CHAPTER III
METHOD OF THE ANALYSIS
3.1 Location
The study was conducted at Canteen Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Medan. The reason why the writer took the location is due the writer is one of student at Faculty of Cultural studies at that University.
The research location is a place where researchers studies. In this study researchers also as a research instrument, conduct research at University of Sumatera Utara campus is located in the Faculty of Cultural Studies. This is because the objectstudied is speech or utterances, the researchers prefer the campus to do research. In addition, researchers conducted the study inprivate rooms as well as supported by means of appropriate equipment forsupport the research process.In this study, researchers conducted a study in several weeks, start from 10/10/2014 to 10/02/2015 this is because previous researchersgradually been doing research for then do researchintensified the research object.
3.2 Research Method
the result of the research. Moreover, the results of the research would be better by applying table, graph, draft, picture, etc.
The research was conducted at of Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara there are at English Department, Arabic Department, Japanese Department and Chinese Department.
3.3 Population and Sample
Populasi adalah himpunansemuahal yang ingindiketahuidalampenelitian (Malo,
1985:149). Sample adalahbagiandaripopulasi yang dapatmewakilipopulasi data yang ada
(Malo, 1985: 152).Population data in this study is in the form of dialogue as a whole contained at Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara. In this study, researchers used a sample of some of the data in the form of dialogue with regard to the follow-locutions, illocutionary, and perlocution.
The population of this research are 300 students, the population in data is sentence which obtained from 32 respondents, Arikunto(2006:12) says that sample is purposed by taking the subject not based on the level, random, or domain but it’s taken based on the certain purpose. Thus, the researcher took sample based on the sentences which speech act sentence.
Sampel adalah bagian dari jumlah dan karakteristik yang dimiliki oleh populasi
tersebut(Sugiyono2011:120). Sedangkan menurut pendapat lainnya, yang dimaksud sampel atau
contoh adalah sebagian atau wakil populasi yang diteliti (Arikunto, 2010: 174).
Penentuan besarnya sampel dalam penelitian ini didasarkan pada pendapat Arikunto
“Untuk sekedar ancer- ancer, maka apabila subyeknya kurang dari 100, lebih baik semua sehingga penelitiannya adalah penelitian populasi.Selanjutnya apabila subyeknya besar dapat diambil antara 10-15% atau 20-25% atau lebih.”
Based on the concept mentioned above, because the population of more than 100, the researchers took samples of 10-15%. With the sample number was expected to meet the requirements of the sampling.
3.4 Data Collecting Methods
In this study, researchers collected data based dialogue reflected at Faculty of Cultural Studies Canteen University of Sumatera Utara.
Metode yang digunakan dalam pengumpulan data yaitu metode simak (Sudaryanto,
1993: 133).
Refer to the method is a method by means of listeninga language. The techniques used in this method, which is a technique ListenProficient involved free. In this technique, the researchers not involved in the dialogue, conversations,or reward speech. So, the researchers did not participate in the talks process those peoplewho is speaking in the dialogue.
After that, the researchers also uses techniques Record. In this technique, researchersrecord all the data found in the data card and using mediacomputer as a place to store data that is then followed byclassification (Sudaryanto, 1993: 135).
CHAPTER IV
DATA ANALYSIS AND FINDINGS
4.1. Presentation of Data
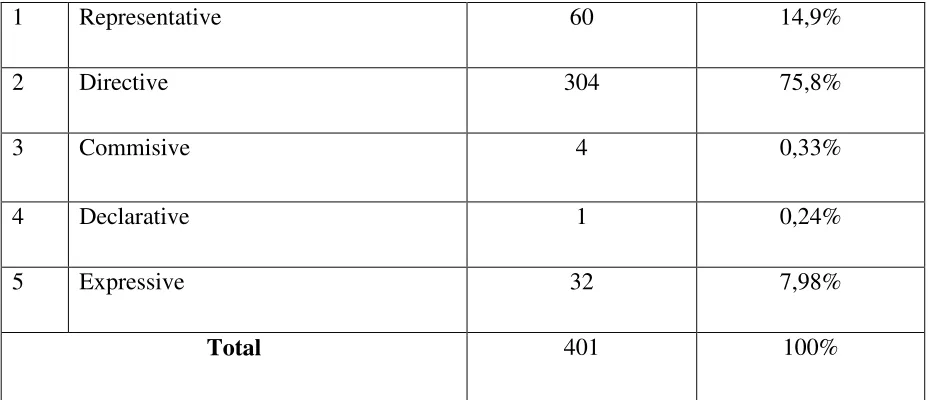
4.1.1.Speech act reflected at Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara.
Many utterances that reflected at canteen Faculty of Cultural studies University of Sumatera Utara, there are:
Conversation at the canteen Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara. 4.1.1.1 Data 1 (English Department 2010)
Ad : Could you order us for two cups of tea, please ! Yu : Yes certainly, ice tea or hot tea?
Ad : Ice tea please.
Yuk : Wait for a while, please. Ad : Thank you
Yu : What would you like to eat? Ad : Fried noodle please
Yu : Okay, it's ready now. 4.1.1.2Analysis of Data I
Ad : Could you order us for two cups of tea, please ! Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires the hearer about coffee because he want to drink that coffee
Yu : Yes certainly, ice tea or hot tea? Direct : Informing, Asking.
Literal : The speaker literally informs the hearer will order that coffee, and the speaker asks what coffee want to order.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker gives information that coffee. Yu : Wait for a while, please.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker informing to the hearer to wait for a while. Ad : Thank you
Direct : Thanking
Literal : The speaker literally thanks the hearer for being so kind to him. Yu : What would you like to eat?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires the hearer about the food want to eat. Ad : Fried noodle please
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker informs the hearer that food Yu : Okay, it's ready now.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker informing that will okay all. 4.1.1.1.3 DataII (English Department 2011)
Ay : Hei Dewi, how are you today?
De : Hei Ayu, I am very fine. How about you?
Ay : I am fine too Dewi. What do you want something to eat for breakfast? De:Yeah I want to eat fried rice with special chicken and egg. How about you?
Ay : I want to eat Nasi Uduk with egg and tempe and very spicy sauce. De : Okay, just wait here, Ayu and I will order.
4.1.1.1.4 Analysis of Data II
Ay : Hei Dewi, how are you today? Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires the hearer about Dewi condition. De : Hei Ayu, I am very fine. How about you?
Direct : Informing and asking
Literal : The speaker literally informs the hearer about her condition.
Ay : I am fine too Dewi. What do you want something to eat for breakfast? Direct : Informing and Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs her condition and he enquires about hearer condition.
De : Yeah I want to eat fried rice with special chicken and egg. How about you? Direct : Informing and Enquiring
Literal : The speaker Literally informs her ordering and enquires about hearer. Ay : I want to eat Nasi Uduk with egg and tempe and very spicy sauce. Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asks the hearer what she wants. De : Okay, just wait here, Ayu and I will order.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker informs the hearer to wait for a while.
Ay : Thank you Wi for doing that . By the way. Why do you seldom breakfast at canteen?
Literal : The speaker literally thanks the hearer and asking about information why the hearer seldom breakfast.
De : Usually I cooked my breakfeast in my renthome. Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs the hearer she is cooked in her rental home.
4.1.1.5 Data III (English Department 2012)
De : Hi Ira, it’s a rest break, why do you just stay in the class? Let’s go to
De : The waiter told me that we might have to wait for little bit long because there are so many orders.
Ir : No problem. I am not in hurry. Hey, tell me about the examination yesterday.. I mean maybe the questions will be the same for my class.
De : Hmmm, when will the exam be held in your class? Ir : Tomorrow morning. It will be the first hour.
De : Ok, you need to study about pronoun, countable noun, un-countable noun, and some tenses. The questions are related to those topics.
Ir : Ok, and then? Any other topic?
De : Hmmm, oh ya I remember it. The conditional sentence appeared for about three questions.
Ira : Thank you Dewi. What are the kinds of those questions. I mean multiple choice or essay?
Ira : Essay! It’s gonna be so difficult. You need to study hard. De : Really? I must prepare it well.
De : May I ask your notes because my notes are not complete enough for the examination.
Ir : No problem. Just visit my home tonight or after school.
De : Ok. Thank you Ira.
Ir : You’re welcome. Our foods are coming, let’s eat.
4.1.1.1.6 Analysis of Data III
De : Hi Ira, it’s a rest break, why do you just stay in the class? Let’s go to the canteen.
Direct : Informing and asking
Literal : The speaker Literally informs and asks the hearer to go to canteen.
Ir : Actually I have to finish my homework. But, no problem, I can do it later. Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs the hearer she will do that homework as pas as possible.
De : That’s a homework, why didn’t you do in your home? Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asks the hearer about that homework. Ir : That’s my bad habit? Any problem?
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs that is speaker habitation to the hearer. De :Owhhhh,, What ails are you?
Direct : Mocking
Ir : What are you going to order? Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The Speaker literally asks the hearer what is her ordering. De : I think meatball and ice tea.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs that the speaker ordering. Ir : Ok, wait a minute, I tell your order.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs that will okay to the hearer. De : Ok, thank you.
Direct : Thanking
Literal : The speaker Literally thanks the hearer for being so kind to him. Ira : No problem.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs that is no problem. A few minutes later.
De : The waiter told me that we might have to wait for little bit long because there are so many orders.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker informs the hearer he might to wait for a while because there adre many orders.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs no problem about that, she is not in hurry. De : Hmmm, when will the exam be held in your class?
Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asks the hearer when they take exam. Ir : Tomorrow morning. It will be the first hour.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs the time of the exam.
De : Ok, you need to study about pronoun, countable noun, un-countable noun, and some tenses. The questions are related to those topics.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs about the topic examination. Ir : Ok, and then? Any other topic?
Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asks her about other topics.
De : Hmmm, oh ya I remember it. The conditional sentence appeared for about three questions.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs about the topic for tomorrow.
Ir : Thank you Dewi. What are the kinds of those questions. I mean multiple choice or essay?
Direct : Thanking and asking
Ir : Essay! It’s gonna be so difficult. You need to study hard. Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker informs the hearer to study hard. De : Really? I must prepare it well.
Direct : Stating
Literal : The speaker literally tells the hearer that he want to study hard to prepare that examination.
Ir : Yes of course. Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs yes.
D : May I ask your notes because my notes are not complete enough for the examination.
Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asks the hearer about the notes. Ir : No problem. Just visit my home tonight or after school. Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker informs the hearer to visit her house. De : Ok. Thank you Ira.
Direct : Thanking
Literal : The speaker literally thanks the hearer.
Ir : You’re welcome. Our foods are coming, let’s eat. Direct : Informing
4.1.1.1.7 Data IV (English Department 2013) Fa : Hey, Good morning, Riah!
Kha : Hello there, Farah! Good morning.
Fa : Wow, I don’t see you very often to be in cantin this early. What makes you come so early this morning?
Kha : That’s actually fine, Farah. My house is kind of far from our Campus, I’m just afraid I would come late if I didn’t come so early.
Fa : But, I think you never come this early before, Riah. It’s just 08.00 AM now. I usually see you come to class around 08.20 AM.
Kha : Yeah, Farah. As a matter of fact, the road where I pass by the bus I take everyday to campus is now under betterment. The betterment process really disrupts the traffic condition, so I always end up trapped in traffic jam lately. Due to the traffic jam, I almost come late everyday to campus. So, during the road betterment I will come to campus earlier than before.
Fa : That’s a smart decision, Riah. You know about our campus rules, right? Kha : Yeah, you are so right, that would be awful. So, what makes you
come this early, Farah? Do you usually arrive at campus this early? Fa : Yes, Riah. I come this early to campus everyday.
Kha : Wow, what a duty! By the way, do you do all the preparation things by yourself? It must be tiring.
Fa : Heehee it won’t happen,
Kha : Heehee I thought that you have to set everything up all alone.
Fa : And… besides of my duty as a student, there are also a few things that please me to be in the campus this early.
Kha : Huh? What are those?
Fa : Humm… I think the air in here is clearer if you breathe in at this early hour. And you may also find some gauze or thin mist around the campus.
Kha : Yeah, you’re right, Vina. I do feel the air is clearer and I think I saw that thin mist you said too.
Fa : Yeah, So, coming earlier to campus isn’t bad, right? Kha : Yup, it’s not that bad.
Fa : And maybe, you could do some homework you forgot to do last night by coming early to the campus.
Fa : Oh, my! I remember I got homework I haven’t finished. I have to finish it before the bell rings. What a great talk, Vina! I’ve got to go, see you later!
Kha : Haha…See ‘ya, Farah! 4.1.1.1.8 Analysis of Data IV
Direct : Greeting
Literal : The speaker literally greets the hearer. Kha : Hello there, Farah! Good morning. Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally gives information on that dialogue.
Fa : Wow, I don’t see you very often to be in cantin this early. What makes you come so early this morning?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquiring the hearer why does hearer come early. Kha : That’s actually fine, Farah. My house is kind of far from our
Campus, I’m just afraid I would come late if I didn’t come so early. Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally Informs the hearer he was afraid to late.
Fa : But, I think you never come this early before, Riah. It’s just 08.00 AM now. I usually see you come to class around 08.20 AM.
Direct : Inforrming
Literal : The speaker literally inform about hearer information.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about speaker habit.
Fa : That’s a smart decision, Riah. You know about our campus rules, right?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer about campus rules.
Kha : Yeah, you are so right, that would be awful. So, what makes you come this early, Farah? Do you usually arrive at campus this early?
Direct : Informing
Literal :The speaker literally informs about hearer condition. Fa : Yes, Riah. I come this early to campus everyday. Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about the speaker.
Kha : Wow, what a duty! By the way, do you do all the preparation things by yourself? It must be tiring.
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally Enquires about hearer preparation the speaker absolutely wonderful about that activities.
Fa : Heehee it won’t happen,
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs that is her habitual.
Kha : Heehee I thought that you have to set everything up all alone. Direct : Informing
Fa : And… besides of my duty as a student, there are also a few things that please me to be in the campus this early.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs her duty as a student to the hearer. Kha : Huh? What are those?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires and want to know what the speaker duty. Farah : Humm… I think the air in here is clearer if you breathe in at this
early hour. And you may also find some gauze or thin mist around the campus.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs her encouragement to campus to the hearer. Kha : Yeah, you’re right.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs the hearer and the speaker absolutely wrapper about that information.
Fa : Yeah, So, coming earlier to campus isn’t bad, right? Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires to the hearer is bad goes to campus early? Kha : Yup, it’s gooooood.
Direct : Information
Fa : And maybe, you could do some homework you forgot to do last night by coming early to the campus.
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires hearer about her homework. Fa : Oh, my! I remember I got homework I haven’t finished. I have to
finish it before entering the class. Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs the hearer she want to do the homework Kha : Haha…See ‘ya, Farah!Hurry !
Direct : Ordering
Literal : The speaker Literally orders the hearer to do the homework as pas as possible.
4.1.1.1.9 Data V (English Department 2014)
Ve : I’ll just have mandi Fitri.
Fi : Fine. I’ll order it right away kak. Ve : Do you take milk with your coffee? Fi : Yes, I take it Kak.
Ve : Is everything okay here?
Fi :Yes, Everything is fine Kak. Kak I want to join my class as pas as possible kak
Ve : Very well then. Have a nice day.
Fi : Thanks ya Kak.
4.1.1.1.10Analysis of data V
Ve : I’ll just have mandi Fitri. Direct : Order
Fi : Fine. I’ll order it right away kak. Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer she will order that. Ve : Do you take milk with your coffee?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literall enquires hearer about drinking. Fi : Yes, I take it Kak.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally inform hearers to takes thar order. Ve : Is everything okay here?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer about condition.
Fi : Yes, Everything is fine Kak. Kak I want to join my class as pas aspossible kak
Direct : Informing and asking
Literal : The speaker literally informs and asks hearer he want to follow the class right now
Ve : Very well then. Have a nice day. Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer to get luck
Fi : Thanks ya Kak.
Direct : Thanking
4.1.1.1.11 Data VI (Arabic Department 2010)
An : Ila aina anta wahyu? Wa : Ila hunaka, limadza?
An : Huna anta tajlis, nasrob awanal nahnu. Wa : Na’am, ajhab amamuka.
An : Ma dza tasrob Wa : Susu dingin. Anta?
An : Ana aidon. Qul awalan maahu. Wa : Naam, Limadza anta la tadhul? An : La ba’sa. Ana kaslan.
Wa : Miroron jiddan anta huna. Laziz naam?
An : Naam, laziz jiuddan huna, Hayya alal asrob qod ta’ti sarobuna. Wa : Naam. Syukron alaika Naam.
An : Naam, la ba’sa dzalik., Wa : Ana Adkhul awalan ilal fasli. An : Tafaddol.
4.1.1.1.12 Analysis of data VI
An : Ila aina anta wahyu?
Direct : Enquiring
Wa : Ila hunaka, limadza?
Direct : Informing and Enquiring
Literal : Th speaker Literally informs and enquires him why?
An : Huna anta tajlis, nasrob awanal nahnu.
Direct : Inviting
Literal : The speaker Literally Invites the hearer to drink there.
Wa : Na’am, ajhab amamuka.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs he will join the table.
An : Ma dza tasrob?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker Literally enquires the hearer what he want to drink.
Wa : Susu dingin. Anta?
Direct : Informing and Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires the hearer what will he drink with question tag.
An : Ana aidon. Qul awalan maahu.
Literal : The speaker literally informs and orders what he will drink
Wa : Naam, Limadza anta la tadhul?
Direct : Informing and Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires why didn’t he join the class.
An : La ba’sa. Ana kaslan.
Direct : Informing
Literally : The speaker literally informs he was lazy.
Wa : Miroron jiddan anta huna. Laziz naam?
Direct : Informing and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs the hearer and enquires him.
An : Naam, laziz jiuddan huna, Hayya alal asrob qod ta’ti sarobuna.
Direct : Informing and asking
Literally : The speaker literally asks to drink because their drinking was coming.
Wa : Naam. Syukron alaika Naam.
Direct : Thanking
Literally : The speaker literally thanks to hearer.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs
Wa : Ana Adkhul awalan ilal fasli.
Direct : Informing and asking
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer he want to join the class.
An : Tafaddol.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer to join the class before.
4.1.1.1 .13Data VII (Arabic Department 2011)
Su : Kaifahalukahi?
Au : Bilkhoir, madzata’malhuna? Su : Saasrobanasohib, anta ilaaina? Au : Ilahunashohib, Madzatasrob? Su : Manisdinginsohib, anta madza? Au : sawaaidonshohib.
Su : aidarsin anta atdkhulba’dinakhi? Au : Filsafatakhi. Anta?
Su : Terjemahanakhi. Ai saah anta tadkhulahki? Au : Sa’atuttasiakhi, anta?
Su : Sawaaidon.
Su : Laziz, Liannanahnunataalamkaifaqolafilhadits, utlubulilmaminal Mahdi ilallahdi, shohikanakhi?
Au :Shohihjiddan. Mahirjiddan anta al-an akhi. Su : AKKKKhh, Wolesazalahakhi.
Au : Hayya ‘alas sarbi, qodja a sarbina. Su : Hayya.Ba’dataallum anta ilaaina? Au : Ilabaitiakhi, Limadz s tadba’ anta? Su : Laa. Saas al faqod.
Au : Owhhh. Okelahakhi, anaawwalanakhinaam, liana dosen fi hadzalyaumbahayaizanataakkhorakhi.
Su : OK. Akhitafaddol.
4.1.1.1.14 Analysis of data VII Su : Kaifahalukahi? Direct : Enquiring
Literally : The speaker literally enquires about hearer news. Au : Bilkhoir, madzata’malhuna?
Direct : Information and Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires hearer doing. Su : Saasrobanasohib, anta ilaaina?
Direct : Informing and enquires
Literal : The speaker literally informs his job and enquires the hearer will do. Au : Ilahunashohib, Madzatasrob?
Direct : Order and enquires
Literal : The speaker literally order and enquires what the hearer drink. Su : Manisdinginsohib, anta madza?
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquirewhat the hearer drink too. Au : Sawaaidonshohib.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs about order. Su : Aidarsin anta atdkhulba’dinakhi?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires about the subject. Au : Filsafatakhi. Anta?
Direct : Informing and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires with anta. Su : Terjemahanakhi. Ai saah anta tadkhulahki?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires to the hearer. Au : Sa’atuttasiakhi, anta?
Direct : Informing and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires the hearer. Su : Sawaaidon.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally Informs the hearer about the time to join the class. Au : Kaifafakkartamahasiswasohib?`
Direct : Enquires
Literal : The speaker literally enquires the hearer about student.
Su : Laziz, Liannanahnunataalamkaifaqolafilhadits, utlubulilmaminal Mahdi ilallahdi, shohikanakhi?
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about student to the hearer. Au :Shohihjiddan. Mahirjiddan anta al-an akhi.
Direct : Supporting
Literal : The speaker literally supports about that answer. Su : AKKKKhh, Wolesazalahakhi.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs to keep quite. Au : Hayya ‘alas sarbi, qodja a sarbina.
Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asking hearer to drink Su : Hayya.Ba’dataallum anta ilaaina?
Direct : Inviting and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer doing after join the class. Au : Ilabaitiakhi, Limada sa tadba’ anta?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires activities after class. Su : Laa. Saas al faqod.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs that is just a question. Au : Owhhh. Okelahakhi, anaawwalanakhinaam, liana dosen
fi hadzalyaumbahayaizanataakkhorakhi. Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asking to hearer he wants to join the class. Su : OK. Akhitafaddol.
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer to wait.
4.1.1.1.15 Data VIII (Arabic Department 2012) Nur : Halooakhi, ilaaina anti?
Fit : Ilalfashli, Limadzaukhti?
Nur : La ba’sa, huna anta ukhti, nasrob au aklawalannahnuqoblanajhabilalfasli. Fit : Okelahukhti, Maaman anti hunahanifan?
Nur : Binafsiukhti, Limadza?
Fit : La ba’sa, miroron anti hunabinafsika?
Nur : Laauti, hadzafaqodbinafsi, qoblahumaaashabina. Fit : Madzata’kuliinaukhti?
Nur : Akaltuukhti, anti faqodlaaba’saanaanjuurukifaqod. Fit : Shohih anti limadza?
Nur : Shohihhhhh. Laasrob Kaman ana, sarobtuhanifanfilbaiti. Fit : la lazizz anti, anaa’murmaa’kimandinaam?
Nur : Laaaa, Lauridanaukhti.
Fit : Laaba’saanaadfakmaakiba’din. Nur : Kholasshohib.
Fit : Oke, liana atilaturdiinahayyailalfsalimaaashabina. Nur : Hayaashohib. Limadza anti la tasrobiina?
Fit : Lianna anti la tasrob, walakinsaatuhulimuqolatiddurus. Hayyaba’dinfaqdba’ da nataallamnahnunajhab Kaman ilahunalinasrobwanakul.
Nur : Okelahukhti. Suqronalannasihatuki.
Literal : The speaker literally greet and enquires where the hearer dos go. Fit : Ilalfashli, Limadzaukhti?
Direct : Informing and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally Informs and enquiring why.
Nur : La ba’sa, huna anta ukhti, nasrob au aklawalannahnuqoblanajhabilalfasli. Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker Literally Asks hearer to company at the canteen. Fit : Okelahukhti, Maaman anti hunahanifan?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer who did company him Nur : Binafsiukhti, Limadza?
Direct : Informing and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires why. Fit : La ba’sa, miroron anti hunabinafsiki?
Direct : Information
Literal ; The speaker literally informs hearer seldom join the class. Nur : Laaukhti, hadzafaqodbinafsi, qoblahumaaashohibina. Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer with her her friend before. Fit : Madzata’kuliinaukhti?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires what she want to eat. Nur : Akaltuukhti, anti faqodlaaba’saanaanjuurukifaqod. Direct : Information
Fit : Shohih anti limadza? Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires about hearer.
Nur : Shohihhhhh. Laasrob Kaman ana, sarobtuhanifanfilbaiti. Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer she will not order anything. Fit : La lazizz anti, anaa’murmaa’kimandinaam?
Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asks hearer abou drinking Nur : Laaaa, Lauridanaukhti.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally Informs She will not order anything. Fit : Laaba’saanaadfakmaakiba’din.
Direct : Offering
Literal : The speaker literally offers hearer drinking Nur : Kholasshohib.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs she will not drink anything. Fit : Oke,thanks
Nur : Hayaashohib. Limadza anti la tasrobiina? Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer why did not drink.
Fit : Lianna anti la tasrob, walakinsaatuhulimuqolatiddurus. Hayyaba’dinfaqdba’ da nataallamnahnunajhab Kaman ilahunalinasrobwanakul.
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about time to join the class. Nur : Okelahukhti. Suqronalannasihatuki.
Direct : Thanking
Literal : The speaker literally thanks to hearer because giving information.
4.1.1.1.17 DataIX (Arabic Department 2013)
Ud : Ma ta’ mal huna? Limadza laa tas rob au takkul? Fa : Ajlis faqod, Maafi fulusi.
Ud : La ba’sa ana adfa’ anta ba’din, qul faqod maa tasrob. Fa : Sa asrob manis dingin laa ba’sa.
Ud : Taddol akhi, laa ba’sa dzalik, qul maaha awwalan sawa nahnu, Fa : Naam akhi, buddan awalan saajhab ila hunaka.
Ud : Naam, Tafaddol akhi. Fa : Kasir fulusuka naam akhi?
Ud : Laa, maujud qolil. Limadza akhi? Fa : Saastair fulusaka shohib.
Ud : Kam akhi?
Fa : Khomsuna faqod, maafi fulusi kaman akhi. Ud : Limadza yas tati’ kadzalik?
Fa : Amsih Do,a fulusii fil baiti liaanna dzalik mafi kaman fulusi. Ud : Idfa’ sarbina hadza shohib, khuz maaka khomsuna
Fa : Syukron katsiron naam shohib.
Ud : Syukron aidon, walakin laisa misla dzalik, anta shohibi.
4.1.1.1.18 Analysis of Data IX
Ud : Ma ta’ mal huna? Limadza laa tas rob au takkul? Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally Enquires what did hearer did and what did hearer want to eat and drink.
Fa : Ajlis faqod, Maafi fulusi. Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer he doesn’t drink becaue of money. Ud : La ba’sa ana adfa’ anta ba’din, qul faqod maa tasrob.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs want to pay hearer. Fa : Sa asrob manis dingin laa ba’sa.
Direct : Requesting
Literal : The speaker Literally Request cool drink
Ud : Taddol akhi, laa ba’sa dzalik, qul maaha awwalan sawa nahnu, Direct : Giving
Literal : The speaker literally gives hearer and the speaker order to hearer to buy that drinking. Fa : Naam akhi, buddan awalan saajhab ila hunaka.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally inform to wait for a while. Ud : Naam, Tafaddol akhi.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer of waiting that order. Fa : Kasir fulusuka naam akhi?
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer about money, he wants to borrow hearer’s money. Ud : Laa, maujud qolil. Limadza akhi?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literal inform and enquires why. Fa : Saastair fulusaka shohib.
Direct : Request
Literal : The speaker literally requests about hearer’s money Ud : Kam akhi?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires how much money wants to borrow. Fa : Khomsuna faqod, maafi fulusi kaman akhi.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer amount of money. Ud : Limadza yas tati’ kadzalik?
Direct : Enquires
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer what happen with him. Fa : Amsih Do,a fulusii fil baiti liaanna dzalik mafi kaman fulusi. Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer cause of money. Ud : Idfa’ sarbina hadza shohib, khuz maaka khomsuna Direct : Order
Literal : The speaker literally orders hearer to pay their drinking and take money. Fa : Syukron katsiron naam shohib.
Direct : Thanking
Ud : Syukron aidon, walakin laisa misla dzalik, anta shohibi. Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer take it easy.
Fa : Maafi nazortu insan mislaka shohib, anta khoir mai, syukron shohib. Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer behavior. Ud : Hayya ilal fasli insa’ dzalik.
Direct : Invite
Literal : The speaker literally invite hearer to go to class.
4.1.1.1.19 Data X (Arabic Department 2014) Fi : Kaifa haluk siti?
Si : Khoir, qodim laa ta’kuliina anti huna. Fi : Naam ana adbakh fi baitii, anti kaifa? Si : Ana aidon, hayya nasrob, madza maaki? Fi : Ana martabe, Anti madza?
Si : Ana juz jeruk. Aina allan baituki? Fi : Fi pajak sore Padang bulan, Aroti?
Si : Laarif aina baituki al an, man shohibuki hunaka?
Fi : Maujud min qoryati, ba’da taalum najhab ila hunaka turidiina? Si : Hayya, maujud film baru laki?
Fi : Maujud, hayya nusahid jamaatan.
Si : Hayya, walakin Mur awwalan lana, kaifa ba’din laa nasrob, khoiru laziz. Fi : Naam, wait for a while,.
Si : Anti tastati billugoh arabiah naam.
Si : Owhhh,, Kadazalik. Kaifa khobar habibuki? Fi : Halahh, nahnu qod nantaqil, khoiru laziz maahu, Si : Limadza?
Fi : Liaana hua playboy, kasir jiddan habibatuhu. Si : Anti kaifa?
Fi : Ana maafi, lianna ana qobih layuurid waladun alayya. Si : Layumkin, anti laaturidiina dzalik.
Fi : Hahha,, Kholas, hayya nasrob,.
Si : Tastahyiina anti, Hayya, laurid ana anjuruki hazinun. Fi : Syuqron, hayya nasrob, la tata kallamiina kaman. Si : Naam shohib.
4.1.1.1.20 Analysis of Data X Fi : Kaifa haluk siti?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer condition
Si : Khoir, qodim laa ta’kuliina anti huna.
Direct : Information and Inviting
Literal : The speaker literally enquires and invites hearer to company him in the cantin
Fi : Naam ana adbakh fi baitii, anti kaifa?
Direct : Information
Si : Ana aidon, hayya nasrob, madza maaki?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer what will she drink.
Fi : Ana martabe, Anti madza?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs his order to hearer and enquires to hearer’s drinking.
Si : Ana juz jeruk. Aina allan baituki?
Direct : Information and Enquires
Literal : The speaker literally informs his order.
Fi : Fi pajak sore Padang bulan, Arofti?
Direct : Informing and Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about her place.
Si : Laarif aina baituki al an, man shohibuki hunaka?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires her friends in at that rent home.
Fi : Maujud min qoryati, ba’da taalum najhab ila hunaka turidiina?
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires hearer did she want to follow to that rent home.
Si : Hayya, maujud film baru laki?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires about new film want to watching at that rent home.
Fi : Maujud, hayya nusahid jamaatan.
Direct : Inviting
Literal : The speaker literally invites hearer to watch together.
Si : Hayya, walakin Mur awwalan lana, kaifa ba’din laa nasrob, khoiru laziz.
Direct : Informing
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about their orders.
Fi : Naam, wait for a while,.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer wait for while.
Si : Anti tastati billugoh injiliziah naam.
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires about her ability in English.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker informs hearer she cannot about English
Si : Owhhh,, Kadazalik. Kaifa khobar habibuki?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires about hearer partner condition.
Fi : Halahh, nahnu qod nantaqil, khoiru laziz maahu.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about that is was the end.
Si : Limadza?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer what is the problem.
Fi : Liaana hua playboy, kasir jiddan habibatuhu.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about the problem.
Si : Anti kaifa?
Direct : Enquiring
Fi : Ana maafi, lianna ana qobih layuurid waladun alayya.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer she don’t have a boyfriends
Si : Layumkin, anti laaturidiina dzalik.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer that is not true about her boyfriend.
Fi : Hahha,, Kholas, hayya nasrob.
Direct : Invite
Literal : The speaker literally invites hearer to drink.
Si : Tastahyiina anti, Hayya, laurid ana anjuruki hazinun.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer is shy.
Fi : Syuqron, hayya nasrob, la tata kallamiina kaman.
Direct : Thanking and inviting
Literal : The speaker literally thanks and invites hearer to drink
Si : Naam shohib.
Literal : The speaker literally informs and let them drink.
4.1.1.1.21 Data XI (Japanese Department 2010) Japanese Department 2010
Go : Haji matte dai ga kune atta toki, o mae ga kou touda. Omoea dasita? Fa : Ha,,. Sore o omoee dasune, omaega taberu? No mu?
Fa : A maku te tsu metae o chao o nonde go hangto sakana o ta beru. Go : Wata shimo sou, omaega chu mong site
Fa : Okee, cotto matene.
Go : To ko ro de itsu sot su gyo suru tsu mori da
Fa : Ma tad a wa ka ta nai ke do, ko toshi no nachi gat su mi sot su gyo su ru tsumori gyo pa o mae wa.
Go : Bo ku ga, ma da ta ku sung ji gyo a tori kae tsana kya na re nai. Fa : To ku bet sui no sikong u kate, mino ten suu wa hya ku go nuu rupiah. Go : Ja, mata kang gae ru. Omae eno seise kiwa na ni.\
Fa : 3,20
Go : So re ga ii yo.
Fa : Sonna ko to luna, issho ni sot su gyo su ru yo. Go : Ja, ta be to kou mo harage he ta
Fa : Sou shi you.
4.1.1.1.22 Analysis of Data XI (Japanese Department 2010)
Go : Haji matte dai ga kune atta toki, o mae ga kou touda. Omoea dasita? Direct : Information
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer cause of that information, the speaker really didn’t like to remind its again.
Go : Ha,,. Sore o omoee dasune, omaega taberu? No mu?
Direct : Order
Literal : The speaker literally orders hearer to get that order as pas as possible.
Fa : A maku te tsu metae o chao o nonde go hangto sakana o ta beru. Direct : Information and order
Literal : The speaker literally Informs and orders hearer to order that order to saler. Go : Wata shimo sou, omaega chu mong site
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer to wait a moment Fa : Okee, cotto matene.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs he wait that Go : To ko ro de itsu sot su gyo suru tsu mori da? Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer and speaker really want to know when the hearer to get graduation.
Fa : Ma tad a wa ka ta nai ke do, ko toshi no nachi gat su mi sot su gyo su ru tsumori gyo pa o mae wa.
Direct : Information
Direct : Order
Literal : The speaker literally orders hearer to get a past examination
Fa : To ku bet sui no sikong u kate, mino ten suu wa hya ku go nuu rupiah. Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer abou the fee Go : Ja, mata kang gae ru. Omae eno seise kiwa na ni? Direct : Reject and enquires
Literal : The speaker literally reject that information and replays to another quiestion.
Fa : 3,20
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs about his score. Go : So re ga ii yo.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally happy hear that information. Fa : Sonna ko to luna, issho ni sot su gyo su ru yo. Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer they will be luck together. Go : Ja, ta be to kou mo harage he ta
Direct : Order
Literal : The speaker literally orders hearer cause the speaker was hungry. Fa : Sou shi you.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs and let the hearer to eat.
She : Mou ta be ta no? Pu : Mou ta be ta nande? She : O mae o ae shi tai
Pu : Bou ku ga no mi mo no wa chu mong suru. She : Sou ka, bo ku a ma ku te su me tai ocha. Pu : Bo ku no chu mong wa, cappuccino. She : Ja, chu mong shi yo nande ta be nai Pu : Sakki, mou ta be ta.
She : Do ko de ta be ta.
Pu : Ko ko data yo, o mae ga a be ru no go os kai yo. She : He,he, Fut sun a wa bo ku ga, konna ji kang nit a be tu. Pu : O mae no chu mong ga kita
She : O,, soka ja ta beo o
Pu : Okee, aishi te ku re te arigatone She : Iee,iee.
4.1.1.1.24 Analysis of Data XII She : Mou ta be ta no? Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer. Pu : Mou ta be ta nande?
Direct : Information and enquire
Literal : The speaker literally informs and he enquires why to the hearer. She : O mae o ae shi tai
Direct : Information
Pu : Bou ku ga no mi mo no wa chu mong suru. Direct : Information and asking
Literal : The speaker literally informs and asking his friend to order the drinking. She : Sou ka, bo ku a ma ku te su me tai ocha.
Direct : Order
Literal : The speaker literally orders hearer to say that to the seller. Pu : Bo ku no chu mong wa, cappuccino.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about his order She : Ja, chu mong shi yo nande ta be nai
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer why didn’t eat Pu : Sakki, mou ta be ta.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer he was eaten. She : Do ko de ta be ta.
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer about the place he get eaten before. Pu : Ko ko data yo, o mae ga a be ru no go os kai yo.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs he eat at that place before. She : He,he, Fut sun a wa bo ku ga, konna ji kang nit a be tu. Direct : Information and order
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about that order also. She : O,, soka ja ta beo o
Direct : Order
Literal : The speaker literally order hearer to eat. Pu : Okee, aishi te ku re te arigatone
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally want to eat She : Iee,iee.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally lets the hearer to eat.
4.1.1.1.25 Data XIV (Japanese Department 2012) Fe : Do koe ku no, Sho ku de de sa be rou Ar : E’, iko ubp kwa ta be tai.
Fe : Na ni o ta be tai? Ar : Go hang to sakana.
Fe : Na nio nomu, isshp ni shii mon suru. Ar : Sume tae mi ru ku da.
Fe : Chotto matte ne, chu mong shitoku kata ne, nan de? Ar : E,,, ki nou mondai ga atta.
Fe : Donna nandae ? na jae hana sa ha katta no? Ar : Nande mo nai mou o watta.
Fe : Souka chuu mong shitta tae be mo no ga kita, ja tabeyou? Ar : Sou, Ta be te ka ra do koe I kuno
Ar :Nande mo nae? Dai ga ku nig a ku ni go go ma de iru to o motta da.
Fe : Iie, dai ga ku no juku ni sang ka shi nai de fu dang no juu gyo u da ke sangka su ru. Ar : Souka
4.1.1.1.26 Analysis of Data XII
Fe : Do koe ku no, Sho ku de de sa be rou Direct : Enquiring and order
Literal : The speaker literally enquires and order hearer to follow him at that canteen Ar : E’, iko ubp kwa ta be tai.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs he want to eat Fe : Na ni o ta be tai?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer what will order Ar : Go hang to sakana.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs abou his order Fe : Na nio nomu, isshp ni shii mon suru. Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer he just want to drink Ar : Sume tae mi ru ku da.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literal informs hearer he will order the seller about that. Fe : Chotto matte ne, chu mong shitoku kata ne, nan de?
Literal : The speaker literally informs about his drinking Ar : E,,, ki nou mondai ga atta.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer to wait as pas as posiible. Fe : Donna nandae ? na jae hana sa ha katta no?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires Hearer about the day before. Ar : Nande mo nai mou o watta.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about problem before. Fe : Souka chuu mong shitta tae be mo no ga kita, ja tabeyou? Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires about the problem Ar : Sou, Ta be te ka ra do koe I kuno
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer his problem was clear. Fe : Su gu kaeru nande?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer about his activities after eating Ar :Nande mo nae? Dai ga ku nig a ku ni go go ma de iru to o motta da. Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about his activities.
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer he just follow the subject at the campus no external campus, after the class directly go home.
Ar : Souka Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer not problem about that. 4.1.1.27 Data XIV ( Japanese Department 2013)
Ha : Woy, kocchinikoe !
Mu : Nandekurastuni hair a nai no.
Ha : She. Wasakkikurasuganakatta. Koregamesseji, ko de ingshushoku, dhiyou? Mu : Soushi you gengkika, omae?
Ha : E. bokwatsu matte no mi mono o chuumongsuru Medan wakontoyniatsuui. Mu : souka? Kono ta bi o maewadokkoniita ho ka.
Ha : Ni hon da zo, zoudandayo. Co wa at sui wake da ne. Mu : O maewatsu me tai no mi mono o chuumongsuruyo ne. Ha : sou, Tsu me tai no me mono
Mu : Ta be mono wa? Isshunichuumongsuruyo Ha : Iya, mou ta be ta yo. Dai gakuwadou Mu : Ii yo. Kitai ho you da.
Ha : dou, site ?riyo shin o kangaeteyo.
Mu : Sakkimuukangaeteta no de kyoudaegakunikitanda Ha : Iizo
Mu : Dai gakuniiku no o maji me ninaru you mi tippusougashiete. Ha : Dai gakuniiku no o maji me ninaru you nitippusu o gashiette. Mu : Tpiiusuganaeyo de modaigakwa nib a me no ie da to omou Ha : souka? Deng sou, arigatho
4.1.1.1.28 Analysis of data XV (Japanese Department 2013)
Ha : Woy, kocchinikoe !
Direct : Calling
Literal : The speaker literally calls the hearer when the hearer walks through in front of the canteen.
Mu : Nandekurastuni hair a nai no.
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer what they want to do.
Ha : She. Wasakkikurasuganakatta. Koregamesseji, ko de ingshushoku, dhiyou?
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer information of the class
Mu : Soushi you gengkika, omae?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires about condition of hearer.
Ha : E. bokwatsu matte no mi mono o chuumongsuru Medan wakontoyniatsuui.
Direct : Asking and informing
Mu :Souka? Kono ta bi o maewadokkoniita ho ka.
Direct : Enquiring and mocking
Literal : The speaker literally enquires and mocking he is crazy the speaker does not mean literally about the style of that language.
Ha : Ni hondazo, zoudandayo. Co wa at sui wake da ne
.Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about his place with the kidding.
Mu : O maewatsu me tai no mi mono o chuumongsuruyo ne.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about their order at that canteen.
Ha : Sou, tsu me tai no me mono
Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally ask about the cold drinking.
Mu : Ta be mono wa? Isshunichuumongsuruyo
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer about lunch.
Ha : Iya, mou ta be ta yo. Dai gakuwadou
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer he was eaten before and he does not eat again. Mu : Ii yo. Kitai ho you da.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about academic condition.
Ha : Dou, site ?riyo shin o kangaeteyo.
Direct : Reprimanding
Literal : The speaker literally reprimand the hearer that he vey care about his friend.
Mu : Sakkimuukangaeteta no de kyoudaegakunikitanda
Direct : Pleading
Literal : The speaker literally pleads himself to hearer that he is coming to campus.
Ha : Iizo
Direct : Supporting
Literal : The speaker literally supports hearer about hearer information.
Mu : Dai gakuniiku no o maji me ninaru you mi tippusougashiete.
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires about hearer tips on the campus..
Mu : Tippusuganaeyo de modaigakwa nib a me no ie da to omou.
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer the campus is his second house.
Ha : Souka? Deng sou, arigatho
Direct : Thanking
Literal : The speaker literally thanks the hearer for being so kind to him.
Mu : Bo kwabokiyachigaishoni sot sugyoshitai. No ni mono gakita. No mou.
Direct : Exhorting and asking
Literal : The speaker literally exhorts the hearer to tell about graduation and asks hearer to drink.
Ha : No mou. No dogaka wait a ne.
Direct : Inviting
Literal : The speaker literally invites hearer to drink.
4.1.1.1.29 Data XV (Japanese Department 2014)
Fe : Do komoikanai de yo no mi nageranamikadhukudaenitsuitesoudanshi tai. Ri : E. nannoshukudai? Me zuurashiina.
Fe : Bo kwanihong go gawakaranaiyo. Haji mette ben kyousurukara.
Ri : Souka, bo kun go o naji day o daiji ne no wa ben kyousuruyo, nani p no mi tai? Fe : Tsu me taiocha o no mitaibokugaka o maegachuumongsuru
Ri : Bo kuyo. Chotto matte chuumongsuruka ro.
Fe : Ni kong go gokkaichi bang me no sam ta kugotta no? Ri : Sou, o mae wan am bang me ka?
Fe : Sambang me
Fe : Ho nittuemonihong go gakkani, zeni hair u to omotta.
Ri : Ii ne, dokkonimo hair u ka a manikinishinaidaeyp do koiyo,hoka no ko to ka n gaenai de Fe : Tsou ho ka no ku to kannai, to kuni ho kanodaigakuniuturu.
Ri : Ii yooma e no hanashi kite motto moeteru Fe : No mi maogakitayo. No mou.
Ri : E. No mou.
4.1.1.1.30 Analysis of data XVII (Japanese Department 2014)
Fe : Do komoikanai de yo no mi nageranamikadhukudaenitsuitesoudanshi tai.
Direct : Calling and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally calls hearer to come to him and enquires homework.
Ri : E. nannoshukudai? Me zuurashiina.
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer about what homework.
Fe : Bo kwanihong go gawakaranaiyo. Haji mette ben kyousurukara.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about his problems in the campus.
Ri : Souka, bo kun go o naji day o daiji ne no wa ben kyousuruyo, nani p no mi tai?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Fe : Tsu me taiocha o no mitaibokugaka o maegachuumongsuru
Direct : Asking and Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally asks and enquires who want to buy their order.
Ri : Bo kuyo. Chotto matte chuumongsuruka ro.
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires about the first choice in that campus.
Fe : Ni kong go gokkaichi bang me no sam ta kugotta no?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires hearer about his choice.
Ri : Sou, o mae wan am bang me ka?
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about his score.
Fe : Sambang me
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about his score
Ri : Icchi bang ne ni sent a kwanani?
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer about his choice.
Fe : Ho nittuemonihong go gakkani, zeni hair u to omotta.
Direct : Information and pleading
Literal : The speaker literally informs and pleads about his choice.
Ri : Ii ne, dokkonimo hair u ka a manikinishinaidaeyp do koiyo,hoka no ko to ka n gaenai de
Direct : Pleading
Literal : The speaker literally pleads hearer information before.
Fe : Tsou ho ka no ku to kannai, to kuni ho kanodaigakuniuturu.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearers he will be there until graduate.
Ri : Ii yooma e no hanashi kite motto moeteru
Direct : Pleading
Literal : The speaker literally pleads hearer about his opinion.
Fe : No mi maogakitayo. No mou.
Direct : Supporting
Literal : The speaker literally supports hearer about his answer.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer he is very happy cause hear that language.
4.1.1.1.31 Data XVII (Chinese Department 2010) Ed : Zhongchao, yi hun, you wo he shenme?
Sup : Shi dang women wancheng hou, lin - nu daxuesheng tai zao gao liao shishibingfei ruci. Ed : Wo xie 8 ge yue jihua.
Sup : Ge yue, wo xiele yige jihua, zhishi geile women?
Ed : Wo xiang zizai - xiang aja, ziiran wo hai mei zhunbei hao jianyi. Su : Owhh,Kebutlah, rang women mei geren
Ed : Wo yijing zhege qiye, ni zai nali? Su : Hao yijing ACC?
Ed : Hai meiyou, wo hai kanguo yi ben shu, du perputakaan. Ed : Hao, he lu shi ni ma?
Su : Wo he nurdin xie dao.
Ed : Bentar shi de, wo de di yi xiang yiian.
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer to waitb him Su : Oke – Oke
Ed : Rencananya ni xiang gongzuò zai nali?
Su : Wo xiang caiqu yexie jiaoya, rang pian jiao zai cunli, wo yong. Ed : Owhh, ni de zhiye sengya xianran shanyao wohai zai piao. Su : Suizhe ta de yiqie.
Ed : Zhe hen rongyi - wo xiwang ni hui xihuan. Su : Āmen, ni xiang chee ngwei yi ming jiaoshi ma?
Ed : Shi a, shubu xiwang jintian de gongzuo, renhe shihou wo xiang chengwei yi ming laoshi.
Su : Ń, meiyou she me, ku man hen kuai wo jiu xiang qu deng wo de pengyou shanyao, yinwei wo laile.
Ed : Owh, meiyou she me, zhe shi hen zhongyao de, wome di yi. Su : Haole, ni zenme ba laike?
Ed : Shide, wo xiang zhe baleklah, ruguo shi dehua wo de yian shi kending de. Su : Hao ba,TTDJ
Ed : Ya, aku mau baleklah ini, kalau gitu aku gerak dulu ya. Su : Oke, TTDJ
Ed : Xiexie.
4.1.1.1.32 Analyis Of Data XVIII(Chinese Department 2010) Ed : Zhongchao, yi hun, you wo he shenme?
Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asks hearer to company him.
Sup : Shi dang women wancheng hou, lin - nu daxuesheng tai zao gao liao shishibingfei ruci.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearers when get graduation.
Ed : Wo xie 8 ge yue jihua.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about graduation.
Sup : Ge yue, wo xiele yige jihua, zhishi geile women?
Direct : Information and asking
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer and asks him to get graduate together.
Ed : Wo xiang zizai - xiang aja, ziiran wo hai mei zhunbei hao jianyi.
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about his desire.
Su : Owhh,Kebutlah, rang women mei geren
Direct : Supporting
Literal : The speaker literally supports hearers to get graduate together.
Ed : Wo yijing zhege qiye, ni zai nali?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires about hearer’s thesis.
Su : Hao yijing ACC?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about his thesis.
Ed : Hai meiyou, wo hai kanguo yi ben shu, du perputakaan.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about his condition.
Ed : Hao, he lu shi ni ma?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires about his drinking
Su : Wo he nurdin xie dao.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about his order.
Ed : Bentar shi de, wo de di yi xiang yiian.
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer to waitb him
Su : Oke – Oke
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer wait him.
Ed : Rencananya ni xiang gongzuò zai nali?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer about job in the future.
Su : Wo xiang caiqu yexie jiaoya, rang pian jiao zai cunli, wo yong.
Direc : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearers about the job.
Ed : Owhh, ni de zhiye sengya xianran shanyao wohai zai piao.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer is tremendous.
Su : Suizhe ta de yiqie.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer that is same.
Ed : Zhe hen rongyi - wo xiwang ni hui xihuan.
Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asks hearer to get the same profit
Su : Āmen, ni xiang chee ngwei yi ming jiaoshi ma?
Literal : The speaker literally enquires about the teacher.
Ed : Shì a, shubu xiwang jintian de gongzuo, renhe shihou wo xiang chengwei yi ming laoshi.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer he wish he was a teacher.
Su : Ń, meiyou she me, ku man hen kuai wo jiu xiang qu deng wo de pengyou
shanyao, yinwei wo laile.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about their order.
Ed : Owh, meiyou she me, zhe shi hen zhongyao de, wome di yi.
Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asks hearer to talking together.
Su : Haole, ni zenme ba laike?
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer he can’t this time to talking so much because his friend will come to his house.
Ed : Shide, wo xiang zhe baleklah, ruguo shi dehua wo de yian shi kending de.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer no problem about that.
Su : Hao ba,TTDJ
Direct : Enquiring
Ed : Ya, aku mau baleklah ini, kalau gitu aku gerak dulu ya.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer he wants to go home as pas as possible.
Su : Oke, TTDJ
Direct : Warning
Literal : The speaker literally warns hearer to be careful on the way.
Ed : Xiexie.
4.1.1.1.33 XX Data Chinese Department 2011 Da : Hai, you jiushi: You she me gushi ma? Yog : Shì de, gini gini ajalah, bushi yige gushi. Da : Ruguo xie zhege,koq hen shao kesuxing. Yog : Shi de, wo yizhi wufa chenghao
Da : Du putong, ni anshi wo renwei Yog : Bu, wo bushi anshi ni
Da : Wo xie de biaoti buneng fangsong.
Yog : Ta, zi ran da xin de quanli, women yao wancheng suoyou, Da : Wo ye juede er shi caiqu dandu yige qingsong
Yog : Ni xiang he shenme yang de gushi shi, zhang - zhang de gushi jue jue jue yinjiu Da : Wo he cappucion aja.
Yog : Hao ba zhishi geile women, shui zhege mingling? Da : Wo!
Yog : Okeee, qing.
Da : Danshi wo yijing zhunbei hao zhi yin jia, shi de, henduo shihou wo xi kesi Yog : Ta, zhe shi hen zhongyao de yinliao xian xie dao.
Yog : Hao ba zai lushàng-Okay xiaoxin mei cuo Da : Duoxie.
4.1.1.1.34 Analysis Of Data XXI (Chinese Department 2011) Da : Hai, you jiushi: You she me gushi ma?
Direct : Calling and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally clalls and enquires about hearer condition
Yog : Shì de, gini gini ajalah, bushi yige gushi.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about his condition as usually
Da : Ruguo xie zhege,koq hen shao kesuxing.
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer where is him before
Yog : Shi de, wo yizhi wufa chenghao
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer hi was lazy cause of the title of the thesis
Daa : Du putong, ni anshi wo renwei
Direct : Mocking
Literal : The speaker literally mocks hearer. The speaker does not mean literally mocks hearer.
Yog : Bu, wo bushi anshi ni
Direct : Protesting
Da : Wo xie de biaoti buneng fangsong.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer he doesn’t get title
Yog : Ta, zi ran da xin de quanli, women yao wancheng suoyou,
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer about their friend will graduate.
Da : Wo ye juede er shi caiqu dandu yige qingsong
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer that he wish he was graduate as pas as possible.
Yog : Ni xiang he shenme yang de gushi shi, zhang - zhang de gushi jue jue jue yinjiu
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer about their drinking
Da : Wo he cappucion aja.
Direct : Information and Asking
Literal : The speaker literally informs and asks hearer about his order.
Yog : Hao ba zhishi geile women, shui zhege mingling?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires who will order that.
Da : Wo!
Direct : Information
Yog : Okeee, qing.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer to get that message as pas as possible.
Da : Danshi wo yijing zhunbei hao zhi yin jia, shi de, henduo shihou wo xi kesi
Direct : Asking and Information
Literal : The speaker literally asks and informs hearer that he will go go home as pas as possible.
Yog : Ta, zhe shi hen zhongyao de yinliao xian xie dao.
Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asks hearer to drink before going home.
Da : Women yijing wancheng di yici heju, wo ba laike ba?
Direct : Information and asking
Literal : The speaker literally informs and asks him to get out from that place.
Yog : Hao ba zai lushàng-Okay xiaoxin mei cuo
Direct : Information
]Literal: The soeaker literally informs hearer be careful on the way
Da : Duoxie.
Direct : Thanking
Literal : The speaker literally thanks hearer because him so kind to him.
4.1.1.1.35 Analysis Of Data XXII (Chinese Department 2012) Put : Ni dinggoule shenme?
Put : Ba wo leng duzi yiren, ni de gongzuo shi ruhe wancheng AQUA? Suc : Wo yijing wancheng, fanyi renwu?
Put : Ta, qinfen yy ci zhixing renwu ba?
Suc : Halahh,, zhengchang zai shihe xinqing dehua, ni hai meiyou shuo wan, sihu? Put : Jin wan wo zuo de shiqing, jiu ni shuo tongyang de yinliao, xiongdi?
Suc : Ta jiandan de zaici de daolai, zhexie haocai ni qu bu qu? Put :Wo xiang pajus zai li na.
Suc :Xiang gouwu baba, ni zai nali?
Put : Wo xiang mai xie, wo de xiezi yijing kaishile zhege posui de yuanyin. Ni yao qu nali? Suc : Wu huilai ajalah shi de, wo ganjue bushufu, yin wei bushi you shi shenme?
Put : Ta, bushi wo xiang ni yao zaodian lai.
Suc : Zhe shi zenme hui shi ge men. Zhe bi qian shi bu cunzai. Put : Halahhh, ni ya suoyi, wo taunyale henduo qian.
Suc : Meiyou la shuo, women da xin dinggou ci yuehui, rang women xian he, mingtian nidedao shenme ne?
Put :Danshi mingtian women bu hui qu yesu, dan shangsheng. Suc : Aduhh, ni gangcai shuo yihou wo de xinxi shi de ganxie. Put : Wo yijing o zhuyì SI na, zenme yang, women de yundong? Suc : Yundong shi ruci.
Put : Jianyao ya rang wo xian fu qian.
Suc :Hao ba, name wojia luan ya, zaiijian jiedao he anquan gouwu. Put : Lebay bei hupo xian ni, hao ba shi de
4.1.1.1.36 Analysis Of Data XXIII (Chinese Department 2012) Put : Ni dinggoule shenme?
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer about her order.
Suc : Wo xiang mubei zhi fang ru pokat shi de, ni dianle shenme?
Direct : Asking and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally asks and enquires what will she order.
Put : Ba wo leng duzi yiren, ni de gongzuo shi ruhe wancheng AQUA?
Direct: Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally Informs and enquires hearer about the homework.
Suc : Wo yijing wancheng, fanyi renwu?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs and enquires about her home work was finished
Put : Ta, qinfen yy ci zhixing renwu ba?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer that she is deligent.
Suc : Halahh,, zhengchang zai shihe xinqing dehua, ni hai meiyou shuo wan, sihu?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer that her homework.
Put : Jin wan wo zuo de shiqing, jiu ni shuo tongyang de yinliao, xiongdi?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer she will do that homework tonight and enquires about their order.
Direct : Information and Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer ready for ordering and enquires her where she will go after drinking.
Put :Wo xiang pajus zai li na.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer she will go with her friend later.
Suc :Xiang gouwu baba, ni zai nali?
Direct : Enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally enquires hearer what will they shop.
Put : Wo xiang mai xie, wo de xiezi yijing kaishile zhege posui de yuanyin. Ni yao qu nali?
Direct : Information and enquiring
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer she will buy shoes and enquires where hearer will go.
Suc : Wu huilai ajalah shi de, wo ganjue bushufu, yin wei bushi you shi shenme?
Direct : Asking
Literal : The speaker literally asks hearer she will go home first.
Put : Ta, bushi wo xiang ni yao zaodian lai.
Direct : Information
Literal : The speaker literally informs hearer she want to follow speaker.
Suc : Zhe shi zenme hui shi ge men. Zhe bi qian shi bu cunzai.
Direct: Information