MARKETING MANAGEMENT
12th edition
6
Analyzing
Consumer Markets
6-2
Chapter Questions
• How do consumer characteristics influence
buying behavior?
• What major psychological processes
influence consumer responses to the
marketing program?
• How do consumers make purchasing
decisions?
6-3
Emerging Trends in Consumer Behavior
Metrosexual –
6-4
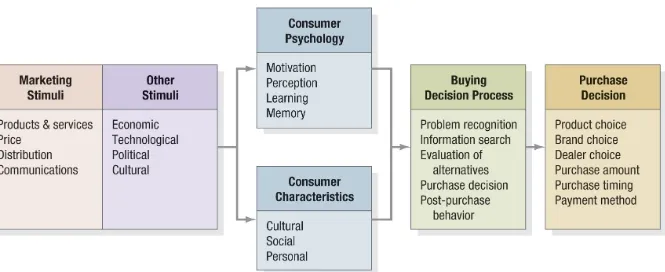
What Influences Consumer Behavior?
Cultural Factors Cultural Factors
Social Factors Social Factors
6-5
Culture
The fundamental determinant of
a person’s wants and behaviors
acquired through socialization
processes with family
6-7
6-8
Fast Facts About American Culture
• The average American:
– chews 300 sticks of gum a year
– goes to the movies 9 times a year
– takes 4 trips per year
6-9
Social Classes
Upper uppers
Lower uppers
Upper middles
Middle class
Working class
6-10
Characteristics of Social Classes
• Within a class, people tend to behave alike
• Social class conveys perceptions of inferior
or superior position
6-11
Social Factors
Reference groups
Social
roles Statuses
6-13
Family
• Family of Orientation – Religion
– Politics
– Economics
• Family of Procreation – Everyday buying
6-14
6-15
Roles and Statuses
6-17
Behavior changes according to life cycle stage
•Family
•Psychological
6-19
Lifestyle Influences
Multi-tasking
Time-starved
6-20
Figure 6.1
6-21
Key Psychological Processes
Motivation
Memory Learning
6-22
Motivation
Freud’s Theory
Behavior is guided by subconscious motivations Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Behavior is driven by
6-23
6-24
6-25
Perception
Selective Attention
Subliminal Perception Selective Retention
6-26
6-27
6-28
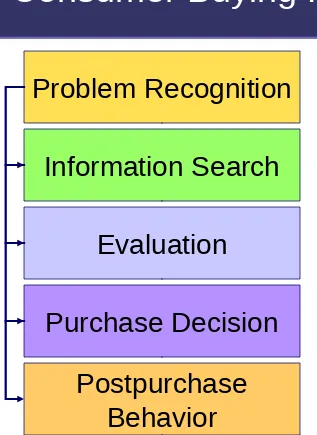
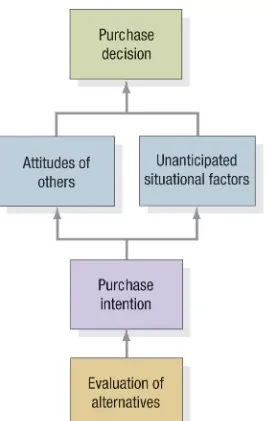
Figure 6.4 Consumer Buying Process
Problem Recognition
Information Search
Evaluation
Purchase Decision
6-29
6-30
Sources of Information
Personal
Experiential Public
6-31
6-32
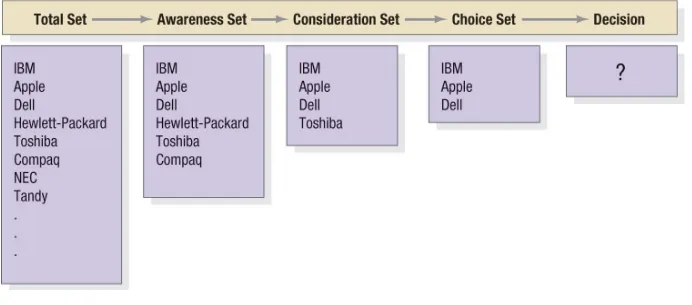
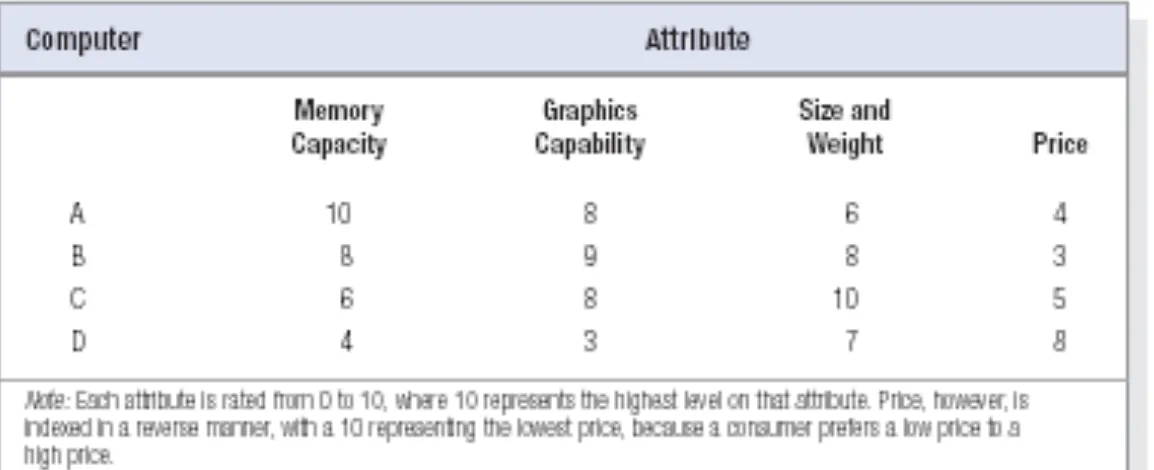
[image:32.720.78.655.163.398.2]6-33
6-34
Non-compensatory Models of Choice
• Conjunctive
• Lexicographic
6-36
6-37
Other Theories of
Consumer Decision Making
Involvement • Elaboration Likelihood Model • Low-involvement marketing strategies • Variety-seeking buying behavior Decision Heuristics • Availability • Representativeness • Anchoring and
6-38
Mental Accounting
• Consumers tend to…
– Segregate gains
– Integrate losses
6-39
Marketing Debate
Is Target Marketing Ever Bad?
Take a position:
1. Targeting minorities is exploitative.
2. Targeting minorities is a sound
6-40
Marketing Discussion
What are your mental accounts?
Do you have rules you employ in
spending money?