i
DESIGNING ENGLISH INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS FOR EXTRACURRICULAR ENGLISH CLUB USING COMMUNICATIVE LANGUAGE TEACHING
IN SMP NEGERI 1 MUNTILAN
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain theSarjana PendidikanDegree
in English Language Education
By
Fransiska Lianita Damayanti Student Number: 051214112
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
iv
“We cannot all do great things.
But we can do small things with great love.”
(Mother Teresa)
vii ABSTRACT
Damayanti, Fransiska Lianita. (2010) Designing English Instructional Materials for Extracurricular English Club using Communicative Language Teaching in SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan.Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
This study was conducted to design English Instructional materials that can be used to teach extracurricularEnglish ClubinSMP Negeri 1 Muntilan. The purpose of the design was to help students to communicate effectively both in oral and written form. There are two problems stated in this study. The first one is “What does the designed set of materials for extracurricular look like?” The second one is “What are the students’ responses to the implementation of the designed materials?”
The research method used in this study was Research and Development (R&D). There are ten steps in R&D. The researcher applied five steps of R&D. The first step was research and information gathering. In this step, the researcher conducted needs survey called pre-design survey. The second step was planning. The third step was conducting preliminary testing. The fourth step was conducting field testing. In this step, the researcher conducted an evaluation survey on the designed materials called post-design survey. The fifth was revising the product. In order to design the materials, the researcher adapted Kemp’s Instructional Design Model. The steps are stating the learner characteristics, considering goal, topics, and general purposes, specifying the learning objectives, listing the subject content, selecting teaching learning activities and resources, evaluating.
The final version of the designed materials, the researcher developed eight units in the syllabus but only three units in the research and implemented one unit. Each unit covered six sections, namely, a).Warm-Upfor listening and vocabulary, b). Speak-Up for speaking, c). Think-It for reading, d). Language Focus, e). Catch-It for speaking, f). Work-It-Out for writing. The post-design survey was conducted to evaluate the designed materials. The researcher used five points of agreement to obtain the participants’ opinions on the designed materials. The result of the survey was calculated using the measurement of central tendency. The mean of post-design survey was 3, 76. This meant that the designed materials were good, acceptable for teaching extracurricular. To solve the second problem, the researcher distributed the questionnaire. The mean of this survey was 4, 24. This meant that the students’ responses of the implementation were good in giving materials, students enjoyed the activities, and students became more confident.
viii ABSTRAK
Damayanti, Fransiska Lianita. (2010) Designing English Instructional Materials for Extracurricular English Club using Communicative Language Teaching in SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan.Yogyakarta: Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Penelitian ini dilaksanakan untuk menyusun materi pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris yang dapat digunakan untuk mengajar ekstrakurikuler English Club di SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan. Tujuan dara dibuatnya materi tersebut adalah untuk membantu siswa agar mampu berkomunikasi secara efektif baik lisan maupun tulisan. Ada dua masalah yang dirumuskan dalam penelitian ini. Yang pertama adalah “Bagaimana materi untuk ekstrakurikuler disusun?” Yang kedua adalah “Bagaimana tanggapan siswa terhadap implementasi materi tersebut?”
Metode penelitian yang dipakai adalahResearch and Development(R&D). Terdapat sepuluh langkah yang terdapat dalam R&D. Penulis hanya menggunakan lima langkah dari R&D. Yang pertama adalah penelitian dan pengumpulan data. Pada langkah ini, peneliti melakukan analisa kebutuhan yang disebut survei sebelum penyusunan materi. Langkah kedua adalah perencanaan. Langkah ketiga adalah pengembangan produk awal. Langkah keempat adalah pengujian awal. Pada langkah ini, peneliti melakukan evaluasi pada desain materi yang disebut survei sesudah pembuatan materi. Langkah kelima adalah perbaikan pada produk. Untuk penyusunan materi, peneliti mengadaptasi model instruksional Kemp. Langkah-langkah tersebut adalah menentukan karakteristik peserta didik, menentukan topic, tujuan umum dan tujuan pembelajaran, menentukan isi materi, memilih aktivitas belajar-mengajar, dan mengevaluasi.
Hasil akhir dari penyusunan materi, peneliti mengembangan delapan unit pada silabus tapi hanya tiga unit yang dikembangakan dalam penelitian dan mengimplementasikan satu unit. Setiap unit terdiri dari enam bagian yaitu: a). Warm-Up untuk mendengarkan dan perbendaharaan kata, b). Speak-Up untuk berbicara, c). Think-It untuk membaca, d). Language Focus, e). Catch-It untuk berbicara, f). Work-It-Out untuk menulis. Survei setelah penyusunan materi dilakukan untuk mengevaluasi materi. Penulis menggunakan lima poin persetujuan untuk mendapatkan opini dari partisipan atas materi yang disusun. Hasil dari survei dihitung menggunakan kecenderungan nilai tengah. Rata-rata pada survei setelah materi disusun adalah 3, 76. Hal ini berarti bahwa materi yang disusun adalh bagus, dapat diterima untuk mengajar ekstrakurikuler. Untuk menyelesaikan masalah yang kedua, penulis menyebar kuesioner. Rata-rata dari survei ini adalah 4, 24. Hal ini berarti bahwa respon siswa akan peng-implementasi-an adalah bagus dalam pemberian materi, dan siswa menikmati aktivitasnya, dan siswa menjadi lebih percaya diri.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
First of all, I would to give my greatest gratitude and praise to my Lord, Jesus Christ, for His endless love, blessing, and grace during the process of completing my thesis. He always gives me strength when I am weak.
My deepest gratitude goes to my major sponsor, Gregorius Punto Aji, S.Pd., M.Hum. for his kindness and willingness to help in writing my thesis. I can finish this thesis because of him. I believe that I would not able to finish my thesis without his patience, support, and guidance.
I would like to thank to Christina Lhaksmita Anandari, S.Pd., M.Ed. for her time to evaluate the materials. Without her suggestions and opinions, I could not make the better materials.
I would like to thank to an extracurricular teacher, Anita Kartika, S.Pd. who has given me time, help, and willingness so that I can complete my thesis. I would like to give thank to English teacher ofSMP Negeri 1 Muntilanfor the time to evaluate the materials. And I also thank all of the English Club students for their willingness to help me conduct my research.
My greatest love and gratitude go to my mother. I thank her for her never ending love, support, prayer, guidance, and patience. She always understands me. We always share everything.
x
Tunggorono 1C where I can feel the second family, “Spring” and “Saraswati” members.
The last but not least, I thank all of the people whose names cannot be mentioned one by one for their prayers and supports.
xi STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ………... LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH… ABSTRACT ………...
ABSTRAK………...
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ……….…. TABLE OF CONTENTS ……….…... LIST OF TABLES ………. LIST OF FIGURES ………..………. LIST OF APPENDICES ………..………..
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION
A. Research Background ………...
B. Problem Formulation ………
C. Problem Limitation ………...
D. Research Objectives………..
E. Research Benefits ……….
F. Definition of Terms ………..
xii
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
A. Theoretical Description ………
1. Instructional Design Models: Jerold S Kemp’s Model ……… 2. Research and Development ………. 3. Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)………. a. The Principle of CLT ………. b. Learner Roles ………. c. Teacher Roles ………... d. The Role of Instructional Materials ………... 4. Task-Based Learning ...……… 5. Syllabus ……… 6. Speaking Skill ……….. a. The Nature of Speaking ………. b. Teaching Speaking ……….
B. Theoretical Framework ………
CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY
A. Research Method ………..
B. Research Participants ………
C. Research Instruments ………
D. Data Gathering Technique ………
E. Data Analysis Technique ………..
F. Research Procedure ………..
xiii
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH FINDING AND DISCUSSION
A. The Design of Materials for Extracurricular English Club in SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan ………. 1. Learners’ Characteristics ………. 2. The Competence Standard, Topics, and Basic Competences …….. 3. The Learning Objectives and Subject Content ……… 4. Teaching Learning Activities ……….. 5. Materials Evaluation and Revision ……….. B. The Students’ Responses to the Materials ………
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS
A. Conclusion ………
B. Suggestions ………...
1. For English Teacher ………. 2. For the Other Researchers ………...
REFERENCES ……….. APPENDICES ………...
35 35 38 41 42 48 51
53 54 54 54
xiv
LIST OF TABLES
Page 3.1 Table of the Data Needed ………...
4.1 The Result of Pre-Design Survey (Question no 1-5) ………... 4.2 The Result of Pre-Design Survey (Question no 6) ………... 4.3 The Basic Competencies ……….. 4.4 The Learning Objectives / Achievement Indicators ……… 4.5 The Result of Pre-Design Survey (Question no 7-10) ………. 4.6 The Topics and Activities ……… 4.7 The Description of Participant of Post-Design Survey ……… 4.8 The Result of Post-Design Survey ………... 4.9 The Result of the Materials’ Implementation ………..……
xv
LIST OF FIGURES
Page 2.1 Kemp’s Instructional Design Model ………...
2.2 The Adapted Kemp’s Instructional Design Model ………. 3.1 The Relationship between R&D and ID ………..
xvi
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page Appendix ASurat Permohonan Ijin Penelitian……….
Appendix B Questionnaire of Pre-Design Survey ………. Appendix C The Result of Pre-Design Survey ……….. Appendix D The Result of Interview with the Teacher ………. Appendix E Questionnaire of Post-Design Survey ………... Appendix F Questionnaire of Materials’ Implementation ……… Appendix G General Description of the Materials ……… Appendix H Syllabus ………. Appendix I Lesson Plan ………. Appendix J Teacher’s Manuals ……….. Appendix K Students’ Handout ……….
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents the introduction of this study. There are six parts covered: research background, problem formulation, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits, and definition of terms.
A. Research Background
Nowadays, English becomes the most important language as a means of communication. Many people are expected to be able to speak English. As many people know that English language learning has been given to children in the earlier age. It is done because there is no age limitation for children to learn English. In the pre-elementary level students learn English but the level is still Basic English. In the next level, students learn more complex English. It is possible that many schools facilitate their students by English language learning. In the favorite school, the extracurricular has been taught to improve speaking ability. These schools facilitate their students by giving language laboratory so that students can practice there.
appropriate materials so that students are interested in joining this extracurricular. There are a lot of materials in teaching speaking for students. The materials chosen depend on the indicators achievement that the teachers want to achieve.
Extracurricular which is held out of regular school activity is an optional activity. Students may join this course or not because it is based on students’ willingness to improve their ability. English Club is one of the extracurricular activities. It is done in SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan. The purpose of this activity is to improve students’ speaking ability so that they can speak English fluently. Students’ courage in speaking English is also taught here in order to make students to be brave to express their idea. Because this school often join English competition, this extracurricular is very important. It helps students to be able to speak English fluently so that they will win the competition.
In addition, students often feel less confident when they have to speak English in front the class or share their experience with others. This case is one of the problems that the researcher should avoid because the success of the learning depends on the students themselves. If they do not want to speak, the course will be useless. Teacher should be able to build students’ character so that they dare to speak. This course becomes the place for students to improve their ability and they will be more confident. Speaking usually starts from interaction of two people or more speaking about something. To make students can interact to each others, teachers should be a good motivator.
The design materials here become useful for teachers because the learning activity will be more organized. Although the purpose of this extracurricular is to improve students’ courage in speaking, the fixed material is also needed so that there is a correlation between the purpose and the material given. The material is designed based on the students’ needs and interests. The researcher believes that it is difficult to design the material. However, material in speaking is really needed. Students should know the language function based on their level of learning.
often practice it. However, there are still many students who are not confident to practice their English.
The purpose of this research is to design English instructional materials for extracurricular English Clubin Junior High School. The most important factor to learn English is the student's motivation on achieving the materials in teaching learning process. If students’ motivation is good and the materials are interesting, the learning process will be successful. These designed materials will be useful because this school has the program of extracurricular English Club.
B. Problem Formulation
This research intends to find out the answers to the research questions stated in the research problem. They are:
1. What does the designed set of materials for extracurricularEnglish Clubin SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan look like?
2. What are the students’ responses to the implementation of the designed materials?
C. Problem Limitation
confident in speaking English so that they win the competition which is held annually.
D. Research Objectives
Like the researcher said before, this research intends to find out the answers to the research questions stated in the research problem. The research objectives are:
1. to find out the appropriate materials for extracurricular English Club by using the correct way to design a set of English instructional material. 2. to present the designed set of English instructional materials that can make
students more interested about extracurricularEnglish Club.
3. to know the students’ responses to the implementation of the materials designed.
E. Research Benefits 1. For Students
This research will help students in exercising which materials are suitable in extracurricularEnglish Club. Since the researcher observe the students first, the material will be appropriate to the students’ needs and interests. Then this material makes the students be more enthusiastic in speaking activity.
2. For Teachers
the teachers in giving materials or activities to the students. If the learning activity is not good enough (students less enthusiastic in joining the extracurricular activity), the materials should be changed in this teaching learning activity. Creative teachers are needed to make the teaching learning activity more interesting.
3. For Readers
This research helps the readers to know the appropriate materials for extracurricular English Club by using the correct way in designing the English Instructional material.
4. For Researcher
This research will help me (the researcher) to make the material which is appropriate for extracurricularEnglish Clubin SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan. The way to design the materials is important to the next study. Hopefully, the English instructional design model can worthwhile contribute to teach extracurricular English Clubin SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan.
F. Definition of Terms
There are four terms that will be defined in this research 1. Instructional Material Design
design is the actual planning of activities the teacher will bring about the desired ends.
2. Instructional Material
In this study, instructional material means a set of units and a set of teaching – learning media, which is used by teacher and learners as the focus of discussion in the teaching learning process. The instructional material can help defining the goals of the syllabus and the roles of teacher and learners within the instructed process (Wright, 1987).
3. Extracurricular English Club
Extracurricular is the activity which is done when the regular school activity is over (out of school regular activity). All students can join this activity based on their willingness. This activity is aimed at improving students’ ability in speaking English so that they can be more fluent in speaking English.
4. Junior High School
8 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter is intended to review some theories related to the issue of the study and to formulate the theoretical framework. Therefore, the researcher divides this chapter into two major sub-headings namely theoretical description and theoretical framework. The theoretical description provides the theoretical issues related to the problem, whereas the theoretical framework explains the thread of the theories to formulate the orientation of the study.
A. Theoretical Description
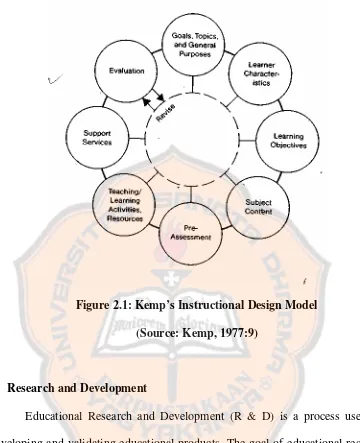
1. Instructional Design Models: Jerrold S. Kemp's Model
Kemp states that in building a successful program, there must be an approach called the systems approach which involves the development of an overall plan incorporating parts of a process in a sequential pattern (1977:6). Thus, there are three questions which are considered as the essential elements to construct an Instructional Design Plan (1977: 8). They are objectives (what must be learned?), activities and resources (what procedures and resources will work best to reach the desired learning levels?), and evaluation (how will we know when the required learning has taken place?). There are eight steps in Kemp’s Instructional Design Models. The steps are:
system or institution. The educational program is then developed to serve these goals. Topics are chosen for study within curriculum area or courses that are used to state the general purposes.
Step 2. State the Learner Characteristics
Enumerate the important characteristic of the learner for whom the instruction is to be designed. Each learner should be recognized and respected the student as an individual. Each person should be assisted in pursuing learning at his or her own pace, on his or her schedule and with his or her selection of learning experiences and material. The planner should obtain information about the learners’ capabilities, needs, and interest.
Step 3. Specify the Learning Objectives
Specify the learning objectives to be achieved in terms of measurable student’s behavioral outcomes. Learning objectives is concerned with learning as the outcome of instruction.
Step 4. List the Subject Content
List the content which has close relationship to the objectives and to the student’s needs. Subject content is the traditional starting point for teaching that is usual in subject-centered teaching. Content in most subject areas is dynamic and changing, and is being recognized as traditional courses are combined around contemporary “theme topics”.
Step 5. Develop Pre-assessment
the objectives students may already have achieved. It is called as ‘pretest’ and the final evaluation called a ‘posttest’.
Step 6. Select Teaching / Learning Activities and Resources
Select teaching/learning activities and instructional resources that will treat the subject content so students will accomplish the objectives. You determine the most efficient and effective methods and then select materials to provide learning experiences that will utilize the content associated with each objective.
Step 7. Coordinate Support Service
These services include funds, facilities, equipment, and personal whose time must be scheduled for participation in the instructional plan. There are many interrelated elements in any instructional situation and each needs careful consideration during the appropriate planning step.
Step 8. Evaluate Student’s Learning
Evaluate student’s learning in terms of their accomplishment of objectives, with a view to revising and re-evaluating any phases of the plan that need improvement.
Figure 2.1: Kemp’s Instructional Design Model (Source: Kemp, 1977:9)
2. Research and Development
Educational Research and Development (R & D) is a process used for developing and validating educational products. The goal of educational research is not to develop products, but rather to discover new knowledge or to answer specific questions about practical problem (Borg and Gall 1983: 772). Based on Borg and Gall, the steps in research and design are:
1) Research and information collecting-includes review of literature, classroom observations, and preparation of report of state of the art.
3) Develop preliminary form of product – includes preparation of instructional materials, handbooks, and evaluation devices.
4) Preliminary field testing – conducted in from 1-3, using 6-10 subjects. Interview, observational and questionnaire data collected and analyzed. 5) Main product revision – revision of product as suggested by the
preliminary field-test results.
6) Main field testing – conducted in 5 to 15 schools with 30 to 100 subjects. Quantitative data on subjects’ precourse and postcourse performance are collected. Results are evaluated with respect to course objectives and are compared with control group data, when appropriate.
7) Operational product revision – revision of product as suggested by main field test results.
8) Operational field testing – conducted in 10-30 schools involving 40 to 200 subjects. Interview, observational and questionnaire data collected and analyzed.
9) Final product revision – revision of product as suggested by operational field test results.
10) Dissemination and implementation – report on product at professional meetings and in journals.
3. Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) a. The Principles of CLT
because this is suitable in teaching speaking. Littlewood (1981:1) states, “One of the most characteristics features of communicative language teaching is that it pays systematic attention to functional as well as structural aspects of language.” It means that using procedures where learners work in pairs or groups employing available language resources in problem-solving tasks. Communicative Language Teaching is a theory of language that starts from a communicative model of language and language use, and that seeks to translate this into a design for an instructional system, materials, teacher and learner roles and behaviors, classroom activities and techniques. The goal of Communicative Language Teaching as Hymes said (1972) in Richards and Rodgers (2001:159), is as communicative competence. His theory about communicative competence is a definition of what a speaker needs to know in order to be communicatively competent in a speech community. As stated by Richards and Rodgers (2001:161), some of the characteristics of this communicative view of language as follow:
1. Language is a system for expression of meaning
2. The primary function of language is to allow interaction and communication
3. The structure of language reflects its functional and communicative uses. 4. The primary units of language are not merely its grammatical and
structural features, but categories of functional and communicative meaning as exemplified in discourse.
described as task principle: activities in which language is used for carrying out meaningful tasks promote learning (Johnson 1982). The third element is described as meaningfulness principle: language that is meaningful to the learner supports the learning process (Richards and Rodgers, 2001:161). In designing the materials, at least there are two principle used by the researcher.
b. Learner Roles
Communicative Language Teaching emphasizes on the processes of communication, rather than mastery of language forms. It leads to different roles for learners from those found in more traditional second language classrooms. Breen and Candlin as cited in Richards and Rodgers (2001:161), in describing the learner’s role within Communicative Language Teaching in the following terms:
The role of learner as negotiator – between the self, the learning process, and the object of learning – emerges from and interacts with the role of join negotiator within the group and within the classroom procedures and activities which the group undertakes. The implication for the learner is that he should contribute as much as he gains, and thereby learn in an interdependent way. (1980:110)
c. Teacher Roles
The success of the study is not far from people who teach the lesson. In this case, teacher has many roles in teaching English by using Communicative Language Teaching. Breen and Candlin as cited in Richards and Rodgers (2001: 167) the teacher roles in Communicative Language Teaching in the following terms:
1) Facilitator
2) Participant
Teacher should act as an independent participant within the learning-teaching group. Teacher is as a guide and as a resource within the classroom.
3) Needs Analyst
Teacher assumes a responsibility for determining and responding to learner language needs. It may be done formally through administering a needs assessment instrument where teachers are expected to plan group and individual instruction that responds to the learners’ needs.
4) Counselor
Teacher is expected to exemplify an effective communicator seeking to maximize the meshing of speaker intention, hearer interpretation, through the use of paraphrase, confirmation, and feedback.
5) Group Process Manager
Teacher is expected to manage the communication among learners in group. Teacher’s responsibility is to organize the classroom as a setting for communication and communicative activities.
d. The Role of Instructional Materials
Materials have the primary role of promoting communicative language use. There are three kinds of materials currently used in CLT:
1) Text-based materials
Communicative approach such as: dialogue, drills, visual cues, taped cues, pictures, sentence fragments to initiate conversation.
2) Task-based materials
A variety of games, role plays, simulations and task based communication are the example of this materials. These typically are in the form of one-of a kind item: exercise handbooks, cue cards, activity cards, pair communication practice materials, and student-interaction practice booklets. Students have to communicate each other to complete the task.
3) Realia
Such kinds of realia are signs, magazines, advertisements, newspaper, graphic and visual resource. These materials build the communicative activities.
4. Task-Based Learning
Task-Based Learning is one of Process-Based Communicative Language Teaching approaches. According to Agustien (2004:30), the claim of Task-Based Learning is that language learning will result from creating the right kinds of interactional processes in the classroom, and the best way to create these is to use specially designed instructional tasks.
ordering, comparing, sharing personal experience, creative tasks. Those are the kinds of communicative task which goal is as communicative competence.
5. Syllabus
In designing the materials, teacher needs syllabus as the measurement of the students needs. A syllabus is a document which says what will (or at least what should) be learnt (Hutchinson: 80). Yalden (1983:110) provides six types of syllabus as follows:
Type 1. Structural-Functional
In this type of syllabus, there is a separation of the two components of form and communicative function. That is why this syllabus is relatively easy to be implemented. Language forms are taught first before the teacher introduces the language functions.
Type 2. Structures and Functions
This type provides a structural progression in a communicative framework. Brumfit states that since cultural and linguistics meaning is customarily negotiated between users of language, it is more sensible to provide them directly. His solution then is to retain form (grammar and pronunciation) as the organizing principle since we can successfully generalize about it, but not about what people should do and mean.
Type 3. Variable Focus
communicative competence such as: structural, functional, instrumental. Type 4. Functional
The objective of this type is in terms of communicative function. The objectives determine the functions needed, and the functions determine the selection and sequencing of grammatical materials.
Type 5. Fully Notional
This type is applicable for the learners who already have adequate proficiency of English but still need to be specified in a new particular purpose. All components of this syllabus - socio cultural, semantic, linguistics as well as psycho-pedagogical – are united together.
Type 6. Fully Communicative
This type is also called as learner generated syllabus. The learners become the source of input. Communication is the primary objective and the linguistic competence should be a part of communicative competence.
6. Speaking Skill
a) The Nature of Speaking
influences other human beings (Rivers,1968:162).In other word, speaking activities can express students own ideas, wishes, opinions, attitudes, information, etc. Speaking is usually done by two or more speakers, facing each other and paying attention and responding to what is said rather than how correctly it is said (Nunan, 1989:31).
b) Teaching Speaking
According to Bushman (1986:25) the general purpose for speech study in English Class is to develop students who can participate satisfactorily in everyday situations that demand oral work. Nowadays, people are expected to speak English fluently in working environment. That is why the teaching of speaking skill cannot be separated from the idea of teaching communicative ability. Rivers (1968:160) said that the teaching of the speaking skill is more demanding on the teacher than the teaching of any other language skill. Rivers added that students in a foreign-language class will not learn to speak fluently merely by hearing speech, so it is important to the teacher to give more opportunities for practicing the speaking skill. The teacher needs to use his imagination in devising situations that provoke the students to the use of the language in the expression of his own meaning.
B. Theoretical Framework
A teaching learning process needs an instructional material to guide it. It is needed especially by the teacher to make the teaching learning activity be more organized. The teacher would be more ready in handling the class when teacher has prepared the instructional materials.
First of all, the researcher uses Research and Development as the method for doing the research. There are five steps of Research and Development that the researcher will be used. In addition, the researcher not only uses Research and Development but also uses Instructional Design. Here, the researcher adapts Kemp’s Instructional Design Model because the researcher tries to make it in linear step, not circular. Those two guidelines of design will complete each other so that the researcher can make a good design. However, the researcher still needs theory of learning in teaching. Then, Communicative Language Teaching is chosen because it helps the researcher to provide the principle to develop activities that are integrated in the materials. The focus of this study is speaking. Speaking activities can express students own ideas, wishes, opinions, attitudes, and information.
task-based materials. This kind of material is advantageous for the students because they are student-centered. The topics of the material can be chosen by getting learners’ characteristic.
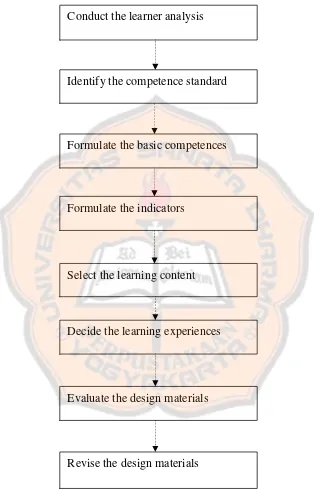
These are the steps of designing the materials that the researcher uses: Step 1. Conduct the Learner Analysis
The researcher conducts the learning analysis to know the students interest, needs, and difficulties in learning English so that the researcher could design the suitable materials for them.
Step 2. Identify the Competence Standard
The researcher identifies the competence standard because it is the basis for the rest of the steps.
Step 3. Formulate the Basic Competences
Specify the basic competences to be achieved in terms of measurable student behavioral outcomes.
Step 4. Formulate the Indicators
The indicators can be used as the guide to choose the learning materials and decide the learning experiences. Indicators are adapted from the basic competences which are used in the level of study.
Step 5. Select the Learning Content
Step 6. Decide the Learning Experiences
Set and list the learning experiences which support each indicator. Step 7. Evaluate the Design Materials
The design materials evaluation is done by distributing the questionnaire to the participants. The participants gave their judgments, comments, opinions, suggestions toward the designed materials.
Step 8. Revise the Design Materials
This following figure describes the linear step adapted from Kemp’s Model.
Figure 2.2: The Adapted Kemp’s Instructional Models Conduct the learner analysis
Identify the competence standard
Formulate the basic competences
Formulate the indicators
Select the learning content
Decide the learning experiences
Evaluate the design materials
24 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The purpose of this chapter is to present the method used to answer the questions stated in Chapter 1. The discussion is presented into six major parts, namely research method, research participants, research instruments, data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A. Research Method
This research was an educational research and development (R&D) in which the research process is used for developing the designed materials. Borg and Gall (1983: 772) stated that educational research and development (R&D) is a process used to develop and validate educational products. According to Borg and Gall (1983: 775), there was a cycle to be followed:
1. Research and information gathering.
2. Design the preliminary product.
Getting the data collected, the researcher constructed preparation of the materials, handbooks, and evaluation devices.
3. Conduct preliminary testing.
This step required expert verification to analyze the product. The designed materials were given to the teachers and lecturer to be analyzed. The researcher gave the questionnaire to the teachers and lecturer so that they were willingness to give comments and suggestions about the first designed materials. There were four English teachers and one lecturer who became the participant in this post-design survey in order to get validity of the materials.
4. Conduct field testing.
The next step was the implementation of the first product revision. It would be conducted in the school by the researcher. In this step, the researcher distributed the questionnaire to the students to get the students’ responses to the implementation of the designed materials.
5. Revise the product.
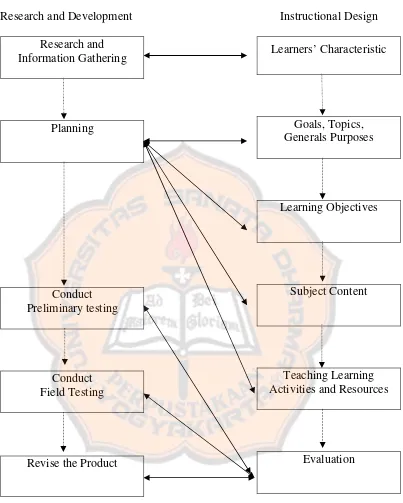
Research and Development Research and Information Gathering
Planning
Conduct Preliminary testing
Conduct Field Testing
Revise the Product
Instructional Design Learners’ Characteristic
Goals, Topics, Generals Purposes
Learning Objectives
Subject Content
Teaching Learning Activities and Resources
Evaluation
The next step of the design
The relationship between R & D and ID
B. Research Participants
1. Participants in Research and Information Gathering
The first step, the research participants were students of SMP Negeri Muntilan. The researcher distributed questionnaires to collect information which was useful in designing the materials, such as the students' characteristics, the students’ ability, the methods used, and the class activities. Besides, the researcher conducted interview to the English teacher in order to know the goal of this course.
2. Participants in Preliminary Testing
In preliminary testing, the research participants were the English teachers in this school and a lecturer. It was needed to gain information about the activity of extracurricular English Club. The teachers evaluated the design product and gave suggestion to the researcher. There were four English teachers and one lecturer who became the participants in this post-design survey in order to get validity of the materials.
3. Participants in Field Testing
C. Research Instruments
There were two kinds of instruments used in this study. 1. Instrument in data collecting
According to Oxford Advanced Learner’ Dictionary (Hornby, 1995:952), questionnaire is a written or printed list of questions to be answered by a number of people, especially as part of a survey. According to Ary, Jacobs, and Razavieh (1990:418) as cited in Hanani (2005), a questionnaire is an instrument of the study to gather information through the respondents' written responses to a list of questions. The questionnaire was written in Indonesian language which the purpose was to avoid misunderstanding of students. In this section the researcher used closed-ended questions so that the answer is appropriate with the researcher wants. This questionnaire is to gain data about the students and the teaching learning activities. Then, the research problem could be solved accurately.
2. Instrument in preliminary testing
The next instrument was questionnaire which was distributed to English teachers and also the lecturer to obtain the evaluation and suggestion. The researcher asked the teachers and lecturer to evaluate the designed materials. The teachers and lecturer gave comments about the designed materials.
3. Instrument in field testing
In field testing, the researcher distributed questionnaire to ask students' responses and suggestion about the implementation of the materials design. The questions were about whether the designed materials were interesting or not.
D. Data Gathering Technique
researcher revised the product based on the students' feedback to produce the final product. The following table was the framework of the data needed.
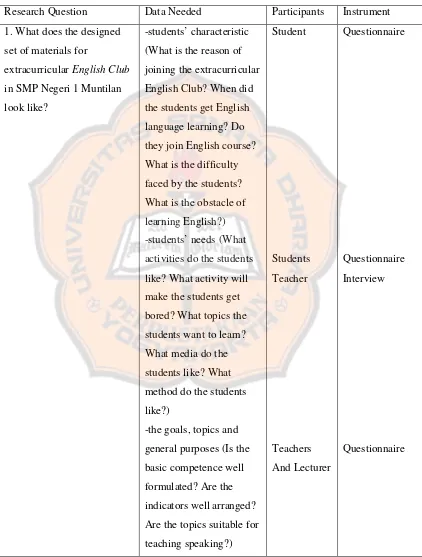
Table 3.1. Table of the Data Needed
Research Question Data Needed Participants Instrument
1. What does the designed set of materials for
extracurricularEnglish Club in SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan look like?
-students’ characteristic (What is the reason of joining the extracurricular English Club? When did the students get English language learning? Do they join English course? What is the difficulty faced by the students? What is the obstacle of learning English?) -students’ needs (What activities do the students like? What activity will make the students get bored? What topics the students want to learn? What media do the students like? What method do the students like?)
-the designed materials (Are the tasks well elaborated? Are the pictures interesting enough? Does it suit the students’ level? Is Task-Based Learning
developed in the materials? ) 2. What are the students’
responses to the implementation of the designed materials?
- Is the topic interesting? - Is the implementation interesting?
-Do the students enjoy join this course?
-Do the students want to learn English more? -Are the activities interesting?
-Do the students get bored?
Students Questionnaire
E. Data Analysis Technique
Data analysis is a process to shift, organize, summarize and synthesize the data to arrive at some results and conclusion of the research (Selinger and Shohamy, 1989: 201). Data from questionnaire and interview were analyzed to find out the students’ needs about the activity of this course. The conclusion was made related to the data gathering.
The Mean (M) is the average point (X) which is obtained by counting the sum of the score (∑X) then it is divided by the number of subjects (N).
The formula is:
M = the average points ∑X = the sum of the score N = the number of subject
The estimation of the participants’ opinions on the designed materials used five points of agreement and disagreement namely:
1: if the participants strongly disagree with the statement 2: if the participants disagree with the statement
3: if the participants neither agree nor disagree with the statement 4: if the participants agree with the statement
5: if the participants strongly agree with the statement
The data were presented in the form of table in which the participants opinions, statements, and the mean.
Statements No Participants opinion
1 2 3 4 5
N Mean
The data showed whether the designed materials were good, acceptable or not. 1.01 – 2.50 = poorly design and not acceptable
The design materials were good and acceptable if the mean was more than 75%. The design materials were good but needed revisions if the mean was 50% up to 75%. The design materials were poor and not acceptable if the mean was below 50%.
The researcher made all list about the participants comments and suggestions. The researcher revised the designed materials in order to make the better form.
F. Research Procedure
There were some steps in finishing this study. First of all, the researcher conducted survey by distributing the questionnaire and conducting an interview. After finishing the survey, the researcher continued to the next step, research and development. The steps of research and development were:
1. Research and Information Gathering
a. Preparing the questionnaire for the students and interview for the teacher. b. Distributing questionnaires to all students and conducting an interview. 2. Designing the Product
Make the first product based on the feedback of the questionnaire and interview.
3. Preliminary Testing
a. Distributing the proposed designed materials along with the second questionnaire to the teachers of extracurricular English Club and also the lecturer
4. Revising the designed materials to produce the product. Making revision based on the suggestions.
5. Field testing
a. Testing the proposed materials.
b. Distributing the questionnaire to the students about their response to the implementation of the designed materials.
6. Revising
35 CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING AND DICUSSION
This chapter will answer the two problems stated in the Chapter 1. There are two parts in this chapter. The first part is the design of the materials and the second part is the students’ responses to the materials.
A. The Design of Materials for Extracurricular English Club in SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan
This part is to answer the first problem ‘What does the designed set of materials for extracurricular English Clubin SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan look like?’. This design consisted of five elements which are taken from Kemp’s models. The elements of designing the materials, namely: learners’ characteristics; competence standard, topics, and basic competences; the learning objectives and subject content; the teaching learning activities; and materials evaluation and revision. Those elements can be seen as follow:
1. Learners’ Characteristics
learning process using English. The data presentation of students’ characteristic can be seen as follows:
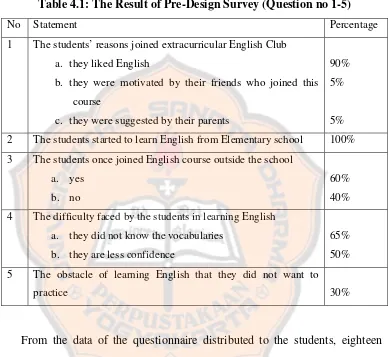
Table 4.1: The Result of Pre-Design Survey (Question no 1-5)
No Statement Percentage
1 The students’ reasons joined extracurricular English Club a. they liked English
b. they were motivated by their friends who joined this course
c. they were suggested by their parents
90% 5%
5% 2 The students started to learn English from Elementary school 100% 3 The students once joined English course outside the school
a. yes b. no
60% 40% 4 The difficulty faced by the students in learning English
a. they did not know the vocabularies b. they are less confidence
65% 50% 5 The obstacle of learning English that they did not want to
practice 30%
students (50%) said that they are less confident when speaking. Six students (30%) said that their obstacle in learning English when they did not want to practice.
It could be seen that most students had learnt English when they were in the Elementary School. It can be seen in the table that 90% of the students joined extracurricular English Club because they liked to learn English. Only 60% of students who joined English course before, so the level of knowledge of the students was different. Then, the researcher should give the materials in the level of less difficulty. If the researcher gives the materials based on the students who are expert in English, others students will be difficult to follow the learning activity. Other characteristic of the students was they were lazy to practice their English. In this case, teacher should be a good motivator so that students were interested in learning English. Students said that their obstacle of learning English were they did not know the meaning of the vocabularies and they less confident to speak English. They were afraid if they made mistake. People can not learn without make any mistake. This case that would be the problem should be solved by the researcher. Knowing the students characteristics, the researcher get the students’ needs.
From the discussion above, it can be concluded in the simple way that the students’ characteristics as follow:
1. They like English so they are motivated to join this course.
3. Some of them have ever joined English course so they have some basic knowledge.
and the students’ needs as follow:
1. They need more vocabularies so that they know the meaning of English vocabulary.
2. They need more practice in order to make them be more confident.
3. They need more practice so that they will be more fluent in speaking English.
2. The Competence Standard, Topics, and Basic Competences
After deciding the goal, the researcher selected the topics. The topics selection was based on the students’ needs inferred from the questionnaire in the pre-design survey.
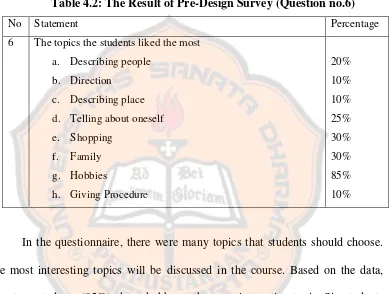
Table 4.2: The Result of Pre-Design Survey (Question no.6)
No Statement Percentage
6 The topics the students liked the most a. Describing people
b. Direction c. Describing place d. Telling about oneself e. Shopping
f. Family g. Hobbies
h. Giving Procedure
20% 10% 10% 25% 30% 30% 85% 10%
about Oneself, Describing People, Describing Place, Giving Direction, and Giving Procedure. Because the materials would be implemented, there were only three topics which were developed. After stating goal and the topics, the researcher formulated the general purposes called Basic Competence.
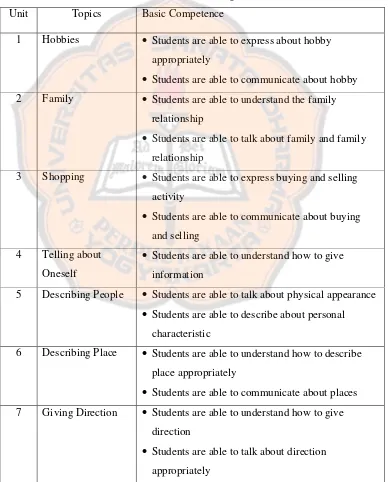
Table 4.3: The Basic Competences
Unit Topics Basic Competence
1 Hobbies Students are able to express about hobby appropriately
Students are able to communicate about hobby 2 Family Students are able to understand the family
relationship
Students are able to talk about family and family relationship
3 Shopping Students are able to express buying and selling activity
Students are able to communicate about buying and selling
4 Telling about Oneself
Students are able to understand how to give information
5 Describing People Students are able to talk about physical appearance Students are able to describe about personal
characteristic
6 Describing Place Students are able to understand how to describe place appropriately
Students are able to communicate about places 7 Giving Direction Students are able to understand how to give
direction
8 Giving Procedure Students are able to understand how to give procedure appropriately
Students are able to talk about procedure
3. The Learning Objectives and Subject Content
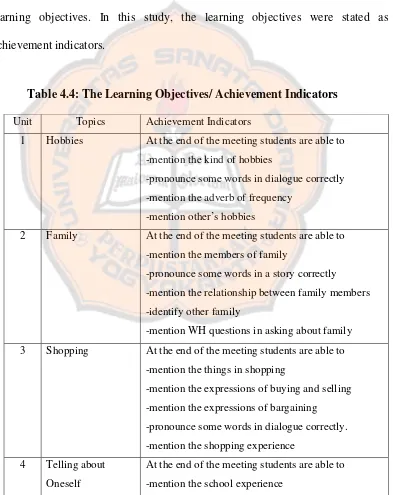
After formulating the Basic Competences, the researcher specified the learning objectives. In this study, the learning objectives were stated as achievement indicators.
Table 4.4: The Learning Objectives/ Achievement Indicators
Unit Topics Achievement Indicators
1 Hobbies At the end of the meeting students are able to -mention the kind of hobbies
-pronounce some words in dialogue correctly -mention the adverb of frequency
-mention other’s hobbies
2 Family At the end of the meeting students are able to -mention the members of family
-pronounce some words in a story correctly -mention the relationship between family members -identify other family
-mention WH questions in asking about family 3 Shopping At the end of the meeting students are able to
-mention the things in shopping
-mention the expressions of buying and selling -mention the expressions of bargaining
-pronounce some words in dialogue correctly. -mention the shopping experience
4 Telling about Oneself
-mention the biography
-use Simple Past in expressing about experience -use Simple Future in a short paragraph
-mention their dreams in the future
5 Describing People At the end of the meeting students are able to -mention the expressions of feeling
-mention the physical appearance -mention the personal characteristics -use adjectival word in sentences -identify their idols
6 Describing Place At the end of the meeting students are able to -mention the expressions of admiration -pronounce the words correctly
-mention the language in describing place -make paragraph about describing place -identify the places students have ever visited 7 Giving Direction At the end of the meeting students are able to -mention the expressions of giving direction -pronounce the words correctly
-mention the vocabularies in giving direction -make direction to others
8 Giving Procedure At the end of the meeting students are able to -mention the expressions of giving procedure -pronounce the words correctly
-mention the procedural words
-make procedure of making something -mention the steps of giving procedure
4. Teaching Learning Activities
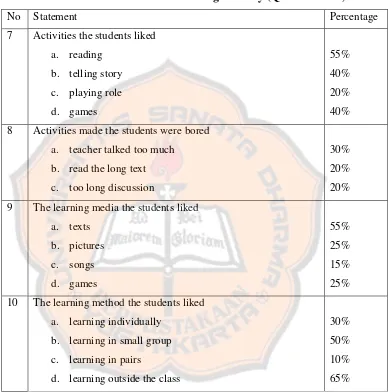
activity the students get bored. The presentation of the data gathered can be seen as follow:
Table 4.5: The Result of Pre-Design Survey (Question 7-10)
No Statement Percentage
7 Activities the students liked a. reading 8 Activities made the students were bored
a. teacher talked too much b. read the long text c. too long discussion
30% 20% 20% 9 The learning media the students liked
a. texts 10 The learning method the students liked
a. learning individually b. learning in small group c. learning in pairs
d. learning outside the class
30% 50% 10% 65%
students felt bored. Although most students (55%) liked using text as their media, the researcher chose Task-Based materials. Thirteen students (65%) liked learning outside the class, but it considered to the topic being discussed. If in the learning activity needs more places to explore, they might do it outside the class. The other ten students (50%) liked studying in the small group that might consist of three to four students.
In designing the material, the researcher tried to percentage the four skills were listening 10%, speaking 60%, reading 20%, and writing 10%. It can be seen that most students liked reading. Listening was given to make students common hearing English conversation. The focus of this study was speaking so this skill has the biggest percentage. Doing more practice, students would be more fluent and confident. Reading was given because most students liked reading. So the researcher always gives passage in each topic but in small portion. Then, writing was given as measurement between students’ pronunciation and writing. The four skills have their own role so they should be included in the learning activity. In teaching learning activity, the researcher tried to avoid talk too much in front of the class. The action would made students get bored. The most interesting media chosen by the students was text. But the researcher would use pictures and games in the learning activity. Learning in small group that consists of three or four students would be the first alternative in teaching learning activity.
Pre-activity
In this section, teacher introduces class about Warm Up and Speak Up. The purpose of this section is to prepare students about the topic they will learn. The activity in this section is still simple because it will motivate students to the learning process.
Warm Up!
Warm Up! is the activity which stimulates students to explore the topic being discussed. The activities in this section such as listening to the recording, filling in the blanks, and guessing the activities from the pictures.
Speak Up!
Speak Up! is a warming up activity in order to make students wants to speak English. The kind of activity in this section is small games by finding their friends based on the instruction.
Whilst-activity Think It!
Think It!is the activity which stimulates students to think (use their brains) based on the topic being discussed. The activity in this section is answering the questions based on the text, or solving the problem based on the situation. This section will use students’ creativity.
Language Focus
Catch It!
Catch It!is the activity which done to be more understand about the theory that the students have learnt in Language Focus. The activity in this section is playing role where students will work together mutually.
Post-activity Work It Out!
Work It Out!is the last activity of the course. The activity in this section is written activity. Students can write their experience, arrange the word into good sentence. Then, students share the result to their friends in front of the class. The framework of the learning activity can be seen in the following table.
Table 4.6: The Topics and Activities
Unit Topics Activity
1 Hobbies 1. Pre-activity
Warm-Up!
(Guess the picture) Speak-Up!
(Small games: Finding friends) 2. Whilst-activity
Think It!
(Question and answer based on the text ) Language Focus
(Explain the theory by the teacher) Catch It!
(Role play: My friends’ hobbies) 3. Post-activity
Work It Out!
good sentence.)
2 Family 1. Pre-activity
Warm-Up!
(Listen to the recording) Speak-Up!
(Small games: Finding friends ) 2. Whilst-activity
Think It!
(Question and answer based on the text) Language Focus
(Explain the theory by the teacher) Catch It!
(Role play: Uniting Family) 3. Post-activity
Work It Out!
(Written activity and share: Make Family tree)
3 Shopping 1. Pre-activity
Warm-Up!
(Listen to the recording) Speak-Up!
(Small games: puzzle) 2. Whilst-activity
Think It!
(Question and answer based on the text) Language Focus
(Explain the theory by the teacher) Catch It!
(Role play: Buying and selling activity) 3. Post-activity
Work It Out!
5. Materials Evaluation and Revision
The researcher knows that the designed materials needed to be improvement. Then, the researcher distributed the questionnaire as the post design survey. This questionnaire distributed to four English teachers and one lecturer. The purpose of this questionnaire was to get comment and suggestions about the designed materials.
Table 4.7: The Description of Participants of Post- Design Survey Educational background Teaching Experience (years) Group of participants
S1 S2 <10 10-20 >20
The lecturer of Sanata Dharma University
- 1 1 -
-The teacher of SMP 1 Muntilan
Table 4.8: The Result of Post- Design Survey
No Statement N Mean
1 The basic competences are well formulated 5 3,6
2 The indicators are well formulated 5 3,2
3 The materials match the basic competences and indicators 5 3,8
4 The topics are well arranged 5 4
5 The topics are suitable to teach speaking for extracurricular in Junior High School
5 4
6 The content of materials is relevant to the theory of Task-Based Learning
5 4
7 The tasks are well elaborated and sufficiently varied to facilitate the students to understand the topic being discussed
5 3,6
8 The pictures are interesting enough to attract students’ attention
5 3.8
9 The level of difficulty suits the students’ level 5 3.8 10 Task Based Learning is developed in the materials 5 3.8
Answering the closed-ended questions, the participants also gave comments and suggestions for the improvement of the designed materials.
The general comments from the participants: a. The designed materials were very good.
b. It only needs the addition in the learning activities. c. Grammar needs to be revised.
d. Please be careful with the use of symbols.
Language Teaching. The second suggestion was that the researcher should give not only written test but also spoken test in the post-activity. Actually, it was written in the teacher manual that after students did the exercise, students share the result to their friends in front of the class. The third suggestion was that the researcher should give many kinds of example to enlarge the students’ vocabulary. In this case, the researcher only gave those vocabularies because the researcher, then, ask the students to find the other vocabularies related to the topic. And the last was the researcher should reduce and omit the mistakes of minimum requirements. The researcher knew that this mistake so crucial in designing materials. Getting the comments and suggestions about the designed materials, the researcher continued to revise the product to get the better materials. The revision and improvement on the designed materials based on participants’ suggestions would be discussed here. The researcher accepted almost the suggestions. The researcher agreed to revise the grammar because this mistake so crucial. The researcher also should check and re-check again to avoid the minimum requirements in this study. Based on the result of the post-design survey, the researcher should reformulate the indicators. By reformulate the indicators, the learning objectives would be clearer.
List of the revisions of the designed materials: 1. Revision of the grammar.
Hopefully, by doing those revisions the teaching learning process would be more successful than before.
From data of the participants’ opinion, it was found that the means ranged from 3.51 – 5.00. It was also found that the average means was 3.76. It could be concluded that the materials design were good and acceptable for the students of extracurricularEnglish Clubin SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan.
B. The Students’ Responses to the Materials
To get the data about the students’ response to the implementation of the designed materials, the researcher distributed the questionnaire to all of the students of extracurricularEnglish Club. The questionnaires were distributed after the researcher revised the designed from the post-design survey.
Table 4.9: The Result of the Materials’ Implementation
No Statements N Mean
1 I enjoy joining extracurricularEnglish club 20 4.5
2 I like to the topic explained 20 4.1
3 I was more enthusiastic to the learning activity 20 4.2 4 The materials suited the students’ understanding 20 4.1
5 The teaching learning activities were so vary 20 4.5
6 The learning processes were so enjoyable 20 4.25
7 I was not feel bored in this extracurricular 20 3.95
8 I became more confident to this learning activity 20 4
9 The language used was understandable 20 4.3
From the data above, it can be said that most of students enjoy joining extracurricular English Club. They liked the topics being discussed because the learning activities were so vary. The language was understandable by the students. They became more confident in this course. There was one student who did not like the topic being discussed and less confident. There were three students who felt bored to the learning activity.
Students’ opinion in the implementation of the designed materials: 1. I liked this activity because I felt comfortable.
2. This activity made me more motivated in learning English. 3. I got more vocabularies in this course.
4. I became more enthusiastic and confident to speak in front of the class. 5. These activities made me feel learning by playing.
6. We can interact to each others.
Some students commented that they felt bored when the instruction was not understood by the students. The teacher always asks the students whether they know the instruction or not. When students had not understand the instruction yet, they teacher explained it again.
53 CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS
This chapter consists of two parts. The first part is the conclusion of the study. The second is the suggestions that are expected to help the English teachers of SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan in teaching extracurricular English Club and for other researchers.
A. Conclusion
This study was to design of English instructional materials for English Club in SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan. There were two problem formulations in this study. Those problems were (1) What does the designed set of materials for extracurricular English Club in SMP Negeri 1 Muntilan look like? (2) What are the students’ responses to the implementation of the designed materials?
In the syllabus, it was covered eight units but only three units were developed in the research. The researcher implemented one unit. They were Hobbies, Family, and Shopping. The more complete design can be seen in the appendix.
To answer the second research problem, the researcher distributed questionnaire to the students. It was conducted to get the response whether the materials design were interesting and acceptable. From the statistical data, it was found that the means ranged from 3.51 – 5.00. It was also found the average means was 4.24. It could be concluded that students enjoyed and liked learning activities as the researcher implemented in extracurricularEnglish Club.
B. Suggestions
The researcher has some suggestions to the English teacher and other researcher who conduct the same study.
1. Suggestion for English teacher
In teaching extracurricular, it should be better if the teacher know the students needs. Materials that suit the students’ needs will help the learning activity be more success. Then, teacher should know the approach that will be used in teaching extracurricular like Communicative Language Teaching. This approach will help teacher in managing their students and leads teacher to be more creative in designing the materials. In this approach, there are many role of teacher that will very be useful in teaching learning activity and teacher should pay attention to the roles.
2. Suggestion for the other researcher
REFERENCES
Agustien, H. I. R. 2004. Language and Language Learning. Singapore: SEAMEO-Regional Language Centre.
Borg and Gall. 1983. Educational Research an Introduction. New York: Longman.
Brown, D. 2004.Language Assessment Principles and Classroom Practices. New York: Longman.
Bushman, J. H.Teaching English Creatively. Springfield: Charles C Thomas. Danarti, D. 2008.50 Games for Fun. Yogyakarta: Penerbit ANDI.
Hutchinson, T and Waters, A. 1987. English for Specific Purposes: A Learning Centered Approach. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Hornby, A. S. 1995. Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary. London: Oxford University Press.
Kemp, J. E. 1977. Instructional Design: A Plan for Unit and Course Development. Belmont: Fearon Pitman Publishers USA.
Leo, S. 2006.English for Leisure Time.Jakarta: Gramedia Pustaka Utama. Lewis, G. 1999.Games for Children. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Luoma, S. 2004. Assessing Speaking. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Noar, G. 1953. The Junior High School Today and Tomorrow. New York:
Prentice Hall.
Nunan, D. 1989.Designing Tasks for the Communicative Classroom. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Richards, J. 1997.New Interchange. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Richards, J. 2001. Curriculum Development in Language Teaching. Cambridge:
Cambridge University Press.
Rivers, W. M. 1968. Teaching Foreign-Language Skills. Chicago and London: The University of Chicago Press.
Rivers, W. M. 1983. Communicating Naturally in a Second Language. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Wenden, A and Robin, J. 1987. Learners Strategies in Language Learning. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Sources from the internet:
http://images.search.yahoo.com/search/images?p=surfing&ei=utf-8&y=Search&fr=yfp-t-701&xargs=0&pstart=1&b=21&ni=20, accessed on January 25th, 2010
Kuesioner
Nama :
Kelas :
1. Apa alasan Anda mengikuti ekstrakurikuler Bahasa Inggris?
a. Karena senang dengan Bahasa Inggris
b. Karena ikut teman sehingga termotivasi untuk ikut
ekstrakurikuler
c. Karena disuruh orang tua
2. Kapan mulai belajar Bahasa Inggris?
a. SD
b. SMP
3. Pernahkah mengikuti kursus Bahasa Inggris?
a. Ya pernah
b. Belum pernah
4. Kesulitan apa yang Anda alami dalam belajar Bahasa Inggris?(pilihan
boleh lebih dari satu)
a. Kosakata yang belum dimengerti
b. Kurang percayadiri dalam berbicara
c. Lain-lain………..
5. Hambatan apa yang Anda alami dalam belajar Bahasa Inggris?
a. Tidak adanya buku penunjang
b. Tidak adanya kemauan untuk berlatih
c. Lain-lain………
6. Apa topik yang menarik untuk dipelajari ekstrakurikuler Bahasa Inggris?
(pilihan boleh lebih dari satu)
a. Describing people
b. Direction