THE EFFECT OF USING MONITORING, QUESTIONING,
AND REPREDICTING STRATEGY ON STUDENTS’
READING COMPREHENSION
A THESIS
Submitted to Fulfill the Partial Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
By:
DORMAULI SAMOSIR
Registration Number: 209121015
ENGLISH AND LITERATURE DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGES AND ARTS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
First of all the writer would like to express her praises to the Almighty God,
Jesus Christ, for the love and blessing so the writer has finally completed this thesis.
This thesis is aimed to fulfill one of the requirements for the degree of Sarjana
Pendidikan of English Department, Faculty of Languages and Arts, State University of
Medan.
During the process of writing, the writers realizes that she cannot accomplish
without God blessing and supporting from many people, therefore the writer would like
to express her sincere gratitude to:
1. Prof. Dr. Ibnu Hajar Damanik, M.Si., the Rector of State University of Medan.
2. Dr. Isda Pramuniati, M.Hum., the Dean of Faculty of Languages and Arts, State
University of Medan.
3. Prof. Dr. Hj. Sumarsih, M.Pd., the Head of English and Literature Department,
Rika, S.Pd., M.Hum., the Secretary of English Department, Dra. Masitowarni
Siregar, M.Ed., the Head of English Education Program, and all lecturers.
Thanks for their support and advice during her academic years.
4. Prof. Dr. Berlin Sibarani, M.Pd., the thesis supervisor for great care, guidance,
and advices during the process of accomplishing this thesis.
5. Dr. Anni Holila Pulungan, M.Hum., Dra. Tjut Ernidawati, M.Pd., and Dra.
Rahmah, M.Hum., her reviewers, thanks for their advices and constructive
suggestions that improve this thesis.
6. Drs. Gunawan Simanjuntak, the headmaster of SMP Trisakti 2 Medan, and also
the English teacher, Drs. A. Tumanggor, who had helped her in conducting the
iii
7. Her beloved parents, J. Samosir and A. Sitinjak for their love, motivation,
patience, prayers, and financial support.
8. Her beloved sisters, Jerni Ivanna and Nurhijah and her beloved brothers
Saruwekdi, Yan Sofian, and Petrus Tri Boy. Thanks for their support, prayers,
motivation and care.
9. Her best friends, Febrina Manalu and Yustina Situmorang. Thanks for their
support, love, prayer, and care.
10.Her beloved friends, students of English Department, specially Carla, Dewi,
Orli, Elma, Rasta, Sahat, Survey, Nurdiana, Ellis, Bintang and her classmates
Regular C '09, her friends PPLT 2012 SMAN 1 Sei Bamban specially Dayfreeri, ‘Lang Agus, Freddy, and K Fenty, her friends in UK-KMK Santo Martinus
Unimed, and also her boarding house friends, Paulina, Juni, Rohani, Swi,
Mega, Patris, Eta, Dewi, Titin, Eka, Tetty, Iko and Tari. Thanks for their
motivation, care, and laugh.
The writer hopes this thesis will be useful for those who read it, especially for
the students of English Department.
Medan, March 2014
ABSTRACT
Samosir, Dormauli. 209121015. The Effect of Using Monitoring, Questioning, and Repredicting Strategy on Students’ Reading Comprehension. A Thesis. Medan: English Department, Faculty of Languages and Arts, State University of Medan. 2014.
vi
LIST OF TABLES
Page
Table 1.1 The English Score of Eight Grade Students of SMP Trisakti 2 Medan ... 3
Table 3.1 The Research Design ... 27
Table 3.2 Teaching Procedure in Experimental Group ... 29
Table 3.3 Teaching Procedure in Control Group ... 30
Table 3.4 Table Specification ... 31
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page
Appendix A The Score of Pre Test and Post Test by the Students of Experimental Group ... 45
Appendix B The Score of Pre Test and Post Test by the Students of Control Group ... 46
Appendix D The Calculation of t-test ... 50
Appendix E The Percentage Points of The T Distribution ... 53
Appendix F Reading Comprehension Test ... 54
Appendix G Answer Key ... 60
Appendix H Lesson Plan ... 61
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. The Background of the Study
Reading is one of the four language skill that is very important. Reading is
the most important activity in any language class. According to Zare et al., (2013)
Reading is a cognitive activity in which the reader takes part in a conversation with the
author through the text. Reading means to understand the meaning of printed words.
Understanding information in the text is, of course, the whole purpose of reading.
According to Westwood (2001) a cognitive-constructivist view of reading
emphasis that it is a process in which readers actively search for and make
meaning for themselves in what they read.
Reading is a very complex skill and for this reason it is not surprising to
find that some children encounter difficulties in learning to read (Westwood
2001:25). So, the students require an active interaction with the text. The students
glean the information from the text and what they have already known. It means
that the students link to their experience or background knowledge. In addition,
Meyer and Ray (2011) state that reading comprehension involves actively
constructing new understandings by building relationships among the parts of text
and between the text and one's pre-existing knowledge.
Reading comprehension is an important skill which has to be mastered by
students. It is important because reading comprehension is the basis of nearly all
learning and a basic requirement to progress in life. According to Jalilifar et. al.,
(2008) for many language learners reading is ranked first among the academic
2
In reading skill, students are expected to get knowledge and understand
about the context that has explained in the text. Students do not only read the text,
but also understand the information from the text that they read. The purpose of
reading comprehension is to get some skills in understanding the text. So, it is
useless if we do not have reading comprehension because it involves the
competence to find some information in reading text.
In fact, reading is not as easy as people think. It is not easy to have the
ability of drawing meaning from the text and interpret the information
appropriately. So the students have problem in reading comprehension. This
problem can be affected by some factors. It can be from the students themselves
(internal factor) and also from the teacher (external factor).
The reading comprehension problem which is affected by students
themselves can be seen from the students’ view about reading comprehension
class. While doing teaching practice in SMA N 1 Sei Bamban, the writer asked the students’ opinion about reading class. They said that reading class is boring
activity. They must translate the difficult words in to Indonesian in order to
understand the text.
And the reading comprehension problem which is affected by teacher can
be seen from the way of teacher who uses the conventional method. The writer
found the same case when she observed how English teacher taught reading in
SMA N 1 Sei Bamban. The teacher asked the students to read the passage then,
find out the difficult words and translate it into Indonesian language. After that,
3
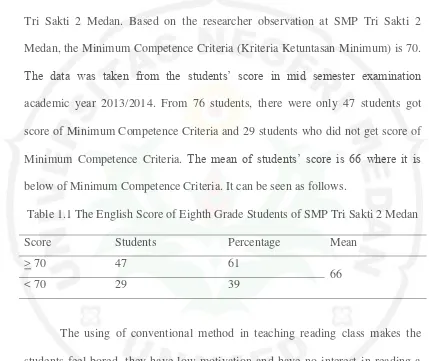
The problem of the students in comprehending a text also happen in SMP
Tri Sakti 2 Medan. Based on the researcher observation at SMP Tri Sakti 2
Medan, the Minimum Competence Criteria (Kriteria Ketuntasan Minimum) is 70. The data was taken from the students’ score in mid semester examination
academic year 2013/2014. From 76 students, there were only 47 students got
score of Minimum Competence Criteria and 29 students who did not get score of
Minimum Competence Criteria. The mean of students’ score is 66 where it is
below of Minimum Competence Criteria. It can be seen as follows.
Table 1.1 The English Score of Eighth Grade Students of SMP Tri Sakti 2 Medan
Score Students Percentage Mean
> 70 47 61
66
< 70 29 39
The using of conventional method in teaching reading class makes the
students feel bored, they have low motivation and have no interest in reading a text. Students who are not interest in reading can’t gain information and improve
their knowledge. In other hand, people especially students are expected to increase
their interest in reading and try to develop their reading comprehension. Reading
comprehension can developed when reading interest increase too.
Considering the condition above, the writer is interested in applying
Monitoring, Questioning, and Repredicting Strategy which is developed by Duffy
(2009:107) to teach reading comprehension. Monitoring, Questioning, and
Repredicting are strategic heart of the comprehension process. Monitoring,
4
Comprehension starts when students anticipate meaning by predicting ahead of
time what they will find in a passage. Then students move into a text, they
monitor, they question, and when necessary they abandon they prediction they
made earlier and make a new prediction. The readers talk to themselves about the
meaning they are building.
Based on the explanation above, the writer is interested in conducting a
research on the effect of using Monitoring, Questioning, and Repredicting strategy on students’ reading comprehension.
B. The Problem of the Study
Based on the background of the study above, the problem is formulated as
the following: “Does Monitoring, Questioning, and Repredicting Strategy
significantly affect the students’reading comprehension?”
C. The Scope of the Study
This study focuses on using Monitoring, Questioning and Repredicting
Strategy on students’ reading comprehension in descriptive text especially on
literal and interpretative reading.
D. The Objective of the Study
5
E. The Significance of the Study
The findings of the study are expected to have both theoretically and
practically importance in reading comprehension.
1. Theoretically, the findings of this study is expected to enhance the theories
of reading comprehension.
2. Practically, the findings of the study is expected to give feedback to:
a. The teachers who teach English, it can be used as one alternative
strategy to teach reading.
b. The students, it helps them to develop their reading skills and good
reading comprehension after they learn by using Monitoring,
Questioning, and Repredicting Strategy.
c. The researcher, it will be basic information in conducting further
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS
A. Conclusion
Based on the research finding, the researcher concludes that there is a
significant effect of applying Monitoring, Questioning, and Repredicting Strategy on students’ reading comprehension, since students’ achievement in reading
comprehension taught by applying Monitoring, Questioning, and Repredicting
Strategy is higher than without applying Monitoring, Questioning, and
Repredicting Strategy. Therefore, alternative hypothesis (Ha) is accepted and null
hypothesis (Ho) is rejected. This is supported by the data analysis results in which
the t-observed (5.12) is higher than the t-table (2.00) at the significant level of
0.05.
B. Suggestions
Based on the conclusion above, the researcher gives some suggestions for
those who are interested in teaching reading as follows:
1. English teachers are suggested to use Monitoring, Questioning, and
Repredicting Strategy in their teaching learning process in order to
improve the students’ reading comprehension
2. Students are advised to have more practice in reading and applying
Monitoring, Questioning, and Repredicting Strategies.
3. The researchers who are interested in doing a research related to the study
should try to apply Monitoring, Questioning, and Repredicting Strategy on
41
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S. 2003. Prosedur Penelitian :SuatuPendekatanPraktik: Edisirevisi V. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Antonacci, Patricia & Callaghan Cathrine. 2011. Strategies for Middle and Secondary Classroom. California: Sage Publications, Inc.
Best, J.W. 2002. Research in Education. New York: Prentice-hall.
Blanton, W. E., Wood, K. D., & Taylor, D. B. 2007. Rethinking Middle School Reading Instruction: A Basic Literacy Activity. Reading Psychology, 28, 75- 95.
Broek et. al. 2001. Inferential Questioning: Effects on Comprehension of Narrative Texts as a Function of Grade and Timing. Journal of Educational Psychology, Vol. 93, No. 3, 521-529
Burns, Roe & Rose. 1984. Teaching Reading in Today’s Elementary Schools. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Cain, Kate & Oakhill, Jane. 2006. Assessment matters: issues in the measurement of reading comprehension. British Journal of Educational Psychology Vol.76
Duffy, Gerald G. 2009. Explaining Reading: A Resource for Teaching Concepts, Skills, and Strategies. New York: The Guildford Press.
Ginting, Lady. 2010. The Use of Questioning Strategy in Improving Students’ Achievement on Reading Comprehension. Unpublished Thesis. Medan: State University of Medan.
Guthrie et. al. 2004. Motivating Reading Comprehension: Concept-Oriented Reading Instruction. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Ihedioha, Silas. 2012. Effectiveness of Transmitter of Knowledgeand
Conventional Teaching Models on Secondary School Students’ Achievement
on Circle Geometry and Trigonometry. Accessed on December 02nd, 2013
from http://www.emis.de/journals/GMN/.../4_GMN-2232-V12N1. 314211701.pdf
43
Lapp, Flood & Farnan. 2004. Content Area Reading and Learning Instructional Strategies. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Mathirajan et. al. 2006. Management Research Methodology. New Delhi: Dorling Kindersley, Ltd
Meyer, Bonnie J. F & Ray, Melissa N. 2011. Structure Strategy Interventions: Increasing Reading Comprehension of Expository Text. International Electronic Journal of Elementary Education, 4(1), 127-152.
McNamara, Danielle S. 2007. Reading Comprehension Strategies: Theories, Interventions, and Technologies. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Myers, Miriam. 2006. Standards-Based Reading Comprehension. Huntington Beach: Beach City Press.
Nasution, Rika. 2011. The Effect of Prediction Strategy on the Students’ Reading Comprehension. Unpublished Thesis. Medan: State University of Medan.
National Reading Panel. 2000. Teaching Children to Read: An Evidence- Based Assessment of the Scientific Research Literature on Reading and its Implications for Reading Instruction. Washington, DC: National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
Pardiyono. 2007. Pasti Bisa Teaching Genre-Based Writing. Yogyakarta: Andi Offset
Priyana, Irjayanti & Renitasari. 2008. Scaffolding English for High Junior School. Jakarta: Pusat Perbukuan Departemen Pendidikan Nasional
Tankersley, Flood & Farnan. 2003. The Threads of Reading: Strategies for Literacy Dvelopment. Alexandria: The Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.
Territona, Rona. 2009. The Effect of Comprehension Monitoring Strategy on
Students’ Reading Comprehension. Unpublished Thesis. Medan: State
University of Medan.
Thiede et al. 2003. Accuracy of Metacognitive Monitoring Affects Learning of Texts. Journal of Educational Psychology, Vol. 95, No. 1, 66–73
44
Westwood, Peter. 2001. Reading and Learning Difficulties: Approaches to Teaching and assessment. Victoria: Acer Press.
Westwood, Peter. 2008. What Teachers Need to Know about Reading and Writing Difficulties. Victoria: Acer Press.
Zare et. al. 2013. The Relationship between Reading Comprehension and Reading Strategy Use among Malaysian ESL Learners. International Journal of