commit to user
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY MASTERY
BY USING “PLAY SCHOOL DVD”
(A Classroom Action Research to the First Grader of Kalam Kudus Christian Primary School in the 2010/2011 Academic Year)
A Thesis
Written to Fulfill One of the Requirements of Graduate Degree of English Education of Sebelas Maret University Surakarta.
ARSIDI PUSPANINGDYAH
S890809001
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
SEBELAS MARET UNIVERSITY
SURAKARTA
commit to user
i APPROVAL
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY MASTERY BY USING
“PLAY SCHOOL DVD”
(A Classroom Action Research to the First Grader of Kalam Kudus Christian
Primary School in the 2010/2011 Academic Year)
By:
ARSIDI PUSPANINGDYAH
NIM: S890809001
This thesis has been approved by the Board of Consultants of English Education
Department, Graduate School of Sebelas Maret University Surakarta.
Consultant I Consultant II
Dr. Sujoko, M.A. Drs. H. Tarjana, M.A.
The Head of English Education Department
Graduate School
Sebelas Maret University
Dr. Ngadiso, M.Pd
commit to user
ii
BOARD OF EXAMINERS
This thesis has been examined by the Board of Thesis Examiners of the English Education Department Graduate School of Sebelas Maret University, Surakarta
On July 29, 2011
Board of Examiners: Signature
1. Chairman: 1. _____________________
Dr. Ngadiso, M.Pd
NIP. 19621231 198803 1 009
2. Secretary: 2. _____________________
Dr. Abdul Asib, M.Pd
NIP.19520307 198003 1 005
3. Examiners I: 3. _____________________
Dr. Sujoko, M.A
4. Examiners II: 4. _____________________
Drs. H. Tarjana, M.A
The Director of Graduate Degree of The Head of Graduate School of
Education Program of English Education Department of
Sebelas Maret University Sebelas Maret University
Prof. Drs. Suranto, M.Sc.,Ph.D Dr. Ngadiso, M.Pd
commit to user
iii MOTTO
commit to user
iv
DEDICATION
This thesis is dedicated to my parents who have given me their love,
commit to user
v
PRONOUNCEMENT
This is to certify that I myself write this thesis entitled, “Improving
Students’ Vocabulary Mastery By Using Play School DVD (A Classroom Action
Research To The First Grader Of Kalam Kudus Christian Primary School In The
2010/2011 Academic Year)”.
It is not plagiarism or made by others. Anything related to other’s work is
written in quotation, the source of which is listed in reference.
If then this pronouncement prove wrong, I am ready to accept any
academic punishment, including the withdrawal or cancellation of my academic
degree.
Surakarta, July 2011
commit to user
vi ABSTRACT
Arsidi Puspaningdyah, S890809001, “ Improving Students’ Vocabulary Mastery by Using Play School DVD ( A Classroom Action Research to the First Grader of
Kalam Kudus Christian Primary School in the 2010/2011 Academic Year)” . A
Thesis. Surakarta: English Department Graduate School Sebelas Maret University, 2011.
The objectives of this research are to know whether Play School DVD can improve students’ vocabulary mastery and to know the strengths and weaknesses when Play school DVD is applied to improve the students’ vocabulary mastery. The subject of the research was the first grader of Kalam Kudus Christian Primary School in the 2010/2011 academic year.
The procedures of the research consist of planning, action, observation, and reflection. In collecting the data, the researcher used questionnaire, interview, field notes, and test. To analyze the quantitative data, the researcher applied a descriptive statistics. It was used to compare the scores and means of the pre-test and post-test. The pre-test was conducted in the pre-research while the post-test was conducted at the end of Cycle 1 and 2. The result of the test was used to know how well the students’ vocabulary mastery is. To analyze the qualitative data, the researcher analyzed the improvement of the teaching learning process by analyzing the results of questionnaire, interview, and field notes using Constant Comparative Method.
The applying Play School DVD in the process of teaching and learning vocabulary can solve the students’ problem in mastering the four aspects in vocabulary. The result of the tests shows that Play School DVD can improve the students’ mastery in vocabulary. The improvement can be found by comparing the average score of the Pre-test and of Post-tests in Cycle 1 and 2. The average score of the Pre-test is 38.87, Post-test 1 is 66.58, and Post-test 2 is 86.25. The results of questionnaire, interview, and field notes show the strength and the weaknesses of Play School DVD. The strength when Play School DVD is applied in teaching vocabulary are: (a) it can attract the students’ attention that make them concentrate on the lesson; (b) it triggers the students’ curiosity and interest; (c) it can motivate the students to learn English; (d) it is an effective media to teach vocabulary; (e) it helps the students to get or learn real English. The weaknessess when Play School DVD is applied in teaching vocabulary are: (a) teachers can be passive and leave his/her job to the DVD; (b) long and monotonous DVD will be boring.
commit to user
vii
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The researcher would like to praise her Lord, Jesus Christ, who has
enabled and strengthened her to finish this thesis. The researcher would also give
a great gratitude and appreciation to:
1. Prof. Drs. Suranto, M.Sc. Ph.D. The director of Graduate School of
Sebelas Maret University.
2. Dr. Ngadiso, M.Pd. The head of English Education Department Graduate
School of Sebelas Maret University.
3. Dr. Abdul Asib, M.Pd. The secretary of English Education Department
Graduate School of Sebelas Maret University.
4. Dr. Sujoko, M.A. The first consultant who has guided and supported the
researcher so that she could finish writing this thesis.
5. Drs. H. Tarjana, M.A. The second consultant who has given his time and
patience advising the researcher in this thesis.
6. Wiwoho, M.Pd. The headmaster of SD Kristen Kalam Kudus who has
given the researcher permission to conduct the research.
7. Ferdinand Nicholas Boonde, M.Pd. The researcher’s collaborator who has
given help, assistance, supports, and suggestion in carrying the action of
the researcher.
8. The first graders of class E as the subjects of the research for their
cooperation during the action.
The researcher realizes that this thesis is still far from being perfect.
Therefore, she will accept all constructive criticism mindfully and constructing
suggestion is needed for the progress of the next study. May this thesis will be
useful to increase the quality of the educational activities.
Surakarta, July 2011
Arsidi Puspaningdyah
commit to user CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
English as a local content has already been applied in Kalam Kudus
Christian Primary School since 2006. Before that, English had just been taught as
an extracurricular material. The importance of English language and the increase
of competitors, in this case the growing number of international primary school in
Surakarta, have motivated Kalam Kudus to increase its quality, especially in
English language teaching and learning.
Based on Depdiknas (2006: 402-403), the purposes of teaching English in
the primary school are to develop students’ communicative competence orally in
school context and to raise students’ consciousness about the importance of
English. It means that to be good in English, primary school students should be
able to use English orally to interact with the others in school context. Students
should know about the English vocabulary in order to use it in communicating
with the others.
Notion and Waring in Cameron (2001: 72) state that vocabulary is central
to the learning of a foreign language at primary level. Gower, et al. (1995:142)
also states that vocabulary is important to students, and that it is more important
than grammar for communication purposes, particularly in the early stages when
commit to user
language. It means that learning vocabulary takes the important role in teaching
foreign language especially in the early stage. Realizing the importance of
vocabulary in teaching English, the English teaching in the first and second grades
in Kalam Kudus primary school has been emphasized on vocabulary mastery. The
vocabulary teaching is focused to help the students build up the knowledge of
words in ways that will enable them to use language efficiently and successfully.
According to Ur (2010), the students should master at least 1000 items of
vocabulary by the end of the sixth grade. Whereas Notion and Waring (2001: 75)
give higher qualification about students’ vocabulary mastery in a year. They state
that a realistic target for children learning a foreign language might be around 500
words a year. Mastering vocabulary itself, as stated by Thornbury (2002: 15),
means mastering both its form and its meaning. Furthermore, Cameron (2001: 78)
states that knowing about word involves knowing about its form (how it sound,
how it is spelt, the grammatical changes that can be made to it), its meaning (its
conceptual content and how it relates to other concepts and words) and its use (its
patterns of occurrence with other words, and it particular types of language use).
From that statement above, it can be concluded that the ideal condition of
the vocabulary mastery of the first graders is they are able to spell, to pronounce,
to understand the meanings of words, and to use the words in sentences. The
students should get, at least 60, the passing grade.
To cover the ideal condition that has been stated above, the English
teachers in Kalam Kudus Primary school had applied some techniques and used
commit to user
problems still occurred, especially in Class I E. They did not know how to
pronounce and write the word correctly and sometimes they forgot about the
meaning. They also had difficulties in using the words they had learnt to construct
a simple, basic sentence. Those problems always arose and made them get low
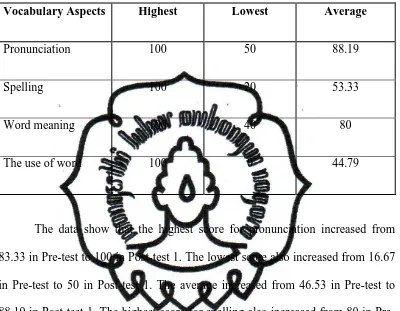
scores in doing the test. Below is the result of their pre-test based on the
indicators.
Table 1.1 The Students Score Viewed from the Skills
Indicator Highest Lowest Average
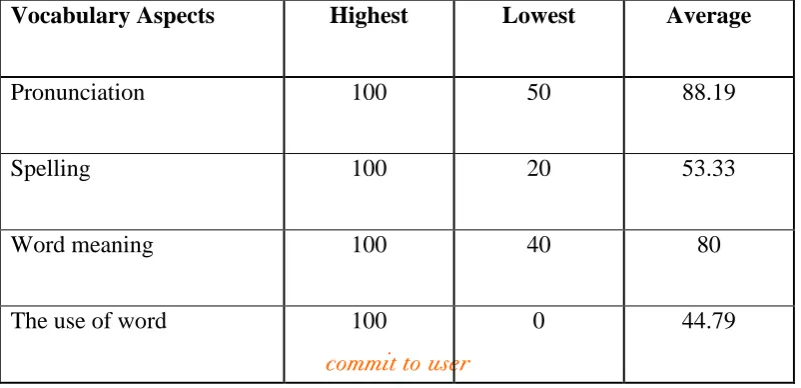
Pronunciation 83.33 16.67 46.53
Spelling 80 0 34.17
Word meaning 80 35 59.17
The use of word 100 0 15.625
There were some factors causing these problems. The first factor came
from the students. The students had difficulties in memorizing the words and their
meanings. The students found the process of teaching and learning boring and
uninteresting that made them not serious in doing the process. The students also
felt unconfident to say the words because they were afraid of mispronouncing the
words. They needed to be motivated. The second factor came from the teachers.
The teachers themselves sometimes only reviewed the words that had been taught
to the students twice. Of course, this is not enough. Webb in Ur (2010) gives the
evidence that the learners need, at least, ten or may be more meaningful
commit to user
than ten times to review a new item. Besides, the teachers should equip
themselves with various interesting media in order to make the teaching-learning
process more interesting. The third factor came from the condition of the class.
There were 24 students in the class. This number was actually quite big. The
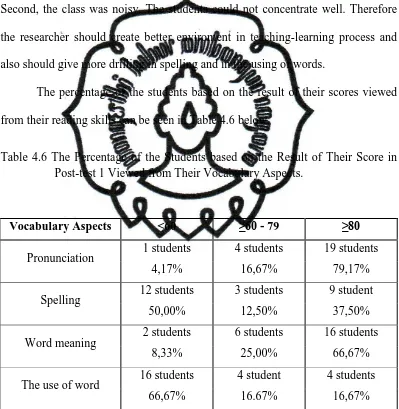
teacher in fact found difficulties in controlling the class. The result was the class
became so noisy. This condition made the process of the teaching and learning
ineffective because the teacher spent too much time to manage the class and calm
the students. Sometimes her efforts did not work.
Based on the problems stated above, in this research the writer proposes to
teach English vocabulary using Play School DVD as a media. Play School is
Australia's most successful regular television program for pre-school children.
Play School aims to extend the child's interest and encourages participation. Each
program contains a story, some songs (both traditional and new) and a variety of
play ideas with things to make and do.
The use of Play School DVD can be the solution to the problems because
Play School DVD provides pictures of the language-in-use. It can make
impossible experiences possible for its viewers and provides stimulation through
its dominant sense. According to Harmer (2001:38), children understanding
comes from what they see and hear, and, crucially when they have a chance to
touch and interact with. It means that listening to some words is not enough. The
children also need to see and interact with the words that are learnt to make a
commit to user
Based on the background above, it is believed that the use of Play School
DVD as the media in teaching English is an effective solution to overcome the
problem of improving students’ vocabulary mastery. Play School DVD consists of
some interesting sequences that can attract the students’ attention and make them
interesting to learn English. The DVD has colorful and clear pictures of the words
that are going to be learnt. It helps the students to have clear understanding about
the meaning of the words that are going to be learnt and also helps the students
easier in memorizing the word. The players in the DVD are native speakers. They
will help the students in having a good and correct pronunciation and spelling.
The students also learn how the words are constructed into sentences through the
conversation in the DVD. Therefore, the writer would like to conduct a research
about teaching vocabulary by using Play School DVD in Kalam Kudus Christian
Primary School under the title “Improving Students’ Vocabulary Mastery by
Using Play School DVD ( A Classroom Action Research to the First Grader of
Kalam Kudus Christian Primary School in the 2010/2011 Academic Year)”.
B. Problem Statement
Based on the background of the study, the writer wanted to identify
whether the use of “Play School DVD” can improve students’ vocabulary
mastery. The problems can be formulated as follows:
1. Can “Play School DVD” improve the students’ vocabulary mastery?
2. What are the strengths and the weaknesses of the implementation of Play
commit to user C. The Objectives of the Study
Based on the background of the study and the formulation above, there are
some objectives to be achieved in this study, namely:
1. Identifying whether “Play School DVD” improves the students’ vocabulary
mastery.
2. Identifying the strength and the weaknesses of the implementation of “Play
School DVD” in improving students’ vocabulary mastery in the first grader
of Kalam Kudus Primary School.
D. The Benefit of the Study
The result of the research is expected to be able to give some benefits to
the students, the teachers, and other researchers.
1. To the researcher
The result of this research can be used to improve the teaching and
learning vocabulary in her class. By doing the research, the researcher will
know whether or not Play School DVD is an effective media to improve
students’ vocabulary mastery.
2. To the students
It can help the students to learn vocabulary in an interesting way. By
using Play School DVD as the media in learning English especially in
learning vocabulary, the students will learn a real model of English in terms
of pronunciation, spelling, word meaning, and the use of word in a sentence.
commit to user 3. To the English teachers
It is hoped that by understanding the result of the study, English
teachers will enrich their techniques in teaching vocabulary. They will get
knowledge about teaching vocabulary using Play School DVD and use it as
the alternative media to help the students improve their vocabulary mastery.
4. To other researchers
The result of the study helps other researchers in developing the
techniques in teaching vocabulary. It can be used as a reference for those who
want to conduct a research in English teaching process, especially in teaching
vocabulary to young learners. Other researchers can also use it as a
comparative resource to conduct another research about vocabulary mastery.
The writer hopes that other researchers can use this study on a bigger scope in
commit to user CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter consists of the following sections: the theoretical
descriptions, rationale, and action hypothesis. The theoretical descriptions consist
of the explanation of vocabulary, the nature young learners, and the notion of Play
School DVD.
A. Vocabulary
1. The Nature of Vocabulary
Richard (2001:4) states that vocabulary is one of the most recognized
components of language. While Hornby (1994: 1425) adds that vocabulary is total
number of words that make up a language. Furthermore, Nunan (2005: 121) states
that vocabulary is the collection of words that an individual known. Clear
definition is given by Crystal. He states that vocabulary of a person is defined
either as the set of all words that are understood by that person or the set of all
words likely to be used by that person when constructing new sentences (Crystal,
2003: 2)
From the definition above it can be defined that vocabulary is a collection
of words that used by a person to construct sentences. Mastery means natural or
acquired facility in specific activity (http://www.answers.com/topic/mastery).
Hornby (1995: 721) states that mastery is complete knowledge or great skill.
commit to user
with the two experts, Quirk, et al. (1991: 644) states that mastery is great skill or
knowledge in a particular subject or activity.
According to the discussion above, it can be constructed that vocabulary
mastery is the competency to comprehend a collection of words and apply them to
construct sentences.
2. Some Aspects of Vocabulary
Thornbury (2002: 15) states that at the most level, knowing a word
involves knowing its form and its meaning. Cameron (2001: 78) states that
knowing about word involves knowing about its form (how it sound, how it is
spelt, the grammatical changes that can be made to it), its meaning (its conceptual
content and how it relates to other concepts and words) and its use (its patterns of
occurrence with other words, and it particular types of language use). Moreover,
Ur (1996: 60-62) states that there are some aspects of vocabulary that should be
taught or mastered by students in learning foreign language, as follow:
a. Form: pronunciation and spelling
The learner has to know what a word sound like (its pronunciation) and
what it looks like (its spelling). These are fairly obvious characteristics, and
one or the other will be preserved by the learner when encountering the items
for the first time. In teaching, teacher need to make sure that other these
aspects, both pronunciation and spelling, are accurately presented and
commit to user
b. Grammar
The grammar of new item will be necessary to be taught if this is not
obviously covered by general grammatical rules. An item may have an
unpredictable change of form. Certain grammatical context may have some
idiosyncratic way of connecting with this information at the same time as
teachers teach base form. When teaching the new verb, for example, the
teacher must give also its past form, if this is irregular (think, thought).
Similary, when teaching about noun, the teacher may wish to present its
plural form, if it is irregular (tooth, teeth).
c. Aspect of Meaning: denotation, connotation, appropriateness
The meaning of a word is primarily what it refers to in the real world, its
denotation; this is often the sort of definition that is given in dictionary. For
example, dog denotes a kind of animal; more specifically, common, domestic
carnivorous mammal; and both dark and moist mean slightly wet.
A less obvious component of the meaning of an item is its connotation; the
association, or positive or negative feeling it evokes, which may or may not
be indicated in a dictionary definition. The word dog, for example, as
understood by most British people, has positive connotation of friendship and
loyalty.
A more subtle aspect of meaning that often needs to be taught is whether a
particular item is the appropriate one to use in a certain context or not. For
commit to user
denotation with cry, but it is more formal, tends to be used in writing more
than speech, and is in general much less common.
d. Aspect of meaning: meaning relationship
How the meaning of one item relates to the meaning of others can also be
useful in teaching. There are various such of relationship: here are some of
the main ones.
1) Synonym; item that means the same, or nearly the same; for example
bright, clever, smart may serve as the synonym of intelligent
2) Antonym: item that means the opposite; rich is the antonym of poor.
3) Hyponym: item that serves as specific examples of general concept: dog,
lion, mouse are hyponyms of animal.
4) Co-hyponym or co-ordinates: other items that are the ‘same kind of
thing’; red, blue, green and brown are co-ordinates.
5) Superordinates: general concepts that ‘cover’ specific items; animal is the
superordinates of dog, lion, mouse.
6) Translation: words or expressions in the learners’ mother tongue that are
more or less equivalent meaning to the item being taught.
e. Word formation
Vocabulary items, whether one-word or multy-word, can often be broken
down into their component ‘bits’. Exactly how these bits are put together is
commit to user
The teacher may wish to teach the common prefixes and suffixes; for
example, if learners know the meaning of sub-, un-, and –able, this will help
them guess the meaning of words like substandard, ungrateful, and
untranslatable. Another way vocabulary items are built is by combining two
words (two nouns, or gerund and noun, or a noun and verb) to make one item.
For example: bookcase, follow-up, swimming pool.
From the explanation above it can be concluded that vocabulary mastery
means the ability to spell and pronounce the words correctly, understand the
meaning of words, and use the words in a correct sentence.
commit to user
Based on the four types of vocabulary above, it can be concluded that high
frequency words need to be given more attention in teaching English vocabulary
especially in elementary level. As Nunan (2003: 136) states that learners need to
learn low frequency words but, except for special needs, they are best learned
after the high frequency words are known. Nation in Linse (2005: 122) also states
that teachers should facilitate vocabulary learning by teaching learners useful
commit to user
own. What is meant by useful words here are words that children are likely to
encounter-words that occur in high frequency words.
4. The Advantage of Learning Vocabulary for Children
Vocabulary becomes the main part in language learning. Notion and
Waring in Cameron (2001: 72) state that vocabulary is central to the learning of a
foreign language at primary level. Gower, et al (1995:142) state that vocabulary is
important to students. It is more important than grammar for communication
purposes, particularly in the early stages when students are motivated to learn the
basic words they need to get by in the language. Wilkins in Thornbury (2002:13)
supports this idea. He states that without grammar very little can be conveyed,
without vocabulary nothing can be conveyed. Furthermore Nation in Schreuder
and Weltens (1993:115) states that good vocabulary knowledge enables
comprehension.
Based on the statement above, it can be concluded that vocabulary is
important for the learners, especially children, to learn a language.
5. Teaching Vocabulary
Nation (1974: 18-19) states that there are three things that must be taught
in teaching a word. They are the form of word, the meaning of word, and the form
and the meaning of word go together. Furthermore, Nation explains that there are
some ways to teach the form of word.
commit to user a. The teacher teaches the form of word visually.
The examples of teacher teaches the form of word visually are by showing
the form of word, showing the mouth movements involves in saying the
word, by showing hand movements that draw the letters of word in the air, or
by showing wooden or plastic letters that spell the word.
b. The teacher teaches the form of word tactilely.
Teaching the form of word tactilely means that the learners use their sense
of touch. The examples of teaching the form of word tactilely are teaching the
form of word by using letters made of wood, cardboard, sand paper, and so
on, so the learners can feel the shape of the letter that make up the word, by
using a system of writing like Braille, or by writing the word, letter by letter,
on the learner’s hand.
c. The teacher teaches the form of word aurally
The example of teaching the form of word aurally are teaching the form of
word by saying the word or by producing the word in morse code or some
other aural code.
Nunan also explains about some ways to help the learners understand the
meaning of words. They are:
a. Demonstration
In demonstration, teacher explains the meaning of word by showing an
commit to user b. Picture
Teacher uses photographs, blackboard drawings, illustrations cut from
magazine or newspaper to teach the meaning of word. Cameron (2001: 85)
adds moving images from TV, video or computer to teach the meaning of
word.
c. Explanation
To explain the meaning of word, the teacher gives description, gives
synonyms or opposites, puts the word into defining context, and translates the
word.
In teaching vocabulary, the teacher is not only teaching the form and the
meaning but also helping the learners to connect the form of a word with its
meaning by presenting the form and the meaning together, so that the learners
know that the words are connected to each other.
Cameron (2001:87-89) states that when learners know about a new word,
either the form or the meaning of this word, their vocabulary process has begun.
The word has entered the learner’s short term memory and the next teaching issue
is how to build up the memory of the word so that it is available for use in the
longer term. Memorizing activities are needed at the point if learning new words
for the first time, and at regular intervals to recycle vocabulary, so that it stays
commit to user
There are some organizational networks that are given by Cameron to
make strong memory connections:
a. Thematic organization of vocabulary
b. Organization of vocabulary through relations of wholes to parts
c. Organization of vocabulary in general to specific hierarchies
d. Organization of vocabulary through words and antonyms
6. Motivation in Learning Foreign Language
Motivation in the classroom is an essential component. Grolnick and Ryan
(1992:227) explore the central purpose of education. They state that the more
significant than the attainment of specific contents taught in schools is the growth
within each child of an interest and curiosity about the world around him or her
and the development of a confidence and sense of competence in learning. Such a
framework recognizes that achievement in school is a short-term goal whereas the
enhancement of the motivation to learn is an ongoing lifelong one.
Motivation is the energy which supports students in achieving their need
(Brown, 200: 161). Wlodkowski and Jaynes (1990:6) explain that in the broadest
sense, motivation is a value and a desire for learning. Furthermore, Gardner in
William and Burden (1997: 116) defines motivation as combination of effort plus
desire to achieve the goal of learning the language plus favorable attitudes
towards learning the language. Bonia (1997: 3) gives clear definition by stating
that student’s motivation refers to a student’s willingness, need, desire, and
commit to user
From the statements above, it can be concluded that motivation is the
power of the students for achieving the objectives of learning and mastery the
language.
There are two kinds of motivation; intrinsic motivation and extrinsic
motivation.
a. Intrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic motivation is motivation which appears without needing internal
stimulus, because it has been internal to the person that is suitable with
his/her need. Intrinsic motivations are inherent in learning situations and meet
pupil needs and purposes. Therefore, intrinsic motivations can be said as a
kind of motivation in which the learning activities started and continued
based on internal drive and absolutely related to learning activities. As
Brophy (1998: 126) states that intrinsic motivation applies students value (or
can learn to) participate in the activity, and emphasizes on students’ interest
in engaging these activity willingly.
b. Extrinsic Motivation
Extrinsic motivation is the motivation that appears because there is
stimulus/ incentive from outside the individual. It is a kind of motivation in
which learning activities started and continued based on external drives which
are not absolutely related to learning activities. Extrinsic motivation
stimulates students to engage in classroom activity effort fully because
commit to user
B. The Nature of Young Learner
1. The Definition of Young Learner
The age of the students is a major factor for teacher in making decisions
about how and what to teach. People of different ages have different needs,
competences, and cognitive skill.
According to Linse (2005: 2) young learners are defined as children
between ages 5-12. Meanwhile Harley, et al. in Cameron (2001: 15) state that
young learners is a group of children (7-8 years) that are studying a foreign
language, they seem to pay more attention to sound and prosody ( the music of an
utterance), whereas other elder children (12-14) are more attentive to cues of word
order. Furthermore Brumfit (1997: 67) states that young learners is a group of
children level of age five to six, where they learn language without reading and
writing.
From the explanation above it can be concludes that young learners is a
group of students level of age five to fourteen, where in every stage they have
some characteristics suitable to their level of age.
2. Young Learners’ Characteristics in Learning Language
Young children, especially those up to the ages of nine or ten, learn
differently from older children, adolescents, and adult. Harmer (2001:38) states
that children learn in the following ways:
commit to user
b. They often learn indirectly rather than directly – that is they take in
information from all sides, learning from everything around them rather that
only focusing on the precise topic they are being taught.
c. Their understanding come not just from explanation, but also from what they
see and hear and, crucially, have a change to touch and interact with.
d. They generally display an enthusiasm for learning and a curiosity about the
world around them.
e. They have a need for individual attention and approval from the teacher.
f. They are keen to talk about themselves, and respond well to learning that uses
themselves and their own lives as main topics in the classroom.
g. They have a limited attention span; unless activities are extremely engaging
they can easily get bored, losing interest after ten minutes or so.
In line with Harmer, Scotts and Ytreberg (p. 1-3) determine the characters
of children from five to seven years old in learning the language as follow:
a. They can talk about what they are doing.
b. They can tell you about what they have done or heard.
c. They can plan activities.
d. They can argue for something and tell you why they think what they think.
e. They can use logical reasoning.
f. They can use their vivid imaginations.
g. They can use a wide range of intonation patterns in their mother tongue.
commit to user
Furthermore, Scotts and Ytreberg note other characteristics of the young
language learner.
a. They know that the world is governed by rules. They may not always
understand the rules, but they know that they are there to be obeyed, and the
rules help to nurture a feeling of security.
b. They understand situations more quickly than they understand the language
used.
c. They use language skills long before they are aware of them.
d. Their own understanding comes through hands and eyes and ears. The
physical world is dominant at all times.
e. They are very logical-what you say first happens first.
f. They have a very short attention and concentration span.
g. Young learners sometimes have difficulty in knowing what fact is and what
fiction is.
h. Young children are often happy playing and working alone but in the
company of others.
i. Young children love to play, and learn best when they are enjoying
themselves. But they also take themselves seriously and like to think that what
they are doing is ‘real’ work.
Based on the explanation above, the researcher can conclude that children
need to be taught in different way due to their age, background and need to learn.
commit to user
C. Play School DVD
1. The Notion of Play School DVD
Play School is Australia's most successful regular television program for
pre-school children. It is broadcasted every weekday throughout the year on
ABC1 at 9.30 am and 3.00 pm and ABC2 at 4.30 pm.
The first program was broadcasted on July 18, 1966 at 10.05am in NSW
and Victoria only, but soon was broadcasted around the country. In December that
same year, Play School began afternoon transmissions as well as mornings, a
practice that continues to this day. Now 40 years on, over one million children
view Play School each week.
Play School aims to encourage a child to wonder, to think, to feel and to
imagine. The program shows two warm, caring people taking the time to be with
one child. They address the child directly and personally. Into this relationship are
woven the stories, songs and activities that form the fabric of Australian children's
culture. Play School is successful because it satisfies our basic human need to
interact with other people and to be valued by them.
Play School aims to extend the child's interest and encourages
participation. Each program contains a story, some songs (both traditional and
new) and a variety of play ideas with things to make and do.
commit to user
2. The Procedure of Teaching Vocabulary by Using Play School DVD
There are several steps that will be done in teaching vocabulary by using
play school DVD. First, the teacher plays some sequences of Play School DVD.
Second, the teacher shows up some pictures that demonstrate the meaning of the
words shown up on the segment of Play School DVD.
The third step is the teacher plays the segment of Play School DVD. The
teacher asks the students to listen to the pre taught vocabulary. When the students
think that they hear one of the words from the pre taught vocabulary, they raise
their hands. The teacher pauses DVD and then asks the students what word he/
she heard. The teacher rewinds the DVD so that the students can listen to the
word again. The teacher pauses DVD and asks the students to imitate what is said
by the native in the DVD. By doing this activity, it is hope that the students will
practice on how to pronounce the words correctly and acknowledge the word
when it is constructed in a sentence. The teacher also encourages the students to
interact with the Play School presenters by singing along and doing action as
requested.
Fourth, the teacher shows the pictures of the pre taught vocabulary again
and asks the students to spell the word. The teacher then writes the word on the
board and asks the students to pronounce it. The fifth step is the teacher plays the
segment of Play School DVD again and pauses on the segment where the pre
taught vocabulary used. The teacher says the phrase or sentence where the pre
commit to user
The final step is the teacher asks the students to make a phrase or sentence
based on the word of pre taught vocabulary (Uni-Bridge English Language
Program Curriculum 2010/2011 Level 1 School Program).
3. The Advantages of the Using of Play School DVD
Using video to support the teaching and learning process will offer some
unique instructional features. Video gives student one more way to experience
abstract content. Judy (2003: 309) states that video make impossible experiences
possible for their viewers and provide stimulation through our dominant sense. It
provides the opportunity to show the students phenomena that would be either
impossible or dangerous to view personally.
The advantages of video, in this case is the advantages of Play School
DVD, in learning the language are obviously explained by Harmer (2001: 282).
There are some reasons why video can add a special, extra dimension to the
learning experience:
a. Seeing language-in-use
It means that the students not only hear the language but also see the
language itself. The language is conveyed through expressions, gestures, and
other visual clues.
b. Cross-cultural awareness
Video uniquely allow students a look at situations far beyond their
commit to user
British ‘body language’ when inviting someone out, or how American speaks
to the waiter. Video is also a great value in giving students a chance to see
such things as what kinds of food people eat in other countries, and what they
wear.
c. Motivation
For all the reasons so far mentioned, most students show an increased level
of interest when they have to see the language in use as well as hear it, and
when this is coupled with the interesting task.
In line with Harmer, Allan (1991: 48-49) states that there are four
advantages of using video in language teaching and learning. They are:
a. Video presents realistic ‘slice of life’
Video can allow the students to see the ways people communicate visually
as well as verbally. It shows obviously the example of language in use. So,
video is a good means of bringing ‘slice of living language’ into the
classroom.
b. Video gets students talking
The right video material can get the students talking. Its vivid presentation
of settings and characters can be used to set scene for role play. It also can
present a case with such impact that it sparks off fierce debate. So that video
can be a stimulus to genuine communication in the classroom by bringing out
commit to user c. Video provides visual support
Video helps the students in understanding a foreign language because the
students are not only listening to the words but also see the word used. Video
helps the students concentrate because it provides a focus of attention while
they listen.
d. Video offers variety and entertainment
As people expect to enjoy the experience of viewing, so do the students.
They bring the same expectations to the experience of viewing video in the
classroom. The combination of variety, interest and entertainment that can
derive from video makes it an aid which can help develop motivation in
learners.
4. The Disadvantages of the Using of Play School DVD
Watching a video can also be a passive experience. Judy (2003: 311) also
states that watching motion video can be a passive even boring experience for the
learner. That is why teaching methods must be used which instead turn it into a
springboard for student action and interaction.
E. Rationale
Vocabulary takes an important role in learning the language, especially for
commit to user
that the student cannot use the language because knowing the vocabulary means
knowing its form, its meaning, and knowing how to use it.
Based on pre observation stated in the background of the study, it was
found that the students got difficulty in spelling and pronouncing words correctly,
they found it difficult to memorize the meaning of the word and construct the
word into a simple, basic sentence.
There were some reasons why such problems occurred. First, it happened
because the students only had short term memories about the words they learnt so
that they often forgot about the word, either the form or meaning easily. Second,
they felt unconfident to say the word. They were afraid of mispronounce the
word. Third, they had difficulty in using the word to construct sentence. The last
reason was that they got bored with technique that was usually applied in the
teaching learning process, in which they only memorized the word and had test
about it.
To overcome such a condition, a good media in teaching vocabulary was
needed. As stated in the previous section that young learners understanding come
through hands and eyes and ears and that the physical world is dominant at all
times. Play School DVD enables students to have an experience with the real
picture of the word. Besides, it enables students to see language in use. It also
provides the students with songs and activities to interact with. So, it is hoped that
by using Play School DVD, the students will have full understanding about the
commit to user
Watching the Play School DVD, the students will hear how each word is
pronounced by the native speaker. The same word will be pronounced again and
again so that the students will get a clear and right pronunciation. Through this
step, it is hoped that the students’ problems in pronouncing will be solved. The
teacher then will show some pictures related to those words. The teacher will ask
the students to spell and write the word. Through this step, it is hoped that the
students’ problem in spelling will be solved.
The procedures in teaching vocabulary by using Play School DVD also
help students to memorize the word well. Repeating the words and showing their
pictures several times through the activities in Play School DVD will help the
students to acquire the words well. From the Play DVD School, the students will
also learn how certain words are put in a simple sentence. Students will use it as a
model to make a simple and basic sentence using the words they have learnt. It is
hoped that the students’ problem in making simple basic sentence can be solved.
Based on the explanation above, it can be assumed that Play School DVD
can help the students to improve their vocabulary mastery.
F. Action Hypothesis
Related to the previous description of the related theories and the basic
assumption above, the researcher formulates the action hypothesis as follows: The
commit to user CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In this chapter, the researcher elaborates a research methodology including
setting of place and time of the research, the subject of the research, the method of
the research, the procedure of research, technique of collecting data, and
technique of analyzing data. They would be explained in the following parts:
A. The Setting and Time of the Research
This research was carried out at Kalam Kudus Christian Primary School
Surakarta, Central Java. This school is located at two different places. The first
until the fifth grade is located at Jl. S. Parman 42, Surakarta. The sixth grade is
located at Jl. R.M Sangaji 24, Surakarta in the same place with Kalam Kudus
Christian Junior High School.
Kalam Kudus Christian Primary School which is located at Jl. S. Parman
40 has 20 classes which are divided into Grade 1 until Grade 5. Each grade has 5
classes. Each class consists of 28 to 30 students. Because of lack of class, the first
and the second grade go to school in shift. The first grade’s lessons are from 07.00
until 10.10 and the second grade’s lessons are from 10.15 until 13.30. The period
commit to user
This classroom action research was conducted from November 2010 up to
April 2011. Below is the time table.
Table 3.1 The Time Table of the Research
NO ACTIVITIES MONTH/YEAR
3. Preparing the instruments V
4. Conducting the research V V
Kudus Christian Primary School. They were 24 students. They came from almost
the same social and economic status. Almost all of their parents were
commit to user C. The Method of the Research
In this research, the researcher used action research method. Related to
the action research method, there are some definitions of action research. Wallace
(1998:4) explains that action research is “done by systematically collecting data
on your (teachers) everyday practice and analyzing it in order to make some
decisions about what your practice should be. While McKernan (2003:5) defines
action research as a systematic self-reflective scientific inquiry that is done by
practitioners to improve practice.
The researcher used action research because the researcher wanted to
solve problems in teaching vocabulary as well as the attempt to know the students
improvement in mastering vocabulary by using Play School DVD.
D. The Procedure of Action Research
The researcher used action research as a spiral steps that consist of four
stages. As stated by Richard (1996: 13), the four stages are planning, action,
observation, and reflection. In each cycle, the procedures of research were as
follows:
1. Planning
After identifying the problems, the researcher and the collaborator made a
plan about what kind of activities that would be carried out in the action. It
included making the lesson plan, preparing the material, and preparing
observation sheets to record students’ activities.
commit to user 2. Action
The researcher gave pre-test and post-test to the students. The researcher
taught vocabulary using Play School DVD which followed the steps in the lesson
plan. There were two cycles in this research in which each cycle consists of three
meeting.
3. Observing
The activity was observing the teaching and learning process done by the
researcher and the students. It included the interaction between the teacher and the
students, the way the teacher explained the material, and the way she answered the
students’ questions. So, everything that happened during the teaching and learning
process would be recorded. In this activity, the collaborator took an important
role. He was the one who observed the teaching and learning process and took
note. As stated by Nunan (1992:120) that collaborator is needed to create multiple
perspectives and to broaden interaction.
4. Reflection
Doing the reflection, the researcher together with the collaborator and
some students as the representatives evaluated the process of the teaching and
learning and the result of the implementation of Play School DVD in teaching
vocabulary. The result of the reflection was used to make the next cycle better
commit to user The scheme of Action Research is reflected as follows:
E. Data Sources
The data of the research were collected from the procedure and activities
of teaching and learning process using the Play DVD School and the scores of
vocabulary test. The result of the teaching in the form of post-test was compared
with the pre-test.
Action
Observing
Reflection
Planning
commit to user The sources of the data in this research were:
1. Event
It was all the action of the teaching and learning process using Play DVD
School which was done in two cycles. It also included the activity of doing tasks
and exercises.
2. Documents
They were books and teaching materials used by the teacher in teaching
English. Other documents such as students’ previous test result and works were
also taken and analyzed.
3. Information Data
Information data means all the data that were taken from interview and
questionnaire.
F. Technique of Collecting Data
There were two kinds of data, quantitative and qualitative, that were
needed for the research. The researcher collected quantitative data by giving tests.
The researcher gave the students a pre-test and a post-test in order to know their
vocabulary mastery before and after being taught using Play DVD School. It was
to know whether the students’ vocabulary mastery improved or not. The questions
commit to user
The qualitative data were collected by doing observation, interview, and
giving questionnaire.
1. Observation
In observation, the researcher asked the collaborator to observe the process
of the teaching and learning process done by the researcher and the students. The
collaborator watched and noted all the activities happened during the process. He
made the report in the form of field note.
2. Interview
The researcher interviewed the students and collaborator about their
personal perception, experiences, opinion, and ideas related to the teaching and
learning process in the class.
3. Questionnaire
To get more comprehensive data, the researcher also gave the students
questionnaire to fill in. The researchers used closed-ended items questionnaire as
suggested by Burns (2010: 82). These are items which there is limited choice of
answer. The researcher gave the students a statement and they should give their
commit to user G. Technique of Analyzing Data
To analyze the quantitative data, the researcher applied a descriptive
statistics, comprising the highest and lowest score and finding the mean. To
measure the students’ mastery on the vocabulary test, the researcher used the
percentage correlation formula as follow:
Where:
S = the students’ mastery in %
R = the students’ right answer
N = the maximum number of the whole answer
SM = Standard Mark (100)
After analyzing the scores of the written test, the researcher compared the
mean of the pre-test and of the post-test result by using the formula:
∑ 葈
Where:
ᰀ = mean (the score)
SX = the total score
commit to user
The qualitative data were analyzed by using Constant Comparative
Method as suggested by Strauss and Glasser in Lincoln and Guba (1985:339).
Constant Comparative Method or CCM is analyzing the data by comparing one
category to another constantly. They say that in general, the data analysis proceses
include data reduction, data classification, data synthetis, and ended by action
hyphotesis. The following is a brief step related to the statement above;
1. Comparing incidents applicable to each category.
In this step all incidents occurred in the data will be coded into as many as
categories as possible.
2. Integrating categories and their properties.
The researcher will begin to note the relationship among the concept. For
these relationships to emerge, however, it will be necessary for the researcher
to have noticed all the concepts.
3. Delimiting the theory.
It refers to the theory and category reduction from the result of two previous
steps. As the patterns of relationship among concepts become clearer, the
researcher ignores some of the concept initially noted but evidently irrelevant
to the inquiry. When the numbers of categories are reduced, the theory itself
becomes simpler.
4. Writing the theory.
This is the final step that the researcher is making the final judgment of his
commit to user CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULT AND DISCUSSION
A. Introduction
As has been mentioned in Chapter I, the purposes of the research are to
know whether the use of Play School DVD improves students’ vocabulary
mastery and to find the strengths and weaknesses when Play school DVD is
applied in teaching vocabulary to the first graders of Kalam Kudus Christian
Primary School.
According to the result of the preliminary study, the first graders of
Kalam Kudus Christian Primary School, especially Class IE, had difficulties in:
(a) pronouncing words; (b) memorizing words, both the forms and their meanings,
and (c) using words in a sentence.
From the preliminary study, it was found out that the problems arose
because of three aspects. The first one came from the students. They had
difficulties in memorizing the words and their meanings. The students found the
process of the teaching and learning boring and uninteresting that made them
unserious in doing the process. The students also felt unconfident to say the words
because they were afraid of mispronouncing them. The second aspect was from
the teacher. The teachers sometimes only reviewed the words that had been taught
to the students twice to four times. Besides, the teachers should equip themselves
commit to user
more interesting. The last aspect was the classroom situation. There were 24
students in the class. This number was actually quite big. The teacher in fact
found difficulties in controlling the class. The result was the class became so
noisy. This condition made the process of the teaching and learning ineffective
because the teacher spent too much time to manage the class and to calm the
students which were sometimes did not work. Therefore, a new technique is
needed to work out those problems. The researcher decided to use Play School
DVD as the media in conducting this action research.
B. Preparation of Action Research
To identify the students’ problems in vocabulary mastery, the researcher
observed the class to see the teaching-learning process done by the teacher and the
students, and conducted a pre-test.
A pre-test was conducted on Tuesday, February 28th, 2011. The purpose of
doing the pre-test was to identify the students’ vocabulary mastery. Before the test
was applied, it had been tried out in another class. The purpose was to get a valid
and reliable instrument.
The total number of students was 24 and all of them joined the pre-test.
According to the result of the pre-test, it can be concluded that the students’
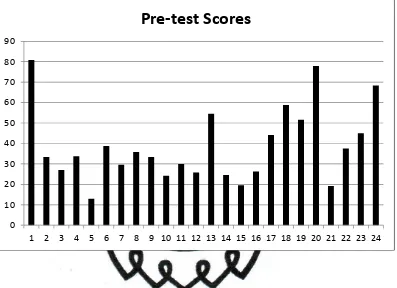
vocabulary mastery was low. It was shown by their scores. Below is the chart of
commit to user Figure 4.1
The Chart of Pre-test Scores
The chart shows that one student got 80.83. Two students got above 60,
and 21 students got below 60. The highest score is 80.83 and the lowest is 12.92.
Those resulted 38.87 for the average of this test. A complete data about students’
pre-test result can be found in Appendix 6.c.
Another important consideration was about the students’ score viewed
from their skills. The average of students’ score in pronouncing the word was
46.53, in spelling the word was 34.17, in understanding word meaning was 59.17,
and in using the word in a sentence was 15.625. For more complete data, it can be
found in Table 4.1. 0
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
commit to user
Table 4.1. The Students’ Scores on Vocabulary Mastery on Pre-test Viewed from Their Aspects.
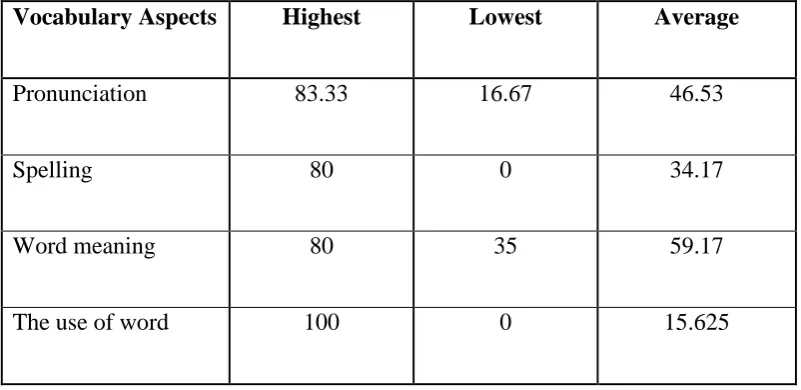
Vocabulary Aspects Highest Lowest Average
Pronunciation 83.33 16.67 46.53
Spelling 80 0 34.17
Word meaning 80 35 59.17
The use of word 100 0 15.625
The percentage of the students based on the result of their scores viewed
from their vocabulary aspects can be seen in Table 4.2 below.
Table 4.2 The Percentage of the Students Based on the Result of Their Scores Viewed from Their Vocabulary Aspects.
Vocabulary Aspects <60 ≥60 – 79 ≥80
Pronunciation
18 students 4 students 2 students
75.00% 16.67% 8.33%
Spelling
17 students 5 students 2 students
70.83% 20.83% 8.33%
Word meaning
10 students 12 students 2 students
41.67% 50.00% 8.33%
The use of word
21 students 1 student 2 students
commit to user
The level of the students’ vocabulary mastery can be seen in the following
table.
Table 4.3 The Level of Students’ Vocabulary Mastery Based on Their Pre-test Result
Percentage Interpretation Number of students
(N=24)
81-100 Very good -
61-80 Good 3 students
41-60 Fair 5 students
21-40 Poor 13 students
1-20 Very poor 3 students
From the table above, it can be seen that the vocabulary mastery of 21
students (87.5%) were low and 3 students (12.5%) were at Good level.
C. Research Implementation
1. Description of Cycle 1
In Cycle 1, the researcher carried out four meetings. Cycle 1 was
conducted from March 2nd to March 14th, 2011. After the fourth meeting, Post-test
1 was carried out. Each cycle consisted of planning, action, observation, and
commit to user a. Planning Action
The researcher and the collaborator prepared for the action. The
preparation included: designing lesson plans, preparing assessment, preparing
Play School DVD, preparing pictures and preparing observation list. The lesson
plans were designed for four meetings. It consisted: (1) General Instructional
Goals; (2) Specific Instructional Goals; (3) Learning Source; (4) Material; (5)
Teaching and Learning Activities; and (6) Assessment. The vocabulary material
for the first meeting was “Animal”, for the second meeting was “Dinosaur’s Parts
of the Body”, for the third meeting was “Fruits and Vegetable”, and for the fourth
meeting was “Color”. All the materials were taken from Play School DVD.
After designing lesson plan, the researcher and the collaborator prepared
the assessment. The assessments were in the form of multiple choice and essay
with 16 questions that covered the instructional objectives in the lesson plan. The
next activity was preparing Play School DVD. The researcher chose suitable
sequence from Play School DVD. She then searched the pictures that were
suitable with the play. After that, the researcher and the collaborator prepared
observation instrument. The collaborator and the researcher would use field note
in observing the teaching and learning process done by the researcher and the
commit to user b. Action
1) First meeting
The first meeting was on Wednesday, March 2nd, 2011. The researcher and
the collaborator entered the class at 10.55 A.M. The class was so noisy. The
students had just finished having their break. It needed about 10 minutes to calm
down the students and made them ready to have a lesson. The researcher then
greeted the students. The researcher prepared all the media and learning sources.
She turned on the LCD and plugged in to her note book.
In pre-vocabulary activity, the researcher played the Play School DVD.
When she played the Play School DVD, the students were so happy. They sat on
their seat and watched it enthusiastically. When the researcher stopped the play in
order to go to the next step on her research, some of the students said,” Lho miss,
jangan dimatikan”. The students loved watching Play School DVD.
After playing the DVD, the researcher showed some animal’s pictures to
the students. She asked the students to pay attention to the pictures. The
researcher wanted the students to recognize the picture when they saw it on the
DVD. So, on this step, the researcher did not allow them to speak out what picture
it was.
In whilst-vocabulary activity, the researcher played the Play School DVD
again. The researcher then asked the students to raise their hand every time they
heard or saw some kind of animals mentioned in the DVD. At first the children
commit to user
or saw any kind of animals mentioned on the DVD. So, the researcher paused the
DVD and gave the model to the students. Having been sure that the students
understood what to do, the researcher played the DVD again. When she played
the DVD, some students then raised their hands. The researcher then paused the
DVD, asked the students what they had heard. She continued the DVD and did the
same steps until all animals had been mentioned by the students.
The researcher then stuck the pictures on the board and asked the students
to spell the word. But, only some students did the spelling. The researcher then
encouraged the other students to do the spelling. She asked the passive students to
spell the word. The researcher corrected the students when they misspelled the
words. She then wrote the word on the board, below the picture. The researcher
played the DVD again and asked the students to repeat after the native speaker on
the DVD saying the name of every animal in the pictures. Then the researcher
showed the pictures to the students one by one. First she showed the picture of a
lion, and then asked the students by saying, “What picture is it?” The students
answered it by only saying, ”lion”. Then the researcher gave the model. She said,
“It is a lion.” The researcher showed another picture and asked the students to
answer it as the model she gave.
In post-reading activity, the researcher gave the assessment to the students
and they were given 10 minutes to finish it. Next, the researcher showed the
picture to the students and asked them to say the names of the animals in the