STUDENTS’ RESPONSES TO THE USE OF MIND MAPPING TO INCREASE THEIR ABILITY IN ORGANIZING IDEAS
IN WRITING DESCRIPTIVE TEXT
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Vincentia Berlian Prima Hendraputri Student Number: 121214062
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
i
STUDENTS’ RESPONSES TO THE USE OF MIND MAPPING TO INCREASE THEIR ABILITY IN ORGANIZING IDEAS
IN WRITING DESCRIPTIVE TEXT
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Vincentia Berlian Prima Hendraputri Student Number: 121214062
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
ii
iv
“Of all things, knowledge is the best,
because it is not subject to liability and
cannot be stolen, because it cannot be
bought, and cannot
be destroyed” –
Hitopadesa
v
vi
vii ABSTRACT
Hendraputri, Vincentia Berlian Prima. (2016). Students’ Responses to the Use of Mind Mapping to Increase Their Ability in Organizing Ideas in Writing Descriptive Text. Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
This research was about the use of mind mapping implemented in SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. The aim of this research was to find out students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping to increase their ability in organizing ideas in writing descriptive text.
The researcher formulated three problems of this study: (1) what are students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping to increase their ability in organizing ideas in writing descriptive text?; (2) what are students‟ improvements after using mind mapping?; and (3) what are students‟ suggestions to the further implementation of mind mapping?
This research employed qualitative research. The researcher used case study as the research design of this research. The participants of this research were thirty (30) students and an English teacher of class 7J SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. The researcher used triangulation in order to enhance the reliability, validity, and trustworthiness of this research. The researcher conducted observation, distributed questionnaire and conducted an interview. The researcher conducted an observation together with the peer-observer. After that, the researcher distributed the questionnaire to the students of class 7J SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. The researcher also conducted an interview with the English teacher and five (5) students of class 7J. The researcher employed the coding strategy and presented the data in a form of narrative description.
The result of this study indicated that students were interested in using mind mapping. Moreover, the students realized that the use of mind mapping did not only help them to improve their ability in organizing their ideas in writing descriptive text but also gave many advantages in improving their writing skill. The implementation of mind mapping should be maintained well. There were several suggestions from the students and also from the teacher to the implementation of mind mapping.
viii ABSTRAK
Hendraputri, Vincentia Berlian Prima. (2016). Students’ Responses to the Use of Mind Mapping to Increase Their Ability in Organizing Ideas in Writing Descriptive Text. Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
Penelitian ini meneliti tentang penggunaan mind mapping yang di laksanakan di SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta.Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk mengetahui respon siswa pada penggunaan mind mapping untuk meningkatkan kemampuan mereka dalam menyusun ide-ide untuk menulis teks deskripsi.
Di dalam penelitian ini, peneliti membuat tiga rumusan masalah: (1) Apa respon siswa terhadap penggunaan mind mapping untuk meningkatkan kemampuan mereka dalam mengatur ide-idenya untuk menulis teks deskripsi?; (2) Apa sajakah peningkatan siswa setelah menggunakan teknik mind mapping?; (3) Apa saran siswa untuk pelaksanaan praktik mind mapping di kemudian hari?
Penelitian ini menggunakan metode penelitian kualitatif.Peneliti menggunakan penelitian studi kasus sebagai desain penelitian.Peserta dalam penelitian ini sebanyak tiga puluh (30) siswa dan seorang guru Bahasa Inggrisdari kelas 7J SMP Negerri 15 Yogyakarta. Peneliti menggunakan strategi triangulasi untuk meningkatkan reabilitas, validitas, dan akuntabilitas di dalam penelitian ini. Peneliti melakukan observasi, menyebar kuesioner dan melakukan wawancara. Peneliti melakukan observasi bersama dengan seorang pengamat yang lain. Seteah itu, peneliti membagikan kuesioner kepad semua siswa kelas 7J SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. Peneliti juga melakukan wawancara dengan guru Bahasa Inggris dan lima (5) orang siswa dari kelas 7J. Peneliti menggunakan strategi pengkodean dan menyajikan data dalam bentuk deskripsi narasi.
Hasil dari penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa siswa tertarik menggunakan mind mapping. Penggunaan mind mapping tidak hanya mampu membantu mereka dalam meningkatkan kemampuan mereka mengatur ide-idenya dalam menulis teks deskirpsi, namun juga memberikan banyak manfaat untuk meningkatkan keterampilan menulis mereka. Para siswa dan guru Bahasa Inggris juga memberikan beberapa saran dalam pelaksanaan mind mapping berikutnya.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to express my greatest gratitude to the one and
only Jesus Christ my Almighty Lord and Mother Mary, who have given an
amazing life with great parents and friends for me.
I would like to express my deepest gratitude to my beloved advisor, Bapak
Drs. Pius Nurwidasa Prihatin, M.Ed., Ed.D for his knowledge, patience,
suggestion, guidance, and sharing during the process of the research and thesis
writing from the beginning until the end. I also want to apologize for all the
mistakes I have made during the process of this thesis. My thankfulness also goes
to all lecturers and all of the teachers of SMP N 15 Yogyakarta for their
lessons and values that they gave to me.
I would also like to thank the big family of SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta
who has given me the opportunities to do the research. I especially thank the
English teacher who helped me conduct the research in his class. I would also like
to express huge gratitude to all of the students of class 7J SMP Negeri 15
Yogyakarta Academic Year 2015/2016 who participated in my research by filling
the questionnaire and being my interviewees.
I dedicate this final thesis especially to my beloved parents, Fx. Hendro
Dwi Raharjo and Cecilia Vonny Indrasari, for their prayer, endless love,
inspirations, and motivation in finishing my thesis. I also thank my sister,
x
My gratefulness also goes to my best friends, Gregorius Purna
Nugrahanto, Yohana Sri Widiastuti, Desy Kurnia Lestari, Luciana Novita
Awis, Gisella Maya Saputri, Yohana Vita Lelita, Tessa Murena Paramita
Ayu Nyoman Aryani and Hilarius Raditya Priambada Purba for their
support, encouragement and prayers. I also want to express my gratitude to all
PBI students, especially the students in batch 2012 Class C.
Finally, I would like to give all my gratitude to everyone whom I cannot
mention one by one who always gives me love, care and support to finish my
thesis.
xi
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN ... vi
1. The English teacher of SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta ... 6
2. The other students or readers... 6
3 Future researchers ... 7
F. Definition of Terms ... 7
1. Responses ... 7
2. Writing ... 8
3. Ability in Organizing Ideas ... 8
4. Mind Mapping Technique ... 9
5. Descriptive Text ... 9
xii
Page
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 11
A. Theoretical Description ... 11
1. Responses ... 11
2. Writing Skill ... 13
a. Definition of writing ... 13
b. Aspects of Writing Skill ... 14
c. Teaching Writing ... 16
3.Ability in Organizing Ideas ... 17
4.Mind Mapping Technique ... 18
a. Definition of Mind Mapping ... 18
b. Types of Mind Mapping ... 19
1) Mind mapping software ... 20
2) Hand-writing mind maps ... 20
c. Benefits of Mind Mapping ... 21
5. Descriptive Text ... 22
D. Research Instrument and Data Gathering Technique ... 30
1. Questionnaire ... 31
2. Interview ... 34
3. Observation ... 37
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 39
1. Data Reduction Strategy ... 39
2. Data Display Strategy ... 41
xiii
Page
F. Research Trustworthiness ... 43
G. Research Procedure ... 44
CHAPTER IV: RESULT AND DISCUSSION ... 47
A. Study Site ... 47
B. Data Reduction Strategy ... 49
a. Coding ... 50
b. Themes Development ... 52
C. Data Display ... 54
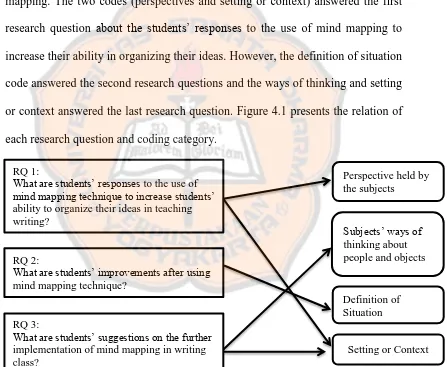
1. The students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping to increase their ability in organizing ideas in writing descriptive text. ... 55
2. The students‟ improvements after using mind mapping technique. ... 62
3. The students‟ suggestion on the implementation of mind mapping. ... 67
D. Conclusion Drawing and Verification ... 71
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION ... 75
A. Conclusions ... 75
B. Recommendations ... 78
1. For further researcher ... 78
2. For the English teacher or future English teacher ... 78
REFERENCES ... 79
xiv
LIST OF TABLE
Page
Table 2.1: Aspects of Micro and Macro Skills ... 14
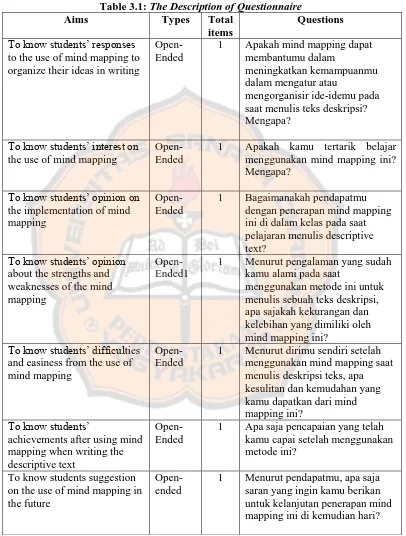
Table 3.1: The Description of Questionnaire ... 33
Table 3.2: The Observation Schedule ... 38
Table 3.3: Type of Code Family ... 40
Table 4.1: Themes and Coding Scheme ... 53
xv
LIST OF FIGURE
Page
Figure 2.1: Stage on Writing by Harmer (2007) ... 16
Figure 2.2: Example of Software Mind Mapping ... 20
Figure 2.3: Example of Hand-writing Mind Mapping ... 21
xvi
LIST OF APPENDICES
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
This chapter provides an introduction about the discussion of this paper. This chapter is divided into six parts. They are research background, research problem, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits, definition of terms, and the significance of the study.
A. Research Background
Writing is one of four important skills in learning English and it is a skill that the students has to master if they want to be professional writers. According to Weigle (2002), writing has become an essential tool for students in today‟s
global community. However, Tiedt (1989) says that “from all the language skills, writing is the most difficult and it is a hard work” (p. 6). Writing difficulties lie not only in generating and organizing ideas, but also in translating those ideas into a readable text (Richards & Renandya, 2011).
The researcher conducted a study related to writing skill because writing becomes the most difficult skill than other skills. The students generally find many difficulties when they want to write a paragraph in writing sections. Baskoff (1969) says that students face three problems in writing. The problems lie in “what to say, how to organize, and how to say” (p. 3). This fact happens when a
the difficulties about how to start writing something, how to organize their ideas, and how to choose the right vocabulary. However, the students and the teacher should find a way to solve those problems to make them successful in writing.
In this research, the researcher used mind mapping to help the students to solve their problems in writing, especially in organizing their ideas. Buzan (2002) says that mind mapping is a graphic representation of ideas and it shows the ideas which are generated around a central theme and how they are interlinked. The users of mind mapping will create a diagram or map of keywords, phrases, concepts, facts, and figures. Mind mapping can be used for generating, visualising, organising, note-taking, problem-solving, and decision-making. Farrand, Hussain, and Hennessey (2002) also state that mind mapping improves the long-term memory of factual information. Buzan (2006) states that mind mapping is a powerful graphic technique which provides a universal key to unlock the potential of the brain. Moreover, a study by Al-Jarf (2009) also has a clear statement about the use of mind mapping. Al-Jarf (2009) states that mind mapping offers a powerful approach for improving the ability of anyone to generate, visualize, and organize the idea. Those statements support that mind mapping is a useful technique to help students or people organize the ideas in writing.
skill, the researcher conducted a preliminary study. The preliminary study was in the form of informal interview related to the situation of the class. From the English teacher‟s explanation, the students‟ writing ability of grade 7 SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta still needed an improvement. Students tended to find lots of difficulties in writing a certain type of text including a descriptive text. To write a descriptive text, students should have good vocabularies in order to describe something or someone in a good way so that they will not make mistakes in selecting the appropriate words. From the English teacher‟s explanation, the students found some difficulties about how to start describing someone or something because they had many ideas in their mind. The students said that they did not know how to organize their ideas and even some of them got stuck in finding an idea. Based on all of those problems, students assumed that writing as a daunting task, and it made writing less interesting. Therefore, the teacher should find a better way to teach the students how to make a good descriptive text.
In teaching writing, teachers are demanded to plan appropriate classroom activities that support the learning of a specific writing skill effectively at every stage ‒ planning, drafting, revising, and editing. Seow (2002) mentions that at the
possible without worrying about how to use them. It is very useful to help writers organize their thought, whether they have too many ideas or too few ideas.
Considering the issue above, the researcher tries to have a case study research about mind mapping technique. Furthermore, the researcher conducted a case study research on the students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping to increase their ability in organizing ideas in writing descriptive text. The aim of this research is to find out the students‟ responses, whether mind mapping increase students‟ ability in organizing their ideas effectively or not, based on the student‟s responses. Besides, this research is to obtain the strengths and
weaknesses of mind mapping based on the students and teacher‟s point of view. The aim of this researcher is to help the teacher to know about the effectiveness of the mind mapping. This research is beneficial for the teacher to know students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping, students‟ improvement, students‟ perception of the strengths and weaknesses of mind mapping and students‟ suggestions. Furthermore, the teacher can conduct more interesting
materials when teaching English, especially in writing skill.
B. Problem Formulation
There are three problem formulations in this research. The problems are presented as follows.
3. What are students‟ suggestions for further implementation of mind mapping in a writing class?
C. Problem Limitation
Since the researcher conducted research about students‟ responses, the researcher focused and limited the problems on the students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping. Besides the identification of the students‟ responses, the
researcher also obtained the students‟ improvements and suggestions after using mind mapping technique. The participants of this study were the students of 7J class SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta who had an experience in using mind mapping. The researcher also asked the English teacher of 7J class about students‟
responses to the use of mind mapping.
D. Research Objectives
Based on the research problems above, the researcher has the research objectives of this study. The objectives of this study are presented as follows. 1. To find out students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping to increase their
ability in organizing ideas in writing descriptive text.
2. To find out students‟ achievement after using mind mapping technique
E. Research Benefits
This research is expected to give some contributions and benefits to English language teaching, especially for:
1. The English Teacher of SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta
Since this research focuses on students‟ responses, it is beneficial for the English teacher of SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. As stated previously, this research provides a research about students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping to increase their ability in organizing ideas in writing a descriptive text. The result of students‟ responses about mind mapping will be varied. The English teacher can use the students‟ responses in developing their writing skill through mind mapping technique. This research also presented students‟ suggestion on the use of mind mapping. The students‟ suggestions give the contribution to the
English teacher of SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta in implementing better learning material in writing. This research can also reflect to the teachers whether the use of mind mapping has improved the students‟ ability in organizing ideas or not.
2. The other Students or Readers
mapping so that it can really help the readers to increase their ability in organizing their ideas. The readers can also use the result of this research to be their consideration and knowledge when they want to use mind mapping especially in writing.
3. Future Researchers
This research is expected to support other researchers to do further discussions which are related to the topic of the use of mind mapping in teaching writing. The future researchers can develop this research into a classroom action research using the same topic, which is the use of mind mapping, to increase the students‟ ability in organizing ideas in writing descriptive text. Moreover, the
future researchers can also make some modules for the research and development.
F. Definition of Terms
In order to clarify the concepts and avoid misinterpretation, the researcher provides the definition of several key-terms which are used in writing this research. The key-terms are presented as follows.
1. Responses
2. Writing
There are four basic skills of the English language learning, namely listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Those four basic skills are divided into receptive and productive skills. Writing belongs to productive skills because it requires the writer to produce a written product.
Zamel (2007) states that writing is the process of discovering meaning and producing something in a written form so that people can read and perform it or use it. Moreover, writing is a way of sharing personal meanings and writing course emphasizes the power of the individual to construct his or her own views on a topic (Richards, 2003). It means that something which is provided in written form will be used by people to discover the meaning of the writing.
Writing is how to produce a written product. However, to make a written product, the writer should have some processes. It means that the writer should have a good skill to organize their ideas which can help them to make the best written product. It can also help the reader to understand the meaning easily.
3. Ability in Organizing Ideas
4. Mind Mapping Technique
Michelco (1998) notes that mind mapping is an organized brainstorming method and it makes learning, note-taking, and organizing ideas become simpler and easier. Buzan (1993) states that mind maps attempt, visually and graphically, to portray a relationship of ideas or concepts. To create a mind map, someone usually starts in the middle of the page with the central theme/main idea and from that point, he or she works outward in all directions to create a growing diagram composed of keywords, phrases, concepts, facts, and figures.
Buzan (1996) states that mind map, as well as encouraging the infinite continuous flow of ideas, enables the brain to be awake and alert by making the brain uses its skills. It means that by using the mind mapping technique, students tend to use their brain to organize and specify their ideas before doing the writing tasks and it can also develop students‟ thinking skill. Anderson et. all (1993) state that mind mapping also activates the imagination, the combined use of words and symbols which increases the creativity as well as thinking skill.
5. Descriptive Text
G. Research Significant
This study has significant of discovering students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping to increase their ability in organizing ideas especially in writing descriptive text. This research presented detail information about students‟
11 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In order to give a fundamental theory of this research, this chapter presents a discussion on the related literature as a theory based upon the research that has been conducted by the researcher. The discussion includes theoretical description and theoretical framework.
A. Theoretical Description
This theoretical description is concerned with theories that are related to the keywords used in this research. There are three major points that will be discussed in this part, namely responses, mind mapping, and writing. The theoretical descriptions are presented as follows.
1. Responses
The main term which is used in this research is responses. Responses are discussed at first to answer the first question in the research problems. In this chapter, the researcher does not only discuss the definition of responses but also the related theories to the responses.
students‟ act or feeling on the use of mind mapping by knowing their responses.
Dollar and Miller says that “response refers to any act or thought related to the satisfaction or reduction of a drive” (as cited in Braun, 1979, p.426). In this study, the drive means the enthusiasm of the students to learn and make the description text with mind mapping. Their responses determined their satisfaction of the use of mind mapping whether mind mapping help them to increase their ability in organizing their ideas in writing or not. All of the students‟ responses were based on their own experience when using mind mapping. The students‟ responses will determine the effectiveness of mind mapping.
There are two kinds of response namely unconditioned response and conditioned response (Pavlov, 1927). Unconditioned response is the reflex response evoked by stimulus without any learning required. Besides, conditional response is an automatic response established by training to an ordinary neutral stimulus. In this research, the conditioned research can be seen when the students were given the mind mapping technique before they were making the descriptive text. The students were given the tasks related to mind mapping more than once and it has repeated continuously in the class.
and action of the students. Therefore, the students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping can determine the effectiveness of mind mapping.
2. Writing Skill
a. Definition of writing
In this research, the researcher only focused on writing skill. Furthermore, there are some definitions of writing stated by some experts. Writing can be defined as a series of contrast (Nunan, 2003). At first, writing is both a physical and a mental act. At the most basic level, writing is the physical act of committing words or ideas to some medias. On the other hand, writing is the mental work of investing ideas, thinking about how to express them, and organizing them into statements and paragraphs that will be clear to a reader. Zamel (1982) states that writing is the process of discovering meaning and it is producing something in written form so that people can read and perform it or use it. Moreover, writing is a way of sharing personal meanings and writing course emphasizes the power of the individual to construct his or her own views on a topic (Hyland, 2003). It means that something which is provided in written form will be used by the people to discover the meaning of the writing.
in doing the pre-writing steps that some of the students are extremely unconfident and unenthusiastic writers. One of the reasons is because they think that they do not have anything to say and cannot come up with the ideas. It was linear to the situation that the students of SMP Negeri 15 faced. They could not find the right ideas and organize their ideas into the structural paragraph.
It can be concluded that writing is a process of organizing ideas in which the writer is demanded to perform creativity in using the language skills to produce a written text. The writer should have a good skill to organize their ideas which can help them to make the best written product. It can also help the reader to understand the meaning easily.
b. Aspects of Writing Skill
The writer should have the best writing skill in producing a written product. Brown (2004) divides the aspects of writing skill into two main skills namely micro and macro skills of writing. Brown also mentions several important aspects of both skills. The aspects of micro and macro skills explained by Brown (2004) are presented as follows.
Table 2.1: Aspects of Micro and Macro Skills
MICRO SKILL MACRO SKILL
1. Producing graphemes and orthographic pattern of English
2. Producing writing at an efficient rate of speed in order to suit the purpose 3. Producing an acceptable core of words
and use appropriate word order pattern 4. Usig acceptable grammatical system (tenses, agreement, pluralization,
3. Conveying links and connection between events and communication (such as relation as mid idea, supporting idea, new information, given information, generalization, and exemplification)
discourse implied meanings of writing accurately in using prewriting devices, writing with fluency in the first drafts, using paraphrases and synonyms soliciting peer and instructor feedback, and using feedback for revising and editing.
Besides two skills explained by Brown (2004), writing also involves several sub skills namely spelling correctly, forming letters correctly, writing legibly, punctuating correctly, using correct layouts, choosing the right vocabulary, using correct grammar and using paragraph correctly. All of the writing skills should be introduced in every stage of writing composition to the students or writers. Therefore, the students or writers can produce the best writing products by obeying those skills of writing.
c. Teaching Writing
There are two approaches in teaching writing (Harmer, 2001). The first approach is focusing on the product of writing process and the second approach is focusing on the writing process itself. However, teacher should pay attention to the various stages of writing process.
Writers need some processes to produce a written product. The experienced writers also plan what they are going to write. Harmer (2004) says that before starting to write or type, they try and decide what they are going to say. Some experts also discuss the process of writing. Rumisek and Zemach (2005) say that writing process goes through several steps to produce a written product. Moreover, Nation (2009) also has the similar view about writing process. Nation explains that one way of focusing on different aspects of writing is to look at writing as a process. It means that writing process incorporates some stages structurally. Harmer (2007) states that the stages on writing are planning, drafting, revising, and final drafting as can be seen in Figure 2.1.
Based on the Harmer‟s explanation, the researcher can conclude that
writers revisit a certain stage from the stage of planning until the last stage which is final version. In the classroom activity, when the students want to write something, the first stage that they should do is the planning stage. In the planning stage, students can use mind mapping to produce or obtain the new ideas. In the drafting stage, students choose the optimal ideas to be included in the piece of writing. Editing means that students should put everything together in a coherent and cogent manner, whereas for the revising stage, students are asked to check their written work again. The students can produce the good final version after they have already done all of the stages.
3. Ability in Organizing Ideas
Ability is the fact that somebody is able to do something. Ability can be improved by doing the exersises. It means that ability in writing skill can also be improved by doing some assignments which are related to writing skill. Purves (1988) explains that students themselves commonly identify language difficulties, particularly an inadequate grasp of vocabulary or grammar and to convey their ideas in appropriate and correct English (as cited in Hyland, 2003).
help the students develop effective paragraph through the creation of the topic sentences, supporting sentences, and transition. Moreover, students are guided to produce connected sentences (Hyland, 2003). The connected sentences gave the students or writers a paragraph coherence and demonstrate their writing skill. 4. Mind Mapping Technique
a. Definition of Mind Mapping
Michelco (1998) says that mind mapping is an organized brainstorming method and it makes learning, note-taking, and organizing ideas become simpler and easier. Buzan (1993) states that mind maps attempt, visually and graphically, to portray a relationship of ideas or concepts. In order to create a mind map, someone usually starts in the middle of the page with the central theme/main idea and from that point, he/she works outward in all directions to create a growing diagram composed of keywords, phrases, concepts, facts, and figures.
Buzan (1996) says that mind map, as well as encouraging the infinite continuous flow of ideas, enables the brain to be awake and alert by making the brain uses its skills. It means that by using mind mapping technique, students tend to use their brain to organize and specify their ideas before doing the writing tasks. Furthermore, it can also develop students‟ thinking skill. In addition, Anderson, et. al (1993) state that the method also activates the imagination, the combined use of words and symbols and also increases the creativity as well as thinking skill.
themselves both verbally and visually. Therefore, when learners use the mind map, they may use graphic representation which may help in the brainstorming process. Brainstorming process helps the students to think although they do not have any ideas in their mind. The students or writers only need to write down all of things in their mind without thinking about the text organization until their creativity has found. By using brainstorming process, writer can find the most appropriate ideas to be used in the mind mapping.
McGriff (2007) also finds that relating images to concepts is a creative task which requires thinking instead of memorizing. Adam and Mowers (2007), in a recent study, show that students who could express their learning with visual skills had a 40% higher retention rate than that of just verbal learners. This study shows that the use of mind mapping technique is a useful strategy to support students during writing tasks. Moreover, a study by Toi (2000) has a clear explanation about the use of mind mapping in increasing students‟ writing skill.
Toi in his study found that the application of mind mapping in planning is a useful writing strategy that can improve students‟ writing skill. Therefore, the researcher used the mind mapping as the technique to increase students‟ ability in organizing
ideas and also their writing skill.
b. Types of Mind Mapping
computer software. Both types of mind mapping can help someone to organize their ideas. The explanations below are the examples of those two types of mind mapping.
1) Mind mapping software
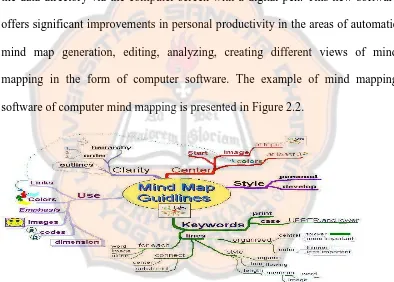
Tonny and Buzan (2003) state that mind mapping software or usually called as computer mind mapping is the „digital link‟ that allows people to input the data directory via the computer screen with a digital pen. This new software offers significant improvements in personal productivity in the areas of automatic mind map generation, editing, analyzing, creating different views of mind mapping in the form of computer software. The example of mind mapping software of computer mind mapping is presented in Figure 2.2.
Figure 2.2: Example of Software Mind Mapping
2) Hand-Writing Mind Maps
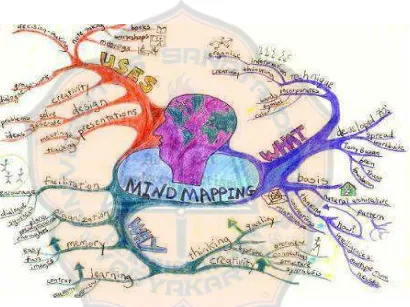
creativity. The writer will draw the mind mapping with their own hands. This hand-writing mind maps give a free decision to the writers to make their mind mapping as interesting as they want. It means that each writer will produce different types of hand-writing. The example of hand-writing mind maps is presented in Figure 2.3.
Figure 2.3: Example of Hand-writing Mind Mapping
c. Benefits of Mind Mapping
be found from using mind mapping. The benefits of mind mapping are presented as follows.
1) Someone can easily add some ideas in the mind mapping or add another link that related to the mind topic in a mind mapping
2) Mind mapping can help someone to concentrate on the information structure and relationship among the ideas.
3) By using the mind mapping, someone can really see the connections and similarities in the information
5. Descriptive Text
Mind mapping technique becomes one of many techniques which are trusted as the writing strategy. It means that mind mapping will be appropriate to be used in several kinds of text especially a descriptive text. According to Gerot and Wignell (1994), a descriptive text is a kind of text with a purpose to give information. The context of a descriptive text is the description of particular things, for example animals, persons, objects, appearances, landscapes, or natural phenomenon.
B. Theoretical Framework
The researcher implemented the main theories in this research in order to address the research problems which were about students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping, students‟ improvement after using mind mapping, and students‟
suggestion to the further implementation of mind mapping. The explanation of the main theories presented as follows.
1. Research question 1: Students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping.
The first research question is about students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping to increase ability in organizing their ideas in writing descriptive text. Students‟ responses will be various. Therefore, the researcher focuses on the
students‟ action and thought (McKechnie, 1981). Moreover, the researcher also
discusses about students‟ perception and ways of thinking (Braun, 1979). The students‟ responses will be about the students‟ satisfaction in using mind mapping
as well as their experiences (Braun, 1979). In this research, the experiences are about the use of mind mapping in writing a descriptive text.
In line with the students‟ responses, the researcher uses the research from
Pavlov (1972) about the unconditioned and conditioned response. The researcher also sees their responses as their motivation in using mind mapping when writing a descriptive text as it is stated by Garrison (2004).
appropriate technique to help them in organizing their ideas (Mayers, 2005). Therefore, in order to answer the second research questions, the researcher uses the explanation from McGriff (2000), Buzan (2007), and Edward (2011) about the advantages that the students‟ or people can get after implementing mind mapping.
25 CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY
In this chapter, the researcher discusses about the methodology employed in this research. There are six parts discussed in this chapter namely research method, research participants, research instrument, data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A. Research Method
This research discussed about the student‟s responses on the use of mind mapping technique to increase their ability in organizing their ideas when writing descriptive text. Therefore, the method which was used in this research was a qualitative research. According to Maanen (1979), qualitative research is an umbrella term covering an array of interpretive techniques which seek to describe, decode, translate, and otherwise come to terms with the meaning, not the frequency, or certain more or less naturally occurring phenomena in the social world (as cited in Merriam, 2009). Furthermore, Denzin and Lincoln (2005) state that qualitative researchers are studying things in their natural settings, attempt to make sense of, or interpret, and phenomena in terms of meanings people bring to them.
characteristics of the real-life event, such as small group behavior, school performance and individual life cycles (Yin, 2009). Moreover in this research, the researcher wants to know about the use of mind mapping in the class. Cohen, Manion and Morison (2011) state that the strategies and instruments for the data collection which were used by the researcher were survey (distributing questionnaires), interview, and observation. Yin (2003) says that case studies can establish cause and effect (“how” and “why”); indeed one of the strengths is that
they observe effects in real contexts. Thus, in this research, the researcher tried to know students‟ responses and the effects on the use of mind mapping.
a. Definition of case
When conducting the case study research, the researcher should know what a case in case study research means. According to Miles and Huberman (1994), case is a phenomenon of some sorts occurring in a bounded context. Miles and Huberman (1994) also stated that the case is, “in effect, your unit of analysis”. The first research question was about students‟ responses to the
use of mind mapping to organize their ideas in writing. Therefore the case in this research was the students‟ responses from 7J class to the use of mind mapping to organize their ideas in writinga description text.
b. Bounded case
will be focused on one topic. According to Baxter and Jack (2008), “in order to avoid that problem, several authors including Yin (2003) and Stake (1995) have suggested that placing boundaries on a case can prevent this explosion from occurring” (p.546). Suggestions on how to bind a case include: (a) by time and place (Creswell, 2003); (b) time and activity (Stake (2003); and (c) by definition and context (as cited in Miles & Huberman, 1994). Based on the explanation above, the researcher collected the case by choosing the context and providing some definitions of the case. In this case, the researcher had a study about the students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping to organize their ideas. Therefore, the established boundaries need to include a concise def inition or explanation of responses and mind mapping.
The strategies and instruments for the data collection used by the researcher was survey. Ary et. al (1990) state that a survey is a kind of research method for gathering data ranging from physical counts and frequencies to attitudes and opinions by asking questions of a group of individuals called respondents. Surveys are also useful for gathering factual information, data on attitudes and preferences, beliefs and predictions, opinions, behavior and experiences – both past and present (Weisberg et al., 1996; Aldridge & Levine, 2001).
the research instruments helped the students to express their responses about the use of mind mapping based on their experiences. The researcher also used the peer-observer to conduct an observation in the class. All of the instruments gave deep information to answer both the research questions.
B. Research Setting
This research took place in SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. The research was done in class 7J. The researcher chose SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta and VII J to conduct this research because the researcher did the teaching practice (Program
Pengalaman Lapangan/PPL) there. Therefore the researcher knew about the
students‟ problems in learning English, especially in writing skill. In order to
answer the research questions, the researcher distributed questionnaires. The researcher also observed the students together with the peer-observer to know about the students‟ responses through their behavior. After that, the researcher interviewed some students and the English teacher to know the students‟ responses and achievement to the use of mind mapping.
held after the students finished answering the questionnaires. The second section was the interview with the teacher which was held on June 16th, 2016.
C. Research Participants
The respondents for this research were the students from SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta class 7J. The researcher only used one class which had an experience in using mind mapping technique. The researcher only chose class 7J because of this class fulfilled the criteria that the researcher had. The researcher had three criteria that should be fulfilled by the respondents. The three criteria were students of 7J had already experienced using mind mapping technique, the researcher knew students‟ characteristic and all of the students were cooperative.
their experiences on the use of mind mapping (before and after using mind mapping) based on their level of understanding. The students who became the research participants agreed to be interviewed and they also wanted to share their experiences in using mind mapping.
The researcher also conducted an interview session with the English teacher of 7J. In the interview, the researcher got the deeper data about students‟ feeling and responses on the use of mind mapping based on the teacher point of view. The teacher knew about students‟ changes before knowing about mind mapping and after using mind mapping. It helped the researcher to know about students‟ improvement from the teacher point of view.
D. Research Instrument and Data Gathering Technique
In this research, the researcher used triangulation as a technique to gather the data. Triangulation was first borrowed in the social science to convey the idea which says that to establish a fact, the researcher needs more than one source of information (Bogdan and Biklen, 1982). It means that many sources of data are better in a study than a single source. Therefore, the researcher decided to use the triangulation in this study.
particularly in qualitative research. Therefore, the researcher could reduce the research bias in this research.
1. Questionnaire
As the first instrument, the researcher used questionnaire as the technique to gather the data. According to Lodico et. al (2006), “a survey or questionnaire is the main tool of instrument used to collect data in a survey research” (p.159). Weisberg et al. (1996) and also Aldridge and Levine (2001) state that surveys are useful for gathering factual information, data on attitudes, and preference, beliefs and predictions, opinion, behavior, and experiences – both in the past and present. Since the aim of this study was to know about students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping, the first instrument that the researcher used in this research was questionnaires. The questionnaires were the main instrument of this study.
According to Wilson and McLean (1994), questionnaire is a widely used and useful instrument for collecting survey information (as cited in Cohen, Manion, Marisson, 2011). By distributing the questionnaire, the researcher could obtain students‟ thoughts, feelings, attitudes, beliefs, values, responses,
personality, and behavioral intentions (Johnson and Christensen, 2011). The students or respondents were suggested to answer all the questions briefly and honestly based on their experiences in using mind mapping. They should return the questionnaires back to the researcher together with their answers to the researcher.
questions. The researcher chose the open-ended questions for the questionnaires in this study. Cohen, Manion, and Morrison (200) concluded that “open ended questions enable participants to write a free account in their own terms, to explain and qualify their responses and avoid the limitation of pre-set categories of response” (p.382). Therefore, by distributing a questionnaire with open-ended questions, the respondents gave the researcher the brief and wide data to be analyzed.
There were seven questions in the questionnaire and the respondents should answer all of the questions based on their experiences and feeling in using mind mapping. Cohen, Manion, and Morrison (2000) state that “questionnaires simply put the open-ended questions and left a space (draw lines) for a free response” (p.392). The respondents answered all the questions in the space or the lines which were given by the researcher. If the spaces were not enough, the respondents could answer it in the other page of the paper so they could answer all the answer freely based on their experiences in using mind mapping.
answer the second research question. The descriptions of the questionnaire can be menggunakan mind mapping ini? Mengapa?
Before the researcher distributed the questionnaires, the researcher piloted the questionnaires. The researcher tested the questionnaire to some students to ensure that the questions made sense to participants and to avoid problems in the questionnaire that might lead to biased answers. After the researcher finished piloting the questionnaire, the researcher distributed the questionnaires to the respondents. The questionnaires were distributed in the end of the class in the last meeting. This questionnaire helped the researcher to know about students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping. The responses told their improvements after using mind mapping.
In giving responses in each question on the questionnaire, the respondents were asked to answer those questions based on their experience or their feeling in using mind mapping. The respondents should answer it honestly based on the real condition that they faced.
2. Interview
The second data gathering technique was interview. Interviewing is a way to collect data as well as to gain knowledge from individuals (Patton, 1990). He adds that the purpose of interview is to find out what is in and on someone else‟s mind. Kvale (1996) defines interviews as “ … an interchange of views between two or more people on a topic of mutual interest, sees the centrality of human interaction for knowledge production, and emphasizes the social situated of research data.” Creswell (2008) states that an interview survey is a form on which
questionnaire and also gain more data or responses from them. The researcher adapted the procedures of interviewing someone by Tuckman (1992) as it is cited from Cohen, Manion, and Morrison (2000).
The interviewer should inform the participant of the nature or purpose of the interview, being honest yet without risking biasing responses, and should strive to put the participant at ease. The conduct of the interview should be explained (what happens, and how, and the structure and organization of the interview), how responses may recorded (p.421)
Cohen et. al (2000) says that “once the data from the interview have been collected, the next stage is analyzing them by coding or scoring” (p.427). Thus for this research, the researcher would analyze all of the data through coding.
The researcher conducted a one-on-one interview in this research. John Creswell (2008) says that “one-on-one interviews are also useful for asking sensitive questions and enabling interviewees to ask questions or provide comments that go beyond the initial questions” (p.387). Therefore, by conducting the interview, the researcher knew about students‟ responses deeply.
information about their feeling on the use of mind mapping. The researcher can also ask more question based on their answers to dig their answers deeply.
A good interview is when the subjects can talk freely about their point of view in the interview section (Briggs, 1986). Therefore, the researcher can get rich data from the respondents‟ perspective in the form of words. Thus, if the
researcher thought that there were some answers that did not complete yet, the researcher would ask more about it.
The questions that had been given in the interview sections helped the researcher to know deeply about students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping
to increase their ability in organizing their ideas in writing. This section also helped the researcher to find out the respondents‟ achievement and suggestion on the use of mind mapping.
3. Observation
Simpson and Tuson (2013) say that observation is a highly flexible form of data collection that can enable the researcher to have access to interactions in a social context. By conducting the observation the researcher could see students‟ behavior through mind mapping. Observation also helped the researcher to see what exactly happened in the class. Observation is more than just looking. It is looking and noting systematically people, events, behaviors, settings, artefacts, routines and so on (Marshall & Rossman, 1995; Simpson & Tuson, 2003). It means that the researcher could find the original responses from the students through their behavior. Robson (2002) says that what people do may differ from what they say they do, and observation provides a reality check; observation also enables a researcher to look afresh at everyday behavior that otherwise might be taken for granted, expected or go unnoticed.
Before conducting the observation, the researcher explained about the purpose, the things that the peer-observer did and also clarified the questions so that the peer-observer did not find the difficulties when answered the questions in the observation guideline. The researcher also prepared an observation guideline for the peer observer. The peer observer and the researcher observed the situation in the class based on the observation guideline that has been prepared before. Therefore, the researcher got the valid data which were needed for this research. By using the observation guideline, there was a correlation from the result between the peer observer and the researcher‟s observation. The peer-observer
had an ability to observe the respondents and write down all the things that she or he knew.
In fact, the researcher conducted the observation for four times in order to know deeply about students‟ feelings and responses on the use of mind mapping through their behavior, attitude and the real condition in the class. Table 3.2 shows the date of observation that the researcher did.
Table 3.2: The Observation Schedule
No Activity Date Time
1 Observation 1 Tuesday, March
29th , 2016
08.35 a.m. – 10.50 a.m. 2 Observation 2 Thursday, 31st
March, 2016
08.35 a.m. – 10.50 a.m. 3 Observation 3 Tuesday, April
E. Data Analysis Technique
In order to complete the data analysis, the researcher used some steps which were adapted from Miles and Huberman (1984). They state that the data analysis consists of three con-current flows of activity namely data reduction, data display, and conclusion drawing or verification.
1. Data Reduction Strategy
Based on Tesch (1990), data reduction is a form of analysis that sharpens, sorts, focuses, discards and organizes data in such a way that final conclusion can be drawn and verified (as cited in Miles & Huberman, 1994). In qualitative research, the researcher obtained data from different sources using data collection techniques assortment (triangulation). While collecting the data, the researcher got plenty of data so the researcher had to record the result carefully in details. The amount of the data which had been collected was complex. As stated by Miles & Hubberman (1984), the activity in qualitative data analysis performs interactively and runs continuously until complete, so that the data was already saturated. When the data was already completed, the researcher did the next step which was data reduction. The data obtained by the researcher was very varied so the researcher made some techniques to draw conclusions of the research that had been done.
similar information. More than this, it enables the researcher to search and retrieve the data in terms of those items that bear the same code” (p.559). Kerlinger (1970) says that coding has been defined as the translation of questions responses and respondents‟ information to specific categories for the purpose of analysis (as cited in Cohen, Manion, & Marisson, 2000). It means that by using coding, the researcher will have same code to analyze the data. The researcher had to categorize the respondents‟ answers through some categories in coding.
The researcher used the variation of codes from the types of code family suggested by Bogdan and Biklen (2003). The researcher used this type of code families because it consisted of specific topics that were relevant for reviewing the questionnaire and interview data. The type of code family by Bodgan and Biklen (2003) is presented in Table 3.3.
Table 3.3: Type of Code Family
Code Family Descriptions
Setting/Context Codes General information on the setting topic, or subject Definition of Situation Codes To place units of data that tell you how the subjects
define the setting of particular topic.
Perspectives held by Subjects Codes oriented toward ways of thinking all or some subjects share that are not as general as their overall definition of the situation but indicate orientations toward particular aspects of a setting.
Subjects‟ ways of thinking about People and Objects
The subjects‟ understanding of each other, of outsiders, and of the objects that make up their world.
Process Codes Words and phrases that facilitates categorizing sequences of events, changes over time, or passages from one type or kind of status to another.
Activity Codes Codes that are directed at regularly occurring kinds of behavior.
Event Codes It is directed as units of data that are related to specific activities that occur in the setting or in the lives of the subjects you are interviewing.
Strategy Codes The tactics, methods, techniques, maneuvers, ploys, and other conscious ways people accomplish various things.
Relationship and Social Structure Codes
data that direct you to cliques, friendships, romance, coalitions, enemies and mentors/students.
Narrative Codes It describes the structure of talk itself.
Method Codes It isolates material pertinent to research procedures, problems, joys, dilemmas and the like.
Developed From Bogdan and Biklen (2003)
Bodgan and Biklen (2003) say that after the researcher read the questionnaire and transcribe the recorded interviews, the researcher read the transcripts over and over again several times in order to get ideas for a coding scheme. It means that the researcher needed to record and sort all the answer before deciding the coding scheme. The researcher used this coding to analyze all the answers from the three instruments in this research. After coding all the data, the researcher used the narrative descriptive to display the data.
2. Data Display Strategy
Miles and Huberman (1994) state that data display has been considered as an important step during the qualitative data analysis. They also say that the most frequent form of displaying qualitative data in the past was extendeed text. Therefore, the researcher displayed the data in the form of a text. The results of a qualitative study should include themes derived from the data, a thorough description of the themes, and multiple perspectives from participants or detailed descriptions of the settings or individuals to support these themes (Creswell, 2009).
3. Conclusion Drawing Strategy
the qualitative analyst begins to decide what thing mean – it is nothing regularities, patterns, explanations, possible configurations, causal flows, and preposition.
In this research, the researcher focused on the students‟ responses, students‟ achievement and students‟ suggestion to the use of mind mapping. The
researcher also combined the answer from all of the data, which were from questionnaire, interview and the peer observer.
Based on the questionnaire, the researcher read all of the answers from the result of the questionnaire. The researcher also made some guidelines which consisted of the questions that had been chosen in the data reduction. All of the answers for the questions were recorded as the final answer. The researcher concluded the answers by making a criterion for each question. Those answers helped the researcher to answer the first problem formulation. As in the last question, the researcher also made some criteria based on the answers. If there were similar answers in the questions, they were noted as one answer. The last question was the data for answering the second problem.
Based on the peer observer, the researcher mixed and matched all of the answer from the peer observer and the researcher‟s result. The result from the peer observer and the researcher were considered as one result. If there were different answers from the peer observer and the researcher, those answers would be presented only based on the real condition.
The researcher drew the conclusion from the interview, questionnaire and the result of the peer observer that had been returned by the students. Those data completed the data triangulation and presented only based on the real condition. The result answered both of the problem formulations on this research.
F. Research Trustworthiness
In order to make sure the trustworthiness in this study, the researcher used various strategies to attempt the trustworthiness. According to Brewer and Hunter (1989), the use of different methods in concert compensates for their individual limitations and exploits their respective benefits. Therefore, the researcher used more than one source of data, which was triangulation to increase the credibility or to minimize the research bias and prove the trustworthiness.
trustworthiness because the data from the observation did not only come from the researcher‟s point of view but also from the peer-observer‟s point of view.
G. Research Procedure
There were several procedures to conduct this research. The first was the researcher decided the subject of the study which was mind mapping. In order to find some information related to mind mapping, the researcher conducted the library review. The researcher tried to find information which was relevant to the study.
The next step was generating the problem formulation. In order to answer the problem formulation, the researcher conducted the techniques to collect the data. In this research, the researcher conducted a qualitative research methodology. In order to obtain the validity and reliability of the study, the researcher conducted a triangulation strategy. The triangulation that the researcher used in this research was questionnaires, observation and interview.
answers that are related to students‟ responses and suggestions. In the interview section, the respondents verified and completed their answers. The researcher also asked some questions in order to complete the data. The answers from both questionnaires and the interview were gathered into one and they were presented based on the real situation.
The researcher also conducted an interview with the English teacher to know about the students‟ responses from the teacher‟s point of view. The researcher made an appointment with the teacher and did the interview section. After that, the researcher made the interview transcript and gave it back to the teacher to make sure that the transcript was based on the real condition.
The last instrument was observation. In this study the researcher involved a peer-observer to increase the validity. The researcher also mixed and matched the observation‟s result from the peer observer and the researcher. The researcher combined the result and did the data reduction again. The researcher only used the data which were related to students‟ responses and suggestions on the use of mind mapping. After that the researcher answered the research questions by using the data that the researcher obtained.
In the data analysis, the researcher used the data analyzing technique from Miles and Huberman (1994). Based on Miles and Huberman (1994), there are three parts to analyze the data namely data reduction, data display, and conclusion or verification. The result was not only from the researcher‟s interpretation but
47 CHAPTER IV
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents research finding and discussion to answer the research questions about the students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping, students‟ improvement after using mind mapping and students‟ suggestion on the
further implementation of mind mapping. Each problem was discussed and analyzed using theories that were stated in the review of related literature. This chapter also consists of the description and discussion of the study site and of the students‟ responses to the use of mind mapping.
A. Study Site
they were confused, they only wrote anything that they had in their mind without thinking of the text organization. They tended to make an unorganized text because they did not know what to do. The problem came because they did not have the right technique to help them to solve this problem. Therefore, the researcher introduced mind mapping as a technique to help them solve their problem in organizing their ideas.
The research was conducted on the students of 7th grade of 15 Junior High School Yogyakarta especially in class 7J because 7J fulfilled the criteria that the researcher had before. The number of the students in 7J was 31 students with 20 female students and 11 male students. The study was conducted in three phases, which were observation class by the researcher and peer-observer, questionnaire for the students, a formal interview with the English teacher of 7J and an informal interview with some students of 7J class.
From the interview section, the researcher also wanted to know deeper about the students‟ improvement after using mind mapping.
B. Data Reduction Strategy
Based on the explanation in chapter III, in qualitative research, researchers obtained data from different sources using data collection techniques assortment (triangulation). While collecting the data, the researcher got plenty of data so the researcher had to record the result carefully in details. The amount of the data which had been collected was complex therefore the activity in the qualitative data analysis performs interactively and runs continuously until complete, so that the data is already saturated (Miles & Hubberman, 1984).
The data obtained by the researcher varied so the researcher used some techniques to draw the conclusions of the research that had been done. Therefore, the researcher conducted a data reduction by reading the research data as many as possible. The data were in the form of observation from the researcher and peer-observer, the students‟ answers of questionnaire and interview transcripts. After