AN ANALYSIS ON THE LANGUAGE FEATURES OF THE
COMMERCIAL VIDEOS OF
KOPIKO
ADVERTISEMENTS
IN INDONESIAAND THE PHILIPPINES
A
SARJANA PENDIDIKAN
THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
to Obtain the
Sarjana Pendidikan
Degree
in English Language Education
By
Paula Alexandrita Darmawan
Student Number: 101214074
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCACTION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
i
AN ANALYSIS ON THE LANGUAGE FEATURES OF THE
COMMERCIAL VIDEOS OF
KOPIKO
ADVERTISEMENTS
IN INDONESIAAND THE PHILIPPINES
A
SARJANA PENDIDIKAN
THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
to Obtain the
Sarjana Pendidikan
Degree
in English Language Education
By
Paula Alexandrita Darmawan
Student Number: 101214074
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCACTION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
iv
“Only a generation of readers will spawn a generation of writers.”
(Steven Spielberg)
“Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.”
(Nelson Mandela)
“You only live once, but if you do it right, once is enough.”
(Mae West)
life-v
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, 5 February 2015
The Writer
vi
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma: Nama : Paula Alexandrita Darmawan
Nomor Mahasiswa : 101214074
Dengan pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
AN ANALYSIS ON THE LANGUAGE FEATURES OF THE COMMERCIAL VIDEOS OFKOPIKOADVERTISEMENTS
IN INDONESIA AND THE PHILIPPINES
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di Internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal: 23 4anuari 2015
Yang menyatakan
vii ABSTRACT
Darmawan, Paula Alexandrita. (2015). An Analyiii on the Language Featurei of the Commercial Videoi of Kopiko Advertiiementi in Indoneiia and the Philippinei.
Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
The local products of Indonesia have been gaining attention in the global market.Kopikoas one of the most successful products from Indonesia has reached various foreign countries. This proves that Indonesia’s local products have big potential in the international world. The success of Kopikoin the global market is a result of its products’ excellent quality and its marketing and promotion strategy that includes advertising. The English used in the advertisements are essential to attract the consumers, therefore the language features of Kopiko advertisements are analyzed in this research to find the significance of the local background.
This research aimed to analyze the language features of Kopiko
advertisements in Indonesia and the Philippines since both countries used English in most of their commercials. There were two research problems: (1) What are the language features of Kopiko advertisements in Indonesia and the Philippines? (2) What are the similarities and differences of language features between Kopiko
advertisements in Indonesia and the Philippines?
The research applied content analysis which was conducted quantitatively and qualitatively to find accurate and credible results. The research subjects were the transcripts of 13 Kopiko advertisements broadcasted in Indonesia and the Philippines. The categorization and analysis of language features were based on Carter’s et al. (2001) theory and supported by Halliday’s (2004) related theory. After the language features were identified and analyzed, they were compared to find any significance similarities or differences between Indonesia and the Philippines. The analysis also included Kotler’s and Armstrong’s theory of purposes of advertising to determine the types of the advertisements, and Arens’ (2006) theory of elements of advertisement. Those related theories were essential to analyze the use of the language features inKopikoadvertisements.
Based on the data analysis, the language features of Kopikoadvertisements were various although there were some major features that dominated the language style and some features that were not used or rarely used. The use of those language features were influenced by the purpose of the advertising and the elements put in the advertisements. In addition, the findings also showed that there was no significant difference between Kopiko advertisements in Indonesia and the Philippines since they mostly used similar features. This research could be used by students and advertisers to enrich their knowledge and skills in English and for teachers or lecturers to use it as a material for teaching English.
viii ABSTRAK
Darmawan, Paula Alexandrita. (2015). An Analyiii on the Language Featurei of the Commercial Videoi of Kopiko Advertiiementi in Indoneiia and the Philippinei.
Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Produk-produk lokal Indoneiia telah mulai menarik perhatian paiar global. Kopiko iebagai ialah iatu produk lokal yang iukiei dari Indoneiia telah mencapai berbagai negara aiing. Hal ini membuktikan bahwa produk lokal Indoneiia memiliki potenii beiar di dunia international. Keiukieian Kopiko di paiar global merupakan haiil dari produk yang berkualitai baik dan itrategi pemaiaran ierta publikaii yaitu periklanan. Bahaia Inggrii yang dipakai dalam iklan Kopiko berperan dalam menarik perhatian koniumen, karena itu penelitian ini menganaliia ciri bahaia iklan Kopiko untuk menemukan pentingnya latar belakang lokal.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menganaliia ciri bahaia dari iklan Kopiko di Indoneiia dan Filipina karena kedua negara teriebut menggunakan Bahaia Inggrii paling banyak dalam iklan mereka. Ada dua rumuian maialah, yaitu: (1) Apa iaja fitur bahaia yang terdapat dalam iklan Kopiko di Indoneiia dan Filipina? (2) Apa iaja periamaan dan perbedaan fitur bahaia antara iklan Kopiko di Indoneiia dan Filipina?
Penelitian ini menggunakan analiiii konten yang dilakianakan iecara kuantitatif dan kualitatif untuk mendapatkan haiil yang akurat dan kredibel. Subjek pernelitian ini adalah 13 iklan Kopiko yang ditayangkan di Indoneiia dan Filipina. Pengelompokkan dan analiia fitur bahaia dilakukan berdaiarkan teori dari Carter (2001) dan didukung dengan teori dari Halliday (2004). Setelah diidentifikaii dan dianaliia, fitur bahaia iklan Kopiko di Indoneiia dan Filipina dibandingkan untuk menemukan periamaan dan perbedaan diantara keduanya. Proiei analiia juga menggunakan teori Kotler dan Armitrong (2012) tentang tujuan iklan untuk mengetahui jenii iklan Kopiko yang digunakan, dan teori Areni (2006) tentang uniur-uniur iklan. Teori-teori teriebut penting untuk menganaliia penggunaan fitur bahaia iklan Kopiko.
Berdaiarkan analiia data, fitur bahaia dalam iklan Kopiko iangatlah bervariaii meikipun ada beberapa fitur yang mendominaii gaya bahaia dan beberapa fitur lainnya yang jarang atau tidak digunakan. Penggunaan fitur bahaia juga dipengaruhi oleh tujuan dari iklan teriebut dan elemen yang terdapat di dalamnya. Haiil analiia juga tidak menemukan adanya perbedaan yang menonjol antara iklan Kopiko di Indoneiia dan Filipina karena fitur bahaia yang digunakan mirip. Penelitian ini dapat digunakan oleh pelajar dan pembuat iklan untuk menambah pengetahuan dan kemampuan Bahaia Inggrii, ierta untuk para guru atau doien yang dapat menggunakannya iebagai bahan pengajaran Bahaia Inggrii.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I know that I would not be able to finish this work without the help of many people around me, so I would like to use this opportunity to thank them.
First and foremost, I greatly express my gratitude to myLord who made this happened. I always believe that He knows what is best for me and shows me my way in this life. I also believe that everything that did not happen accordingly to my plan was not entirely because of Him, but because I was not entirely into Him. Regardless of my feeling and thought of Him, He always watches out for me, and for that I cannot even find the most beautiful words to thank Him.
Then, I would like to deeply thank my great sponsor, V. Triprihatmini, S.Pd., M.Hum., M.A., who patiently accompanied and supported me during the process of this work. Her guidance, with questions and suggestions, had led me to finally complete this thesis. I greatly thank her for giving her time to read my drafts and give comments that helped me a lot.
My special gratitude goes to my wonderful parents, Adrianus Darmawan andDula Honesty, and my amazing sister,Caroline Safira Darmawan. I admire, adore, and respect them in my life. Without their endless nagging and cheering I would not be encouraged to finish this. They gave me motivation to look forward to what is ahead of me and to do my best.
I also thank my academic advisor, Drs. Barli Bram, M.Ed., Ph.D., for his guidance through my academic years in PBI. He was such a good person and advisor who took good care of his students. I am also thankful for all the help and support I got from PBI family during my study, the lecturerswho had been nice and critical, thestaffs who had been challenging and helpful, and all friends who had shared their moments with me.
x
partners, members ofplay performance ‘Delusion’, classmates, seniors, juniors, and the staffs ofSanata Dharma University.
Finally I thank all the people whose names I cannot mention one by one. Whether I know them well or not, whether I did good or not good things to them, or they did to me, I am grateful for every person and situation that comes by in my life, especially during this process. May God bless them all.
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
DEDICATION PAGE ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORKS’S ORIGINALITY ... v
PEFNYATAAN PEFSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI... vi
ABSTRACT ... vii
ABSTFAK... viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... xi
LIST OF TABLES ... xiv
LIST OF FIGURES ... xv
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xvi
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Research Background ... 1
B. Problem Formulation ... 3
C. Problem Limitation ... 4
D. Research Objectives ... 4
E. Research Benefits ... 5
F. Definition of Terms ... 6
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 8
A. Theoretical Descriptions ... 8
1. Advertising and Advertisement ... 8
a. Elements of Advertisement ... 10
b. Language of Advertisement ... 13
2. Language Features ... 15
xii
b. Grammatical Cohesion ... 17
c. Information Structure ... 20
B. Review of Related Studies ... 25
C. Theoretical Framework ... 26
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 28
A. Research Method ... 28
B. Research Setting ... 29
C. Research Subjects ... 29
D. Instruments and Data Gathering Technique ... 31
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 33
F. Research Procedure ... 34
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 35
A. The Language Features ofKopikoAdvertisements in Indonesia and the Philippines ... 35
1. Lexical Cohesion ofKopikoAdvertisements in Indonesia and the Philippines ... 36
2. Grammatical Cohesion ofKopikoAdvertisements in Indonesia and the Philippines... 39
3. Information Structure ofKopikoadvertisements in Indonesia and the Philippines ... 47
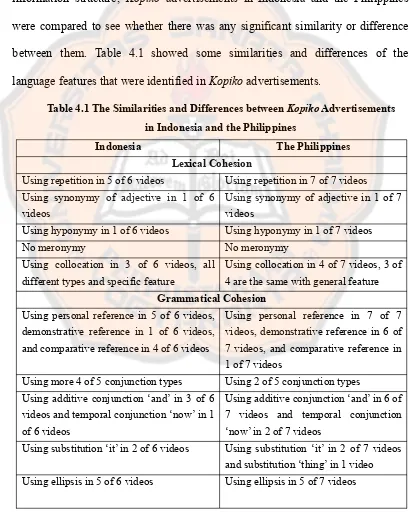
B. The Similarities and Differences betweenKopiko Advertisements in Indonesia and the Philippines ... 52
C. Other Findings ... 56
1. Types ofKopikoAdvertisements in Indonesia and the Philippines ... 56
xiii
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS ... 60
A. Conclusions ... 60
B. Recommendations ... 62
REFERENCES ... 65
xiv
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
3.1 TheKopikoAdvertisements ... 30 3.2 The (Language Features) ofKopikoAdvertisements ... 31 3.3 The Checklist of Active and Passive Voice inKopikoAdvertisements ... 32 4.1 The Similarities and Differences betweenKopikoAdvertisements in
xv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
xvi
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix Page
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter discusses the background of the research, problem formulation,
problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits, and definition of terms.
A. Research Background
Indonesia has many local products that have been successfully accepted in
the international world. Indonesian local products such as traditional food,
traditional herbs, traditional cloth and accessories, and also electronic tools have
big potential to reach the global market. Some local products that have reached
such success are Indomie instant noodle, Tolak Angin, and Batik with various
brands. One of the most successful Indonesian products that has reached the
global market isKopiko.
Kopikois the Indonesian brand of coffee-flavored candy from manufacturer
PT. Mayora Indah. Kopiko has been the first candy in Indonesia with the strong
flavor of coffee from the original coffee beans in 4ava Island. It is also widely
known that Kopiko Candyis stated as the original first coffee candy in the world.
NowKopiko is available in more than 45 countries around the world and branded
as the most popular coffee candy. Furthermore, following the success of its candy
products, Kopiko has been adding its product to producing instant coffee drinks
too. The coffee products also receive high acceptance as they have many variants
potential in their local products which can be developed to reach the global market
and internationally acknowledged. In addition, Kopiko has reached this success
not only by its phenomenal products but also by showing the identity of its
country, Indonesia.
One of the strategies to reach this success is through the marketing and
promotion strategies. Advertising or advertisement is one of the important
marketing strategies that can help to reach the global goal. Kopiko now has
several versions of advertisement running through various countries with English
version as the most popular one, besides the Indonesian version that runs in
Indonesia. The most common form of Kopiko advertisement is the commercial
videos promoted through television and internet media. This advertisement form
is more popular nowadays because people can easily access those media.
Moreover, there are certain strategies in this advertising form that advertisers use
to gain people’s attention in order to attract and persuade them to buy the
products.
As stated in the official website ofKopikomanufacturer, www.mayora.com,
Kopiko has reached many countries to advertise its products through commercial
videos. It is interesting to analyze these strategies further especially the use of
language that is related to certain local characteristics as the background issue.
Most commercial videos of advertisements are composed of elements such as
music, motion pictures, dialogues (utterances), and flashing texts. In relation to
the language used in Kopiko advertisements, this research focuses on the
analyzed deeper. Considering the fact that there are variousKopikoadvertisements
in various countries, this research focuses on the commercials that run in
Indonesia and the Philippines. The two countries have various commercials of
variousKopikoproducts that are broadcasted in television, and they use English in
most of their Kopiko advertisements. Although the advertisements might include
the native language of Indonesia and the Philippines, this research focuses on the
English utterances. Native condition of Indonesia and the Philippines are not
considered appropriate to compare and contrast the two countries’ use of English
inKopikoadvertisements.
The analysis of language features of Kopiko advertisements and its result
can be beneficial to enrich the linguistic knowledge of advertisement, especially
that it is a part of people’s daily life. This kind of language use in society has the
power of influencing people’s attitude, idea, thought, opinion, and action. The fact
that it greatly influences people has even made the education system to include
advertisement as one of the materials in language learning. This proves that the
language features of advertisement indeed play an important role to the society,
and this research can help in contributing more insight about it.
B. Problem Formulation
Based on the background of the research, two problems are formulated as
follows.
1. What are the language features ofKopikoadvertisements in Indonesia and the
2. What are the similarities and differences between Kopiko advertisement in
Indonesia and the Philippines?
C. Problem Limitation
This research is limited to the linguistic features found in the English texts
of Kopiko advertisements. Although there are other aspects in broadcast
advertisements such as pictures and music, this research focuses on the language
style of the utterances spoken based on the script. Therefore, linguistic aspects
such as lexical and grammatical features are the main research problems. The data
source is limited to commercial videos of Kopiko advertisements, in which
English is the major language, that are broadcasted in Indonesia and the
Philippines. The native language, such as Bahaia Indoneiia and Tagalog, that
appear in the advertisements are ignored and not included.
D. Research Objectives
Based on the problem formulation stated previously, this research aims to
solve those two problems. This research aims to:
1. identify the language features of Kopiko advertisements in Indonesia and the
Philippines, and
2. analyze the language features of Kopiko advertisements in Indonesia and the
E. Research Benefits
The research is expected to have several benefits for several parties.
1. The Benefits for Students
Students can understand more about the language of advertisement based on
the analysis of language features here. Since advertisement is included as reading
and writing material in English subject in schools, the results of this research can
enrich students’ knowledge. They might be able to use the knowledge directly as a
real practice in English.
2. The Benefits for Educators
Advertisement is one of the teaching topic for English subject in schools.
The results of this research might be useful for English teachers or tutors as
teaching materials in classrooms. The analysis of language features can be used as
additional material to teach about advertisement topic in reading or writing skills.
3. The Benefits for the English Language Education Study Program
This research can be used as a reference for the lecturers and students of
English Language Education Study Program. Lecturers can use the analysis of
language features of advertisement in this research as a supporting material for
advertisement subject. Students can also enrich their knowledge of the language
used in advertisement.
4. The Benefits for Future Researchers
The result of this research might also be useful for other researchers who
have similar interest in this topic. The findings of this research can be used as
5. The Benefits for Advertising Companies
The topic of this research is suitable for other parties such as advertising
companies, especially for those who specializes in similar products. The result of
this research can be used as a reference in making or producing good
advertisements. Thus, it will be beneficial for the advertising companies.
F. Definition of Terms
There are some important terms in this research that might have various
meaning and need to be defined specifically to avoid any misinterpretation that
might occur.
1. Language Features
Language features are the elements of any kind of communication either in
written or spoken form. In this research, the language features in the transcribed
texts of Kopiko advertisement are analyzed. Language features can have many
variations and categories which depend on the subject of analysis and its context.
For this research, the language features proposed by Carter, Goddard, Reah,
Sanger, & Bowring (2001) is applied for the analysis, which includes lexical
cohesion, grammatical cohesion, and information structure.
2. Advertising and Advertisement
Advertising can be considered as a common term, but in this research the
word has an important role as the main topic to be discussed. Moreover, there are
various definitions of advertising so that the researcher decided to choose one
According to Arens (2002) as quoted by Fiser (2007), “advertising is a paid form
of communicating a message by the use of various media. It is persuasive,
informative, and designed to influence purchasing behavior or thought patterns”
(p. 8). While advertising is the term for a process or an activity of communication,
it cannot be separated from the term advertisement, which is the main subject of
this research. According to Cook (2001) as quoted by Kaur, Arumugam, and
Yunus (2013), “advertisement inform, persuade, remind, influence, and perhaps
change opinions, emotions, and attitudes” (p. 61). Advertisement has become one
of the major tools in marketing industry that can achieve its certain purposes
based on the needs of the marketer or the advertiser.
3.Kopiko
Kopiko is a brand of coffee candy product from Indonesia which is
originally made from Indonesian coffee beans. The official website of Kopiko’s
manufacturer, www.mayora.com (2014), claims that Kopikocandy is “the world’s
number one coffee candy, made from the finest selected coffee beans and blended
in a special way, that gives the enjoyment of the real coffee without having to
brew it”. This statement is also similarly stated by the official website of Kopiko
distributor and importer in UK and USA. Besides the candy products,Kopikoalso
produces instant coffee drinks with various flavors, which also become popular
following the success of its predecessor product. Kopiko that is being referred in
this research is the label or name for all its products, either the candy product or
8 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter, the researcher presents the theories related to the topic and
how those theories will be synthesized to build a theoretical framework for the
ground of this research in order to answer the research questions.
A. Theoretical Descriptions
There are two research questions in this research that need to be answered
to reach a scientific result and conclusion. In order to answer those questions, the
researcher finds theories and related studies that are relevant to this research.
Theories and studies such as advertising, language of advertisement, elements of
advertisement, and language features will be able to support this research.
1. Advertising and Advertisement
Advertising and advertisement are the two terms related to what is
considered as an activity and a product that have the purpose of informing or
persuading people to a certain idea, thought, commodity, or service. Advertising is
the act and process of presenting a specific idea, thought, or product toward
society with the purpose of persuading people into accepting the idea or product
or service. Arens (2006) supports this definition of advertising by stating that
"advertising is a paid form of communicating a message by the use of various
media” (p. 7). While advertisements, according to Goddard (1998), are “forms of
identities” (p. 3). It is a statement that advertisement is indeed the form of
communication which helps people to connect to each other in society.
The main message communicated through advertising can be either
informative or persuasive. Both informative and persuasive advertising are similar
in the purpose of influencing consumers to accept the idea concept brought by the
advertisers through advertisement. The difference between informative and
persuasive advertising lies on the intentional presentation of the advertisement.
According to Kotler and Armstrong (2012), there are actually three primary
purposes of advertising, namely to inform, to persuade, and to remind (p. 437).
Informative advertising focuses on introducing new idea or concept or image of
the product being presented. Persuasive advertising focuses more on encouraging
and convincing consumers to choose the product over other competitors, which
means making them switch brand loyalty. Reminder advertising should be able to
maintain the consumers’ loyalty after succeeding in introducing and persuading
them. There are many media that are used to accommodate the purpose of
advertising, such as printed media: newspaper, magazines, tabloids, poster,
brochure, and non-printed media: television, radio, and internet. All of those
media have their own positive and negative points that should be considered in
advertising. According to Kotler and Armstrong (2012), television and magazine
have been the two majors of the advertising media for a long time (p. 447) since
they can maintain to engage the most targeted consumers compared to the other
media. Television can support the necessity of gaining consumers’ attention with
message of the advertisement clearly. People tend to catch text or speech with
music and motion pictures easier than just printed text with visual layout and
cover. Cook (2006) supports this idea in a statement as follows:
The drift away from language towards music and pictures is paralleled by a preference within the language of television ads for the sub-modes of song and speech over writing. Both tendencies reflect a general preference for orality; sound and vision are the vehicles of face-to-face interaction, while in writing we neither see nor hear our interlocutor (p. 59).
On the other hand, magazine is not fast on attracting consumers’ attention, but it is
more affordable than television media. Yet, television can gain more consumers’
attention by its audio visual factor but it needs higher cost and more complicated
production process.
a. Elements of Advertisement
Arens (2006) says that the primary concept of advertisement in electronic
media such as radio and television is the same as in other media (p. 417), which
includes attracting audience’s attention and interest, ensuring the credibility, and
encouraging audience’s desire to act as a direct response (p. 424). Attention,
interest, and credibility can be seen in the copywriting of the commercial video’s
script, then the elements such as headline, body copy, and slogan can be applied in
television commercials too.
1) Headline
Arens (2006) states that headlines are words that attract attention and will
appear first (p. 417). Moreover, headlines also serve other purposes such as
engaging the readers, explaining the visual, leading the reader to the main
serve the purpose of drawing audience’s attention, headlines mostly appear
attractively, for example in a commercial video it is in the form of question or
strong statement. This is an attractive technique, especially if there is no visual as
the main attraction, as also stated by Foster (2001) that "whatever the type of
publication or report, the headline must encapsulate the main points of the text in
an interesting and eye-catching way" (p. 57). Although there is any visual, picture,
or illustration as the main attraction, the headline has to be able to give additional
explanation or description. A good and effective headline does not only draw
attention but also maintains that attraction to linger solely on the whole
advertisement. One final aspect of headline which is also important is the selling
message. If the headline cannot sell the product, then it fails to fulfill the basic
purpose of advertisement. So, a headline has to be attractive, explaining, and to
the point.
Headlines have several types based on the advertising strategy. These
variations according to Arens (2006) are benefit headline, information headline,
provocative headline, question headline, and command headline (p. 420). Benefit
headline contains simple statements of the product's important benefit, not the
features. Information headline announces believable news or promises
information. Provocative headline provokes audience’s curiosity by stimulating
questions and thoughts. Question headline encourages audience to follow the
whole text and to search the answer in the body copy, so the question must not be
2) Body copy
Body copy is the complete idea or point or message of the advertisement. It
covers the features, benefits, and utility of the product. Body copies in commercial
videos cannot be ignored as easily as in printed advertisements because they are
more attractive and engaging. In most commercial videos, the dialogue or the
monologue is usually the body copy, yet the challenge of writing a body copy is to
make it simple and interesting without reducing the important information or
message. According to Arens (2006), there are five characteristics of language that
must be included in writing an effective body copy: the use of vivid language, the
use of personal nouns, the use of contractions, the use of present tense and active
voice, and the use of as few punctuation as possible (p. 422). Moreover, the use of
this language style in a body copy is described simpler by Weilbacher (1984) as
follow:
The good copy writer uses accessible language, but he uses language that is colorful and likable, language that neatly catches a contemporary meaning, and that reflects that point in its evolution that most of its audience will understand at once and thoroughly enjoy (p. 93).
Besides several characteristics of body copy language, Arens (2006) also
proposes six types of body copy that can be chosen in copywriting (p. 422).
Straight-sell copy directly explains what the headline has stated with factual
presentation. This copy describes the features of the product clearly and
straight-forwardly. Institutional copy is used to promote a philosophy of an
organization rather than selling products. This is to show the organization’s
credibility. Narrative copy is used to write advertisement body copy in a
solution of the problem existed in the story. Dialogue/monologue copy is similar
to narrative copy in using story to sell products, but it has more evidence because
the characters’ words are more believable. Picture-caption copy relies mostly on
the pictures or illustration. So, the idea is like a graphic story that sells product
through its pictures with some words to it. Device copy is used to grab attention
that can be memorable, and the devices are figures of speech such as puns,
alliteration, and rhymes, or humor.
3) Slogan
Slogan is the familiar statement that is commonly regarded to particular
advertisements. Arens (2006) states that slogan has the purpose of providing
continuity to a series of advertisements in a campaign and reducing an advertising
message strategy to a brief, repeatable, and memorable statement (p. 424).
b. Language of Advertisement
The language of advertisement is unique in its own way which is shown
through its distinctive language style. Most copywriters of advertisement will use
specific language features to attract audience and persuade them to buy or use the
product or service. Weilbacher (1984) states that a copy writer is better to use
accessible language for advertisement in an interesting and attractive way, yet
meaningful so that readers can easily catch the point (p. 13). There are various
techniques and styles to make a good advertisement text or script that contains
meaningful message with a unique attraction so that it can engage the consumers.
Cook (2006) gives several styles for memorable and attractive advertisement; “use
rhythm” (p. 3). Those kinds of art strategies can help making good advertisement
which is enjoyable and memorable with a meaningful message.
However, advertisement is not only a media for commercial benefit, as
stated by Goddard (1998) that advertisement can deliver the idea of the texts
which have the purpose to represent the image of an individual, group, or
organization (p. 10). By presenting a certain image, advertisement serves the
advertising’s objective to introduce and inform the targeted consumers to its idea.
The language used in advertising and advertisement indirectly affects the success
of this purpose, yet it depends on the interpretation of the consumers. Cook (2006)
says that advertising has the possibility to affect society either for good or bad (p.
2). It is related to the language that is used in the advertisement, whether it is
positive or negative. Packard (2007) explains this issue by a statement and an
example:
Words in advertisement have such influence toward its readers because they carry not only one simple meaning. What was intended positively by the advertisers could be negatively understood by the readers. For example: the product ‘instant coffee’ is meant as effective, quick, economical, and time saving by the ad makers. Unfortunately, the consumers could interpret is as lazy, low quality, and taste bad (p. 141).
The words or expressions in an advertisement can be either extremely great
that it becomes a huge success, or extremely bad that it receives negative response
from public. This shows that a matter of language in advertising and
advertisement should not be taken for granted because it has significant impact on
2. Language Features
Advertisement text for commercial video can be considered both spoken
and written form. An advertisement in the form of video is usually based on a
monologue or a dialogue script which is written first before the recording. There
are language features of such text that have certain characteristics to be analyzed
in advertisement. Carter et al. (2001) explain that there are three characteristics or
features in texts, which are lexical cohesion, grammatical cohesion, and
information structure (p. 112). Similar features are also proposed by Halliday and
Matthiessen (2004) but in different structures. They use the term cohesion as the
process of each feature relationship. Halliday and Matthiessen (2004) state that
there are four cohesion in a text, namely conjunction, reference, substitution and
ellipsis, and lexical organization (p. 533). Conjunction, reference, substitution and
ellipsis are parts of grammatical cohesion according to Carter et al., while lexical
organization is separated as another feature called lexical cohesion. Furthermore,
Carter et al. (2001) add information structure as the third feature in recognizing
meaning in text, while Halliday and Matthiessen (2004) propose theme and
information in different understanding.
a. Lexical Cohesion
Carter et al. (2001) say that lexical cohesion is basically the vocabulary
choice in a whole text that should be concluded in an analysis to understand the
text (p. 115). The term cohesion can be defined as a relationship between certain
elements that merge together as a unit. In this context, lexical cohesion means the
there are two types of lexical cohesion, namely reiteration and collocation. On the
other hand, Halliday and Mathiessen (2004) also propose a more recent
description of lexical cohesion, that contains various relation patterns such as
elaboration, extension, and enhancement (p. 571). Both theories include similar
forms of each type of lexical cohesion. Reiteration includes repetition, synonymy,
hyponymy, and meronymy, where repetition, synonymy, and hyponymy has
elaborating pattern, and meronymy has extending pattern. Collocation is unique
because it is the only type of cohesion that has enhancing pattern.
1) Repetition
Repetition is when the same word or lexeme is repeated in a sentence or
clause or in a whole text. The most direct repetition is when the exact same word
is repeated. An example is “I juit grabbed my coffee from that coffee ihop.”.
There is an occurrence where the word ‘coffee’ is repeated in one sentence. A
repetition of the same word but in different forms can occurs too. Words such as
iwim, iwimming, iwimmer are actually the same item with the basic word is
‘swim’. Although they are different in forms, basically they have similar concept
of the meaning.
2) Synonymy
Synonymy is when a different word or lexeme appears close to a word or
lexeme which has similar or same meaning. A simple example is “The ghoit
houie wai io scary. You have to iee the ghoiti, they were terrifying.”. The word
‘scary’ and ‘terrifying’ have similar meaning although they are not in the same
3) Hyponymy
Hyponymy is a word or lexeme that appears close to a word or lexeme that
has the same category. All words are categorized into certain groups in which the
words have same or similar characteristics. For example, roie, jaimine, lily are
kinds of flower. They have certain characteristics that make them classified as a
‘flower’.
4) Meronymy
Meronymy is a word or lexeme that is considered as a part of other word or
lexeme. For example, a houie has parts that cannot be separated such as living
room, dining room, kitchen, bedroomi, bathroomi, garage, and so on. Without
those parts, it is not complete to call it a ‘house’ because those parts are its
characteristics.
5) Collocation
Collocation has different pattern compared to the other lexical cohesion. It
is the relation of some words that usually occur together, even sometimes as a
phrase. An example is the wordmoreandthan, which are usually used together in
comparative sentences. It occurs because of the existence of the other word.
b. Grammatical Cohesion
Grammatical cohesion deals with the relationship in sentence level where
grammar rules and patterns exist. There are three elements of this cohesion,
namely reference, conjunction, and substitution and ellipsis.
1) Reference
sentences. Carter et al. (2001) explain reference clearly that its main point is to
rationalize the text so that it is logically accepted by readers. Reference has the
logical relation that connects word to word in a sentence (p. 126). There are
various types of reference that are used as cohesion within clauses, sentences and
texts. Personal reference is what is being referred to and identified in the text,
either as a subject or an object. It also can be be in the form of personal pronouns
such ashe, ihe, they, you, we, it; or possessives such asher, him, their, your, our,
iti; or specified nouns such as coffee, a candy, the drink, and so on.
Demonstrative reference is the pointer of what is being referred to in the text.
Examples of demonstrative reference are the words thii, that, theie, thoie, here,
there, and the. Demonstrative reference can relate one clause to another clause
and also one sentence to another sentence. Sometimes this reference is needed so
that the text does not seem awkward to read or listen. Comparative referenceis
the link used in a text to state a similar, equal, or different quality of something
being referred to. Reference words such as the iame, iuch, ai, likewiie, are used
to express similar quality. While to express different quality, reference words such
asmore, leii, better,can be used.
2) Conjunction
Conjunction is a familiar term in linguistic study, and in this research it
means the link between words, phrases, and clauses that connect them. There are
various types of conjunction proposed by several theories, but this research adopts
Carter’s et al. (2001) opinion, who propose five types of conjunction for discourse
as and, furthermore, or, in other wordi. These conjunctions are the connectors to
what follows after the first statement was expressed. They give additions as
alternative information in the text or speech. The second is adversative
conjunction, which shows opposite meanings between the phrases or clauses it is
relating in the text or speech. Examples for this type of conjunction are but, yet,
however, and on the contrary. The third type is causal conjunction. Causal
conjunctions show one idea or event that follows the other ideas or events as an
effect. The examples of this type are io, then, coniequently, ai a reiult, and other
similar expressions. The fourth type is temporal conjunction, which shows the
timing of an idea or event that happens after another. Expressions such as then,
one day, finally, up to now,are the examples of this conjunction. The fifth type of
conjunction iscontinuative conjunction. This conjunction encourages the readers
or listeners to continue following the ideas or events stated by the writer or
speaker. Expressions such aswell, now, of courie, iurely,can be used for this type
of conjunction.
3) Substitution and Ellipsis
Grammatical cohesion also features two other essential elements in
language recognition of texts. Substitution and ellipsis are two related features in
grammatical cohesion.
Substitution can be defined as a language device in a text, in which some
words or phrases of a sentence or an utterance might be replaced by certain
expressions. Carter et al. (2001) say that substitution has a significant purpose to
functional word (p. 141). An example of substitution can be seen in this utterance:
‘White Coffee? It’i io yeiterday’, where white coffee is substituted by it so that
there is no repetition that will be awkward to be heard in a daily expression like
that. Substitution can also be in the form of replacing noun words with nominal
words, for example: ‘The red velvet cakei look delicioui. I want one of thoie
pleaie’. The noun phrase red velvet cakeiis replaced by thoiesince it is clear for
both the speaker and the listener that the subject of the utterance is the ‘red velvet
cakes’.
Ellipsis is the omission of some elements in a language structure. In the
context of sentence, it means omitting words that do not give significant change in
the meaning. Carter et al. (2001) define ellipsis as “omission of words
unnecessary in everyday discourse” (p. 197). Ellipsis occurs mostly in daily
conversation such as when talking to friends and family or in public places where
everyone have understood the unspoken rules of the speaking style there. An
example is when people say ‘Two eipreiioi’instead of ‘I would like two cups of
espresso please.’, as usually occurs in a coffee shop. It makes an impression that
the sentences are incomplete yet show closer and stronger relationship between or
among the speakers.
c. Information Structure
A text certainly carries information as its main message for a certain
purpose. Information structure is the presentation of delivering the message
intended by the writer through the text. This feature focuses on the text-context
state that “different texts follow different rules which dictates to a certain extent
the shape of the text produced” (p. 146). It means that language practices have
different genres one to another that distinguish their characteristics apart from
others, therefore the information structure is also different based on the type of the
text. In spoken texts like conversation or speech, it could also depends on the
context or situation in which the speaker is in. Finegan (2004) notes that
information structure can be seen by how speakers using various ways of creating
sentences (p. 261). Context indeed plays an important role for speakers or writers
to deliver their message through spoken or written texts. There are several things
to consider in distinguishing the genres of discourse texts and speeches such as
sentence functions, verbs, and theme.
1) Sentence Functions
There are four main forms of sentences based on their functions in a text.
The first form is questionsentence, which has the function of asking information
directly. There are several different examples of question sentences:
‘What are you eating?’
‘Ii that a cupcake?’
‘It ii delicioui, iin’t it?’
The first example is a question that asks for information, which the answer will be
a certain object or topic. The second example is a simple yes-no question to
confirm the state of the object being referred to. The third example is also asking
for confirmation with a slightly different sentence structure which is called
The second form of sentence is statement, which is for explaining or
describing information. This form is generally used in daily conversation and
writing, for examples: ‘I read linguiitic booki everyday.’, ‘The ihop ii cloied at
night.’, and ‘There are penguini at the zoo now.’. More than one kind of
information can be delivered in one sentence of statement. The third isimperative
or command sentence, which is used to command information or action.
Imperative sentences do not need to be exclamative because the main function is
to ask others to do something, for examples:‘Buy thii now.’,‘Try thii new recipe.’,
‘Get thoie paperi pleaie.’. As seen in those examples, there is no need to put a
subject at the beginning of the sentence or put an exclamation mark at the end of
the sentence. Exclamation mark can be used in the last form of sentence,
exclamation, which its function is expressing emotion directly. Some examples of
this sentence function are: ‘Firit in Indoneiia!’, ‘New flavor!’, and ‘Perfect!’.
Based on those examples, a single word and a simple phrase can be a meaningful
sentence since it carries the emotion expressed by the speaker or writer.
2) Verbs
Beside the functions of sentences, another element to understand the
information structure of a text or speech is by looking at the verbs used in its
sentences. Tense and voice are used in analyzing the verbs in sentences because
they depend on the genre of the text and they give significant meaning of the
information they carry. According to Carter et al. (2001), “tense refers to the way
verbs are used to signal time”, which means that the verb of a sentence can show a
the three main tenses are as follows:
‘One Pirection performed a ipectacular itage lait night.’
‘One Pirection performi in front of thouiandi of fani.’
‘One Pirection ii performing their lateit iingle thii weekend.’
The first sentence shows an information that an action has been done, seen by the
use of ‘-ed’ form for the verb. The second sentence indicates that the information
is in present tense. The last sentence indicates that the information is about an
upcoming action that is expected to definitely happen in the near future.
Voice is the way a verb deliver the information, either in active or passive
sentence structure. An information delivered in active voice can be changed into
passive voice, with the same essence of the meaning. Yet, there are several certain
verbs that cannot be conversed into passive voice, such as cry, rain, walk, which
are called intransitive verbs. Here are some examples of active and passive voice:
‘He watched a movie.’(active voice, past tense)
‘A movie wai watched by him.’(passive voice, past tense)
‘The ticketi are iold out.’(passive voice, present tense)
‘They iell out the ticketi.’(active voice, present tense)
‘She runi away from home.’(active voice, present tense, intransitive verb)
The first and second example show how the difference and conversion of active
and passive voice. Both active and passive voice sentences from each example
have the same information, the difference between them is that the form of the
sentence structure brings different perspectives or points of view. While in active
front of the sentence, then followed by the verb which is added by a ‘to be’. On
the other hand, the third example shows a type of sentence with intransitive verb
that cannot be conversed into passive voice. Some passive forms omit the original
subject of the active form because they make the sentence shorter and more
effective to use.
3) Theme
Theme is also a part of the information structure to understand a text. What
is meant by theme is the main idea of the information of a text or speech. Theme
can be analyzed by looking at the links between clauses or sentences that usually
exist at the beginning and at the end of a sentence. The links have similar function
as conjunction but they are connecting the context of the text, not just a part of
sentence structure. Carter et al. (2001) explain the work of theme in a text clearly
as follows:
Theme refers to the first part of a sentence, which is where the subject matter of the sentence is usually laid out for the reader. It covers all the material before the main verb. When sentences are woven tightly together, the end of one sentence (called the ‘focus’) can become the theme of the next. But themes have to have some continuity across sentences, otherwise a text that
lookitightly knit can make complete nonsense (p. 152).
An example that can describe the use and work of theme in a text is presented as
follows:
‘A driver delivered a package to your room thii afternoon. The package
ieemi big and heavy, and on the top of it ii the gift card from your iender. I
think it’i one of your admireri.’
The expression ‘on the top of it’ connects the main information of the sentence
B. Review of Related Studies
There are several studies that are related to the topic of this research. Those
studies are similar in some ways to this research, and the researcher finds them
helpful to support this research. The first related study is “Stylistic Analysis of the
Magazine Advertisement: Atkins Chocolate Chip Granola Bar”, written by Min Li
(2009). The study aims to analyze the language style of specified advertisements
based on the linguistic description, textual analysis, and contextual analysis
aspects (p. 63). Some parts of the three aspects used in the particular study are
similar to this research, therefore they are used as references that help the
researcher understands the concept of language features and text and context.
The second related study is “An Analysis on the Language Style of
Utterances in Magnum Advertisements”, written by Permatasari (2014). The
related study focuses on analyzing the language style of Magnum advertisements
and the power relation they have based on the language features such as lexical
features and syntactical features. Those two features are used as the ground in
categorizing and conducting the data analysis. It is a reference for this research,
which uses three categories of language features based on different theories.
While Permatasari uses Grey’s theory of language style of advertisement, this
research uses Carter’s et al. and Halliday’s theory of language features of
discourse, which are applied to advertisement. The particular study’s subject is
similar to this research, the commercial videos that are transcribed for the data
analysis. While the Magnum advertisements are taken from international
advertisements are taken from Indonesia and the Philippines, where the
commercials use English as either the main language or second language. The
research procedure of the study by Permatasari is used as a reference for this
research since it has similar data and categories for the analysis process.
C. Theoretical Framework
After reviewing the theories and related studies, the researcher will use
them to help answering the research questions. The theories and reviews of related
studies about language features are used to answer the first research question
which is what the language features of the Kopiko advertisements are. This
research question focuses on finding the language style, structure, pattern, and
format of the text of the advertisement. There are three language features of text
that are considered to be relevant to support this question and can be related
directly to reviews of the language of advertisement and the elements of
advertisement. Therefore, the theories and reviews of related studies about
elements of advertisement are also used to support the answer more accurately. As
stated in previous section, there are three specific elements in advertisement
according to Arens (2006) that can be used to identify the language features of
advertisement. The two reviews are combined to help answering the first research
questions. Therefore, the answers to this research question will not be out of the
scope of limitation.
The second research question is about the distinctive language features of
research question is to analyze the similarities and differences of the language
features that are identified in each advertisement from Indonesia and the
Philippines. The findings of similar and different features between the two
versions ofKopikoadvertisements are also related to the same theories and studies
that are used for the first research question. For the first question, those theories
and related studies are used to discover the surface or first layer of this research
which is the linguistics aspect of advertisement. Then, for the second question,
those theories and related studies are used to do deeper analysis to find whether
there is any significant influence based on country background that show how
28 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents a rationale for the methods of research and analysis.
The researcher describes the methods of research and analysis, outlines the
procedure in gathering and analyzing the data, and reveals the boundaries of the
research. This chapter comprises the research method, research setting, research
subjects, instrument and data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and
research procedure.
A. Research Method
This research focuses on the language features of advertisements, therefore
content analysis method will be used to conduct this research. Ary, 4acobs, and
Sorensen (2010), define content analysis as a research method that is used to
identify certain features of written or visual materials such as textbooks,
newspapers, speeches, advertisements, and other kinds of documents (p. 457).
This research will identify the particular linguistic features of the English that is
used in commercial videos of Kopiko advertisements in Indonesia and the
Philippines.
Content analysis deals with the language practice in society such as
advertisements and focuses on its characteristics which have special meaning and
specific purpose. By using this method, the researcher will be able to reach the
advertisements' language and to analyze them to find their distinctive
characteristics that show the purposes of the advertisements and the similarities
and differences between Indonesia version and the Philippines version. This is
also supported by Krippendorff (2004), who states that “content analysis provides
new insights, increases a researcher’s understanding of particular phenomena, or
inform practical actions” (p. 18). Since content analysis is conducted to analyze
and identify the meaning behind specific characteristics of a material or
document, it serves the purpose of this research which deals with language and its
practice in social life. Content analysis focuses on the text being analyzed as a
whole, which means its structure, its meaning, its relationship among each
elements, and also its context. This research methodology is appropriately used
for this research considering the research problems, the research objectives, and
the primary data.
B. Research Setting
The research was conducted from October 2014 to November 2014 for the
data gathering. The data gathering included collecting the commercial videos
needed as the primary data of Kopiko products’ advertisements. Then the data
analysis was conducted from November 2014 to December 2014.
C. Research Subjects
The subjects of this research will be the transcripts of the commercial
researcher focuses on two popular products from Kopiko brand which are candy
and instant coffee drink. Those products are most well-known in society all
around the world in which countries haveKopiko products distributed there. The
advertisements are taken from several versions of Kopikocommercial videos that
are broadcasted through television and internet media. There are Indonesia
version and the Philippines version of Kopiko advertisements which all have
English utterances and texts as the main language used in the advertisements.
Some of the advertisements use full English as the language, while several others
mix English with the country’s native language. The advertisements are chosen
based on the presence of utterances and the majority use of English, therefore the
presence of native language in several advertisements is ignored since the main
focus of this research is the English utterances and texts.
There are 13 commercial videos of Kopikoadvertisement in Indonesia and
the Philippines that are taken as primary data in this research. Table 3.1 shows the
data of the advertisements for the research.
Tabel 3.1 TheKopikoAdvertisements
Video Country
Kopiko 78olong version Indonesia
Kopiko White Mocha Indonesia
Kopiko Brown Coffee Indonesia
Kopiko 78oshort version 1 Indonesia Kopiko 78oshort version 2 Indonesia
Kopiko Candy Indonesia
Kopiko Cafe Blanca The Philippines
Kopiko LA Coffee The Philippines
Kopiko Brown Coffee The Philippines
Kopiko Astig 3in1 The Philippines
Kopiko Coffee The Philippines
D. Instruments and Data Gathering Technique
The instruments of this research are the primary data, which are the
commercial videos of Kopikoadvertisements from Indonesia and the Philippines;
observation sheets that are categorized based on the categories of language
features to analyze the data; and the researcher as the doer of the observation and
analysis. The examples of the observation sheets are presented in table 3.2 and
table 3.3.
Table 3.2 The Language Features ofKopikoAdvertisement
Video Language FeatureX
Kopiko 78olong version (Indonesia) Kopiko White Mocha (Indonesia) Kopiko Brown Coffee (Indonesia) Kopiko 78oshort version 1 (Indonesia) Kopiko 78oshort version 2 (Indonesia) Kopiko Candy (Indonesia)
Table 3.3 The Checklist of Active and Passive Voice inKopikoAdvertisement
Video Active Voice Passive Voice
Kopiko 78olong version (Indonesia) Kopiko White Mocha (Indonesia) Kopiko Brown Coffee (Indonesia) Kopiko 78oshort version 1 (Indonesia) Kopiko 78oshort version 2 (Indonesia) Kopiko Candy (Indonesia)
Kopiko 3in1 Astig Na Kape (the Philippines) Kopiko Brown Coffee (the Philippines) Kopiko Cafe Blanca (the Philippines) Kopiko LA Coffee (the Philippines) Kopiko Brown Coffee (the Philippines) Kopiko Astig 3in1 (the Philippines) Kopiko Coffee (the Philippines)
This research uses content analysis method and deals with documents
namely Kopiko advertisements as the primary data. Therefore the technique of
collecting the primary data is an important procedure. The advertisements are
taken from several versions of Kopiko commercial videos broadcasted in
Indonesia and the Philippines, which are advertising two main products, namely
coffee candy and instant coffee drink. The commercial videos are collected from
www.youtube.com and chosen based on the use of English as the major language.
After that, the videos are transcribed into written texts in the form of dialogue or
monologue, which can be seen in Appendix A. There are few native languages
that are spoken in several versions of the advertisements, but they are not
analyzed in this study. The native language are not transcribed since this research
focuses on the English being used in the videos. After all the primary data needed
E. Data Analysis Technique
This research, which uses content analysis as the methodology, will employ
qualitative and quantitative data. The data analysis technique is a combination of
both types. Krippendorff (2004) states that quantitative data (numbers) is needed
in content analysis but not a definite criteria, while qualitative data (verbal) is the
text itself and the basic measurement for the research findings (p.87). The
qualitative data are the categories of language features, while the quantitative data
are the frequency of appearance of each features in all advertisements that will be
presented in percentage numbers. This research categorizes the primary data,
namely the transcripts of Kopiko advertisements, into groups that have various
characteristics of language features as stated in the previous chapter. This
categorization is conducted to help the researcher analyze the data, especially to
find the unique features of the language inKopikoadvertisements. The categories
that are used for this identification are the language features based on lexical
cohesion, grammatical cohesion, and information structure. The researcher
identifies the language features in each advertisement that are compatible with
the characteristics of each category. After the features found in the advertisement
language are identified and put in their categories, they are analyzed further to
find the similarities and differences that distinguish the English versions of
Indonesia and the Philippines. After identifying and analyzing the language
features of the advertisements, the researcher uses the reviews of related theories
and studies to conduct further analysis. The reviews will support the research
F. Research Procedure
This section summarizes the procedure of this research. First, the
researcher finds the issue of the research topic and formulates the problems. This
step includes finding the topic which is an analysis on the language features of
Kopiko advertisements and formulating the two research questions. Second, the
researcher works on the library study to find the theories and studies related to
this research. Third, the researcher decides the methodology for conducting this
research which is content analysis that includes both qualitative and quantitative
data. Fourth, the researcher collects the sources of the primary data which are
several versions of Kopiko commercial videos that are broadcasted in Indonesia
and the Philippines. Fifth, the researcher transcribes the utterances from the
commercial videos into written texts as the primary data. Sixth, the researcher
classifies the primary data into three categories to identify the language features
of the advertisements. Seventh, the researcher begins to analyze the categorized
primary data to find the answers to the research questions. Eighth, the researcher
uses the reviews of related theories and studies to support the data analysis in
order to answer the research questions. Finally, the research findings and the
35 CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter discusses the research findings that have been analyzed based
on the research methodology to answer the research questions. This chapter is
divided in three parts. The first part discusses the language features of the
primary data, Kopiko advertisements. The second part discusses the distinctive
features of Kopiko advertisements between Indonesia and the Philippines to see
their similarities and differences. The third part discusses other findings of the
analysis that are related to the previous findings.
A. The Language Features of Kopiko Advertisements in Indonesia and the
Philippines
The analysis of the language features ofKopiko advertisements was based
on the theory from Carter et al. (2001) and Halliday and Matthiessen (2004)
about the language features of texts in discourse context. Since advertisement is a
form of discourse, especially that in this research the advertisement was taken
from commercial videos, those features can be used to analyze the language of
Kopiko advertisements in the perspective of text and related context. This is
appropriate considering the fact that the advertisements are from different
countries which use English as the main language. There are three features to
analyze in this research, namely the lexical cohesion, the grammatical cohesion,