Departemen Patologi Anatomi Fakultas
Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera Utara Medan - 2011
Blok BBS 2
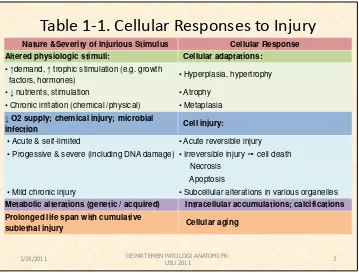
Table 1-1. Cellular Responses to Injury
Nature &Severity of Injurious Stimulus Cellular Response Altered physiologic stimuli: Cellular adaptations:
• demand, trophic stimulation (e.g. growth
factors, hormones) • Hyperplasia, hypertrophy
• nutrients, stimulation • Atrophy
• Chronic irritation (chemical /physical) • Metaplasia
O2 supply; chemical injury; microbial
infection Cell injury:
• Acute & self-limited • Acute reversible injury • Progessive & severe (including DNA damage) • Irreversible injury ➙cell death
Necrosis Apoptosis
• Mild chronic injury • Subcellular alterations in various organelles
Metabolic alterations (genetic / acquired) Intracellular accumulations; calcifications Prolonged life span with cumulative
sublethal injury Cellular aging
Stresses/pathologic stimuli the cell
Adaptation
• Atrophy
• Hypertrophy
• Hyperplasia
• Metaplasia
Irreversible injury & dies
Perubahan sel & jaringan
Agenesis
Aplasia
Hypoplasia
Atrophy
Hypertrophy
Hyperplasia
Metaplasia
Dysplasia
Anaplasia
Granuloma
•
Complete absent of
organ
•
e.g. :
– Renal agenesis
– Ovarial agenesis
– Tubal agenesis, etc.
Agenesis
Aplasia
•
Is present
•
But never develops
•
e.g. :
– Lung aplasia with tissue
•
Developved incompletly
•
But the tissue histhologicaly normal
•
e.g. : microcephaly
Hypoplasia
•
Decrease in the:
–
Size
–
Function of a cell
•
But not dead
Causes of atrophy :
1. functional demand (immobilitation in fracture, prolonged
bed rest)
2. Inadequate supply O2 (ischemia)
3. Insufficient nutrients (starvation, inadequate nutrition, chronic disease)
4. Interruption of trophic signals transmitted by chemical
mediators (endocrine system/neuromusculator transmission)
e.g. : thyroid, adrenal cortex, ovarium, testis.
5. Persistent cell injury by chronic inflamation
e.g. : chronic gastritis, prolonged pressure 6. Aging : brain, heart (Senile Atrophy)
!"#$ #% & '(! )* + ,)-# '(."*)/0 & 1' 2 !3 $ )* + %"2 ( '( $#! 1( $! "$ $#()'+ )-# '(."*)0 & )* + %"2 ( '( !&"$$ ( !&'$ $#()'+ ( '!"$4 1' 2 !3 $ !& )5 ' %"$."$4
The mechanism of atrophy :
e.g. :
• Insulin
• Tyroid stimulating hormon
• Glucocorticoids
Synthesis
Catabolism
↑ Hormones
•
size of cell accompanied by ↑ functional
capacity
•
Is a response to trophic signals
•
Commonly a normal procesess
… hypertrophy
Physiological (hormonal) hypertrophy
• in puberty
• production of sex hormon
• Hypertrophy breast tissue
• Abnormal hormon production in cancer
Functional demands
• Exercise
• Pathological conditions (myocardial cell) • Kidney hypertrophy on surgical removed
-# '(."*) "$ '$ '( ' '.6' $! !# ' & '+ . 7 ,8& '(! '!!' 98/0
7'(."' )* + '$$#! ( 4 $ ('! 5 %"2(#* #$$ !": !" * %"++ "$ !& . % !0 ;"'2+ )* + ++ 5 "< !# #)1 $ '! %#( ++ !&'! ." .0
↑
! &"4& ( )'4$"%" '!"#$
↑ '(."' )* + ++ = $* + "0
7'(."' )* + ++ '$$#! .":". '.'1!
Hyperplasia
the number of cells in an organ / tissue
Physiologic hyperplasia
• Hormonal hyperplasia
• Compensatory
hyperplasia
Pathologic hyperplasia
• ↑ hormonal / growth
factor stimulation
• e.g. :
• Endometrial
hyperplasia
Metaplasia
1 adult cell type another adult cell type
(convertion of 1 differentiated cell type of another)
Usually reversible if the stimulus is removed
• Squamous metaplasia of the bronchial epithelium to tobacco
• Lower oesophagus by reflux acidic gastric
• Endocervical metaplasia
# ! #))#$ " !& ( 1+' ) $! #% ' 4+'$.*+'( 1"!& +"*) 2- ' >*')#* ++0
7 ++*+'( '+! ('!"#$ "$ !&
"< 5 &'1 = #(4'$"<'!"#$ #% !& ++*+'( #)1#$ $! #% ' !" *
1. Size & shape of cells
variation
2. Nuclei : >>, irregular & hyperchromatism
3. Disorderly arrangement of the cells within the
epithelium
Dysplasia
& )# ! #))#$ "$ !& (:"? = 2(#$ &*
Dysplasia is a preneoplastic lession
•
Normal cell
primitive cell
•
E.g. : Malignant cell
–
Carcinoma
–
Sarcoma
–
Adenocarcinoma
–
Lymphoma
–
Etc.
Anaplasia
2 principal pattern of cell death :
• Commonly : coagulative necrosis • Cellular swelling
• Protein denaturation • Organellar breakdown • Cell rupture
NECROSIS
• Regulated event • Programmed death
APOPTOSIS
Term
Definition
Necrosis
Antemortem pathologic cell death
Apoptosis
Antemortem programmed cell death
CAUSES OF CELL INJURY
Hypoxia
Physical Agent
Chemical and drugs
Microbiology Agents
Immunologic Reaction
Genetic Defects
Nutritional Inbalance
Aging
• Anemia
• Ischemia
• Intoxication CO2
• Aerobic oxidative
respiration
• Mechanical trauma
• Extreme temprature :
heat, cold
• Radiation: X-ray, sun light
• Electric shock
• Athmosphere pressure
Hypoxia Physical Agent
• Sufficiently concentrated :
Glucose, Salt, O2
• Air pollutants
• Insecticides
• Asbestosis
• Ethanol
• Cellular metabolism (i.e.
waste products)
• Tape worms
• Rickettsia
• Virus
• Bacteria
• Fungi
… CAUSES OF CELL INJURY
Chemical agent & drugs Microbiology Agents
… CAUSES OF CELL INJURY
•
Anaphylactic reaction
•
Autoimmune diseases
Genetic Defects
• Congenital malformation • Sickle cell anemia
• G-6-PD
Nutritional Imbalance
• Protein calori insufficiency • Vitamins defficiency • DiabetesAging
Cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on :• Injury type • Duration • Severity Current Status : • Nutritional • Hormonal • Adaptibility
of the cell
Intercellular systems :
• Cell membrane integrity • Aerobic
respiration • Protein synthesis • Integrity genetic
apparatus
O2& oxygen derived free radicals :
• Ischemic • Hypoxic
injury
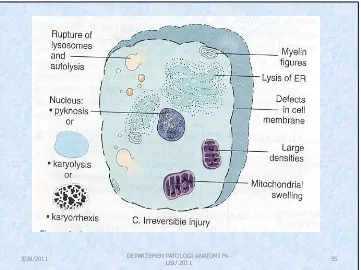
The ultrastructural features of these stages of cell injury. Normal cell & changes in reversible & irreversible cell injury
•
Reduced of :
– Oxidative
phosphorylation in mitochondria
– Activity Na Pump
•
Cellular swelling
•
Loss of microvilli
Glycogen depleted ↓ protein synthesis
Formation of cell surface blebs
•
Severe vacuolization of
mitochondria
•
Damage of :
– Mitochondrial matrix
– Plasma membrane
•
Swelling of lysosomes
•
Accumulation of
amorphous calcium
•
Rich dentities in
mitochondrial matrix
Figure 1-6.
Cellular features of
Feature Necrosis Apoptosis
Cell size Enlarged (swelling) Reduced (shrinkage) Nucleus Pyknosis → karyorrhexis
→ karyolysis
Fragmentation into nucleosome-size fragments
Plasma membrane Disrupted Intact; altered structure, especially orientation of lipids
Cellular contents Enzymatic digestion; may leak out of cell
Intact; may be released in apoptotic bodies
Adjacent inflammation Frequent No
Physiologic or pathologic role
Invariably pathologic (culmination of irreversible cell injury)
Often physiologic, means of eliminating unwanted cells; may be pathologic after some forms of cell injury, especially DNA damage
1. Reversible acute cell injury
2. Necrosis (cell death after irreversible injury)
3. Apoptosis (cell death by suicide)
4. Subcellular alteration as a respond to chronic or persistent injury stimuli
5. Intracellular accumulations of a number of substance
Morphologic changes that follow cell death in living tissue
1. Intense eosinophilia of the dead cell is due to
loss of RNA & coagulation of protein
2. Nuclei undergo:
1. Pyknosis 2. Karyorhexis 3. Karyolysis
Leaving a shrunken cell devoid of nucleus
3. Protein may be liberated from the dead cell
Necrosis
& )#(1&#+#4" '11 '('$ #% $ (# " "
!& ( *+! #%
$!"'++- 1(#
@
0 $<-)'!" ."4
!"#$ #% !& ++
0
$'!*('!"#$ #% 1(#! "$
Autolysis
: is a cell death by hydrolitic
enzymes
Nuclear Changes: This nucleus is faded -- karyolysis.
Karyolytic nuclei suggest that cells have died (undergone necrosis).
('4) $! . $* + " *44 ! !&'! ++ &': ." .0 '(-#((& ?" " !& ! () * . %#( !&" "( *) !'$ 0 & $* + * "$." '! . 2- !& +'(4 '((#3 )'- 2 *$. (4#"$4 9'(-#((& ?" 0 &
Morphologic changes in reversible and irreversible cell injury (necrosis).
#()'+ 9".$ - !*2*+ 3"!& :"'2+ 1"!& +"'+ ++
'(+- ,( : ( "2+ / " & )"
(#!" ,"(( : ( "2+ / "$6*(-#% 1"!& +"'+ ++
Types of Necrosis
Depends on :
•
&
!(* !*('+ 1(#! "$ = $<-)'!" 1(#! "$ !&*
2+# 9"$4 ++*+'( 1(#! #+- "
•
7'&'( ! (" !" #% &-1#?" . '!& #% ++ "$ '++
!" *
? 1! !& 2('"$
040 @
-# '(."'+ $%'( !"#$ ,# +* "#$ #% '(! ("'+
*11+-/
Coagulative Necrosis
•
">* %' !": 7#++">*'!":'
(# "
• '. !" *
• 11 '( )" +">*".
• *+! #% ." #+*!"#$ #% !" * 2- !& ' !"#$ #% &-.(#+-!" $<-)
040@ ( 2('+ "$%'( !"#$5 $ (# " '* . 2- 2' ! ("'+ "$%0
•
7' #*
(# "
• '. ++
• #() ')#(1&#* 1(#! "$' '* )'
• # #("4"$'+ '( &"! !*( '$ 2 $ ,&" !#+#4" /
• #%! = 3&"! ( )2+"$4 ( ') &
Coagulative & liquefactive necrosis
0 ".$ - "$%'( !
, #'4*+'!": $ (# " / B0
">* %' !": $ (# " ,9".$ '* . 2- %*$4'+ "$% !"#$/0
• Gumatous Necrosis
• Dead tissue, it is firm & rubbery like caseous necrosis in the
spirochetal infection syphilis.
• Hemorrhagic Necrosis
• Dead tissue suffused with extravasated red cell, when cell
death is due to blockage
• Fat Necrosis
• Not really necrosis.
• Focal areas of fat destruction tipically occuring following
pancreatic injury /after trauma to fat for (ex. in the breast)
• Describes foci of hard yellow material seen in dead adipose
•
Fibrinoid Necrosis
•
Fibrin deposited in damage necrotic vessel
walls in hypertension and vasculitis
•
Gangrene
•
Extensive tissue necrosis ; is complicated to
a variable degree by secondary bacterial
infection
APOPTOSIS
• Responsible for the programmed cell death in several
important physiology processes
• Including :
– During embryogenesis (in implantation, organogenesis, &
developmental involution)
– Hormon dependent physiologic involution (endometrium,
lactating, prostate after castration)
– Cell deletion in proliferating population (intestinal crypt
epithelium / cell dead in tumor)
– Deletion of autoreactive T cell in the thymus,
cell death of cytokine starved lymphocytes
Apoptosis of epidermal cells in an
immune-mediated reaction
A. Apoptotic cells are visible in the epidermis with eosinophilic cytoplasm and small, dense nuclei.
B. High power of apoptotic cell in liver in immune-mediated hepatic cell injury.
Granuloma
•
Special type of chronic inflamation in tissue
reaction.
•
Cause :
infection :
TBC fungal syphilis,etc
non-infection :
sarcoidosisCrohn’s disease
NECROBIOSIS
(#2"# " " 1&- "#+#4" '+ . '!& #% ' ++5 '$.
'$ 2 '*
. 2- (!'"$ #$."!"#$
! '$ 2 ". $!"%" . 2#!& 3"!& 3"!&#*! $ (# "
* & ' @
• B' #1&"+"'
• (-!& )' #(
… Necrobiosis
•
Gradual cell damage
•
Progressive
•
Singly / small group cells
•
Reversible (+/-)
•
Example :
–
Hepar cell
deg.
–
Cell death
healing
fibrosis.
Alterations in structure & function that may lead
to cell death, or at least diminished capacity of the
cell to respond an injury
•
Reduced cell in :
–
Pleomorphic vacuolated mitochondria
–
Repair of chromosomal damage
… Cellular Aging
Morphologic alteration in :
• Pleomorphic vacuolated mitochondria
•
endoplasmic reticulum
• Disorted Golgi Apparatus
• Accumutaion of lipofuscin pigment
Cellular senescence is multifactorial :
The cumulative effects of :
1. Extrinsic influences : free radical damage
DEGENERATION
Cloudy swelling
Fatty
change Hydropic Atropy
Hyaline
Mucoid
Amyloid
CalcificationC-.(#1" &'$4
#% 4
!'!"#$'+
)#+
! ! &"4& ( )'4$"%" '!"#$ !& "$!(' -!#1+' )" %'! .(#1+ ! '( +
" " #) !") 1(#! "$ .(#1+ ! '11 '( 3"!&"$ !& -D!#1+' ) #% " 9 ++ 0 & .(#1+ ! '11 '( &#)#4 $ #* 5 4+' -5 2 '. +"9
!(* !*( '$ '1 '('$ 9$#3$ ' 8&-'+"$ 0E