Read the following instruction carefully
before you answer the questions. Answers
are to be marked on a
SEPARATE O.M.R.
SHEET
1.
Please write your Centre Code No.
and Roll No. very clearly (only one
digit in one block) as given on your
admission card and even zeros
appearing in the Centre Code No.
and Roll No. should be correctly
written in the appropriate blocks on
O.M.R. Sheet.
Example:
National Means Cum Merit Scholarship Examination 2013
j k"V “h; l kŁku o ; ks
X; r k N k=ko ‘f k i j h{ kk
2013
th(For students studying in Class 8 )
d { kk v kBo ha
e s
a
v Ł; ; u j r fo | kfFkZ
; ks
a
d s
fy ,
State Council of Educational Research and Training Haryana, Gurgaon
j kT; ’ kS
f{ kd v u q
l a
Łkku , o a
i zf’ k{ k. k i fj "kn ~
g fj ; k. kk] x q
M+
x k¡o
(
)
Time Allowed :
3 Hours
Maximum Marks :
180
i z’ u ksa d s m kj n su s l s i g y s fu Eu fy f[ kr fu n sZ’ kksa d ks Ł; ku l s i f< +, A m kj , d v y x v ks-, e -v kj - ’ khV i j v afd r d j u s g SaA
1.
v i u k d sUn z d ksM u Ec j r Fkk j ksy u Ec j t Sl k fd v ki d s i zo s’ k& i =k e sa fn ; k x ; k g S] Li "V r ; k …, d p kS[ kV s e sa d so y , d v ad ‰ fy f[ k, A ; g k¡ r d fd v ki d s d sUn z d ksM u Ec j r Fkk j ksy u Ec j e sa v i u s o ky s ’ kwU; d s v ad Hkh v ks-, e -v kj - ’ khV i j l g h p kS[ kV s e sa fy [ ks t k, ¡Amn kg j . k
Scheme
Code
State
Code
Year
Centre Code
Roll No.
3
2 7
1 3
l e ; %
3
?ka
V s
i w
. kk–
d %
180
Instructions to the Candidates
i j h{ kkfFkZ
; ks
a
d s
fy , fu n s
Z
’ k
Scheme Code
State Code
Year Centre Code Roll No.
3
2 7
1
3
1
1
3
1
1
2
4
Ld he d ksM
j kT; d ksM
o "kZ d sUn z d ksM v u q e kad
2.
This test has two parts. Part I as well
as part II consist of 90 questions in
each.
3.
Each question carries one mark.
4.
Since the time allotted to the two parts
of this question-paper is very limited,
you should make the best use of it by
not spending too much time on any
question.
5.
Extra page has been provided for
rough work at the end of question
paper.
6.
Do not mark more than one answer of
any question on OMR sheet
otherwise answer will be cancelled.
7.
Avoid cutting/over writing/use of fluid
etc. on OMR Sheet.
8.
Attempt each question, there is no
negative marking in this test.
Note:Do not write anything except the
Roll Number and rough work
anywhere in the booklet.
2.
; g i j h{ kk n ks Hkkx ksa e sa g SA i zR; sd Hkkx e sa90
i z’ u g SA3.
i zR; sd i z’ u d k , d v ad g SA4.
p wafd b l i z’ u & i =k d s n ksu ksa Hkkx ksa d s fu ŁkkZfj r l e ; l hfe r g S] b l fy , b l d k v fŁkd r e l n qi ; ksx d hft , v kSj fd l h i z’ u i j c g qr l e ; u y x kb , A5.
i z’ u i qfLr d k d s v ar e sa(Rough)
j Q d k; Z d s fy , v fr fj Dr i ‘"B fn ; k x ; k g SA6.
v ks-, e -v kj - ’ khV i j fd l h Hkh i z’ u d s , d l s v fŁkd m kj e kd Z u d j sa o j u k m kj fu j Lr g ks t k, x kA7.
v ks-, e -v kj - ’ khV i j d fV ax @v kso j j kb fV ax @ ¶ y wM d k i z; ksx u d j saA8.
i zR; sd i z’ u g y d hft , ] b l i j h{ k. k e sa d ksb Z u d kj kRe d v ad u u g ha g SAu ksV % b l i qfLr d k e sa v i u k v u q e kad fy [ ku s v kSj j Q d k; Z d j u s d s v fr fj Dr v kSj d qN u g ha fy f[ k, A
Directions : (Q. 1 to 4)
The numbers have been arranged under
some rule. Based on that rule, which
number will come in place of the
question mark?
Q.1
196, 169, 144, 121, 100, ?
(1)
64
(2)
81
(3)
91
(4)
36
Q.2
3, 9, 27, 4, 16, 64, 5, 25, ?
(1)
50
(2)
75
(3)
100
(4)
125
Q.3
2, 5, 10, 17, 26, 37, 50, ?
(1)
65
(2)
60
(3)
55
(4)
75
Q.4
91, 76, 89, 78, 87, 80, 85, 82,?
(1)
83
(2)
84
(3)
85
(4)
86
PART-I
…Hkkx
-I
‰
MENTAL ABILITY TEST
c kS
f) d ; ks
X; r k i j h{ k. k
Questions: 1 to 90
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
1
l s4
‰v ad fd l h fu ; e d s v kŁkkj i j fy [ ks x , g SaA ml h fu ; e d s v kŁkkj i j i z’ u o kp d fp Ug d s
LFkku i j d kSu l k v ad v k, x k\
i z-
1
196, 169, 144, 121, 100, ?
(1)
64
(2)
81
(3)
91
(4)
36
i z-
2
3, 9, 27, 4, 16, 64, 5, 25, ?
(1)
50
(2)
75
(3)
100
(4)
125
i z-
3
2, 5, 10, 17, 26, 37, 50, ?
(1)
65
(2)
60
(3)
55
(4)
75
i z-
4
91, 76, 89, 78, 87, 80, 85, 82,?
(1)
83
(2)
84
(3)
85
Directions : (Q. 5 to 7)
How many triangles are there in each
figure?
Q.5
(1)
16
(2)
13
(3)
9
(4)
7
Q.6
(1)
11
(2)
13
(3)
15
(4)
17
Q.7
(1)
5
(2)
6
(3)
8
(4)
10
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
5
l s7
‰fu Eu fy f[ kr i zR; sd v kd ‘fr e sa f=kHkqt ksa d h l a[ ; k fd r u h g S\
i z-
5
(1)
16
(2)
13
(3)
9
(4)
7
i z-
6
(1)
11
(2)
13
(3)
15
(4)
17
i z-
7
(1)
5
(2)
6
(3)
8
Directions : (Q. 8 to 11)
A series of small letters are given which
follow a certain pattern. However some
letters are missing from the series. You
have to find out the right set of letters
from alternatives that can be inserted
into the blanks of the series.
Q.8
a__b a__b__b__a__b
(1)
a b a a b
(2)
a b b a b
(3)
a a b b a
(4)
b b a b b
Q.9
b a__c b__b__b a b__
(1)
a c b b
(2)
b a c c
(3)
b c a a
(4)
c a b b
Q.10 __a a__ b a__b b__a b__a a b
(1)
a a a b b
(2)
b a b a b
(3)
b b a a b
(4)
b b b a a
Q.11 c c c b b__a a __c c__b b b a a__c
(1)
a c b c
(2)
b a c a
(3)
b a b a
(4)
a c b a
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
8
l s11
‰v ax zst +h o . kZe ky k d s N ksV s v { kj ksa d h , d J ‘a[ ky k
n h x b Z g S] t ks , d fu f’ p r e e sa g SA d qN v { kj
J ‘a[ ky k l s x k; c g SaA v { kj ksa d k , d l g h l e wg
u hp s fn , x , fo d Yi ksa e sa l s N k¡fV , ] ft u l s fj Dr
LFkku ksa d h i wfr Z d h t k l d sA
i z-
8
a__b a__b__b__a__b
(1)
a b a a b
(2)
a b b a b
(3)
a a b b a
(4)
b b a b b
i z-
9
b a__c b__b__b a b__
(1)
a c b b
(2)
b a c c
(3)
b c a a
(4)
c a b b
i z-
10 __a a__ b a__b b__a b__a a b
(1)
a a a b b
(2)
b a b a b
(3)
b b a a b
(4)
b b b a a
i z-
11 c c c b b__a a __c c__b b b a a__c
(1)
a c b c
(2)
b a c a
(3)
b a b a
4 3
144
11 9
9801
15 6
?
916
3 4
49
2 3
?
1 5
Directions : (Q. 12 to 16)
In each of the following figures,
numbers are written according to some
patterns and one number is missing,
shown by question mark. Find the
missing number that replaces the
question mark.
Q.12
(1)
125
(2)
215
(3)
251
(4)
512
Q.13
(1)
1216
(2)
2250
(3)
8100
(4)
11036
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
12
l s16
‰u hp s n h x b Z i zR; sd v kd ‘fr e sa , d fu f’ p r e
v u ql kj d qN l a[ ; k, ¡ fy [ kh x b Z g SA b u e sa l s , d
l a[ ; k y qI r g S] ft l s i z’ u fp Ug l s n ’ kkZ; k x ; k
g SA y qI r l a[ ; k K kr d j ks t ks i z’ u fp Ug d s
LFkku i j mi ; qDr g ksA
i z-
12
(1)
125
(2)
215
(3)
251
(4)
512
i z-
13
(1)
1216
(2)
2250
(3)
8100
(4)
11036
4 3
144
11 9
9801
15 6
?
916
3 4
49
2 3
?
Directions : (Q. 17 to 20)
In each of the following questions,
among all the alternatives marked (1),
(2), (3) and (4), select the one which
satisfies the same condition of
placement of the dot(s) as in Fig. (X)
Q.17
(X) (1) (2)
(3)
(4)
Q.18
(X) (1) (2)
(3)
(4)
Q.19
(X) (1) (2)
(3)
(4)
Q.20
(X) (1) (2)
(3)
(4)
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
17
l s20
‰u hp s fn , x , i zR; sd i z’ u e sa p kj fo d Yi ksa
(1),
(2), (3)
o(4)
e sa l s d kSu l h v kd ‘fr , sl h g S t ks v kd ‘fr(X)
e sa n ’ kkZ, x , fc an qv ksa d s LFkku d h fLFkfr l s e sy [ kkr h g S\i z-
17
(X) (1) (2)
(3)
(4)
i z-
18
(X) (1) (2)
(3)
(4)
i z-
19
(X) (1) (2)
(3)
(4)
i z-
20
Directions : (Q. 21 to 23)
In each of these questions, choose the
correct mirror image of the figure (X)
from four alternatives given alongwith it.
Q.21
(X) (1) (2) (3) (4)
Q.22
(X) (1) (2) (3) (4)
Q.23
(X) (1) (2) (3) (4)
Directions : (Q. 24 to 26)
In each of these questions, choose the
correct water image of the figure (X)
from the four alternatives given
alongwith it.
Q.24
(X)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
21
l s23
‰fn , x , i z’ u ksa e sa l s v kd ‘fr
(X)
d ks n i Z. k e sa n s[ ku s i j d Sl h fn [ kkb Z n sx h] l kFk fn , x , p kjfo d Yi ksa e sa l s l g h m kj N k¡fV , A
i z-
21
(X) (1) (2) (3) (4)
i z-
22
(X) (1) (2) (3) (4)
i z-
23
(X) (1) (2) (3) (4)
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
24
l s26
‰fn , x , i z’ u ksa e sa v kd ‘fr
(X)
d ks i ku h e sa n s[ ku s i j d Sl h fn [ kkb Z n sx h] l kFk fn , x , p kjfo d Yi ksa e sa l s l g h m kj N k¡fV , A
i z-
24
(X)
(1)
(2)
Q.25
(X)
(1) (2) (3) (4)
Q.26
(X)
(1) (2) (3) (4)
Directions : (Q. 27 to 30)
In these questions, different positions of
a dice are given. Answer the question
followed by figures?
Q.27
Which number is opposite to 4?
(1)
2
(2)
1
(3)
3
(4)
6
Q.28
Which number is opposite to 3?
Q.29
Which number is opposite to 2?
(1)
4
(2)
3
(3)
5
(4)
1
Q.30
Which number is opposite to 6?
(1)
1
(2)
2
(3)
3
(4)
4
Directions : (Q. 31 to 35)
Q.32 Drama: Character : : ?
(1)
Farming : Loan
(2)
Game : Players
(3)
North : Direction
(4)
Classroom : Blackboard
Q.33 Reading : Knowledge : : ?
(1)
Climb : Mountain
(2)
Play : Football
(3)
Worship : God
(4)
Effort : Success
Q.34 Sun : Mars : : ?
(1)
School : Classroom
(2)
Field : Well
(3)
Earth : Moon
(4)
Ship : Boat
Q.35 Storm : Wind : : ?
(1)
Happiness : Deeds
(2)
Tide : Moon
(3)
Waves : Sea
(4)
Anger : Weep
i z-
32
M“ke k % i k=k % % \(1)
[ ksr h % _ . k(2)
[ ksy % f[ ky kM+h(3)
m kj % fn ’ kk(4)
d { kk& d { k % ’ ; ke i Œi z-
33
i B u % K ku % % \(1)
p < +u k % i o Zr(2)
[ ksy u k % Q qV c kWy(3)
i wt k % Hkx o ku(4)
i z; kl % l Q y r ki z-
34
l w; Z % e ax y x zg % % \(1)
fo | ky ; % d { kk d { k(2)
[ ksr % d wv ka …u y d wi ‰(3)
i ‘Fo h % p Un ze k(4)
l e qn zh t g kt % u kSd ki z-
35
r wQ ku % g o k …i o u ‰ % % \(1)
i zl Uu r k % d k; Z(2)
To kj HkkV k % p Un ze k(3)
r j ax sa % l e qn zQ.36 Pointing to a boy, Meena says, "He
is the son of my grandfather's only
child." How is the boy related to
Meena?
(1)
Cousin
(2)
Brother
(3)
Uncle
(4)
Nephew
Q.37 P o i n t i n g t o a l a d y i n t h e
photograph, Vandana told her
friend, "She is the daughter of my
mother." How is the Vandana
r e l a t e d t o t h e l a d y i n t h e
photograph?
(1)
Sister
(2)
Son
(3)
Nephew
(4)
Daughter
Q.38 Pointing to a boy in a photograph
Raju says, "He is the son of my
mother's only son." How is Raju
related to that boy?
(1)
Uncle
(2)
Brother
(3)
Cousin
(4)
Father
Q.39 A man said, "This girl is the wife of
the grand son of my mother." Who
is the man of the girl?
(1)
Grand Father
(2)
Father
(3)
Father-in-Law
(4)
Husband
i z-
36
e hu k u s , d y M+d s d h v ksj b ’ kkj k d j r s g q, d g k] o g e sj s n kn k d s , d e k=k c Pp s d k y M+d k g SA ml y M+d s d k e hu k l s D; k fj ’ r k g SA(1)
p p sj k Hkkb Z(2)
Hkkb Z(3)
p kp k ; k r k¯(4)
Hkfr t k@Hkku t ki z-
37
o Un u k u s Q ksV ksx zkQ e sa , d e fg y k d h v ksj b ’ kkj k d j r s g q, v i u s fe =k l s d g k]o g e sj h e kr k d h c sV h g SA Q ksV ksx zkQ e sa e fg y k l s o Un u k d k D; k fj ’ r k g S\
(1)
c g u(2)
c sV k(3)
Hkfr t k(4)
c sV hi z-
38
Q ksV ks e sa , d y M+d s d h v ksj b ’ kkj k d j r s g q, j kt w u s d g k] o g e sj h e kr k d s , d e k=k c sV s d k c sV k g SA j kt w d k ml y M+d s l s D; k l Ec UŁk g S\(1)
p kp k(2)
Hkkb Z(3)
p kp k d k y M+d k(4)
fi r ki z-
39
, d v kn e h u s d g k] ; g y M+d h e sj h e kr k d s i kS=k d h i Ru h g SA ml y M+d h d k o g v kn e h d kSu y x r k g S\(1)
n kn k(2)
fi r k(3)
l l qjQ.40 Q the Son of M was married to N,
whose sister O was married to P,
the brother of Q. How is O related
to M?
(1)
Sister
(2)
Daughter-in-Law
(3)
Sister-in-Law
(4)
Daughter
Q.41 A man starts from a point and
moves 3 km North, then turns to
West and goes 2 km. He turns
North and walks 1 km and then
moves 5 km towards East. How far
is he from the starting point?
(1)
11 km
(2)
5 km
(3)
10 km
(4)
8 km
Directions : (Q. 42 to 43)
A vehicle starts from point B and runs 10
km towards north, turns to its right and
runs 15 km. It then turns to its right again
and runs another 10 km to reach point C.
Q.42. After reaching point C, how far is
the vehicle from the starting point
B?
(1)
25 km
(2)
15 km
(3)
10 km
(4)
35 km
i z-
40 M
d k y M+d kQ
g S v kSj ml d h ’ kkn hN
l s g qb Z Fkh] ft l d h c g uO
d hP
l s ’ kkn h g qb Z Fkh] t ksQ
d k Hkkb Z g SAO
d kM
l s D; k l Ec UŁk g S\(1)
c g u(2)
i q=ko Łkq(3)
HkkHkh(4)
c sV hi z-
41
, d v kn e h , d fc Un q …t x g ‰ l s p y u k v kj EHk d j r k g S v kSj m kj d h v ksj3
fd e h- p y r k g S fQ j o g i f’ p e d h v ksj e qM+d j
2
fd e h- t kr k g SA o g m kj d h v ksj1
fd e h- p y r k g S v kSj fQ j i wj c d h v ksj ?kwe d j5
fd e h- p y r k g SA o g v i u s v kj fEHkd LFkku l s fd r u k n wj g S\(1)
11
fd eh-(2)
5
fd eh-(3)
10
fd eh-(4)
8
fd eh-fu n sZ’ k …i z-
42
l s43
‰, d o kg u
B
LFkku l s p y u k v kj EHk d j r k g S v kSj10
fd e h- m kj d h v ksj n kSM+r k g S v kSj fQ j v i u s n kfg u h v ksj e qM+d j15
fd e h- n kSM+r k g SA ; g fQ j v i u s n kfg u h v ksj e qM+d j n wl j h c kj10
fd e h- LFkkuC
i j i g qap u s d s fy , n kSM+r k g SA i z-42
LFkkuC
i j i g q¡p u s d s c kn o kg uv kj fEHkd LFkku
B
l s fd r u k n wj g S\(1)
25
fd eh-(2)
15
fd eh-(3)
10
fd eh-Q.43. After taking the second turn, in
which direction will the vehicle be
moving?
(1)
North
(2)
East
(3)
South
(4)
West
Directions : (Q. 44 to 45)
Shaloo ran 20 m to the east from his
starting point A, then he turns left and
ran for 15 m, then turned right and went
25 m and then turned right again and
went 15 m on point B.
Q.44 How far was Shaloo at last from the
starting point A?
(1)
45 m
(2)
35 m
(3)
25 m
(4)
15 m
Q.45 In which direction he may be at last
from his starting point A?
(1)
East
(2)
West
(3)
North
(4)
South
i z-
43
n wl j h c kj e qM+u s d s c kn o kg u fd l fn ’ kk e sa t k j g k g ksx k\(1)
m kj(2)
i wj c(3)
n f{ k. k(4)
i f’ p efu n sZ’ k …i z-
44
l s45
‰’ kky w v i u s v kj fEHkd LFkku
A
l s20
e h- i wj c d h v ksj n kSM+k] fQ j o g c ka; h v ksj e qM+r k g S v kSj15
e h- n kSM+r k g S fQ j n ka; h v ksj e qM+k25
e h- p y k v kSj fQ j v Ur e sa n ka; h v ksj e qM+d j15
e h-p y d j LFkkuB
i j x ; kAi z-
44
’ kky w v i u s v kj fEHkd LFkkuA
l s v Ur e sa fd r u h n wj Fkk\(1)
45
eh-(2)
35
eh-(3)
25
eh-(4)
15
eh-i z-
45
v i u s v kj fEHkd LFkkuA
l s v Ur e sa fd l fn ’ kk e sa o g g ks l d r k g S\(1)
i wj c(2)
i f’ p e(3)
m kjDirections : (Q. 46 to 50)
The Diagram shown below represents
four types of literates which knows
English, Hindi, Punjabi and Sanskrit.
Based on above information solve the
questions given below.
Q.46 People who can read and write
Hindi, Sanskrit and Punjabi are
represented by
(1)
E and B
(2)
K and F
(3)
E and K
(4)
J and K
Q.47 People who can read and write all
languages are represented by
(1)
J
(2)
K
(3)
E
(4)
F
Q.49 People who cannot read and write
English, Punjabi and Sanskrit are
represented by
(1)
A
(2)
B
(3)
C
(4)
D
Q.50 People who do not know English
and Punjabi but are familiar with
Hindi and Sanskrit both are
represented by
(1)
A
(2)
B
(3)
C
(4)
E
Directions : (Q. 51 to 52)
A person has his wife, two married sons
each having 5 children including two
girls.
Q.51 How many female members are in
the family?
(1)
5
(2)
6
(3)
7
(4)
8
Q.52 How many members are in the
family?
(1)
15
(2)
16
(3)
17
(4)
18
i z-
49
y ksx t ks v ax zst h] i at kc h v kSj l aLd ‘r i < + v kSj fy [ k u g ha l d r s g Sa mUg sa i zd V fd ; kt kr k g S&
(1)
A
(2)
B
(3)
C
(4)
D
i z-
50
y ksx t ks v ax zst h v kSj i at kc h u g ha t ku r s] i j Ur q fg Un h v kSj l aLd ‘r n ksu ksa l s i fj fp r…t ku u s o ky s‰ g Sa mUg sa i zd V fd ; k t kr k
g S&
(1)
A
(2)
B
(3)
C
(4)
E
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
51
l s52
‰, d O; fDr d s i fj o kj e sa ml d h i Ru h] n ks ’ kkn h’ kqn k c sV s , o a i zR; sd c sV s d s
5
c Pp s g Sa] ft u e sa n ks&n ks y M+fd ; k¡ Hkh ’ kkfe y g SaAi z-
51
i fj o kj e sa d qy fd r u h e fg y k l n L; g Sa\(1)
5
(2)
6
(3)
7
(4)
8
i z-
52
i fj o kj e sa d qy fd r u s l n L; g Sa\(1)
15
(2)
16
(3)
17
?
?
?
?
?
?
Directions : (Q. 53 to 56)
Complete the series of Problem Figures
among the Answer Figures.
Q.53 Problem Figures
Answer Figures
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Q.54 Problem Figures
Answer Figures
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Q.55 Problem Figures
Answer Figures
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
53
l s56
‰l e L; k v kd ‘fr ; ksa d h J s. kh d ks m kj v kd ‘fr ; ksa e sa l s i wj k d j ksA
i z-
53
l e L; k v kd ‘fr ; k¡mRr j v kd ‘fr ; k¡
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
i z-
54
l e L; k v kd ‘fr ; k¡mRr j v kd ‘fr ; k¡
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
i z-
55
l e L; k v kd ‘fr ; k¡mRr j v kd ‘fr ; k¡
?
?
Q.56 Problem Figures
Answer Figures
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Directions : (Q. 57 to 61)
In these problems, there is a group of
four figures marked serially 1 to 4. Out of
these four figures three are similar in
some way and one is different. Find the
one which is different.
Q.57
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Q.58
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Q.59
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Q.60
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Q.56
l e L; k v kd ‘fr ; k¡m kj v kd ‘fr ; k¡
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
57
l s61
‰b u l e L; kv ksa e sa p kj v kd ‘fr ; ksa d k , d l e wg g SA b u v kd ‘fr ; ksa d ks
1
l s4
r d e kad fn ; k x ; k g SA p kj e sa l s r hu v kd ‘fr ; k¡ fd l h i zd kj l s l e ku g S v kSj , d v kd ‘fr fHkUu A b u e sa t ks fHkUu g S ml s K kr d j ks&i z-
57
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
i z-
58
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
i z-
59
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
i z-
60
O N O
side, how many persons are there
in the row?
Q.64.
Mobile phone is related to...?
(1) Temperature
Q.66. Bulb is related to?
Q.67.
Highway is related to ?
(1) Transportation
(2) Communication
(3) Civilization
(4) Mobilization
Directions : ( Q 68 to 71)
The following questions are based on
the given letter series. Answer the
questions keeping in view the given
letter series.
E Y C I F O H Q A T J D L N R P M G V S Z K
Q.68. If FG is related to IV and TZ is
related to AK then QV is related
to:-(1) OZ
(2) HS
(3) HZ
(4) OS
Q.69.
If DELHI is written as. TZJFY and
MOST is written as RIGQ. Then in
the same way PRANK will be
written
as-(1) LNHDS
(2) NLDHS
(3) NLSDH
(4) NLHDS
Q.70.
If FT is coded as RS and MZ is
coded as FA then which will be
coded as ML?
(1) IQ
(2) HC
(3) OC
(4) HO
i z-
67.
j kt i Fk d k l Ec U/ k g S&(1)
i fj o g u(2)
l ap kj(3)
l H; r k(4)
x fr ’ khy r kfu n sZ’ k …i z-
68
l s71
‰fu Eu fy f[ kr i z’ u v ax zst h o . kZe ky k d h v { kj J ‘a[ ky k i j v k/ kkfj r g SaA J ‘a[ ky k d ks Ł; ku e sa j [ kr s g q, i z’ u ksa d k m kj n hft , A
E Y C I F O H Q A T J D L N R P M G V S Z K
i z-
68.
; fnFG
d k l Ec U/ kIV
l s g ks r FkkTZ
d k l Ec U/ k
AK
l s g ks r ksQV
d k l Ec U/ k g ksx k&(1) OZ
(2) HS
(3) HZ
(4) OS
i z-
69.
; fnDELHI
d ksTZJFY
r FkkMOST
d ksRIGQ
fy [ kk t kr k g ks r ksPRANK
d ks fy [ kk t k, x k&(1) LNHDS
(2) NLDHS
(3) NLSDH
(4) NLHDS
i z-
70.
; fnFT
d ksRS
l s r FkkMZ
d ksFA
l s i zn f’ kZr fd ; k t kr k g ks r ks fd l d ksML
l s i zn f’ kZr fd ; k t k, x k\
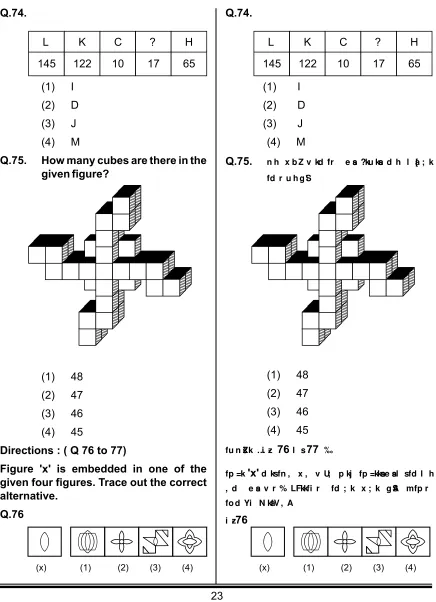
L
145
K
122
C
10
?
17
H
65
L
145
K
122
C
10
?
17
H
65
Q.74.
(1)
I
(2)
D
(3)
J
(4)
M
Q.75.
How many cubes are there in the
given figure?
(1)
48
(2)
47
(3)
46
(4)
45
Directions : ( Q 76 to 77)
Figure 'x' is embedded in one of the
given four figures. Trace out the correct
alternative.
Q.76
Q.74.
(1)
I
(2)
D
(3)
J
(4)
M
Q.75.
n h x b Z v kd ‘fr e sa ?ku ksa d h l a[ ; k fd r u h g S\(1)
48
(2)
47
(3)
46
(4)
45
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
76
l s77
‰fp =k
'x'
d ks fn , x , v U; p kj fp =kksa e sa l s fd l h , d e sa v r % LFkkfi r fd ; k x ; k g SA mfp r fo d Yi N kafV , Ai z-
76
(x) (1) (2) (3) (4) (x) (1) (2) (3) (4)
Q.77
Directions : ( Q 78 to 81)
In the questions below, are given two
statement followed by the conclusions
numbered I and II. Decide which of the
given conclusions logically follows from
the two given statements disregarding
commonly known facts. Give answer(1)
if only conclusion I follows, (2) if only
conclusion II follows, (3) if either I or II
follows and (4) if neither I nor II follows.
Q.78 Statements: Some chairs are
rabbits. Table is a
chair.
Conclusion: I) Some rabbits are
chairs.
II) Table is not a
rabbit.
Q.79
Statements: All questions are
answers. Some
a n s w e r s a r e
problems.
Conclusion: I) Some problems
are questions.
II) Some answers
are questions.
Q.80 Statements: Some shoes are
shirts. All shirts
are caps.
Conclusion: I) Some shoes are
caps.
II) Some shoes are
not shirts.
i z-
77
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
78
l s81
‰fu Eu fy f[ kr i z’ u ksa e sa i zR; sd e sa n ks o Dr O; ksa d s i ’ p kr ~ n ks fu "d "kZ
I
oII
fn , g SaA l ke kU; K kr r F; ksa d k Ł; ku u j [ kd j fn , x , n ks o Dr O; ksa i j v k/ kkfj r r kfd Zd fu "d "kks– d ks fu / kkZfj r d j saA ; fn fu "d "kZI
e k=k fu d y s r ks(1), II
e k=k fu d y s r ks(2), I
v Fko kII
e sa l s d ksb Z , d fu d y s r ks(3),
uI
o u g hII
fu d y s r ks m kj(4)
n hft , Ai z-
78
o Dr O; % d qN d qfl Z; k¡ [ kj x ks’ k g SaA e st , d d ql hZ g SAfu "d "kZ %
I)
d qN [ kj x ks’ k d qfl Z; k¡ g SAII)
e st [ kj x ks’ k u g ha g SAi z-
79
o Dr O; % l Hkh i z’ u m kj g SaA d qN m kj l e L; k, ¡ g SaAfu "d "kZ %
I)
d qN l e L; k i z’ u g SaAII)
d qN m kj ] i z’ u g SaAi z-
80
o Dr O; % d qN t wr s d e ht g SaA l Hkh d e ht sa V ksfi ; k¡ g SaAfu "d "kZ %
I)
d qN t wr s V ksfi ; k¡ g SaAQ.81 Statements:
A l l p l a n t s a r e
f l o w e r s . S o m e
flowers are pens.
Conclusion: I) All plants are
pens.
II) Some plants are
pens.
Directions : ( Q 82 to 85)
In each of following questions three of
four words/numbers in alternative
series are same in any way and form a
group which one of this group does not
belong to it?
Q.82
(1) 23-32
(2) 34-43
(3) 45-54
(4) 64-46
Q.83
(1)
5
(2) 7
(3) 9
(4) 11
Q.84
(1)
BCEH
(2) ABCE
(3) PQSV
(4) EFHK
Q.85
(1)
GEDC
(2) AZYX
(3) ONML
(4) TSRQ
i z-
81
o Dr O; % l Hkh i kS/ ks Q wy g SaA d qN Q wy i Su g SaAfu "d "kZ %
I)
l Hkh i kS/ ks i Su g SaAII)
d qN i kS/ ks i Su g SaAfu n sZ’ k …i z-
82
l s85
‰fu Eu fy f[ kr i zR; sd i z’ u e sa p kj fo d Yi ksa e sa l s r hu fd l h i zd kj l s , d l e ku g Sa r Fkk , d l e wg d h j p u k d j r s g SaA d kSu l k , d fo d Yi ml l e wg d s v Ur x Zr u g ha v kr k g SA
Q.82
(1) 23-32
(2) 34-43
(3) 45-54
(4) 64-46
Q.83
(1)
5
(2) 7
(3) 9
(4) 11
Q.84
(1)
BCEH
(2) ABCE
(3) PQSV
(4) EFHK
Directions : ( Q 86 to 87)
In each of the following questions
arrange the given words in a meaning ful
s e q u e n c e a n d t h e n c h o s e t h e
appropriate sequence amongst the
alternatives given below in each
question.
Q.86
(a) Service
(b) Advertisement
(c) Application
from
(d) Appointment
(1)
a, b, c, d
(2)
b, a, d, c
(3)
d, a, b, c
(4)
b, c, d, a
Q.87
(a)
Dressing
(b) Wound
(c) Accident
(d) Doctor
(1)
b, c, a, d
(2)
c, b, a, d
(3)
c, b, d, a
(4)
a, b, c, d
Q.88 Which diagram represents
India, Haryana and Rohtak?
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
fu n sZ’ k …i z-
86
l s87
‰fu Eu fy f[ kr i zR; sd i z’ u ksa e sa ’ kCn ksa d ks v FkZi w. kZ e c
i z-
86
(a)
u kSd j h(b)
fo K ki u(c)
v ko sn u i =k(d)
fu ; qfDr(1) a, b, c, d
(2) b, a, d, c
(3) d, a, b, c
(4) b, c, d, a
i z-
87
(a)
e j g e i V ~V h(b)
p ksV(c)
n q?kZV u k(d)
MkDV j(1) b, c, a, d
(2) c, b, a, d
(3) c, b, d, a
(4) a, b, c, d
i z-
88
d kSu l h v kd ‘fr Hkkj r ] g fj ; k. kk r Fkk j ksg r d d ks i zn f’ kZr d j r h g S\(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Q.89
In a certain language FOR
stands for 'old is gold' ROT
stands for 'Gold is Pure' and
ROM stands for 'Gold is Costly'
How is Pure old gold is costly'
be written?
(1) TFROM
(2) FOTRM
(3) FTORM
(4) TOMRF
Q.90
If (+) means (x), (-) means (+), (x)
means (÷) and (÷) means (-) then
9x4+2-5x10÷3 is equal to .
(1) 2
(2) 3
3
(3) 5
/4
l
(4) 21
/
3i z-
89
; fn fd l h l kad sfr d Hkk"kk e sa'old is
gold'
d ksFOR
l s'Gold is Pure'
d ksROT
l s r Fkkgold is costly
d ksROM
l s i zn f’ kZr fd ; k t kr k g ks r ks]Pure old gold is costly
d ks fd l i zd kj i zn f’ kZr fd ; k t k, x k\(1) TFROM
(2) FOTRM
(3) FTORM
(4) TOMRF
i z-
90
; fn(+)
l s r kRi ; Z(x)
; fn
(-)
l s r kRi ; Z(+)
; fn(x)
l s r kRi ; Z(÷)
; fn(÷)
l s r kRi ; Z(-)
g ks r ks9x4+2-5x10÷3
c j kc j g S(1) 2
(2) 3
3
(3) 5
/
4l
PART-II
…Hkkx
-II
‰
SCHOLASTIC APTITUDE TEST
’ kS
f{ kd { ke r k i j h{ k. k
Questions: 91 to 180
Physics
Q.91
A bat can detect its obstacle in
his path by
(1) viewing
(2) listening
(3) smelling
(4)
detecting reflected sound
Q.92
Ice glacier always melts
(1)
from upper layer
(2)
from lower layer
(3) all
around
(4)
from middle layer
Q.93
A point object is placed in the
principle axis is a concave
mirror quite far away from the
pole and moved at a constant
-1
speed of 1ms towards the pole.
Its image also moves. It is found
that the object and the image
cross each other at a distance 60
cm from the pole. From the
given detail in passage, the focal
length of the mirror is
(1)
30 cm
(2) 40
cm
(3) 50
cm
(4) 60
cm
Physics
i z-
91
p e x kn M+ v i u s j kLr s e sa v ku s o ky s v o j ks/ kksa d k i r k y x kr k g S(1)
n s[ kd j(2)
l qu d j(3)
x a/ k d k v kHkkl d j d s(4)
i j ko fr Zr / o fu d k v kHkkl d j d si z-
92
c Q Z d s Xy sf’ k; j g e s’ kk fi N y u k ’ kq: g ksr s g SaA(1)
¯ i j h l r g l s(2)
fu p y h l r g l s(3)
l Hkh l r g l s , d l kFk(4)
c hp d h l r g l si z-
93
v o r y n i Z. k d s e q[ ; v { k i j fc Un q-1
o Lr q d ks n i Z. k d s / kzqo d h v ksj
1ms
d s l e ku o sx l s p y k; k t kr k g SA o Lr q d k i zfr fc Ec Hkh p y r k g SA ; g i k; k t kr k g S fd o Lr q v kSj ml d k i zfr fc Ec / kzqo d s60
l se h d h n wj h i j fe y r s g SaA i g j s e sa fn , O; k[ ; ku v u ql kj n i Z. k d h Q ksd l n wj h g ksx h(1) 30
l se h(2) 40
l se h(3) 50
l se hQ.94
If two media has equal refractive
index and light is incident
normally at one of the boundary,
which of the following options
s h o w s c o r r e c t f o r m o f
refraction.
Q.95 In the following question, a
statement of assertion (A) is
given and followed by a
corresponding statement of
reason (R) just below it. Of the
following statements, choose
the correct answer.
(A) An iron needle is attracted
to the ends of a bar magnet
but not to the middle region
of the magnet.
(R) Material making up the ends
of a bar magnet is different
from that of middle region.
(1) If both assertion and reason
are true, reason is the correct
explanation of assertion.
(2) If both assertion and reason
are true, reason is not the
c o r r e c t e x p l a n a t i o n o f
assertion.
(3) Assertion is true but reason is
false
i z-
96
; fn g e v i u s fo | qr mi d j . kksa d ksQ.96
If we want to keep our electrical
appliances safe against over
(4)
Use of electric meters
Q.97
For a child sitting in a swing,
w h i c h o f t h e f o l l o w i n g
represents variation of kinetic
energy with time.
Q.98
How will the reading in ammeter
of a figure given below be
affected if another identical bulb
B is connected in parallel with
2bulb B . The voltage in the mains
1is maintained at a constant
value.
(1) The reading will be reduced to
half
(2) The reading will be double of
previous one
(3) The reading will not be
affected
i z-
99
d kWy eI
o d kWy eII
e ssa r F; ksa d k l g hQ.99
Match the entries of column I
with that of column II.
Column I
Column II
A. White light
P. dispersion by
incident in
water droplets
prism
in atmosphere
B. Two prism
Q. white light
placed with
refracting
angle opposite
with respect to
another
C. Laser light
R. No dispersion
incident on
Q.100 Two ebonite rods, one A rubbed
with polythene and other B with
wool are brought near the
positively charged electroscope
one by one. The possible effect
on leaves of electroscope will be
With A
With B
(1) Increases
Decreases
(2) Increases
Increases
(3) Decreases
Decreases
i z-
101
v ki d ks fd l h c an c r Zu e sa v K kr o Lr q c an d j d s fn ; k t kr k g SA l e ku : i l s¯ "e k n su s i j v ki r ki e ku o l e ; e sa
; fn u hp s fn [ kk; k x ; k x zkQ i zkI r d j r s
g ks] r c x zkQ e sa n ks { kSfr t j s[ kk, a
fn [ kk, ax h
(1)
B ksl o Lr q(2)
r j y o Lr q(3)
x Sl(4)
r j y o x Sli z-
102
o Lr q d ks B . Mk fd ; k t k l d r k g SA(1)
p ky u } kj k(2)
l ao g u } kj k(3)
fo fd j . k } kj k(4)
mi j ksDr l Hkh } kj ki z-
103 12g
d kc Zu d k] v kWDl ht u d h l e qfp r e k=kk e sa n g u d j u s i jCO
2 d h e k=kk c u sx h(1)
32 g
(2)
44 g
(3)
88 g
(4)
22 g
Q.101 You are given a closed metal
container with an unknown
substance. By supplying heat at
constant rate and plotting a
graph between temperature and
time, if you get a graph as
shown, then two horizontal lines
indicates
(1) Solid
substance
(2) liquid
substance
(3) gas
(4)
liquid and gas
Q.102 A body can be cooled by
(1) Conduction
(2) Convection
(3) Radiation
(4)
All of the above
Q.103
When
12 g of carbon is
completely burnt in sufficient
quantity of oxygen, the amount
of CO formed is
2(1)
32 g
(2)
44 g
(3)
88 g
(4)
22 g
Temp
Time
r ki e ku
Q. 104 A plastic which is bad conductor
of heat and electricity is used to
manufacture electrical switches
and handles of utensils. The
plastic may be
(1)
P. V. C.
(2)
Malemine
(3)
Polyethene
(4)
Bakelite
Q.
105 W h i c h o f t h e f o l l o w i n g
electronic configuration can be
of a metal
(1) 2, 8, 5
(2) 2, 8, 4
(3) 2, 8, 1
(4) 2, 6
Q. 106 Reaction 2H O
2 22H O + O is
2 2an example of
(1) Combination reaction
(2) Neutralization reaction
(3) Decomposition reaction
(4) Displacement reaction
Q.107 Solution of calcium hydroxide
o n a d d i n g a d r o p o f
phenolphthalein indicator turns
(1) Pink
(2) Red
(3) Yellow
(4) Blue
i z-
104
, d I y kfLV d t ks m"e k o fo | qr d k d qp ky d g S] fo | qr fLo p o c j r u ksa d s g SaMy c u ku s d s d ke v kr k g SA ; g I y kfLV d g ks l d r k g S(1)
i o lh-(2)
e sy ke kb u(3)
i ksy hb Fkhu(4)
c sd ky kb Vi z-
105
fu Eu e sa l s d kSu l k b y SDV “ksfu d fo U; kl , d / kkr q d k g ks l d r k g S(1)
2, 8, 5
(2)
2, 8, 4
(3)
2, 8, 1
(4)
2, 6
i z-
106
v fHkf ; k2H O
2 22H O + O
2 2fu Eu e sa l s fd l d k mn kg j . k g S
(1)
l a; kst u v fHkf ; k(2)
mn kl hu hd j . k v fHkf ; k(3)
v i ?kV u v fHkf ; k(4)
fo LFkki u v fHkf ; ki z-
107
d SfYl ; e g kb M“ksDl kb M+ d s fo y ; u e sa Q hu ksy ¶ Fksy hu l wp d d h , d c wan Mky u s i j fo y ; u d k j ax g ks t kr k g S(1)
x qy kc h(2)
y ky(3)
i hy kQ.108 Which allotrop of carbon is used
as an adsorbent
(1) Coal
(2) Diamond
(3) Graphite
(4) Charcoal
Q.109 Which of the following metal
does not react at all with water
(1) Ni
(2) Mg
(3) Zn
(4) Ca
Q.110 Oxidation process involves
(1)
gain of electrons
(2)
Loss of electrons
(3)
Addition of hydrogen
(4)
Removal of oxygen
Q.111
Milk of magnesia is
(1) Colloid
(2) True solution
(3) Homogenous mixture
(4) Suspension
Q.112
Which out of following is not an
organic acid
(1) Formic acid
(2) Citric acid
(3) Ethanoic acid
(4) Carbonic acid
i z-
108
d kc Zu d k d kSu l k v i j : i v o ’ kks"kd d s : i e sa i z; ksx fd ; k t kr k g S(1)
d ks; y k(2)
g hj k(3)
x zsQ kb V(4)
p kj d ksyi z-
109
fu Eu e sa l s d kSu l h / kkr q t y l s d ksb Z Hkh v fHkf ; k u g ha d j r h(1)
Ni
(2)
Mg
(3)
Zn
(4)
Ca
i z-
110
v kWDl hd j . k f ; k e sa g ksr k g S(1)
b y SDV “ksu i zkIr d j u k(2)
b y SDV “ksu [ kksu k(3)
g kb M“kst u d k l a; ksx(4)
v kWDl ht u d k g V ku ki z-
111
fe Yd v kWQ e SfXu f’ k; k g S(1)
d ksy kb M(2)
fo y ; u(3)
l e kax h fe J . k(4)
fu y ac ui z-
112
fu Eu e sa l s d kSu l k d kc Zfu d v Ey u g ha g S(1)
Q ksj fe d v Ey(2)
fl fV “d v Ey(3)
, Fkksu ksb d v EyQ.113
Match the Column
Column-1
Column-2
A. Acidic
salt
I. NaCl
B. Basic
salt
II. Na CO
2 3C. Neutral
salt
III.
NH Cl
4(1) A-I, B-III,
C-II
(2) A-II,
B-III,
C-I
(3) A-III,
B-II
C-I
(4) A-III,
B-I,
C-II
Q114 Which of the following is a
Prokaryotic cell?
(1) Spirogyra
(2) Amoeba
(3) Rhizopus
(4) Escherichia
Coli
Q.115
Which of the following is not a
viral disease?
(1)
Chicken Pox
(2) Polio
(3) Hepatitis
A
(4) Tuberculosis
Q.116
Main cause of soil erosion is
(1) Afforestation
(2) Less
rain
(3)
Thinning of Ozone layer
(4) Deforestation
i z-
113
d kWy e d k fe y ku d j sa d kWy e &1
d kWy e &2
A.
v Ey h; y o . kI. NaCl
B.
{ kkj h; y o . kII. Na CO
2 3C.
mn kl hu y o . kIII. NH Cl
4(1) A-I, B-III,
C-II
(2) A-II,
B-III,
C-I
(3) A-III,
B-II
C-I
(4) A-III,
B-I,
C-II
i z-
114
fu Eu e sa l s d kSu i zksd Sfj ; ksfV d d ksf’ kd k g S\(1)
Li kb j ksx k; j k(2)
v e hc k(3)
j kb t ksi l(4)
b l p j fp ; k d ksy hi z-
115
fu Eu e sa l s d kSu l h fo "kk. kq t fu r c he kj h u g ha g S\(1)
p sp d(2)
i ksfy ; ks(3)
fg i sV kb fV lA
(4)
r i sfn di z-
116
Hkwfe d V ko d k e q[ ; d kj . k g S(1)
o u j ksi . k(2)
d e o "kkZ(3)
v kst ksu i r Z d k i r y k g ksu kQ.117
Match the diseases of column A
with their causing organism in
column B
Column A
Column B
a. Measles
i. Bacteria
b. Cholera
ii. Virus
c. Malaria
iii. Protozoa
d. Rust of wheat iv. Fungus
(1) a -iv,
b-iii,
c-i,
d-ii
(2) a -ii,
b-i,
c-iii, d-iv
(3) a -i,
b-iii,
c-iv, d-ii
(4) a -i,
b-ii,
c-iii, d-iv
Q.118 Algin is taken from
(1) Bacteria
(2) Algae
(3) Fungi
(4) Protozoa
Q.119 The process of removing
unwanted plants from the fields
is called
(1) Sowing
(2) Harvesting
(3) Irrigation
(4) Weeding
Q.120 Which of the following releases
the toxic substance 'tuberculin'
(1)
Bacteria
(2) Virus
(3) Algae
(4) Fungi
i z-
117
d kWy eA
d h c he kfj ; ksa d k d kWy eB
e sa fy [ kh x b Z mu d s d kj d t ho ksa l s fe y ku d j sad kWy e
A
d kWy eB
a.
[ kl j ki.
t ho k. kqb.
d kWy j kii.
fo "kk. kqc.
e y sfj ; kiii.
i zksV kst ksv kd.
x sag w d h j LViv.
Q Q wan(1) a -iv, b-iii, c-i,
d-ii
(2) a -ii,
b-i,
c-iii,
d-iv
(3) a -i,
b-iii, c-iv,
d-ii
(4) a -i,
b-ii,
c-iii,
d-iv
i z-
118
, y fx u fu Eu e sa l s fu d ky k t kr k g SA(1)
t ho k. kq(2)
’ kSo ky(3)
Q Q wan(4)
i zksV kst ksv ki z-
119
[ ksr l s v o kafN r i kS/ kksa d ks g V ku s d h i zf ; k d g y kr h g SA(1)
c qv kb Z(2)
d V kb Z(3)
fl ap kb Z(4)
[ kj i r o kj fu ; a=k. ki z-
120
fu Eu e sa l s fd l d s } kj k g kfu d kj d …fo "kSy k‰ i n kFkZ ^V ; wc j D; wfy u * N ksM+kt kr k g S\
(1)
t ho k. kq(2)
fo "kk. kq(3)
’ kSo kyQ.121 Which nutrient increases in soil
due to crop rotation?
(1) Zinc
(2) Sulphur
(3) Nitrogen
(4) Calcium
Q. 122 Which of the following method
of irrigation helps in maximum
conservation of water?
(1) Chain
pump
(2) Rahat
(3) Drip
system
(4) Sprinkler
system
Q.123 The structure bearing 'genes' in
the cell are called as
(1) Nucleolus
(2) Nucleus
(3) Chromosomes
(4) Ribosomes
Q. 124 Match column A with column B
Column A
Column B
i. Gram seed
a. Urea
ii. Rice (Paddy) b. Karif crop
iii. Fertilizer
c. Silos
iv. Storage
d. Rabi crop
which is the most appropriate
combination
(1) i-a, ii-b, iii-c, iv-d
(2) i-d, ii-c, iii-b, iv-a
(3) i-d, ii-b, iii-a, iv-c
(4) i-b, ii-a, iii-c, iv-d
i z-
121
Q l y p . k l s fe Œh e sa fd l i ks"kd d h e k=kk c < + t kr h g S\(1)
ft ad(2)
l YQ j(3)
u kb V “kst u(4)
d SfY’ k; ei z-
122
fu Eu fy f[ kr e sa l s fd l fo f/ k } kj k fl ap kb Z d j u s l s i ku h d k l o kZf/ kd l aj { k. k g ksr k g S\(1)
p su i ai(2)
j g V(3)
fM“i l a; a=k(4)
fN M+d ko l a; a=ki z-
123
d ksf’ kd k e sa t hUl d s / kkj d d ks d g k t kr k g S(1)
d sfU d k(2)
d sU d(3)
x q. kl w=k(4)
j kb c ksl ksEli z-
124
d kWy eA
d k fe y ku d kWy eB
l s d j ks d kWy eA
d kWy eB
i.
p u ka.
; wfj ; kii.
p ko y …/ kku ‰b.
[ kj hQ Q l yiii.
mo Zj dc.
l kb y ksiv.
HkaMkj . kd.
j c h d h Q l y mi ; qDr fo d Yi d kSu l k g SAQ. 125 Out of 23 pair chromosomes in
Q.126 Choose the rational number
which does not lie between
rational numbers and
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Q. 127 150 is what percent of 30?
Q.129 At the rate of m meters per s
seconds, how many meters does
a cyclist travel in x minutes?
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Q.130 If x+5>2 and x-3 <T, then the value
of x lie between which of the
2
Q.133 The product of integers w, x, y
and z is 770 and if 1 < w < x < y < z
Q.135 If the altitude of an equilateral
triangle is 3 cm then its area is
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Q. 137 If n is a positive integer then
n (n + 1) ( n + 2) is
(1)
Even only when n is even
(2)
Even only when n is odd
(3)
Odd whenever n is odd
(4)
Divisible by 4 whenever n is
even.
Q.138 Mary's income is 60% more than
Tim's income and Tim's income is
40% less than John's income
what percent of John's income is
Mary's income?
(1)
124%
(2)
120%
(3)
96%
(4)
80%
Q.139 In the fig shown, the value of v + x
+ y + z + w is
(1)
45
°
(2)
90°
(3)
180°
(4)
360°
i z-
137
; fn , dn
?ku kRe d i w. kk–d g S r ksn (n + 1) ( n + 2)
g ksx k\(1)
l e d so y r c t cn
l e g ksx k(2)
l e d so y t cn
fo "ke g ksx k(3)
fo "ke t cn
fo "ke g ksx k(4)
4
l s fo Hkkft r t cn
, d l e l a[ ; k g ksx hi z-
138
e sj h d h v k; fV e d h v k; l s60%
v f/ kd g SA i j ar q fV e d h v k; t kWu d h v k; l s40%
d e g S r ks t kWu d h v k; e sj h d h v k; d k fd r u s i zfr ’ kr g S\(1)
124%
(2)
120%
(3)
96%
(4)
80%
i z-
139
fn , x , fp =k e sav + x + y + z + w
d k e ku g kssx k\(1)
45
°
(2)
90°
(3)
180°
(4)
360°
z
v x
y
w
z
v x
y