THE ERROR ANALYSIS AND ITS NATURE
FOUND IN FOREIGN LANGUAGE LEARNERS’ WRITING
Dwi Rahayu
The lecturer of STKIP PGRI Pacitan E-mail: [email protected]
Abstract:
It is a kind of library research which aims at revealing: (1) the definitions of error analysis; (2) the sources of error; (3) error taxonomy and linguistic category; (4) relevant research of error analysis. The strategy of this research is modified from George (2008: 66) through the following phases: (1) motivation or assignment; (2) topic selection; (3) research questions (brainstorming); (4) research plan (strategy); (5) reference works & databases (tools & tactics); (6) sources; (7) evaluation; (8) drafting & revising. Error is one of the lerners’ interlanguage prosess where the learners make unnecessary items to be included or even ommit the necessary items. Those issues are virtually unique to note and being ongoing research that has never ended. This research is carried out to have more affinity for the students’ error so then the teachers can be responsive in giving his or her policy in Eglish teaching strategy priority. Based on the relevant research findings, the frequent errors made by the students are in using participles and past costumes (the highest error is past simple) it may be caused of the frequent usage of the basic grammar used by the students. It implies that drilling on the frequent error is a must and becomes priority to focuse.
Key Words: Error Analysis (EA), Writing
In modern society, English becomes more important as a tool of communication. English as a global language sets the important role in teaching English at school from elementary school to senior high school and even in university. From these facts, students are not only expected to speak English fluently but they also have to be able to fulfill four language skills namely listening, speaking, reading, and writing. These four skills are integrated and related to each other.
Writing as one of the four skills are important as stated by Heaton (1975: 138) writing skill are more complex and difficult to teaching, requiring, and mastering not only of grammatical and rhetorical devices but also conceptual and judgment, because of the difficulties of writing, some efforts have been done to solve the problem.The main objective is to make the writing become easier to learn for the students. In addition, writing
includes the most important activity in the entire world that one will be remembered and referred of their writing, even when their bodies are no longer being in this world. Writing activity can’t be separated from the progressing world including sciences, informations, educations, and business.
METHODS OF THE RESEARCH
It is kind of library research that is aimed at finding out the theories through the analysis of the theories or relevan researches. It needs to establish the strategy or tool of that enquiry so-called search strategy modified from George (2008: 66) through the following phases: (1) motivation or assignment; (2) topic selection; (3) research questions (brainstorming); (4) research plan (strategy); (5) reference works & databases (tools & tactics); (6) sources; (7) evaluation; (8) drafting & revising. To acquire trustworthiness, the prerequisitite should be fulfilled to get the validity of the data using triangulation of relevant research. The researcher uses the relevant research to enrich the data in order to have strong inference. The method used to analyze the data is through the following phases (1) domain analysis; (2) taxonomic analysis; (3) componential analysis; (4) finding out the culture theme (conclusion). The method is hidden, where the researchers of the relevant researches had applied those methods to infer the research findings.
RESERACH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS
The Definitions of Error Analysis
Before discussing about error analysis, it should be understood what error is, which is commonly compared to mistake. Corder (1967 1971 in James, 1998: 78) associates the error compared to mistake distinction to the issue of competence and performance. In this way, errors are seen as failures of competence and mistakes as failures of performance. Corder argues that mistakes are of no significance to the process of language learning since they do not reflect a defect in our knowledge and they can occur in L1 as well as L2 (Corder, 1967: 166-167 cited in James 1998: 78-79). On the other
hand, errors “Are of significance; they do reflect knowledge; they are not self-correctable; and only learners of an L2
make them” (James 1998: 79). In
addition, Edges in James (1998: 80-81) states mistake as slips occured as a consequence of processing problems or carelessness. The learner is usually able to self-correct if he or she has a chance to do so. Then, what is error analysis?
In conformity with Richards and schmidts (2002: 184)
The error analysis is the study and analysis of the errors made by second language learners. Error analysis may be carried out in order to: a) identify strategies which learners use in language learning, b) try to identify the causes of learner errors, c) obtain information on common difficulties in language learning, as an aid to teaching or in the preparation of teaching materials. Error analysis is developed as a branch of applied linguistics in the 1960s, and set out to demonstrate that many learner errors were not due to the learner’s mother tongue but reflected universal learning strategies.
It means that error is produced by second language learners in the process of acquiring the target language and error analysis functions to be an aid of teaching and learning process and developed as a branch of applied linguistics. While, Hastuti in Khalawi (2011: 37) states that error analysis is process based on the learner’s error with a clear objective and the target is clear. And the object of learning is language. It is true that the target should be based on the language study not to be trapped in different object. And the result of the analysis should reflect the aid of better target and improvement.
errors according to their source, and evaluation or justification of seriousness level of the error. Based on the last definiton of error analysis, the researcher of EA should be procedural noticing the aspect of source and kind of error the students make and giving strong justification on his or her research.
Based on those expert definitons, error analysis is developed as a branch of applied linguitics that is procedural to reveal aspect of source and kind of error that are made by the second or foreign language learners with clear objetive and target, namely as the aid of teaching and material preparation.
The Source of Error
In conformity with Brown (1987: 178) errors are divided to be: (1) interlingual error, characterized by a lot of interlingual transfer from the native language or interference; (2) intralingual error, it is one which results from faulty or partial learning of the target language, rather than from language transfer. Intralingual errors may be caused by the influence of one target language item upon interlingual error another.
For example a learner may produce He is comes, based on a blend of the English structures He is coming, He comes (Richards and Schmidt, 2002: 185); (3) communicative strategies, are retro-actively determined by discourse activity carried out by speakers. Some variation is to be expected, which in the end modifies or qualifies the pre-existing frame (Rouveyrol et al, 2005: 292). While Brown (1980: 178) states that a communicative strategy is the conscious employment of verbal mechanism for communicating idea when precise linguistic forms for some reason is not readily available to the learner at a point in communication. It means that the learners will have difficulty in distinguishing slank, jargon, formal, informal, or non formal language.
Error Taxonomy and Linguistic Category
Error taxonomy classifies errors according to observable surface features of the errors without referring to their underlying causes or sources. Error based surface strategy taxonomy is discussed in the following issues (Dulay, 1982: 150): (1) omission, means that an item which must be present in a well-formed utterance is absent. There is an evidence that grammatical morphemes (e.g. noun and verb inflections, articles, prepositions) are omitted more often that content morphemes which carry the meaning (Dulay et al. 1982: 154-155). For instance, in the sentence *My father policeman the grammatical morphemes “is” are omitted; (2) addition, is the second category of surface strategy taxonomy and also the opposite of omission. The presence of an extra item which mustn't be present in a well formed utterance is characteristic for additions. Dulay divides them into three categories: (a) double markings, as in *Did you went there?, (b) regularization, e.g.* sheeps, *cutted, and (c) simple addition; (3) misformation, is “The use of the wrong form of the morpheme or structure” (Dulay et al. 1982: 158) that consist of (a) regularizations an irregular marker is replaced by a regular one, as in *sheeps for sheep, (b) Archi-forms refer to the use of one member of a class of forms instead of using all the members, e.g. using this in the situations when either this or these should be used, (c) alternating forms are represented by “Free alternation of various members of a class with each other”, as in *those dog and this cat are used interchangeably; (4) misordering, occurs where a thirtynine morpheme or a group of them is incorrectly placed, as in *I get up at 6 o'clock always, where always is misordered.
which is affected by the error. Among language components we count phonology, syntax and morphology, semantics and lexicon, and discourse (Dulay et al. 1982: 146). It is used as either the only one or combined with some other taxonomy that is useful in organizing the collected data.
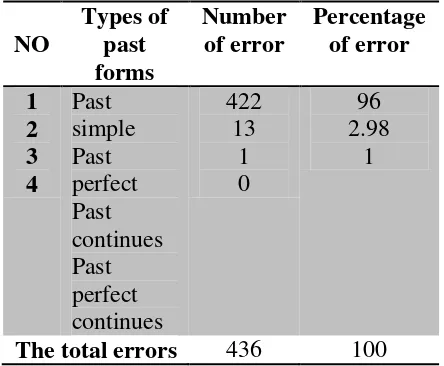
Relevant Research of Error Analysis The first research was carried out by Hasan Khalawi, the students of English department Nusantara university Kediri on September 15th 2011 entitled “The Error Analysis on The Use of Past Tense Found in The Students’ Recount Writing at The Fourth Semester of English Department Students” had found the following display in his research:
Table I. Classification of Errors Based on Type of past form
NO
Types of past forms
Number of error
Percentage of error
1 2 3 4
Past simple Past perfect Past continues Past perfect continues
422 13
1 0
96 2.98
1
The total errors 436 100
Table II. Classifying Error Based on Types of Errors
N O
Types of errors
Number of errors
Percentage of errors 1
2 3 4
Omission Inclusion Malformati on
Disorderin g
60 27 269
85
13.6 6.12 61 19.2
The total errors
441 100
The second research was carried out by Nurul Susanti the student of English department Sarjana Wiyata Taman Siswa University Yogyakarta had gotten her research findings as follow:
Table III. Error Research Findings
N O
SUB CATEGORIES
PROBL EMS
%
1 Participles 95 39%
2 Past costumes 116 48%
3 Conditions 5 2%
4 Causatives 1 1%
5 Affirmative agreement
0 0%
6
Relative pronouns which refer to person and things
2 1%
7
Modifier of cause in clauses of clause and result
0 0%
8 Adverb of
Manner
3 1%
9 Time modifiers 8 3%
10 Cause connectors 12 5%
TOTAL 242 100
%
However, based on the minimal comparison between the both researcher, it has already been revealed that the students have more difficulty in using participles and past costumes (the highest error is past simple) it may be caused of the frequent usage of the basic grammar used by the students. It implies that drilling on the frequent error is a must and becomes priority to focus.
CONCLUSION AND IMPLICATION Conclusion
learners with clear objetive and target, namely as the aid of teaching and material preparation; (2) the source of errors is divided to be three aspects based on Brown (1987: 178) those are: (a) interlingual error characterized by a lot of interlingual transfer from the native language or interference, (b)
intralingual error caused by the influence of one target language item upon interlingual error another; and (c) communicative strategies, are retro-actively determined by discourse activity carried out by speakers indicated by the difficulty of using slank, jargon, formal, informal, or non formal language; (3) the frequent errors made by the students based on the relevant reseraches are the use of participle and past costumes (the highest error is past simple) it may be caused of the frequent usage of the basic grammar used by the students.
Implication
Based on the research findings, it implies that EA is important to be carried out continuously. It is because, the individual difference or class uniqueness is various in particular time and study. The advanced technology and ICT may affect the different assumption about what kinds of errors frequently made by the students. In addition, the teachers can use drilling strategy to enhance and focused on the frequent error made by the students, those are participle and past costumes (simple past) using many exposures in advance (talking using many participle and past simple tenses), after that, the students are drilled.
Bibliography
Brown, H. Douglass. (1987). Principle of Language Learning and Teaching. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Dulay, H., Burt, M. & Krashen, S. (1988). Language Two. New York: Oxford University Press.
George, W. Mary. (2008). The Elements of Library Research. New Jersey: Princeton University Press.
Heaton, J. B. (1975). Writing English Language Test. London: Longman Group.
James, Carl. (1981). Contrastive Analysis. Harlow: Longman
Khalawi, Hasan. (2011). The Error Analysis on The Use of Past Tense Found in The Students’ Recount Writing at The Fourth Semester of English Department Students of STKIP PGRI Pacitan: A Thesis. Kediri: Unpublished.
Nurul, W Susanti. (2006). Problem of Using Grammar Among The Third Semester Students of Sarjanawiyata Tamansiswa University Yogyakarta: A Thesis. Yogyakarta: Unpublished.
Rouveyrol et al. (2005). A Linguistic toolbox for discourse analysis: toward A Multidimensional Handling of Verbal Interaction. London: Sage Publications.
Richards, Jack C, and Richards schmidt. (2002). Longman Dictionary of Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics. Longman.