THE SUITABILITY OF ENGLISH
SYLLABUS AND THE STUDENTS’ NEED
IN
ACCOUNTING PROGRAM AT SMKN 1
BANGKALAN
THESIS
Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the
degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By:
Sunnatul Mufarrohah
NIM D75213102
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHER TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN TULISAN
Saya yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini:
Nama : Sunnatul Mufarrohah
NIM : D75213102
Semester : VIII (Delapan)
Jurusan : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Fakultas : Tarbiyah dan Keguruan UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya
ABSTRACT
Mufarrohah, Sunnatul. (2017). The Suitability of English Syllabus and Students’ Needs in Accounting Program at SMKN 1 Bangkalan. A thesis. English Teacher Education Department, Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, State Islamic University Sunan Ampel Surabaya. Advisors: Rakhmawati, M.Pd. and Mokhamad Syaifudin, M.Ed, Ph.D.
Key words: students’ needs, English for specific purposes (ESP), syllabus
ABSTRAK
Mufarrohah, Sunnatul. (2017). Kesesuaian Silabus Bahasa Inggris dan Kebutuhan Siswa di Kelas Akuntansi di SMKN 1 Bangkalan. Skripsi. Pendidikan Guru Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Sunan Ampel Surabaya. Pembimbing: Rakhmawati, M.Pd. Dan Mokhamad Syaifudin, M.Ed, Ph.D.
Kata kunci: kebutuhan siswa, bahasa Inggris untuk tujuan tertentu (ESP), silabus
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page
TITTLE SHEET ... i
ADVISORS APPROVAL SHEET ... ii
APPROVAL SHEET ... iii
MOTTO... iv
DEDICATION SHEET... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... viii
LIST OF CONTENT ... ix
LIST OF TABLE ... xii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of The Study ... 1
B. Problem of the Study ... 3
C. Objective of The Study ... 4
D. Significance of the Study ... 4
E. Scope and Limitation of the Study ... 4
F. The Definition of Key Term ... 5
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF THE RELATED LITERATURE ... 7
A. English for Specific Purpose (ESP) ... 7
1. The Characteristics of ESP ... 7
2. Types of ESP ... 8
B. Definition of Needs ... 9
C. Definition of Needs Analysis ... 9
2. Procedure of Need Analysis ... 10
D. Students’ Need ... 11
E. Definition of Syllabus ... 12
F. English for SMK ... 13
G. Review of The Previous Studies.. ... 15
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 18
A. Approach and Research Design ... 18
B. Research Presence ... 19
C. Research Location ... 19
D. Data and Source of the Data ... 20
E. Research Instrument ... 21
F. Checking Validity of Findings... 23
G. Research Stages ... 23
H. Data Analysis Technique ... 24
CHAPTER IV: FINDING AND DISCUSSION ... 26
A. Finding ... 26
1. Finding of students’ need in learning English ... 26
a. Overview of target situation analysis ... 26
b. Overview of learning need analysis ... 32
2. Finding of the existing English syllabus ... 44
a. Overview identity ... 45
b. Main competence ... 45
c. Basic competence ... 46
d. Learning material and learning activity ... 49
3. Finding of the suitability of Students’ Needs and English Syllabus ... 52
B. Discussion ... 56
1. Discussion of students’ needs in learning English ... 56
a. Target situation analysis ... 56
b. Learning need analysis ... 58
2. Discussion of the existing English syllabus ... 60
a. Overview identity ... 60
3. Discussion of the suitability of students’ needs and
English syllabus ... 63
a. Target situation analysis ... 63
b. Learning needs analysis ... 64
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 65
A. Conclusion ... 65
B. Suggestion ... 66
REFERENCES ... 68
LIST OF TABLES Page
Table 2.1 Main competence and basic competence in syllabus .... 14
Table 4.1 Students’ goal ... 27
Table 4.2 Students’ necessities ... 28
Table 4.3 Students’ necessities ... 28
Table 4.4 Students’ lacks ... 29
Table 4.5 Students’ lacks ... 30
Table 4.6 Students’ wants ... 31
Table 4.7 Listening input ... 32
Table 4.8 Speaking input ... 33
Table 4.9 Reading input ... 34
Table 4.10 Writing input ... 35
Table 4.12 Type of activity in learning listening ... 36
Table 4.12 Type of activity in learning speaking ... 36
Table 4.13 Type of activity in learning reading ... 37
Table 4.14 Type of activity in learning writing ... 38
Table 4.15 Type of activity in learning vocabulary ... 39
Table 4.16 Type of activity in learning grammar ... 40
Table 4.17 Type of activity in learning pronunciation ... 40
Table 4.18 Setting ... 41
Table 4.19 Learners’ role ... 42
Table 4.20 Teachers’ role ... 43
Table 4.21 The first basic competence of English ... 46
Table 4.22 The second basic competence of English ... 47
Table 4.23 The third basic competence of English ... 48
Table 4.24 The fourth basic competence of English ... 48
Table 4.25 The fifth basic competence of English ... 49
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1 : The Organization of the Needs Analysis
Questionnaire
Appendix 2 : Interview Guideline
Appendix 3 : Students’ Questionnaire
Appendix 4 : Students’ Questionnaire in Bahasa Indonesia
Appendix 5 : Transcript of Teacher’s Interview
Appendix 6 : English Syllabus
Appendix 7 : Surat Tugas
Appendix 8 : Surat Izin Melakukan Penelitian
Appendix 9 : Surat Keterangan Telah Melakukan Penelitian
Appendix 10 : Surat Validasi
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY
As a foreign language in Indonesia, English has its own complexity in teaching and learning. Teaching English as foreign language (EFL) in vocational school needs the suitable syllabus for teaching and learning in order to make it more useful for the learners and not wasting time in teaching to the students.1 To make it more useful, of course, the teachers of English need to consider the basic needs of the students in learning English at their classroom. Accounting Program in vocational school as a subject of this research is a study program which needs its own specification for English subject
in order to match with the students’ target knowledge of accountancy.
English learning in vocational high school (SMK) should be different from regular high school, therefore there is a term of ESP (English for Specific Purpose). ESP is a term that refers to the teaching of English to students who are learning language for a particular work or career.2 This specification of English use will help students to master English as well as what they need in term of specific purpose of the specific program they take in vocational high school. One argument for such a need is that ESP has become an important subject among other subjects to be taught at vocational schools as English has become one of the main means of worldwide communication.
In line with the above definition, ESP then should
meet the students’ specified needs and should make the
students learn something based on their reason for learning. By conducting needs analysis, it will find out the students’ needs in terms of use of the language in the target situation and the
students’ needs in acquiring the language learned. ESP with its
11Suyadi, “English for Specific Purpose for Accounting Student”,International Journal of
Innovation and Research in Educational Sciences, Vol.3 No.2, 2016, 144.
2Brian Tomlinson, Developing materials for Language Teaching, (London: Continuum,
2
emphasis on needs analysis as a starting point in language program design was an important factor in language curriculum development in vocational high school.3 This step helps the curriculum planners or learning provider knows whether the
content of the programs is relevant with the learners’ need or
not.4
Some students may not have a specific purpose for learning a foreign language, and they attend the program just for fun or to pass an exam. Need analysis is a process to identify what students require to learn in the target situation and how the students learn the target language among the period of training time.5 As a result, needs analysis was warmly welcomed by ESP teachers as an approach to course design,
which focused on students’ needs.6 Needs assessment or need
analysis is a part of curriculum development and is normally required before a syllabus can be developed for language teaching.
Regarding the English teaching and learning process, SMKN 1 Bangkalan uses curriculum 2013. The school is using syllabus which was adopted from the model that given from the government. The syllabus of teaching ESP for Accounting students is considered very crucial due to the fact that the existing syllabus being used is not based on the needs analysis in the field, but rather than on the teacher judgment. Consequently, the teaching of English tends to be very general
instead of content-based since the teachers’ mastery on ESP for
accounting field is inadequate. Students are not highly motivated to learn English as the instruction materials are not interesting for them and do not have any relationship with their field of study. The failureof the studentsinrecruitmenttestis due to the low mastery of English instead oftheir mastery of
3Laurence Anthony, “Defining English for Specific Purposes and the Role of the ESP Practioner”, (Japan, Okayama University of Science), 15
4 B. martin, Assessing Students’ language needs in a need analysis,2003. 115. Accessed on
April 23, 2017 from http://www.paaljapan.org/resources/PAL9/pdf/ Balint Martin.pdf.
5Hyun Hyo Kim, “Needs Analysis for English for Specific Purpose course Development for Engineering Students in Korea”, International Journal of Multimedia and Ubiquitous
Engineering, Vol.8, No.6, 2013,2.
6David Nunan, “The Impact Of English As A Global Language On Educational Policies
3
content subjects. ESP Syllabus, like any other syllabus, consists of a description of what will be included in the program, or program objectives.7
Kitao states that in designing the program, especially for designing English syllabus, something to be considered is
students’ need.8 By analyzing student`s need, the program designer can understand what and how the program should be conducted. However, the syllabus for teaching English for Accounting does not create by finding out the student needs as the previous step. Therefore, it may indicate that the syllabus does not cover the student needs yet.
This study investigates the needs of the students and the suitability of the existing English syllabus which is conducted in accounting program at SMKN 1 Bangkalan. SMKN 1 Bangkalan is chosen as the place for doing research because it is the oldest vocational high school that exists in Bangkalan. The school aims towards high quality school which is proven by some cooperation with both domestic and foreign institution as a place for students’ apprenticing. The accounting program selected in SMKN 1 Bangkalan because the program is the most favorite program in that school, and got many trophies in joining the contest. The researcher observes that accounting program has bigger chance to use English in the future career than other program in SMKN 1 Bangkalan. B. Problems of the Study
Based on the background of the study that has been explained, the researcher decides to have two research questions as following:
1. What are the students’ needs in learning English in accounting program at SMKN 1 Bangkalan?
7 Ms. Veena. P, “Importance of Needs Analysis in Curriculum Development for Vocational Purpose”, International Journal of English Language, Literature and
Humanities Vol. IV, (India, Loyola Academy Hyderabad, 2016), 440
8L. Iftihaturrahmah., Undergraduate Program: “A Survey Of The Need Analysis Of Kejar
Paket C.
4
2. To what extent does the existing English syllabus meet the
students’ needs in learning English in accounting program
at SMKN 1 Bangkalan? C. Objectives of the Study
Related to the statement of the problems, there are also two objectives of the study here, there are:
1. To find the needs of students in Accounting program at SMKN 1 Bangkalan
2. To describe the suitability of the existing English syllabus
with the needs of the students in teaching English in accounting program.
D. Significance of the Study
1. For teacher
It is expected that the result of this research give some inputs in teaching English based on students need which can be used as a model to design the effective and efficient English teaching-learning process at the school.
2. For School Principal
Hopefully the result of this study can inform the school principal to support and improve the quality of the next English teaching and learning process.
3. For Future Researcher
This research provides valuable references to conduct further research in developing material used in teaching English for SMK.
E. Scope and limitation of the Study
Related to the problem that has been explained, the scope of this study is the analysis of the language skills that mostly needed by the students and the types of data that will be used by the students in learning English in accounting program at SMKN 1 Bangkalan. By knowing the needs of the students, the teacher can match the suitable material in teaching English. Choosing the suitable material in teaching English is neede to
5
F. Definition of the Key Terms
To avoid misunderstanding in reading this study, the researcher provides the definition of key terms as follows:
1. ESP
Hutchinson and Waters define ESP as an approach rather than a product, meaning that ESP does not involve a particular kind of language, teaching material or methodology.9 It is said that ESP is an approach to language learning, which is based on learner need, because
the content and method are based on the learner’s reason
for learning. In this research, ESP should be seen as an approach to language teaching which is directed by specific and apparent reason for learning English.
2. Needs Analysis
According to Hutchinson and Waters, needs analysis
is the base of „necessities’ and „wants’, which are a
classification between what students have to know and what the students fell they have to know.10 Need analysis in this research means that an activity for getting information to meet the needs of the students. Needs analysis helps in collecting and analyzing data for
determination of what learner’s want and need to learn.
3. Students’ Needs
In ESP, students’ needs are often described in terms of
performance that is in terms of what the students will be able to do with the language at the end of study.11 In this
research, the students’ needs can be seen by conducting
need analysis. The information would also be needed about the different kinds of activities the students would be using the language, the language functions involved, the situations, and which of the four language skills would be needed.
9 Tom Hutchinson and Alan Waters, English for Specific Tom Hutchinson and Alan
Waters, English for Specific Purpose (New York, Cambridge University Press,1987),80Purpose (New York, Cambridge University Press,1987),6
10
Jack C. Richards, Curriculum Development in Language Teaching (New York: Cambridge, Cambridge university press,2001),51
6
4. English Syllabus
A syllabus is a document which says what will (or at least what should) be learnt.12 Hyland define syllabus design as a plan of what is to be achieved through teaching and learning, identifying what will be worked on in reaching the overall program aims and providing a basis for evaluating students’ progress.13 This research analyzes the English syllabus of accounting program at SMKN 1 Bangkalan to know the suitability of the syllabus and the
students’ need.
5. Accounting Students
Accounting Program is a study program which needs its own specification of material for English subject in
order to match it with the students’ target knowledge of
accountancy.14 Accounting students are those who are
studying a study program in vocational schools. The
information of the students’ needs was taken from accounting students at SMKN 1 Bangkalan as a subject in this research
12 Tom Hutchinson and Alan Waters, English for Specific Purpose (New York, Cambridge
University Press,1987),80
13 Sebastian Jeczelewski, “Need Analysis, Course Design and Evaluation of Business English”. University of Iceland, 2016, 14.
14Suyadi, “English for Specific Purpose for Accounting Student”.International Journal of
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF THE RELATED LITERATURE
A. English for Specific Purpose (ESP)
ESP is a way of teaching and learning English for specialized subjects with some specific vocational and educational purposes in mind.1 ESP programs are narrower in focus than general English language teaching (ELT) programs
because the center is on analysis of learners’ needs.2
in ESP, English is taught for specialized learners with some specific vocational and educational purpose in mind. Considering the definitions, it can be concluded that ESP is very important to be taught because it has been specific to support students learning English for a certain area.
1. The Characteristics of ESP
Duddley - Evan explains that ESP has some characteristics. The characteristics are divided into two groups according its ´absolute´ and ´variable´ attributes.3
a. The absolute characteristics are:
1) ESP is designed to meet specific needs of the learner.
2) ESP uses of the underlying methodology and
activities of the discipline it serves.
3) ESP is centered on the language (grammar, lexis,
and register), skills, disprogram and genres appropriate to these activities.
b. The variable characteristics are seen in five points:
1) ESP is designed for specific disciplines.
2) ESP uses specific teaching situations, a different methodology from that of general English.
1Mohammed Mizel Tahir, “English For Specific Purposes (ESP) And Syllabus Design”,
98. (http://www.iasj.net/iasj accessed: on February 04, 2017).
2Helean Basturkmen, Developing Courses in English for Specific Courses, (New Zealand:
Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), 3.
3Milevica Bojović,, Teaching Foreign Language for Specific Purposes: Teacher
8
3) ESP is designed for adult learners, either at a tertiary level institution or in a professional work situation.
4) ESP is generally designed for intermediate or
advanced students.
5) Most ESP programs assume some basic
knowledge of the language system, but it can be used with beginners.
2. Types of ESP
Carter points out that English for Academic and Occupational Purposes serves professional and vocational
purposes.4 However, Hutchinson and Waters have drawn a
“Tree of ELT”, which demonstrates the subdivisions of
ESP. In this tree, ESP is divided into three branches:
a. English for Science and Technology (EST)
b. English for Business and Economics (EBE)
c. English for Social Studies (ESS).
Each area mentioned above is again divided into branches as English for Academic Purposes (EAP) and English for Occupational Purposes since Hutchinson and Waters underline that there is no certain distinction between EAP and EOP (English for Occupational
Purposes).5 The reasons why we cannot have a sharp
distinction between them are that people can work and study at the same time, the language which is taught in a learning environment (for academic purposes) can be used by the learner in an occupational settings in getting job. This might be the reason why EAP and EOP are classified under the same kind of ESP.
Regardless of the kind of programs, vocational learners are trained in practical English vocabulary in a particular field as well as the working knowledge of specific skills and best practices which are necessary for their profession
4D. Carter, “Some Propositions about ESP”,
The ESP Journal, vol.2, 1983, 133.
5 Tom Hutchinson and Alan Waters, English for Specific Purpose (New York, Cambridge
9
B. Definition of Need
Needs are often described as the difference between what learners can presently do in a language and what they should be able to do. According to Hutchinson
and Waters, needs may be divided as „target needs’ and
„learning needs’.6
1. Target needs or target situation needs are what the learner
needs to do in the target situation (language items, skills, strategies, subject knowledge, etc)
2. Learning needs are what the learner needs to do in order to
learn (the condition of the learning situation).
Target needs include what learner need to know and do in target situation in order to perform effectively. There are three kinds of target needs: necessities, lacks and wants. The
term “necessities” identifies what students' have to know to
function in the target situation effectively. The term “lacks” refers to the gap between what the learners know already and what the learners do not know. Therefore, to know the gap,
there are some comparisons between the students’ current
proficiency and the required proficiency to cope with the target situation. In order to identify students' weaknesses their
previous knowledge should be examined and, finally, “wants”
reflect what students think they need. Learning needs analysis, on the other hand, is concerned with language learning. It should also be noted that students' motivation for learning will be guaranteed when learning needs are satisfied.
C. Definition of Need analysis
Procedures used to collect information about learners’
needs are known as need analysis.7 Brown attempts to define the term as the activities that are involved for gathering information that will act as the foundation for developing a curriculum which will meet the learning needs of a particular
6Tom Hutchinson and Alan Waters, English for Specific Purpose (New York, Cambridge
University Press,1987),59.
7Jack,C, Richard, Curriculum Development In Language Teaching, (Cambridge University
10
group of learners.8 According to Johns the very first step of a course design is what we call needs analysis which provides validity and relevancy for the other subsequent course design activities.9
1. The Purpose of Need Analysis
According to Richards on his discussion toward needs analysis, says that the first step in conducting a needs
analysis is to
decide exactly what its purpose or purposes are. The following are some of the major purposes of needs analysis:10
a. To find out what language skills that mostly needed by
the learner for particular role.
b. To determine whether the program design has
addressed the need of student`s potential.
c. To determine which group of students which is most needed in a certain training program.
d. To identify a gap between what students are able to do
and what they need to be able to do.
e. To collect information what problems commonly
faced by the students
2. Procedures of Needs Analysis
When performing a need analysis, the ESP practitioner can pick out numerous strategies, but needs to keep in mind that every procedure affects the type of the information obtained.11 Schutz and Derwing, introduced eight detailed stages to perform a needs assessment. These stages are:12
8 J. Brown, The elements of language curriculum: A systematic approach to program
development, New York: Heinle&Heinle Publishers, 1995, 134.
9 A. M Johns, English for specific purposes (ESP): Its history and contributions. In M.
Celce-Murcia (Ed.), Teaching English as a second or foreign language (2nd ed., pp. 67- 77). New York: Newbury House, 1991, 234
10Jack,C, Richard, Curriculum Development In Language Teaching, (New York:
Cambridge University Press, 2001), 53
11Jack,C, Richard, Curriculum Development In Language Teaching, (New York:
Cambridge University Press, 2001), 51
11
a. Determining if the goal is directly related to
establishing the purpose of the study specifically in order to determine appropriate outcome.
b. By setting the limits on the target population, the researcher is able to specify the target population of the investigation in order to carry out more pragmatic decisions regarding costs, place and length of the project.
c. Delimiting the framework of examination involves
outlining the limitations of the research mainly to increase its potency.
d. Choosing the data collecting device includes picking out proper information gathering instruments.
e. Gathering evidence consists of compiling the
necessary information via the data collecting device that will be used in this process.
f. Evaluating the data, the analyst the data based on his
own observations and calculations.
g. By deciphering the outcome, the analyst interprets the
data developed from the technique of information analysis.
h. Lastly, the criticism of the research portion involves writing down recommendations for additional studies and clarifying the drawbacks of the research.
Clearly this is not the only available method to conduct an appropriate needs analysis. Nevertheless, it has been applied numerous times and the ESP practitioner willing to use it will not be compelled to deal with additional errors arising from using a different method. D. Students’ Need
12
In ESP, students’ needs are often described in terms of
performance of what the students will be able to do with the language at the end of study.13 In this research, the students’ needs can be seen by conducting need analysis. Whereas in a general English subject the goal is usually an overall mastery of the language that can be tested on a global language test, the goal of an ESP is to prepare the learners to carry out a specific task or set of tasks.
In accounting program, the students need learning English that could help their basic knowledge in accountancy such knowing how to operate the conceptual framework of accounting, knowing how the procedures of basic accounting is, how to do the journal as a report, how to do ledger report, bank reconciliation statement and how the capital and revenue transactions should be done.14 All the basic knowledge of accountancies should be mixed with the English skills in order to meet the English performance of accounting.
In order to determine the learners’ needs as the starting
point for developing ESP programs, a number of approaches were suggested. The students, teachers, and employers could all
be involved in determining the students’ needs. The
information would also be needed about the different kinds of activities the students would be using the language, the language functions involved, the situations, and which of the four language skills would be needed.
E. Definition of Syllabus
The syllabus can be defined as a guide for teachers and learners by providing goals to be achieved. Furthermore, the syllabus can also be termed as a permanent record, a learning tool and a contract between several partners such as learners, teachers and institutions.15 For Allen, Syllabus is that subpart of curriculum which is concerned with specification of what units
13 Jack C. Richards, Curriculum Development in Language Teaching (New York:
Cambridge, Cambridge university press,2001),33
14Suyadi, “English for Specific Purposes for Accounting Students”,
International Journal of Innovation and Research in Education Sciences.Vol.3 No. 2, 2016, 145.
13
will be taught.16 Syllabus is one of the ways to applying the already existing curriculum to the personal needs of teachers and learners. Hyland define syllabus as a plan of what is to be achieved through teaching and learning, identifying what will be worked on in reaching the overall program aims and
providing a basis for evaluating students’ progress.17
Moreover, syllabus is a statement of content which is used as the basic for planning various kinds of programs, and that the task of the syllabus designer is to select and grade this content. As a conclusion, syllabus is an aid made by a teacher for guidance in teaching process in the whole program for period of time. Syllabus is a notion devoted to teaching methodology, mainly aimed at selecting and grading content. F. English for SMK
English for SMK or English for vocational purposes (EVP), under the umbrella of English for specific purposes (ESP), has gained its prominence because more and more English language programs are geared for those who would like to learn English, which is relevant to their vocations. The overarching goal of ESP instruction is to help specialist learners function well in workplaces or vocational higher education settings where English serves as a medium of
communication.18
English syllabus in SMK is a reference of the courses that used by the teacher as a guideline for conducting the teaching and learning process. A syllabus should be developed
by each school that conforms to schools’ vision, situation, and
mission. The Government also states that syllabus is a set of plan which covers main competence, basic competence, materials, activities, assessment, time allocation, and learning resources.19 Therefore, a syllabus is a plan or a reference that
16Mohamed MizelTahir, “English for Specific Purposes (ESP) and Syllabus Design”, ELT
Methodolody, 122, (http://www.iasj.net/iasj accessed: on February 04, 2017.
17 Sebastian Jeczelewski, “Needs Analysis, Course Design and Evaluation of Business
English, University of Iceland, 2006, 14.
18Handoyo Puji Widodo, “Teaching English for Specific Purpose (ESP): English for
Vocational Purpose (EVP), English Language Education, vol.5, 279.
19
14
used by teachers in leading a teaching-learning process of a program and it includes six elements.
The Standard of Education Content, the content of the main of competency and the basic competency of English for SMK are written as follows:
Table 2.1
Main Competence and Basic Competence in Syllabus
Main Competence Basic Competence
3. Memahami, menerapkan, menganalisis pengetahuan faktual, konseptual, prosedural dan meta kognitif berdasarkan rasa ingin tahunya tentang ilmu pengetahuan, teknologi, seni, budaya, dan humaniora dengan wawa san kemanusiaan, kebang saan, kenegaraan, dan peradaban terkait penyebab fenomena dan kejadian, serta menerapkan penge tahuan prosedural pada bidang kajian yang spesifik sesuai dengan bakat dan minatnya untuk meme cahkan masalah.
3.8 Menganalisis fungsi sosial, struktur teks, dan unsur kebahasaan untuk menyatakan dan menanyakan tentang pengandaian jika terjadi suatu keadaan/kejadian/peristiwa di waktu yang akan datang, sesuai dengan konteks penggunaannya.
3.9 Menganalisis struktur teks dan unsur kebahasaan untuk melaksanakan fungsi sosial teks ilmiah faktual (factual report ) dengan menyatakan dan menanyakan tentang teks ilmiah faktual tentang orang, binatang, benda, gejala dan peristiwa alam dan sosial, sederhana, sesuai dengan konteks pembelajaran di pelajaran lain di Kelas XI
3.10 Menganalisis fungsi sosial, struktur teks, dan unsur kebahasaan dari teks eksposisi analitis tentang topik yang hangatdibicarakan umum, sesuai dengan konteks penggunaannya. 3.11 Menganalisis fungsi sosial, struktur
teks, dan unsur kebahasaan dari teks biografi pendek dan sederhana tentang tokoh terkenal, sesuai dengan konteks penggunaannya. 3.12 Menyebutkan fungsi sosial dan
kebahassaan dalam lagu 4. Mengolah, menalar, dan
menyajidalam ranah konkret dan ranah abstrak terkait dengan pengem bangan dari yang dipelajarinya di sekolah secara mandiri, bertindak secara efektif dan kreatif,
15
serta mampu menggunakan metoda sesuai kaidah keilmuan
4.13 Menangkap makna dalam teks ilmiah faktual (factual report), lisan dan tulis, sederhana, tentang orang, binatang, benda, gejala dan peristiwa alam dan sosial, terkait dengan mata pelajaran lain di Kelas XI.
4.14 Menangkap makna dalam teks eksposisi analitis tentang topik yang hangat dibicarakan umum
4.15Menangkap makna teks biografi pendek dan sederhana tentang tokoh terkenal
4.16 Menangkap pesan dalam lagu
Source: Permendikbud RI Nomor 24 Tahun 2016 As stated above, the English subject is a compulsory lesson which is expected to form the totality of Indonesians in the context of working people.20 It means that the knowledge and basic skill in English should support the competence of the skill program.
G. Review of The Previous Study
There were some previous studies that had been done under the topic of curriculum development that discuss about need analysis and syllabus design.
First, The study conducted by Latifah Kusumaningrum
about An Analysis on the Learners’ Needs of English for
Specific Purpose at SMKN 2 Sragen.21 The objectives of the study are to find the real needs of the students of SMKN 2 Sragen, to compare the existing syllabus based on the needs analysis, and the syllabus. The type of the study is descriptive qualitative study. The object of this study is the learners’ needs of English for Specific Purposes taught in SMKN 2 Sragen. In this study the writer uses questionnaires and document. In her research, the writer takes 40 students of SMK N2 Sragen as respondents. The writer analyzes the data based on the real needs and student needs to propose a suitable syllabus. Then
20
Permendiknas no.22/2016
21Latifah Kusumaningrum, “An Analysis on the Learners’ Needs of English for Specific
16
she compared with the existing syllabus. The writer sees the
syllabus does not satisfy the students’ real need especially in
speaking and listening. The students have difficulty the material because the material of speaking and listening skill taken from recorded material which is not easy to be understood.
Second, a study conducted by Tri Yuana focused on
learners’ needs of English for specific purposes at SMK Tri
Guna Bhakti Surabaya.22 The research which was done by the
researcher was designed as descriptive qualitative research. The data was gained from questionnaire and observation checklist with eleventh grade of the accounting students of the school as the subjects of the study or target population of needs analysis. The results of the study showed the needs of the accounting students of SMK Tri Guna Bhakti Surabaya is being able to communicate in English better in the subject area of accounting. Most of the students argued that the English teaching and learning process in the classroom is not really effective because the learning materials are not related to the accounting study program
Third, a study entitled “The Development of English Syllabus and Lesson Plans at SMKN 8 Malang” was done by
Henry Istiqomah.23 The research aimed to analyze English
syllabus and lesson plans at SMK Negeri 8 Malang. The
subject of the study was the Vice Principal of Curriculum Affairs and three English teachers. The research is descriptive qualitative research and used questionnaires and interview guide to collect all data and information. The findings indicated that the development of English syllabus and lesson plans at SMK Negeri 8 Malang was influenced by the vision and missions of the school and the curriculum use for English subject which combined the curriculum of SMK and SMA. The formats of the syllabus and lesson plans followed the criteria of KTSP syllabus and lesson with character values.
22Tri Yuana, “An Analysis on The Learners’ Needs of English for Specific Purposes at
SMK Tri Guna Bhakti Surabaya”, State University Surabaya, 2013.
23 Henry Istiqomah, “The Development of English Syllabus and Lesson Plan at SMKN 8
17
Fourth, the study which was done by I Made Wartina discusses about Designing English Syllabus for the Eleventh Grade Students of Agribusiness Food Crops and Horticulture Department at SMK Negeri 1 Kuripan.24 The study aims to identify reading materials needed by the eleventh grade students of the AFCH department at SMKN 1 Kuripan, and designing appropriate English syllabus for teaching reading. The data are gathered from questionnaires, interview guides and documents. The obtained data are analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively using descriptive statistics. The study reveals that the needed reading materials deal with topics in the agricultural fields, such as: soil preparation, crop cultivation, operating farm tractor, pests’ control, and irrigation. The appropriate type of syllabus is competency-based syllabus with
KTSP syllabus format.
Fifth, a study conducted by Adi Purwanto was about Developing English Syllabus for the Restaurant Department in SMKN 1 Pogalan, Trenggalek.25 In this study, the English syllabus is developed based on the educational research and development (R and D) because the objective of the study is to develop a model syllabus. The product of this study is an English syllabus for the Restaurant Department, an example of instructional material, and one lesson plan.
Those are the previous studies about need analysis and syllabus design. The difference between this study and those previous are that in this study the researcher focus on the needs of the students and the suitability with the existing syllabus in ESP classroom which is represented by accounting program at SMKN 1 Bangkalan.
24 Maria Guerrero, “English for Specific Purposes Curriculum Design for Latino
Immigrant Parents”, 2007
25
Adi Purwanto, “Developing English Syllabus for the Restaurant Department in SMKN 1 Pogalan, Trenggalek”, English Language Education, The state University of Malang,
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Approach and Research Design
Research design is a plan for collecting and analyzing evidence that will make it possible for the researcher to answer the questions, he or she has posed. Based on the research questions and objectives of the study, the approach of this research was qualitative. Beverley Han cock said that qualitative research is concerned with developing explanations of social phenomena. This research concerned with social phenomena dealing with student needs in learning ESP. According to Dawson, qualitative research explores attitudes, behavior, and experiences through such methods as interviews
or focus groups.1 This research applied qualitative approach to
find out the answer dealing with the teacher’s knowledge and experiences of process in designing syllabus. It would be proven through interview and analysis of syllabus as a real product.
As of the design of the research, Suryana stated that descriptive research is used to identify and classify the elements or characteristics of the subject.2 It means that descriptive design is used to describe the detail condition of research subject, so the problem could be identified clearly. Therefore, the research design of this study was descriptive-qualitative research because the main concern of this research
was to know the students’ need and the syllabus design for
accounting program at SMKN 1 Bangkalan. It explained that descriptive research would be described narratively and interprets. It is also related to the variable of this study which
was dealing with students’ need and the way of teacher in
designing the syllabus.
1Chaterine Dawson, “A Practial Guide to Research Methods”.,(United Kingdom: Advision
of How to book.Ltd,2007),15
2Suryana, Model Prakantis Penelitian Kualitatif dan Kuantitatif, (Jakarta: Universitas
19
Suharsimi stated that descriptive research describes the reality of research variable and condition.3 It means that this study would like to describe the process done by the teacher in
knowing the students’ need and designing syllabus through
descriptive design. B. Research Presence
In this study, the researcher was as nonparticipant researcher. It means that the researcher did not take part of the research which could be influenced the finding. In this research, the researcher collected the data and provided as research instrument by interpreting from theory about need analysis and English syllabus within the fact of the problem in the field. The main source of the data was questionnaire that given for the students for accounting program at SMKN 1 Bangkalan, the researcher interviewed the English teacher of accounting program dealing with her knowledge in teaching English.
In this research, the researcher presence was very transparent. The participant knew that they were being observed. The participant could see easily that the researcher came to the participants to distributes a questionnaire and interview them. Therefore, the participants knew that the researcher was collecting data from them.
C. Research Location
The researcher chosen SMKN 1 Bangkalan located at Jl. Kenanga 2 Bangkalan. The school is the oldest vocational high school in Bangkalan and has many specific programs. The school has high quality which is proven by some cooperation with both domestic and foreign institution as a place for
students’ apprenticing. The favorite program in that school is
accounting program. The teacher of that school said that accounting has a big chance to work for the students after graduating from the school. The study was conducted in the eleventh grade of accounting students at SMKN 1 Bangkalan. The subject of this research was the students of accounting program consist of 27 females and 9 males, and also one English teacher of accounting program.
20
D. Data And Source Of Data
The data of this study are about the students’ needs
and the existing syllabus. The data was found from the source of data, they are:
1. Eleventh grade students.
Eleventh grade students are the key source to find the data of students’ needs. They are considering as the source of data to find students’ needs in learning ESP at accounting program at SMKN 1 Bangkalan. The students consist of 27 females and 9 males.
The researcher took all the accounting students. There are 36 students as the research subject of eleventh grade students, consist of 27 females and 9 males students. This was based on the teacher that the eleventh grade did not have significantly difference characteristic and ability. This was supported by the result of the middle test that showed their ability. Therefore, the samples were considered enough to find the relevance result.
Moreover, to confirm the questionnaire result, some students are interviewed especially for them who do not state clearly their argument in the questionnaire. The interview is related to their needs in learning English for accounting.
2. The English teacher for accounting program.
The English teacher was considering as the key source of data about English for accounting syllabus. There was one English teacher who taught English in accounting program. The teacher taught all classes in accounting program, there were two classes, she has been taught English in accounting program for more than ten years. The researcher found data about syllabus from the teacher through interview.
3. The English Syllabus
21
E. Research Instrument
Research instrument is tool or device to guide the researcher for gathering data during the research process. To collect the data, this study used three instruments, they were:
1. Questionnaire
Questionnaire is one of the most common instruments used. They are relatively easy to prepare, they can be used with large numbers of subjects, and they obtain information that is relatively easy to tabulate and analyze.4 Questionnaire is useful in gathering data for the big number of participants. Moreover, because student needs was an abstract thing, it could not be seen by observation. Therefore, student needs questionnaire was important to analyze the participant feeling and mind.
In the case of the present study, it is decided to conduct the needs analysis by means of a questionnaire, because filling in a form or questionnaire is not time-consuming, although it is considered to be the most traditional and even the most boring way of doing needs analysis.5
Questionnaire items made up of 20 questions classified under two major sections according to Tom Hutchinson - Allan Water and David Nunan. The aim of the questionnaire is to collect data about target situation analysis and learning need analysis. The target situations analysis was divided into four aspects, those are: goals, Necessities, lacks, and wants. The learning needs questionnaire was divided into 5 aspects, those are: learning input, procedures, setting, learners’ role, and
teachers’ role. Those questionnaires were suited to the
condition of English for Accounting at SMKN 1 Bangkalan. In addition, it is matched to the theory of students’ needs in learning ESP and needs analysis stated in second chapter. The questionnaire can be seen in the appendix 3.
4 Jack C. Richards, Curriculum Development in Language Teaching (New York:
Cambridge, Cambridge university press,2001), 60.
5Alex Case, 15 ways to do needs analysis, 43. Available at http://edition.tefl.net/ideas/
22
2. Interview guideline
Interview is a good way to find out the participant`s mind and feeling.6 In the interview section, the instrument that was used by the researcher was interview guideline. The interview was designed by the researcher itself by considering some theories about learning needs analysis and syllabus.
In this study, the researcher did the two sections of interview. The first section was the interview to the eleventh grade students. This was a way to confirm the
participants feeling and mind dealing with students’ needs.
In this section the researcher used in depth interview because the researcher needed to collect the information about what the participant mean deeply.
The second section was the interview to the teacher. In this section the researcher used formal-semi structured interview because in the interview section both researcher and participant knew that they were there to generate data based on guiding questions. However, this was possible to have additional question during the interview section. The researcher could ask some additional points when there was unclear information. The question for interview could be seen in appendix 2.
3. Document studies
Document study is used to guide the researcher takes the document needed in the study.7 In this study, the document needed to be analyzed was syllabus of English for accounting program for eleventh grade in SMKN 1 Bangkalan. The syllabus was analyzed based on the criteria by the list of student needs. The student needs` criteria were gotten from the result of questionnaire and interview.
6Abdur Rahman, Undergraduate Program: “the implementation of reading aloud to vary
the pronunciation practice for students of senior high school in Mamba`us sholihin muslim
boarding school gresik” (Surabaya: state Islamic university sunan ampel surabaya, 2011), 30
7
23
F. Checking Validity of Finding
Checking validity of findings is one of the important things in figuring out accurate results problem. To find out the valid and reliable data, the researcher used valid and reliable
instrument. Validity refers to the appropriateness,
meaningfulness, and usefulness of the instrument to collect the data.8 In this study, the instruments had been validated by the experts.
The questionnaire and interview guideline as the instrument in this study has been validated by Ana Nurul Laila, S.Pd, M.TESOL. Moreover, because the participants are not from English department, to make the participant easy to understand the questionnaire, the researcher translated the questionnaire from English to Bahasa.
In addition, to make the data is reliable, the researcher used camera and recorder to get the concrete fact during the research process and it also helped the researcher to analyze the data.
G. Research Stages
1. Preliminary research
In preliminary research, the researcher gathered data from some informants about program of English for specific purposes taught in SMKN 1 Bangkalan. SMKN 1 Bangkalan has many programs to be chosen by the students.
Preliminary research was continued to deeper interview by having interview to the teacher of English for accounting, observing the class, and having interview to some students in English for accounting program. From those activities, the researcher found that the teacher has
problem on facilitate the students’ needs in learning
English. The problems were not only happened to the teacher but also to the students. Based on the informants, the program was not suitable to their expectation because the material of English that taught is general English, they also need to learn English related with their program as
8Sugiyono, Metode penelitian kuantitatif, kualitatif, R&D, (Bandung: Alfa Beta, 2009),
24
accounting students. This indicated miscommunication between the teacher as the learning designer and the students.
2. Development of Research Design
In this stage, the researcher planned some points to make the study well organized. The researcher tried to find the topic, organizing the problems, analyzing the theory
and previous studies related to students’ needs and
syllabus, deciding the research method, and finding the appropriate instruments used in the research. Moreover, the researcher was advised by the advisors to make the study valid and reliable.
3. Research Action
This part was a main part of this research because it was time for researcher to begin collecting the data. In conducting research, the researcher did all of the research procedure. The first was distributing questionnaire to know
the students’ needs in learning English. The researcher also
interviewed some students about their answer in the questionnaire. The interview was an in depth interviewed to make the answer clearer.
The second was interview the English teacher to know
the teacher’s opinion about the existing English syllabus.
Document studies that is English syllabus also analyzed by the researcher to know the suitability of the syllabus and
the students’ needs.
4. Writing the report
In this section, the researcher reflected all of the information that have been collected by reporting the result and finding of the study in terms of interpreting data gathered from all the research instruments. The writing report is in the form of descriptive. This described the
finding of questionnaire and interview about students’
needs.
H. Data Analysis Technique
25
Compiling, disassembling, reassembling (and Arraying), Interpreting, and Concluding.9 However, in this study the data were analyzed in four phase because disassembling and reassembling phase can be combined. The phases are described follows:
1. Compiling: the first instrument, the researcher made table
from the students’ answer in the questionnaire. The
collected data about students’ needs taken by distributing
questionnaire to eleventh grade students who took Accounting program. The second instrument, the researcher transcribed and types the data from the recording of interview process to English teacher into a document for analysis.
2. Assembling: in assembling section the researcher classified
the students’ answer in the table as the criteria to analyze the syllabus.
3. Interpreting: after getting the data of student`s need in learning English in Accounting class, the researcher analyzed the data and explained it narratively. Then, the data of English syllabus also explained narratively based
on the criteria of the lists of students’ needs. The
description that was made by the researcher was based on the data collected from interview and document studies. 4. Concluding: in the last section of analysis data, after
knowing the interpreting section, the researcher could decide whether the syllabus has covered the student needs or not.
9Robert K.Yin, Qualitative research from Start to Finish, 2011, The Guilford Press : new
CHAPTER IV
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter describes and analyzes the data which are obtained during the research process. It includes the result of interview, questionnaire, and document studies analysis. Detailed description of the results obtained from this study is presented.
A. FINDING
Based on the research problems stated in the first chapter, the research finding presents the result of the research based on the statement. They are about English learning need of the students in English Language Teaching Process at SMKN 1 Bangkalan and to what extent the English syllabus meet the English learning need of the students. These data had
been collected by the researcher on 8thof May 2017. Based on
research procedure and data collection technique, the data were collected by distributing questionnaire, doing interviews, and document studies. From those three instruments of collecting data, then the researcher describes the findings to answer the research questions. The findings are described narratively as the following:
1. Finding of the Students’ Needs in Learning English The first research problem, that is to find the students’ needs can be answered by analyzing the questionnaire and interview to some students. There are two sections in the questionnaire, those section are: target situation analysis and learning needs analysis. The data for each section is presented on the table, and the analysis of each section is described after the table. Moreover, the interview to the students is to confirm the unclear opinion stated in the questionnaire. The finding form questionnaire is presented below:
a. Overview of target situation analysis
In this overview section of target situation analysis, there are nine questions below that will be
describes to know the students’ answer about the
27
1) Goals
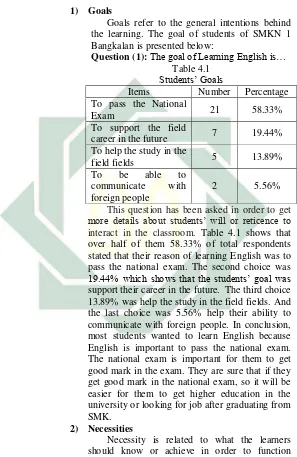
Goals refer to the general intentions behind the learning. The goal of students of SMKN 1 Bangkalan is presented below:
[image:39.420.72.369.66.523.2]Question (1):The goal of Learning English is… Table 4.1
Students’ Goals
Items Number Percentage
To pass the National
Exam 21 58.33%
To support the field
career in the future 7 19.44%
To help the study in the
field fields 5 13.89%
To be able to
communicate with
foreign people
2 5.56%
This question has been asked in order to get more details about students’ will or reticence to interact in the classroom. Table 4.1 shows that over half of them 58.33% of total respondents stated that their reason of learning English was to pass the national exam. The second choice was 19.44% which shows that the students’ goal was support their career in the future. The third choice 13.89% was help the study in the field fields. And the last choice was 5.56% help their ability to communicate with foreign people. In conclusion, most students wanted to learn English because English is important to pass the national exam. The national exam is important for them to get good mark in the exam. They are sure that if they get good mark in the national exam, so it will be easier for them to get higher education in the university or looking for job after graduating from SMK.
2) Necessities
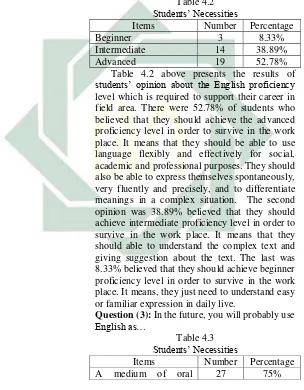
28
effectively in the target situation. In this study, the results of students’ necessities are presented as follows.
Question (2): The English proficiency level
which is necessary for my career is…
[image:40.420.68.372.144.534.2]Table 4.2 Students’ Necessities
Items Number Percentage
Beginner 3 8.33%
Intermediate 14 38.89%
Advanced 19 52.78%
Table 4.2 above presents the results of students’ opinion about the English proficiency level which is required to support their career in field area. There were 52.78% of students who believed that they should achieve the advanced proficiency level in order to survive in the work place. It means that they should be able to use language flexibly and effectively for social, academic and professional purposes. They should also be able to express themselves spontaneously, very fluently and precisely, and to differentiate meanings in a complex situation. The second opinion was 38.89% believed that they should achieve intermediate proficiency level in order to survive in the work place. It means that they should able to understand the complex text and giving suggestion about the text. The last was 8.33% believed that they should achieve beginner proficiency level in order to survive in the work place. It means, they just need to understand easy or familiar expression in daily live.
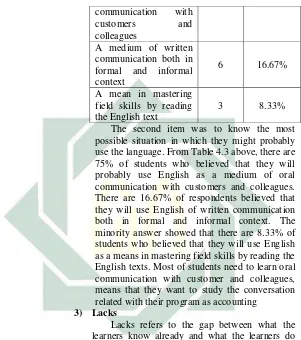
Question (3): In the future, you will probably use English as…
Table 4.3 Students’ Necessities
Items Number Percentage
29
communication with
customers and
colleagues
A medium of written communication both in formal and informal context
6 16.67%
A mean in mastering field skills by reading the English text
3 8.33%
The second item was to know the most possible situation in which they might probably use the language. From Table 4.3 above, there are 75% of students who believed that they will probably use English as a medium of oral communication with customers and colleagues. There are 16.67% of respondents believed that they will use English of written communication both in formal and informal context. The minority answer showed that there are 8.33% of students who believed that they will use English as a means in mastering field skills by reading the English texts. Most of students need to learn oral communication with customer and colleagues, means that they want to study the conversation related with their program as accounting
3) Lacks
Lacks refers to the gap between what the learners know already and what the learners do not know. Therefore, to know the gap, there are some comparisons between the students’ current proficiency and the required proficiency to cope with the target situation.
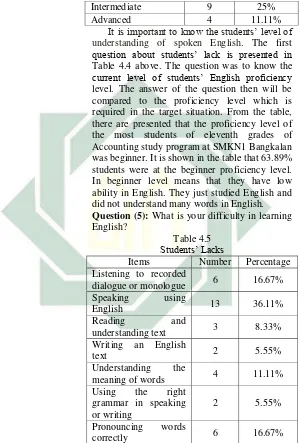
[image:41.420.68.369.65.405.2]Question (4): My current proficiency level of English is…
Table 4.4 Students Lacks
Items Number Percentage
30
Intermediate 9 25%
Advanced 4 11.11%
It is important to know the students’ level of understanding of spoken English. The first question about students’ lack is presented in Table 4.4 above. The question was to know the current level of students’ English proficiency level. The answer of the question then will be compared to the proficiency level which is required in the target situation. From the table, there are presented that the proficiency level of the most students of eleventh grades of Accounting study program at SMKN1 Bangkalan was beginner. It is shown in the table that 63.89% students were at the beginner proficiency level. In beginner level means that they have low ability in English. They just studied English and did not understand many words in English. Question (5): What is your difficulty in learning English?
Table 4.5 Students’ Lacks
Items Number Percentage
Listening to recorded
dialogue or monologue 6 16.67%
Speaking using
English 13 36.11%
Reading and
understanding text 3 8.33%
Writing an English
text 2 5.55%
Understanding the
meaning of words 4 11.11%
Using the right
grammar in speaking or writing
2 5.55%
Pronouncing words
[image:42.420.71.370.70.513.2]31
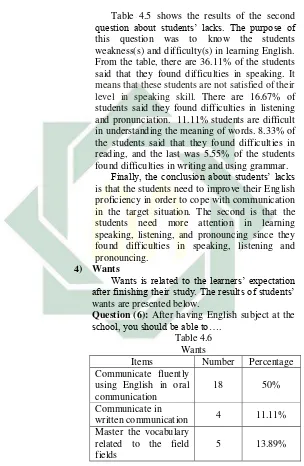
Table 4.5 shows the results of the second question about students’ lacks. The purpose of this question was to know the students weakness(s) and difficulty(s) in learning English. From the table, there are 36.11% of the students said that they found difficulties in speaking. It means that these students are not satisfied of their level in speaking skill. There are 16.67% of students said they found difficulties in listening and pronunciation. 11.11% students are difficult in understanding the meaning of words. 8.33% of the students said that they found difficulties in reading, and the last was 5.55% of the students found difficulties in writing and using grammar.
Finally, the conclusion about students’ lacks is that the students need to improve their English proficiency in order to cope with communication in the target situation. The second is that the students need more attention in learning speaking, listening, and pronouncing since they found difficulties in speaking, listening and pronouncing.
4) Wants
Wants is related to the learners’ expectation after finishing their study. The results of students’ wants are presented below.
Question (6): After having English subject at the school, you should be able to….
Table 4.6 Wants
Items Number Percentage
Communicate fluently using English in oral communication
18 50%
Communicate in
written communication 4 11.11%
Master the vocabulary related to the field fields
[image:43.420.68.372.61.527.2]32
Use the grammar
correctly 9 25%
From Table 4.6, half of the students, 50% of all respondents wanted to be able to communicate using English in oral communication fluently. Therefore, they need to improve their listening and speaking skills. Moreover, they also need some competences which can support them in
communicating using English such as
pronunciation and vocabulary. The second tendency was 25% students who wanted to learn to use grammar correctly.11.11% students said that they wanted to communicate in written communication. Thus, most of students wanted to communicate fluently using English because English as international language, if they can speak English fluently, it will be easier for them to communicate with native English people. Communicate in written communication is the minority of this question.
b. Overview of Learning Needs Analysis 1) Input
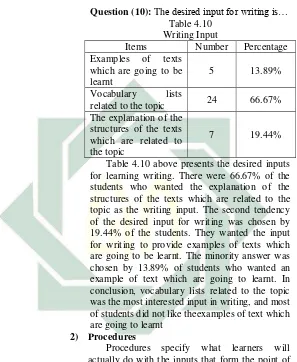
[image:44.420.69.371.65.526.2]Inputs refer to the types of data that will be used by the learners in learning English. The data below provide the description about the desired inputs of the students at SMKN 1 Bangkalan Question (7): The desired input for listening is…
Table 4.7 Listening Input
Items Number Percentage
Monologue and
dialogue 4 11.11%
Monologue and
dialogue with picture 17 47.22%
Monologue and
dialogue with the lists of new vocabularies
6 16.67%
33
Table 4.7 above presents the desired inputs for learning listening. There were 47.22% of the students who wanted the listening input in the form of dialogue with picture as illustration. The second tendency of the desired input for listening was authentic text. It was chosen by 25% of