INCREASING THE STUDENTS’ ABILITY INLISTENING SKILL BY USING ELVES (EXCITE, LISTEN, VISUALIZE, EXTEND AND SAVOR) STRATEGY
AT THE EIGHTH GRADE OF SMP NEGERI 2 LAHOMI IN 2015/2016
THESIS
By:
GRESYOFITA DAELI Reg. Number: 102108054
INSTITUTE OF TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION OF GUNUNGSITOLI FACULTY OF EDUCATION OF LANGUAGES AND ARTS
ABSTRACT
Daeli, Gresyofita. 2016.Increasing the Student’s Ability in Listening Skill by Using ELVES (Excite, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy at the Eighth Grade of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi in 2015/2016. Thesis, Advisors (1) Yasminar Amaerita Telaumbanua, M.Pd, (2) Dra. Nursayani Maru’ao, M.Pd
Key words: Listening Skill and ELVES Strategy
The purpose of the research is to increasethe students’ ability in listeningskill by using ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy at the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi in 2015/2016. In fact most of the students find difficulties in listening comprehension. The problems appeared because of many factors, such as: the students had lack motivation in learning listening, the teacher is rarely used media to teach listening, the students were not able to differentiate the sound produced by their English teacher, the English teacher used inappropriate strategies in teaching descriptive text.In solving the students’ problems, the researcher applied one of the strategies that is by using ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) which is proposed by Wheat (1991:22).
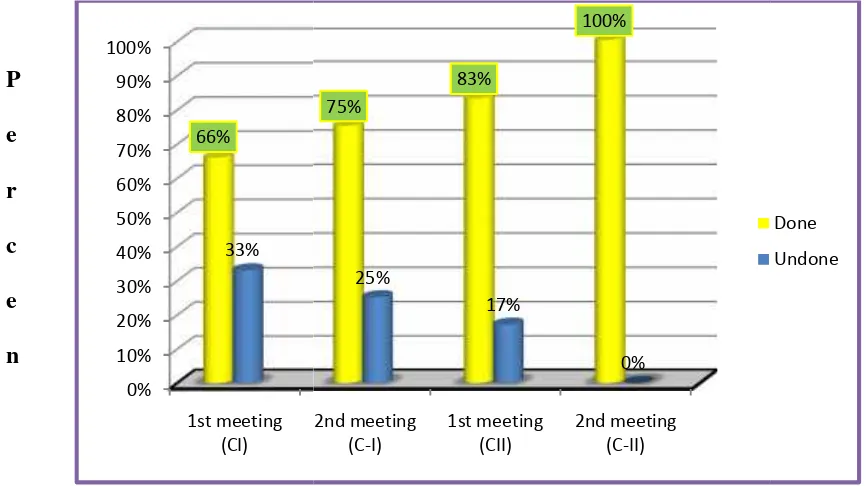
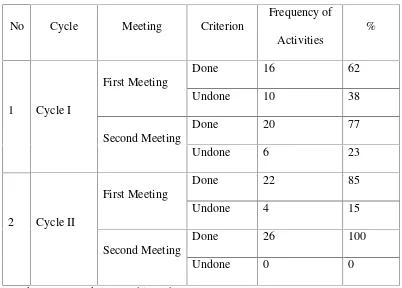
In the first meeting of Cycle I, there were 10 students (66%) did the activities and 5 students (33%) who did not did the activities. In second meeting, there were 20 students (77%) did the activities and there were 6 students (23%) who did not did the activities. The average of the students’ score was 60,38. The highest score 90 and the lowest is 20. Because the students could not achieve the MCC at the school, the researcher continued to the next cycle. Based on the result of the observation sheets for the students in the first meeting of Cycle II, there were 21 students (65%) who did the activities and there were 78 students (25%) who did not did the activities. In second meeting, all the students were did the activities. The average of the students’score was 80. the highest score is 100 and the lowest is 75. It showed that the score of all of the students could reach and higher than MCC (Minimum Competence Criterion) which is 65 points.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, the researcher says thanks to God, for His blessing upon the researcher’s life, so that the researcher is able to compose and accomplish this thesis entitled “INCREASING THE
STUDENTS’ ABILITY IN LISTENING SKILL BY USING ELVES (EXCITE, LISTEN,
VISUALIZE, EXTEND AND SAVOR) Strategy at the Eighth Grade of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi. The researcher is confined and aware that without God’s help, it’s likely that the composition of this thesis cannot reach its completeness.
During her study in IKIP Gunungsitoli until finishing, the researcher has been
supported by many sides, motivating her to study well. Hence, she wants to express her sincere appreciation and thanks to:
1. Mr. Henoki Waruwu, M.Pd., as the Rector of IKIP Gunungsitoli for his best service and advice for students of IKIP Gunungsitoli.
2. Mr. Adieli Laoli, S.Pd. M.Pd., as the Dean of the Faculty of Language, the examiner of research method, who always guides her by giving constructive suggestions in writing this thesis.
3. Miss Yasminar Amaerita Telaumbanua, M.Pd., as the chair of English department
at once as the first advisor, who assists her, gives suggestion and also addition and brilliant ideas in finishing this thesis.
4. Dra. Nursayani Maru’ao, M.Pd as a second advisor, who always helps and gives her motivation,
constructive idea in writing this thesis.
5. Mr. Yaredi Waruwu, S.S., as first examiner, who always suggests the researcher and gives many opinions in finishing this thesis.
7. All of the lecturers in English department of IKIP Gunungsitoli who had taught her well during studying at IKIP Gunungsitoli.
8. Mr. Ikhlas Hia., as the Headmaster of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi, who has facilitated the researcher in collecting the data in his school.
9. Mr.Adrianus Daeli.,S.Pd as the teacher-collaborator, who has given the good contribution to help the researcher in observing her teaching-learning activities in the eighth class (VIII-B) as the subject of the research. All of the students at the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi, especially VIII-B, who helped the researcher in doing her research.
10. Special thanks to her beloved parents, to her dad (Hasatulo Daeli (Alm).) and her mom (Rehana Hia), who have financed her during her study in IKIP Gunungsitoli until finishing this thesis. 11. Her beloved young brothers ( Senjata Daeli, Lisiduhu Daeli, Buterlina Daeli, Antonius Daeli) who
have supported her in finishing this thesis.
12. Her close friend Yupiter Gulo, S.Pd, Estiwati Gulo, S.Pd.,M.Pd, and all of RENARA-NISBAR, who constructive her ever gave criticism and motivation.
Thank you so much for all of your suggestions, advices, supports, motivations, and praying. Your gift is nice memory in her life and she always keeps you all in her heart, may Jesus bless you.
Gunungsitoli, July 2016 The researcher,
Gresyofita Daeli
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Pages
ABSTRACT ... i
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ...iii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ...vi
LIST OF TABLES ………...………...ix
LIST OF GRAPHICS ……….………...x
LIST OF FIGURES ….………...………... xi
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION... 1
A. The Background of the Problem ... 1
B. The Identification of the Problem ... 3
C. The Limitation of the Problem... 3
D. The Formulation of the Problem ... 3
E. The Purpose of the Research... 3
F. The Significance of the Research ... 4
G. The Assumptions of the Research ... 4
H. The Limitations of the Research ... 5
I. The Key Terms Definitions of the Research... 5
CHAPTER II : REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 6
A. Theoretical Framework ... 6
1. Listening ... 6
a. Definition of Listening... 6
b. Principles of Teaching Listening ... 8
d. Types of Listening ... 11
e. Components of Listening ... 12
f. The Habits of Bad Listening ... 13
g. Ways to Become a Better Listener... 15
h. The Assessments of Listening... 16
i. The Syllabus of Listening at the Eighth Grade of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi ... 17
B. ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy... 20
a. The Definition of ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy ... 20
b. The ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy in Teaching Listening... 22
c. The Procedures of ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy ... 23
d. The Advantages and Disadvantages of ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy ... 25
e. The Relationship between Listening and ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy... 26
C. The Latest Related Research ... 27
D. Conceptual Framework ... 28
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHOD... 30
A. The Object of the Action Research ... 30
B. The Setting and Subject of the Research ... 31
C. The Schedule of Implementing the Action ... 32
D. The Procedures of Action Research... 34
F. The Techniques of Analyzing the Data... 40
CHAPTER IV : RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS…………....43
A. Research Findings...…………..………...…... 43
1. Research Setting ... 43
2. The students’ Ability in Reading Comprehension by using ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor ) Strategy... 44
a. Cycle I ... 44
b. Cycle II ... 54
B. Research Findings Discussions ... 67
1. The Common Response of the Research Problem... 67
2. The Analysis and Interpretation of Research Findings... 68
3. The Research Findings versus the latest Research ... 71
4. The Research Findings versus Theory ... 73
5. Research Findings Implication... 74
6. The Analysis of Research Findings Limitation ... 74
CHAPTER V : Conclusions And Suggestions ... 75
A. Conclusions ...75
B. Suggestions ...76
REFERENCES... 77
APPENDICES ...78
LIST OF TABLES
Tables Pages
1. The Condition of the Eighth Class Students of SMP NEGERI 2 LAHOMI In 2015/2016...31 2. The result of students’ Evaluation sheet ... ...52 3. The Students’ Ability in Listening Skill Based on Intelligibility Aspect
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
1. The Conceptual Framework...29 2. Implementation of Action by using ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize,
Extend and Savor) strategy to Increase the Students’ Ability in Listening
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. The Background of the Problem
Listening is one of four skills in English. In learning foreign language, certainly students want to be able to communicate in English. So the students must be active to hear before holding a conversation to the other people. This is supported by the opinion of Nunan (2003: 24) that affirms, “Listening is an active, purposeful process of making sense of what students hear”. Student can make a
good conversation with others by listening because she or he needs to listen before giving a response. Listening is assuming greater importance in foreign language classroom. A student can understand instructions and explanations of his or her teacher by listening well. As Rost (2003: 200) points out, “Listening is vital in the language classroom because it provides input for the learner.
Without understanding input at the right level, learning cannot begin.” In other words, listening is very important in teaching and learning process.
In the syllabus of theKTSP 2006at the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi, the students are expected to comprehend the meaning in very simple of short monolog functional text in descriptive and recount texts to interact with the environs. The basic competence hopes the students to respond the meaning in very short functional text accurately, fluently, and acceptable to interact with the nearer environs. In other words, the students should pass on listening if they get at least 65 points or more.
the students were not able to differentiate the sound produced by their English teacher, the English teacher used inappropriate strategies in teaching descriptive text.
In solving the students’ problems, the researcher applied one of the strategies that is by using
ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor). According to Wheat (1991:22), “a read-aloud activity that can be used by teachers to the students to increase the awareness of own past experiences. So, by using ELVES in teaching-learning process in the classroom gives the positive impact towards the teacher and the students. The researcher will apply the ELVES strategy to increase the student ability in listening comprehension.
Based on the explanations above, the researcher investigates this research entitled “Increasing the Students’ Ability inListening Skill by Using ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy at the Eighth Grade of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi in2015/ 2016”.
B. The Identification of the Problem
Based on the problem, the researcher identifies as follows. 1) The students lacks of motivation in learnings listening. 2) The teacher rarely used media in teaching listening.
3) The students were able to differentiate the sound produced by English teacher. 4) The students felt difficult to construct some sentences in English.
5) The English teacher used in appropriate strategies in teaching listening.
C. The Limitation of the Problem
D. The Formulation of the Problem
The problem of the research is formulated, “How does ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) strategyto increase the students’ ability in listening skill at the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi in 2015/2016?”
E. The Purpose of the Research
The purpose of the research is to increasethe students’ ability in listeningskill by using ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy at the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi in 2015/2016.
F. The Significances of the Research
The findings of the research are signified for:
1) The researcher, to get knowledge to use ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) in increasing the students’ ability in listening skill.
2) The students, as an important source to increase their ability in listening skill by using ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) strategy.
3) The English teacher, as an input for them to vary their strategies in teaching listening.
4) The next researchers, as a comparison with the other strategy in increasing the students’ ability in listening.
G. The Assumptions of the Research
The researcher has some assumptions of the research, they are: 1) Listening is one of the skills that has to be mastered by the students.
2) ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) is an interesting strategy in teaching listening.
H. The Key Terms Definitions of the Research
To avoid missunderstanding of the definition of research, the researcher classifies the terms used, they are:
1. Listening skill is one of English skills which can be used in listening activity to listen the material as well as possible.
2. ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) is the reseacher activity to increase the students’ ability in listening skill by teaching descriptive text which describes about a place as a
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Framework
1. Listening
a. Definition of Listening
According to Mc Erlain (1999:78), “Listening to a language can be defined as the ability to
receive and decode oral communication by processing a language sample, in addition byYtreberg (2003:21) says, “It is quite clear that listening is the skill that children acquire first, especially if they have not yet learn to read”. When the students start to learn a foreign language, it is going in mainly
through their ears and what the students hear is their main source of the language, also give them as much visual back-up as possible through facial expression, through movement, through mine and through pictures.” Based on the expert‘s opinion, in other words, listening is a basic skill that important
to master. Listening may to be the first skill which train by the students in learning foreign language. Diamond (2001:745) says, “Listening is essential for success, listening is an intense, active
processing a language sample.” Related to these definitions, Helgensen in Nunan (2003: 24) affirms,
“Listening is an active, purposeful process of making sense of we hear.”
Listening along with reading is a receptive skill. That is, it requires a person to receive and understand incoming information (input). Because Listening is receptive, we can listen to and understand things at a higher level then we can produce (Helgense in Nunan, 2003: 24). For this reason, people sometimes think of it as a passive skill. However, listening is very active. As people listen, they process not only what they hear but also connect to ather information which already known. Listening is one of the skills in learning English that should be mastered by the students. Therefore, listening is learned by the students in the classrooms to achieve the optimal result that has been set and arranged in the syllabuss of Junior High School SMP N 2 Lahomi.
b. Principles of Teaching Listening
According to Harmer (1998:99-100), when teaching listening skill the teachers have to know the principles.
There are some principles of teaching listening skill, they are: 1) The tape recorder is just as important as the tape.
2) Preparation is vital to engage the students with the topic and the task that will be discuss.
The teacher needs to prepare her/himself before they teach a lesson into the class. They will be prepared for any problems, noises, accents that come up when they are teaching the students. That way, the teacher can judge whether students are able to engage and cope the topic or task that will be discussed.
3) Once will be not enough for the students to learn the language features.
In listening subject, the students need to hear the sounds more than ones because the students want to hear it again to pick up the things they miss in the first time and teacher should give them a chance to study some of the language features. If using a tape recorder or directly the teacher becomes as a speaker that produces the sounds, the first listening is often just to give the students an idea of what the listening material sounds like, so the subsequent listening is easier for the students.
4) Students should be encouraged to respond the content of a listening, not just to the language. As with reading, the most important part of listening practice is to draw out the meaning, what is intended, or what impression it makes on the students. In other words, the students should be encouraged to respond the content of the material.
5) Different listening stages demand different listening task.
There are the different things we want to do with the listening text. We need to set the different task for different listening stages. It means that, for a first listening, the task needs to be fairly straightforward and general so the students’ understanding and response can be successful.
6) Good teacher exploit listening texts to the full.
script for a new activity. Listening the music or stories is a clues for it. The listening then becomes an important event in teaching sequence rather than just an exercise.
From the explanation, it is concludes that the teacher should pay attention for all the things that can support the listening subject because it is not only about hearing of something but also understanding the spoken knowledge by considering the situation in the class. The teacher needs to ensure that students are well prepared for listening and able to hear what they are listening to. For the listeners, they have to understand how to differentiate the situation when the spoken language produced, context, and how to use the language in the real world.
c. Model of the Listening Process
Flowerdew and Miller (2005:24) assert that there are 3 models that have been developed to explain how the listening process functions for adults
1. Bottom-up processing
The bottom-up processing model assumes that listening is a process of decoding the sounds that one hears in a linear fashion, from the smallest meaningfull units (phonemes) to complete texts. According to this view, phonemic units are decoded and linked together to form words, words are linked together to form utterances, and utterances are linked together to form complete meaningful texts.
2. Top-down processing
In this reconstruction process, the listener uses prior knowledge to make sense of what he or she hears. It can be concluded that top-down process involves knowledge that a listener brings to a text.
3. Interactive processing
Intercative processing is the combination of top-down and bottom-up data. Pre listening activities are good ways to make sure it happens. Before listening, the students can braisntorm vocabulary related to a topic. In the process, they base their information on their knowledge of life (top down information) as they generate vocabulary and sentences (bottom-up).
It is concluded that an interactive processing the information will be process applying the ELVES strategy by combining the bottom-up and top-down data. In the research, the researcher imitated all of these models of processing information in teaching listening to the students.
d. Types of Listening
Different situations require different types of listening. There are some types of listening according to Kline (2009) as follows:
1) Informative listeningis the name we give to the situation where the listener’s primary concern is to understand the message. Informative listening, or listening to understand, is found in all areas of our lives.
2) Relationship listening. The purpose of relationship listening is either to help an individual or to improve the relationship between people.
4) Critical listening. The ability to listen critically is essential in a democracy. The subject of critical listening deserves much more attention than we can afford it here.
5) Discriminative listening. It may be the most important type, for it is basic to the other four. By being sensitive to changes in the speaker’s rate, volume, force, pitch, and emphasis, the
informative listener can detect even nuances of difference in meaning.
e. Components of Listening
Barker in Moore (2005:359) describes the listening process as having four components as follows:
1. Hearing
Hearing is psychological. It is the nonselective process of sound waves striking the eardrums. 2. Attending
Although listening is started by a psychological process of hearing, it quickly becomes a psychological one as students decided whether to focus on, or attend to, what teacher say. Listening involves focusing on the speaker and the message being transmitted.
3. Understanding
Understanding involves the mental processing of received information. During this phase, students must actively judge the worthiness of message and the relevance of the information, as well as select and organize the information received.
4. Remembering
Remembering is the fourth component of the listening process. The recall of information is directly related to how the information is evaluated.
rehearsed. Of course, the more times they hear any piece of information, the better they will retain it; similarly, rehearsed information is more often remembered.
f. The Habits of Bad Listening
Some students are poor listeners because they have developed bad listening habits. Moore (2005: 362) explains these bad habits as follows:
1) Pseudeolistening
Pseudeolistening is an imitation of listening. Good pseudeolistening look you in the eye, nod a smile in agreement, and even answer questions occasionally. In others words, they give the appearance of attentiveness, but, in reality, they are thinking about other things.
2) Insulated listening
Some students avoid listening when they do not want to deal with an issue or when it takes mental exertion to understand what is being said.
3) Selective listening
Selective listeners attend only to a teacher’s remarks that interest them. Such students automatically case listening when the message is of little interest.
4) Attribute listening
Attribute listeners are more interested in the delivery and/or the physical appearance of the teacher. These students are often more concerned with critizing the teacher’s style of delivery of physical appearance than with listening to the message.
5) Stage hogging
6) Devensive listening
Devensive listeners take innocent remarks as personal attacks. Teenagers are notorius for being devensive listeners. They often take parental or teacher remarks about their behaviors as being distrustful shooping.
It can be concluded that those bad habits are some factors that make the students become poor listeners. Therefore, they should be avoided by the students. It should be that the students have to practice working on such bad habits above if they are to become better listeners. To become a better listener, it is not born that way. Below, the researcher discusses about the ways to become a better listener.
g. Ways to Become a Better Listener
Virtually, everyone listens. However, few do it well. Basic to the improvement of listening ability is awareness of the need for improving the skill (Moore, 2005: 359). According to Lucas (1992: 36-41), there are six ways to become a better listener, they are:
1) Take listening seriously
The first step improvement is always self-awareness. Analyze your short comings as a listener and commit yourself to overcoming them. Good listeners are not born that way. Like any other skill, it comes from practice and self disclipine.
2) Resist distraction
Our attention can stray even in the best circumstances. Whenever you find this happening, make a conscious effort to pull your mind back to what the speaker is saying. Then force it to stay there.
Don’t let negative feelings about a speaker’s appearance or delivery keep you from listening to
the message. Try not to be misled if the speaker has an unusually attractive appearance. 4) Suspend judgment
Unless we listen only to people who think exactly as we do, we are going to hear rhings with whice we disagree. When this happen, our natural inclination is to argue mentally with the speaker or to dismiss everything he or she says.
5) Focus your listening
Skilled listener needs to focus on what is the speaker said 6) Develop note-taking skills
When done properly, note-taking is an excellent way to improve your concetration and to keep track of a speaker’s ideas. It almost forces you to become a more attentiveand creative listener. On the other hand, become a better listener should follow the step as have been explained become a more attentive and creative listener.
h. The Assessments of Listening
The researcher assesses the students’ ability in listening based on the expert’s opinion as suggested by Nation (2001:344) saying, “There are some tests to assess listening, as follows: true or
false test, vocabulary depth test, matching test, multiple-choice test, and transition test”.
Based on the kinds of listening test, the researcher uses matching test to know the students’ ability in listening skill by applying ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy.
Note: S = Score
R = Right answer
Finally, the researcher applies the formula suggested by Cartier and friends in Brown (2004:1-8)to find the students’mark, as follows:
′ :Obtained score
Total score x 100
After getting the mark, the researcher classifies the mark according to the degree of ability such as presented below:
0 - 39 is classified as fail 40 - 59 is classified as less 60 - 74 is classified as enough 75 - 84 is classified as good 85 - 100 is classified as very good
i. The Syllabus of Listening skill at the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi
Based on the syllabus of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi at the eighth grade students’ in which the
researcher wants to make a research in increasing the students’ ability in listening comprehension
through ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy, there is a type of text which learned by the students in learning material that is descriptive text.
1. Descriptive Text
Description is a strategy for presenting a verbal potrait of a person, person or thing (Crimmon and John, 1967: 163). According to Brereton (1982: 59), there are two types of description that are most useful, they are description of a place and description of a person.
2. Description of a Place
In this case, the text is used to describe a place such as a room, a house instead of something as large as a city or a country. (Brereton, 1982: 59). Descriptive text creates such a vivid impression of the place to make the listener see what the author seen. In order to show the place, the text must be in the concrete details.
Example:
MY HOUSE
I live in a small house. It has five rooms: there are two bedrooms, a living room, a bathroom, and a kitchen. Indeed it is a small house; but I like living in here for wasting my spare time.
When the door is open, I can see the living room. It is so small with only three chairs and a table, nothing else. I prefer reading a novel in this room.
My bedroom is in the left side of the living room. In this room there is a night table next to the bed, a TV, a radio, and a computer. When being bored of reading, I usually play online games, chat with my friends via Facebook and so on.
Next to my bedroom is my mother's. I do not know what is inside because I never come in to see it. In the right side of the living room there is the kitchen. In the kitchen I have everything I need when I get hungry. It is very pleasure when my mother cooks; the smell fills my whole house.I know it is a very small house; but it is the best place I have ever seen.
3. Description of a Person
In this case, the text is used to describe a person or someone. It is nearly same as the description of a place in whice it must be in the concrete details. However, in this text, it describes about a person.
Example:
MICHAEL DOUGLAS
Michael Douglas is a very famous and popular American actor. He is about sixty years old. He is a slim person and he is average height. He has got light brown eyes and short fair hair.
His wife is a very beautiful British actress who is named Catherine Zeta-Johns, she has got green eyes and long straight black hair. They have got a daughter who is two years old. They all live in the United States Of America.
Adopted from A Plan for Writing by John C. Brereton
A description text has two main parts, they are identification and description. The structure of a text is called thegeneric structure.
1. Identification
This part identifies a particular thing to be described. For example, in the first text above (description of place), the author told about My House, not houses in general.
Identification usually answers the following question: 1) What is the topic of the text?
2. Description
This part describes the parts and characteristics. For example, in the first text above (description of place), the author describes about:
1) The parts of My House (the main building and two wings) and 2) The characteristics of My House: size (large, tall)
The language features includes the use of: 1) Specific participant (person) or place 2) Simple present tense
However, the researcher just teaches the students to increase their ability in listening by teaching descriptive text. To know the students’ ability in listening, the researcher provided assessment to get the students’ ability in listening through ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) strategy, so that the researcher could analyze the cases or problems that would be shown.
B. ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy
a. The Definition of ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy
maintain initial excitement about reading”. In other words listening is the excitement of desiniging the
students knowledge to study.
However, ELVES is not only device or materials, but also the other things that enable the students to get knowledge. Gerlach and Ely in Sanjaya (2008: 163) point out, “a medium, conceived is any person, material or events that creates condition which enable the learner to acquire knowledge, skill and attitude.
Regarding the definition above, it seems that the last definition stated by Gerlach is more general than the first one. Then, Smaldino et al (2008: 6) assert, “ ELVES is anything that carries
information between a resource and receiver.”
Harjanto (2008: 247) formulates ELVES for learning. He says:
“...as the carriers of messages, from some transmitting source (with may be a human
being or an intimate object), to the receiver of the message (which is or is our case is the learner).”
Inspired from some of the definitions above, the researcher concludes that ELVES is used to carry message from the resource to the receiver of message in order to stimulate their thought, feeling, attention and motivation so teaching and learning process can be done optimally.
There are many kinds of ELVES that can be used in the teaching and learning process. Because of that, strategy have been classified in to some classification in order that they are in orderliness and more specific.
bring about a change of emphasis in teaching, from the teacher directed approach to a facilitated approach, is to change the medium of instruction”. In other words, ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) strategycan be used to teach listening.
There are many good reasons for encouraging the students to imagine the picture while listen. In the first place, they got to see ‘language in use’. This allows them to see a whole lot of paralinguistic
behavior. For example, they can see how intonation matches facial expression and what gestures accompany certain phrases (e.g. shrugged shoulders when someone says I don’t know). The sound from the story has a number advantages, they are recorded materials allows the students to hear a variety of different voices apart from just their bown teacher’s and also it gives them an opportunity to ‘meet’ a range of different characters’ especially where ‘real’ people are talking. (Kearsley, 2001:
304).
Regarding to the expert’s opinions, it is concluded that ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) strategy especially in descriptive text can be used to teach and practice listening by having the students listen and imagine the picture.
c. The Procedures of ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy
ELVES can be classified into some classifications. According to Peterson (2008:6), there are five procedure of ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy used in learning, they are :
1) Excite, the listening experience should start with a discussion that focuses on the listener's experience.
3) Visualize, students are encouraged to create mental images as they listen to stories. These visual images are shared.
4) Extend, students are asked to extend the meaning of the story by bridging past knowledge with the new knowledge gained from the story.
5) Savour, this savouring allows for reflection provided for students to reflect on their about what has been read. Time is thoughts and feelings about the story. The savouring might be as simple as a discussion or it might involve an individual or class project.
According to Weat (2008: 6), there are several procedure of ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy as follows:
1) Excite, discuss appropriate experiences that your listeners might have had associated with the story, and ask them to share their experiences.
Do all animals sleep at the same time at night? Look at the title and picture on the book cover. What do you think will happen in the story?
2) Listen, have your listeners take part during the oral reading of the story.
Raise your hand when you hear me read something that proves you were right when we discussed the story earlier and predicted what would happen.
3) Visualize, help your listeners construct visual images while listening to the story.Tell me how big you think the mother raccoon is in the story? Show me with your hands. Tell me what the pond looks like. How big is it?
4) Extend, encourage your listeners to use the information from the story as a "pi.ictor" of future situations that they might encounter.
5) Savor, savoring the story allows the listeners to reflect on the central meaning of the listening experience.Would you lik(o trade places with one of the animals in this story? Which a imal would you be. Why did you choose thatanimal? Let's do a research project by using some referencebooks to learn more about the animal you choose.
However, both of the steps for the experts opinions are nearly same. Therefore, the researcher has modified these steps in teaching listening to the eighth grade students class B of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi, they are:
1) The researcher invited the students to listen the experience should start with a discussion. 2) The researcher invited the students to discuss the text earlier and predict what would happen. 3) The researcher choosed the students to look at the title picture on the book cover.
4) The researcher asked the students what they think and describe the picture.
5) The researcher choosed the students to raise hand when hear something that proves you were right.
6) The researcher invited the students to encourageand create mental images as they listen to the text.
7) The researcher extended the meaning of the story by bridging past knowledge with the new knowledge gained from the text.
8) The researcher allowed for reflection provided for the students to reflect on their knowledge about what has been read.
d. The Advanteges and Disadvantages of ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy
3) The motion can be slowed or sped.
4) The presentation of ELVES can be repeated.
5) ELVES is the strategy of teaching learning process which highlight in listening skill and speaking.
6) ELVES have been available in great quantities.
7) It can be owned by students discussion or individually. 8) It can be used anywhere and anytime.
ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy also has some disadvantages, they are:
1) It needs specialist to mention it.
2) It needs long time to imagine the picture. 3) It needs treatment.
4) It is easy to be broke down.
Based on the expert’s opinion, it can be concluded that the advantages of ELVES (Excite,
Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) make the students become active, fun and joyful during in the teaching-learning process. While disadvantages are the students needed a lot of time to follow the strategy and creatively and it is considered to the teacher in the school when implementing it.
e. The Relationship between Listening Skill and ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy
Listening is one of the important skills in learning English that should be learned by the students. According to Yteberg (2003: 30), the most obvious ‘listen and ELVES (Excite, Listen,
Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy the teacher begins the lesson by giving some instructions to the students. Perhaps with act of teacher statement, in this strategy, the students can be more active. Listen and ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy designed for both young and very young learners of English. It may be a helpful resource to supplement course design, provide more listening comprehension practice, as a filler or ice-breaker, or as a way to introduce a touch of fun in our lessons (Hana Svecova, 2006). This strategy increases the students’ ability in listening comprehension.
The aim of this strategy is to help young learners to understand language through listening to instructions and performing them with their bodies (Mabel Lee, 2006: 89). By this strategy the students do not just listen but also performs the instruction with the picture of their material. In other words, if the students can describe the same thing with the instruction, the students have understood and can listen well.
Based on the expert’s opinion, it is concluded that listening and ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) strategy makes the students more active by describing a picture based on the instructions from the teacher.
C. The Latest Related Research
The latest related research was investigated by Ratya (2012) with the title of the thesis is, “Increasing the Students’ Ability in Listening through ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and
Ratya and the researcher has similarity in doing the research, such as the researcher and Ratya take listening as the skill of research and take the similar strategy that will be applied in solving the students’ problem in listening that is Listenskill.
C. The Conceptual Framework
Basically, there are four major language skills that should be mastered by the students, they are listening, speaking, reading and writing. In this research, the researcher chooses one of them, that is listening.
When the researcher observed at the eighth class b students of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi, the most crucial problem that should be solved is the teacher’s strategy in teaching listening to the students.
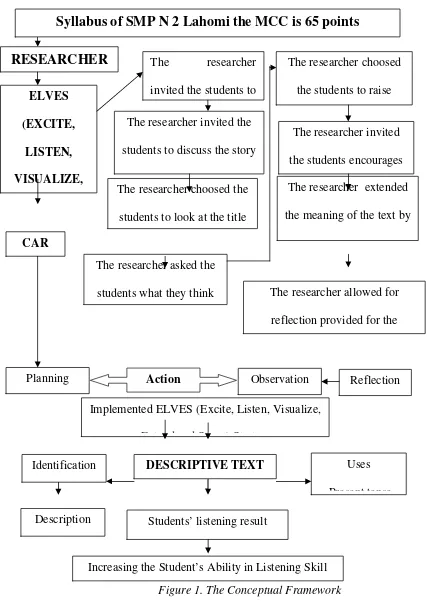
Figure 1. The Conceptual Framework
Increasing the Student’s Ability in Listening Skill
Syllabus of SMP N 2 Lahomi the MCC is 65 points
Planning Observation Reflection students to look at the title
The researcher asked the students what they think
The researcher invited the students encourages The researcher extended the meaning of the text by
bridging past knowledge
The researcher allowed for reflection provided for the
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
A. The Object of the Action Reseach
In conducted the research, the researcher used the Classroom Action Research (CAR). CAR focuses on developing, improving, or increasing the quality of the students. In teaching learning process. In this case the researcher want to found the appropriate technique which can make a better condition in the classroom. CAR is a research that can be used by teacher to evaluate what did they do in teaching learning process.
As Ebbutt in Wiriaatmadja (2007: 12) affirms that action research is a systematic study about the improvement of educational practice that is done by teacher through some improving actions based on their reflection of the previous action’s result. On the other hand Classroom Action Research is done by the teacher in order to improve and increase the quality of the teaching and learning processes and also the students’ learning result by doing actions continuously based on the observation and reflection
of the previous action. Futhermore, Aqip (2008: 3) states the Classroom Action Research (CAR) is a research done by the teacher in his or her own classroom. This statement means that Classroom Action Research gives a large opportunity for the teacher to do some improvement actions in his/her own classroom. The goal is not only the students’ result, but also to improve the quality of the teaching and
learning processes.
It is concluded that the object of action in the research is the students’ ability in listening skill
B. The Setting and Subject of the Research
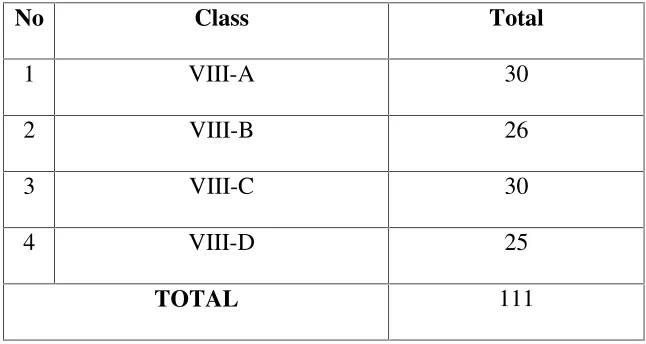
The setting of the research is SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi that is located on Jl. Lahomi km 4 Lahomi village. The total number of teachers was 20 persons and two of them were English teachers. It is consisted of 10 classes and 410 students. The subject of the research was VIII-B (eighth class B students which was consisted of 26 students. The researcher chooses the class because the students in the class had problems in listening Skill.
The real condition of the eighth grade students of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi can be seen as follows. Table 3.1
THE CONDITION of the EIGHTH CLASS STUDENTS of SMP NEGERI 2 LAHOMI in 2015/2016
No Class Total
1 VIII-A 30
2 VIII-B 26
3 VIII-C 30
4 VIII-D 25
TOTAL 111
C. Schedule of Implementation Action
Based on the planning, the researcher conducted the research around 2 months. It started on October untill November 2015 based on the syllabus of the Eighth Grade of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi.
D. The Procedures of Implementation Action
In doing the research, the researcher arranges the procedures of action implementation in two cycles. The cycle consisted of some activities, they are:
1) Planning is to determine the material, lesson plan, field note, evaluation sheet, and observation sheet for the researcher and students.
2) Action is the process of teaching-learning activities through ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) strategy.
3) Observation is to search evidence or collecting data about the students’ and the researcher’s activities during teaching-learning process.
4) Reflection is making a revision about the teaching-learning result, and containing the improvement plan to the next cycles.
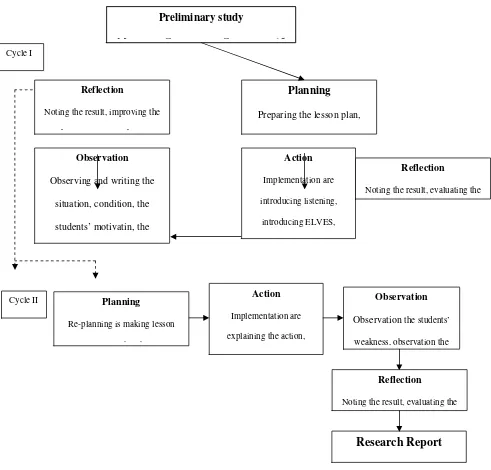
Figure 2 : Implementation of Action by using ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize,
Extend and Savor) strategyto Increase the Students’ Ability in Listening Skill.
Based on Figure 2, it shows that a cycle consists of planning, action, observation and reflection. First is planning consists of the plans that the researcher is going to do. It’s all about the preparation
needed in doing the researcher such as lesson plan, descriptive text, observation sheet, evaluation sheet and pictures. Second is action is about the realization of theory treatments that have been planned before, such as introducing listening, introducing ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy, teaching descriptive text, giving example and giving task. Third is observation is searching the students’ and the researcher’s activities and also the weaknesses found during the teaching and
learning processes. Fourth is reflection. In this session, the researcher will decide whether go to the next cycle or not. It will be based on the data analysis that is gotten.
D. The Procedures of Action Research
In the research, each sycle consists of two meetings. It depend on the teaching procedure, action implementation and the lesson plan (syllabus). To make it clear, the researcher gives the explanation about the activities that are done by the researcher. The cycles of the research are as follows:
1. Cycle I
The cycle consisted of two meetings. Each meeting followed CAR procedure above as explained by the researcher.
a) First Meeting
1. Planning
In doing cycle I in the first meeting, the researcher prepared many things, such as: lesson plan, descriptive text and observation sheet. The planning’s steps are didto avoid the misconception of the
action that will be done in the classroom. 2. Action
The teaching-learning process consisted of pre teaching-learning, whilst teaching-learning, and post teaching-learning. For the meeting in the classroom, the researcher greeted the students, introduced herself to the students, and checked the present list. Futhermore, the researcher explained the students about listening. Then, the researcher introduced the students about the strategy used in the classroom to teach listening that is ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) strategy that consisted of descriptive text. Then, the researcher activated the students’ background knowledge about the descriptive text. The students’ gave their opinions. Futhermore, the researcher gave the students the
example of descriptive text with the title “My House”. The researcher explained the students about the descriptive text, the generic structure of descriptive text, including the tense used in the descriptive text. The researcher implemented the procedureof ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) strategy.
gained from the text. Finally, the researcher allowed for reflection provided for the students to reflect on their knowledge about what has been read.
3. Observation
In observation, the researcher did some activities such as searching the students’ activities
during the teaching and learning processes, paying attention to the students’ activities, paying attention
to the researcher’s activities, searching about the students’ listening ability and observing the
weaknesses during the teaching and learning processes. 4. Reflection
In reflection, the researcher did some activities such as nothing the result of the observation, evaluating the result of the observation, analyzing the result of the observation, and improving the weaknesses during the teaching and learning processes.
b) Second Meeting
The meeting conducted on September 2015, which needs the allotted time 2 x 40 minutes. The procedure, as follows:
1. Planing
In the second meeting, the researcher prepared many things, such as: lesson plan, the students’
evaluation sheet and observation sheet, field notes. The planning’s steps are done to avoid the misconception of the action that done in the classroom.
2. Action
the strategy used in the classroom to teach listening that is ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy that consisted of descriptive text. Then, the researcher activated the students’ background knowledge about the descriptive text. The students’ give their opinions. Futhermore, the
researcher gave the students the example of descriptive text with the title “My House”. The researcher explained the students about the descriptive text, the generic structure of descriptive text, including the tense used in the descriptive text. The researcher implemented the procdureof ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy.
The researcher invited the students to listen the experience should start with a discussion. Then, the researcher invited the students to discuss the story earlier and predict what would happen. After that, the researcher choosed the students to look at the title picture on the book cover. Next, the researcher asked the students what they think and describe the picture. Then, the researcher choosed the students to raise hand when hear something that proves you were right. After that, the researcher invited the students to encourage and create mental images as they listen to the text. Next, the researcher extended the meaning of the story by bridging past knowledge with the new knowledge gained from the text. Finally, the researcher allowed for reflection provided for the students to reflect on their knowledge about what has been read.
3. Observation
In observation, the researcher did some activities such as searching the students’ activities during the teaching and learning processes, paying attention to the students’ activities, paying attention
to the researcher’s activities, serching about the students’ listening ability in teaching and learning processes.
4. Reflection
In reflection, the researcher did some activities such as noting the result of the observation, analyzing the result of the observation, evaluating the result of the observation, and improving the weaknesses during the teaching and learning processe.
2. Cycle II
This cycle did if the result of Cycle I cannot achieve the MCC and it will be designed by considering the weakness and the strength, while if the result of Cycle I will be successful, the research stops in Cycle I and reports the result.
E. The Instruments of Collecting Data
In collecting the data, the researcher used instruments, as follows: 1) Observation sheet
Observation sheet is used to look for the qualitative data. Qualitative data is obtained from the researcher’s and students’ activities when conducting the teaching-learning activities in the classroom.
This sheet will be checked list by the teacher-collaborator whether it is done or undone. 2) Field notes
3) Evaluation sheet
Evaluation sheet is used to evaluate the students’ ability in comprehending narrative text through ELVES. In this evaluation, the researcher applies matching test as tool in gaining the data if consisted of 20 items question.
F. The Techniques of Data Analyzing Data
After the researcher collected the data by observing the students’ and the researcher’s activities and also testing the students’ ability in listening, the researcher will analyze the data gotten from the
implementation of action in each cycle. The data that will be analyzed are quantitative and qualitative data. Quantitative data will be analyzed by the score of the students’ evaluation paper. Qualitative data
took from the observation form. It is aimed to know the development that has been achieved and it can be used as the input of reflection of what has been done in action or implementation.
There are three steps analyzed the data in the research, namely:
1. Reduction of data is evaluating and classifying the data based on the information and it must be organized according to the statements of this research.
2. Explanation of data is the data that have been organized by the researcher must be classified to get the meaning in the table, graphic or narration forms
To find the students’ ability related to the quantitative data, the researcher analyzed the data by scoring
all of the students’ answers. Then, the researcher used the formula written byPurwanto, (2006: 103) as follows:
Which:
PD : Percentage degree
F : Frequency of the researcher’s and students’ activities have been already done T A : Whole activities of the researcher and the students
100 : Constant and maximal number of percentage.
Then it is classified as Nurgiyantoro (2001:399) says, to the following scale (%) 1) For the researcher’s activities
0% - 39% : the degree of teaching level is fail. 40% - 59% : the degree of teaching level is less. 60% - 74% : the degree of teaching level is enough. 75% - 84% : the degree of teaching level is good. 85% - 100% : the degree of teaching level is very good. 2) For the students’ activities
0% - 39% : the degree of the students’ activities level is fail. 40% - 59% : the degree of the students’ activities level is less. 60% - 74% : the degree of the students’ activities level is enough.
PD(%) = F
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS A. The Research Findings
1. The Research Setting
The location of the research was SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi that is located on Jl. Lahomi km 4 Lahomi village. This school has some rooms, such as theheadmaster’s room, teachers’ room, students’ classroom, library, laboratories, canteens, some courts of sports and other buildings. Around this school there were fresh atmosphere because all sides of this school planted by green trees and flowers that can support the teaching learning process.
The subject of the research is eighth class B students consisted of 26 students. In this class, there were 14 girls and 12 boys. The researcher choosed this class because they have weakness in listening ability.
The researcher did the research by the agreement of headmaster of SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi. In doing this research, there are some procedures they are: (a) planning, (b) action, (c) observation, and (d) reflection. During the research, the researcher was helped by Daeli as the teacher collaborator and one of the English teachers in SMP Negeri 2 Lahomi. The teacher collaborator observed all the students and the researcher’s activities in order that the activities could run well and get the valid result.
During conducting the research, all the students were present. The researcher performed this research for two cycles that consisted of four meetings. Each cycle consisted of two meetings.
2. The Students’ Ability in Reading Comprehension by Using ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy
a. Cycle 1
done with 2 x 40 minutes. The researcher did it on October 2015 were the first meeting did on Wednesday, 4thNovember 2015,and the second meeting were done on Friday, 6thNovember 2015. The process of doing the research in Cycle 1, namely:
1). First Meeting
There were some activities that the researcher did in the first meeting of Cycle I, as follows: a) Planning
Before doing the action, the researcher prepared some things such as: lesson plan, material, observation paper for the researcher’s and the students’ during teaching-learning activities, field note, and camera digital.
b) Action
After planning, the researcher conducted the action in the classroom. The first meeting was held on Wednesday, 4thNovember 2015. The time allocation was 2 x 40 minutes. The researcher entered the classroom together with the teacher-collaborator. The teacher-collaborator gave the chance to the researcher to start the activities based on the procedures in lesson plan. The researcher greeted the students and all of them gave responses and introduced herself to the students. Then, the researcher checked the students’attandence list.
The researcher continued in doing the whilst teaching-learning activities. The researcher explained the definition of the students about listening and about the purpose of listening. introduces the material to the students, it is descriptive text that describes about a place. The researcher introduced the material to the students that is descriptive text that described about a place. The researcher activated the student’s background knowledge about descriptive text. The researcher explained the material that
will be taught to the students, that is descriptive text which describes about place.
the students to discuss the text earl choosed the students to look at the t the students what they think and des descriptive text. In the post teachin greeted the students.
c) Observation
The observation was done b classroom. The English teacher obs process; involved the researcher’s and t
1. The result of the students’ obser (b) The students who done activitie (c) The students who had not done a
The result can be seen in Graphi
Graphic 1:The result o he title picture on the book cover about a place. The describe the picture, find out the language features
hing-learning activities, the researcher conclude
ne by the English teacher during the researcher di observed all of the activities happened in teac
and the student’s activities.
observation paper in the first meeting of Cycle I
ties :16 persons (62%) of 26 students done activities: 10 persons (38%) of 26 students
raphic 1 below :
t of the Students’ ObservationSheet the first M
Done Undone
place. The researcher . The researcher asked es and structure of the uded the material and
did the action in the teaching and learning
Based on the result of the stude meeting of Cycle I, as follows:
1) The situation around the class wa 2) Some of the students did not respons 3) Some of the students did not liste 2. The result of the researcher’s obs ` a) Done : 10 activities (66 %
1) The students started to give their own opi 2) The students felt enjoy to follow
by the researcher.
students observation sheets, the researcher found t
was noisy so they could not hear the description of esponse questions from the researcher.
isten the conclusion of material from the researche observation paper in the first meeting of Cycle I:
%) of 15 activities at the first meeting. ( 33 %) of 15 activities at the first meeting.
seen in the following
her Activities were Done and Not Done in first m
ntages found by the researcher in conducting the fir
ir own opinion when the researcher asks them. ow the teaching-learning process with the new tec
d) Reflection
In first meeting, the researcher did not have enough time to evaluate the students’ ability in
listening skill. The researcher decided to evaluate the students in the second meeting. Based on the result of two pieces of the observation paper that was explained in the previous part the researcher should do some improvements in the next meeting, such as:
1) The students listened the researcher explanation.
2) The researcher asked the students to response questions from the researcher. 3) The researcher asked the students to listen concluded material from the researcher.
2). Second Meeting
The researcher continued the activities from the first meeting because of the limitation of the time in the first meeting. It was held on Friday, 6th November 2015. The time allocation used in the second meeting was 2 x 40 minutes.
a). Re-Planning
In second meeting, the researcher prepared a lesson plan, reading text observation sheet for the researcher, observation paper for the students and evaluation sheet.
b). Action
After planning, the researcher conducted the action in the classroom. The second meeting was held on Friday, 6thNovember 2015. The meeting was done in 2 x 40 minutes. The researcher continued the first meeting activities that was to evaluate the students’ ability in comprehending the descriptive text.
gave the instruction to the students how to do the test. The researcher asked the students to answer the questions individually. The researcher walked around the classroom to make sure that all of the students did the task. Sometimes, there were some students who asked questions to the researcher and the researcher gave them the explanation.
The researcher collected the students’ evaluation sheet after making sure that they had finished answering it. The researcher took the conclusion and closed the meeting by greeting the students.
c). Observation
The observation was done by the English teacher-collaborator during the researcher implemented the actions in the classroom. The English teacher-collaborator observed all of the activities happened in the teaching-learning process; involved the researcher’s and the students’ activities.
(1) Based on the result of the observation paper for the students, the students who are active and cooperative in following the teaching-learning process as follows :
The result can be seen in Graphi
Graphic 3: The Students Activities
Based on the result of observa in doing the first meeting in cycle I, a
a) Some of the students did not listen t b) Some of the students did not listen t
(2) Based on the result of the obs (a) Done : 9 activities ( 75%) of
ties were Done and Not Done in Second meeting i
ervation sheet of the students, the researcher found I, as follows:
sten the researcher when the researcher explain the sten the researcher conclusion about the material.
observation sheet for the researcher as follows: ) of 12 activities in second meeting.
25%) of 12 activities in second meeting.
It can be seen in the following graphi
Graphic 4: The Researcher Ac
Based on activities during the the result of observation paper showe
Based on result of two pieces are:
(1) The students have motivation in t (2) The students start to give their at (3) The student able to give their opi
always gave their attention to the (4) Some of the students started to
Activities were Done and Not Done in second m
the teaching-learning process, the teacher collabor howed that the researcher’s activities.
ces of observation paper, the researcher found som
on in teaching learning process.
attention in the researcher explanation.
d) Reflection
After implementing the action above, the researcher evaluated the students’ ability in reading
comprehension by using matching test.
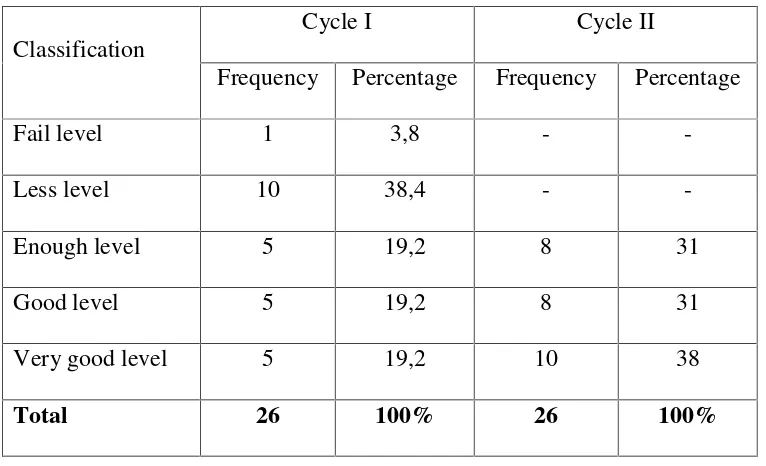
The result of students’ evaluation sheet can be seen in Table 4.1, as follows:
MCC Level Scoring Frequency %
65
Very Good 85-100 5 19,2
Good 75-84 5 19,2
Enough 60-74 5 19,2
Less 40-59 10 38,4
Faill 0-39 1 3,8
Total 26 100%
The data from the table above explained that the students’ ability in listening by using Using ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy in Cycle 1 was enough. It showed that there were 5 students (19,2%)classified in the “verygood” level. There were5 students (19,2%) in the “good” level. There were5 students (19,2%)in the “enough” level. There were10 students (38,4%) in the “less” level and there were 1 student (38%) in the “fail” level. From the total number of students there were 16 students able to achieve the KKM (65) while 10 students still unable to achieve it. In addition, the average of the students’ mark was 60,38. This result was showed that the students were unsuccessful to do the ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) Strategy in comprehending the descriptive text. The result of the students’ ability in Cycle 1 could be viewed in
Graphic 5 : The result of the Stude Visualize, Extend and S
Based on the explanation above
skill by using Strategy in ELVES (Ex enough, which means that Strategy unable to increase the student’s abili
KKM(Minimum Competence Criter 65points could not be achieved by t Therefore, the researcher would cont Cycle II by doing some improvement 1) The researcher praises the student 2) The researcher asks the students t
0%
tudents’ Ability in Listening through Using ELVES nd Savor) Strategy in Cycle I.
above, the researcher concluded that the students’
(Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend and Savor) i y in ELVES (Excite, Listen, Visualize, Extend a bility in listening the descriptive text. It was indic
terion) of the English subject at the eighth grade, t y the students by looking at the average of the stude
continue to the Cycle 2. Therefore, the reseacher ents, namely:
udents for their opinion.
nts to be active in doing the task from the researcher
Less Enough Good Very Good nd and Savor) was still ndicated by looking the
e, theKKMwhich was students’ mark above.
her should continue in
b. Cycle 2
In doing the Cycle 2, the researcher took two meetings. In this cycle, each meeting was done with 2 x 40 minutes. The first meeting did on Wednesday, 18th November 2015, and the second meeting did on Friday, 27thNovember 2015. The process of doing the research in cycle 2 as follows: 1). Meeting 1
The first meeting did on Wednesday, 18th November 2015. At the first meeting the researcher did some activities. It needed 2x40 minutes. The procedures of each phase that the researcher applied as follows:
a. Re-planning
In planning, the researcher prepared lesson, reading text, observation paper for the researcher , observation paper for the students, and the students attendance list. In the re-planning of the first meeting in Cycle II the researcher conducted its procedures similar to the Cycle I. In this meeting, the researcher tried to improve the students’ weakness and difficulties that was found in Cycle 1.
b. Action
The first meeting of Cycle 2 conducted on Wednesday, 18th November 2015. The meeting was done in 2 x 40 minutes. The researcher entered the classroom with the teacher collaborator who sat at the corner. The researcher greeted the students and all of them gave responses and introduced himself to the students. Then, the researcher checked the students’ present list.