ON MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES THEORY FOR THE FOURTH
GRADE STUDENTS IN SD KRISTEN 2 SUMBEREJO KLATEN
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Agung Tri Nugroho
Student number: 071214089
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
DESIGNING IN
ON MULTIPLE I
GRADE STUDEN
Prese
ENGLISH DEPARTM FACULTY
i
G INTEGRATED ENGLISH MATERI
LE INTELLIGENCES THEORY FOR
DENTS IN SD KRISTEN 2 SUMBEREJ
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
esented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Agung Tri Nugroho
Student number: 071214089
H LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PRO TMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUC TY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUC
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
2012
TERIALS BASED
OR THE FOURTH
MBEREJO KLATEN
ents
DESIGNING I
ON MULTIPLE
GRADE STUDEN
Prese
ENGLISH DEPARTM FACULTY
i
G INTEGRATED ENGLISH MATERI
LE INTELLIGENCES THEORY FOR
DENTS IN SD KRISTEN 2 SUMBEREJ
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
resented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requireme to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Agung Tri Nugroho
Student number: 071214089
ISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PRO TMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDU TY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUC
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
2012
TERIALS BASED
OR THE FOURTH
MBEREJO KLATEN
ments
iv
“Take therefore no thought for the morrow: for the
morrow shall take thought for the things of itself.
Sufficient unto the day is the evil thereof.”
Matthew 6:34
This thesis is dedicated to:
My Lord Jesus Christ
My late father, Kuwatno
My mother, Endang Palupi
vii
ABSTRACT
Nugroho, Agung Tri. 2012. Designing Integrated English Materials Based on
Multiple Intelligences Theory for the Fourth Grade Students in SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program,
Sanata Dharma University.
The purpose of this study was to design integrated English materials based on the multiple intelligences theory for the fourth grade students of SD Kristen 2
Sumberejo Klaten. There were problems that occurred in the school. The amount of
English books in the school was limited. Another problem was the fourth grade students had difficulties in learning English especially in vocabulary memorization. There was alsoa benefit of students’ non academic abilities. The English teacher of
the school applied learning activities that could involve students’ multiple
intelligences.
This study was aimed at answering two problem formulations. The first
problem was “How are integrated English materials based on multiple intelligence
theory for the fourth grade students in SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten designed?” The second problem was “What do integrated English materials based on multiple
intelligence theory for the fourth grade students in SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten
look like?”
The research method applied in this study was Research and Development (R&D). There were five major steps in the R&D method. The steps were research and information collecting, planning, developing preliminary form of product, preliminary field testing, and main product revision. In order to answer first problem, the writer adapted Kemp’s and Dick’s instructional design model. The
model was conducting needs analysis; listing topics, stating goals, and stating learning objectives; listing subject content; selecting teaching-learning activity and learning sources; developing syllabus; evaluating materials; and revising materials. The writer also applied Indonesia’s Ministry of Education regulations on Panduan Penyusunan Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Jenjang Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah.
In order to answer second problem, the writer applied theories such as
characteristics of young learners, principles of young learners’ learning, multiple
intelligences, and developing syllabus.
The materials consisted of four units. The design is for grade four of elementary school in semester one. The writer distributed questionnaire to respondents in order to check the feasibility of the materials. The result showed that the ranges of the mean were in 3.3 – 4.3 points which mean the materials were acceptable. The writer expected this study can be a reference for teaching English in elementary school and a reference for conducting similar study.
viii
ABSTRAK
Nugroho, Agung Tri. 2012. Designing Integrated English Materials Based on
Multiple Intelligences Theory for the Fourth Grade Students in SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris,
Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Tujuan penelitian ini untuk menyusun materi Bahasa Inggris terintegrasi berdasarkan teori kecerdasan multiple untuk siswa kelas empat SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten. Ada permasalahan yang terjadi di sekolah. Jumlah buku Bahasa Inggris di sekolah terbatas. Masalah yang lain adalah siswa kelas empat sulit belajar Bahasa Inggris khususnya dalam mengingat-ingat kosakata. Ada juga keuntungan dari kemampuan non-akademik siswa. Guru Bahasa Inggris sekolah tersebut menerapkan aktivitas belajar yang melibatkan kecerdasan multiple siswa.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menjawab dua rumusan masalah. Masalah
yang pertama adalah “Bagaimana materi Bahasa Inggris terintegrasi berdasarkan
teori kecerdasan multiple untuk siswa kelas empat SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten disusun?” Masalah yang kedua adalah “Seperti apa materi Bahasa Inggris
terintegrasi berdasarkan teori kecerdasan multiple untuk siswa kelas empat SD
Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten?”
Penelitian ini menerapkan metode Research and Development (R&D). Terdapat lima langkah utama dalam R&D. Langkah tersebut antara lain penelitian dan pengumpulan informasi, perencanaan, pengembangan produk awal, pengujian awal dan evaluasi produk. Untuk menjawab masalah pertama penulis mengadopsi model disain pembelajaran dari Kemp dan Dick yaitu melaksanakan analisa kebutuhan; merumuskan topik, tujuan umum, dan tujuan khusus pembelajaran; menyusun isi materi; memilih aktivitas belajar mengajar dan sumber belajar; mengembangkan silabus; mengevaluasi materi; dan memperbaiki materi. Penulis juga menerapakan peraturan Menteri Pendidikan Nasional Indonesia tentang Panduan Penyusunan Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Jenjang Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah. Untuk menjawab masalah kedua penulis menerapkan teori lain seperti karakter anak-anak, prinsip belajar anak-anak, kecerdasan multiple, dan pengembangan silabus.
Materi yang disusun terdiri dari empat unit. Materi ini digunakan untuk kelas empat sekolah dasar pada semester pertama. Penulis mendistribusikan kuosioner kepada partisipan-partisipan untuk uji kelayakan materi. Hasil uji menunjukkan bahwa nilai rataan berkisar antara 3.3 – 4.3 yang berarti materi yang disusun sudah layak. Penulis mengharapkan penelitian ini dapat digunakan sebagai referensi untuk mengajar Bahasa Inggris di sekolah dasar dan untuk melaksanakan penelitian serupa.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
My greatest gratitude goes to Jesus Christ. Because of His blessing, I can
finish my thesis entitled Designing Integrated English Materials Based on Multiple
Intelligences Theory for the Fourth Grade Students in SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo
Klaten.
In finishing my thesis, I faced many obstacles and difficulties. However,
these problems could be solved because of others’ help. Firstly, I thank my thesis
advisor, Veronica Triprihatmini, S.Pd., M.Hum., M.A., who has guided me in
finishing my thesis. I thank her for her willingness to help me solve the difficulties
in finishing my thesis and for her time in every thesis consultation. I also thank
Christina Kristiyani, S.Pd., M.Pd., Yuseva Iswandari, S.Pd., M.Ed., and Prasetyanto Adi Wibowo for the willingness in evaluating the designed materials.
I thank the headmaster of SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten, Suprihyem, S.Pd., for
the permission that I could do my research in the school.
I thank my late father Kuwatno and my mother Endang Palupi for their
never-ending love for me. I thank also my older sisters Yulianti Kurniawati and
Rita Oktora for their love and support to me.
I address my thanks to my friends Siska, Noti, Anti, Tika, Ika, Lita,
x
I address my special thanks to Nana, who has been coloring my life with
everything we have shared together. Finally, I thank everyone, whose name cannot
be mentioned here, for helping me finish my thesis.
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGE ... ii
DEDICATION PAGE... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY... v
PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS ... vi
ABSTRACT... vii
ABSTRAK ... viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS... xi
LIST OF TABLES ... xvi
LIST OF FIGURES ... xvii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xviii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION 1 A. Research Background ... 1
B. Research Problem ... 3
C. Problem Limitation... 4
D. Research Objectives ... 4
xii
F. Definition of Terms ... 5
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE 7 A. Theoretical Description ... 7
1. Instructional Design... 7
a. Kemp’s Instructional Design... 7
b. Dick’s Instructional Design... 10
2. Characteristics of Young Learners ... 14
a. Physical Development... 14
b. Social Development ... 14
c. Moral Development ... 14
d. Cognitive Development ... 15
3. Principles of Young Learners’ Learning... 15
a. Learning by Looking at Picture ... 15
b. Learning by Listening and Hearing ... 15
c. Learning by Talking... 16
d. Learning by Reading ... 16
e. Learning by Doing ... 16
f. Learning by Writing... 16
g. Learning by Role Playing and Dramatizing... 16
4. Multiple Intelligences ... 17
a. Musical Intelligence ... 17
xiii
c. Logical-Mathematical Intelligence ... 17
d. Linguistic Intelligence... 17
e. Spatial Intelligence... 18
f. Interpersonal Intelligence... 18
g. Intrapersonal Intelligence... 18
5. Developing Syllabus ... 18
a. Identifying Standard Competence and Basic Competence... 18
b. Identifying Subject Contents... 19
c. Developing Learning Activities ... 19
d. Formulating Indicators ... 19
e. Determining Learning Evaluation... 19
f. Determining Time Allocation ... 20
g. Listing Learning Sources ... 20
B. Theoretical Framework ... 20
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 24 A. Research Method ... 24
1. Research and Information Collecting ... 25
2. Planning ... 25
3. Developing Preliminary Form of Product ... 25
4. Preliminary Field Testing ... 26
xiv
B. Research Setting ... 26
C. Research Participants... 27
D. Instrument and Data Gathering Technique... 27
1. Interview ... 27
2. Observation... 27
3. Questionnaire ... 28
E. Data Analysis Technique... 29
F. Research Procedures... 29
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 31 A. The Steps in Designing Integrated English Materials Based on Multiple Intelligences Theory for the Fourth Grade Students in SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten... 31
1. Conducting Needs Analysis... 31
2. Listing Topics, Stating Goals and Stating Learning Objectives... 37
3. Listing Subject Content ... 41
a. Listening... 41
b. Speaking... 42
c. Reading ... 42
d. Writing ... 42
xv
4. Selecting Teaching/Learning Activities and
Instructional Resources... 43
5. Developing Syllabus ... 43
6. Evaluating Materials ... 44
7. Revising Materials ... 46
B. The Presentation of Integrated English Materials Based on Multiple Intelligence Theory for the Fourth Grade Students in SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten... 47
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS ... 53
A. Conclusions ... 53
B. Recommendations ... 54
1. Recommendation for the English Teacher of SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten... 54
2. Recommendation for future Researchers... 54
REFERENCES... 55
xvi
LIST OF TABLES
Page
Table 4.1. Learning Facilities ... 32
Table 4.2. The Result of Pre Design Questionnaire... 33
Table 4.3. The Result of Interview... 35
Table 4.4. Students’ Needs Analysis... 37
Table 4.5. Learning Goals... 37
Table 4.6. Learning Topics ... 38
Table 4.7. Basic Competences ... 38
Table 4.8. Indicators... 39
Table 4.9. Respondents of Post Design Questionnaire ... 44
Table 4.10. The Result of Post Design Questionnaire ... 45
xvii
LIST OF FIGURES
Page
Figure 2.1. Combination of Kemp’s and Dick’s
Instructional Design ... 13
xviii
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page
Appendix 1. Letter of permission ... 57
Appendix 2. Pre Design Questionnaire... 59
Appendix 3. Post Design Questionnaire ... 62
Appendix 4. Syllabus ... 66
Appendix 5. Presentation of the Materials ... 73
Appendix 6. Teacher’s Guide... 101
Appendix 7. PANDUAN PENYUSUNAN KURIKULUM TINGKAT SATUAN PENDIDIKAN JENJANG PENDIDIKAN DASAR DAN MENENGAH ... 112
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents the introduction of the research. This chapter
consists of six parts, namely research background, research problem, problem
limitation, research objectives, research benefits, and definition of terms.
A. Research Background
English is used as international language. Because of this reason, the needs
for mastering English are increasing. The increasing needs of English affects
elementary schools which formerly did not teach English to students to include
English in the curriculum. Although many elementary schools have been starting
teaching English to the students, there are also many obstacles in teaching it. One
of them is learning source.
Indonesian Ministry of National Education periodically supplies books
called BSE or Buku Sekolah Elektronik for main subjects in elementary schools
which are included in Lampiran Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan Nasional Nomor
22 Tahun 2006 Tanggal 23 Mei 2006. The subjects are religion education, civics,
Indonesian language, mathematics, science, social science, cultural education and
sports (p.8). English, however, is not placed in the main subject which means the
government does not supply books for learning. The schools, therefore, have to
supply English books to support teaching-learning activities. This condition also
occurs in SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten.
In SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten, English is taught starting from grade 4.
Students are required to learn actively by themselves. In the school, there is still a
shortage of English books. The school has only been using the same English
books to support learning activities since 2006. There are no other English books
that support the learning process until now. The teacher only uses the same
English book to teach the students for almost last 5 years. The teacher only uses
other learning sources for teaching references.
The lack of the availability of various English books is an obstacle that the
school has been facing. The use of same English books for a long period affects
learning process in the school. The students can only learn using the same books
for almost last 5 years. The books cannot support the students when they are
doing worksheets. The worksheet, however, is not only from the teacher. Every
semester, the students receive different worksheets from the local government.
Therefore, the books that they have will not support them any more since the
contents are not updated.
In the school, students are also provided with extracurricular activities
such as choir, traditional dance, computer training, and drum band. All students
are attracted to these all activities. They have performed some extracurricular
activities to public such as in Christmas celebration, Easter celebration and also in
church worship on Sunday. Physical conditions of the school support these all
extracurricular activities. The school has a large schoolyard and has also a hall.
These places are used as rehearsals of those extracurricular activities. The English
the extracurricular activities. The teacher exploits their abilities to be used in
teaching-learning process. The teacher often applies various activities in class
such as playing games, singing songs, and role playing.
During teaching-learning activities, English is taught by combining two or
more language skills. For instance, listening and writing are combined in an
activity like listening and filling missing words. Language skills are combined
because the materials to be learned are corresponding to each others. The
combination is also to enable students to learn language skills more effective
because it will save time when two or more skills are combined.
Based on the conditions above, the researcher decides to design integrated
English materials which are relevant to the school’s needs that can help the
learning process. Considering that the students have good abilities outside their
academic abilities, the researcher involves their abilities by applying Gardner’s
theory (1993) on multiple intelligences. The researcher takes the benefits of
students’ non-academic abilities through designing activities based on multiple
intelligences theory. The purpose of designing materials is to provide English
materials that can increase students’ motivation to learn English.
B. Research Problem
In this research, the researcher intends to find out the answers to the
problems that are formulated as follows:
1. How are integrated English materials based on multiple intelligence theory
2. What do integrated English materials based on multiple intelligence theory
for the fourth grade students in SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten look like?
C. Problem Limitation
The researcher focuses on designing integrated English materials for the
fourth grade students. The materials are designed based on students’ multiple
intelligences. The materials combine two or more language skills.
D. Research Objectives
Based on the problem formulation above, the researcher has two
objectives. The objectives of the research are:
1. To describe the process of designing integrated English materials based on
multiple intelligence theory for the fourth grade students in SD Kristen 2
Sumberejo Klaten.
2. To present integrated English materials based on multiple intelligence theory
for the fourth grade students in SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten which can
help the students to learn four skills in language learning.
E. Research Benefits
In accordance with the objectives of the research, this research is expected
1. English Language Education Study Program (ELESP)
This research can be a reference for conducting research and studies in the
scope of English teaching area. This research can also be an example of
research on multiple intelligences theory.
2. ELESP students
This research can provide ELESP students with an example of material design
especially the design on multiple intelligences theory. This research can be a
reference for composing appropriate and interesting English materials in doing
their thesis or in the future when they become a teacher.
3. English teachers
This research can be a reference for English teachers, especially those in
elementary school, to provide appropriate and interesting English materials
based on students’ conditions and needs. The designed materials in this
research can also be implemented in teaching and learning process.
4. Others researcher
This research can be a reference for other researchers to conduct similar
research on designing appropriate English teaching materials based on
students’ conditions and needs. The designed materials can be implemented in
order to conduct similar study.
F. Definitions of Terms
In this section, some terms used in the research are defined to avoid
1. Design
Dick (1989) defines design as “a process to develop a wide variety of
instructional materials” (p.3). In this research, design deals with the process of
creating integrated English materials and also deals with presenting the materials.
2. Integrated English materials
According to Richards and Rogers, integrated materials are materials
which “focus on the integrated communicative skills” (as cited by Negari, 2009,
p.7). In this research, integrated means combining two or more language skills in
one learning activity. Integrated English materials cover four language skills
which are listening, speaking, reading and writing.
3. Multiple intelligences
According to Gardner (1993) human has seven intelligences. They are
musical intelligences, bodily-kinesthetic intelligences, logical-mathematical
intelligences, linguistic intelligences, spatial intelligences, interpersonal
intelligences, and intrapersonal intelligences (pp. 17-26). In this research, the
researcher applies these seven intelligences in order to design the integrated
materials.
4. Fourth grade students
Fourth grade students are those who are in the fourth year in SD Kristen 2
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter presents the discussions of the theories which are related to
this thesis. There are two parts of the discussions. The first part is theoretical
description which discusses the related theories used in this study. The second
part is theoretical framework which discuses the framework of the research.
A. Theoretical Description
In this part, the researcher explains theories on instructional designs,
characteristics of young learners, the principles of young learners’ learning,
multiple intelligences and developing syllabus for young learners.
1. Instructional Design
Instructional design is related to designing materials and teaching-learning
activities for the learners. The models of instructional design are taken from
Kemp’sandDick’s model.
a. Kemp’sInstructional Design
Kemp’s (1977) instructional design plan is designed to answer three
questions considered as “essential elements” of the design (p.8). These questions
asked about the objectives of the instructional design, the activities and resources
being used in the instructional design and the evaluation of the design itself.
In designing the instructional design, Kemp proposes eight parts. The eight
parts are explained as follows:
1) Considering Goals, Listing Topics, and Stating the General Purposes for
Teaching Each Topic
Goals might be derived from society, students, or subject areas. Goals
related to society are those which establish learners’ personal values. Goals
derived from the students are related to students’ educational goals which are
related to the subject matter. Goals which are derived from subject area are related
to the specific purposes of the subject matter.
Goals which have been stated will be a foundation of selecting topics of
teaching-learning materials. After the topics have been selected, the general
purposes of topics are listed. The purposes are the wants of what students should
accomplish in the topics (pp. 13-16).
2) Enumerating Characteristics of the Learners
Learners’ important characteristics are considered for whom the
instruction is to be designed. These characteristics include learners’ capabilities,
needs, and interests. Besides, academic and social factors in the school should also
be considered. Academics factors are those related to academic environment such
as number of students, students’ academic background, students’ level of
intelligence, students’ study habits, and students’ motivation to learn. Social
factors of students involve their age, maturity, talents, relation with others, and
socioeconomic situation. Learning condition are also important considerations.
These conditions involve factors that can affect students’ ability to concentrate,
3) Specifying Learning Objectives
Learning objectives are grouped into three categories, namely cognitive,
psychomotor, and affective. Objectives related to cognitive aspect are those which
related to students’ knowledge and thinking process. Psychomotor aspect is
related to students’ ability of kinesthetic activities such as physical activities.
Affective aspect concerns on students’ attitudes, appreciations, and values (pp.
23-30).
4) Listing Subject Content
The subject content should support each learning objectives. The content
should also relate to the objectives and students’ needs. This stage deals with
selecting and organizing students’ knowledge, skills, and attitudinal factors of the
topics (pp. 43-47).
5) Developing Pre-assessments to the Students
Pre-assessment is used to determine students’ background and present
students’ level knowledge about the topic. The pre-assessment is used to find out
to what extent the students have acquired the necessary prerequisites for studying
the topics and to find out what students have mastered the topics (pp. 50-52)
6) Selecting Teaching/Learning Activities and Instructional Resources
Teaching/learning activities and instructional resources will treat the
subject content so that students will accomplish the learning objectives. The
teaching-learning activities must be efficient and effective. This means that the
7) Coordinating Support Services
Support services cover budget, personnel, facilities, equipments, and
schedules. These components are for carrying out the instructional plan (pp.
84-85).
8) Evaluating Students’Learning
Students’ accomplishment of learning objectives is evaluated. The
evaluation is done in order to provide a view to revising and re-evaluating any
phases of the plan that need improvement (pp. 91-92).
b. Dick’s Instructional Design
Dick (1989) defines instructional design as “a process to develop a wide
variety of instructional materials” (p.3). The examples of instructional materials
are printed materials, computer-assisted instruction, and televised instruction. He
classifies nine stages in designing materials. These steps are explained as follows:
1) Setting Goals
The goals of instruction are based on where they come from, how they are
used, how they can be categorized and how they influence the instruction. The
goals are grouped into four aspects which are students’ knowledge, intellectual
skills, motor skills, and attitudes (pp. 8-13).
2) Writing Objectives
The objectives are more specific than the goals. The objectives indicate
what students should be able to do the instruction. The objectives describe what
the students should demonstrate as a result of the instruction and what students
3) Analyzing Students’Characteristics
In defining the objectives, students’ characteristics such as their skills and
knowledge are analyzed. These skills and knowledge are used as a prerequisite
that the students must have before they get the instruction (pp. 30-33).
4) Developing Test
The purpose of developing tests for students is to measure their progress
whether they have achieved the objectives or not. For the teachers, developing
tests can provide them information regarding the quality of their instruction (pp.
37-38).
5) Selecting Textbook and Other Printed Materials
The selection of textbook and other printed materials enables the teacher to
select materials as well as to identify the strengths and weaknesses of each text.
The materials should also reflect the students’ needs and skills (pp. 53-55).
6) Developing Instructional Activities
The development of instructional activities is to enable students to attain
particular objectives. These instructional activities describe what will be presented
to students, how the activities will be presented and the order of presenting the
instruction (pp. 69-74).
7) Choosing Instructional Media
The instructional media that will be used have to meet practical use,
appropriateness for the students, and suitability to present particular instructional
8) Implementing Instruction
After the materials are ready, they then can be implemented to the
classroom (p. 103). The implementation, then, could result materials revision.
9) Revising Instruction
The materials are revised after the teacher implements them. If students do
not achieve the goals and objectives, the instructional materials have to be revised
(p. 112).
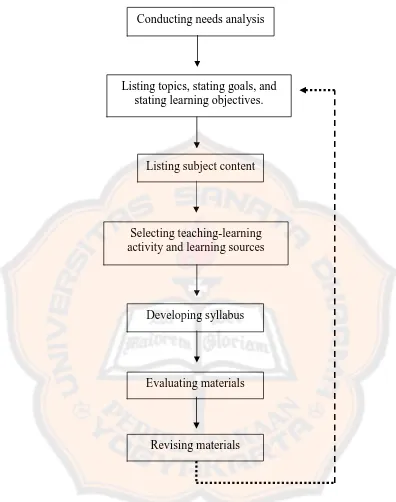
The instructional design which was applied in this research was
combination between Kemp’s and Dick’s theory. The combination was taken
from some steps from Kemp’s and Dick’s theory.Some steps were not included in
this research because the researcher adjusted the instructional design to the results
of needs analysis conducted in the school. The combination of instructional design
of those theories were conducting needs analysis; listing topics, stating goals and
learning objectives; listing subject content; selecting teaching-learning activity
and learning sources; developing syllabus; evaluating materials; and revising
materials. After revising the materials, the step was back to the previous steps if
there were feedbacks to revise the materials. The combination of Kemp’s and
Figure 2.1. Combination of Kemp’s and Dick’sInstructional Design
Conducting needs analysis
Listing topics, stating goals, and stating learning objectives.
Listing subject content
Selecting teaching-learning activity and learning sources
Developing syllabus
Evaluating materials
2. Characteristics of Young Learners
Sandha (2001) proposes characteristics of young learners in their
developments. Young learners are those whose ages are between 6-12 years. He
classifiesyoung learners’ developments into four groups, namely physical, social,
moral and cognitive.
a. Physical Development
According to Sandha (2001) young learners, whose age ranges from 6-12
years, the body and many physiological and neurological aspects are growing.
Physiological and neurological changes affect children’ cognitive development
especially the brain. Bodily changes of the young learners also occur. Girls are
growing faster than boys. Besides, girls also grow faster in terms of puberty than
boys (p. 32).
b. Social Development
Sandha (2001) states that in the social development, young learners of
elementary school have specific characteristics. They like playing and having fun
with their friends. Most social interaction between young learners occurs when
they are playing together (p. 32).
c. Moral Development
Sandha (2001) proposes three stages of young learners’ moral
development. The first is called preconventional manner. In this stage, young
learners react to rewards and punishment. They should be encouraged by being
given rewards. The second stage is called conventional manner. Young learners
should be motivated by maintaining the social interaction among others. The last
stage is called postconventional manner. In the last stage, young learners can
make judgment based on moral principles (p. 33).
d. Cognitive Development
Young learners, as stated by Sandha (2001), learn by concrete example.
They will understand concept of what they are learning if there are concrete
example of it. Teachers should provide example in order to make the learning
process run effectively. Teachers can provide examples such as pictures of fruits,
animals, jobs, etc. (p. 30).
3. Principles of Young Learners’Learning
Noar (1972) states that young learners learn in some ways. These ways are
explained as follows:
a. Learning by Looking at Pictures
Young learners learn by experiencing with pictures. Teaching and learning
activities can include pictures as a visualization of the real objects. They learn by
using their eyes and then they interpret what they see is (p. 32).
b. Learning by Listening and Hearing
Listening and hearing are related to sounds. Young learners learn using
their ears to capture what they hear and listen. The media for learning can be a
c. Learning by Talking
Young learners are talkative in their age. They are also more developing
socially. This can be seen from their behavior that they like talking much with
their friends. Because of this condition, they can be maximized in learning by
talking. The teaching activities can be done through telling stories. They can
experience by themselves in telling stories with their friends (p. 36).
d. Learning by Reading
Reading in young learners’ age should be attractive enough in order to
encourage the young learners to learn. Besides, the level of difficulty should also
be considered. The books being used should be fun for them (p. 37).
e. Learning by Doing
Learning by doing involves young learners to do actively what the teacher
wants to do. Learning activities involve media to stimulate the young learners to
learn. The media can be art work, paper, paints, pencils, clay, plasticine, and other
equipment that can help children learn (pp. 37-38).
f. Learning by Writing
Young learners are given freedom to practice writing. The activities can be
writing letters and words, writing sentences and paragraphs, composing notes to
friends or parents, and creating stories (pp. 38-39).
g. Learning by Role Playing and Dramatizing
Young learners can be engaged in role playing and dramatizing through
practicing stories, fairy tales, or fables that they are familiar with. By doing so,
4. Multiple Intelligences
Gardner (1993) argues that intelligences do not depend only on IQ. He
states that intelligences that are measured by IQ test only cover logic and
language. He adds that human brain has other types of intelligences instead of
logic and language. He proposes that human has seven intelligences.. These
intelligences are explained as follows:
a. Musical Intelligence
Musical intelligence deals with the ability in musical area such as those
related to sounds, tones and rhymes. People with musical intelligence learn
through musical activities like singing (p. 17).
b. Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence
This intelligence deals with the ability in body movements. People who are
good in this area have a well-coordinated body. They can do anything related to
body movement like athletics (pp. 18-19).
c. Logical-Mathematical Intelligence
Logical-mathematical intelligence deals with the ability to think rationally
and logically. People who have this intelligence are good in mathematics and
others area with logic thinking process (pp. 19-20).
d. Linguistic Intelligence
Linguistic intelligence concerns with the ability to use language, whether
in written or spoken form. People who have linguistic intelligence are good in
e. Spatial Intelligence
Spatial intelligence covers the ability related to space. People with this
intelligence are good in three dimensional objects. The areas of this intelligence
are architects, decorators, sculptors, and painters (pp. 21-22).
f. Interpersonal Intelligence
Interpersonal deals with the ability to understand others and work with
others. The learning process can be done through interaction among others (p. 22).
g. Intrapersonal Intelligence
Intrapersonal intelligence deals with the ability to understand oneself.
People with this intelligence can learn and work with themselves well (pp. 24-25).
5. Developing Syllabus
According to Indonesian Ministry of National Education’s regulation on
Panduan Penyusunan Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Jenjang Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah, there are 7 steps in developing a syllabus. The steps are explained as
follows:
a. Identifying Standard Competence and Basic Competence
There are some considerations in identifying standard competence and
basic competence. The identification must consider the hierarchy of difficulty
level, correlation between standard competence and basic competence with the
subject to be learned, and also correlation between standard competence and basic
b. Identifying Subject Contents
In order to achieve the standard competence, the identification of subject
contents can be done with some considerations. These considerations can be
students’ potential, relevance toward local area’s characteristics and toward
students’ needs, students’ development, the benefits to students, students’
knowledge, and time allocation (p. 16).
c. Developing Learning Activities
Learning activities are planned to involve students to use their physic and
mind in learning through interacting with teacher, other students, learning
environment, and learning sources in order to achieve standard competence.
Learning activities must be able to help students learn the subject effectively.
Therefore, learning activities must be developed in good order and must cover
students’ activities and material to be learned (pp. 16-17)
d. Formulating Indicators
Indicators reflect students’ achievement toward standard competence that
can be measured through students’ learning attitude, knowledge, and skills.
Indicators can be developed through students’ characteristics, learning subject,
and local area context (p. 17).
e. Determining Learning Evaluation
Evaluation is aimed at measuring students’ achievement toward indicators
that were stated. The evaluation can be done through test and non-test. The
observation toward students’ attitude, observation toward students’ progression,
and self evaluation (pp. 17-18).
f. Determining Time Allocation
Determining time allocation of every standard competence is based on the
effective week and time allocation of the subject in a week. Time allocation is
only the estimation of the time that students need to master the subject (p. 18).
g. Listing Learning Sources
Learning sources are listed to help students learn the subject. Learning
sources should be based on standard competence, basic competence, subject
contents, and also learning indicators. Learning sources can be from printed
media, electronic media, human resources, learning environment, society, and
culture (p. 18).
B. Theoretical framework
In chapter one, the research question has been formulated. In order to
answer the first research question which is how integrated English materials for
the fourth grade students based on multiple intelligences are designed the
researcher applied the combination of Kemp’s and Dick’s instructional design
model and Indonesian Ministry of National Education regulation on Panduan
Penyusunan Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Jenjang Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah. Because of the condition of the elementary school, the researcher
adjusted the designing steps based on the school’s needs. The steps of designing
1. Conducting Needs Analysis
In this step, the researcher conducted observation to the students and the
environment of the school and conducted interview with the English teacher in the
school. The observation and interview were conducted to know characteristics of
the students and to know learning environment and learning supports. The
researcher also analyzedstudents’ learning needs by distributing questionnaires to
the students.
2. Listing Topics, Stating Goals and Stating Learning Objectives
The process of listing topics, stating goals and stating learning objectives,
were based on the result of needs analysis. Each unit of the designed materials had
a topic, goals, and learning objectives.
3. Listing Subject Content
The subject contents which were designed supported each learning
objective. The subject contents weredesigned by considering students’ needs and
interests so that the students will be motivated to learn through interesting
contents in the materials.
4. Selecting Teaching/Learning Activities and Learning Sources
Teaching/learning activities and instructional resources were selected by
considering theories of multiple intelligences, characteristics of young learners,
and principles of young learners’ learning. The activities and instructional
5. Developing Syllabus
Developing syllabus was based on the Panduan Penyusunan Kurikulum
Tingkat Satuan Jenjang Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah. The content of the
syllabus such as standard competence and basic competence, subject content,
learning activities and indicators were developed based on the result of needs
analysis.
6. Evaluating Materials
The evaluation of the materials was done by distributing questionnaires
about the design. The questionnaires were distributed to the teacher of the school
and some lecturers. The questionnaires are used to obtain respondents’ opinions
and suggestions about the design.
7.Revising Materials
The materials were revised based on the result of the questionnaires. The
revision was done by revising the materials if there is something wrong in the
design and improving the materials.
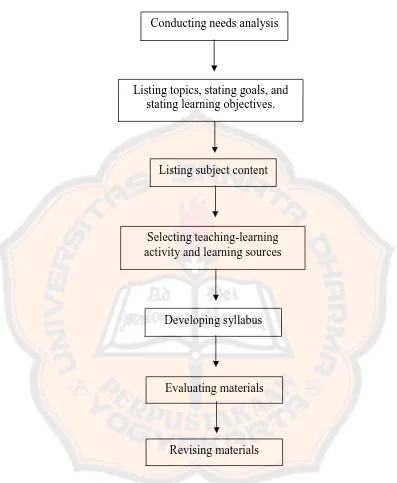
In order to answer second question which is what integrated English
materials based on multiple intelligence theory for the fourth grade students in SD
Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten look like the researcher applied theories on characteristics of young learners, principles of young learners’ learning, and
multiple intelligences. These theories were the references for selecting learning
activities in the materials, selecting colors and pictures, and selecting games and
songs for supporting learning process. The theoretical framework of this research
Figure 2.2. Theoretical Framework
Conducting needs analysis
Listing topics, stating goals, and stating learning objectives.
Listing subject content
Selecting teaching-learning activity and learning sources
Developing syllabus
Evaluating materials
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter discusses the method which is used to answer two problems
formulated in the chapter one. This chapter consists of five parts, namely research
methods, research setting, research respondents, research instruments, and
research procedures.
A. Research Method
This research applied research and development (R & D). Borg (1983)
defines research and development as a process used to develop and validate
educational products which include materials like textbooks and also teaching
method or method for organizing instruction (p. 772). This research combined
qualitative and quantitative method. Qualitative method used instruments which
were observation and interview. Quantitative method used instrument which were
questionnaires.
Research and development had ten major steps. In this research, the
researcher did not apply these ten steps. The researcher took first five steps to
conduct the research. These first five steps already presented the main steps in the
research and development namely development, field testing, and revision. The
five steps are explained as follows:
1. Research and Information Collecting
According to Borg (1983), this step includes “review of literature,
classroom observation, and preparation of report of state of the art” (p. 775). In
this research, the researcher conducted needs analysis through observation,
interview and questionnaire. The researcher observed the classroom to gain
students’ needs and interests. The researcher also interviewed English teacher in
the school to gather information about the students of grade four. The researcher
also analyzed students’ needs by distributing questionnaires to the students. The
questionnaires were aimed at attainingstudents’ needs and interests.
2. Planning
Borg (1983) states that planning covers“defining skills, stating objectives
determining course sequence and small scale feasibility testing” (p. 775). In this
research the researcher listed topics, stated goals and stated learning objectives
based on the analysis of learners’ characteristics and the result ofquestionnaires.
3. Developing Preliminary Form of Product
This step, according to Borg (1983) includes “preparation of instructional
materials, handbooks, and evaluation devices” (p.775).In this step, the researcher
listed subject contents and selected teaching/learning activities. The researcher
also developed a syllabus based on the result of needs analysis. In order to
develop the product, the researcher also referred to some English books for
4. Preliminary Field Testing
According to Borg (1983) preliminary field testing can be conducted
through “interview, observation, and questionnaire” (p.775). In this step, the
researcher distributed questionnaires to the English teacher in the school and also
to some lecturers. The questionnaires were aimed to gain respondents’
evaluations, comments, opinions, and suggestions toward the design.
5. Main Product Revision
Borg (1983) states that the revision of the product is based on the result of
preliminary field testing (p. 775). The result of the questionnaires was used to
improve the design.
B. Research Setting
The research was conducted in SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten. The
research was conducted during July– September 2011. In July the researcher did
observation to the fourth grade students and the condition of the school. In the
first week of August 2011 the researcher interviewed the English teacher in order
to find out the teaching and learning process. In the first week of September 2011
the researcher distributed questionnaires to the students to gain students’ needs
and interests on learning English.
C. Research Participants
The respondents of the needs analysis were 13 students of grade four of
respondents for evaluating the designed material were the English teacher of the
school and 2 PBI lecturers of Sanata Dharma University.
D. Instrument and Data Gathering Technique
The instruments used in this research to gather data were observation,
interview, and questionnaires. The instruments are explained as follows:
1. Interview
In this research, the type of interview that was used was unstructured
interview. According to Ary (1979), unstructured interview is defined as “more
informal” interview (p.174). The interviewer is free to ask questions to the
interviewee and the interviewee is also free to answer the questions (p. 174). In
this research, the researcher interviewed the English teacher of the school. The
interview was conducted to know teaching-learning process and students’
characteristics.
2. Observation
Observation used in this research was nonparticipant observation. Ary
(2002) defines nonparticipant observation as observation in which the observer
observes “without participating or taking any active part in the situation” (p.430).
The researcher, in this research, observed students of grade four while they were
studying English. The researcher did not participate in the teaching process.
However, the researcher only observed in the back of class during
3. Questionnaire
In the pre design step, the questionnaire that was used was structured
questionnaire. According to Ary, structured questionnaire (1979) contains
“questions” and “alternative answers” to the questions (p. 175). The answers to
the questions had to be in-depth responses. The questionnaire distributed to the
students was in multiple choices in order to enable students to answer the
questions without any difficulties. The pre design questionnaire was aimed at
gainingstudents’ learning needs and interests.
In the post design steps, the questionnaire that was used was combination
of structured and unstructured questionnaire. Ary (1979) defines unstructured
questionnaire as questionnaires that donot include “suggested answer” (p. 175). It
means that the respondents are free to give their responses to the questions. In the
post design steps, the questionnaire distributed to the lecturers and English teacher
of the school consisted of nominal scale in the first section and also free answer to
questions in the second section. The questionnaire was aimed at evaluating the
design.
Data gathering technique in the pre-design step was done by distributing
questionnaires to 13 the students of grade four. The questionnaires were to collect
students’ needs and interest on studying English. In the post-design step, the
researcher evaluated the designed material by distributing questionnaires to
English teacher of the school and 2 PBI lecturers of Sanata Dharma University.
E. Data Analysis Technique
In the pre design questionnaires, the researcher analyzed the result of the
questionnaires by applying descriptive measurement. The result of the pre design
questionnaires were calculated with percentage method. The measurement was the
number of students choosing certain answer divided by the total number of the
students then times 100%. The formulation of the calculation is presented as
follows:
∑ 100%
N : the number of students choosing certain answer
∑N : the total number of the students
In the post design questionnaire, the analysis of the result was done with
mean calculation. Ary (1979) states that the mean is calculated with the sum of all
the values divided by the number of the cases. The formulation was presented as
follows (p. 103):
X =
∑X : the mean
∑X : the sum of all the values
N : the number of the cases
F. Research Procedures
In this research, the researcher conducted procedures as mentioned in the
research method. The first procedure was research and information collecting. In
22
this step, the researcher conducted classroom observation and distributed
questionnaires to students which aimed at gaining students’ needs and interests.
The researcher also interviewed English teacher in the school to gather
information about the students of grade four.
The second procedure was planning. In this step, the researcher stated
goals of the materials design, learning objectives and topics which were based on
the analysis of learners’ characteristics and the result ofquestionnaires.
The third procedure was developing preliminary form of product. In this
step, the researcher listed subject contents and selected teaching/learning
activities. In order to develop the product, the researcher referred to some
references of English books for elementary school especially for the fourth grade.
The fourth procedure was preliminary field testing. Preliminary field
testing was conducted through questionnaires. In this step, the researcher
distributed questionnaires to the English teacher and also to 2 PBI lecturers to
gain evaluations, comments, opinions, and suggestions toward the design.
The last procedure was main product revision. The revision of the product
was based on the result of preliminary field testing. The result of the
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter is divided into two parts. The first part is aimed at answering
the first problem formulation stated in chapter 1. This part discusses about the
steps elaborated in designing materials. The second part is aimed at answering the
second problem formulation stated in chapter 1. This part discusses the
presentation of the designed materials.
A. The Steps in Designing Integrated English Materials Based on Multiple Intelligences Theory for the Fourth Grade Students in SD Kristen 2
Sumberejo Klaten
This part presents the steps elaborated in designing materials. The steps
were adapted from Kemp’s and Dick’s instructional model. The steps in designing
the materials are conducting needs analysis; listing topics, stating goals and
stating learning objectives; listing subject content; selecting teaching/learning
activities and instructional resources; developing syllabus; evaluating materials;
and revising materials. Those steps are explained as follows:
1. Conducting Needs Analysis
In this research, needs analysis was done through observation, interview
and questionnaires. The respondents of needs analysis are 13 students of grade
four of SD Kristen 2 Sumberejo Klaten and the English teacher of the school. At
the first time, the researcher conducted observation at the school. The observation
was aimed at gaining learning facilities of the school that can support teaching and
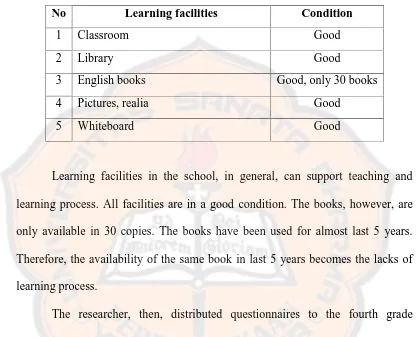
[image:52.595.97.514.191.528.2]learning process. The result of the observation is showed as follows:
Table 4.1. Learning Facilities
No Learning facilities Condition
1 Classroom Good
2 Library Good
3 English books Good, only 30 books
4 Pictures, realia Good
5 Whiteboard Good
Learning facilities in the school, in general, can support teaching and
learning process. All facilities are in a good condition. The books, however, are
only available in 30 copies. The books have been used for almost last 5 years.
Therefore, the availability of the same book in last 5 years becomes the lacks of
learning process.
The researcher, then, distributed questionnaires to the fourth grade
students of the school. The questionnaires were distributed before designing
materials. Therefore, they are called pre design questionnaire. The researcher used
closed questionnaire in order to gain students’ needs and interests about English
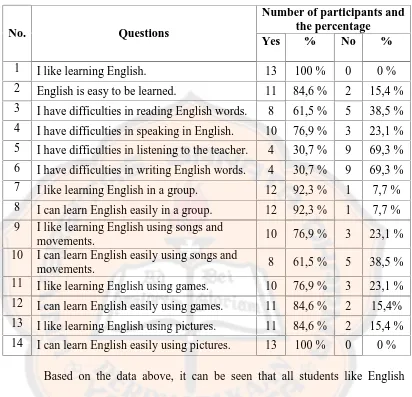
Table 4.2. The Result of Pre Design Questionnaire
No. Questions
Number of participants and the percentage
Yes % No %
1 I like learning English. 13 100 % 0 0 %
2 English is easy to be learned. 11 84,6 % 2 15,4 %
3 I have difficulties in reading English words. 8 61,5 % 5 38,5 %
4 I have difficulties in speaking in English. 10 76,9 % 3 23,1 %
5 I have difficulties in listening to the teacher. 4 30,7 % 9 69,3 %
6 I have difficulties in writing English words. 4 30,7 % 9 69,3 %
7 I like learning English in a group. 12 92,3 % 1 7,7 %
8 I can learn English easily in a group. 12 92,3 % 1 7,7 %
9 I like learning English using songs and
movements. 10 76,9 % 3 23,1 % 10 I can learn English easily using songs and
movements. 8 61,5 % 5 38,5 % 11 I like learning English using games. 10 76,9 % 3 23,1 %
12 I can learn English easily using games. 11 84,6 % 2 15,4%
13 I like learning English using pictures. 11 84,6 % 2 15,4 %
14 I can learn English easily using pictures. 13 100 % 0 0 %
Based on the data above, it can be seen that all students like English
subject. However, not all of the students said that English is easy to be learned.
From the table above, 11 students (84,6 %) stated that learning English is easy and
2 students (15,4 %) stated that learning English is not easy.
Some students still face difficulties in learning English skills. From the
data above, there are 8 students (61,5 %) facing difficulties in reading English
words while 5 students (38,5 %) do not have difficulties. In speaking, it is found
that 10 students (76,9 %) face difficulties and 3 students (23,1 %) stated that they
are 4 students (30,7 %) facing difficulties while 9 students (69,3 %) do not face
difficulties.
Although there are difficulties in learning English, almost all of the
students stated that they like learning English. The data above shows that there are
12 students (92,3 %) who like learning English while a student (7,7 %) does not
like learning English. The data above also shows students’ interests in learning
English. Almost all of the students like learning English in a group. From 13
students, there are 12 students (92,3 %) who like learning English in a group,
while the rest (7,7 %) does not.
There are more than half of the students who like learning English using
some supporting learning media such as songs and movements, games, and
pictures. From the data, there are 10 students (76,9 %) who like learning English
using songs and movements, while the rest students (23,1 %) do not. Songs and
movements used in the lesson can help the students learn the lesson easier. It can
be seen from the data that there are 8 students (61,5 %) who can learn lesson
easily using songs and movements while 5 students (38,5 %) cannot. There are 10
students (76,9 %) who like learning using games and 3 students (23,1 5) who do
not. Using games also affects students to learn easier. From the data, there are 11
students (84,6 %) can learn easily by using games while the rest (15,4 %) cannot.
Pictures also play an important role in helping students learn English. It can be
seen that 11 students (84,6 %) like learning through provided pictures while the
using pictures, the data above shows that all students can learn easily through
pictures.
In the need analysis, the researcher also interviewed English teacher of the
school in order to obtain more information about teaching and learning activities
[image:55.595.105.513.254.753.2]at grade four. The result of the interview is showed as follows:
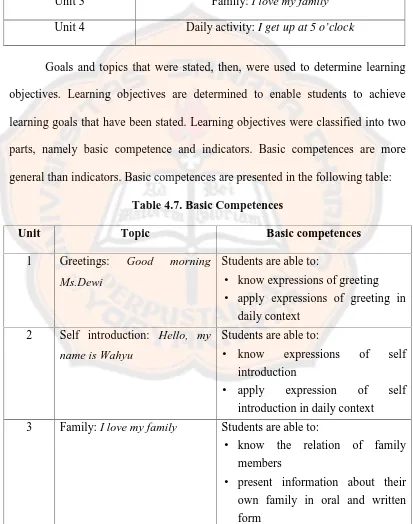
Table 4.3. The Result of Interview
No Questions Answers
1 How long does English lesson in the school last?
There are 2 meetings in a week. Each meeting lasts for 70 minutes or 2 contact hours. In a week there are 140 minutes available for teaching-learning process.
2 What are the activities run in the teaching-learning process?
The activities run are teaching, doing exercises, and discussing. The students are also given tasks and homework in order to help them learn the lesson.
3 What are the techniques applied in the teaching-learning process?
The main technique applied during teaching learning process is drilling. Drilling helps students to memorize the lesson. Others techniques are using pictures, songs, movements, models like replica of fruits and animals, and playing games.
4 What are learning sources used in the class?
Learning process is supported by English book. For grade 4, there are about 30 books from local government. However, unfortunately the book that is used has been used for the last 5 years. So, it only supports a little for teaching-learning process. To support the teaching-learning process I use other books for my teaching references.
semester. 5 What are the difficulties faced during
teaching-learning English?
The first difficulty is on the supporting learning source like book. Because the book is not up-to-date, the learning process may not run effectively.
The second is on the students. The main difficulties that they face are on speaking and reading although they find difficulties also in other skills. Another difficulty is on the memorization of vocabularies. 6 What do you do to solve those
difficulties?
I use drilling to help them memorize English words. I also use realia such as picture and replica. Besides, to refresh their mind, I use games and songs so that they can be attracted again to focus on the lesson after they felt bored or they lost attention.
7 What do you do in order to attract and motivate students to learn English?
The students have good talent like in music, dance, sport, and many others. They have strengths in those talents. So, I often include their talents during the lesson. For example, they can sing a song related to the lesson. Through lesson presented in the song, they can learn it indirectly.
8 What are the topics that are suitable and interesting for grade four?
I think the topics could be greetings and introduction; topics about family; daily activities; anything around the students in daily context like jobs, things in class or house, foods, fruits, vegetables, and clothes. The topics could also be pronouncing the alphabet and numbers.
Based on the data from observation, questionnaires and interview; the
researcher determines students’ needs. Students’ needs analysis are presented as
Table 4.4.Students’ Needs Analysis
Needs To be able to master four English skills and to communicate effectively in daily context.
Lacks Availability of English books, vocabularies memorization, pronunciation, mastering English skills.
Wants To be able to know and use English vocabularies in daily conversation.
2. Listing Topics, Stating Goals and Stating Learning Objectives
The next steps after need analysis are stating goals, listing topics and
stating learning objectives. The goals of materials design are defined into two
parts which are mastering English skills and communicating effectively. The goals
[image:57.595.97.521.139.591.2]are defined in the table as follows:
Table 4.5: Learning Goals
Goals
Students are able to master four English skills, namely
listening, speaking, reading and writing.
Students are able to communicate effectively in daily
context.
After stating learning goals, the researcher then listed topics based on
needs analysis. The materials consist of four topics. The topics were developed
based on the students’ interests and the English teacher’s suggestions. The topics
Table 4.6. Learning Topics
Unit Topic
Unit 1 Greetings: Good morning Ms.Dewi
Unit 2 Self introduction: Hello, my name is Wahyu
Unit 3 Family: I love my family
Unit 4 Daily activity:I get up at 5 o’clock
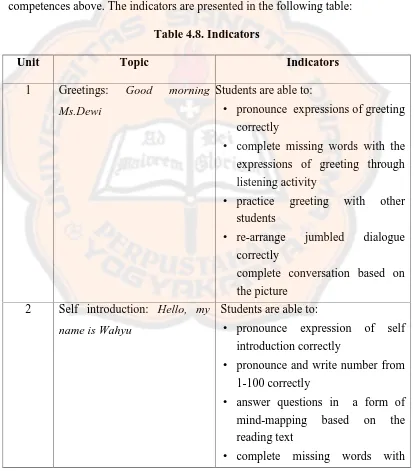
Goals and topics that were stated, then, were used to determine learning
objectives. Learning objectives are determined to enable students to achieve
learning goals that have been stated. Learning objectives were classified into two
parts, namely basic competence and indicators. Basic competences are more
general than indicators. Basic competences are presented in the following table:
Table 4.7. Basic Competences
Unit Topic Basic competences
1 Greetings: Good morning Ms.Dewi
Students are able to:
• know expressions of greeting
• apply expressions of greeting in daily context
2 Self introduction: Hello, my
name is Wahyu
Students are able to:
• know expressions of self introduction
• apply expression of self introduction in daily context 3 Family: I love my family Students are able to:
• know the relation of family members
4 Daily activity: I get up at 5
o’clock
Students are able to:
• know how to present daily activities
• present daily activities in oral and written form
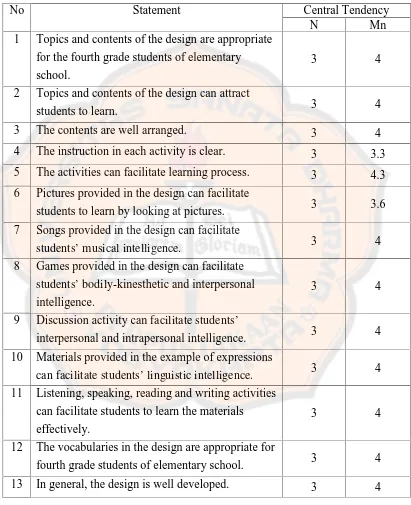
From basic competences in the table above, the researcher then determined
indicators that students should achieve. The indicators were derived from basic
[image:59.595.105.519.275.746.2]competences above. The indicators are presented in the following table:
Table 4.8. Indicators
Unit Topic Indicators
1 Greetings: Good morning Ms.Dewi
Students are able to:
• pronounce expressions of greeting correctly
• complete missing words with the expressions of greeting throug