. Azmi
1, Z. Nawawi
2, M. I. Jambak
2, M. A. B.
Sidik
2, Y. Z. Arief
3, Z. Adzis
3, N. A. Muhamad
31
Tenaga Nasional Berhad, Malaysia,
2Sriwijaya University,
Indonesia,
3Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia
xxiv
PE-05
EXPERIMENTAL AND THEORETICAL
PREDICTION OF OZONE YIELD BY HIGH
FREQUENCY SILENT DISCHARGE
Mochammad. Facta
1, Hermawan
1, Zainal Salam
2, Zolkafle
Buntat
21
Universitas Diponegoro, Indonesia,
2Universiti Teknologi
Malaysia, Malaysia
56
PE-06
TRANSMISSION-LIGHTNING-ARRESTER : A
LOCATION DETERMINATION USING FLASH
M. I. Jambak
2, M. A. B. Sidik
1,2, Z. Buntat
1, Z. Nawawi
2,
R.F. Kurnia
2, Y. Z. Arief
1, A. A. Wahab
3, Z. Ramli
3, M. E.
Ramly
31
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia,
2Sriwijaya
University, Indonesia,
3Tenaga Nasional Berhad, Malaysia
TRACK: ROBOTICS AND CONTROL SYSTEMS
57
RC-01
THE ELIMINATION OF OVERSHOOT CURVE
RESPONSE OF CLOSED LOOP IN
PROPORTIONAL INTEGRAL (PI) CONTROLLER
Azwardi, Cekmas Cekdin
State Polytechnic of Sriwijaya, Indonesia
58
RC-02
PRESSURIZER SIMULATOR
Andri Suryabrata, Tatang Mulyana, Deden Witarsyah
Telkom Unversity, Indonesia
xxv
RC-03
OBSTACLE AVOIDANCE FUNCTIONS ON ROBOT
MIROSOT UPN "VETERAN" YOGYAKARTA
Wilis Kaswidjanti, Hidayatulah Himawan, Awang
Hendrianto Pratomo, Hafidz Fajar Abdur Rahman
UPN "Veteran" Yogyakarta, Indonesia
60
RC-04
DEVELOPMENT OF THE PD/PI EXTENDED
STATE OBSERVER TO DETECT SENSOR AND
ACTUATOR FAULTS
Katherin Indriawati, Trihastuti Agustinah, Achmad Jazidie
ITS, Indonesia
61
RC-05
DESIGN OF MASSIVE ACTUATIRS FOR 3D
ROBOT MANIPULATORS
Felix Pasila, Hans Natalius, Roche Alimin
Petra Christian University, Indonesia
62
RC-06
PATTERN RECOGNITION APPROACH FOR
FORMATION CONTROL OF SWARM ROBOTS
USING FUZZY-KOHONEN NETWORKS
Siti Nurmaini
Sriwijaya University, Indonesia
63
RC-07
STUDY OF VEHICLE MOVEMENT FOR MIXED
TRAFFIC MODELING USING SOCIAL FORCE
MODEL
Rina Mardiati
1,21
Institut Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia,
2Sunan Gunung
Djati State Islamic University of Bandung, Indonesia
xxvi
RC-08
BRIEF REVIEW ON FORMATION CONTROL OF
SWARM ROBOT
Ade Handayani
1, Siti Nurmaini
2, Irsyadi Yani
21
State Polytechnic of Sriwijaya, Indonesia,
2Sriwijaya
University, Indonesia
65
RC-09
REMOTE CONTROL SYSTEM FOR MULTI
MOBILE ROBOT USING A COMBINATION OF
COMPUTER-MICROCONTROLLER
Nanang Ismail
1, Okyza, MP
1, Dimas Widyasastrena
21
SGD State Islamic University, Indonesia,
2Indonesia
Computer University, Indonesia
66
RC-10
DEVELOPMENT OF FUZZY LOGIC BASED
TEMPERATURE CONTROLLER FOR DIALYSATE
PREPARATION SYSTEM
Pratondo Busono, Ario Fitrianto, Teguh Handoyo, Arief
Barkah, Yaya Suryana, Riyanto, Rony Febryarto
Center for Information and Communication Technology
(BPPT) Kawasan PUSPIPTEK Serpong, Indonesia
67
RC-11
SENSORLESS SOLAR TRACKER BASED ON SUN
POSITION FOR MAXIMUM ENERGY
CONVERSION
Syafii, Refdinal Nazir, Muhammad Hadi Putra, and
Kamsory
Andalas Univesity, Indonesia
xxvii
RC-12
REVIEW ON ODOR LOCALIZATION
Nyayu Latifah Husni, Siti Nurmaini, Irsyadi Yani
State Polytechnic of Sriwijaya, Indonesia
69
RC-13
NCTF-FL CONTROLLER FOR PENDULUM
BALANCING SYSTEM
Noor Hisham Jalani
Department of Electrical and Electronic Technology
Advanced Technology Training Centre (ADTEC), Malaysia
70
RC-14
INTEGRATING MICROSOFT KINECT WITH
ARDUINO: REAL-TIME SKELETON HUMAN
TRACKING ON ANDROID PUPPET
I Putu Lesmana
Polytecnic State of Jember, Indonesia
TRACK: TELECOMMUNICATION & WIRELESS
71
TW-01
CAR ENGINE STORAGE AND SPARE PARTS
MANAGEMENT SYSTEM USING RFID
TECHNOLOGY
Evizal Abdul Kadir
1, Siti Mariyam Shamsuddin
1, Sri Listia
Rosa
21
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia,
2Universitas
Islam Riau, Indonesia
xxviii
TW-02
RADIO SUBCARRIER MULTIPLEXING IN
CONJUNCTION WITH OPTICAL MODE DIVISION
MULTIPLEXING FOR 5G NETWORKS
Angela Amphawan, Baseem Khalaf, Wanasiah Tahir,
Hafiza Haron, Rukhiyah Adnan
University Utara Malaysia, Malaysia
,
Kolej Poly-Tech
MARA, Malaysia
73
TW-04
AN EFFICIENT MODULATION AND CODING
SCHEME SELECTION MECHANISM FOR
SINGLE-CELL MODE E-MBMS
Mohd. Algharem
1, Mohd. Hasbullah Omar
1, Ibrahim
Alghamdi
2, Rahmat Budiarto
21
Universiti Utara Malaysia, Malaysia,
2Albaha University,
Saudi Arabia
75
TW-05
MODE DIVISION MULTIPLEXING OF LG AND HG
MODES IN RO-FSO
Angela Amphawan
1, Sushank Chaudhary
1, Hafiza Samad
2,
Jihadah Ahmad
21
Universiti Utara Malaysia, Malaysia,
2Kolej Poly-Tech
MARA, Malaysia
76
TW-07
GAIN ENHANCEMENT OF OCTAGON
MICROSTRIP YAGI ANTENNA UTILIZING 1-D
PHOTONIC CRYSTAL (PCS) COVER
K. Quzwain, A. Ismail, A. Sali, A. R. H. Alhawari
Universiti Putra Malaysia, Malaysia
xxix
TW-08
MDM OF HYBRID MODES IN MULTIMODE FIBER
Angela Amphawan
1, Yousef Fazea
1, Mohd Samsu Sajat
1,
Roslinda Murad
2, Hajar Alias
21
Universiti Utara Malaysia, Malaysia,
2Kolej Poly-Tech
MARA, Malaysia
79
TW-09
SIGNALLING COST MODEL TO EVALUATE
MOBILITY IN MIXED WIRELESS IPV4/IPV6
NETWORKS
Bassam Naji Altamimi
1, Lelyzar Siregar
2, Rahmat Budiarto
31
Taibah University, Saudi Arabia,
2Universitas Sumatera
Utara, Indonesia,
3Albaha University, Saudi Arabia
80
TW-10
A BROADBAND MIMO ANTENNA FOR ACCESS
NETWORK
Teguh Prakoso
1,2, N. Shazwani M. Noor
2, E.H. Hadyan
1,
M.A. Riyadi
1, Razali Ngah
21
Universitas Diponegoro, Indonesia,
2Universiti Teknologi
Malaysia, Malaysia
81
TW-11
MOBILE SPECTRUM EXCHANGE INFORMATION
FOR OFDM BASED COOPERATIVE SPECTRUM SENSING
COGNITIVE RADIO NETWORKS
Arief Marwanto
1,, S. Kamilah S. Y
2,, M. Haikal Satria
21
Universitas Islam Sultan Agung, Indonesia
2
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia
xxx
TW-12
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS ON SIGNAL
STRENGTHS OF HUTCHISON, INDOSAT,
TELKOMSEL AND XL AXIATA OPERATORS BY
APPLYING RF SIGNAL TRACKER SOFTWARE IN
THE AREAS OF THE PROTOCOL STREETS OF
PEKANBARU DISTRICT
Yusnita Rahayu, Chandra, Anhar
University of Riau, Indonesia
Proceeding of International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computer Science and Informatics (EECSI 2015), Palembang, Indonesia, 19 -20August 2015
Computer Anxiety and Computer Attitude towards
Computer Self Efficacy (CSE) Polsri
Telecommunication Engineering Student on Writing
the Final Report
Irma Salamah
Electrical Engineering Politeknik Negeri Sriwijaya Palembang, Sumatera Selatan Email : [email protected]
M. Aris Ganiardi, RD. Kusumanto
Informatics Management, Electrical Engineering Politeknik Negeri Sriwijaya
Palembang, Sumatera Selatan
[email protected], [email protected]
Abstract— Various attitudes emerged and shown by
individuals for the presence of computer. Although many benefits are felt by the computer, but there are some people who feel anxious with the computer (computer anxiety). Computer attitude showed no reaction or behave the computer by pleasure or displeasure against the computer. The phenomenon that arises is computer anxiety and computer attitude can affect a person's expertise in the use or operate the computer. This study aims to examine how the effect of computer anxiety and computer attitude towards computer self efficacy on the 6th semester student telecommunications engineering POLSRI. Samples taken in this study were all students of telecommunication engineering 6th semester POLSRI totaling 89 people. The results showed computer anxiety and computer attitude not affect the computer self-efficacy 6th semester student of telecommunications engineering POLSRI. This is due because the 6th semester student of telecommunications engineering POLSRI have positive feelings to learn the computer either by themselves or through a learning courses.They also realize that the computer provides many benefits. With the computer, the information can be obtained more quickly and efficiently. Computer is a necessity, can enhance human life, and was instrumental in education and employment.
.
Keywords—computer anxiety, computer attitude, computer self efficacy
BACKGROUND
The use of computers in education is needed. Almost all elements of the college requires a computer as a tool in completing the work. Lecturers as teachers demanded to be able to use a computer to provide course materials to students, making research as part of a tri dharma college. Students were always dealing with computers in their tasks, to complete assignments and thesis / final report or searching data via the internet.
Changes in the use of software and computer programs in the completion of the thesis also often cause pressure (stress) within the student [6]. One of the psychological distress experienced by students is computer anxiety. Computer anxiety can be defined as rejection to change. Rejection can be a symptom or something else like a fear of the unknown, fear of failure, or unwillingness to change current state [6]. Computer Anxiety is a person's tendency to be hard, worry,
or fear about the use of computers in the present or in the future [11]
Literature review
Previous Research
Research relating to computerphobia has never been done. The study conducted by [8]; [2]; [13], and [6]. [8] conducted a study titled "The Effect of Computer Anxiety Factor, Computer Attitude and Math Anxiety against Expertise in End User Computing (Survey on Student Programs Accounting Education Yogyakarta State University class of 2004 and class of 2004). The sample used in this study is 61 people. The results showed a significant effect between computer anxiety and End User Computing, significant effect between computer attitude with expertise End User Computing, significant effect between Math anxiety, computer attitude, Math anxiety towards expertise in End User Computing. The study has similarities with this study that use the same independent variables namely Computer Anxiety and Computer Attitude. While the difference is [8] adds another independent variable namely Math anxiety. [2] conducted a study with the title "Computer Anxiety and Characteristics of Personality Type in Student Accounting." The study was conducted on 139 accounting student at the Faculty of Economics and Business Universitas Gadjah Mada. The conclusion of this study showed no anxiety of computer on accounting students. There is a significant correlation characteristics of students with type sensing-intuitive (sensing-sensing-intuitive) and mind-feelings (thinking-feeling) with computerphobia on accounting students. Gender and the IPK does not affect a student computer anxiety.
Research Saiful [2] have in common with this study in one variable computer anxiety. The difference seen from the other independent personality type. Subjects were accounting students of Gadjah Mada University. While in this study conducted in telecommunication engineering students POLSRI.
Proceeding of International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computer Science and Informatics (EECSI 2015), Palembang, Indonesia, 19 -20August 2015
results showed computer anxiety has significant effect on computer use. There are differences in computer anxiety between male and female students. Female students have a computer anxiety level higher than the male students. The results showed that curriculum has a significant effect on the of computer use. The study has similarities with this study that in one independent variable namely Computer Anxiety. While the difference is another independent variable that is gender and curriculum.
While [6] conducted a study on 110 students majoring in accounting Yogyakarta State University is implementing a thesis. The results show computer anxiety and computer attitude affect the use of computer skills of students in the writing.
Computer Anxiety Vs Computer Self Efficacy
Computer anxiety is fear or excessive anxiety to cause physiological consequences to students. Computer anxiety is a picture of the emotional fear, anxiety, and phobias are perceived by the individual to the interact with the computer or when thinking about using a computer.
According [11] definition of computer anxiety is a person's tendency becomes difficult, worry, or fear regarding the use of information technology (computer) in the present or in the future. According [13], the definition of computer anxiety is a particular type of stress was associated with negative beliefs about computers, the problem - a problem in using computers and the rejection of the machine.
According to [15], computer anxiety is a technophobia, where the computer is one of the growing technology in human life.
Computer Anxiety a person's tendency to be difficult,
worry, or fear about the use of computers in the present or future [4]. According to [7] computer self efficacy is defined as “an individual’s judgement of their capability to use a computer.” Research model shown in fig. 1
Computer anxiety associated with computer self efficacy. A person with a high level of anxiety computing will strive to avoid all things computer so will result in lower computing capabilities. Computer anxiety is one of technophobia [12]. Individuals who have a high sense of anxiety that shows a lack of self-efficacy [3]. If individuals feel anxious in the use of computers, then he has a reason to feel anxious that show low self-efficacy. Based on the description above hypotheses can be constructed are as follows:
H1 : computer anxiety affect towards computer self
efficacy Polsri telecommunication engineering student
Computer Attitude Vs Computer Self Efficacy
A number of experts giving a definition of computer attitude. According [16] computer attitude is defined as "a reaction or judgment to the computer by the pleasure or displeasure of the computer." In this case there is a group of people who happy (optimistic) with the development of the computer world. On the other hand a group of people unhappy (pessimistic) with these developments. According
[5] computer attitude shows "reaction or judgment to the computer by the pleasure or displeasure of the computer." The computer attitude shows feeling happy or not happy that involves a person's behavior. It is associated with behavioral theory by [1], which explains that a person's attitude is influenced by external stimuli. In the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) by [1] explained that "the motivation to behave in a certain person with the behavioral intention the best starting behavior and finally can make a person act (Attitude)." TPB focuses on conception attitude (attitude), subjective norms and perceived control explains the differences between the behaviors. [1] add one construct that does not exist in the TRA, which is perceived behavioral control. These constructs are added in an attempt to understand the limitations of the individual in order to perform certain behaviors [4]. If someone believes that the outcome is positive then the execution behavior will have a positive attitude as well. Subjective norms determined by the normative beliefs which is important to referent Individual [17]. Behavior is not only determined by the attitude and subjective norms, but also the individual's perception of control that can be done which is based on control beliefs [9]. Connection with the computer attitude, the attitude theory can explain that the computer attitude is determined by the value of the benefit perceived usefulness and social norms, where these factors are factors that contribute to the acceptance of the technology computer.
Computer attitudes show a reaction or judgment against the computer by pleasure or displeasure against computer [10]. Computer attitude is indicated from the attitude of optimism, pessimism, and intimidation. Computer attitude affects a person's ability to computing. Computer attitude with high aspect optimistic will cause high computing capability, while computer attitude with high the aspects of pessimistic and intimidation that would cause low computing capability. Based on the description above hypothesis can be constructed are as follows:
H2 : computer attitude affect towards computer self efficacy Polsri telecommunication engineering student
RESEARCH METHODS
The research population is all students of 6th semester telecommunications study program State Polytechnic Sriwijaya. Totaling 89 student consisting of 2 regular classes and two non regular classes. The type of data collected is primary data and secondary data. The primary data obtained through interviews with students of 6th semester POLSRI telecommunication techniques, using questionnaire that has been provided. Secondary data is data obtained from the academic Electrical Engineering Department.
Proceeding of International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computer Science and Informatics (EECSI 2015), Palembang, Indonesia, 19 -20August 2015
Fig 1. Research model
Measurement of variables in this study done in order for proposed hypothesis can be tested and research questions can be answered. Two main criteria to test how well the measurement instrument used is by validity and reliability testing. The validity testing of this research done by calculating the correlation between the scores with the help of SPSS applications. Validity testing is also done for each of the questions used in the variable. While the reliability test can only be done after a ensured instrument valid. Reliability testing use the SPSS by looking at the value of coefficient Alpha or Alpha Cronbach.
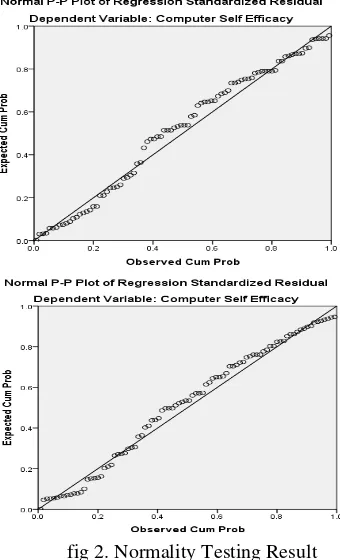
This research has two hypotheses. The hypothesis tested with a simple linear regression analysis. Further, classical assumption testing consist of normality test (Figure 2), multicollinearity and heterocedasticity test (Tables 4 and 5).
CURRENT RESULTS
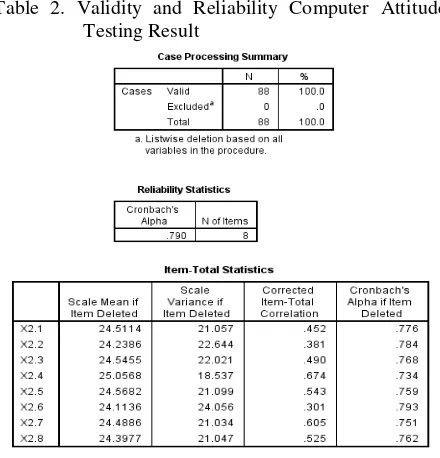
Validity testing in this research is done by calculate correlation between scores by SPSS 20.0. Validity testing is also done for each of the questions used in the variable. While the reliability testing can only be done after a certain instrument validity. Reliability testing in this study use the SPSS 20.0 to see the value of coefficient Alpha or Alpha Cronbach (Tables 1,2, and 3).
Table 1. Validity and Reliability Computer Anxiety Testing Result
Table 2. Validity and Reliability Computer Attitude Testing Result
Table 3. Validity and Reliability Computer Self Efficacy Testing Result
This study has two hypotheses. The hypothesis tested in this study with a simple linear regression analysis. Further, classical assumption testing consist of normality test (Fig 2), multicollinearity and heterocedasticity test (Tables 4 and 5). Computer Anxiety
Computer Self
Efficacy
Proceeding of International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computer Science and Informatics (EECSI 2015), Palembang, Indonesia, 19 -20August 2015
fig 2. Normality Testing Result
Based on the output Normal P-P Plot shows that the distribution of existing data spread evenly all diagonal axis of the graph. In the graph dots spread around the diagonal line, and its distribution follows the direction of the diagonal line. Decision-making, if the data spread around the diagonal line and follow the direction of the diagonal line, the regression model to meet the assumption of normality. Thus the regression model is feasible to used to predict computer self-efficacy by independent variable input.
Table 4. Mulicolinearity Testing Result
Multicolinearity test known from VIF value for each predictor. Requirements to be considered free from multicollinearity is when the VIF predictor value does not exceed 10. The results for the third variable coefficients visible VIF figure does not exceed 10, so that does not happen multikolinieritas. Thus the regression models used
for prediction feasible computer self-efficacy by independent variable input.
Table 5. Heterocedasticity Testing Result
Heterocedasticity testing done using Spearman's rho, from the table above shows that the correlation between computer anxiety, computer attitude, and unstandardized residual generate greater significance value of 0.05. It can be concluded that the regression model did not reveal any problems heterokedasticity.
After the classical assumption testing we do regression analysis (Table 6).
Tabel 6. H1 and H2 Testing Result
For hypothesis 1, T test gives the value -0.432 (< t table, t table = 1.988) with a significance level of 0.667. Because t count < t table with a significance level > 0.05 then partially computer anxiety not affect computer self-efficacy POLSRI students in completing the final task.
Proceeding of International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computer Science and Informatics (EECSI 2015), Palembang, Indonesia, 19 -20August 2015
the computer attitude not affect computer self-efficacy POLSRI students in completing the final task.
From the results of data processing by using SPSS, obtained 2 regression equation: Y = 30.961 - 0.100 X1 and Y = 24.539 + 0.178 X 2.
The constanta in this study 30.961. It has meaning if there is no computer anxiety, computer self-efficacy students will increase 30.961. Coefficient regression X1 -0.100, meaning the addition of one factor of computer anxiety, the computer self-efficacy of students will decrease by 0,100.
The constanta in this study 24.539. It has meaning if there is no computer anxiety, computer self-efficacy students will increase 24.539. Coefficient regression X2 0.178, meaning the addition of one factor of computer anxiety, the computer self-efficacy of students will increase by 0,178.
Results of the hypothesis presented in Table 7.
Tabel 7. Hypothesis Result H1-H2
Hipotesis H1-H2 Uji T Sign Hasil Hipotesis
computer anxiety affect
towards computer self
efficacy Polsri
telecommunication engineering student
t count < t tabel
> 0,05 Not
Accepted
computer attitude affect towards computer self
efficacy Polsri
telecommunication engineering student
t count < t tabel
> 0,05 Not Accepted
Hypothesis H1 is not accepted. These results are not in accordance with the results of research conducted by [6], [13], and [8] who found computer anxiety affect the use of computer skills of students. College students with a low level computer capability have an uncomfortable feeling when
interacting with a computer. For POLSRI
telecommunications engineering students, the computer is not something to be feared. They anticipate the fear of computers by learning by themselves from the internet or courses. In addition the duties of lecturers generally done by a computer. So that the computer anxiety had no effect in
computer capability POLSRI telecommunications
engineering students in the final project.
H2 hypothesis is not accepted. These results are not in accordance with the results of research conducted by [6] and [8] who found the computer attitude affect the use of computer skill of students. This is due because the positive feelings to learn computers. They also realize that now is the era of computerization. Computer provides many benefits to human life. With the computer information can be obtained more quickly and efficiently. They do not think the computer
will control people in the future, because the computer itself is manmade so the man who will remain in control of the computer. For that computer attitude does not affect the ability of telecommunications engineering students POLSRI the final project.
The influence with a very small percentage of the computer anxiety and computer attitude due to some technical aspects such as computer programming languages. Students tend to be lazy to learn computer programming languages because they find it difficult to understand. This is why only a fraction of telecommunications engineering students take final POLSRI related to programming languages.
CONCLUSION
This research is described in the structural model to predict the effects of computer anxiety and computer attitude toward
computer self efficacy POLSRI telecommunications
engineering students. The results show computer anxiety and computer attitude is not affect the ability POLSRI telecommunications engineering students in completing the final task. The percentage student that take the project related computing quite a lot. This is due because the positive feelings to learn the computer either by themselves or through a learning courses.They also realize that the computer provides many benefits. With the computer, the information can be obtained more quickly and efficiently. Computer is a necessity, can enhance human life, and was instrumental in education and employment.
ADVICE
For further research in the same topic can expand the sample to the students POLSRI other departments, develop perspectives studied, for example: testing the effect of the characteristics of respondents to the computer anxiety and computer attitude towards computer self efficacy, and develop variable computer anxiety and computer attitude as the variables that affect the variable computer self efficacy.
REFERENCES
[1] Ajzen, I dan Madden. Prediction of Goal-Directed Behavior: Attitudes, Intentions, and Perceived Behavioral control, Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, Vol. 22, pp. 453-474. (2005)
[2] Ali Syaiful, dan Fadila. Kecemasan Berkomputer (Computer Anxiety) dan Karakteristik Tipe Kepribadian pada Mahasiswa Akuntansi Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta. Simposium Nasional Akuntansi ke‐11 Pontianak. (2008)
[3] Bandura, A.. Self-Efficacy: The exercise of control. New York: W. H. Freeman. (2006)
[4] Chau, P. Y. K., dan Hu, P. J. Examining the Technology Acceptance Model Using Physical Acceptance of Telemedicine Technology, Journal of Management Information Systems, Vol. 16, No. 2, pp. 91-112. (2002)
[5] Dhandung. Pengaruh Computer Anxiety Terhadap Keahlian Akuntan Pendidik Dalam Menggunakan Komputer. Skripsi. (Tidak Dipublikasikan). Universitas Sebelas Maret Surakarta. (2004) [6] Dinar Widya Utomo. Pengaruh Computer Anxiety dan Computer
Proceeding of International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computer Science and Informatics (EECSI 2015), Palembang, Indonesia, 19 -20August 2015
Komputer Pada Penulisan Skripsi. Skripsi. Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta. (2012)
[7] Doyle, E. Computer Anxiety, Self-Efficacy, Computer Experience: An investigation throughout a Computer Science degree. ASEE/IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference, October 19 – 22,(2005)
[8] Dyah Ratna. Pengaruh Faktor Computer Anxiety, Computer Attitude, dan Math Anxiety terhadap Keahlian dalam End User Computing (Survei pada Mahasiswa Jurusan Pendidikan Akuntansi Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta angkatan 2004 dan angkatan 2004). Skripsi (Tidak diterbitkan). Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta. (2007)
[9] Francis, J.J., Eccles, M.P., Johnston, M., Walker, A., Grimshaw, J., Foy, R., Kaner, E.F.S., Smith, L., dan Bonetti, D. Constructing Qustionnaires Based on The Theory of Planned Behaviour. A Manual for Health Services Researches. United Kingdom: Quality of Life and Management of Living Resources. (2004)
[10] Horvat, J., Petric, G., & Mikrut, M. Measuring Computer and Web Attitudes Using Cas and Was Measurement Instruments, MIS Quarterly, 23, 2, pp. 239–260. (2006)
[11] Igbaria, M., & Parasuraman, S. A Path Analytic Study of Individual Characteristics, Computer Anxiety, and Attitudes Towards Microcomputers. Journal of Management373-388. (1989). [12] Indriantoro, Nur. Pengaruh Komputer Anxiety terhadap Keahlian
Dosen dalam Pengunaan Komputer, Jurnal Akuntansi dan Auditing Indonesia. Vol.4, No.2. (2000)
[13] Jayanto Teguh. Pengaruh Computer Anxiety, Gender, dan Kurikulum Perguruan Tinggi Negeri terhadap Keahlian Penggunaan Komputer. Skripsi (Versi Elektronik). Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Brawijaya Malang. (2008)
[14] Kharisma Lanang. Pengaruh Computer Anxiety dan Computer Attitude Terhadap Keahlian Mahasiswa Akuntansi Dalam Menggunakan Komputer Akuntansi. Skripsi (Versi Elektronik). Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Pembangunan Nasional Veteran Jakarta. (2010).
[15] Orr. Barriers to the Treatment of Social Anxiety. Journal of Psychiatry, 1(57), 521-527. (2000).
[16] , D., & Gudono. Pengaruh Faktor Demografi dan Personality terhadap keahlian dalam End User Computing. Jurnal Riset Akuntansi Indonesia, 2(1), 20-36. (1999).