ABSTRACT
Kusumo, Galih. 2007. English Reading Instructional Materials Based on Contextual Teaching and Learning Approach for the seventh Grade Students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
English as an international language has become one of the subjects learnt in Junior High School. There are four main skills developed in English. They are listening, speaking, reading, and writing. In order to master the four skills students need to study and enrich their knowledge. Studying and enriching knowledge can happen if someone reads many books. Thus, students need to be able to read well. The writer chooses Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) to develop the reading skills. CTL is one of the most appropriate methods applied to teach reading since it facilitates the students to be active and learn English in natural context/real situation.
This study was conducted to design a set of reading instructional materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) for the seventh grade of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta. The objectives of this study were to answer two questions which were stated in the problem formulation. The questions were (1) How is a set of reading instructional materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the seventh grade of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta designed? (2) What does the set of reading instructional materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the seventh grade of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta look like?
In this study, the writer adapted R&D cycle (Research and Development method) to answer the research question above. The writer employed five out of ten steps of R&D cycle. They were (1) Research and Information Collecting, (2) Planning, (3) Development of Preliminary Form of Product, (4) Product evaluation, and (5) Main Product Revision.
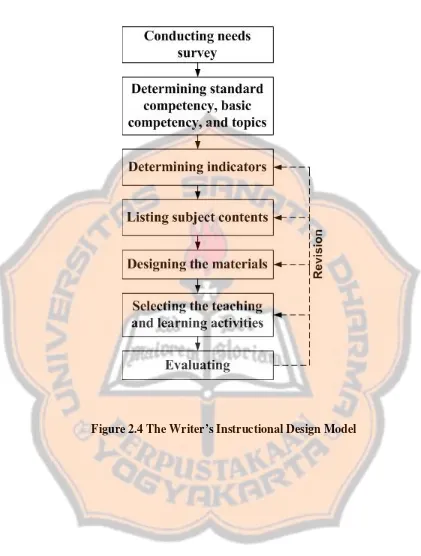
To answer the first question, the writer combined the models of instructional design from Kemp and Yalden. Those models are modified into eight steps, namely, (1) conducting needs survey, (2) determining competency standard, basic competence, and topics, (3) Determining indicators, (4) Listing subject content, (5), Designing the materials (6) selecting the teaching and learning activities, (7) evaluating, and (8) revising.
To answer the second question, the writer designed the final version of the designed materials after making some revisions based on the comments, evaluation, and suggestions from the respondents in the materials evaluation. The materials consist of eight parts. Each part consists of three sections. They are pre-reading, whilst pre-reading, and post reading.
ABSTRAK
Kusumo, Galih. 2007. English Reading Instructional Materials Based on Contextual Teaching and Learning Approach for the Seventh Grade Students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: Program Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Bahasa Inggris sebagai bahasa international telah menjadi salah satu mata pelajaran yang diajarkan di Sekolah Menengah Pertama (SMP). Terdapat empat kemampuan utama dalam Bahasa Inggris, yaitu listening, speaking, reading, writing. Untuk menguasai keempat kemampuan tersebut siswa perlu belajar dan mengembangkan pengetahuan mereka. Untuk belajar dan mengembangkan pengetahuan siswa perlu banyak membaca buku. Oleh karena itu, siswa harus memiliki kemampuan membaca yang baik. Penulis menggunakan pendekatan
Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) untuk mengembangkan kemampuan reading siswa.CTL merupakan metode yang paling tepat untuk diterapkan dalam mengajarreading karena metode ini memfasilitasi siswa untuk menjadi aktif dan mempelajari bahasa Inggris dalam konteks/situasi yang nyata.
Studi ini dilaksanakan untuk merancang seperangkat materi reading
dengan menggunakan metode Contexual Teaching and Learning untuk siswa kelas satu SMP Pangudi Luhur I Yogyakarta. Tujuan dari studi ini adalah untuk menjawab dua (2) pertanyaan yang ada dalam “problem formulation”. Pertanyaan-pertanyaan tersebut adalah (1) Bagaimana seperangkat materi pembelajaran membaca dengan menggunakan metode Contextual Teaching and Learning dirancang? (2) Bagaimanakah bentuk dari seperangkat materi reading dengan menggunakan metodeContextual Teaching and Learningtersebut?
Dalam studi ini penulis mengadaptasi metode lingkaran R&D (Research and Development) untuk menjawab pertantanyaan penelitian di atas. Penulis menerapkan lima dari sepuluh langkah dalam metode R&D. Langkah-langkah tersebut adalah (1) Mengumpulkan penelitian dan informasi, (2) Perencanaan, (3) Pengembangan bentuk awal dari produk, (4) Evaluasi produk, dan (5) Perbaikan utama produk.
Untuk menjawab pertanyaan pertama, penulis menggabungkan model pengajaran dari Kemp dan Yalden. Model-model tersebut kemudian dimodifikasi menjadi delapan (8) langkah yaitu, 1) Mengadakan survey untuk menganalisis kebutuhan siswa, (2) Menentukan dan menetapkan standar kompetensi, kompetensi dasar dan topik-topik, (3) Menetapkan indikator, (4) Merinci isi materi, (5) Merancang materi, (6) Memilih kegiatan pembelajaran dan sumbernya, (7) Mengevaluasi materi, dan (8) Memperbaiki materi.
diterima dan digunakan untuk mengajarkan reading pada siswa kelas satu SMP Pangudi Luhur I Yogyakarta.
Untuk menjawab pertanyaan yang kedua, penulis menyajikan versi akhir dari materi yang dirancang setelah melalui beberapa revisi berdasarkan dari pendapat, komentar, dan saran dari responden dalam langkah mengevaluasi materi. Material yang didisain terdiri delapan (8) unit. Setiap unit terdiri dari tiga bagian, yaitupre-reading, whilst reading, and post reading.
ENGLISH READING INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS
BASED ON CONTEXTUAL TEACHING AND LEARNING APPROACH FOR THE SEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF PANGUDI LUHUR I
JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL YOGYAKARTA
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain theSarjana PendidikanDegree
in English Language Education
By: Galih Kusumo
Student Number: 02 1214 095
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
A Thesis on
ENGLISH READING INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS
BASED ON CONTEXTUAL TEACHING AND LEARNING APPROACH FOR THE SEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF PANGUDI LUHUR I
JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL YOGYAKARTA
By Galih Kusumo
Student Number: 021214095
Approved by:
Major sponsor
C. Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd. August 18, 2007
Co-sponsor
A Thesis On
ENGLISH READING INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS
BASED ON CONTEXTUAL TEACHING AND LEARNING APPROACH FOR THE SEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF PANGUDI LUHUR I
JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL YOGYAKARTA
By Galih Kusumo
Student Number: 021214095
Defended before the Board of Examiners on August 27, 2007
and Declared Acceptable
Board of Examiners
Chairperson Ag. Hardi Prasetyo, S.Pd., M.A. ... Secretary Drs. P.G. Purba, M.Pd. ...
Members C. Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd. ………..
Christina Kristiyani, S.Pd., M.Pd. ……….. F.X. OudaTeda Ena, S.Pd., M.Pd. ...
Yogyakarta, August 27, 2007
Faculty of Teachers Training and Education Sanata Dharma Univeristy
Dean,
It’s just your doubts that bind you,
just drop those thought behind
By All American Reject
STATEMENT OF WORK ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis which I wrote does not contain the works or part of the works of other people, except those cited in the quotations and bibliography, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, August 18, 2007 The writer,
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First and foremost, I would like to thank my almighty Lord Jesus Christ for being always at my side during my life and never leaving me even for a second. He gives me light when I am in the dark; He gives direction when I am lost; and He encourages me when I stop hoping. His love helps me to finish this thesis and to obtain my“Sarjana Pedidikan Degree”.
My deep gratitude goes to C. Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd., my major sponsor, for her patience, support, encouragement, guidance and contribution of
ideas in helping me finish my thesis. At the same time, my gratitude goes to
Christina Kristiyani S.Pd. M.Pd. my co-sponsor, for her guidance, criticisms, and suggestions even when she is busy.
My deep thankfulness goes to Sr. Maureen who has spent her precious time reading and correcting my thesis. I owe her much for her patience, kindness,
and advice when I faced some problems during the time I finished my thesis.
I would like to thank Drs. J. B. Gunawan, M.A., my academic sponsor, for his guidance during the semester I passed in the PBI study program. I also
would like to thank all PBI lecturers, especiallyDian Fransiska Maharani, S.Pd. and Dr. Antonius Herujiyanto for their willingness to be my respondents. Furthermore, I thank them all for teaching and giving me useful knowledge so that
I can be a better person. Besides, I thank the secretariat staff, mbak Tari and mbakDanifor helping and giving information that I need for my study.
Junior High School for their cooperation and giving me suggestions and evaluation for my design. I would also like to thank theseventh grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School for spending their time filling in the questionnaire for my needs survey.
My deepest and sincerest gratefulness goes to my lovely parents, my mom Dra. Tri Subekti,my fatherDrs. Puji Purnomo. M.Si. They have not been tired to encourage me in every condition. They are spirit and light to finish my study soon. I sincerely express my special thank to my brother,Wahyu Pramudita,and my girlfriend, Wieda who always supports me and helps me when I have a problem. The happiness, sadness, and problem we had faced brought us to be more understanding and mature.
My gratitude is extended to all my friends in the PBI students especially Wawan, Udjo, Dedi, Christian, Gede (jix), Dany, Ook, Mawar, Cecil, Cicil, Ila, Ari, Echi, Shasha, Miko, Vivin, Ita, Haryana, Rendi, Gaby, Tomo, Timur, and other friends that I cannot mention one by one. I will never forget their contribution in improving the quality of my life. I hope our friendship will be everlasting.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGE ... ii
BOARD OF EXAMINERS ... iii
DEDICATION PAGE ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK ORIGINALITY ... v
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ... vi
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... viii
LIST OF FIGURES ... xiii
LIST OF TABLES ... xiv
ABSTRACT ... xv
ABSTRAK ... xvii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Problem Identification ... 4
C. Problem Limitation ... 4
D. Problem Formulation ... 5
E. Objectives of the Study ... 5
F. Benefits of the Study ... 5
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE... 8
A. Theoretical Description ... 8
1. Reading ... 8
a. The Nature of Reading ... 8
b. Teaching Reading skill ... 9
1) Pre-Reading Activities ... 9
2) Whilst Reading Activities ... 10
3) Post Reading Activities ... 11
c. Reading Techniques ... 11
1) Skimming ... 12
2) Scanning ... 12
3) Reading with Comprehension ... 12
2. Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) ... 13
a. The definition of Contextual Teaching and Learning ... 13
b. The Importance of Contextual Teaching and Learning ... 13
c. Basic Principle of Contextual Teaching and Learning ... 14
d. The Application of Contextual Teaching and Learning in Class .. 16
3. Curriculum ... 18
a. The 2006 Curriculum for Junior High School ... 18
b. The Nature of English Language Based on 2006 Curriculum ... 18
c. The Goals and Functions ... 19
4. Material Development ... 20
5. Instructional Design Models ... 22
a. Kemp’s Model ... 22
b. Yalden’s model ... 25
B. Theoretical Framework ... 27
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY ... 32
A. Method of the Study ... 32
1. Research and Information Collecting ... 33
2. Planning ... 33
3. Development of Preliminary Form of Product ... 34
4. Product evaluation ... 34
5. Main Product Revision ... 34
B. Respondents ... 35
1. Research and Information Collecting ... 35
2. Product evaluation ... 35
C. Instruments ... 36
1. Research and Information Collecting Instrument ... 36
2. Product evaluation Instruments ... 38
D. Data Gathering Techniques ... 39
1. Research and Information Collecting ... 39
E. Data Analysis Techniques ... 40
1. Research and Information Collecting ... 40
2. Product evaluation ... 42
F. Procedures ... 43
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION... 45
A. Conducting Needs Survey ... 45
1. The Results of the Questionnaires for the English Teachers ... 45
2. The Results of the Questionnaires for Students ... 47
B. Determining Competency Standard, Basic competence, and Topics .. 50
C. Determining Indicators ... 52
D. Listing Subject Contents ... 52
E. Designing the Materials ... 53
F. Selecting Teaching Learning Activities and Resources ... 54
G. Evaluating ... 54
1. The Description of the Respondents ... 55
2. Data Presentation ... 55
3. Respondents’ Comments and Suggestions on the Materials Design .. 57
H. Revising ... 58
1. Response to the Respondents’ Evaluation ... 58
2. The Presentation of the Designed Materials ... 58
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 61
B. Suggestions ... 63
REFERENCES... 64
APPENDICES ... 66
Appendix A: Letter of Permission ... 67
Appendix B: Questionnaire of Research and Information Collecting for Students ... 69
Appendix C: Interview of Research and Information Collecting for teachers 72 Appendix D: Questionnaire for Feedback Gathering ... 74
Appendix E: Syllabus ... 80
LIST OF FIGURES
Page
Figure 2.1 Materials Development Model ... 21
Figure 2.2 Kemp’s Instructional Design Model ... 24
Figure 2.3 Yalden’s Instructional Design Model ... 26
LIST OF TABLES
Page
Table 3.1. The Description of Product Evaluation Respondents ... 36
Table 3.2. The Format of the Presentation of Product Evaluation Results ... 42
Table 4.1. The Results of the Questionnaire for Students ... 47
Table 4.2. The Basic Competencies ... 51
Table 4.3. The Indicators ... 52
Table 4.4. The Results of the Evaluation Questionnaires ... 56
ABSTRACT
Kusumo, Galih. 2007. English Reading Instructional Materials Based on Contextual Teaching and Learning Approach for the seventh Grade Students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
English as an international language has become one of the subjects learnt in Junior High School. There are four main skills developed in English. They are listening, speaking, reading, and writing. In order to master the four skills students need to study and enrich their knowledge. Studying and enriching knowledge can happen if someone reads many books. Thus, students need to be able to read well. The writer chooses Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) to develop the reading skills. CTL is one of the most appropriate methods applied to teach reading since it facilitates the students to be active and learn English in natural context/real situation.
This study was conducted to design a set of reading instructional materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) for the seventh grade of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta. The objectives of this study were to answer two questions which were stated in the problem formulation. The questions were (1) How is a set of reading instructional materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the seventh grade of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta designed? (2) What does the set of reading instructional materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the seventh grade of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta look like?
In this study, the writer adapted R&D cycle (Research and Development method) to answer the research question above. The writer employed five out of ten steps of R&D cycle. They were (1) Research and Information Collecting, (2) Planning, (3) Development of Preliminary Form of Product, (4) Product evaluation, and (5) Main Product Revision.
To answer the first question, the writer combined the models of instructional design from Kemp and Yalden. Those models are modified into eight steps, namely, (1) conducting needs survey, (2) determining competency standard, basic competence, and topics, (3) Determining indicators, (4) Listing subject content, (5), Designing the materials (6) selecting the teaching and learning activities, (7) evaluating, and (8) revising.
To answer the second question, the writer designed the final version of the designed materials after making some revisions based on the comments, evaluation, and suggestions from the respondents in the materials evaluation. The materials consist of eight parts. Each part consists of three sections. They are pre-reading, whilst pre-reading, and post reading.
ABSTRAK
Kusumo, Galih. 2007. English Reading Instructional Materials Based on Contextual Teaching and Learning Approach for the Seventh Grade Students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: Program Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Bahasa Inggris sebagai bahasa international telah menjadi salah satu mata pelajaran yang diajarkan di Sekolah Menengah Pertama (SMP). Terdapat empat kemampuan utama dalam Bahasa Inggris, yaitu listening, speaking, reading, writing. Untuk menguasai keempat kemampuan tersebut siswa perlu belajar dan mengembangkan pengetahuan mereka. Untuk belajar dan mengembangkan pengetahuan siswa perlu banyak membaca buku. Oleh karena itu, siswa harus memiliki kemampuan membaca yang baik. Penulis menggunakan pendekatan
Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) untuk mengembangkan kemampuan reading siswa.CTL merupakan metode yang paling tepat untuk diterapkan dalam mengajarreading karena metode ini memfasilitasi siswa untuk menjadi aktif dan mempelajari bahasa Inggris dalam konteks/situasi yang nyata.
Studi ini dilaksanakan untuk merancang seperangkat materi reading
dengan menggunakan metode Contexual Teaching and Learning untuk siswa kelas satu SMP Pangudi Luhur I Yogyakarta. Tujuan dari studi ini adalah untuk menjawab dua (2) pertanyaan yang ada dalam “problem formulation”. Pertanyaan-pertanyaan tersebut adalah (1) Bagaimana seperangkat materi pembelajaran membaca dengan menggunakan metode Contextual Teaching and Learning dirancang? (2) Bagaimanakah bentuk dari seperangkat materi reading dengan menggunakan metodeContextual Teaching and Learningtersebut?
Dalam studi ini penulis mengadaptasi metode lingkaran R&D (Research and Development) untuk menjawab pertantanyaan penelitian di atas. Penulis menerapkan lima dari sepuluh langkah dalam metode R&D. Langkah-langkah tersebut adalah (1) Mengumpulkan penelitian dan informasi, (2) Perencanaan, (3) Pengembangan bentuk awal dari produk, (4) Evaluasi produk, dan (5) Perbaikan utama produk.
Untuk menjawab pertanyaan pertama, penulis menggabungkan model pengajaran dari Kemp dan Yalden. Model-model tersebut kemudian dimodifikasi menjadi delapan (8) langkah yaitu, 1) Mengadakan survey untuk menganalisis kebutuhan siswa, (2) Menentukan dan menetapkan standar kompetensi, kompetensi dasar dan topik-topik, (3) Menetapkan indikator, (4) Merinci isi materi, (5) Merancang materi, (6) Memilih kegiatan pembelajaran dan sumbernya, (7) Mengevaluasi materi, dan (8) Memperbaiki materi.
diterima dan digunakan untuk mengajarkan reading pada siswa kelas satu SMP Pangudi Luhur I Yogyakarta.
Untuk menjawab pertanyaan yang kedua, penulis menyajikan versi akhir dari materi yang dirancang setelah melalui beberapa revisi berdasarkan dari pendapat, komentar, dan saran dari responden dalam langkah mengevaluasi materi. Material yang didisain terdiri delapan (8) unit. Setiap unit terdiri dari tiga bagian, yaitupre-reading, whilst reading, and post reading.
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter covers six important parts of the thesis: background of the
study, problem identification, problem limitation, problem formulation, objectives
of the study, benefits of the study, and definition of terms.
A. BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY
Nowadays, English is a very important device in communication. English
language is usually found in many places such as in guidebooks, newspapers, and
novels. This happens because English has become an international language. It
means that most countries use English as the first or second language in
communication. Consequently, this reason makes people try to be competent in
English. Some countries have considered that English becomes an important
language. Indonesia is one of them. Most schools in Indonesia have included
English as one of the compulsory subjects to develop students’ knowledge.
Proficiency of English can be achieved by mastering four language skills;
namely speaking, reading, listening, and writing. In order to master the four skills
students need to study and enrich their knowledge. Studying and enriching
knowledge can happen if someone reads many books. Therefore, students need to
ideas. Looking at this fact, reading can be considered as a skill that is important to
be mastered.
Reading will be easier for the reader if the language which is used in the
text uses the language of the reader. If people read in the texts which use their
language, it will be easier for them because they know the structure and meaning
of the language. On the other hand, people who read a book in a foreign language
will consider reading as a difficult activity because the language has different
structure and meaning from their own or native language. As the result, peoples’
interest in reading will decrease.
It is not easy to teach English to the students especially for those in the
Junior High School. Teachers should be more creative and attractive in adapting
texts and making them simple and interesting for the students. The teachers
sometimes take the texts directly from magazines or newspapers directly.
Actually, it is not bad but sometimes some of the vocabulary in those texts is not
appropriate for the students or too difficult for the students especially in the
beginner level. It makes reading considered as a boring subject because they could
not understand the texts and become disinterested to practices reading. Whereas,
reading is one of the important skills to be mastered for the students in the junior
high school.
It is not easy to be a junior high school teacher because the characteristics
high school are needed to support their learning (1953: 31). Therefore, a teacher
should be able to make the situation in the class interesting by providing new and
interesting materials.
Concerning the importance of reading at the Junior high school, a good
program for reading is needed. A good program must be supported by innovative
strategies. Unfortunately, teachers sometimes forget that teaching children is
totally different from teaching adults (Partee, 2006). Some schools still use
traditional methods in their classes. Traditional methods mean that the learning is
focused on the teacher. It makes lecturing become the main strategy in class. This
method makes the study oriented on “memorization” It only makes the students
"memorize" the knowledge for a short time. Study will be meaningful if children
“experience” what they have learnt.
Nowadays, there is a method that has become an issue in education. The
method is called Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL). Unfortunately,there is
no good understanding from the teacher about this method. Contextual Teaching
and Learning (CTL) is a learning concept which helps the teachers to relate the
materials which are taught in the class (theory) to the situation in the students’ real
world. Using this approach the students’ learning will be meaningful for them.
The process of study is conducted naturally in the form of students’ work and
experience, not by transferring knowledge from teacher to the students. Some of
must be memorized. It makes the teacher become the main source in class. It will
make speech uses more often and the students become passive. By using CTL in
class, the teacher can overcome that problem. CTL will encourage the students to
be more active in class.
Based on the reasons above, the writer designed a set of instructional materials which focuses on reading skill, using Contextual Teaching and Learning approach to support the teaching learning process.
B. PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION
A teacher is a person who is responsible for teaching learning process and plays an important role in the class. Therefore, the teacher has a responsibility for creating elements such as materials, and strategies to deliver the materials to the students that are needed to make the teaching learning process succeed. For the teacher, teaching sometimes can be difficult for him/her. “Creating and applying certain techniques must be done by teachers with certain considerations to achieve the purpose” (Richard & Rodgers 1996:15).
The materials made by the teacher must enable students to use language in
their daily life. The teacher should prepare all the materials well, so they can be
used to help the students increase their skill especially in reading.
C. PROBLEM LIMITATION
and Learning that can make a language teaching and learning activities to be communicative and interesting.
D. PROBLEM FORMULATION
Considering the previous explanation about the background and scope of the study, the problems of the study are formulated as follows:
1. How is a set of English instructional reading materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the seventh grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School designed?
2. What does the designed set of English reading materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the first grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School look like?
E. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY The objectives of this study are:
1. To find out how a set of English reading materials using Contextual Teaching
and Learning for the seventh grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High
school is designed.
2. To find out what the designed set of English reading instructional materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the seventh grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School looks like.
1. The Junior High School Teachers.
The teachers are expected to be confident and have no difficulties in teaching English using Contextual Teaching and Learning anymore after learning from the design of this study.
2. Students
Students usually become easily bored and have difficulty since they only have to memorize the lesson without applying it in real life. It can raise students’ boredom and difficulty. Hopefully, this designed material can increase their motivation to learn English.
3. Other Researchers
Hopefully, the result of this study can provide helpful information and give stimulus for further study. Hence, better and more various reading materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) approach will be found.
G. DEFINITION OF TERMS
There are some definitions that the writer had to clarify in order to make the study understandable, the terms are as follows:
1. Design
Design is defined as, “plan to guide education activity in the target situation” (Houle, 1978: 203). In this study, designing means an activity of making some strategies, materials, and teaching-learning activities in the target language. 2. Reading
3. Contextual Teaching and Learning
Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) helps us relate subject matter content to real world situations and motivate students to make connections between knowledge and its applications to their lives, family members, citizens, and workers and engage in the hard work that learning requires (Johnson. 2002: 23). In this study, CTL is a strategy which can help students make connection between language which they have learned and its application.
4. Junior High School Students
8
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter the writer discusses some theories that are relevant in designing reading materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) for the seventh grade of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta. This chapter is divided into two major parts. In the first part, the writer discusses the theoretical description and in the second part, the writer explains the theoretical framework.
A. THEORETICAL DESCRIPTION 1. Reading
a. The Nature of Reading
Goodman (1976) and Smith (1978) as cited by Vacca (1981: 2) proposed that reading is an “active process of deriving meaning”. It means that when
reading the texts readers try to understand the author’s message by interacting
with the text. A reader is a user of language whose task it is to make sense out of what she or he reads. Another view about reading comes from Karlin (1980: 7).
He says that reading is the reconstruction of the ideas of others. It shows us about comprehensive processes in someone’s mind while he/she is reading. He/she
receives thoughts and ideas that are conveyed through written expression.
the writer’s message. From the definition above, the writer concludes that reading
is an active thinking process of the written and printed symbol to build the meaningful interpretation from the writer’s message.
b. Teaching Reading Skill
According to Hughes (1989) there are two sub-skills of reading comprehension. They are macro skill and micro skill. The term “macro skill” refers to understanding the general ideas in the text (e.g., information, gist, argument) while “micro skill” refers to recognizing and interpreting the linguistic features of the text (e.g., referents, word meanings, discourse indicators). In this study, the writer uses micro skill to design the materials.
According to Pearson and Fielding’s generative learning quoted by
Urquhart and Weir (1988:183) there are three phases that are used in teaching
reading. They are pre-reading activities, whilst reading activities, and post reading
activities. Each phase will be further explained as follows:
1) Pre-reading activities
This phase is important. It is to activate student’s knowledge about the text
and motivate student so they will have interest in reading. The basic principles for
pre-reading activities are:
a) Teaching vocabulary
74), vocabulary should be taught in context to effectively guess the meaning of less frequently used vocabulary.
b) Providing essential background information
Adequate preparation for reading a piece of text includes helping students either recall or acquire information necessary for comprehending the text. c) Establishing purpose for reading
Purposes in reading will help the students focus their attention on what to look for as they read and help them to connect their knowledge with new information. The students sometimes are not ready to establish their own reason for reading. Therefore, the teacher must try to encourage them so they will have good reading habits.
d) Motivating students to be able to do the reading
The teacher must try to raise and develop interest of student to reading texts. This is important for the students. Students who have lack of motivation in reading will not be able to achieve all that is needed in reading.
2) Whilst Reading Activities
The activities, in whilst reading, are the activities to lead the students to
understand the content of the reading passage. The activities are as follows:
a) Skimming
It helps the students to gain general ideas of the material by reading the texts quickly and selectively.
b) Scanning
c) Reading for explicitly stated main ideas
It helps the student to find the main idea which is stated explicitly. d) Reading for implicitly stated main ideas
It helps the students to find the main idea which is stated implicitly. e) Reading for details
This activity asked the students to find detailed information from the text. f) Reading between lines
This activity is done by reading each line of the text. It will help the students to have better understanding on how to draw an inference.
g) Deducing meaning from context
This activity requires the students to discover the meaning of a great number of unfamiliar words from the texts.
3) Post Reading Activities
Questions of evaluation and personal responses are also seen as the
important things in post reading activities, relating the text to the outside world.
This activity can be done in an oral or a written way.
c. Reading techniques
Reading technique plays an important role in understanding reading
material (Kustaryo 1988: 3). Reading techniques help the students to be able to
read efficiently. After finding out the purpose or what the students expect to gain
from their reading, students should select the technique that is appropriate. There
are some techniques that can be used by students to achieve their purpose. The
1) Skimming
Skimming is a reading technique that involves students looking through the text rapidly for the general meaning of an article (Thomas, 2002: 28). It is used by the reader to find the idea of what the author is saying in the text without many details. It can be done by knowing the key word which can be the topic, the descriptive adjective, the abstract noun or the functions word. If the reader wants to be able to do skimming, he/she has to understand the organized text, become aware of the main point in a paragraph, and be able to assume the main ideas of a text.
2) Scanning
Scanning is a reading strategy whose purpose is to find specific information from a text. In this technique the readers search for particular specific information that is needed in order to be able to locate the information. The reader has to know information that he/she wants to search, the place to find the information and the way the reader can identify the information at the time he/she sees the information to be able to do scanning. 3) Reading with comprehension
In reading with comprehension, the reader is supposed to be able to
understand everything which has been read. Students need not only skills of
comprehension but also the reader’s experiences and knowledge in this
technique. To be able to do this technique, the reader should understand the
vocabulary, see the relationship among words and concepts, organize ideas,
2. Contextual Teaching and Learning
a. The Definition of Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL)
Contextual Teaching and learning (CTL) is a concept that helps teachers relate the material which is taught to real world situations and motivates students to make connections between knowledge and its applications to their daily life. They do this by using seven main components of study, namely constructivism, questioning, inquiry, learning community, modeling, reflection, and authentic assessment (www.dikdasmen.org). By using this concept it is hoped that the result of the study will be meaningful for students. The teaching learning process happens naturally in the form of students work and activities not just by transferring from teacher to students. Therefore, teachers have to provide a context which is meaningful for content (Purnomo, et al, 2007: 49).
In contextual class, the teacher becomes the facilitator and helps the
students achieve their learning goals. Thus, the teacher should think that the
teaching strategy is more important than giving information.
b. The Importance of Contextual Teaching and Learning
Most of our education is still dominated by a view that knowledge is a set
of fact which must be memorized. As a result, the teaching learning process
focuses on the teacher as the main source of knowledge. Therefore, lecturing
becomes the main strategy to teach. Therefore, a new strategy which can make the
students more active is needed. The strategy not only makes the students
memorize a set of facts but also encourages students to construct knowledge in
Based on the fact above, CTL which emphasizes on constructivism in the
teaching learning process can be promoted as an alternative strategy to make the
students active and encourage the students to construct the knowledge.
c. Basic Principles of Contextual Teaching and Learning
According to Purnomo et al.(2007: 50) there are some principles that must
be applied to make teaching learning process using CTL a success. They are
Problem based learning, authentic instruction, inquiry based learning, project
based learning. The principles will be explained as follows:
1) Problem Based learning
This principle engages learners in problem solving investigations. The students must be able to use information which is available and think critically to solve problems in the real world.
2) Authentic Instruction
Authentic instruction is a contextual approach which is meaningful, for example learning how to sing by singing a song, learning how to sell by selling something, etc.
3) Inquiry Based Learning
Inquiry based learning creates study as an activity to ask ourselves and find the answer by ourselves. The students are encouraged to find the answer by asking themselves.
4) Project Based Learning
According toProject-based Learning(2001) Project based learning focuses
problem solving investigations and other meaningful tasks allowing students
to work autonomously to construct their own learning and culminates in
realistic project. This principle engages students to involve their mental,
physics, nerve, sense and social skill.
5) Work Based Learning
This principle integrated workplace or workplace-like activities and classroom
content (Smith, 2001). Work gives an opportunity to students not only to
know someone’s experience but also experience something different.
6) Service Learning
Emotion of the students is important to be recognized in the teaching
learning process. Emotion determines the process and the result of study.
Positive feeling of student which emerges in the teaching learning process will
accelerate the study.
7) Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning organizes instruction using small learning groups in which students work together to achieve learning goals (Holubes, 2001). Learning together will be better than learning individually. Each student can encourage the other students to learn better. If a student does not understand the lesson, other students can help him.
d. The Application of Contextual Teaching and Learning in Class
1) Constructivism
Constructivism is the philosophy of CTL approach. Constructivism considers that knowledge is not a set of facts, concepts which are ready to be obtained and remembered. Someone has to construct the knowledge and give meaning through real activity (Sungkowo, 2003). In constructivism, knowledge cannot be transferred directly from one person to another person such as teacher to students. Each person should try to interpret the knowledge by himself. Knowledge is not something that can be required instantly. Therefore, teachers have to give an opportunity for the students to study alone and be ready to become the source of information.
2) Inquiry
Knowledge and skills which are obtained by the students are not the result of
remembering a set of facts but the students must discover by themselves.
Learning is not only brain activities but also the relationship with other parts
of bodies. If the teacher only emphasizes brain activities, “sit down, not move
and be silent” approach will happen in class. There are some steps that are
used in inquiry. There are observation, hypothesis, data gathering, and
conclusion.
3) Questioning
Asking is considered an important part in inquiry based learning.
Someone’s knowledge always begins from “asking” for example before
knowing about English, student will ask “what is English?” Questioning can
the attention to unknown aspects. This activity is not difficult to be
implemented in class because it can be done between teacher with students,
students with teacher, students with students, and students with other people
who come into class. Discussion can be used to develop this activity.
4) Learning Community
Learning community suggests that the result of study is obtained through cooperation with someone else. Mejer (2002) said that cooperation in learning something is four times more effective in increasing the student’s achievement than learning by himself/herself. Learning communities need two requirements to make it a success:
a) The communication happens in two ways. b) There is no dominant person in communication. 5) Modeling
In teaching learning process, example from a model that can be imitated is needed. The model is not always the teacher. It can be any one such as, students, or someone outside the class.
6) Reflection
Reflection also becomes an important part in CTL. Reflection is the way of thinking about what has been learned or what is behind what has been learned. Reflection can also mean a response the activity, incident, or knowledge that has been gained.
7) Authentic assessment
Assessment is the process of collecting the data so that the teachers can see the
because it can be used to make sure that the teaching learning process was
done in a good way. Data which are compiled through assessment do not use
to find student’s study. The good teaching learning process should be
emphasized to help the student to learn “learning how to learn”. The
assessments emphasizing on the study process make the data that are compiled
be achieved through real activity. The data which are taken from outside and
inside the class is called authentic.
3. Curriculum
a. The 2006 Curriculum for Junior High School
The 2006 curriculum is the newest curriculum from the National Education Department that was issued in 2006. This curriculum is also used as a guide to teach English. If the 2006 curriculum is compared to the 2004 curriculum, it can be found that actually they are not very different.
b. The Nature of English Language Based on 2006 Curriculum
English is a means to communicate both in oral and written form.
Communicate is to comprehend and to express information, thought, feeling,
through language. The learners are expected to be able to develop science,
technology, and culture. In a heuristic meaning, communicative competence
means discourse competence that is the ability to understand and produce oral or
written texts which can be found in four skills (listening, speaking, reading, and
writing). These skills are used to perceive and create discourse in society life.
able to communicate and have discourse in English in certain literacy level
(Departemen Pendidikan Nasional,2006: 277).
Literary level consists of performative, functional, informational, and
epistemic. In performative level, people are able to read, write, listen, and speak
using symbols. In functional level, people are able to use language to fulfill their
daily needs such as reading newspaper, and manuals. In informational level,
people are able to access knowledge with their language ability while in epistemic
level people are able to express knowledge into the target language (Wells, 1987).
c. The Goals and Functions
English subject has goals and functions as follows:
1) Develop communicative competence in English both orally and written to
achieve functional literacy level.
2) Develop the awareness about the nature and importance of English to increase
the competitiveness of the nation in global society.
3) Develop the understanding of the learners about the relationship between
language and culture.
d. Scope of English Lesson Based On 2006 Curriculum
According to Departemen Pendidikan Nasional(2006: 278) there are
some scopes in English lesson based on 2006 curriculum. They are:
1) Discourse competency that is ability to create and produce oral or written text
which is involved in four skills (Listening, speaking, reading, and writing)
2) Ability to understand and produce not only many short functional texts and monologues but also essays in the form of procedure, descriptive, recount, narrative, and report.
3) Supporting competence, namely linguistic competence (using grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, and writing), sociocultural competence (using formal expressions and grammar in every communication context), strategic competence (overcoming problems in many ways which appear through the process of communication so that the communication still takes place), and discourse competence (using discourse instrument).
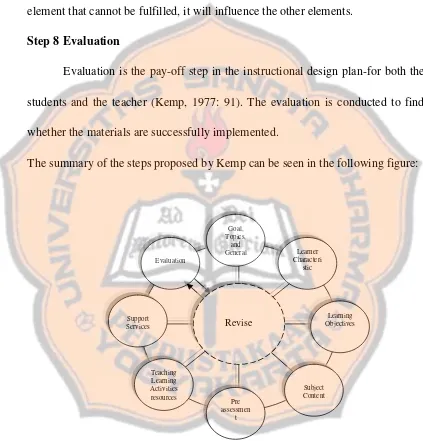
4. Material Development
In designing the materials, the writer used the model proposed by Hutchinson and Waters. The purpose of this model is to provide coherent framework for the integration of the various aspects of learning and it provides enough room for creativity and variety to grow (Hutchinson and Waters, 1994: 108). There are four elements in the model. They are:
a. Input
It can be in form of sound recording, a text, diagram or any piece of communication data, depending on the needs defined in analysis.
b. Content Focus
Language is a means of conveying information and feeling about something. Therefore, to generate meaningful communication non-linguistic content should be exploited.
c. Language Focus
tasks and activities since the models’ aim is to enable students to use language.
d. Task
Materials should be developed to lead towards a communicative task in which learners use content and language knowledge they have built up through the unit.
The summary of the material development proposed by Hutchinson and Waters can be seen in the following figure:
Figure 2.1 Materials Development Model
In this model, task becomes the main focus of the unit. The model is a
vehicle helping the students to do the task. The language and content are drawn
from the input and are selected according to what the students will need to do the
task. It is obvious that the important feature of the model is to create coherence in
terms of both in language and content throughout the unit. This will provide
5. Instructional Design Models a. Kemp’s Model
This model is taken because the structure of the instructional design by Kemp can be applied in all education levels (elementary to colleges). The model can also be used to design a single unit of instructional material.
According to Kemp (1977: 8), a plan is designed to answer these three primary questions:
1. What must be learned? (objectives)
2. What procedures and resources will work best to reach the desired learning level? (activities and resources)
3. How will we know when the required learning has taken place? (evaluation) Kemp (1977: 8-9) offers eight elements in designing the program development. An interdependent is found among eight elements. Kemp’s model is a flexible process. It can move back and forth to the other steps. The steps are: Step 1 Goal, and then list topics, and general purpose.
In making instructional design, a designer should decide the goals of the system, select the topics to be taught by the teacher, and specify the general purposes of each topic. The goals can be obtained from society, students, and subject areas. When the designer selects the topics, he should arrange the topics into chronological order from simple levels to complex levels. The general purposes are made from the topics and explicitly express students’ expectation. Step 2 Learner Characteristics
Step 3 Learning Objectives
Specifying learning objectives is difficult but essential in making instructional design. In this step, teacher is concerned with learning as the outcome of instruction. Learning requires active efforts by the learner. Therefore, objectives should be measurable and unambiguous so that students are able to do objectives.
Step 4 Subject Content
Subject content must be closely related to the objectives and to the students’ need. The subject content includes the organization of the content and task analysis. In organization of the content, the designer prepares the outline of the information that will be taught. Meanwhile, in task analysis, the designer lists all procedural elements that will be taught.
Step 5 Pre-assessment
Pre-assessment is used to find the students’ background and present knowledge about the topic. Therefore, the students do not waste their time on things they already know. There are two kinds of pre-assessments’ tests. They are pre-requisite testing and pre-testing. The designer uses pre-requisite testing to find whether the students have already had a basic knowledge of the topic. In order to find which of the objectives the students have already mastered, the designer can use pre-testing.
Step 6 Teaching/Learning Activities Resources
In this step, teachers should determine the most effective methods to be
used in the teaching learning process and then select the materials to provide
Step 7 Support Services
The support services are budget, personnel, facilities,
equipment and schedules to carry out the instructional plan. If there is one
element that cannot be fulfilled, it will influence the other elements.
Step 8 Evaluation
Evaluation is the pay-off step in the instructional design plan-for both the
students and the teacher (Kemp, 1977: 91). The evaluation is conducted to find
whether the materials are successfully implemented.
The summary of the steps proposed by Kemp can be seen in the following figure:
Figure 2.2 Kemp’s Instructional Design Model
In Kemp, developing an instructional system is continuous process. Each
step in the diagram always requires revision. Therefore, the changes made in one Goal,
Topics, and General
Teaching Learning Activities resources Support Services
Learner Characteri
stic
Learning Objectives
Subject Content Pre
assessmen t Evaluation
element will influence other elements because they are interdependent.
Developing an instructional system Kemp’s model begins with the objective as a
starting point and evaluation as the end.
The writer considered that this model is appropriate for designing reading material. The model is more flexible to be applied and the material is selectively chosen based on the learners’ needs and interest.
B. Yalden’s Model
In Yalden’s model, the syllabus emphasizes the communicative function. This means that it is important to ensure that learners acquire the ability to communicate in a more appropriate way. According to Yalden (1987: 89), there are eight stages offered in language program development.
1) Needs Survey
The purpose of this step is to find the learners’ need and the objectives that are suitable for the learner.
2) Description of the Purpose
The information gathered from the first step was used to determine and to describe the purpose of the program.
3) Selection of Syllabus Types
In this step, a syllabus designer should choose a syllabus that will be used in the language program. The syllabus which is used is the functional syllabus. It means that objective of learning is described in terms of communicative function.
4) Production of Proto-syllabus
5) Production of Pedagogical Syllabus
According to Yalden, this step develops the teaching materials, the learning and testing approaches, testing sequence and decisions on testing instruments. 6) Development and Implementation of Classroom Procedure
The communicative syllabus has changed the teacher’s role. In class, the teacher should consider himself as a facilitator than a leader. Therefore, the teaching learning process should emphasize the learner’s activities rather than the teacher.
7) Evaluation
In this stage, the syllabus designer should assess all competence in a language
program. According to Yalden, evaluation describes three things: the learners,
the teaching, and overall design.
8) Recycling
Recycling is the last step in the process syllabus design. This step is done to
match the goals and students’ performance. If the goals and students’
performance do not match the syllabus, designer should revise the content,
materials, and teaching methodology.
B. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This study focuses on designing a set of reading materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) for the seventh grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta. CTL is a concept that helps students relate the materials which are learnt to real world situations and motivates students to make connections between knowledge and its applications to their daily life. CTL which emphasizes on constructivism in the teaching learning process can be promoted as an alternative strategy to create better learning process.
In developing the materials the writer used the model from Hutchinson and Waters. The model is chosen because the model provides coherent framework for the integration of the various aspects of learning and it provides enough room for creativity and variety to grow.
Here, to develop the design, the writer combined Kemp’s instructional
design model and Yalden’s instructional design model because they can complete
each other. There is no need analysis in Kemp’s models. The use of need analysis
from Yalden’s model can make the design better. Moreover, Yalden’s model
emphasizes communicative function and the process of instructional design model
and the steps in Kemp’s model are continuous.
The new framework is composed of several elements, namely, conducting
a needs survey; determining competency standard, basic competence, and topics;
determining indicators; listing subject contents; selecting teaching and learning
Step 1 Conducting needs survey
The writer adapted this step from Yalden’s model. A need survey was essential in planning the instruction. It could be used to learn about the students’ need. The writer conducted a survey through questionnaires to the seventh grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School and interviewed two English teachers of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School.
Step 2 Determining competency standard, basic competence, and topics The writer adapted this step from Kemp’s model. This step was used to determine the goals of the materials design based on the students’ need. The topics, then, were chosen based on the necessity to achieve the goals. In determining the standard competency, basic competency, and topics the writer developed them from 2006 curriculum.
Step 3 Determining Indicators
This step was adapted from Kemp’s model. According to Kemp (1977: 24) by specifying the indicators, the writer knew specifically whether the basic competence had been achieved or not. The writer made a list of what the learners had to learn in every meeting and at the end of each meeting the students were expected to be able to achieve the basic competence.
Step 4 Listing subject content
This step was adopted from Kemp’s model. The function of this step was to facilitate the achievement of each objective. Therefore, they should be closely related to the objectives of the learner’s needs.
Step 5 Designing the materials
selected. The materials were designed based on the standard competence and basic competence.
Step 6 Selecting the teaching and learning activities
Producing a set of English learning materials for the seventh grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Yogyakarta using CTL was the main focus of this study. The materials were designed based on the principles of the CTL theory as discussed in the previous section. Here, the writer looked for some books to gather relevant teaching learning sources and also the suitable teaching media.
Step 7 Evaluating
Evaluation was done to help the writer gain the final designed materials. The evaluation was done to the whole components of the material. It helped in making any necessary adjustment.
Step 8 Revising
31
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
In this chapter the writer discusses the research methodology that was used to answer the problems presented in Chapter I. There are six points discussed in this chapter. They are: (1) method of the study; (2) respondents; (3) instruments; (4) data gathering techniques; (5) data analysis techniques; (6) procedures.
A. METHOD OF THE STUDY
As it has been stated in the problem formulation in chapter one, this research attempted to solve two major problems. Firstly, it was conducted to find out how a set of English reading material using CTL approach for students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School was designed. Secondly, it was aimed to present the designed materials for students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School.
In this study, the writer applied Research and Development method
(R&D). According to Borg and Gall (1983: 772) R&D can be defined “as a
process used to develop and validate educational products” such as teaching
materials, teaching methods and method for organizing instruction. In addition,
R&D tries to develop research knowledge and incorporate it into a product by
becoming a bridge so that the gap between educational research and educational
practice can disappear (Borg and Gall1983: 771). Research and Development
revised based on the field-test data. Borg and Gall stated that there are ten major
steps that are used in the Research and Development method (R&D) cycle to
develop the products (1983: 775). They are research and information collecting,
planning, development of preliminary form of product, product evaluation, main
product revision, main field testing, operational product revision, operational field
testing, final product revision, dissemination and implementation.
In order to answer the two major problems mentioned above, the writer employed step one until step five. The steps are explained as follows:
1. Research and Information Collecting
Research and information collecting included review of literature,
classroom observation, and preparation of report of state of the art (Borg and Gall, 1983: 775). In this step, describing the designed material as specific as possible
became the important thing. Thus, the writer distributed questionnaires to the seventh grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School and conducted an informal interview for the teachers, and checked the curriculum in order to obtain
the data. The data were used as a source to obtain the students’ needs and information and opinion from the teacher about the topics which were suitable for
the seventh grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School. 2. Planning
In this study, planning included defining skills, stating objectives
and determining sequence. Those aspects would be applied to develop a suitable
syllabus and lesson plans to teach English reading for the seventh grade students
be achieved by the designed material became the important aspect in this step
(Borg & Gall 1983: 779). Objective is the best basis to develop the instructional
materials. Instructional materials can be tested and revised until it was suitable
with the objectives.
3. Development of Preliminary Form of Product
After completing the planning step, the next step was to develop the
preliminary form of product. This step included preparation of instructional
materials, handbooks, and evaluation devices. In this step, designer had to
organize the designed materials so as to permit obtaining as much feedback as
possible. The materials were developed using the model proposed by Hutchinson
and Waters.
4. Product Evaluation
This step is applied to obtain the evaluation for the instructional materials. In this study, the writer used questionnaires to gain the feedback. The feedback would be useful to revise and improve the designed material so that the designed material would work properly. The evaluation was obtained from the seventh grade teachers of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School and English lecturers of Sanata Dharma University.
5. Main Product Revision
After obtaining the evaluation from the product evaluation, the writer
applied the result or suggestions to revise the materials as recommended by the
teachers and lecturers. Thus, the data collected from the product evaluation would
B. RESPONDENTS
There were 121 seventh grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Yogyakarta,
three English teachers and two English lecturers of Sanata Dharma University
who became respondents in this survey research and interview. In conducting this
study, the writer obtained information from the respondents in research and
information collecting to obtain the students’ need and from product evaluation to
improve the designed set of material.
1. Research and Information Collecting
The seventh grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School were
involved in this survey as the respondents of questionnaires to find out the
information about their interest, needs, lacks and wants in reading. It was also
important to know the teaching learning methods that were used in teaching
learning process.
The English teachers of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School was also
involved as the interviewees to collect information. It was done to find out the
students’ need from teachers’ view. Moreover, they were closely related to the
teaching learning process. Thus, their comments provided the information for
designing the materials.
2. Product Evaluation
There were five respondents in this step. They were two English lecturers
of Sanata Dharma University and three English teachers of Junior High school.
However, one English lecturer had Bachelor degree while another lecturer had
Doctor degree. The respondents were competent as shown from their teaching
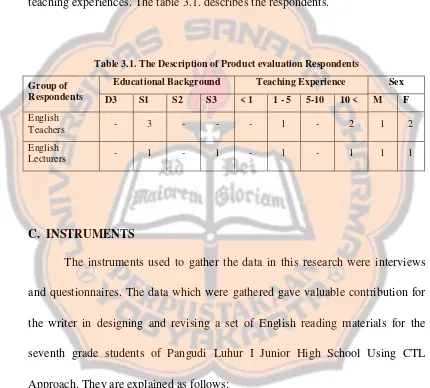
experience. Several respondents had a lot of experiences in teaching, which was
indicated by their teaching experience. All of them had more than two years
teaching experiences. The table 3.1. describes the respondents.
Table 3.1. The Description of Product evaluation Respondents
Group of Respondents
Educational Background Teaching Experience Sex
D3 S1 S2 S3 < 1 1 - 5 5-10 10 < M F
English
Teachers - 3 - - - 1 - 2 1 2
English
Lecturers - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 1 1
C. INSTRUMENTS
The instruments used to gather the data in this research were interviews
and questionnaires. The data which were gathered gave valuable contribution for
the writer in designing and revising a set of English reading materials for the
seventh grade students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Using CTL
Approach. They are explained as follows:
1. Research and Information Collecting Instruments
In the research and information collecting, the writer employed two kinds
of instruments: questionnaire and interview. The first instrument is questionnaire.
“printed form of data collection, which includes questions or statements to which
the subject is expected to respond”. According to Ary et al (1979: 175), there are
two types of questionnaires, structured or closed questionnaires and unstructured
or open questionnaires. A closed questionnaire is a questionnaire, which encloses
the choices of questions while an open questionnaire is a questionnaire, which
does not enclose the expected choices (Ary et al 1979: 175). Here, the writer
combined those two types of questionnaires in order to be able to give more
accurate and appropriate information to design the instructional materials. The
combination of open and closed questionnaires can be called semi-open
questionnaire. It was distributed by the writer to the seventh grade students of
Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School. The questionnaire was used to find the
student’s needs, interests, and difficulties in learning reading.
The second instrument, an interview, was conducted with the English
teachers of Pangudi Luhur I Yogyakarta. Ary et al (1979: 418) stated that
interview is an instrument which allows flexibility since the interviewer is able to
observe the subject as well as the situation and paraphrase the question when
needed. There are two kinds of interview questions, open ended questions and
closed questions. The respondent’s answers in the open-ended question were freer
than in the closed question because the answers are already provided. This
instrument enabled the writer to explore more the answers of the respondents in
appropriate to students’ ability and need. The interviewees were the English
teachers who were considered to know the ability of the students and what the
students needed so the material would be more effective and efficient. Interview
was used to find the teachers’ experience and opinions in teaching English reading
including their techniques, materials, strategies, topic choices and teaching media.
Information from the teacher was useful to develop the material since the teacher
had an experience in teaching reading.
2. Product Evaluation Instruments
1 : strongly disagree with the statement 2 : disagree with the statement
3 : undecided with the statement
4 : agree with the statement
5 : strongly agree with the statement
D. DATA GATHERING TECHNIQUES
In this study, the writer discussed the instrument used in Research and
Information Collecting survey and Product evaluation.
1. Research and Information Collecting
In the Research and Information Collecting, the writer
distributed questionnaires and gathered the data for the survey research from the
students of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta. The data gathered
were closed and open questionnaires. The purpose of distributing the
questionnaires was to figure the learners’ needs, interests and difficulties in
learning reading.
The informal interview was also held to obtain information from the
teachers of Pangudi Luhur I Junior High School Yogyakarta. The questionnaires
were distributed in March, 27 2007 and the informal interview was conducted in
October, 19 2006. The purpose of the informal interview was finding out the
teachers’ experience and opinions in teaching English reading including their
The writer also did library study to find some sources that could be used to
develop the designed materials. This activity was done by finding some books
related to this study.
2. Product Evaluation
In the product evaluation, the writer also used questionnaires. In order to
obtain final version of the materials, questionnaires on the developed materials
were distributed to three English teachers of Junior High School Yogyakarta and
two English lecturers of Sanata Dharma University. The questionnaire for the
designed set of material evaluation was distributed in June 2007. The
questionnaire was intended to figure out the respondents’ opinion and comments
on the designed material. Besides, it was expected that the writer could obtain
evaluation and feedback to improve the designed material so that the writer could
obtain the best final version of the materials.
E. DATA ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES 1. Research and Information Collecting
In the Research and Information Collecting, the analysis of the data was
aimed at solving the problem of what the English reading materials using
Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) for the seventh grade students of
Pangudi Luhur I Yogyakarta looked like. The data here were used to find the
learner’s needs which could be useful to determine whether they needed reading
In this research, a descriptive data analysis was chosen. The data to
evaluate the proposed English reading materials using Contextual Teaching and
Learning (CTL) for the seventh grade studen