i
FOR THE SEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMPKANISIUS PAKEM SLEMAN
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana PendidikanDegree
in English Language Education
By
Francisca Ika Septiani Student Number: 021214108
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
iv OR A PERSON
WHO DOES SOMETHING TO MAKE THE WORLD BETTER. MAYBE YOU CAN’T FIX IT.
BUT AT LEAST YOU DIDN’T DO NOTHING.
(
ANGELINA JOLIE)
my late father Agustinus Tri Antoro (†)
vii
First of all, I would like to dedicate my gratitude to God, Jesus Christ, and Holly Mary for the blessing, love, and the kindness in my life that I could finish my thesis.
I would like to give my great thanks to my major sponsor, C. Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd. and my co-sponsor Christina Kristiyani, S.Pd., M.Pd. for always giving me a lot of advice and attention during the process of writing the thesis and give detailed corrections to improve my thesis.
Next, I would like to thank English teachers of Kanisius Pakem Sleman, Ms. Susi and Ms. Tuti, for their willingness to give valuable suggestions for the designed materials. I also thank Ratna, Yuda, and Wisnu for their help in doing the task of the material.
Special appreciation also goes to all lecturers of English Language Education Study Program for their kindness and patience. They have given me a lot of valuable experiences during my study in this university. I would also like to thank PBI staffs, mba Tari and mba Danik for giving good services.
viii
Meme, Mas Damar, for the great friendship. I thank for all support, help, care, and laugh during the moment we have shared together.
I never forget my lovely friends in PBI 2002: Arai, Regi, Reni, Grace, Cicil, Vivin, Dedi, Udjo, Miko, Ila, Niken, Ratri, Mel, Gabo, and Lintang. These people always supported me to accomplish my thesis. I would like to say thank you for the sad and happy moments to share during our study in university.
My thanks also goes to the teachers and students in Bumble Bee English course. I really enjoy the experience of teaching there. Many thanks go to Frater Edi who give a book “The Secret”. I thank for the motivation and believe that I get from reading the book.
Last but not least, I also thank for those who have given me a hand, whom I have not mentioned.
Francisca Ika Septiani
ix
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES... ii
DEDICATION PAGE ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY... v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS... vi
TABLE OF CONTENTS... vii
LIST OF FIGURES ... xi
LIST OF TABLES... xii
ABSTRACT... xiii
ABSTRAK... xiv
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Problem Formulation... 3
C. Problem Limitation ... 3
D. Research Objectives ... 4
E. Research Benefits ... 4
1. For English teachers... 4
2. For students of Kanisius Pakem... 4
3. For other researchers... 5
F. Definition of Terms ... 5
1. Instructional Materials ... 5
2. Vocabulary... 5
3. Multiple Intelligence Theory ... 6
4. Seventh Grade Students ... 6
5. Kanisius Pakem Junior High School ... 7
CHAPTER II: REVIEWOF RELATED LITERATURE... 8
A. Theoretical Description ... 8
1. Instructional Design Models ... 8
a. Dick & Reiser’s Model ... 9
x
b. The Eight Intelligences... 13
3. Characteristics of Junior High School Students... 15
a. Social Development ... 15
b. Emotional Development... 16
c. Cognitive Development... 16
4. Vocabulary... 16
a. The Four Key Strands in Vocabulary... 16
1) Vocabulary and Meaning-Focused Input ………... 16
2) Vocabulary and Meaning-Focused Output ……… 17
3) Developing Fluency with Vocabulary ……….. 17
4) Vocabulary and Language-Focused Instruction ………... 17
b. Principles of Teaching Vocabulary ……… 18
1) Focus on the Most Useful Vocabulary First ………. 18
2) Focus on the Vocabulary in the Most Appropriate Way ……….. 18
3) Give Attention to the High Frequency Words Across the Four Strands of a Course ……… 18
4) Encourage learners to reflect on and take responsibility for learning ………... 19
B. Theoretical Framework ... 19
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY ... 24
A. Research Method ... 24
1. Research and Information Collecting ……….. 25
2. Planning ……… 25
3. Development of Preliminary Form of Product ……… 26
4. Product Evaluation ……….. 26
5. Main Product Revision ……… 26
B. Research Participants ... 26
1. Research and Information Collecting ... 27
2. Product Evaluation... 27
C. Research Instruments... 28
xi
1. Research and Information Collecting ... 30
2. Product Evaluation ... 30
E. Data Analysis Techniques ... 31
1. Research and Information Collecting ... 31
2. Product Evaluation... 31
F. Research Procedure ... 33
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 36
A. The Process of Designing the Material ... 36
1. Doing Needs Analysis... 36
2. Determining Standard Competences, Basic Competences, and Topics... 39
3. Determining Indicators ... 40
4. Listing Subject Contents ... 40
5. Designing the Materials ……… 40
6. Selecting teaching-learning Activities ………. 41
7. Evaluating ……… 41
8. Revising ……… 42
B. The Presentation of the Designed Materials ... 42
1. The Standard Competences, Basic Competences, and Topics ... 42
2. The Indicators ... 46
3. The Subject Contents ... 48
4. The Materials ……… 49
5. The Teaching-Learning Activities……… 50
6. The Evaluation of the designed materials ……… 50
a) The Description of Respondents ……… 50
b) Data Presentation ……….. 51
c) Respondent’s Comments and Suggestions ………... 53
d) Implementation one-to-one Evaluation ……… 53
7. The Revision of the Designed Materials... . 56
a) Responses to the Respondent’s Evaluation ………. 57
xii
B. Suggestions... 62
REFERENCES ... 64
APPENDICES ... 66
Appendix A. Letter of Permission ... 67
Appendix B. Interview Guideline, Post-design Questionnaire... 70
Appendix C. The Results of Post-design Questionnaire ... 78
Appendix D. The Syllabus ……… 80
Appendix E. The Lesson Plan ... 96
Appendix F. The Learning Activities and Intelligences ... 138
xiii
xiv
Table 3.1 TheDescription of Product Evaluation Respondents ... 27
Table 3.2 The Format of Product Evaluation Results... 32
Table 4.1 The Standard Competences ... 42
Table 4.2 The Basic Competences... 44
Table 4.3 The Indicators ... 46
Table 4.4 The Result of the Evaluation Questionnaire ... 52
xv
Septiani, Francisca Ika. 2008. EnglishVocabulary Instructional Materials Based on the Multiple Intelligence Theory for the Seventh Grade Students of SMP Kanisius Pakem Sleman. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
This study was conducted to design vocabulary materials based on the Multiple Intelligence (MI) theory for the seventh grade students of SMP Kanisius Pakem Sleman. The areas of intelligences to be elaborated in this study are Verbal-Linguistic, Mathematical-Logical, Musical, Visual-Spatial, Bodily-Kinesthetic, Interpersonal, Intrapersonal, and Naturalist Intelligences.
The objectives of this study were to answer two research questions: (1) how is a set of vocabulary instructional materials based on the Multiple Intelligence theory for the seventh grade students of SMP Kanisius Pakem Sleman designed? And (2) what does vocabulary instructional materials based on the Multiple Intelligence theory for the seventh grade students of SMP Kanisius Pakem Sleman look like? The five steps of R & D cycle were employed to answer two questions above. The five steps were: (1) Research and Information Collecting, (2) Planning, (3) Development of the Preliminary Form of Product, (4) Product Evaluation, and (5) Main Product Revision. To answer the first question, the writer adapted Dick& Reiser’s and Kemp’s instructional design models. There were eight steps employed based on Dick & Reiser’s and Kemp’s instructional design models: (1) Doing Needs Analysis, (2) Determining Standard Competences, Basic Competences, and Topics, (3) Determining Indicators, (4) Listing Subject Contents, (5) Designing the Materials, (6) Selecting the teaching-learning Activities,(7) Evaluating, and (8) Revising.
In order to answer the second question, the final version of the designed materials was presented after conducting some revisions based on the feedbacks, comments, and suggestions from the respondents. Based on the evaluation by the English teachers of SMP Kanisius Pakem Sleman and English Education lecturer of Sanata Dharma University; the mean was ranged to 3.3 up to 4.5 on a scale of 1-5. It is concluded that the designed materials are good and acceptable. The final version of the designed materials consists of eight units and each unit consists of four sections, that is Come In Please, Let’s Build the Word, Work It Out, and You Can Do It. In each unit there were four up to six intelligences developed. The detailed presentation of the designed materials can be seen in the Appendix G.
xvi
Septiani, Francisca Ika. 2008. EnglishVocabulary Instructional Materials Based on the Multiple Intelligence Theory for the Seventh Grade Students of SMP Kanisius Pakem Sleman. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Studi ini dilaksanakan untuk merancang materi pembelajaran vocabulary berdasarkan teori kecerdasan ganda bagi siswa kelas tujuh SMP Kanisius Pakem Sleman. Aspek-aspek kecerdasan yang akan dibahas di dalam penelitian ini adalah: kecerdasan verbal-linguistik, matematis-logis, musik, ruang-visual, kinestetik-badani, interpersonal, intrapersonal, dan kecerdasan alam.
Tujuan dari studi ini adalah menjawab dua pertanyaan: (1) Bagaimana merancang materi vocabulary berdasarkan teori kecerdasan ganda bagi kelas tujuh SMP Kanisius Pakem Sleman? (2) Bagaimanakah bentuk rancangan materi vocabulary berdasarkan teori kecerdasan ganda bagi kelas tujuh SMP Kanisius Pakem Sleman? 5 langkah metode siklus R&D dipergunakan untuk menjawab dua pertanyaan diatas. 5 langkah tersebut adalah: (1) pengumpulan informasi dan hasil-hasil penelitian, (2) perencanaan, (3) pengembangan bentuk awal materi, (4) evaluasi materi, dan (5) perbaikan materi utama.
Untuk menjawab pertanyaan pertama, penulis mengadaptasi model pembelajaran dari Dick& Reiser’s. Ada 9 langkah yg diterapkan berdasarkan model pembelajaran Dick&Reiser’s: (1) melakukan survey kebutuhan, (2) menentukan standar kompetensi, kompetensi dasar, dan topik, (3) merumuskan indikator, (4) merinci isi materi, (5) merancang materi, (6) memilih kegiatan belajar mengajar, (7) evaluasi, dan (8) memperbaiki materi .
Untuk menjawab pertanyaan kedua; versi akhir dari materi yang dirancang, diperbaiki berdasarkan masukan, komentar dan saran dari responden. Berdasarkan hasil evaluasi yang diperoleh dari guru-guru bahasa Inggris SMP Kanisius Pakem Sleman dan dosen Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Sanata Dharma; rata-rata yang diperoleh adalah 3.3 sampai 4.5 dari skala 1-5. Maka, dapat disimpulkan bahwa materi yang di rancang ini baik dan dapat diterima. Versi akhir materi yang dirancang terdiri dari delapan unit dan masing-masing unit terdiri atas empat bagian, yaitu, Come In Please, Let’s Build the Word, Work It Out, and You Can Do It. Dalam setiap unit ada empat sampai enam inteligensi dikembangkan. Materi secara detail dapat dilihat pada Apendiks G.
1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter covers six important parts of the thesis: background of the study, problem formulation, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits, and definition of terms.
A. Background of the study
writer believes when teacher provides variety of task based on students’ major intelligence, students will be helped in their part of learning.
In this globalization era, English has become international language in all over the countries. Therefore, students learn English in school. They have to learn English in order to be able to communicate orally and written in their daily life. Junior High School students also learn English as their obligatory subject. However, from the writers’ interview to some junior high school students it is known that they consider English as a difficult subject. They have problems especially in memorizing the meaning of English words. There are several words that have more than one meaning and students are confused to decide the appropriate meaning.
applying the language to communicate with other people. To achieve the purpose, the mastery of vocabulary is important for supporting the communication skill that students need to achieve.
In designing the materials, the writer uses multiple intelligences theory. The writer believes when teacher provides a lot of varieties in learning activities based on students’ way of learning, their understanding on the lesson will be developed. Students who are not good at linguistic skills can be helped if the teacher provides variety on the learning activities based on what they are good at. By developing the eight intelligences in task, students’ major intelligence will be activated and it will help them in learning any kind of subject.
B. Problem Formulation
There are two main problems to discuss in this study:
1.How is a set of English vocabulary instructional materials based on the Multiple Intelligence theory for the seventh grade students of Kanisius Pakem designed?
C. Problem Limitation
This study focuses on how to design English vocabulary instructional materials to teach English. The approach used is Multiple Intelligences that can help students in their part of learning by developing the eight areas of intelligences.
D. Research Objectives This study aims at:
1. Finding out how a set of vocabulary instructional materials based on the Multiple Intelligence theory for the seventh grade students of Kanisius Pakem is designed.
2. Presenting the designed set of materials.
E. Research Benefits
This study is expected to give some benefits. Those is: 1. English teachers
The vocabulary materials can be used as a tool to help English teachers to teach using multiple intelligences theory and develop the student’s intelligences through various activities in English teaching. In addition, these materials can be used as a supplementary material in teaching English. In this study, supplementary means the materials can be used to add or complete the existing materials.
The writer hopes that with the designed materials, the students will experience various activities that can stimulate their intelligences in learning English. They will be able to understand and memorize the words in English. At the end, the students are able to learn and use their eight intelligences independently.
3. Other researchers
It is hoped that through this study, the other researcher will be encouraged to conduct some studies to find new theories in education.
F. Definition of Terms
In this section the writer defines some important terms that is used in this study:
1. Instructional Material
An instructional material is any resource including printed materials of many kinds, audiovisual media, and other items for group and individual uses. The material itself can help and motivate students to understand on the subject given (Kemp, 1977). In this study, instructional material is materials from any kind of resource that is used for group and individual uses. The material itself would be printed materials.
2. Vocabulary
rules combining them) make up a language 2) words known to or used by a person in trade, profession 3) book containing list of words. In this study, the writer refers to Hornby’s definition that is, total numbers of words which (with rules combining them) make up a language.
3. Multiple Intelligence Theory
A theory proposes that there is much intelligence that human has. The intelligences are languages that all people speak and are influenced, in part by the culture into which one is born (Campbel & Dickinson, 1984: xix). Multiple Intelligences theory has been proposed by Gardner (2000) in his book Intelligence Reframed.
There are nine intelligences that people have namely linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, musical, bodily kinesthetic, interpersonal, intrapersonal, naturalist, and existential. In this study the writer will only discuss the eight intelligences. The writer will reflect the intelligences on the design when the topics and materials are possible.
4. Seventh grade students
They are students at the approximate age of 13-15. According to Piaget, (1958) students at this age pass the period of formal operation. It is a period when students are able to think symbolically and can understand meaningfully without seeing the concrete object.
5. Kanisius Pakem Junior High School
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL REVIEW
This chapter presents two major discussions. They are theoretical description and theoretical framework. In the theoretical description, some related theories such as instructional design models, multiple intelligence theory, characteristic of junior high school students, and vocabulary will be developed. The theoretical framework presents the summary of the previous section and illustrates the steps to be taken in constructing the design.
A.Theoretical Description
There are four topics presented in this section: instructional design, Multiple Intelligence Theory, charactheristic of junior high school students, and vocabulary.
1. Instructional Design Model
a) Dick and Reiser’s Model
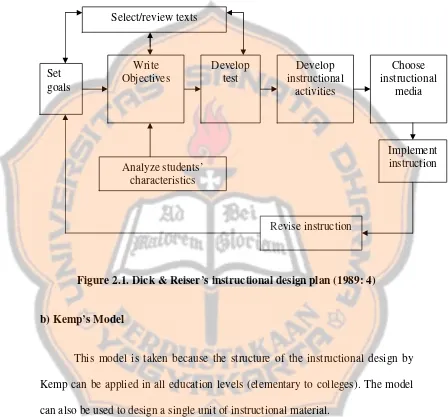
instructional plan. The diagram on Figure 2.1 shows steps to develop effective instruction based on the components previously described.
Figure 2.1. Dick & Reiser’s instructional design plan (1989: 4)
b) Kemp’s Model
This model is taken because the structure of the instructional design by Kemp can be applied in all education levels (elementary to colleges). The model can also be used to design a single unit of instructional material.
Kemp (1977: 8-9) offers eight elements in designing the program development. An interdependent is found among eight elements. Kemp’s model is a flexible process. It can move back and forth to the other steps. The steps are goals; topic and general purposes; learning characteristics; learning objectives;
Set goals
Write Objectives
Develop test
Develop instructional
activities
Choose instructional
media
Implement instruction Analyze students’
characteristics
subject content; pre-assessment; teaching-learning activities and resources; support services; evaluation.
Step 1 Goals, topics and general purposes
In making the design, a designer should identify goals, choose major topics, and listing the general purposes. The goals can be derived from three sources i.e. society, students, and subject areas. After recognizing the goals, major topics should be treated within the content area. Those topics should be consequenced from simple or concrete levels to complex and more abstract levels. The next thing to do is listing general purposes which are made from the goals and explicitly express students’ expectation.
Step 2 Learning characteristics
In order to assure individual’s success in educational program, the designer should recognize and respect the students as an individual learner. It means that the designer must obtain information about the student’s capabilities, needs and interest. The information on student’s characteristic will affect the instructional design emphazised.
Step 3 Learning Objectives
Step 4 Subject content
Students’ learning experiences must closely relate to the objectives and to the students’ needs. Subject content comprises the selection and organizing of the specific knowledge, skills and attitudinal factors of any topic. It is called in term of organizing content. In teaching skill, an organizational procedure called task analysis which refers to logical, step by step description of the job or performance skill is often used.
Step 5 Pre-assesment
In order to plan learning activities, a pre-requisite test is needed. The test is fuctioned as determination whether students have the appropriate background for the topic. The second is to determine which of the objectives students have already achieved.
Step 6 Teaching/learning activities and resources
All the plan have done came to the selection of teaching/learning activities. The designer has to decide the most efficient and effective methods to provide learning experiences. The selection of activities close to the selection of supporting materials which effectively explain and illustrate the subject content.
Step 7 Support services
time instructional plans are being made and selected. The support services includes funds, facilities, equipment and personnel.
Step 8 Evaluation
This is the final step in the instructional design plan for both the students and the teachers. Student’s performance is measured by teachers that have set the criteria for judging the quality of student’s work. When students succesfully achieve them, the educational program is succesfully gained.
Figure 2.2 Kemp’s Instructional Design Model
Goal, Topics, and General
Purposes
Teaching Learning Activities resources Support Services
Learner Characteristic
Learning Objectives
Subject Content
Pre assessment Evaluation
2. Multiple Intelligence Theory
a. The Nature of Multiple Intelligence theory
In his book Frames of Mind (1983), Gardner presented a list of seven intelligences. The first two are ones that have been typically valued in school; the next three are usually associated with arts; and the final two are what Howard Gardner called ‘personal intelligences’ (Gardner, 1999: 41-43). Afterwards in Intelligence Reframed (2000) he added two intelligences. The nine intelligences are linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, musical, bodily kinesthetic, interpersonal, intrapersonal, naturalist and existential. In this study, the writer will only discuss the eight intelligences since the ninth intelligences is quite new and personal.
b. The Eight Intelligences
There are eight intelligences will be discussed in this study. They are described as follows.
1. Linguistic intelligence is the ability of using words in remembering list or process. The person with this intelligence is able to think in words and language to express complex meanings.
3. Musical intelligence posseses a sensitivity to pitch, melody, rhytm, and tone. An individual with musical intelligence has high participation in musical activities such as playing instruments, singing, and composing.
4. Spatial intelligence defines the individual’s ability to transform objects in space. A person who has this intelligence is excellent in reproducing objects in visible forms.
5. Bodily-kinesthetic intelligence is the ability to unite body and mind to perfect physical performance. This intelligence centers on how a person can use his or her body to show high skills of performance.
6. Interpersonal intelligence is the capacity to understand and interact effectively with others. Person with interpersonal intelligence enjoys interacting with others of similar or different ages. He or she often great at group work, team, and collaborative projects.
7. Intrapersonal intelligence refers to the ability to construct an accurate perception of oneself and to use such knowledge in planing and directing one’s life. This intelligence includes of how person uses feelings and thoughts to understand his or herself and other people.
Gardner believes that since each intelligence can be used for good or ill purposes, all eight are inherently value-free (Campbell,1996). Each student has different intelligence therefore the purpose of the school should be to develop intelligences and to help people to reach the goals based on the spectrum of intelligences.
3. Characteristics of Junior High School students
Students of junior high school are between the ages of 13-15. They are considered as adolescence. Konopka (1973) sees adolescence as an important segment of continuing human development. She distinguishes early adolescence (the years from twelve to fifteen), middle adolescence (fifteen to eighteen), and late adolescence (nineteen to twenty two). Usually an adolescent becomes deeply aware of many life issues and questions relating to himself and others, to community and nation. They eagerly take opportunities for a good time, for pleasure and excitement but is also concerned over the expectations of others and his liberty to press for new experiences and adventures (Pikunas, 1973: 242 ). There are several developments happened during the adolescence stage (Pikunas, 1976: (245-256). They are social development, emotional development, and cognitive development.
a. Social Development
b. Emotional Development
The pubertal child begins to experience heightened feelings and undertakes to revise his or her own attitudes. There is an increasing of emotional which is apparent in the various moods experienced by adult. c. Cognitive Development
The cognitive development has developed well during adolescence stage. They begin to feel confident in their own mental ability and enjoy intellectual activity. They are already able with activity of thinking, hypothesizing, and experimenting.
4. Vocabulary
a. The Four Key Strands in Vocabulary
Nation (2002: 267) stated that research on second language acquisition can be interpreted to show that a well-balanced language course should contain four major strands: meaning-focused input, meaning-focused output, fluency development, and language-focused instruction. He added that vocabulary teaching and learning must fit into these four strands. The details of how the vocabulary component fit into the four strands are elaborated as follows.
1) Vocabulary and Meaning-Focused Input
suitably graded input by offering it across a range of genres and topics. Therefore, it is essential that learners have access to simple written and spoken texts.
2) Vocabulary and Meaning-Focused Output
Learning vocabulary from meaning-focused output means learning vocabulary by speaking and writing in which the main attention is on communicating messages. By using vocabulary productively, it can strengthen learning and can push learners to focus on aspect of vocabulary knowledge.
3) Developing Fluency with Vocabulary
The fluency development strand of a course aims to help learners make the best use of what they already know. It is important for each four skills listening, speaking, reading and writing.
There are three conditions required for the development of fluency: (1) it should not involve unfamiliar vocabulary, (2) the learners’ focus is on the message, and (3) the learners are encouraged to reach a higher than usual level of performance through the use of repetition, time pressure, and planning and preparation.
4) Vocabulary and Language-Focused Instruction
on pronunciation and spelling of a word, memorizing collocation, and being corrected for incorrect use of a word.
b. Principles of Teaching Vocabulary
Nation in Practical English Language Teaching (2003:135-41) stated that there are four principles which can be used in teaching vocabulary. They are elaborated as follows:
1) Focus on the Most Useful Vocabulary First
Teaching useful vocabulary before less useful vocabulary gives learners the best return for their learning effort. The most useful vocabulary that is given by the teacher will enable them to master the English word and absolutely same with the effort they have done.
2) Focus on the Vocabulary in the Most Appropriate Way
In this study, the writer will look at the four most important vocabulary learning strategies of using word parts, guessing from context, using word cards, and using dictionaries. Using word parts to help remember words, and using guessing from context are two very important strategies for dealing with low-frequency words. There are two more very important strategies- using word cards for deliberate learning, and looking up words in dictionaries.
3) Give Attention to the High Frequency Words Across the Four Strands of a Course
4) Encourage learners to reflect on and take responsibility for learning
There is an important principle lays behind choosing and learning and that is that learners need to realize that they must be responsible for their own learning. Taking this responsibility requires (1) knowledge of what to learn and the range of options for learning vocabulary, (2) skill in choosing the best options, and (3) the ability to monitor and evaluate progress with those options.
B. Theoretical Framework
Having discussed the theoretical description, in this part the writer will put important points on theoretical framework. Firstly, the study is about the instructional design. The organized plan on the design aims to give direction to the teacher so they can develop effective instruction. The writer uses steps modified from Kemp and Dick& Reiser’s model. The writer adapts this two models since they are completing each other. In Kemp there is no need analysis. The use of need analysis in Dick & Reiser’s can make the design better. Moreover, Dick&Reiser’s model emphasizes on delivering the effective instruction to the learners. However, Dick& Reiser’s model is not flexible whereas Kemp’s model is flexible since there is interdependence among the eight elements.
consideration. Students in this level are already good at handling abstract rules and concept, then it will give consideration for the teacher not always gives concrete object in the activities.
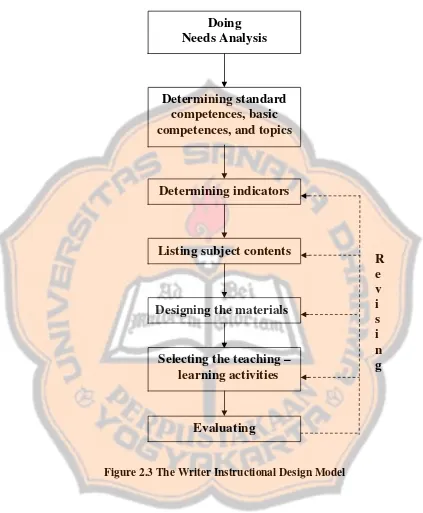
The framework is composed of several elements, namely, doing needs analysis; determining standard competences, basic competences, and topics; determining indicators; listing subject contents; designing the materials; selecting teaching and learning activities; evaluating, and revising.
Step 1 Doing Needs Analysis
The writer adapts this step from Dick & Reiser’s model. A need analysis is essential in planning the instruction. It can be used to learn about the students’ need and special characteristic. The writer conducts a survey by interviewed two English teachers of Kanisius Pakem Junior High School.
Step 2 Determining Standard Competences, Basic competences, and Topics The writer adapts this step from Kemp’s model. This step is used to know the goals of the materials design based on 2006 Curriculum. The topics, then, are chosen based on the necessity to achieve the goals. In determining the standard competences, basic competences, and topics the writer develops them from 2006 curriculum.
Step 3 Determining Indicators
have to learn in every meeting and at the end of each meeting the students are expected to be able to achieve the basic competence.
Step 4 Listing Subject Content
This step is adapted from Kemp’s model. The function of this step is to facilitate the achievement of each objective. Therefore, they should be closely related to the objectives of the learner’s needs.
Step 5 Designing the Materials
In this step, the writer designs the materials utilizing the teaching learning activities and the instructional sources which have been previously selected. The materials are designed based on the standard competences and basic competences. Step 6 Selecting the Teaching and Learning Activities
Producing a set of English learning materials for the seventh grade students of Kanisus Pakem based on Multiple Intelligences theory is the main focus of this study. The materials are designed based on the eight areas of intelligences as discussed in the previous section. As stated by Dick & Reiser’s (1989:4) in planning the activities, teacher should consider the textbook to be one of the available means that could be used in teaching specific objects. Therefore, the writer looks for some books to gather relevant teaching learning sources and also the suitable teaching media.
Step 7 Evaluating
Step 8 Revising
Figure 2.3 The Writer Instructional Design Model
Doing
Needs Analysis
Determining standard
competences, basic
competences, and topics
Determining indicators
Listing subject contents
Designing the materials
Selecting the teaching –
learning activities
Evaluating
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents the methodology used in this study. Referring to the problem formulation, the methodology used is the methods to find out how the material is designed. The major discussions related to the methodology used in this study are: (1) research method; (2) research participants; (3) research instruments; (4) data gathering techniques; (5) data analysis techniques and (6) research procedure.
A. Research Method
This study attempts to answer two major problems. Firstly, it was conducted to find out how a set of English vocabulary instructional materials based on Multiple Intelligences of Kanisius Pakem Junior High School was designed. Secondly, it was aimed to present the designed materials for students of Kanisius Pakem Junior High School.
Research and Development method (R&D) cycle to develop the products (1983: 775). They are research and information collecting, planning, development of preliminary form of product, product evaluation, main product revision, main field testing, operational product revision, operational field testing, final product revision, dissemination and implementation.
In order to answer the two major problems mentioned above, the writer employed step one until step five. The steps are explained as follows.
1. Research and Information Collecting
Research and information collecting includes review of literature, classroom observation, and preparation of report of state of the art (Borg and Gall, 1983: 775). In this step, describing the designed material as specific as possible became the important thing. Thus, the writer conducted an informal interview for the teachers of Kanisius Pakem. The writer also checked the curriculum in order to obtain the data. The data were used as a source to obtain the students’ needs and opinion from the teacher about the teaching of vocabulary which was suitable for the seventh grade students of Kanisius Pakem Junior High School.
2. Planning
instructional materials. Instructional materials can be tested and revised until they were suitable with the objectives.
3. Development of Preliminary Form of Product
After completing the planning step, the next step was to develop the preliminary form of product. This step included preparation of instructional materials, handbooks, and evaluation devices. In this step, designer organized the designed materials so as to permit obtaining as much feedback as possible. 4. Product Evaluation
This step is applied to obtain the evaluation for the instructional materials. In this study, the writer used questionnaires to gain the feedback. The feedback would be useful to revise and improve the designed material so that the designed material would work effectively. The evaluation was obtained from the English teachers of Kanisius Pakem Junior High School and English lecturer of Sanata Dharma University.
5. Main Product Revision
After obtaining the evaluation from the product evaluation, the writer applied the result or suggestions to revise the materials as recommended by the teachers and lecturers. Thus, the data collected from the product evaluation would be used as the basis to obtain the final designed material.
B. Research Participants
and one English lecturer from Sanata Dharma University. Both teacher of Kanisius Pakem was Bachelor graduates. The lecturer had achieved Master Degree. The lecturer chosen to be participant is those who expert in Vocabulary. The respondent was competent since she teach that subject and she also has teaching experience. Several respondents had a lot of experiences in teaching, which was indicated by their teaching experience. All of them had more than two years teaching experiences. The table 3.1. describes the respondents.
Table 3.1. The Description of Product evaluation Respondents Group of
Respondents Educational Background Teaching Experience Sex D3 S1 S2 S3 < 1 1 - 5 5-10 10 < M F English Teachers - 2 - - - 1 1 - - 2
English Lecturer
- - 1 - - 1 - - 1
1. Research and Information Collecting
The English teachers of Kanisius Pakem Junior High School were involved in this survey as the respondents of interview to find out the information about vocabulary teaching. Besides, it also found out students’ needs, lacks and wants in vocabulary from teachers’ view. Moreover, they were closely related to the teaching learning process. Thus, their comments provided the information for designing the materials.
2. Product Evaluation
High School. The respondents’ opinion on the designed material will be used as a feedback to revise the designed material.
C. Research Instruments
The instruments used to gather the data in this research were interviews and questionnaires. The data which were gathered gave valuable contribution for the writer in designing and revising a set of English vocabulary materials for the seventh grade students of Kanisius Pakem Junior High School based on Multiple Intelligences Theory. They are explained as follows.
1. Research and Information Collecting Instruments
2. Product Evaluation Instruments
In the product evaluation, the writer only used one instrument that is questionnaire. The questionnaire was distributed to two of the English teachers of Junior High School and one lecturer of the English Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. The questionnaire was used to gain respondents’ opinions and comments on the designed material. Therefore, the writer could obtain feedback and evaluation to design suitable English vocabulary materials using Multiple Intelligences Theory for the seventh grade students of Kanisius Pakem Junior High School. In the product evaluation survey, the writer used likert scale items type and open ended question. The likert scale is one of the most widely techniques to measure attitudes. It assessed attitude toward a topic by presenting a set of statements about the topic and asking respondents to indicate for each whether they strongly agree, agree, are undecided, disagree, or strongly disagree (Ary et al., 2002). Therefore, the writer used likert scale to measure the assessment of the respondents’ opinions on the designed materials. There were five points of agreement as follows:
1 : strongly disagree with the statement 2 : disagree with the statement
3 : undecided with the statement 4 : agree with the statement
D. Data Gathering Techniques
In this study, the writer discussed the instrument used in Research and Information Collecting survey and Product evaluation.
1. Research and Information Collecting
In the Research and Information Collecting, the writer held informal interview to obtain information from the teachers of Kanisius Pakem Junior High School. The informal interview was conducted in June 2008. The purpose of the informal interview was to find out the teachers’ experience and opinions in teaching English vocabulary including their techniques, materials, strategies, topic choices and teaching media.
The writer also did library study to find some sources that could be used to develop the designed materials. This activity was done by finding some books related to this study.
2. Product Evaluation
E. Data Analysis Techniques
1. Research and Information Collecting
In the Research and Information Collecting, the analysis of the data was aimed at solving the problem of what the English vocabulary materials based on Multiple Intelligences Theory for the seventh grade students of Kanisius Pakem looked like. The data were used to find the learner’s needs on vocabulary which could be useful to determine the appropriate teaching of vocabulary for seventh grade students.
In this research, a descriptive data analysis was chosen. The data to evaluate the proposed English vocabulary materials based on Multiple Intelligences Theory for the seventh grade students of Kanisius Pakem was gained from the interviews. The interview with the teacher tried to reveal the teachers’ opinion about difficulties in teaching vocabulary, techniques, strategies, media, and the students’ characteristics. The data from the interviews helped the writer to develop appropriate materials for students’ abilities and needs.
2. Product Evaluation
Dharma University. The obtained data were used to make improvement and revision to the material. Afterwards, the writer revised and improved the material.
The second one was about the descriptive statistic data about the participants’ statements. In this study, the writer used five points of agreement. The data were measured by central tendency. The descriptive statistics would be presented as follows:
Table 3.2. The Format of the Presentation of Product Evaluation Results
No Respondents’ opinion on Central Tendencies
Number Mean Median Mode
The data gathered were interpreted using statistics to find the median, mode, and mean. Median (Mdn) is the midpoint of any ordered set of scores. Mode is the most frequent score in a distribution. The mean (X) is the average point which is obtained by counting the sum of the score (∑X) then it is divided by the number of the subjects (N) (Brown, 1989:66). The formula is:
X = Σ X N Where:
X = the mean
The designed material would be good and acceptable if the score of the mean from the questionnaire was above 3.50. The designed material would need a revision for the designed material if the score of the mean is below 3.50.
F. Research Procedure
The following part is the procedure in conducting the study. The steps are research and information collecting, planning, development of preliminary form of product, product evaluation, and main product revision.
Step 1. Research and Information Collecting
In this step, the writer did an informal interview to English teacher of Kanisius Pakem Junior High School for finding the need analysis. In this study, the writer also did the library study to gather relevant sources related to this study. Step 2. Planning
In this step, the writer determined standard competences, basic competences, and topics, determined the indicators, and listed subject contents. Step 3. Development of Preliminary Form of Product
Step 4. Product Evaluation
In this step, the writer distributed questionnaires to the two English teachers of Kanisius Pakem and one English lecturer to obtain feedback or suggestions for the instructional materials.
Step 5. Main Product Revision
Doing Needs Analysis
Determining Indicators Listing Subject Contents
Designing the Material
Selecting the Teaching Learning Activities
Evaluating
Revising
Figure 3.1. The Relationship of R&D and Instructional Design Models
Research &
Information Collecting
Planning
Development
of Preliminary Form
of Product
Product Evaluation
Main Product Revision
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this chapter, the writer discusses the research results and the discussion of the procedures of this study. There are two parts to discuss in this chapter. The first part discusses about the processes of designing the material. The purpose of this part is to answer the first question which is stated in chapter 1. In order to answer the first question, the writer employed the design model of the study.
The second part concerns with the designed materials. This part aims to answer the second question of the study. The writer shows the result of processes designing the materials. In addition, the writer also includes the results of the evaluation of the designed materials done by two teachers of Kanisius Pakem and one lecturer of English Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. The feedbacks from teachers and lecture were used to revise and improve the designed material.
A. The Process of Designing the Material
In this part, the writer discusses the steps which were conducted during the processes of designing the materials. The explanation of each step is as follows. 1. Doing Needs Analysis
teachers of Kanisius Pakem Sleman. The interviews were conducted on June 2, 2008 in Kanisius Pakem Sleman. There were eight items which were given to the English teachers. The problems questioned in the interview were:
a. Students’ difficulties in learning English vocabulary. b. Teachers’ strategies to cope with such problems. c. Vocabulary task in student books.
d. Teaching methodology preferred by students. e. Teaching methodology not preferred by students.
f. Teaching media have been applied and preferable by students. g. Topics needed to enhance vocabulary learning.
h. Teachers’ understanding on Multiple Intelligences Theory.
The detailed information about the result of the interview can be seen below: a. Students’ difficulties in learning English vocabulary
b. Teachers’ strategies to cope with such problems
The strategies often used by teachers to cope with vocabulary problems were various based on the troubles occur. The teachers often applied several strategies to cope with such problems. They were doing repetition, giving reading task and the students guessing the word meaning from the contexts. c. Vocabulary task in students’ book
The vocabulary tasks in students’ book did not fulfill students’ need. The activities included in students’ book were monotonous and the task for vocabulary was very limited. Moreover, the vocabulary in the students’ book was not related to the theme given. This condition made the teacher have to make a list of words based on the theme discussed.
d. Teaching methodology preferred by students
Teaching methodology preferred by students was discussion and role play. By doing role play and discussion, students could practice their knowledge of vocabulary and find the meaning of the word together with their friends. The activities liked by students showed that their major intelligences are bodily- kinesthetic, linguistic and intrapersonal. Besides the methodology, the topics should attract students’ attention. When the topics fitted the student interest, their motivation would increase.
e. Teaching methodology not preferred by students
would not appropriate since the students would be more passive and only accept the vocabulary given.
f. Teaching media have been applied and preferable by students
The teachers stated that media had strong influence for vocabulary teaching. Providing media in vocabulary task would make students learn faster and they could memorize the words easily. For vocabulary teaching, there were many medias that could be used. Some of them were songs, picture, video, and the everyday situation. Most students would be interested when teachers could provide a media for the teaching learning process. g. Topics needed to enhance their vocabulary learning
The topics needed for students had to suit with the curriculum. Some of the topics were description, memo, notice, things around them and was liked by them.
h. Teachers’ understanding on Multiple Intelligences Theory
The teachers stated that they had heard about Multiple Intelligences Theory. Unfortunately, they did not really understand what Multiple Intelligences Theory was and its application in teaching learning process.
The purpose of the designed materials was to develop students’ English vocabulary. Besides, the materials were expected to activate students’ eight areas of intelligences. Therefore, the goal of the course was to develop students’ English vocabulary by providing learning activities that could activate the eight intelligences.
3. Determining Indicators
After determining the standard competences, basic competences, and topics, the next step was to determine the indicators for each unit.
4. Listing Subject Contents
In this study, the subject contents were based on the results of needs analysis, standard competences, basic competences, topics, and indicators. Furthermore, the learning activities based on eight intelligences were also used in this step, that is linguistic, logical-mathematical, musical, spatial, bodily kinesthetic, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalist intelligence.
5. Designing the materials
6. Selecting teaching-learning activities
In this study, the writer selected the teaching learning activities based on the Multiple Intelligence Theory. The writer developed and varied the activities in order to develop students’ eight intelligences and provide students the enjoyable teaching learning activities.
7. Evaluating
In evaluating the designed materials, the writer distributed the designed materials and the post-design questionnaire to the teachers and lecture. The teachers were two English teachers of Kanisius Pakem Sleman and the lecture was the lecture of English Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. The aim of this step was to obtain feedbacks, comments, and evaluation from the participants so that the writer would be able to revise and present the final version of the designed materials.
8. Revising
After gaining the evaluations from the participants on the designed materials, the writer revised the materials. The revisions were based on the feedback and the suggestions from the participants. After doing the revisions, the writer presented the final version of the vocabulary instructional materials.
B. The Presentation of the Designed Materials
In this part, the writer discusses the results of the material development. The explanations are as follows.
1. The Standard Competences, Basic Competences, and Topics
The writer determined the standard competences based on 2006 curriculum. Since vocabulary can be learned through four skills (reading, speaking, listening, writing skills) the designed material had to suit to the standard competences of the four skills. The standard competences for the four skills are presented as follows.
Table 4.1 Standard Competences
Skills Standard Competences
Listening
• Understanding the meaning in simple short functional oral text to interact
with the nearest environment.
• Understanding the meaning in oral simple functional text and simple short
monolog in a form of descriptive and
Skills Standard competences
Listening • environment.
Speaking
• Expressing the meaning in simple transactional and interpersonal
dialogue to interact with the nearest environment
• Expressing the meaning in simple short functional oral text to interact with the nearest environment.
Reading
• Understanding the meaning in simple short functional written text related to
the nearest environment.
• Understanding the meaning in simple short essay in a form of descriptive and
recount to interact with the nearest
environment.
Writing
• Expressing the meaning in simple short functional written text to interact with
the nearest environment.
• Expressing the meaning in functional written text and simple short essay in a
form of descriptive and recount to interact with the nearest environment.
After determining the standard competences, the topics were listed by the writer. The topics were based on 2006 curriculum to the seventh grade of Junior High school. There were eight topics developed. They are arranged as follows.
Unit 2 : Family
Unit 3 : Instruction Unit 4 : Things Around
Unit 5 : Housing Unit 6 : Jobs Unit 7 : Hobbies
Unit 8 : Past Event
After stating the topics, the writer formulated the basic competences. The basic competences were taken from 2006 curriculum. They are presented as follows.
Table 4.2. The Basic Competences
Skills Basic Competences
Listening
2.1. Responding meaning in simple short
functional oral text accurately and fluently
to interact with the nearest environment.
8.2. Responding the meaning in simple
short monolog accurately and fluently to
interract with the nearest environment in a form of recount.
Speaking
3.1. Doing interaction with the nearest environment involving: greeting other
students,introducing themselves/someone,
giving instruction or forbidding.
Skills Basic Competences
Speaking
environment involving: asking &giving information.
4.1. Expressing meaning in simple short functional oral text to interact with the
nearest environment.
9.2. Expressing meaning in simple
transactional dialogue (to get things done) and interpersonal (socialize) using many
language styles to interact with the nearest
environment involving: expressing likes
and dislikes.
Reading
Writing
5.2. Responding the meaning in simple
short functional written text acccurately
and fluently related to the nearest
environment.
11.2. Responding the meaning and
rhetorical steps accurately and fluently in a simple short essay related to the nearest
environment in a form of recount.
6.1. Expressing the meaning of ideas in
simple short functional written text using
many kinds of writting style accurately
and fluently to interract with the nearest
environment.
6.2. Expressing the rhetorical steps in
simple short functional written text using
many kinds of writing style accurately and
Skills
Writing
Basic Competences
12. 2. Expressing meaning and rhetorical
steps in a simple short essay using many
kinds of writing style accurately and fluently to interact with the nearest
environment in a form of descriptive and
recount.
2. The Indicators
In the 2006 curriculum, indicators were used to check whether the basic competences had been achieved or not. The indicators were formulated for each unit by the writer. The indicators are stated as follows.
Table 4.3. The Indicators
Topic Meeting Indicators
Introduction 1
At the end of the meeting students are able to:
1. Greet other students. 2. Introduce themselves.
3. Write personal identity.
1
At the end of the meeting students are able to:
1. Mention members of family. 2. Talk about their family members. Family
2
At the end of the meeting students are able to:
1. Identify the information includes in the text. 2. Identify the language style in the text.
3. Make a short paragraph.
4. Write paragraph about family accurately and
Meeting
1
Indicators
At the end of the meeting students are able to:
1. Respond on the giving instruction by imitating
the pictures.
2. Identify how to give instruction.
3. Give instruction to other students. 4. Apply the words of instruction in real life. Topic
Instructions
2
At the end of the meeting students are able to:
1. Identify the meaning of notices.
2. Create a response to a sample of memo.
3. Express on giving instruction through dialogue.
1
At the end of the meeting students are able to:
1.Mention part of living things around.
2. Identify how to describe things.
3. Identify the structure of personal letter. 4. Write a letter about describing things.
5. Write a descriptive text. Things Around
Housing
1
At the end of the meeting students are able to:
1. Mention things at home. 2. Describe things at home.
3. Compose words on describing their dream
house.
4. Use rhetorical steps in writing descriptive
text.
Jobs 1
At the end of the meeting students are able to:
1. Ask and answer about jobs.
2. Apply the words of asking and giving
Topic
Jobs
Meeting
2
Indicators
At the end of the meeting students are able to:
1. Identify information in the text.
2. Identify language feature in the text.
3. Identify the correct description.
4. Write a text about jobs.
1
At the end of the meeting students are able to:
1. Express likes and dislikes.
2. Apply the expression of likes and dislikes. Hobbies
2
At the end of the meeting students are able to:
1. Arrange the jumbled sentences to make a
good paragraph.
2. Express their hobby in a form of writing.
Past Event 1
At the end of the meeting students are able to:
1. Respond the use of past tense by singing the
song.
2. Identify the use of past tense. 3. Identify information includes in text.
4. Identify the verb and structure of recount text.
5. Write a recount text.
6. Use rhetorical steps in writing recount text.
3. The Subject Contents
The first section was Come In Please. It was the pre-activity to activate students’ prior knowledge and introduce students to the topic. In this section, the teacher used a picture or asked students to answer the questions related to the topic. Let’s Build the Word was the second section. This section was for learning the vocabulary related to the topic. In this section, the students were provided various tasks which helped them to understand and memorize the vocabulary. The third was Work It Out. This section dealt with students’ learning activities to activate their intelligences. The activity was developed based on the eight intelligences. The fourth was You Can Do It for the post activity. In this part, students were asked to make a short writing based on the topics. This activity could also remind them with the materials they have learned. Some units also provided list of words or things that should be remembered by students, namely Keep in Mind. Keep in Mind could be found in Let’s Build the Word.
4. The Materials
5. The Teaching-Learning Activities
This step was dealing with the teaching and learning activities that were appropriate to accomplish the basic competences and indicators. The teaching and learning activities were developed based on eight areas of intelligences. The learning activities and intelligences being developed were presented in Appendix F.
6. The Evaluation of the Designed Materials
The writer planned to evaluate the materials since the writer realized that the designed material needed to improve. To do this, the writer distributed the materials and the questionnaires to the respondents. There were three respondents that were chosen by the writer. They were one English lecturer of Sanata Dharma University and two English teachers of Kanisius Pakem Junior High School. The writer hoped that the respondents could give feedback and evaluation of the materials so that the writer could revise the materials and present the final designed materials. Evaluation consisted of four parts. They were the description of respondents, data presentation, the respondents’ comments and suggestions on the Materials Design, and implementation one to one evaluation with learners.
a. The Description of Respondents
Evaluation survey. They gave feedback, evaluations, and some comments about the designed materials. They were also considered as input to revise the materials so that the writer could present the final design.
b. Data Presentation
The writer distributed questionnaires to the respondents to obtain the evaluation on the designed material. The purpose of the questionnaire was to gain feedback about the designed material so that the writer could obtain the appropriate materials for the seventh grade students of Kanisius Pakem. The likert scale was used by the writer to show the respondents’ opinions on the designed materials. The degrees of agreement from the respondents were expressed in number. The number ranged from 1 to 5. There were five degrees of agreement. The five degrees of agreement are as follows.
1 : strongly disagree with the statement
2 : disagree with the statement
3 : undecided with the statement
4 : agree with the statement
5 : strongly agree with the statement
Table 4.4. The Results of the Evaluation Questionnaire
Central Tendencies No Respondents’ opinion on
N Mean 1 The Basic Competence is well formulated. 3 4
2 The indicators are well formulated. 3 4
3 The contents are appropriate for the seventh grade students of Kanisius Pakem.
2 4,5
4 The topics are well arranged. 3 4
5 The materials are able to attract students’ interest in learning English.
3 4,33
6 The activities are well elaborated. 3 4
7 The activities are developed based on the eight areas of intelligences.
3 4
8 The number of activities in each unit has been sufficient for the time given.
3 3,66
9 The steps in giving instruction are clear and helpful for the teacher and student.
3 3,33
10 There are various activities, materials, and media that support learning.
3 4
11 Generally, the contents are well arranged. 3 4
N : Number of respondents
Mean : Indicators of central tendency of the sources set. The Mean was counted using the formulation below:
X = Σ X
N
time given and (2) the instructions of the materials. Therefore, there were some revisions that should be done to improve the designed material.
c. Respondents’ Comments and Suggestions on the Materials Design The writer also distributed open-ended questionnaires to obtain the respondents’ comments, criticism, and feedback on the designed materials. There were two questions asked. The questions asked about the comments or opinions and suggestions or expectations about the designed materials. There were six points of feedback and suggestions from the respondents.
1) The vocabulary materials were good and helpful for both students and teachers to practice their vocabulary. They could develop the eight areas of intelligences.
2) The vocabulary materials were interesting for the students of Junior High School. It was caused by the various activity and colorful pictures used. 3) It would be better if the writer completed the design with teachers’ notes
on how to deliver the materials and the short summary of them.
4) There were some grammatical mistakes and instructions should be revised. 5) The pictures from unit 1 (one) and 2 (two) were not related to the topic. 6) The pictures of object in unit 3, 4 and 5 could not be understood. d. Implementation One- to -One Evaluation with Learners
instruction, and to obtain initial performances indications and reactions to the content by learners.”
In this research, the writer implemented a unit to the seventh grade