ABSTRACT
Kristianti, Yulia Dewi. 2015. The Students’ Use of Computer Software to Develop Listening Media in Language Teaching Media Class. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Nowadays, teachers are expected to be able to use technology in order to support their teaching and learning strategies. Listening as one of the language skills requires technology in order to create the materials. It is important that preservice teachers in English Language Education Study Program know how to develop good listening materials by using appropriate media such as computer software.
This study investigated the use of computer software to develop the listening media in Language Teaching Media class of the English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University. There are two research questions formulated in this study, those are 1) how do students in Language Teaching Media class develop listening media?, 2) what are the students’ perceptions on the use of software to develop listening media in Language Teaching Media class?
This study employed mixed method which was the combination between qualitative and quantitative method. The participants of this research were the fifth semester students who joined the Language Teaching Media course academic batch 2012 at English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University. A questionnaire and an interview were the instruments that were used to gather the data. The questionnaire was used to answer the research questions number one and two. Meanwhile the interview was used to support the results and to gain more information.
The results showed that students in Language Teaching Media class applied some steps in the instructional design. Their lesson plans consisted the topics of the lesson, the target classes, the indicators, and the objectives. Since the media that were not adjusted to the lesson plan could not reach the learning goals that had been settled. The students also made their best in developing listening media by considering some factors that influenced the listening skill. The second result, which was about the students’ perceptions on the use of computer software, tended to have positive results. The available software helped students to improve the quality of listening media they had made. The software was applicable and easy to be used so that they could spend time more efficiently on editing and learning the media. Overall, the available software used in Language Teaching Media class was still satisfying.
ABSTRAK
Kristianti, Yulia Dewi. 2015. The Students’ Use of Computer Software to Develop Listening Media in Language Teaching Media Class. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Dewasa ini, para guru diharapkan mampu untuk menggunakan teknologi agar dapat mendukung strategi belajar mengajar. Listening sebagai salah satu dari kemampuan-kemampuan berbahasa membutuhkan teknologi dalam pembuatan materinya. Sangat penting bagi para calon guru Bahasa Inggris untuk mengetahui bagaimana mengembangkan listening materials yang baik dengan menggunakan media yang tepat, seperti computer software.
Penelitian ini menyelidiki penggunaan computer software di kelas Language Teaching Media, program studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma, untuk mengembangkan listening material. Terdapat dua pertanyaan penelitian dalam studi ini, yaitu 1) bagaimana siswa di kelas Language Teaching Media mengembangkan listening media?, 2) bagaimana persepsi siswa tentang penggunaan software yang terdapat di kelas Language Teaching Mediauntuk mengembangkan listening media?
Metode yang digunakan adalah metode campuran yang mana merupakan gabungan antara metode kuantitatif dan kualitatif. Peserta dalam penelitian ini merupakan mahasiswa semester lima angkatan 2012 yang mengikuti kelas Language Teaching Media di program studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma. Kuesioner dan wawancara adalah alat yang digunakan untuk mengumpulkan data dalam penelitian ini. Kuesioner digunakan untuk menjawab pertanyaan penelitian nomor satu dan dua sedangkan wawancara digunakan untuk mendukung hasil kuesioner dan mendapatkan lebih banyak informasi.
Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa para siswa di kelas Language Teaching Media menerapkan beberapa langkah dalam desain pembelajaran. Rencana pelaksanaan pembelajaran mereka terdiri dari topik pembelajaran, target kelas, indikator, dan tujuan pembelajaran. Karena media yang tidak disesuaikan dengan materi pembelajaran tentunya tidak dapat mencapai tujuan yang telah ditetapkan. Para siswa di kelas Language Teaching Media melakukan yang terbaik dalam membuat listening media dengan mempertimbangkan beberapa faktor yang dapat mempengaruhi kemampuan listening pendengarnya. Hasil dari pertanyaan kedua, yaitu mengenai persepsi siswa terhadap software yang tersedia di kelas, cenderung menunjukkan hasil yang positif. Softwareyang tersedia membantu para siswa untuk meningkatkan kualitas listening media yang mereka buat. Software tersebut dapat dan mudah digunakan sehingga siswa dapat menggunakan waktu mereka secara efisien dalam mengedit dan belajar mengenai learning media. Secara keseluruhan, siswa puas akan software yang tersedia di kelas Language Teaching Media.
THE STUDENTS’ USE OF COMPUTER SOFTWARE TO
DEVELOP LISTENING MEDIA IN LANGUAGE TEACHING
MEDIA CLASS
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN Thesis
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Yulia Dewi Kristianti Student Number: 111214065
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
i
THE STUDENTS’ USE OF COMPUTER SOFTWARE TO
DEVELOP LISTENING MEDIA IN LANGUAGE TEACHING
MEDIA CLASS
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN Thesis
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Yulia Dewi Kristianti Student Number: 111214065
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
vi ABSTRACT
Kristianti, Yulia Dewi. 2015. The Students’ Use of Computer Software to Develop Listening Media in Language Teaching Media Class. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Nowadays, teachers are expected to be able to use technology in order to support their teaching and learning strategies. Listening as one of the language skills requires technology in order to create the materials. It is important that preservice teachers in English Language Education Study Program know how to develop good listening materials by using appropriate media such as computer software.
This study investigated the use of computer software to develop the listening media in Language Teaching Media class of the English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University. There are two research questions formulated in this study, those are 1) how do students in Language Teaching Media class develop listening media?, 2) what are the students’ perceptions on the use of software to develop listening media in Language Teaching Media class?
This study employed mixed method which was the combination between qualitative and quantitative method. The participants of this research were the fifth semester students who joined the Language Teaching Media course academic batch 2012 at English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University. A questionnaire and an interview were the instruments that were used to gather the data. The questionnaire was used to answer the research questions number one and two. Meanwhile the interview was used to support the results and to gain more information.
The results showed that students in Language Teaching Media class applied some steps in the instructional design. Their lesson plans consisted the topics of the lesson, the target classes, the indicators, and the objectives. Since the media that were not adjusted to the lesson plan could not reach the learning goals that had been settled. The students also made their best in developing listening media by considering some factors that influenced the listening skill. The second result, which was about the students’ perceptions on the use of computer software, tended to have positive results. The available software helped students to improve the quality of listening media they had made. The software was applicable and easy to be used so that they could spend time more efficiently on editing and learning the media. Overall, the available software used in Language Teaching Media class was still satisfying.
vii ABSTRAK
Kristianti, Yulia Dewi. 2015. The Students’ Use of Computer Software to Develop Listening Media in Language Teaching Media Class. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Dewasa ini, para guru diharapkan mampu untuk menggunakan teknologi agar dapat mendukung strategi belajar mengajar. Listening sebagai salah satu dari kemampuan-kemampuan berbahasa membutuhkan teknologi dalam pembuatan materinya. Sangat penting bagi para calon guru Bahasa Inggris untuk mengetahui bagaimana mengembangkan listening materials yang baik dengan menggunakan media yang tepat, seperti computer software.
Penelitian ini menyelidiki penggunaan computer software di kelas Language Teaching Media, program studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma, untuk mengembangkan listening material. Terdapat dua pertanyaan penelitian dalam studi ini, yaitu 1) bagaimana siswa di kelas Language Teaching Media mengembangkan listening media?, 2) bagaimana persepsi siswa tentang penggunaan software yang terdapat di kelas Language Teaching Media untuk mengembangkan listening media?
Metode yang digunakan adalah metode campuran yang mana merupakan gabungan antara metode kuantitatif dan kualitatif. Peserta dalam penelitian ini merupakan mahasiswa semester lima angkatan 2012 yang mengikuti kelas Language Teaching Media di program studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma. Kuesioner dan wawancara adalah alat yang digunakan untuk mengumpulkan data dalam penelitian ini. Kuesioner digunakan untuk menjawab pertanyaan penelitian nomor satu dan dua sedangkan wawancara digunakan untuk mendukung hasil kuesioner dan mendapatkan lebih banyak informasi.
Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa para siswa di kelas Language Teaching Media menerapkan beberapa langkah dalam desain pembelajaran. Rencana pelaksanaan pembelajaran mereka terdiri dari topik pembelajaran, target kelas, indikator, dan tujuan pembelajaran. Karena media yang tidak disesuaikan dengan materi pembelajaran tentunya tidak dapat mencapai tujuan yang telah ditetapkan. Para siswa di kelas Language Teaching Media melakukan yang terbaik dalam membuat listening media dengan mempertimbangkan beberapa faktor yang dapat mempengaruhi kemampuan listening pendengarnya. Hasil dari pertanyaan kedua, yaitu mengenai persepsi siswa terhadap software yang tersedia di kelas, cenderung menunjukkan hasil yang positif. Software yang tersedia membantu para siswa untuk meningkatkan kualitas listening media yang mereka buat. Software tersebut dapat dan mudah digunakan sehingga siswa dapat menggunakan waktu mereka secara efisien dalam mengedit dan belajar mengenai learning media. Secara keseluruhan, siswa puas akan software yang tersedia di kelas Language Teaching Media.
viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to thank Jesus Christ for His wonderful blessing
and guidance so that I can finish this thesis. I thank him for blessing on me.
I dedicate my deepest gratitude to my sponsor, Concilianus Laos Mbato,
M.A., Ed.D., for his guidance and patience during the process of this thesis. His advice and his encouragement from the beginning until the end of the thesis
completion become my spirit. My sincere appreciation also goes to all PBI
lecturers who always teach me patiently during my study, especially to Chosa Kastuhandani, M.Hum., who allows me to conduct research in his class. Besides, he is a great academic advisor and also a father for me.
I would like to express my gratitude to my lovely mom and dad,
Marcelina Yatin and Handreanus Dulrahmin. They always give everything I need. They give the best for me so that I can live my life happily and spiritfully. I
would not become I am right now if it is not because of their sacrifice. Besides, I
also give my gratitude to my sister, Noviana Puji Rahayu, who has taught me to
be a strong and an independent woman.
My thankfulness also goes to the greatest person in my life, who patiently
listens to my complaint during the process of finishing this thesis, Andy Widya
Purwanto. His love, care, and support is really helpful for me to bear the tough condition.
My sincere appreciation is also addressed to my great friends, Ocha,
ix
of being friend is. Also, I thank all my friends from PBI class B batch 2011, who
have given beautiful memories during my study in Sanata Dharma University.
However, this thesis cannot be accomplished without a great person who
tries to do the best in her life, I, myself. Without encouraging and motivating
myself, I will never finish this thesis. Lastly, my gratitude also goes to all
everyone who has helped me in completing this thesis.
Sincerely,
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... iv
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Description ... 8
1. Perception ... 8
a.Definition of Perception ... 8
b.Factors Influencing Perception ... 10
2. Listening Media ... 11
a.Factors that Influence Listening Skill ... 11
b.Learning Media ... 14
D. Instrument and Data Gathering Technique ... 24
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 27
xi
CHAPTER IV. DATA ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
A. Data Analysis ... 31
1. Students’ Steps in Language Teaching Media Class to Develop Listening Media ... 31
2. Students’ Perceptions on the Use of Computer Software to Develop Listening Media in Language Teaching Media Class ... 38
B. Discussion ... 50
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS A. Conclusions ... 57
B. Recommendations ... 58
REFERENCES ... 60
xii
LIST OF FIGURE
xiii
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1: Typical Stimulus Choices for Instructional Events ... 15
Table 2.2: Candidate Media for the Types of Stimuli ... 16
Table 3.1: Sample of the Questionnaire Form ... 25
Table 3.2: Participants’ Rating Scales Responses... 28
Table 4.1: Steps in Designing Listening Material ... 32
Table 4.2: The Factors that Influence Listening Skill ... 35
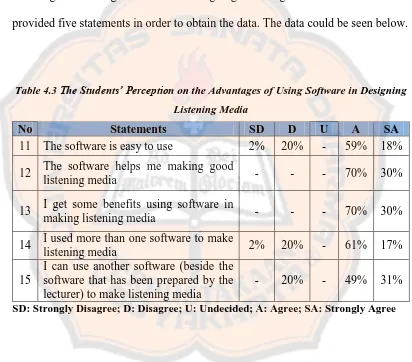
Table 4.3: The Students’ Perception on the Advantages of Using Software in Designing Listening Media ... 39
xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix A
Questionnaire ... 64
Appendix B
Blueprint of the Questionnaire ... 68
Appendix C
Raw Data of Open-Ended Questions ... 73
Appendix D
The Transcript of the Interview... 82
Appendix E
1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This study discusses the students’ use of computer software to develop
listening media in the Language Teaching Media class. This chapter consists of
six parts, namely, the research background, the research question, the problem
limitation, the research objectives, the research benefits, and the definition of
terms.
A. Research Background
Listening is one of language skills needed to be learned. Brownell (1996)
states, good communication starts with good listening skill, not speaking (p. 6).
Nunan (2003) also states that listening is a receptive skill that expects someone to
receive and understand incoming information or input. It is important for students
to be skilled listening skill. That is why listening is taught in school.
The one who is responsible in creating or preparing listening media is the
teacher. Good listening media can motivate students in learning English. In order
to create good listening media, a teacher must be skilled in English and in the
process of making learning media. To make the listening media, a teacher must
2
It is important that preservice teachers in the English Language Education
Study Program know how to develop good listening media by using appropriate
software. Supporting that argument, Gagne and Briggs (1979) state that a stimulus
is the main factor in selecting a learning medium. Types of stimulus need to be
considered in terms of the specific instructional events being planned. Choice of
stimulus may vary considerably even within a single lesson for a group of
learners.
It is also important to have information about the preservice teachers’
perceptions, especially in English Language Education Study Program, on the
computer software they are using in Language Teaching Media class which might
be helpful for the lecturers in improving the quality of the learning process. The
researcher identifies the students’ perception on the use of computer software to
develop listening media in Language Teaching Media class because the lecturer
keeps using the same software in the class. This research can also be the
evaluation for the software used in Language Teaching Media class.
In order to explain the definition and the factors influence perception, the
researcher uses a theory proposed by Altman. Altman (1985) states that there are
four factors that influence perception. Those four factors are the selection of
3
B. Research Questions
This study is expected to answer research questions of this study. There
are two research questions addressed in this study. The researcher formulates the
research questions as follows.
1. How do students in Language Teaching Media class develop listening media?
2. What are the students’ perceptions on the use of software to develop listening
media in Language Teaching Media class?
C. Problem Limitation
In conducting this study, the researcher intends to limit the discussion on
the process of developing listening media. The researcher focuses on the students’
perceptions on the use of computer software to develop listening media in
Language Teaching Media class. The researcher focuses on answering questions
as stated in the research questions. In more specific, the researcher chooses class
B and class E in Language Teaching Media course of English Language
Education Study Program as the research participants.
D. Research Objectives
There are two objectives in this research. The first objective is to examine
4
second is to investigate students’ perception on the use of software to develop
listening media in Language Teaching Media class.
E. Research Benefits
This research is under educational scope. The researcher expects that the
findings of the research can give contributions for the education development.
There are some benefits for students of the English Language Education Study
Program, the lecturers of Language Teaching Media class, and the future
researchers.
1. Students of English Language Education Study Program
The lecturer’s intention in using specific software to develop listening
media is expected to be understood by the students. Moreover, it can be used to
raise students’ awareness of the importance of being independent learners. This
research investigates how listening media are developed; whether students have
the awareness of making good listening media by considering some factors which
influence their listening skills and also steps they take. Hence, through this study,
the students of English Language Education Study Program are supposed to raise
their awareness of the importance of developing good listening media that affect
the listening skill of the listeners.
2. Language Teaching Media Lecturers
This research provides information about students’ perception on the use
5
feedback for the lecturers in developing other software in teaching. If the results
show that the available software is still relevant with the students’ needs, the
lecturers can keep the software and try to improve on other aspects. If the software
is not relevant with the students’ needs, the lecturers must provide other software
that is accessible for the students. This research is also good as the reference to
evaluate the learning process and to improve lecturer’s teaching performance in
the class.
3. Future Researchers
This research provides the data that might be beneficial for future
researchers which is related to the use of computer software to develop listening
media in Language Teaching Media class. The researcher expects that this study
can inspire others. They might discuss any information dealing with the topic that
the researcher discusses. Moreover, other researchers can finish this study if there
are any deficiencies that can be filled.
F. Definition of Terms
There are some terms used in this study. The researcher will give a clear
explanation of the terms to avoid misunderstanding in discussing the research
topic. The terms are the perception, the language teaching media, the computer
6
1. Perception
The definition of perception is derived from some experts. George and
Jones (2008) state that perception is the process when people select, organize, and
interpret the input from their senses. Altman, Valenzi, and Hodgetts (1985) define
that perception is how stimuli are selected and classified by a person so that it can
be interpreted clearly (p. 85). Perception is a process that makes human
understand the environment around them. The perception in this study is a view
from someone in facing reality.
2. Language Teaching Media
Language teaching media or also known as Language Teaching Media is
one of the compulsory courses in English Language Education Study Program,
Sanata Dharma University. Based on the academic guideline, this course aims to
develop students’ abilities to be creatively and innovatively develop and utilize
varieties of media to facilitate language teaching. In the initial process of learning,
students are expected to explore knowledge of the concepts, nature or
characteristics, and purposes of media in general and media for language teaching.
Having sufficient theoretical foundation, students are expected to be creatively
and innovatively develop media for language teaching in the following categories:
conventional media, word processor, digital audio production, digital video
7
3. Computer Software
Computer refers to a machine that is able to process information according
to a set of instructions. The computer capabilities are defined, enabled, and
constrained by the hardware (physical components) and software (programs) that
comprised a particular computer system (Newby, 2000).
Computer software in this research refers to the computer software used
by students in Language Teaching Media class. The available software that is
used in the class was Audacity and Photostory.
4. Listening Media
A medium refers to anything that carries information between a source and
receiver (Smaldino, Lowther, & Russell, 2012). In addition, Smaldino, et al.
(2012) state, if those messages contain information with an instructional purpose,
they are considered as educational media. Media that are used in the instructional
design are elected by the condition of objectives, content, and instructional
methods. Kemp (1980: 7) says that the media are not only used as supplementary
to, or in support of, instruction, but are the instructional input itself. It will give
the most effective and efficient learning.
Listening media in this research are made by the students in Language
Teaching Media class batch 2012. The listening media are made by using specific
8
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter, the researcher presents some theories that are used in
conducting this research. This chapter is divided into two sections. The first
section is the theoretical description and the second one is the theoretical
framework.
A. Theoretical Description
In this section, the researcher uses theories that directly relevant to the
research are presented. There are five basic theories that are going to discuss.
Those theories are perception, listening media, instructional design, and electronic
learning.
1. Perception
This section is divided into two parts. The first one is definition of
perception. The second is the factors that influencing perception.
a. Definition of Perception
Based on Huffman (2000), perception is a process of selecting, organizing,
and interpreting sensory data into useful mental representations of the world.
George and Jones (2008) also have the same meaning with Huffman but in the
9
and interpret the input from their senses. It means that through perception, people
try to choose an object then set it up into their mind and interpret it. Robbins
(2001) states that perception is a process by which people organize and interpret
their sensory opinions in order to give interpretation to the environment around
them. It also means that by giving perceptions is giving opinions also. Perception
is also the process whereby an individual becomes aware of the world around
oneself (Kemp, 1980).
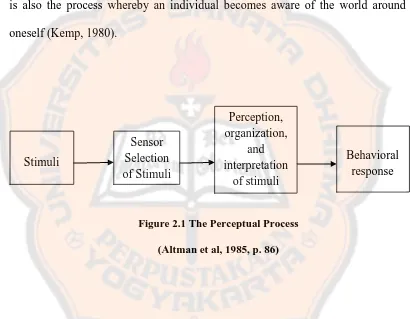
Figure 2.1 The Perceptual Process
(Altman et al, 1985, p. 86)
Based on the Figure 2.1, perceptions appear because there are stimuli at
the beginning of the process. Just like Altman, Valenzi, and Hodgetts (1985)
define that perception is the way a stimulus is selected and classified by a person
so that it can be interpreted clearly. In other words, perception is a someone’s
view in facing the reality. Perception is a process that makes people understand
the environment around them. Sensor Selection of Stimuli
Perception, organization,
and interpretation
of stimuli
Stimuli Behavioral
10 b. Factors Influencing Perception
Altman et al. (1985) state that there are four factors that influence
perception. Those are the selection of stimuli, the organization of stimuli, the
situation, and the self-concept. The explanations are as follows.
1) Selection of Stimuli
Generally, every person will only focus on a small number of stimuli. This
is known as a selection. It is one of the reasons people perceive things in different
ways. People select the certain or the specific stimuli.
2) Organization of Stimuli
Altman (1985) states that organization of stimuli is the second factor that
influence perception. The brain makes effort to select certain items of information
and then put them together in a meaningful way (p. 87). After the information is
gathered, it has to be organized to be meaningful.
3) Situation
Altman (1985) says that the situation which influences someone to
perceive can be in a form of someone’s familiarity with, expectations about, a
situation, as well as his or her past experiences (p. 89). It is related with the
situation which is the combination of past experience with the expectation
happened. So perception is also affected by the experience.
4) Self-concept
Altman (1985) states that the self-concept is the way an individual feels
11
as a self-describing expression or an internal view of oneself see himself, not as
what he says about himself or what other people see him (p. 81). It means that
self-concept is the way we look inside ourselves. It is the image of ourselves and
it is essential to determine what we perceive and do.
2. Listening Media
Communication can be effective if there are good listeners. When at least
two people listen to each other and understand each perspective then information
is created. Brownell (1996) states that an effective communication begins with
listening, not speaking. It is also stated by Nunan (2003), listening is a receptive
skill that expected someone to receive and understand incoming information or
input (p. 23).
For most students, listening is seen as the most difficult skill (Riddell,
2001). However, this becomes a duty for teachers to help the students to improve
their listening skill. In order to help students, a teacher must be proficient in
developing listening media.
a. Factors that Influence Listening Skill:
Brownell (1996) says that there are some factors influencing listening
skills (p. 48). Those factors are:
1) Personal Style of the Listeners
A personal style does affect listening ability. Impatient, high-energy, and
anxious person will seek information that comes in neat packages. A more patient,
12
as listening more effectively. Effective listeners are open-minded and interested in
a wide variety of subjects. They tend to like people and had a generally positive
attitude.
2) Intelligence
Nichols (1948) realizes that the best predictor of effective listening is
cognitive ability. Intelligence as a listening variable interacted with a number of
other factors such as personality, motivation, attitude, and interest in the subject
(Kelly, 1963). People had different listening strengths and weaknesses. While
intelligence might be a significant factor in listening to difficult lecture material,
listening and participating effectively in conversations took a different set of
abilities (Bostrom, 1990).
3) Willingness from the Listeners
“Willingness” to listen is a key to concentration and accurate interpretation
(Cegala, 1981; Daley & McCroskey, 1984). Most people could improve their
listening effectiveness simply by devoting more efforts and energy to the activity.
Kelly (1970) also states that unless you are open-minded and sincerely interested
in your partner, you are likely to block and distort information.
4) Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and stress have a profound effect on the ability to listen well.
Phillips (1977), for instance, defines communication reticence as it is related to
listening as the inability to follow a discussion or to participate in a relevant
13
questions that have already been answered or making statements unrelated to the
current topic of discussion. The anxiety of the listeners is more likely a
consequence of the fear of misunderstanding or misinterpreting the speaker.
5) Gender
Goleman (1978) is among the first to suggest that females perform better
on tasks that involved verbal ability, while men perform best when visual skills
are involved. Women are also thought to be more sensitive to nonverbal cues,
suggesting that they are more likely to take these variables into account in
listening situations (Tannen, 1990; Borisoff & Merrill, 1991). This shows that
gender affects someone’s skill.
6) Culture
An individual’s culture, background, role, and other variables determine
his unique perspective. As a teacher in school who deals with diversity, it
becomes essential to recognize and value individual differences in perception and
view-point. Different cultures bring different perspective.
7) The Clarity of the Speakers
Message and speaker variables both affect listening. The clarity of the
organization have a significant impact on the ability to comprehend and recall the
information that heard. A speaker’s mannerisms and delivery have an impact on
her credibility and affect the attention, comprehension, and retention (Beatty &
14
8) The Stimuli
Short, William, and Christie describe listening to a person speaking will
improve the listening retention and concentration rather than a videotape. This is
due to an interesting concept called “social presence,” which is the physical
presence of another human being is in itself stimulating (as cited in Brownell,
1996, p. 23). Although we know that the addition of visual stimuli improve some
listening behaviors, the accuracy of comprehension might decrease with added
stimuli. In addition, when verbal and visual messages conflicted, most people will
choose the visual channel (Leathers, 1979).
b. Learning Media
Educational media and instructional design develop along separate but
converging pathways. Choosing a medium must be adjusted to the instructional
design. These are the theories of learning media.
1) Definition of Learning Media
Smaldino, Lowther, and Russell (2012) state that medium refer to anything
that carries information between a source and receiver. In addition, they state if
those messages contained information with an instructional purpose, they are
considered as educational media. Media that are used in the instructional design
are selected by the condition of objectives, content, and instructional methods.
Kemp (1980: 7) states that media are not only used as supplementary to, or in
support of, instruction, but are the instructional input itself. It will give the most
15
As stated by Roblyer and Edward (2000), there are various forms of
media. Media can be in a form of pictures, sound, motion video, animation, or text
items combine in a product whose purpose is to communicate information. The
impact of using media in education also varies (Roblyer & Edward, 2000:166). By
using media, students can have motivation to learn, since most people enjoy using
them. Media are also flexible , people can draw on such diverse tools that they
truly offer something to students who excell in intelligence. Because of that
flexibility, the media can also develop and improve students’ creativity and
critical thinking skills. The research also shows that various form of media and
their respective selection and utilization processes directly have impact to what
learners perceive and how they retain and recall information (Kozma, 1991).
2) Factors in Media Selection
As stated by Gagne and Briggs (1979), a stimulus is the main factor in
selecting learning media. Types of stimulus is needed to be considered in terms of
the specific instructional events being planned. Choice of stimuli might vary
considerably even within a single lesson for a group of learners. Some typical
stimulus choices for various instructional events as follows:
Table 2.1 Typical Stimulus Choices for Instructional Events (Gagne and Briggs, 1979)
Instructional Event Type of Stimulus
a. Gaining attention Unusual sounds; startling visual b. Information about
16
Instructional Event Type of Stimulus
c. Guiding learning
Spoken or written words; demonstration; sample products or
performance d. Providing feedback Spoken or written words e. Enhancing retention and
transfer Variety of media and examples
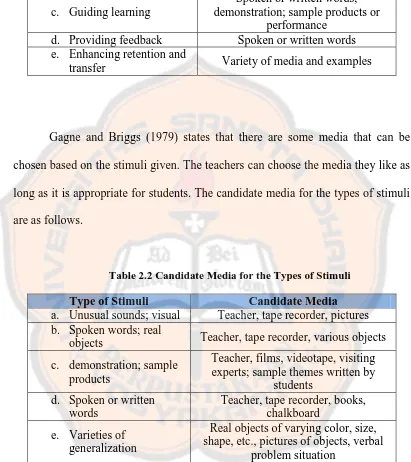
Gagne and Briggs (1979) states that there are some media that can be
chosen based on the stimuli given. The teachers can choose the media they like as
long as it is appropriate for students. The candidate media for the types of stimuli
are as follows.
Table 2.2 Candidate Media for the Types of Stimuli
Type of Stimuli Candidate Media
a. Unusual sounds; visual Teacher, tape recorder, pictures b. Spoken words; real
objects Teacher, tape recorder, various objects
c. demonstration; sample
Real objects of varying color, size, shape, etc., pictures of objects, verbal
problem situation
3. Instructional Design
Instructional design is “the systematic and reflective process of translating
17
activities, information, resources, and evaluation” (Smith & Ragan, 2005).
Instructional design can not be separated from learning. As stated by Newby
(2000), learning is a process of acquiring new knowledge and skills through the
interdependent sub-processes of planning, implementation, and evaluation. While
instruction is the process of helping students learn through the deliberate
arrangement of information, activities, methods, and media. Gagne and Briggs
(1979) also state that instruction is a human undertaking whose purpose is to help
people learn. Instruction is a set of events which affects learners in such a way
that learning is facilitated. So it can be concluded that the instructional design is a
process of developing plans for instruction through practical application of
theoretical principles.
In order to create instructional design, instructional technology is needed.
Instructional technology for teaching and learning has an important role to
increase learning by designing lessons that use instructional technology, including
computers and other media (Newby, 2000). Instructional technology also has been
defined as “applying scientific knowledge about human learning to the practical
tasks of teaching and learning” (Heinich, Molenda, & Russel, 1993, p. 16). Thus,
instructional technology interpreted and implemented basic research of human’s
learning to generate instructional design principles and processes that teachers and
students cannot apply to increase learning effectiveness.
To design an instruction, there are three basic elements that teacher must
18
objective contains the goal that has to be reached by the students, what students
must learn from a study. The second is the teaching and learning strategies in
which teachers must set a plan to conduct the learning process. The procedures
and the resources are required to accomplish the learning. The last one is the
evaluation. The evaluation has an important role in seeing the first step of this
element, which is objective, whether it has been reached or not.
4. Electronic Learning
Today, we are living in the era of technology. A technology has an
important role in many aspects of living. Technology, especially computer and
other electronic tools, has tremendous impact in society. Evenmore nowadays,
education is using technology in supporting learning process. E-learning is one of
the keys to solve our global challenges, transforming our expectations, our
employees, and the way we do business (Ubell, 2010).
Newby (2000: 45) states that software consists of computer programs, sets
of instructions to the computer’s processor that tell it how to perform a particular
task, such as editing text or presenting a computer-based lesson. There are two
basic categories of software: systems software and applications software. Systems
software is the basic operating software that tells the computer how to perform its
fundamental functions. While applications software included programs are
designed to perform specific functions for the user, from the processing text, to do
19
Authoring software is the term for the programs that are used to develop
multimedia and web applications. We live in a complex environment of sights and
sounds. Increasingly computer applications can reflect the complexity and
richness of the real world by incorporating multimedia. Multimedia involves the
use of a variety of media formats (text, visual, audio, video) in a single
presentation or product. Authoring software allows teachers or students to develop
multimedia applications.
B. Theoretical Framework
This research focused on students’ perception on the use of computer
software to develop listening media in Language Teaching Media class. There
were some objectives that were going to be reached through this research. The
first one was how the listening media was produced by the students and the
second one was to investigate students’ perception on the use of computer
software to develop listening media in Language Teaching Media class. In order
to gain the answer of research questions, this research employed four major
theories. Those theories are the perception, the listening media, the instructional
design, and the electronic learning.
First, the researcher elaborated the theories of listening and instructional
design in order to explain how the real practice of developing listening media and
it would be compared to the theory of listening itself. The researcher wanted to
20
factors that influenced listening skill. It was important because listening was the
way of effective communication, just like Brownell (1996) states that effective
communication begins with listening, not speaking. So that later, the target
listeners could gather much information clearly and precisely based on the
listening media that had been made by their teachers.
The researcher also wanted to investigate whether or not the students set a
plan in making their listening media. For teachers, there were three basic elements
that they must pay attention to (Kemp, 1980: 6). The first one was the objectives.
The objectives contained the goals that had to be reached by the students, what
students must learn from a study. If the teacher did not set a goal for the students,
the teacher could not know the direction of where they were going to. They could
not know what the purpose of learning was. The goal of learning was important to
gain students’ motivation in learning English.
The second element of instructional design was the teaching and learning
strategies in which teachers must set a plan to conduct a process of learning. The
procedures and the resources were required to accomplish the learning. After
teachers set their goals of learning, the second thing the teachers must do was
drawing the way how they went to reach the aims. The way the teachers were
going to make included the tools that helped them to reach the aim of learning.
Here the theory of learning media was also needed. By using the theory of
learning media, the researcher could see whether students in Language Teaching
21
supplementary to, or in support of, instruction, but are the instructional input itself
as stated by Kemp (1980: 7).
The last element of instructional design was the evaluation. Evaluation had
an important role in seeing the first step of this element, which was objectives,
whether it had been reached or not. For teachers, evaluation was important
because they could reflect on the process that had happened in their class. The
teachers could decide whether their students got new knowledge and understood
the media or they got nothing from the learning process, especially in listening
class.
To answer the second research question, the researcher elaborated three
theories. Those theories were the perception, the learning media and the electronic
learning (E-learning). In order to explain the definition and the factors influencing
perception, the researcher used theory proposed by Altman et al. (1985). There
were four factors influencing perception and those were the selection of stimuli,
the organization of stimuli, the situation, and the self-concept. Theory of learning
media combined along with the theory of perception was aimed to gain the data
whether it was suitable in developing listening media. The researcher combined
the perception theory with the electronic learning (E-learning) theory in order to
gain deeper information on the use of software in Language Teaching Media
22
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents a rationale for the research method and analysis. The
researcher describes the methods of the research analysis, outlines the procedure
in gathering and analyzing the data, and reveals the boundaries of the research.
This part is divided into six parts, namely, the research method, the research
setting, the research participants, the instrument and data gathering technique,
data analysis technique, and research procedure
A. Research Method
The researcher used mixed method in this study. Mixed method was the
combination between a quantitative and a qualitative method. As stated by Gall,
Gall and Borg (2006), mixed method is a technique that combines both qualitative
and quantitative methods in the design of a single study (p. 32). In 2006, Lodico,
Spaulding, and Voegtle conclude that a mixed method combines the strength of
both qualitative and quantitative research. It provides both an in-depth look at
context, processes, and interactions and a precise measurement of attitudes and
outcomes (p. 282). It was also supported by Creswell (2009) when the quantitative
and qualitative data are used together in the research; a mixed method approach
23
In this study, the mixing process occurred in the data collections were in the form
of the questionnaire and interview.
B. Research Setting
The study took a place at Sanata Dharma University. To be exact it was at
the English Language Education Study Program. The settings of this research are
in the Language Teaching Media classes. There are two classes, class B and class
E. Every class had different schedule. Both of the classes are held on Friday, class
B started the class at 07.00 AM and class E at 10.00 AM. These classes were held
on the fifth semester. The researcher distributed the questionnaires on 28
November 2014. Meanwhile, the interview was conducted on 4-5 June 2015.
C. Research Participants
The participants of this research were the students of the English
Language Education Study Program. The Language Teaching Media students of
the academic year 2012 were chosen as the primary research participants. The
researcher took 49 students from the Language Teaching Media subject classes,
those were class B and class E.
In this case, the researcher employed the purposive sampling. As stated by
Singleton and Straits (1999), the purposive sampling belongs to the
24
representative or the typical of the population based on their judgments. The
researcher selected the participants as the sample because they had experiences in
making listening media using appropriate software in Language Teaching Media
class. Moreover, those two classes are taught by the same lecturer. That were the
reasons the researcher only took those two classes out of five Language Teaching
Media classes.
D. Instrument and Data Gathering Technique
In order to obtain the data for this research, the researcher used
questionnaire. The questionnaire is used to answers the research questions. The
following part describes the instruments used in this research.
1. Questionnaire
In this research, a questionnaire was distributed to investigate the answer
to the first and the second research question. The first question was the steps
students took to make the listening media. Then the second question was about the
students’ perceptions on the use of software in making listening media.
The researcher chose a questionnaire to obtain the explanation about the
students’ perceptions on the use of software in making listening media and the
process. Gall, Gall, and Borg (2006) define questionnaires as the printed forms
that ask the same questions of all individuals in the sample and for which
25
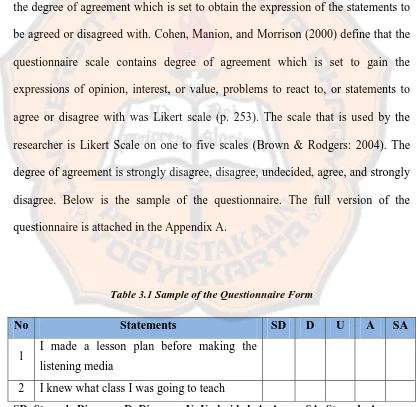
In order to obtain the detailed information, this questionnaire was divided
into two parts, the close-ended and the open-ended questions. Van Dalen (1979)
states a close-ended question consists of concrete questions and a choice of
possible answer (p. 126). The close-ended question is also called as fixed-choice
question and this requires the respondents to choose on response from the
provided options, as state by Singleton and Straits (1999). The researcher provides
the degree of agreement which is set to obtain the expression of the statements to
be agreed or disagreed with. Cohen, Manion, and Morrison (2000) define that the
questionnaire scale contains degree of agreement which is set to gain the
expressions of opinion, interest, or value, problems to react to, or statements to
agree or disagree with was Likert scale (p. 253). The scale that is used by the
researcher is Likert Scale on one to five scales (Brown & Rodgers: 2004). The
degree of agreement is strongly disagree, disagree, undecided, agree, and strongly
disagree. Below is the sample of the questionnaire. The full version of the
questionnaire is attached in the Appendix A.
Table 3.1 Sample of the Questionnaire Form
SD: Strongly Disagree; D: Disagree; U: Undecided; A: Agree; SA: Strongly Agree
No Statements SD D U A SA
1 I made a lesson plan before making the listening media
26
The second part of the questionnaire was an open-ended question. As
stated by Singleton and Straits (1999), an open-ended question requires
respondents to answer the questions in their own words in a written form.
Students were given a chance to answer the questions freely. It was supported by
Van Dalen (1979), “the open-form questionnaire permits the participants to
answer freely and fully in their own words and their own frame of reference” (p.
126).
2. Interview
In this research, an interview was conducted for a specific purpose which
was to strengthen the written observation (questionnaire) or as confirmation. This
purpose was also supported by Patton (2002) who mentions that the main purpose
of an interview is to obtain a specific kind of information. DeMarrais (2004)
defines an interview as a process of conversation engagement between a
researcher and a participant. Zimmerman and Rodrigues (1992) state that
interviewing is a structured process of questioning others (p. 106). They also say
that the interview can help the researcher to obtain the data that cannot be gained
by the observation and questionnaire.
Therefore, the interview in this research was conducted after processing
the questionnaire. The researcher only interviewed some participants who needed
to have more explanation since only some students who made unclear statements
in the questionnaire. By analyzing the results of the questionnaire, there were only
27
was conducted in approximately 5-10 minutes for each participant. Gall, Gall, and
Borg in 2006 concluded, “a sample in which all members of the accessible
population had an equal chance of being selected” (p. 168). In addition, the
researcher conducted interview on 4-5 June 2015.
E. Data Analysis Technique
The data analysis dealt with the questionnaire’s results. The researcher
examined the results of the questionnaire by counting the number of ticks from
every degree of agreement. Then, the researcher grouped the data and presented in
percentage mode. Moreover, the results of the data were interpreted descriptively.
Wiersma (1995) states that the low value represents negative responses and the
high value represents positive responses (p. 183). Next, the researcher made a
classification for the results of the percentage. The students had negative
perceptions if the result of percentage was less than the results of positive
percentage. Then the students had positive perceptions if the results of positive
percentage were higher than the results of the negative percentage. The data were
presented in form of table (see Table 3.2, p. 28).
In order to count the percentage from every degree of agreement, the
following formula is used:
∑
Note:
28
Table 3.2 Participants’ Rating Scales Responses
No Statements Degree of Agreement
SD (%) D (%) U (%) A (%) SA (%)
1. Statement 1 2. Statement 2
Etc.
SD: Strongly Disagree; D: Disagree; U: Undecided; A: Agree; SA: Strongly Agree
For the open-ended questions, the researcher grouped, clustered, and
classified the same answers and then interpreted then, whereas the data from the
interview were transcribed in the written form. Then, the researcher categorized
the results based on some related theories. From the existing theories, the
researcher gathered the final results which answer the research questions. Next,
the interview data were integrated and displayed in descriptive form.
F. Research Procedure
In conducting the research, the researcher took some steps which were
necessary to the research procedures. Below are the eight steps that must be
followed by the researcher.
1. The researcher selected the topic and formulated the research problems. In
this step, the researcher brainstormed many topics and discussed them with
the lecturer. Then the researcher decided the topic that was interesting to be
conducted. Next, the researcher formulated research questions that were
29
2. The researcher found and wrote the review of related literature. In this step,
the researcher read many theories related to the topic of research and tried to
understand what those theories were about. After that, the researcher wrote
the review of the theories.
3. The researcher selected the appropriate methods that could be applied in this
research. In this step, the participants were also selected by purposive
sampling. The researcher also made the instrument to be applied in gathering
the data. Those were the questionnaire and the interview.
4. The researcher asked the permission to the lecturer to conduct the research in
the Language Teaching Media class. In this step, the researcher met the
lecturer and asked the permission. The researcher also asked the time to start
the research.
5. The researcher distributed the questionnaire to all students. The questionnaire
was given to 49 students and it consisted of open-ended and close-ended
questions.
6. The researcher started to process the results of the questionnaire. In this step,
the researcher interpreted the data and made the detail information
descriptively. The researcher also selected some interesting points that needed
more information through interview.
7. The researcher did interview. In this step, the researcher did the interview
30
8. The researcher reported the results and draw conclusions of the research. In
this step, the researcher reported the results in written form and wrote the
conclusions of the research. The researcher also gave suggestions to the
students in English Language Education Study Program, the Language
31
CHAPTER IV
DATA ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter consists of two sections. Those are the data analysis and the
discussion. The first section analyses and discusses the raw data of the
questionnaire and interview. The discussion explains the relation between the raw
data and the supported theories in order to answer the research questions.
A. Data Analysis
The data analysis is meant to answer both research questions. Therefore,
there are two discussions in this section. The first one is how students in
Language Teaching class develop listening media. Then the second section
discusses the students’ perceptions on the use of computer software to develop
listening media in Language Teaching Media class.
1. Students’ Steps in Language Teaching Media Class to Develop Listening Media
The researcher employed both questionnaire and interview to gather the
data about students’ steps in Language Teaching Media class to develop listening
media. Close-ended questionnaire was meant to measure student’s state of
agreement or disagreement, while open-ended questionnaire was to obtain the
32
a. The Steps and Considerations in Developing Listening Media based on the Questionnaire
In this part, the researcher identified the students’ steps and the factors
they considered before developing listening media. Making listening material
could not be separated from the instructional design. The instructional design was
important in order to make teaching material more settled and well-prepared.
Preservice teachers were expected to be able to make learning media without
forgetting the essence of teaching. The statements were below.
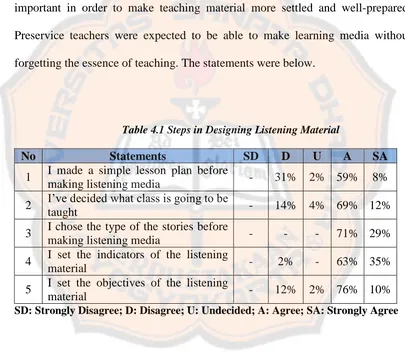
Table 4.1 Steps in Designing Listening Material
No Statements SD D U A SA
1 I made a simple lesson plan before
making listening media - 31% 2% 59% 8%
2 I’ve decided what class is going to be
taught - 14% 4% 69% 12%
3 I chose the type of the stories before
making listening media - - - 71% 29%
4 I set the indicators of the listening
material - 2% - 63% 35%
5 I set the objectives of the listening
material - 12% 2% 76% 10%
SD: Strongly Disagree; D: Disagree; U: Undecided; A: Agree; SA: Strongly Agree
Table 4.1 presented the steps that the students took in designing listening
material. The statement number one investigated whether students made lesson
plan. From the data above, we knew that there were four students (8%) strongly
33
student (2%) stated that he was undecided. However, there were 15 students
(31%) disagreed that they made a simple lesson plans before making the listening
media. Yet, none of the students (0%) strongly disagreed. It showed that most of
the students (more than 60%) agreed that they made lesson plans before making
the listening media.
The research statement number two was about student’s decision in what
class or grade they were going to teach. There were six students (12%) strongly
agreed and 34 students (69%) agreed with the statement. There were two students
(4%) stated that they were undecided and seven students (14%) disagreed with the
research statement. Similar to the previous statement, none of the students (0%)
strongly disagreed with the statement. From the students’ choices, the researcher
concluded that most of the students (more than 80%) decided the class first before
making the listening media.
The third research statement was about the type of the stories the
respondent chose before making listening media. There were 14 students (29%)
strongly agreed, and 35 students (71%) agreed to the research statement. Yet,
there were no disagreed, strongly disagreed, and undecided. The researcher could
conclude that all students (100%) agreed that they chose the type of the stories
before making the listening media.
The fourth research statement was about the indicators that students made
before making listening media. There were 17 students (35%) strongly agreed,
34
disagreed. None of them (0%) strongly disagreed with the research statement. The
data also showed 0% on the undecided column. From the students’ choices, the
researcher concluded that 98% of the total students made indicators before
making the listening media.
For the last research statement on this topic discussed the objectives that
the students made before making the listening media. There were five students
(10%) strongly agreed and 37 students (76%) agreed with the research statement.
Meanwhile only one student (2%) stated that he was undecided, and six students
(12%) disagreed with the research statement. Yet, none of them strongly
disagreed with the research statement. Since the data showed that 86% of the
students agreed to the research statement, hence the researcher concluded that
they set the objectives before developing the listening media.
The factors that influenced the listening skill also should be considered
before developing listening media. This was important since the listening media
was going to affect students’ understanding towards the listening material. In the
factors that influence listening skill discussed the students’ ability to comprehend
their understanding about listening itself. If the students comprehended the
factors, it meant that they were able to design listening media. If the students
knew what the factors were, they could make some considerations in making their
listening media and the results would be good. The statements which contained
this topic discussion were the statements number 6 until 10. The following table
35
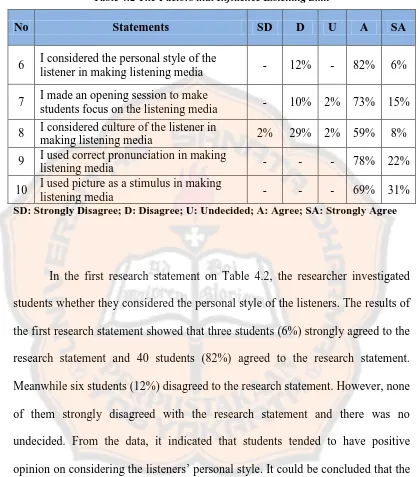
Table 4.2 The Factors that Influence Listening Skill
No Statements SD D U A SA
6 I considered the personal style of the
listener in making listening media - 12% - 82% 6%
7 I made an opening session to make
students focus on the listening media - 10% 2% 73% 15%
8 I considered culture of the listener in
making listening media 2% 29% 2% 59% 8%
9 I used correct pronunciation in making
listening media - - - 78% 22%
10 I used picture as a stimulus in making
listening media - - - 69% 31%
SD: Strongly Disagree; D: Disagree; U: Undecided; A: Agree; SA: Strongly Agree
In the first research statement on Table 4.2, the researcher investigated
students whether they considered the personal style of the listeners. The results of
the first research statement showed that three students (6%) strongly agreed to the
research statement and 40 students (82%) agreed to the research statement.
Meanwhile six students (12%) disagreed to the research statement. However, none
of them strongly disagreed with the research statement and there was no
undecided. From the data, it indicated that students tended to have positive
opinion on considering the listeners’ personal style. It could be concluded that the
students considered the personal style of the listener in designing the listening
media.
Then, for the second research statement was used to investigate students