i
THE CORRELATION BETWEEN STUDENTS’ READING INTEREST ON TEXTS-RELATED PICTURE AND THEIR READING
COMPREHENSION (A Study of the Seventh Grade Students of MTsN 12 Pitalah)
THESIS
Submitted to English Teaching Education Department Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher Training as One of the Requirements for Obtaining
Bachelor Degree in English Teaching Department
ANNISA MULIYANA Reg. No. 15 300 4000 10
ENGLISH TEACHING DEPARTMENT
TARBIYAH AND TEACHER TRAINING FACULTY STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
BATUSANGKAR 2019
vii
Correlation between Students’ Reading Interest on Texts-Related Picture and Their Reading Comprehension (A Study of the Seventh Grade Students of MTsN 12 Pitalah)”.
Permasalahan yang dibahas dalam penelitian ini adalah terdapatnya hubungan antara minat siswa membaca teks bahasa Inggris yang bergambar dengan kemampuan Reading Comprehension mereka. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui hubungan antara minat siswa membaca teks bahasa Inggris yang bergambar (variabel bebas), dengan kemampuan Reading Comprehension mereka (variabel terikat).
Penelitian ini adalah penelitian korelasi. Populasi dalam penelitian ini adalah siswa kelas Tujuh MTsN 12 Pitalah yang berjumlah 117 siswa yang berasal dari empat kelas. Pengambilan sample dilakukan dengan teknik Stratified
Proportional Random Sampling. Berdasarkan teknik tersebut, terpilih 92 siswa
dari populasi sebagai sample dan 22 siswa sebagai tried-out sample. Penelitian ini menggunakan dua instrumen pengumpulan data, yaitu angket dan dokumen hasil belajar mereka dalam Reading Comprehension. Angket digunakan untuk mengetahui minat siswa membaca teks bahasa Inggris yang bergambar. Skor hasil belajar mereka digunakan untuk mengetahui kemampuan Reading Comprehension mereka. Sebelum diuji coba angket berisi 44 items. Setelah
angket diuji coba terdapat 26 items valid dan 18 items tidak valid. Selanjutnya angket diberikan kepada 92 orang sample penelitian untuk mengumpulkan data. Setelah angket dianalisis, selanjutnya dicari hubungan antara minat siswa membaca teks bahasa Inggris yang bergambar dengan kemapuan Reading
Comprehension mereka, dengan menggunakan perhitungan SPSS 16 dan rumus
korelasi Pearson Product Moment.
Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa terdapat hubungan antara minat siswa membaca teks bahasa Inggris yang bergambar dengan kemampuan Reading
Comprehension mereka di MTsN 12 Pitalah. Berdasarkan data yang diperoleh
bahwa nilai rxy (0.276) lebih tinggi dari r-table (0.207) dengan tingkat signifikansi 5 %. Kesimpulannya terdapat hubungan positif antara variable X dan
variable Y dan berdasarkan table “r” product moment interpretation antara
minat siswa membaca teks bahasa Inggris yang bergambar dengan kemampuan pemahaman membaca mereka pada categori 0,20-0,40 dari hasil rxy 0,276 terdapat korelasi yang rendah.
viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
COVER PAGE ... i
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN SKRIPSI ... ii
THESIS ADVISORS’ APPROVAL ... iii
THESIS EXAMINERS’ APPROVAL ... iv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... v
ABSTRAK ... iv
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... vii
LIST OF TABLES ... ix
LIST OF APPEDINCES... x
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Problem ... 1
B. Identification of the Problem ... 3
C. Limitation and Formulation of the Problem ... 3
D. Definition of the Key Terms ... 3
E. Purpose of the Research ... 4
F. Significance of the Research ... 4
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 5
A. Review of Related Theories………..5
1. Reading Comprehension ... 5
a. Definition of Reading Comprehension ... 5
b. Importance of Reading Comprehension ... 6
c. Factors Influencing Reading Comprehension ... 7
d. Purposes of Reading Comprehension ... 8
2. Texts-Related Picture ... 9
a. Definition of Texts-Related Picure ... 9
b. Functions of Texts-Related Picure ... 10
c. Teaching Reading by using Texts-Related Picture ... 10
ix
3. Students‟ Reading Interest ... 14
a. Definition of Reading Interest ... 14
b. The Types of Reading Interest ... 14
c. Indicators of Students‟ Reading Interest ... 15
4. The Relationship between Texts-Related Picture and Reading Comprehension ... 20
B. Review of Relevant Studies ... 22
C. Conceptual Framework ... 23
D. Hypoyhesis ... 23
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 25
A. Research Design ... 25
B. Population and Sample... 25
1. Population ... 25
2. Sample ... 26
C. Technique of Data Collection ... 28
1. Research Instrument ... 28
2. Research Procedures ... 32
D. Technique of Data Analysis ... 33
1. Descriptive Statistic ... 33
2. Inferential Statistic ... 35
3. Correlation Statistic ... 35
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION... 38
A. Research Finding... 38
1. Data Descriptive ... 38
2. Data Analysis ... 43
3. Testing Hypothesis ... 46
x
CHAPTER V: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 50
A. Conclusion ... 50
B. Suggestion ... 50
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 52
ix
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1: Indicators of Reading Interest ... 17
Table 2: Indicators of Students‟ Reading Interest ... 18
Table 3: Population of the Research ... 26
Table 4: Distribution of Sample ... 27
Table 5: Categories Statement of the Questionnaire Answer and the Score ... 29
Table 6: Interpretation the Students Score of Students‟ Reading Comprehension ... 34
Table 7: The Level of Correlation Score... 36
Table 8: Scores of Students‟ Reading Interest on Texts-Related Picture ... 39
Table 9: The Data of the Questionnaire ... 40
Table 10: Frequency Data Distribution of Students‟ Reading Interest on Texts-Related Picture ... 40
Table 11: Scores of Reading Comprehension ... 41
Table 12: Descriptive Statistic of Students‟ Reading Comprehension ... 42
Table 13: The Categorize of Students‟ Reading Comprehension ... 42
Table 14: Testing Normality of Data Result ... 43
Table 15: Result of Testing Homogenity ... 44
Table 16: The Table of Correlation ... 45
Table 17: The Level of Significance ... 45
xii
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1: Syllabus ... 56
Appendix 2: Table of Specification of Reading Interest Questionnaire ... 68
Appendix 3: Questionnaire for Tried-Out ... 70
Appendix 4: Students‟ Responses Sheet of Tried-Out ... 75
Appendix 5: Attendance List of Filling Tried-Out ... 80
Appendix 6: Validity of Tried-Out ... 81
Appendix 7: Reliability of Tried-Out ... 84
Appendix 8: Comparative Table of The Items of Questionnaire ... 89
Appendix 9: Questionnaire of Sample ... 92
Appendix 10: Students‟ Responses Sheet of Sample ... 95
Appendix 11: Attendance List of Filling Sample ... 98
Appendix 12: Students‟ Score of Reading Comprehension ... 102
Appendix 13: Documentations Photos for Data Collection ... 106
56 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Problem
Reading comprehension is an important part in our learning especially learning English. Because reading is a major source in learning English, students will comprehend English components through reading English text. Reading also helps the students to get some knowledge and new information, so that it can make the students comprehend the text.
Anderson (2003: 68) explains that reading comprehension is a process where the readers try to combine and make a connection about the information from a text that they read with their own background knowledge to build a meaning. It means that to get a comprehension in a reading a text, the readers have to read first, and then they connect what they read with their knowledge about that text.
Arkian (2008: 77) stated that reading comprehension as the most widely used technique are studied from various vantage points. Nunan (2003:68) argues that the goal of reading is comprehension. Comprehension is what entices the reader to continue reading. Moreover, Brassell and Rasinski (2008:18) explain that reading comprehension is the ability to take information from written text and do something with it in a way that demonstrates knowledge or understanding of that information.
Based explanation above, it can be conclude that reading comprehension is the ability to understand what they read and also the process that finding information and interpreting.
Moreover, Dawson and Bamman (1963: 220) state factor that can influence students‟ reading comprehension is reading interest. Reading interest is one of the key of someone to be successful in their pursuing knowledge. Many countries strive for their communities to improve reading interest. Interest is powerful factor for increasing reading comprehension, promoting the reading habit, and producing a generation book lovers. However, students‟ interest and excitement about what they are learning is one of the most
2 important factor in education. In short, the higher interest will make the
readers more creative about reading actively and thinking about material. In addition to this, Sari (2017:118) explains that there are some teachers who have conducted a research in improving English skills by using pictures as media. A study conducted by English teacher found out that pictures give a good effect on the students‟ reading of texts.The picture given by the teachers have to relate with the texts. The teachers show the picture and discuss it with the students. Picture also presumed to attract students attention, motivation, and interest toward reading material as well as improve their reading comprehension. Texts- related picture as an important role in teaching and learning process especially in teaching reading comprehension in the classroom. Texts – related picture can be interesting media for teaching reading comprehension. Then, teaching reading comprehension by using texts- related picture can apply in three stages; pre, whilst, and post. By using texts- related picture teacher can also create enjoyable classroom atmosphere.
Based on the writer‟s observation it seems that some of the study of the seventh grade students of MTsN 12 Pitalah have reading interest on texts-related picture. the teacher find that picture to make students interesting and motivating to study English. In addition, it would be helpful for students to comprehend the content of the reading text. Example:
Related to the phenomenon above, the researcher is motivated to conduct a research to find out the correlation between student‟s reading
Mr Jarot
Mr Jarot is my uncle. He is a farmer in the country. He is 50 years old. He is tall and handsome. He has round eyes, a pointed nose, and thick lips. He has straight hair. He is very strong. His arms and legs are strong. His skin is brown. He is very diligent. He is also smart and honest. He is a good person and we love him very much.
3 interest on texts-related picture and their reading comprehension at a study of
the seventh grade students of MTsN 12 Pitalah.
B. Identification of the Problem
Based on the explanation at the background of the problem above, reading comprehension is the ability to take information from written text and do something with it in a way that demonstrates knowledge or understanding of that information. Factor that can influence students‟ reading comprehension is reading interest. Reading interest is one of the key of someone to be successful in their pursuing knowledge. Many countries strive for their communities to improve reading interest. Interest is powerful factor for increasing reading comprehension, promoting the reading habit, and producing a generation book lovers.
In fact the researcher found some of the studies of the seventh grade students of MTsN 12 Pitalah have reading interest on texts-related picture. The teacher finds that picture to make students interesting and motivating to study English. In addition, it would be helpful for students to comprehend the content of the reading text.
C. Limitation and Formulation of the Problem
In this research, the problem is limited to the students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture and its relation with their reading comprehension. Based on the limitation of the problem above, the problem can be formulated in the following question:” is there any correlation between students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture and their reading comprehension?
D. Definition of the Key Terms
To avoid the ambiguity and misunderstanding on this research, the key terms are defined as follow:
1. Students‟ reading interest is one of the best predictors of a child‟s growth in reading. reading interest has a strong positive relationship with the
4 success of students both in school and life. When students read, they will
gain more knowledge and this will help them to have wider and broader perspectives on certain issues.
2. Texts-related picture is based on a simple logic of three possibilities of how picture and text relate to one another and relies on penetrating observations rather thanon any specific realizations.
3. Reading comprehension is the ability to take information from written text and do something with it in a way that demonstrates knowledge or understanding of that information.
E. Purpose of the Research
The purpose of this research is to figure out whether there is a correlation between the students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture and their reading comprehension.
F. Significance of the Research
The result of this research hopefully was useful for the students, teacher and researcher.
1. The Teacher
It is expected that this researcher can give information to the teacher MTsN 12 Pitalah on students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture and its correlation with students reading comprehension.
2. The Students
The result of this research is to get information from the students seventh grade students MTsN 12 Pitalah about students‟ reading interest on texts –related picture and their reading comprehension.
3. The Researcher
The researcher can improve her knowledge from this research. This research can give valuable knowledge and experience to the researcher. Besides that, it is done as requirement to get Undergraduate Deegre (S1) at IAIN Batusangkar.
56 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Review of Related Theories
1. Reading Comprehension
a. Definition of Reading Comprehension
Kintsch (1998) and van Dijk and Kintsch (1983) defined reading comprehension as the process of creating meaning from text. The purpose is to get an understanding of the text rather than to acquire meaning from individual words or sentences. The outcome of reading comprehension is the mental representation of a text meaning that is combined with the readers‟ previous knowledge. This is called a mental model (Johnson-Laird, 1983) or a situation model (Kintsch, 1998). This model defines what has been learned (RAND Reading and Study Group, 2002). Keenan, Betjemann, and Olson (2008) expressed that reading comprehension needs the successful expansion and arrangement of a lot of lower-and higher-level processes and skills. Accordingly, there are many sources for possible comprehension break and these sources are different based on the skill levels and age of readers.
Harris & Hodges (1995: 51) stated that reading comprehension is the construction of the meaning of a written text through of a reciprocal interchange of ideas between the reader and the message in the particular text. Anderson (2003: 68) explains that reading comprehension is a process where the readers try to combine and make a connection about the information from a text that they read with their own background knowledge to build a meaning. It means that to get a comprehension in a reading a text, the readers have to read first, and then they connect what they read with their knowledge about that text.
6 Arkian (2008: 77) stated that reading comprehension as the
most widely used technique are studied from various vantage points. Nunan (2003:68) argues that the goal of reading is comprehension. Comprehension is what entices the reader to continue reading. Moreover, Brassell and Rasinski (2008:18) explain that reading comprehension is the ability to take information from written text and do something with it in a way that demonstrates knowledge or understanding of that information.
Based explanation above, it can be concluded that reading comprehension is the ability to understand what they read and also the process that finding and interpreting.
b. Importance of Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension is an important part in our learning especially learning English. Because reading is a major sources in learning English, the students will comprehend English components through reading English text. Reading also helps the students to get someknowledges and new information, so that it can make the students comprehend the text.
Next Bronsky (2000:2) mentions that some importance of reading those are:
1) To include good habits and values in children at young age. 2) To enhance the children‟s ability
3) To comprehend various concept with immense case. 4) To the develop citical thinking skill in children.
5) To improve their person vocabulary. Command on the language, and communication skill.
6) To show that children who read are able to concentrate on their lesson more properly than those who do not.
7 Reading comprehension is very importance to improve
students‟ reading skill. Reading comprehension also important because in reading process, the students can identify some particular words, sentences and passages of the text. Then if the students are able to understand the content of text, they will get many information from the text.
c. Factors Influencing Reading Comprehension
Dawson and Bamman (1967: 220) also state some factors which can influence reading comprehension as follows:
1) Intelligence
The number of ideas that reader understands and the depth of his understanding will be largely dependent upon his general capacity to learn. The slow learning or dull-normal child cannot be expected to show the same reactions nor gained the same appreciation as the bright child when they read together for pleasure or to gain information. The rate at which he associates what he reads with his knowledge or experience will be influenced by this thing, which we commonly call intelligence. 2) Experience
Children differ in the depth and breadth of their experiences, much of the teaching of comprehension skills is concerned with providing experiences for children through which they may respond to books. The boy or girl with limited experiences may have difficulties in comprehending many of the ideas and activities with which other children are familiar before they come to school.
3) Mechanics of reading
If children have all mastered the skills of word attack and word meaning, if they have learnt to handle books properly, if they have learnt to read from left to right on a line of print, and if
8 all of these skills are performed smoothly, then comprehension
should be easier for them. 4) Interest and interest span
It is true that someone responds quickly to what he reads if he is interested in the topic or at least familiar with it. The average person is interested in those things which he is related to his best aptitudes. Interest span is related to the personality factors. Interest span in the child is also most directly related to the purposes he has for reading at early stages of reading, the teacher will establish those purposes carefully, through discussion of children‟s experiences, visual aids, and relating to immediate needs.
5) Skills of comprehending
Another factor which influences the depth and amount of comprehension is the skills which the child has developed for that purpose. Like all reading skills, the ability to comprehend what we read develops gradually from the simple to the complex skills.
Based on the explanation above, it can concluded that there are many factors influence reading comprehension. They are: Intelligence, experience, mechanics of reading, interest and interest span and then skills of comprehending
d. Purposes of Reading Comprehension
Readers who want to read English texts have some purposes. According to Harmer (2001:99) there are three purposes of reading for students. Firstly, students want to be able to read text in english either for theire careers, for study purposes or for pleasure. When they do not comprehend about what they have read, maybe it can be a problem totheir career or their study. Secondly, reading is useful
9 for language acquisition. Comprehension provides that students
more or less understand what they read. Lastly, reading has positive effect on students‟ vocabulary knowledge, grammar or punctuation and their writing.
Based on the explanation above, it can concluded that there are many purposes of reading comprehension. They are: students want to be able to read text in english either for theire careers, reading is useful for language acquisition, reading has positive effect on students‟ vocabulary knowledge, grammar or punctuation and their writing, created motivation and interest.
2. Texts-Related Picture
a. Definition of Texts-Related Pictures
In many media one can find picture and text existing and working together. Both picture and text express information and when these two modes are placed together their information content likely relates to each other.
Marsh and White (2003), state that texts-related pictures is illustrators or librarians and lacks a theory of how pictures and text are structured and how they function. Even in electronic media, however, pictures most often occur in combination with text and, not much attention has been paid to analysing the semantic relations that allow them to interact with the surrounding text and create more or less coherent, meaningful wholes that may be called multimodal texts. Most of the work that has been done on text and picture relations has either been based on practitioners‟ brilliantintuitions (e.g. McCloud, 1993; Horn, 1998).
Barthes‟ (1977), foundational study of texts-related picture is based on a simple logic of three possibilities of how picture and text relate to one another and relies on penetrating observations rather thanon any specific realizations. Barthes identified three possible
10 texts-related picture: text supporting picture („anchorage‟), picture
supporting text(„illustration‟), and the two being equal („relay‟). Karsono (2014: 192) stated that, the use of pictures is important because it may give a significant impact in teaching learning process, especially in teaching English reading skills that had been conducted in some schools. The use of texts-related pictures may also create an interesting situation in the classroom.
Peeck (1993) lists a number of reasons why pictures should facilitate learning, including increasing motivation, focusing attention, depth of processing, clarification of text content, dual-coding theory, distinctive endual-coding, decreasing interference/decay, processing support for the type of information typically extracted from a specific type of text (e.g., Waddill et al., 1988; Waddill and McDaniel, 1992), and serving as mental models (e.g., Glenberg and Langston, 1992; Gyselinck and Tardieu, 1994).
b. Functions of Texts-Related Pictures
Marsh and White (2003), explain that the 3 general pictures functions from the first level represent 3 types of strength of relation between pictures and text. The first contains functions of pictures that express littlerelation to the text. The second contains functions of pictures expressing a close relation to the text. The last contains functions of pictures where the picture expresses more information than the text expresses (Marsh and White describe this as “functions that go beyond the text). One can describe a relation between picture and text by more than one function. One can combine different functions to create a more detailed description of the relationship.
c. Teaching Reading by Using Texts-Related Picture
Sari (2017: 123), explains that in teaching reading comprehension to junior high school students, the teacher should
11 give the picture to that is related to the text in order to make students
easier in comprehending the text. There are several kinds of text that the students should be mastered by the students in this curriculum; they are descriptive, recount, report, procedure, and narrative text.
For example in descriptive text, especially describing person the teacher chooses a picture of a famous person such as, Agnes Monica. While, to describe place the teacher use the picture that is describing common room like, classroom, teacher room and etc. Then, in describing thing the teacher choose a picture of animal such as, cat, dog, etc.
1) Preparation
To improve the students‟ reading comprehension in understanding of the texts, it needs innovation and creation to motivate them while learning reading skill. Therefore, the teachers need to prepare the material and interesting media that can help them in teaching.
2) Material
The material that can be used in teaching is the appropriate materials that will be learned by the students. In selecting the material, the teachers have to see the syllabus first as a guide for them in teaching. Instead of that, the materials that will be taught by the teachers have to appropriate to the curriculum. Based on curriculum for junior high school, there are two kinds of monologue texts used for teaching English from the first grade. The texts are descriptive text, and procedure text. The teachers should prepare the material well when they want to teach the texts. Appropriate material will make the teaching process successful.
3) Media
Besides preparing well material, the teachers also need the interesting media that will be used in the teaching process.
12 In selecting the media, the teachers have to be creative. The
media that will be used by the teachers have to be interesting for the students. For example; picture. The teachers can use this picture to teach reading. Before they give a model of texts to the students, it is better for the teachers to show the picture that related to the texts first. For example; in teaching descriptive text, the teachers show the picture of person, thing, and place. So, it is not difficult for the students to comprehend the text that will be given in whilst-teaching activity by the teachers.
4) Teaching Procedures
Like the other teaching, this strategy has some steps in implementing the teaching learning process, which have to be obeyed by the teacher. Generally, the activities in teaching learning process are divided into three phase, pre-activity, whilstactivity, and post activity.
Example : Describing person (a) Pre- Teaching activity
The teacher will give pictures that are related to the text and ask the students to answer some questions and describe the pictures itself.
The steps are: (1) Greetings; (2) Reviews the previous lesson; (3) Checks homework ; (4) Leads the students to the new topic; (5) Teacher shows person picture and give questions Questions: Who is she?, What come to your mind if you see this picture?, What does she look like?, What does her eye look like?, What does her nose look like?, What does her lips look like?
(b) Whilst -Teaching Activity
In this step, the teacher will show one text to the student that is related to the picture that is given by the
13 teacher. The teacher will ask the students to read and
comprehend the text. Then, the teacher read the text and continues by the students. And teacher gives some questions that related to the text.
The steps are: (1) The teacher shows another picture that is related to the text that will be given.; (2) Teacher shows the text about my Diva. My Diva Agnes Monica is a famous pop singer. Most people in Indonesia know her. She certainly looks like an angel. She is tall, slim and beautiful. Her hair is black. She has small eyes, pointed nose and thin lips. She wears fashionable clothes, its color is grey. Her personality is as good as her voice. She is confident. She is also generous. She gives a lot of money to charity.; (3) Teacher asks the student to read the text.; (4) Teacher points some of student to read aloud.; (5) Teacher asks students difficult word.; (6) Teacher explains about descriptive (generic structure; identification and description).; (7) Teacher gives the students some questions based on the text. What is the title of the text?, What kind of the text?; What are the generic structures on the text?, Who is Agnes Monica?, Who is my diva?, What does she look like?, What about her body?, What does her nose look like?, What does her hair look like?, What does her eye look like?, What does her lips look like?,What does she wear?, What is the purpose of the text?
(c) Post – Teaching Activity
(1) Teacher and students conclude the lesson.
(2) Teacher give homework to the students (try to read descriptive text about someone)
14 3. Students’ Reading Interest
a. The Definition of Reading Interest
According to Mc Kool (2007), reading interest is defined as readings done when students are outside the school compound. Furthermore, the US Department of Education (2005) defined reading interests as whether or not students like to read in their spare time or at home or whether they like to go to the library. Besides, reading interest is also defined by the number of books read in a month and the number of times students read in a week and the favourite genres and types of English reading materials.
According to research conducted by Taylor, Frye and Maruyama (1990), Anderson, Fielding and Wilson (1988), Stanovich (1986) and Walberg and Tsai (1984), reading interest has a strong positive relationship with the success of students both in school and life. When students read, they will gain more knowledge and this will help them to have wider and broader perspectives on certain issues. Besides, Anderson, Fielding and Wilson (1988) found that students‟ reading interest is one of the best predictors of a child‟s growth in reading. In addition, other research also revealed that reading interest has been linked and related to vocabulary development, comprehension, fluency as well as general intellectual development (Guthrie & Wigfield, 2000; Taylor, Frye & Maruyama, 1990; Anderson, Fielding & Wilson, 1988; Stanovich, 1986).
b. The Types of Reading Interest
Hidi (2007: 3) has distinguished two types of reading interest that reflect distinct areas of research focus, they are:
1) Individual Interest
Individual interest develops slowly, tends to be long lasting, and is associated with increased knowledge and value, personal significance, positive emotion, high value, and increased
15 knowledge. For the examples is a student may have a personal
interest in reading comic, novel, or short story. 2) Situational Interest
Situational interest, on the other hand, is evoked by something in the immediate environment, and consequently may or not have a long-term effect on individual‟s knowledge and value. For examples in the case of reading, such as hot topic on text, magazine or story that famous of the reader.
c. Indicators of Students’ Reading Interest
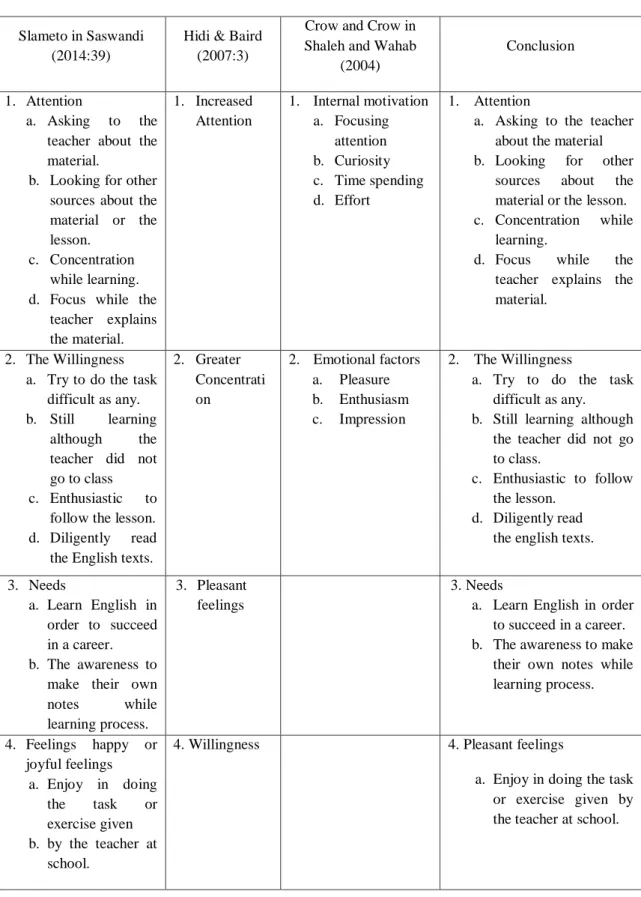
According to Slameto in Saswandi (2014 : 39) indicators of students‟ reading interest are as follows:
1) Attention
a) Asking to the teacher about the material.
b) Looking for other sources about the material or the lesson. c) Concentration while learning.
d) Focus while the teacher explains the material. 2) The Willingness
a) Try to do the task difficult as any.
b) Still learning although the teacher did not go to class. c) Enthusiastic to follow the lesson.
d) Diligently read the English book. 3) Needs
Needs is a condition in the person of a student who driving him to certain activities in order to achieve a goal. For examples:
a) Learn English in order to succeed in a career.
b) The awareness to make their own notes while learning process.
16 4) Feelings happy or joyful feelings
a) Enjoy in doing the task or exercise given by the teacher at school.
b) Always enthusiastic to follow the lessons. c) Take a note from the material.
5) Teaching Materials and Teachers‟ Good Attitudes.
a) Teachers‟ attention makes the students motivated in learning English.
b) Students feel that learning English is fun.
c) Have a high enthusiastic to the lesson and the teacher.
d) Teachers‟ explanation make the students understand about the lesson.
6) Participation
a) Ask if do not understand the material. b) Always do the task given by the teacher. c) Answer the question from the teacher.
Many studies cited by Hidi & Baird (2007: 3) have shown that cognitive performance as measured by many different indicators improve with personal reading interest. Typical indicators of interest are:
1) Increased Attention
Attention is the concentration or activity of our souls towards observation, the understanding, and so on by ignoring the others. Students who is interested in texts-related picturewill pay attention more on it.
2) Greater Concentration
Concentration is exclusive attention to one object: close mental application. Concentration can also refer to something that clustered together or to density or strength of a solution.
17 3) Pleasant feelings
A students has pleasant feeling of reading on texts-related picture , so they will always read the text happily. They are not forced of every reading on texts-related picture that they want to read, such as magazines, story or news paper.
4) Willingness
Willingness is a motivational desire directed to the purpose of life controlled by thought. For example, a man who wants to be a soldier will have a strong will and full attention to learn how to be a good soldier.
Crow and Crow in Shaleh and Wahab states that there three indicators of reading interest. They are internal motivation, social motive, and emotional factors. The writer develops those indicators into reading interest indicators as follow:
Table 1
Indicators of Reading Interest
No Indicator Sub-indicator
1. Internal motivation Focusing attention
Curiosity
Time spending
Effort
Concluding
2. Emotional factors Pleasure
Enthusiasm
Impression
Based explanation above, it can concluded that indicators of students‟ reading interest:
18 Table 2
Table of Indicators of Students’ Reading Interest Slameto in Saswandi
(2014:39)
Hidi & Baird (2007:3)
Crow and Crow in Shaleh and Wahab
(2004)
Conclusion
1. Attention
a. Asking to the teacher about the material.
b. Looking for other sources about the material or the lesson.
c. Concentration while learning. d. Focus while the
teacher explains the material. 1. Increased Attention 1. Internal motivation a. Focusing attention b. Curiosity c. Time spending d. Effort 1. Attention
a. Asking to the teacher about the material b. Looking for other
sources about the material or the lesson. c. Concentration while
learning.
d. Focus while the teacher explains the material.
2. The Willingness a. Try to do the task
difficult as any. b. Still learning
although the teacher did not go to class c. Enthusiastic to
follow the lesson. d. Diligently read
the English texts.
2. Greater Concentrati on 2. Emotional factors a. Pleasure b. Enthusiasm c. Impression 2. The Willingness
a. Try to do the task difficult as any. b. Still learning although
the teacher did not go to class.
c. Enthusiastic to follow the lesson.
d. Diligently read the english texts.
3. Needs
a. Learn English in order to succeed in a career. b. The awareness to
make their own notes while learning process.
3. Pleasant feelings
3. Needs
a. Learn English in order to succeed in a career. b. The awareness to make
their own notes while learning process. 4. Feelings happy or joyful feelings a. Enjoy in doing the task or exercise given b. by the teacher at school.
4. Willingness 4. Pleasant feelings
a. Enjoy in doing the task or exercise given by the teacher at school.
19 Slameto in Saswandi
(2014:39)
Hidi & Baird (2007:3)
Crow and Crow in Shaleh and Wahab
(2004) Conclusion c. Always enthusiastic to follow the lessons.
d. Take a note from the material.
Take a note from the material
5. Teaching Materials and Teachers‟Good Attitude a. Teachers‟ attention makes the students motivated in learning English. b. Students feel that
learning English is fun.
c. Have a high enthusiastic to the lesson and the teacher. d. Teachers‟ explanation make the students understand about the lesson.
4. Teaching Materials and Teachers‟ Good Attitude. a. Teachers‟ attention
makes the students motivated in learning English.
b. Students feel that learning English is fun. c. Teachers‟ explanation make the students understand about the lesson.
5. Participation a. The students ask
if they do not understand the material.
b. The students always do the task given by the teacher.
c. Answer the question from the teacher.
6. Participation
a. The students ask if they do not understand the material.
b. The students always do the task given by the teacher.
c. The students answer the question from the teacher. 7. Internal motivation a. Curiosity b. Time spending c. Effort d. Concluding
20 8. Emotional factor
a. Impression
4. The relationship Between texts-related picture and Reading Comprehension.
a. Effects of Pictures on Reading Comprehension
According to Jenkins &Pany (1981:171), “since pictures in text activate readers‟ background knowledge, they have a positive effect on text comprehension”. Elster (1998 : 68) gives support by adding that pictures are a „scaffold‟ which nurture attention and motivate talks and comments. Haring and Fry (1979) had children read a short story paired with or without illustrations and then to write down everything they could remember about it. They found that the children who had read the story with the pictures performed better on recalling more details and concluded that pictures improved reading comprehension.
Klinger (2000) maintained that since pictures are more complicated and unique than the words that label them, more time and attention is needed to determine a picture. Thus, one looks at pictures for a long time before naming them, which makes pictures more memorable than words. Brookshire et al., (2002) measured comprehension by asking children questions about the text that required them to recall certain facts about the story. They found that those who had seen the text with pictures answered more questions correctly and concluded that illustrations improved comprehension. Free (2004) studied using pictures and words together to improve reading comprehension. The findings of the study indicated that text pictures significantly influenced reading comprehension.
21 b. The Part of Text Depicted by Pictures
Early in 1979, Omaggio (1979: 107) first conducted a study with a group of learners of French as a second language to look at their use of a variety of pictures while working on a reading comprehension task. Omaggio (1979: 107) found that all pictures were not equally effective in enhancing comprehension in the second language. Instead, the most effective picture was the one depicting information from the beginning paragraph(s) of the reading text.
c. Learning Task vs. Picture
In 1983 in Yu (2015: 6) , Levin studied the pictorial strategies employed by students in reading and pointed out that the degree to which a picture facilitated reading comprehension depended on the relationship between the learning task and kinds of pictures provided. For instance, when a reading text requires its readers to understand the complex relationships within the text, a relational picture illustrating the relationship among information from the text, instead of a detailed picture depicting a particular piece of information, is more helpful for reading comprehension.
Later, Waddill, McDaniel and Einstein (1992: 472) further confirmed Levin‟s findings in their study, which showed that a picture effectively increased the recall of information from a reading text only when that information was invited to be processed, that is, when what the picture depicted was directly related to the task content and component processes. To be more specific, the facilitation function of a picture depends on the relationship between the type of the picture and the type of the learning task.
d. Content and Language vs. Pictures
In 1999 in Yu (2015 : 6) , Gyselinck and Tardieu proposed that the effect of pictures on reading comprehension largely
22 depended on the quality of the repetition effect. In this sense, when
the information depicted in the picture also appears in the text, it helps to reduce readers‟ cognitive load. When the picture provides information that is difficult to be understood through the text, it promotes readers‟ reading comprehension. Therefore, it is argued that pictures should match the reading text to help readers understand both its content and language.
Pan and Pan (2009: 186) investigated the reading comprehension learners of English as a foreign language, which further confirmed the proposition of Gyselinck and Tardieu (1999). Pan and Pan (2009:186) suggested that a picture which closely reflected the structure and complexity of the text had a more facilitative effect. Which means, on one hand, the information integration between the text and the picture can improve reading performance of readers. On the other hand, the facilitative function of the picture diminishes or disappears when it does not positively match with the linguistic complexities of the reading text.
B. Review of Relevant Studies
The researcher has found some research that have relevancy with the problem discussed in this study. Dian Probo Astomo SRN: 113221069 did a research entitle: A Correlation Study between Students‟ Interest of Reading on English Text and Translation Ability toward Reading Comprehension at the Fifth Semester Students of English Education Department in the State Islamic Institute of Surakarta in the Academic Year of 2016/2017. Mahardhika A, K.2203067 did a research entitle: A correlational study between the students‟ interest in game activities, vocabulary mastery, and their reading comprehension of seventh grade students of SMP N 8 Surakarta. The similarity with the problem that researcher analyze with the study above is both of research are study about factor affect reading. The different are previous research do the research about A Correlation Study between
23 Students‟ Interest of Reading on English Text and Translation Ability toward
Reading Comprehension and A Correlational Study between the Students‟ Reading Interest in Game Activities, Vocabulary Mastery, and Their Reading Comprehension, but this research will try discuss about the correlation between students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture and their reading comprehension at a study of the seventh grade students of MTsN 12 Pitalah.
C. Conceptual Framework
As explained before, there are some factors that influence reading comprehension. One of them is reading interest. Reading interest may influence students‟ reading comprehension. Based on the discussion above, the research is conducted in order to know whether there is positive correlation between students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture and their reading comprehension. The conceptual framework can be seen as follows:
Figure 1. Conceptual Framework
D. Hypothesis
Based on the previous explanation above, the hypothesis are:
Ha = There is significant correlation between students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture and their reading comprehension.
Ho = There is no significant correlation between students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture and their reading comprehension.
Students‟ Reading Comprehension Students‟ Reading Interest
56 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Research Design
In this research the researcher used quantitative research. According to Gay (2012: 7) a quantitative research is the collection and analysis of numerical data to describe, explain, predict, or control phenomena of interest. However, a quantitative research approach entails more than just the use of numerical data. At the outset of a study, quantitative researchers state the hypotheses to be examined and specify the research procedures that will be used to carry out the study. They also maintain control over contextual factors that may interfere with the data collection and identify a sample of participants large enough to provide statistically meaningful data. In this research design the researcher used the correlational research. According to Gay (2000: 321) a correlation research describes in quantitative term the degree to which two variables are related which has purpose to determine relationship to make a prediction. This research designed to describe the correlation between students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture and their reading comprehension. The design of this research can be drawn as follow:
X = Students‟ Reading Interest on texts-related picture Y = Students‟ Reading Comprehension
= Correlation
Y X
26 B. Population and Sample
1. Population
A group of participant that identified as an object of observation was call population. According to Gay (2000: 102), population is the group of interest of researcher, the group which she or he would like the result of the study to be generalized. Here, the population of this research was the seventh grade students of MTsN 12 Pitalah. They are divided into four classes. The description of population of this research can be seen in following table:
Table 3
Population of the Research
No Class Number of Students
1. VII B 30 2. VII C 28 3. VII D 30 4. VII E 29 Population 117 2. Sample
Based on the number of population above, the researcher selected a number of students as the sample of this research. Sample is representative respondent of population. It should be selected randomly into several students as the sample. According to Gay (2000:121), sampling is the process of selecting a number of individual for a study in such a way that they represent the larger group from which they select.
The population of this research was 117 students. Gay ( 2000:322), suggest the sample size in correlational studies not less than 30 person. The sample of this research was taken by applying stratified proportional random sampling. The researcher used this technique because as state by
27 Gay (2000:121). Stratified proportional random sampling is the process of
selecting a sample in the same proportion that they exist in the population before taking the sample, the researcher analyzed the students mark, then devided the mark into four classes namely, high, average, and low. The calssification found by finding the standard deviation of the mark, the criteria to classify them as suggeste by Anas (2005:176), as follow:
≥ 87 High M + 1 SD 71-86 Average M – 1 SD ≤ 70 Low M = 78,4 SD = 8
Based on formulated, the researcher got 24 students as high group, 74 students as average group and 19 students as low group. The researcher choose the sample randomly and it based on their classification. Then the researcher took 80% of the population as sample and 20% of the population as tried out respondents. The researcher choose the sample randomly and it base on their classification. Then the researcher make a code for each population and chooses it randomly. Consequently, the researcher got 95 students as the sample and 22 students as the tried out respondents. The sample of the research can be seen in the following table
Table 4
Distribution of Sample
Class Population Sample 80% Sampling Technique
H A L H A L
VII B 4 22 4 3 18 3 Stratified
Proportional Random
28 VII D 8 15 7 6 12 7 Sampling VII E 6 20 3 5 16 2 Amount 24 74 19 19 60 16 Total 117 95 Note: Population = 117 Total sample = 95
Try out = population – sample =117 – 95
= 22 students
C. Technique of Data Collection 1. Research Instrument
There are two instrumens used in this research. The first instrument is questionnaire that used to see student‟s reading interest on texts-related picture. The second instrument is document that used to measure the students‟ reading comprehension.
a. Questionnaire
According with Arikunto (2002: 102), he stated that questionnaire is a list of question that given to the persons to give their responses concerning the questions. The main pupose of the questionnaireis to get information which relevant to the research purpose. This questionnaire used to measure the students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture.
The researcher conducted the questionnaire for try out on September 03, 2019. The total items of questionnaire were 44 items. There were 22 students taken as the tried out. The researcher conducted the questionnaire for sample on September 11, 2019. The total items questionnaire 26 items. There were 95 students taken as
29 the sample of this research, but only 92 follow it and 3 of them did
not came because several reasons.
The step of likert scale are: First, collecting amount of item/statement that is relevant with the case that will be research. Second, the item are evaluate by respondents that must choose one of categories starting from Gay (2000: 156), explaining that a likert scale ask paticipants to respond a series of statement they a strong agree (SA), agree (A), undecite (U), disagree (D), or strongly disagree (SD) with each statement.Indonesia language, strongly agree or sangat setuju (SS), agree or setuju (ST), undecide or ragu-ragu (RG), disagree or tidak setuju (TS) and strongly disagree or sangat tidak setuju (STS). The questionnaire is write Indonesia language to make easier for respondents to understand.
The score is give base on the type of each item. If the items is positive, the score arrange SA= 5, A=4, U=3, D=2, and SD=1. If the items is negative, the score arrange SA=1, A=2, U= 3, D= 4, and SD= 5 the score can be explained as follow:
Table 5
Categories Statement of the Questionnaire Answer and the Score
Categories Statement Positive Negative Sangat Setuju (SS) 5 1 Setuju (ST) 4 2 Ragu-ragu (RG) 3 3 Tidak Setuju (TS) 2 4
30 The higher score shows the more supporting to the interest and
the lower score reflect the more people that do not support the interest.
In constructing the questionnaire, the researcher considers the validity and reliability of the test.
1. Validity
According to Gay (2000:191), validity is a degree to which a test measure what it is suppose to measure. To find out the validity of questionnaire, the researcher will use construct validity. The questionnaire was constructed base on the relevant theories formulate on the table of specification that propose by expert and also consulte with the researcher‟s advisors.
After tried out of questionnaire, the researcher used microsoft excel to find the validity of the questionnaire. Then the researcher got the validity of questionnaire where there were 44 items in the questionnaire. From the data, the researcher found 26 items were valid, and 18 items were invalid.
Testing the validity of the questionnaire was not only done through an evaluation by the validator, but also carried out through the steps put forward by Muhidin (2008:31) namely:
a. Adds the student answer score.
b. Test the validity of each statement by means of each statement expressed as variable X and the total answer becomes variable Y.
c. Calculate the value of rtable (; n - 2), n = number of samples, in the product moment table.
d. Calculate the calculated value, with the steps of making a helper table statement item number 1 and calculate the calculated value.
31 The validity of the questionnaire was calculated using the
Product Moment Correlation formula as follows, Arikunto (2006:170)
rxy = n∑XY-∑x∑Y
√ √ Where:
rxy : The coefficient correlation n : Number of respondent ∑X : Score item
∑Y : Sum score item : Squared of score item
Squared of sum of score item. 2. Reliability
Beside the validity, a good questionnaire should have reliability. Gay (2000:169), Explaining that reliability concerns to what can depend on the result could be produced consistently. Relability is the degrees to which a questionnaire consistently measure whatever it measures, the more reliable a test is, the more convidence the researcher can have that the score that will be obtained from administration of the questionnaire are essentially the same score that will be obtained if the test are re-administer.
After getting the score, the researcher will use product moment formula as suggest by Anas (2005:206) as follow:
rxy = n∑XY-∑x∑Y
32 Where:
n : The students
rxy : The coefficient correlation between variable X and Y
∑XY : The total score of cross product XY ∑X : The sum of X
∑Y : The Sum of Y : The squared of X : The squared of Y
Then, to know whether the questionnaire is reliable or not, the researcher analyzed the questionnaire by using split half method as suggest in order to get the reliability of the questionnaire, To see the reliability used the Alpha method proposed by Arikunto (2006:196) as follows:
r11 = ( ) ( 1
)
Where:
r11 : Reliability coefficient n : The number of items
12 : The sum of variance scores of each item
12 : Total variance
And then, the researcher analyze by using split half methods as propose by Gay (2000:174):
r total test = 2 r split half 1 + r split half Where:
r total test : Correlation between score of each half test
33 r split half : Reliability of coefficient
From the result of tried out questionnaire the reliability of the test was 0,9865. It means that questionnaire was reliable.
b. Document
According Bull (2008: 132) document is official paper giving information, evidence, etc. And computer file contains text and has a name that identifies it. To got the data about students‟ reading comprehension, the researcher took the reading comprehension score and got the english teacher.
2. Research Procedure
In collecting the data from the sample, the researcher conducted several steps, they are:
a. Preparation
1) Finding the research problem that the researcher interested in.
2) Collecting the sources and references related with the research problem
3) Writing thesis proposal
4) Consulting and revising the proposal to the advisors 5) Preparing questionnaire with the advisor
6) Revising the questionnaire 7) Having the seminar proposal
8) Consulting and revising proposal after seminar to the advisors b. Operation
1) Getting licence to do the research
2) Permitting to the lecturer for collect the data from the sample of the research
3) Trying out the questionnaire 4) Revising the questionnaire
34 5) Giving the questionnaire to sample of the research
6) Collecting the questionnaire from the sample of the research c. Post operation
1) Coding the questionnaire 2) Tabulating the data
3) Correlating students reading comprehension scores with the result of questionnaire
4) Analyzing the data 5) Interpreting the result
6) Making conclusions and suggestions.
D. Technique of Data Analysis
A set of data collection analyzed descriptive and inferential statistics. According to Anas (2005:4), the data of quantitative research that was collected can be analyzed by aiding of descriptive statistics and inferential statisticsdepend on the purpose of the research. This research focus on correlation research. Therefore, the research used both of statistics.
1. Descriptive Statistics
According to Arikunto (2002:297), descriptive statistics functions to group unarrange data become good unarrangement data and easy to interpret. Sudijono (2000:78), proposed that mean, median , modus are mostly used in statistical measurement to measure the central tendency of the data. The researcher used SPPS version 16 as the aid in analyzing the data.
After getting the description of the data the researcher categorizes the levels of students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture based on the formula that is suggested by Anas (2005: 176), as follow:
High M + 1 SD
35 M – 1 SD
Low
Where: M : Mean
SD : Standard Deviation
To interpret the students reading comprehension, the researcher used the criteria that suggested by Arikunto (2002:245), as follow:
Table 6
Interpretation the Students Scores of Students’ Reading Comprehension
No Interpretation Score 1. Very good 80-100 2. Good 66-79 3. Sufficient 56-65 4. Poor 40-55 5. Very poor 0-39
At last, from the mean score of questionnaire and the criteria above, the researcher knew and described how is the students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture and their reading comprehension.
2. Inferential Statistics
According to Arikunto (2002: 298), inferential statistics functions to generalize research result toward sample or population. Inferential statistics in form of correction analyze was conducted in order to see the correlation beween student‟s interest on texts-related picture and their reading comprehension. Before using a statistics technique (here is a
36 product moment), a researcher has to fulfill requirements. Those
assumption are normality and homogeneity by using inferential statistics. a. Normality test is examining the normality of distribution data
(sample) that analyzed. Normality distribution means each variable of two setsof number is normally distributed. Testing normality by applying One-Sample Kolmogrov-Smirnov formula is calculated by the aid of computer program called SPSS 16.
b. Homogeneity test is examining the sample homogeneity in same population. This test is used to see whether the sample that is taken from the population had the same characteristic or not. The testing homogeneity also used the Chi-Square by the aid of SPSS computer program version 16.
3. Correlation Analysis
This technique that used to analyze data of correlation research is product of the moment correlation technique by Karl Pearson. According to Anas (2005: 190), product moment correlation is one of technique that are usually used to look for correlation of two variables.
The formulation of product moment as follow:
rxy = n∑XY-∑x∑Y
√ √ Which :
rxy : Index correlation of “r” product moment n : Number of cases
X : Students‟ attitude toward assignment variable
Y : Students‟ reading comprehension variable ∑X : Amount scores of variable X
37 ∑XY : Multiple result of total score of variable X
and Y
To help the researcher to analyze the data, the researcher used computation system of SPSS 16 version program to got the result of the variable correlation. Then, to interpret the correlation of the variables from product moment correlation (rxy) accounting.
The first method, it used table of the level correlation can be seen in the table below:
Table 7
The Level of Correlation Score “r” scores Interpretation
0,00 – 0,20 Variable X and Y have very low correlation
0,20 – 0,40 Variable X and Y have low correlation
0,40 – 0,60 Variable X and Y have sufficient correlation
0,60 – 0,80 Variable X and Y have strong or high correlation
0,80 – 1,00 Variable X and Y have very strong and high correlation
The second method, to interpret the level correlation score (r), the first thing to do is looking for “df” or “db” by the formulation below as suggest by Anas (2005: 194),:
Where “N” is amount of samples and “nr” is amount of variables. Then, it has to consult to table velue of product moment with determine “df” and acquire “r” with significance 5% or 1%, moreover, the researcher has to compare the significance of the “rxy” or “ro” with “rt” to show the result. If “rxy” is higher than “rt”, there is correlation between
38 the variables. While, if “rt” is higher than “rxy”, there is no correlation
56 CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING AND DISCUSSION A. Research Finding
1. Data Description
This chapter discusses the description, data analysis and discussion on the correlation between students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture and their reading comprehension (a study of the seventh grade students of MTsN 12 Pitalah), data taken from the score of questionnaire and reading comprehension score. The researcher divided into four classes that the total number of students is 117.
a. The Description of Students’ Reading Interest on Texts-related Picture.
Students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture was the independent variable of this correlation research. The data of the research was the students‟ scores of questionnaire. The questionnaire consists of students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture. The total questionnaire were 26 items those were developed by using five choices “Likert scale” in order to assess the subject of the study on their levels of agreement or disagreement in quantifiable manner.
The test was given to describe students‟ reading interest on texts-related picture . After taking the data, the researcher gave a code for each answer sheet of respondents. After that, the researcher scored the questionnaire. The scores were given based on the type of each item. For the positive item, the scores were arranged as follows: Strong agree =5, Agree =4, Undecide =3, Disagree =2, Strong disagree =1. Whereas for the negative item, the scores were arranged as follows: Strong agree =1, Agree =2, Undecide =3, Disagree =4, Strong disagree =5.
39 Based on the scoring, the researcher got scores of students‟
reading interest on texts-realated picture. It can be seen in following table:
Table 8
Scores of Students’ Reading Interest on Texts-Related Picture Res Score Res Score Res Score Res Score
1 66 25 76 49 91 73 77 2 91 26 84 50 93 74 74 3 89 27 94 51 95 75 86 4 73 28 79 52 82 76 83 5 95 29 94 53 112 77 101 6 77 30 75 54 84 78 61 7 103 31 97 55 87 79 89 8 74 32 88 56 77 80 96 9 111 33 62 57 97 81 81 10 118 34 107 58 90 82 89 11 83 35 99 59 106 83 87 12 115 36 87 60 108 84 84 13 76 37 73 61 80 85 92 14 89 38 99 62 82 86 90 15 83 39 87 63 85 87 90 16 112 40 73 64 91 88 93 17 91 41 99 65 84 89 95 18 86 42 86 66 77 90 90 19 90 43 92 67 99 91 105 20 90 44 95 68 86 92 118 21 109 45 86 69 80 22 126 46 88 70 117 23 105 47 117 71 77 24 92 48 88 72 67 TOTAL 8,297 Note:
Res : Respondent of questionnaire
Score : The score of students‟ reading interest on texts- related picture.