i
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ SPEAKING SKILL
THROUGH FOCUS GROUP DISCUSSION (FGD)
TECHNIQUE
(A Classroom Action Research for the Second Grade
Students of SMPN 2 MERTOYUDAN in the Academic
Year of 2017/2018)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a partial fulfillment of the
requirements for the degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd)
English
Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
By:
ISTI WULAN KHOSIDAH
NIM. 113-13-147
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
ii
DECLARATION
“In the name of Allah the Most Gracious and the Most Merciful”
In the name of Allah,
Hereby, the researcher declares that this graduating paper is written by the
researcher herself. This paper does not contain any materials which have been
published by other people; and it does not cite any other people‟s ideas except the
information from the references.
The researcher is capable to account her graduating paper if in the future it
can be proved of containing others‟ idea or in fact that the researcher imitates the
others‟ graduating paper. Likewise, this declaration is written by the researcher to
be understood.
Salatiga, August 25th2017
The researcher,
IstiWulanKhosidah
iii
Salatiga, August 29th 2017
Mashlihatul Umami, S.Pd.I, M.A
The lecturer of English Education Department
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR‟S NOTE
Case: Isti Wulan Khosidah‟s Graduating Paper
Dear,
Dean of Teacher Training and Education
Faculty Assalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb
After reading and correcting Isti Wulan Khosidah‟s graduating paper entitled “IMPROVING STUDENTS’ SPEAKING SKILL THROUGH FOCUS
GROUP DISCUSSION (FGD) TECHNIQUE (A Classroom Action Research of the Second Grade of SMPN 2 MERTOYUDAN in the Academic Year of 2016/2017)”, I have decided and would like to propose that this paper can be accepted by the Teacher Training and Education Faculty. I hope this paper will be
examined as soon as possible.
Wassalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb.
Counselor,
iv
A GRADUATING PAPER
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ SPEAKING SKILL THROUGH FOCUS
GROUP DISCUSSION (FGD) TECHNIQUE
(A Classroom Action Research for the Second Grade Students of SMPN 2 MERTOYUDAN in the Academic Year of 2017/2018)
WRITTEN BY: ISTI WULAN KHOSIDAH
NIM: 113 13 147
has been brought to the board of examiners of English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty at State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga on September 15th, 2017, and hereby considered to complete the requirements for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd.) in English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty.
Board of examiners
Head : Noor Malihah, Ph.D
Secretary : Mashlihatul Umami, M.A
First Examiner : Hammam, Ph.D
Second Examiner : Sari Famularsih, M.A
Salatiga, September 15th , 2017
Dean of Teacher Training and
Education Faculty
Suwardi, M.Pd.
v
MOTTO
ِرْسُعْلا َعَم َّنِإَف
اًرْسُي
﴿
٥
﴾
اًرْسُي ِرْسُعْلا َعَم َّنِإ
﴿
٦
﴾
“
Karena sesungguhnya sesudah kesulitan itu ada
kemudahan. Sesungguhnya sesudah kesulitan itu ada
kemudahan.
”
vi
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is dedicated to:
1. My beloved mother (Kartini) and Father (Ismail), thanks for your all of the
prayer, struggle and support.
2. My beloved brother (Joko) and sister (Sani), thanks for your motivation
and support.
3. My beloved best friend (Lia Anggraeni, Siti Muzaiyanah and Sawitri),
thanks for your help, motivation and support.
4. My big family in Najma (Endang, Sugiarti, Naba ul Kusna, Muntoyah,
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of Allah, The Most Gracious and The Most Merciful, The Lord
of Universe. Because of Him, the researcher could finish this graduating paper as
one of the requirement for Sarjana Pendidikan in English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies
(IAIN) Salatiga.
Secondly, peace and salutation always be given to our prophet Muhammad
SAW who has guided us from the darkness to the lightness. However, this success
would not be achieved without supports, guidances, advices, helps, and
encouragements from individual and institution, and the researcher somehow
realize that an appropriate moment for me to deepest gratitude for:
1. Rahmat Hariyadi, M. Pd. as the Rector of State Institute for Islamic
Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
2. Suwardi, M. Pd. as the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
3. Noor Malihah, Ph. D. as the Head of English Education Department
4. Mashlihatul Umami M. A., as a counselor who has educated, supported,
directed and given the researcher advices, suggestions, and
recommendations for this thesis from beginning until the end.
5. All of the lecturers in English Education Department. Thanks for your
education
6. All of the staffs who have helped the researcher in processing of
viii
7. Mr Aziz Amin Mujahidin, M. Pd as the Headmaster of SMP N 2
Mertoyudan.
8. All of teachers and students, especially for my teacher counselor Mrs.
Ninik Satriyati, S. Pd., thanks for your kindness, help, guidance and
advice.
9. Mrs. Rindarti, S. Pd as the English teacher of second grade SMP N 2
Mertoyudan, thanks for your help.
10.Students of VIII F SMPN 2 Mertoyudan, thanks for their cooperation
during the teaching learning process.
11.My beloved family, especially my parents and my sister also my brother
who always support and advise me.
12.My best friends (Lia, Muza, Sawitri), thanks for being by my side for your
support and success for you all.
13.All friends in wisma Najma, Najwa, Safira and Zahra.
14.All of my close friend who I could not mention one by one.
15.All of my friend in IAIN Salatiga, especially for English Department in
the cohort of 2013, from A until E class whose names cannot be
mentioned one by one, thanks for being my friends.
16.The big family of LDK and Mahasiswa Al Khidmah Kota Salatiga.
Thanks for everything.
Finally this graduating paper is expected to be able to provide useful
ix
accept more suggestions and contributions from the readers for the improvement
of the graduating paper.
Salatiga,August 25th2017
The researcher,
Isti Wulan Khosidah
x
ABSTRACT
Khosidah, Isti Wulan. 2017. IMPROVING STUDENTS‟ SPEAKING SKILL THROUGH FOCUS GROUP DISCUSSION (FGD) TECHNIQUE (A Classroom Action Research of the Second Grade of SMPN 2 Mertoyudan in the Academic Year of 2017/2018). Counselor: Mashlihatul Umami, M.A.
Keywords: Focus Group Discussion (FGD), Improving Speaking Skill
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE ... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTE ... iii
STATEMENT OF CERTIFICATION ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... x
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... xi
LIST OF FIGURES ... xiii
LIST OF TABLES ... xiv
LIST OF CHARTS ... xv
CHAPTER 1 : INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Research ... 1
B. Statement of the Problem ... 4
C. Objectives of the Study ... 4
D. Limitation of the Study ... 5
E. Benefits of the Study ... 5
F. Definition of the Key terms ... 6
xii
CHAPTER II : THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Review of Previous Research... 9
B. Focus Group Discussion (FGD) ... 12
C. Speaking Skill ... 19
CHAPTER III : METHOD OF RESEARCH
A. Setting and Time of Research ... 28
B. The Subject of the Research ... 30
C. Method of Research ... 32
CHAPTER IV : DATA ANALYSIS
A. Implementation of Research ... 43
B. Improvement of Students‟ Speaking Skill through
Focus Group Discussion (FGD) Technique in SMPN
2 Mertoyudan ... 61
C. Analysis and Discussion ... 71
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
A. Conclusions ... 75
B. Suggestion ... 76
REFERENCES
xiii LIST OF FIGURES
xiv LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1 Oral Proficiency Scoring Categories Grammar ...25
Table 2.2 Oral Proficiency Scoring Categories Vocabulary ...25
Table 2.3 Oral Proficiency Scoring Categories Comprehension ...26
Table 2.4 Oral Proficiency Scoring Categories Fluency ...26
Table 2.5 Oral Proficiency Scoring Categories Pronunciation ...26
Table 2.6 Oral Proficiency Scoring Categories Task ...27
Table 3.1 The Time of Research at SMP N Mertoyudan ...30
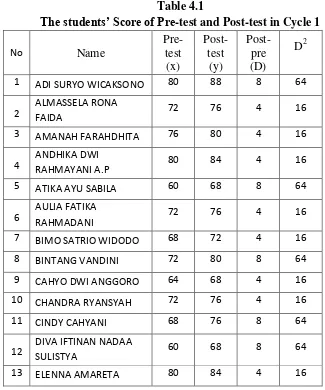
Table 4.1 The Students‟ Score of Pre-test and Post-tes in Cycle 1 ...61
Table 4.2 The Students‟ Score of Pre-tes and Post-tes in Cycle 2 ...66
xv LIST OF CHART
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter contains introduction of the graduating paper which consist of
many parts that explain what will we talk about in this graduating paper. The
contains of this introduction are background of the study, research question,
objectives of the study, benefits of the study, limitation of the study, definition of
keyterms, review of previous research and the outline of the research.
A. Background of The Study
Looking at the developing science and technology in our country, the
language becomes the main point. Language can be used to support them.
Language is considered to be a system of communicating with other using
sounds, symbols, and words in expressing a meaning, idea, or thought.
Language has an important thing in human activity to interact with other
people.
There are many languages that can be used to communicate with
other people in this world. One of them is English, English is the
international language in this world. English helps people to communicate
with other people from different countries background. The final objective
of teaching and learning process is the students are expected to master
four skills of language. English has been taught since the kindergarten
2
especially in Indonesia cannot comprehend English well because they do
not have background about the English language yet.
According to Fauziati (2008) as quoted by Wahyuni (2013) said that
one of the ways of communication is through speaking. Most of students
get difficulties to speak English although they have a lot of vocabulary and
can write them well. The problem is they are not confident and be afraid to
make mistake when speak up.
Based on the researcher‟s interview and observation in SMP N 2
Mertoyudan, most of students in the second grade have some problems in
speaking ability. They are afraid to speak English in front of class.
Speaking becomes a difficult subject to be learnt, because students are not
accustomed to speak English. They will be nervous when speak in front of
class because they are afraid if they make some mistakes, the teacher will
be angry. They are also shy with the other friends if they speak in wrong
pronounciation.
After the researcher observed the students in several meetings, the
researcher found some factors that showed why this condition happened.
The students did not have a good motivation to speak. When they have
limited vocabulary, they would be difficult to speak in English well. The
technique that the teacher used in teaching speaking is not attractive. The
teacher asked students to come in front of the class and asked them to
3
To make the students have strong motivation to learn English
language especially in speaking skill, the teacher should take the best
technique. In this case, the teacher uses Focus Group Discussion as
technique in teaching learning process. Focus Group Discussion technique
can help students to improve their speaking skill. Students have more self
–confidence to speak English because all of students have opportunity to
express their idea. In addition, students must not come in front of class to
speak up, as a result they are not nervous and be afraid again. According to
William (2012:56) proposes that:
“Facilitator or moderator should always remind themselves of the potential dangers that groupthink can pose on the outcome of FGD by ensuring fair distribution of opportunities to all participants to voice out their perspective. FGD participants voluntary assumption of leadership roles and overly assertiveness should be professional discouraged. Individual participants in FGD should be discouraged as much as possible from socially distancing themeselves from the others, in order not to influence or dictate indirectly the outcome of responses ”
In Focus Group Discussion (FGD) students can analyze and
understand the selected topic that be discussed. Harmer (2001:273) stated
that some discussion just happen in the middle of lessons and can provide
some of the most enjoyable and productive speaking in language classes.
One of the best ways of encouraging discussion is to provide activities
which force students to reach a decision.
From the clarification above, the researcher is interested in
conducting the research that will generate from the problem. So, it is the
4
Speaking Skill through Focus Group Discussion (FGD) Technique (A
Classroom Action Research of the Second Grade of SMPN 2 Mertoyudan
in the Academic Year of 2017/2018)”.
B. Research Question
Based on the phenomenon above, this research is aimed to give answers on the following problems:
1. Is the implementation of Focus Group Discussion (FGD) technique improve students’ speaking skill for the second grade students of SMPN 2 Mertoyudan in the Academic Year of 2017/2018?
2. How far is the improvement of Focus Group Discussion (FGD) technique for the students’ speaking skill for the second grade students of SMPN 2 Mertoyudan in the Academic Year of 2017/2018?
C. Objectives of the Study
The purposes of the study are:
1. To find out whether the implementation of Focus Group Discussion (FGD) technique can improve students’ speaking skill for the second grade students of SMPN 2 Mertoyudan in the Academic Year of 2017/2018.
2. To find out the improvement of Focus Group Discussion (FGD) technique in students’ speaking skill for the second grade students of SMPN 2 Mertoyudan in the Academic Year of 2017/2018.
5
This study concerns the use of Focus Group Discussion (FGD) technique to improve students’ speaking skill. The population is the students of 8th grade
students’ of SMPN 2 Mertoyudan in the academic year 2017/2018. E. Benefits of the Study
This research hopefully will be useful for the teachers, students and researcher. There are the benefits of the research:
1. Theoretical benefit
The result of this research can be used as the reference for
those who want to conduct research in English teaching to build
students‟ speaking skill and create an active class by teacher. Giving
English teachers a new experience to use Focus Group Discussion
(FGD) to improve the students‟ speaking skill.
2. Practical benefit
a. For another researcher :
This research can contribute to another researcher to find
out and determining the best technique to improve students‟
speaking skill.
b. For students :
1. It can improve the speaking skill in attractive way.
2. The students more interest to speak up in every situation.
c. For the teachers :
6
2. This research can improve the teachers‟ ability especially about
the application of Focus Group Discussion (FGD) in teaching
speaking.
d. For the researcher
From this research, the researcher can learn some ways to give motivation for the students to improve student’s speaking skill.
F. Definition of the Key terms
Avoiding some incorrect interpretations of this research title, it is important for researcher to explain the key terms used. Therefore, the researcher gives some description and explanation of the key terms to make the reader understand the study easier.
1. Focus Group Discussion (FGD)
According to Bader and Rossi (2002:2) Focus Group is the label given to a special type of group interview that is structured to gather detailed opinions and knowledge about a particular topic from selected participants.
According to Viji (2014:6) Focus Group Discussion (FGD) is a good way to gather together people from similar background or experiences to discuss a specific topic of interest. The group is guided by moderator or facilitator who introduces the topic of discussion and helps participants in the group give their idea.
7
which members of group talk freely and spontaneously about a certain topic.
2. Speaking Skill
Brown (2004:140) defines speaking as a productive skill that
can be directly and empirically observed; those observations are
invariably colored by the accuracy and effectiveness of a
test-takers listening skill, which necessarily compromises the
reliability and validity of an oral production test.
According to Nunan (2011:68) as quoted by Puspasari
(2016), speaking is such a normal part of our daily lives that we
rarely think of all the things we need to do communicate
effectively – not, that is, unless, something is wrong. (Nunan,
2011:68).
G. The Outline of the Research
The first chapter is about introduction of background of the study, limitation
of the study, statement of the problem, objectives of the study, benefit of study,
definition of the key terms, the review of previous research and the outline of the
research.
The second chapter concerns with the theoretical framework which consists
of the general concept of teaching speaking skill and applying Focus Group
Discussion (FGD) technique.
The third chapter extends the methodology of research. It discusses
8
technique of collecting data, technique of analysis data and the general situation
of SMP N 2 Mertoyudan.
The fourth chapter is the data analysis, it consists of field note of cycle
I, II and III and discussion of cycle I, II and III. This chapter explains the result
of the research.
The fifth chapter is closure which consists of conclusion of the research
and suggestion from the researcher.
The last part is bibliography and appendixes.
9
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
H. Review of Previous Research
In this research, the writer takes review of related literature from the
other research.
Rusydina (2016) have conducted a research in line with the current
research. She conduct a research about the effectiveness of mind mapping and
group discussion to increase the students‟ speaking ability (a quasi
experimental research of the eighth grade students of smp negeri 1 bawen in
academic year of 2015/2016). She concludes that both of mind mapping and
group discussion method are effective for students‟ speaking skill of eighth
grade students in SMP N 1 Bawen in academic year 2015/2016. The
discussion method is reputed as the exact method in speaking because in
discussion the students have to try and talking about their opinion in group.
Group Discussion is the method that makes the students have to be active to
talk more. The teacher has to make the student remember about the purpose
of this method, so the students can discuss the topic and use the time
effectively.
Another research is also conducted by Riyanto (2015). He conduct a
research about improving speaking skill through small group discussion (a
classroom action research for the third grade students of vocational secondary
10
there is statement from Kindsvatter (1996:242) “A small group discussion
divides the large classroom into small groups of students to achieve specific
objectives which permit students to assume more responsibility for their own
learning, develop social and leadership skills and become involved in an
alternative instructional approach”. The researcher said that the students have
high responsibility after they got this technique, they can think about the
importance of responsibility, it is indicated when they get a role in a group.
The students take roles to keep the discussion running well. The increasing
thing is not only students‟ responsibility but also the social connection among
others. It is proven when the students share their ideas each other, asking
something to their friends, solving the problem in a group and being
cooperative group.
Mulyo (2015) also conducts a research about the use of spontaneous
group discussion to improve students‟ skill in speaking of the eleventh year of
smk diponegoro salatiga in the student academic year 2014/2015 (a classroom
action research). In her research, the researcher concludes that
implementation of spontaneous group discussion can enhance students‟
interest in learning English especially speaking. The students‟ response is
good. They are attracted in the strategy and the media used in the class. They
feel happy and regard that English is fun during English teaching learning
process. In the process of learning using Spontaneous Group Discussion,
students more interest followed in the learning process. Students are given
11
accompanied students in the learning in order to the group of discussion run
well. The members of group discussion more active and interactive join the
learning and want to know about new information or the material more.
Hasan (2015) also conducts a research about the use of picture and
group discussion to increase speaking skill (classroom action research of the
first grade students of smk saraswati salatiga in the academic year of
2015/2016). In his research, the reseacher concludes that the students‟
speaking skill can increase through picture and group discussion technique.
The students can be creative and great in make and retelling stories. Almost
all of students seriously pay attention to the teacher‟s explanation and active
in engaging in the learning process, such as asking question, responding
question.
Sasmita and Gurning (2012) also conducts a research about improving
students‟ achievement in writing recount text through focus group discussion
(FGD). In their research, the researchers conclude that Focus Group
Discussion is one of good method that can invite the students to be active,
have good motivation and do high activity. Many students got bored and lazy
when the teaching learning process. Because, they are said that English study
is so boring and difficult. However, the researcher invites the students to
know about focus group discussion method. So, the students have the
motivation and want to know how about focus group discussion in learning
process. Finally, the lazy students have a motivation to learn, and they have
12
to write especially writing recount. And all of the students got high score in
teaching learning process through focus group discussion.
I. Focus Group Discussion (FGD)
1. The Definition of Focus Group Discussion
According to Morgan (1997:12) as quoted by Gibbs (1997:2), Focus
Group is form of group interviewing but it is important to distinguish
between the two. Group interviewing involves interviewing a number of
people at the same time, the emphasis being on question and responses
between the researcher and participants. However, Focus group relies on
interaction within the group based on topics that are supplied by the
researcher.
According to Vaughn and colleagues (1996) as quoted by Puchta and
Potter (2004:6) Focus Group usually contains the two following core
elements:
a. A trained moderator who sets the stage with prepared question or
an interview guide.
b. The goal of eliciting participants‟ feeling, attitudes and
perceptions about a selected topic.
Focus Group can be used in the context of participatory and action
research, with the intention to foster social change.
According to Marsela (2015:233) discussion is active learning when
the participants exchange ideas. Discussion may happen at any level
13
According to Viji (2014:6) Focus Group Discussion (FGD) is a good
way to gather together people from similar background or experiences to
discuss a specific topic of interest. The group of participants is guided by
moderator or facilitator who introduces topics of discussion and helps the
group to participate in a lively and natural discussion among them.
Focus Group Discussion (FGD) is a groupthink allows the individual
participants to pose their ideas or opinions also poses their responses
about the opinion from others.
2. The Elements of Focus Group Discussion (FGD) a. Facilitator or moderator.
Facilitator plays an important role in determining the success of
focus group. According to Gibbs (1997) as quoted by Masedah (2012:
66)
„Moderators will need to process good interpersonal skills and personal qualities, being good listener, non-judgmental and adaptable. These qualities will promote the participants‟ trust in the moderator and increase the likelihood of open, interactive dialogue.‟
In selecting a person to moderate a focus group, it is important
that this person have these qualities:
1)Knowledgeable: be familiar with the discussion topic.
2)Ability to speak the language spoken of the area.
3)Cultural sensitivity, including not acting as a judge, a teacher, does
14
with what is said, and not putting words in the participants‟
mouths.
4)Interesting people: be able to make the participants to more focus
and give their attention just in the topic of discussion.
5)Sensitive men and women: listen attentively to what is said and
how it is said.
6)Inclusive: encourage members to contribute by using eye contact,
body language and directly asking for their input.
7)Open and flexible: respond to what is important to the participants.
8)Respect for participants: receive all of the participants‟ opinion.
The facilitator or moderator has to ensure that in the
groupthink there is fair distribution of all participants to voice out
their perspectives. Besides that, moderator is expected to deal the
arguments in the group and ensuring that essential topics are
covered in the time available.
b. Number of Participants
Focus Group Discussion (FGD) is made up of people with certain
heterogeneous characteristics and similar levels of understanding of a
topic. Bloor et al. (2001:20) said that, in considering heterogeneity of
the group, attention should also be given to the desired depth of
information to be achieved from the focus group. Bringing together a
very diverse range of people may mean that the range of views,
15
topic can be explored in depth. Thus, groups which are too diverse in
relation to a particular topic may result of discussion that provides an
insufficient depth of information.
Litosseliti (2003:32) suggested that the group should consist of
between six to ten participants. Bloor et al. (2001:26) believed that the
group should consist of between six and eight participants as the
optimum size for focus group discussion. The optimum size of the
group may reflect the characteristics of participants as well as the
topic being discussed.
The size of the group may be decided according to the quality of
topic that be discussed. Bloor et al. (2001:27) group of small size have
been successfully used in studies of sensitive behaviour. Smaller focus
group is more appropriate if the topic is a very complex. According to
Morgan (1995) as quoted by Bloor (2001:27) said that, small group
may be desirable with certain types of research topics or certain types
of participants. Small focus group or mini focus group with four to six
participants is better to explore the knowledge. Participants are easier
to express their ideas and opinion, also the setting is more comfortable
for participants. Cameron (1995) as quoted by Bloor (2001:27) argued
that sufficient space is needed to accommodate mobility aids and
participants must be able to be seated close enough to each other to
see and hear each other clearly. Small focus group is selected to
16
discussed. Besides that, the discussion is easier to control and allow
the participants to contribute their insight and experience.
Based on the advantages mentioned above, small group shows
the greater potential, because it is easy to handle, the communication
is clearer, the participants more focus and less misunderstanding.
c. Questions during focus groups.
The quality of questions asked in a focus group can make a large
difference in the kind of information obtained. Krueger (1988) gives
some tips on how to handle open‐ended and dichotomous questions in these discussions:
Open‐ended questions are most appropriate at the start of the discussion because they allow participants to answer from different
angles. Open‐ended questions give the participants opportunities to express their thoughts and feelings based on their specific situations.
Krueger warns that some questions may appear to be open‐ended but are really closed‐ended because they include phrases such as “satisfied”, “to what extent”, or “how much”.
Dichotomous questions are ones that can be answered by a
“yes” or “no” or other similar two‐alternative items. As yes‐no questions are dead‐ends, they usually do not trigger the desired group discussion. They also tend to elicit vague responses that do not lead to
an understanding of the key issues being discussed (Moulton and
17 3. Technique of Focus Group Discussion
Before the focus group discussion begins, the facilitator should
obtain the background information of participants such as their age,
background knowledge about the topic, skill and other pertinent
information. The type of information to collect depends on the FGD topic.
Once this is done, this sequence of steps is carried out:
a. After a brief introduction, the purpose and scope of the discussion
is explained.
b. Participants are asked to give their names and short background
information about themselves.
c. The discussion is structured around the key themes using the
questions about the topic prepared in advance.
d. During the discussion, all participants are given the opportunity to
participate.
e. Use a variety of moderating tactics to facilitate the group. Among
these tactics that the moderator can use include:
1) Stimulate the participants to talk to each other, not necessarily
to the moderator.
2) Encourage shy participants to speak.
3) Discourage dominant participants through verbal and
nonverbal cues. The following may be used when the situation
permits:
18
(2)Politely intervene by saying, “Maybe we can discuss that in
another occasion...”
(3)Look in another direction
(4)Take advantage of a pause and suggest that the subject can
be discussed in detail in another session
4) Pay close attention to what is said in order to encourage that
behavior in other participants.
5) Use in‐depth probing without leading the participant. 3 Guidelines in Conducting Focus Group Discussion (FGD)
a. Focus Group Discussion is began with an introduction that
explains the purpose and topic of discussion.
b. Duration of discussion usually about 45 minutes and conveys the
expectation that everyone will contribute in the discussion.
c. After the introduction, the moderator allows the members to
introduce themselves to encourage their confidence.
d. The discussion is going on and all of the members of group have to
give their opinion or idea.
e. Moderator reinforces the members‟ arguments, but don‟t suggest
what is expected or acceptable. The reinforcement can be done by
saying “okay. Let me write that down”.
f. Allow the other participants to give their response. Make sure that
19
g. At the end of the discussion, the moderator makes summary about
the result of discussion. Report the summary to participants.
h. Always thanks to the participants for their participation and ask
them if they have any questions for you.
4 Advantages of Focus Group Discussion (FGD)
According to Masedah (2012: 64) there are some advantages to be
gained through the use of Focus Group Discussion (FGD.
1) Focus Group Discussion (FGD) can cover a large number of
people in the same group.
2) An efficient way of gaining a large amount of information and
particular opinions from a small number of people in a short
time.
J. Speaking Skill
1.The Definition of Speaking Skill
Teaching English always involves four basic skills. They are
listening, speaking, reading and writing. Speaking is one of the skills that
have to be mastered by students in learning English. It is an essential tool
for communicating in order to they can express their idea. So, as
teachers, we have a responsibility to prepare the students as much as
possible to be able to speak in English in the real world outside the
classroom. According to Richards (2008) as quoted by Nirmawati (2015)
said that the mastery of speaking skills in English is a priority for many
20
Consequently learners often evaluate their success in language
learning as well as the effectiveness of their English course based on how
much they feel they have improved in their spoken language proficiency.
Brown (2001:140) said that, speaking is productive skill that can be
directly and empirically observed those observations are invariably
colored by the accuracy and effectiveness of a test-taker‟s listening skill,
which necessarily compromises the reliability and validity of an oral
production test.
Goh (2007:4-6) stated that speaking is important for language
learners. Besides the role it plays in communication, speaking can also
facilitate language acquisition and development. English as international
language is now used by learners to communicate with native as well as
other non-native speakers of language. Learners from different countries
must also have relevant cultural knowledge when speak to one another.
According to Chaney (1998:13) as quoted by Aziz (2015:23-24)
said that speaking is the process of building and sharing meaning through
the using of verbal and non-verbal symbols, in a variety of contexts.
From the definition above, it can be concluded that speaking is a
crucial part in the second language learning and teaching. Speaking is the
basic skill of the language that must be mastered by language learner to
communicate with other people.
21
According to Harmer (2001:269-271) the ability to speak fluently
presupposes not only a knowledge of language features, but also the
ability to process information and language on the spot. The elements of
speaking that speakers have to competent in the speaking skill, they are:
a. Connected speech: effective speakers of English need to be
able not only to produce the individual phonemes of English
but also to use fluent connected speech. In connected speech
sound are modified (assimilation), omitted (elision), add
(linking). It is for this reason that we should involve students in
activities designed specifically to improve their connected
speech.
b. Expressive devices: native speakers of English change the pitch
and stress of particular parts of utterance, vary volume and
speed and show what and how they are feeling to whom they
are talking to.
c. Lexis and grammar: spontaneous speech is marked by the use
of a number of common lexical phrases, especially in the
performance of certain language function.
d. Negotiation language: effective speaking benefit from the
negotiator language. We use to seek clarification and show the
structure of what are saying. They use the negotiation language
22
are saying in order to be clearer, especially when they can see
that they are not understood.
If part of a speakers productive ability involves the knowledge of
language skills such as those discussed above, success is also dependent
upon the rapid processing skills that necessitates.
a. Language processing: effective speakers need to able to
process language in their own heads and put it into logical
order so that it comes out in forms that are not only
comprehensible, but also convey the meanings that are
intended. Language processes involves the retrieval of words
and phrases from memory and their assembly into syntactically
and propositionally appropriate sequences. One of the main
reasons for including speaking activities in language lessons is
to help students develop habits of rapid language processing in
English.
b. Interactive with others: most speaking involves interaction
with one or more participants. This means that effective
speaking also involves a good deal of listening, an
understanding of how the other participants are feeling.
Knowledge of how linguistically to take turns or allow others
to do.
c. Information processing (on the spot): quite apart from our
23
information they tells us the moment we get it. The longer it
takes for the penny to drop the less effective we are as instant
communicators. However, it should be remembered that this
instant response is very culture-specific and it is not prized by
speakers in many other language communities.
3.Types of Speaking Skill
Brown (2001:141-142) said that there are five basic types of
speaking. They are:
a. Imitative.
This type of speaking performance is the ability to imitate a
word or phrase or possibly a sentence. (e.g., "Excuse me." or
"Can you help me?") to clarity and accuracy.
b. Intensive.
This second type of speaking frequently employed in
assessments context is in the production of short stretches of
oral language designed to demonstrate competence in a narrow
band of grammatical, phrasal, lexical or phonological
relationships.
c. Responsive.
This type includes interaction and test comprehension but at
the somewhat limited level of very short conversations,
24
and the like. The stimulus is usually a spoken prompt in order
to preserve authenticity.
d. Interactive.
Interaction can take the two forms of transactional language,
which has the purpose of exchanging specific information, or
interpersonal exchanges, which have the purpose of
maintaining social relationships.
e. Extensive.
Extensive oral production tasks include speeches, oral
presentations, and storytelling, during which the opportunity
for oral interaction from listeners is either highly limited or
ruled out altogether.
4.Assessments of Speaking
Speaking skill is generally recognized in analysis of speech
processes that are pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, fluency and
comprehension. Here the band scores of oral proficiency scoring
categories in speaking skill (Brown, 2004: 172-173). It can be seen on
the tables below:
Table 2.1
Oral Proficiency Scoring Categories Grammar Score Proficiency Description
25
2 Can usually handle elementary constructions quite accurately but does not have thorough or confident control of the grammar.
3 Control of grammar is good, able to speak the language with sufficient structural accuracy to participate effectively in most formal and informal conversations on practical, social, and professional topics.
4 Able to use the language accurately on all levels normally pertinent to professional needs. Errors in grammar are quite rare.
5 Equivalent to that of an educated native speaker.
Source: Brown. 2004. Language Assessment Principles and classroom practice. New York: Pearson Education,Inc.
Table 2.2
Oral Proficiency Scoring Categories Vocabulary Score Proficiency Description
1 Speaking vocabulary inadequate to express anything but the most elementary needs.
2 Has speaking vocabulary sufficient to express him simply with some circumlocutions.
3 Able to speak the language with sufficient vocabulary to participate effectively in most formal and informal conversations on practical, social and professional topics. Vocabulary is broad enough that be rarely has to grope for a word.
4 Can understand and participate in any conversation within the range of his experience with a high degree of precision of vocabulary
5 Speech on all levels is fully accepted by educate native speakers in all its features including breadth of vocabulary and idioms, colloquialisms and pertinent cultural references.
Source: Brown. 2004. Language Assessment Principles and classroom practice. New York: Pearson Education,Inc.
Table 2.3
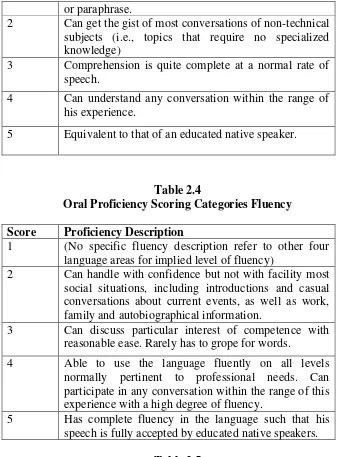
Oral Proficiency Scoring Categories Comprehension Score Proficiency Description
26 or paraphrase.
2 Can get the gist of most conversations of non-technical subjects (i.e., topics that require no specialized
5 Equivalent to that of an educated native speaker.
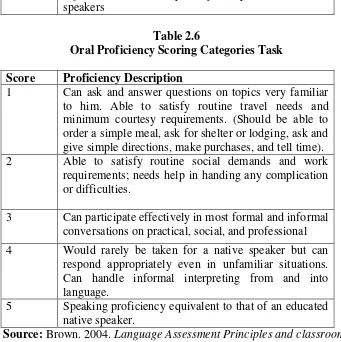
Table 2.4
Oral Proficiency Scoring Categories Fluency Score Proficiency Description
1 (No specific fluency description refer to other four language areas for implied level of fluency)
2 Can handle with confidence but not with facility most social situations, including introductions and casual conversations about current events, as well as work, family and autobiographical information.
3 Can discuss particular interest of competence with reasonable ease. Rarely has to grope for words.
4 Able to use the language fluently on all levels normally pertinent to professional needs. Can participate in any conversation within the range of this experience with a high degree of fluency.
5 Has complete fluency in the language such that his speech is fully accepted by educated native speakers.
Table 2.5
Oral Proficiency Scoring Categories Pronunciation Score Proficiency Description
1 Errors in pronunciation are frequent but can be understood by a native speaker used to dealing with foreigners attempting to speak his language.
2 Accent is intelligible though often quite faulty.
3 Errors never interfere with understanding and rarely disturb the native speaker. Accent may be obviously foreign.
27
5 Equivalent to and fully accepted by educated native speakers
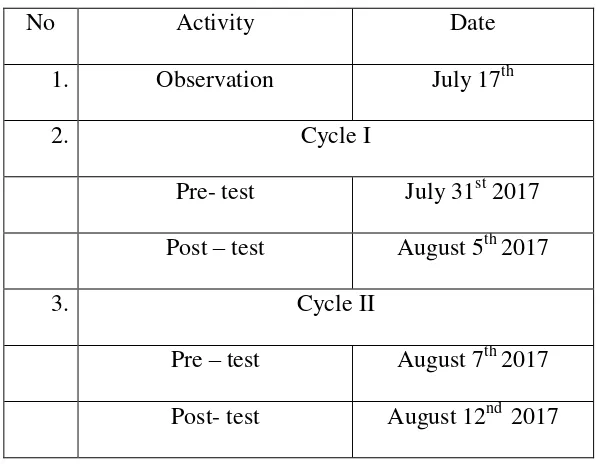
Table 2.6
Oral Proficiency Scoring Categories Task Score Proficiency Description
1 Can ask and answer questions on topics very familiar to him. Able to satisfy routine travel needs and minimum courtesy requirements. (Should be able to order a simple meal, ask for shelter or lodging, ask and give simple directions, make purchases, and tell time). 2 Able to satisfy routine social demands and work requirements; needs help in handing any complication or difficulties.
3 Can participate effectively in most formal and informal conversations on practical, social, and professional
4 Would rarely be taken for a native speaker but can respond appropriately even in unfamiliar situations. Can handle informal interpreting from and into language.
5 Speaking proficiency equivalent to that of an educated native speaker.
Source: Brown. 2004. Language Assessment Principles and classroom practice. New York: Pearson Education,Inc.
However, there are six components usually used to analyze
speech performance, they are grammar, vocabulary, comprehension,
fluency, pronunciation and task. The scoring also can include accuracy,
articulation, eye contact, expression, intonation and gesture of the
speaker. The researcher uses those speaking scoring rubric to collect
28 CHAPTER III
METHOD OF RESEARCH
A. Setting and Time of Research
This research is implemented in SMP N 2 Mertoyudan. The further
explanation about this school is described as follows:
1. The General Situation of SMP N 2 Mertoyudan
This classroom action research is conducted at SMP N 2
Mertoyudan. The school was built on July 18th 1984. The location
is at Danurejo village, Mertoyudan subdistrict, Magelang regency
and West Java. The number of phone is (0293) 326086. The e-mail
of the school is [email protected] . SMP N 2
Mertoyudan consists of 18 groups of learning with 571 students, 40
teachers, 13 staffs and 6 cleaning services. This school is also
completed with some supporting infrastructures, there are language
laboratory, SCIENCE laboratory, library, auditorium, mosque and
gazebo.
2. Vision and Mission
a. Vision
Excellent in the science and technology, have a conception of
environment and be based on faith and piety.
29
1) Fulfilling standard of graduate competence by formulate
the academic and non academic performance and be a
students‟ having a certain character.
2) Fulfilling standard of contain by implementing the basic
competence, standard competence, indicators, basic
material that can be materialized in the syllabus.
3) Implementing learning based problem solving and scientific
to develop students‟ potential.
4) Improving the teachers‟ competence and staff of education
by workshop, in-house training, coaching and education.
5) Fulfilling the adequate tools and infrastructure to support
learning process and education service.
6) Implementing management based on expert school.
7) Fulfilling the standard of funding by empowering all of
potential that can support the excellent learning.
8) Developing assessment system that can measure all of the
students‟ ability.
9) Creating the superior environment and culture in order to
make all member of school is comfortable and safe.
10)Implementing the pioneering effort to be excellent school
that can be signed by the success of academic and
30
educations, cohesive teamwork of teachers and strong
students‟ character.
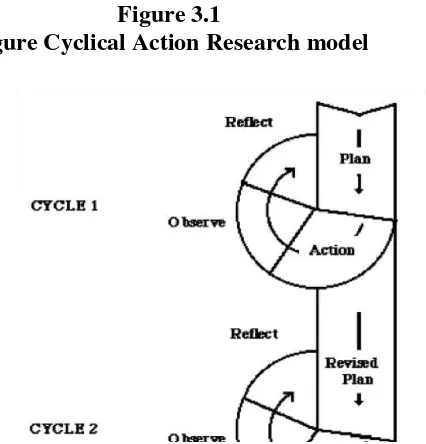
3. Time of research
The time of the research is July 17th - August 12nd 2017. Schedule
of the research is as follows:
Table 3.1
The time of Research at SMP N 2 Mertoyudan
No Activity Date
1. Observation July 17th
2. Cycle I
Pre- test July 31st 2017
Post – test August 5th 2017
3. Cycle II
Pre – test August 7th 2017
Post- test August 12nd 2017
B. The Subject of the Research
In this research, the researcher chooses SMP N 2 Mertoyudan as
subject of the study especially the eighth grade students. The students in
second grade are divided into six groups, A-F. However, the researcher
takes one class in F group. The number of participants is 33 students. They
are 25 girls and 8 boys. Their native language is Indonesian language.
31
English lesson at least two meetings in a week. Each meeting consists of
two hours lesson, an hour lesson is 40 minutes.
1. Population
According to Arikunto (2010:173), a population is all elements
processing one or more attributes of interest. Population is all
individual that participate in the research.
In this research, the population is all of students in the second
grade of SMP N 2 Mertoyudan in the academic year of 2017/2018.
The total number of population is 200 students. They are 81 male and 119 female.
2. Sample
Based on Arikunto (2010:174) “sample is a part of population of
the observation”. The researcher takes one class of the sample in the
second grade students of SMP N 2 Mertoyudan. From the total of the
population of 180 students, the researcher takes F class in eighth group
as the sample of this research. It consists of 25 female and 8 male.
3. Sampling Technique
In this research, the researcher uses purposive sampling in order
to reach a targeted sample quickly. The researcher takes this sampling
technique because it has a purpose in choosing that class as the sample.
The reasons of taking students in F class of eight grades are
because, students in this class have high motivation to master English
32 C. Method of Research
1. Type of Research
In this research, the researcher uses classroom action research
method. Arikunto (2006:2-3) said that Classroom Action Research is
made by three words that can be explained:
a. Research is an activity to find out accuracy the subject of
study using method and the rule of methodology to get the
data or information which benefit to improve the interesting
and important thing for researcher.
b. Action is some activities deliberately done by having specific
purpose.
c. Class is a group of students in the same time receive the same
lesson from teacher.
The aim of action research is to understand the situation in the
class and improve the teachers‟ skill to cope the problem learning in
the class.
2. The Definition of Classroom Action Research
Kemmis and Carr (1986) as quoted by Basrowi and Suwandi
(2008:26) said that classroom action research (CAR) is a form of
self-reflective inquiry undertaken by participant and a social (including
educational) situation in order to improve the rationality and justice of
their own social or educational practices, their understanding of these
33
Hopkins (1993:59) said that classroom action research is the
practical action research because this research involves the teachers‟
practices. The problem is about teachers‟ problem in the class when
learning process happen.
According to the definition above, it can be concluded that
classroom action research is action research in educational field that
can be done in the class in order to improve or repair learning quality.
A reflective research to help a teacher find out what is happening in his
or her classroom and to use that information to take action for future
information.
3. The Characteristics of Classroom Action Research
According to Syamsuddin and Damianti (2011:197) the
characteristics of classroom action research are:
a. It examines problem which are deemed problematic by
researcher in teaching learning process.
b. The researcher can give treatment which planed action to solve
the problems and improve the quality, so the subject can get the
implication.
c. The steps of research in the form of cycle.
d. Classroom action research used collaborative approach.
e. The procedure of research is on-the-spot which designed to
34
Basrowi and Suwandi (2008:34-36) said that the characteristics
of classroom action research are:
a. An Inquiry on Practice from Within
An effort to find out the problem of learning by observing
and understanding the class. Therefore, the researcher can
understand the main problem in the class and she can
determine some actions that can be done.
b. A Collaborative Effort between School Teachers and Teacher
Educators
The actions in classroom action research should also be
collaborative to the broader knowledge on teaching.
Collaboration helps foster insight through discussion and
comparison the action.
4. The Principles of Classroom Action Research
Hopkins (1993:81) states that the principles of Classroom
Action Research are:
a. The climate of interaction between teacher and observer needs to
be non-threatening, helping and one of mutual trust.
b. Focus of the activity should be on improving classroom practice
and reinforcing of successful strategies.
c. Process depends on the collection and use of objective
35
d. Observer and teacher are engaged in a mutual process of
professional development that can lead to improvement in teaching.
5. The Procedures of Research
Classroom Action Research consists of some cycle. Kemmis and
Taggart (1998) as quoted by Hopkins (1993:48) said that where a
sequential program for teachers intending to engage in action research
is outlined in some detail. The procedures of Classroom Action
Research in each cycle are:
a. Planning
The activities in the planning are:
1. Preparing lesson plan, making action plan, preparing
materials and designing the steps in doing the action.
2. Preparing list of students‟ names and scoring.
3. Preparing sheets for classroom observation (to know the
situation of the teaching learning process when the
technique is applied)
4. Preparing teaching equipments.
5. Preparing test (pre-test and post-test)
b. Action
1) Giving pre-test
2) Teaching speaking.
36
4) Giving opportunity to the students to ask about
difficulties.
5) Giving post-test.
c. Observation
Observing is the activity of observing the data collected
in the class to know how far the action effect have reach target.
In this step, the researcher observed teaching learning process.
Then identified and analyzed the data collected during the
learning process.
d. Reflecting
Reflecting is the activity of evaluating critically the
progress of the students. Analyzing the action in order to
remember what happened that has been written in observation.
In this step, the researcher could observe whether the action
activity result any improvement.
The model which is used in implementation of this
research based on Kemmis and Mc Taggart (1998:14) in
Hopkins (1993:48) as follows:
Figure 3.1
37 6. The Technique of Collecting Data
The method that can be used by researcher to obtain the necessary
data in composing and writing this graduating paper are:
a. Test
The researcher uses test to know the students‟ ability
and to detect how far student can improve their speaking skill.
Arikunto (2010:193) said that test is a series of question or
other instrument which are used to measure the individual or
group skill, knowledge, intelligence, capability or talent. The
test was separated into two items, there are:
1) Pre-test is test which can be done before giving
treatment, there is Focus Group Discussion
(FGD).
2) Post-test is test which can be done after giving
treatment of Focus Group Discussion (FGD) in
improving speaking skill.
38
According to Hopkins (1993:140) stated that documents
include memos, letters, examination papers and newspaper
clippings surrounding a curriculum or other educational
concern can illuminate rationale and purpose in interesting
ways.
The researcher takes some documentation to make the
data was complete. Besides make a note, the researcher takes
documents by photographs. Hopkins (1993:142) said that
photographs with or without audiotape are useful ways of
recording critical incidents in classrooms or of illustrating
particular teaching episodes.
c. Observation
Arikunto (2010:199) said that observation is a method of
collecting data by focusing on an object using all of the five
senses.
The researcher uses this method to know the students‟
custom of teaching learning activity in the school area
directly. Hopkins (1993:91) stated when teachers observe
each other teach, all of them often require a simple ways of
gathering information on basic topics, such as questioning
techniques and classroom management.
The purpose of observation is to perceive the nature and
39 7. The Technique of Data Analysis
After collecting data, the next step of the research is analyzing the
data. There are two ways to analyze the data. They are:
a. Descriptive Technique
A descriptive technique is used to know the students
behavior during the teaching learning process. The researcher
describes all activities that happen in the classroom. In
descriptive technique, the researcher analyze the observation„s
sheet which has been made by the observer.
b. Statistical Technique
A statistical technique is used to know the extent to using
the focus group discussion to improve the students‟ speaking
skill the result of pre-test and post-test. This research is
calculated based on Sudijono (2006):
1) Mean
A set of numbers you had collected, add them up
and then divide the total by the number of items, you
would end up with the mean (Sudijono, 2010:79). This
formula is used to know the average of students‟ score.
The formula is:
Mx =
40 M : Mean
∑x : Sum of students‟ score
N : Number of observations in sample
2) SD (Deviation Standard)
First step, the researcher calculates SD, the formula is:
SDD =
Explanation:
SD : Deviation standard for one sample t-test
D : Differences between pre-test and post-test
N : Number of observations in sample
3) T-test
After calculating the SD, the researcher calculates t-test to
know if there are any significant differences or not
between pre-test and post-test.
TO =
Explanation
TO : T-test for the differences of pre-test and post-test
SD : Deviation standard for one sample t-test
41
N : Number of observations in sample
4) Percentages score
According to Sudijono (2010:42-43), percentages score is the
frequency in the percentage digit form. The researcher uses this
formula to get the percentage digit in the score. The formula is:
P = X 100%
Explaination:
P : Percentages
F : Frequency
N : Number of observations in sample
The standard score (the minimum of passing criteria) is 76. If
students have low mark from the standard, they can be assumed
that they have not passed. While, students who passed the standards
42
CHAPTER IV
DATA ANALYSIS
This chapter focuses on analyzing the data collection. The researcher
collects the data from the second grade students of SMP N 2 Mertoyudan. It
shows the finding of the data collected since the beginning until the ending of the
research. The findings consist of the results of pre-test and post-test from the
classroom action research. In this implementation, the researcher arranges two
cycles which use the treatments Focus Group Discussion (FGD) to improve
students‟ speaking skill.
A. Implementation of Research
In this research, the treatment was done by the English teacher of
SMP N 2 Mertoyudan. The teaching learning process was observed by the
researcher. The researcher arranged two cycles, each cycle consists of
planning, action, observation and reflection. The whole steps of this
research are explained in the description below:
1. Cycle I
a. Meeting I
1) Planning
Before conducting the research, the researcher prepared the
instruments of the research, they are:
a) Material for teaching activity, making lesson plan, and
43
b) List of students‟ name and scoring.
c) An observation sheet for classroom observation (to know the
situation of teaching learning process when the technique was
implemented).
d) Pre-test.
2) Implementation
The cycle 1 was divided into two parts. The first part, the
researcher conducted pre-test on July 31st 2017 and the second
part, conducted post-test on August 5th 2017.
The teacher, Mr. Danu, and the researcher (observer), Wulan
entered the classroom. Some of students were surprised with their
coming, because the teacher came with unfamiliar person. Then,
the teacher explained the purpose of researcher on that class and
introduced the researcher.
The situation of the classroom was crowded, because the
students have taken the sport lesson before. So, the teacher waited
them to prepare the English lesson. Mr Danu began the lesson by
greeting the students and reciting Basmallah together. Before the teacher conveyed the objective of the lesson, he gave apperception
to describe the material that would be learned. Mr Danu showed
the slide presentation (PPT) about the material. He asked the
students about the definition of descriptive text but they were not
44
who answered, but the class was quiet. Finally, he pointed one of
them to answer the question. Maya answered, she said
“menggambarkan teks Pak (describing text sir)”. Then, teacher
asked one of boys, Farhan, to answer the question. He said
“merincikan teks(detail the text)”. After that, the teacher explained
it, He said “Maya and Farhan‟s opinion are true, but the
appropriate meaning of descriptive text is the text which describing
something or someone”. Teacher asked students to observe the
picture describe it in order to get more understanding about
descriptive text. Teacher gave an opportunity for students to
express their idea about describing picture. All of students could
make some sentence to describe the picture, but they are afraid to
express their idea orally. Teacher had to point some students to
speak up by mentioning the student‟s number. Mila, who are
pointed, must express her opinion. She said “There are many cars
in the road”.
The teacher showed descriptive text about the existence of
people in the class. He read sentence by sentence carefully and all
of students repeat it well. After that, the students were guided by
teacher identified the characteristic and language feature that could
be used to describe someone or showing the existence of someone.
Teacher explained all of the material, then, asked students to make