Brain Research 879 (2000) 200–203
www.elsevier.com / locate / bres
Short communication
Retention of spatial information in hippocampally damaged rats
overtrained on a cartographic task
a,b ,
*
Juan M.J. Ramos
a
´ ´ ´
Departamento de Psicologıa Experimental y Fisiologıa del Comportamiento, Facultad de Psicologıa, Universidad de Granada, 18071 Granada,
Spain
b
´
Instituto de Neurociencias Federico Oloriz, Universidad de Granada, Granada, Spain
Accepted 5 July 2000
Abstract
Hippocampal rats were overtrained on a cartographic task until they reached a performance equal to that of the control group. Twenty-four days later, during a retraining period, lesioned rats showed a profound retention deficit as compared to controls. However, Expt. 2 shows no retention deficit when a guidance strategy is used to acquire the spatial task. These results suggest that the hippocampus is crucial for long-term retention / consolidation of allocentric spatial information. 2000 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.
Theme: Neural basis of behaviour
Topic: Learning and memory: systems and functions
Keywords: Retention; Consolidation; Long-term memory; Spatial memory and hippocampus; Amnesia
It has recently been suggested that the formation of sition of spatial tasks based on the use of a place or
long-term memories requires transitory interactions be- cartographic strategy. For this reason, in this study
hip-tween the hippocampus and the neocortex [3]. According pocampally lesioned rats were overtrained until they
to this model, these interactions may lead to the formation reached a performance equal to that of the control group.
of a long-lasting cortical memory representation which This permitted us to evaluate, during a later period of
would allow for long-term memory [1]. In support of this retraining, the retention of the spatial information acquired
consolidation model, several studies using non-spatial in the training phase.
paradigms have shown a temporally-graded retrograde In Experiment 1, 21 naive male Wistar rats (280–320 g)
amnesia following hippocampal damage in rats [2,5] and were individually housed in a room with constant
tempera-monkeys [15]. However, when spatial tasks are used, the ture and a 12:12 h light–dark cycle. The animals were
results have been contradictory, observing in some cases a food-deprived to 85% of the normal body weight during
flat retrograde amnesia [7, for review see 9] and in others a the training period. Rats were randomly assigned to a
temporally-graded retrograde amnesia [6,11,13]. Conse- hippocampus (HIP, n512) or to a control group (CON,
quently, it has been difficult to dissociate, using lesion n59). Under sodium pentobarbital anaesthesia (50 mg /
methods, the participation of the hippocampus in the kg), the rats was placed in a David Kopf stereotaxic
performance / retrieval of the task from its possible contri- apparatus. The dorsal hippocampus was damaged at four
bution to the consolidation / retention of spatial informa- different anteroposterior sites in relation to the interaural
tion. The present study was therefore undertaken to zero point [10]: AP515.9, L561.6, V516.5; AP514.8,
investigate whether the hippocampus is necessary for long- L562.5, V516.5; AP513.8, L563.2, V516.5; AP51
term retention of cartographic information. It is a well- 3.0, L564.0, V515.4. Bilateral electrolytic lesions were
established fact that hippocampal lesions impair the acqui- made by passing 2 mA DC cathodal current for 15 s
through a monopolar stainless steel electrode insulated with INSL-X except for the 0.5 mm tip. Control rats were
*Tel. / fax:134-958-243-763.
E-mail address: [email protected] (J.M.J. Ramos). treated similarly, but no current was passed.
J.M.J. Ramos / Brain Research 879 (2000) 200 –203 201
After a 10-day recovery period, all rats were handled on clockwise direction from trial to trial in order to prevent
seven successive days for 5 min each. On the following the animals from using olfactory signals to reach the goal
day the behavioural training began using a four-arm plus- arm. Rats were trained until they reached a learning
shaped maze as apparatus. Each arm of the maze was criterion of at least 14 correct trials on two consecutive
60310 cm. They were connected to an octagonal central days (87%). However, in the acquisition phase there was a
platform 35 cm in diameter. A schematic diagram of the limit of 22 consecutive days of training. The subjects that
maze and cues in the testing room has been presented did not reached the criterion before that point were
elsewhere [11]. During the training procedure animals excluded from the experiment. After reaching criterion, the
received eight trials per session and one session per day. rats remained in their respective cages for 24 days, and
At the beginning of a trial, the rat was placed at the end of were not tested in any way. Starting on day 24 the animals
one of the arms used for starting (S, N and E), with its received retraining on the spatial task learned during the
back to the central platform. The order in which the initial training phase. The procedure used during the
different starting arms were used was randomized in each retraining phase of testing (retention) was identical to that
daily session. Two 45-mg food pellets (P.J. Noyes Com- of training (acquisition). After the behavioural procedure,
pany Inc., UK) were placed in the food cup at the end of the rats were deeply anaesthetized with sodium
pentobarbi-the west arm. After a choice was made and pentobarbi-the rat passed tal and perfused intracardially. Several days later, the
the mid-way point of the chosen arm with all four of its brains were frozen and coronal sections were stained with
limbs, a wooden cube measuring 10310310 cm was Cresyl Violet.
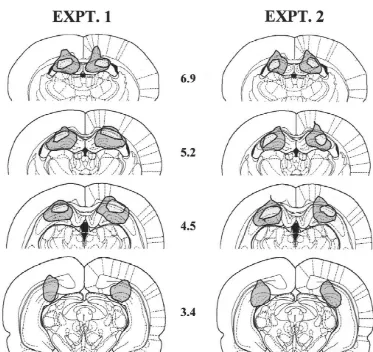
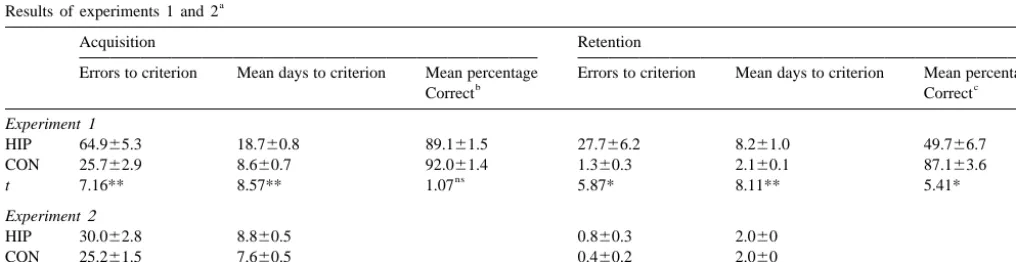
placed by the experimenter just behind the rat. In this way Histological analysis in this Experiment and the
follow-the animal remained at follow-the end of follow-the chosen arm for 5–7 ing one revealed appropriately positioned bilateral lesions
s. Then the rat was picked up and confined in a box for an (Fig. 1). At the most rostral levels of the lesion only lateral
intertrial interval of 30 s. The maze was rotated 908 in a aspects of CA3 field were damaged. At the level of the
202 J.M.J. Ramos / Brain Research 879 (2000) 200 –203
ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus and of the dorsal hippocampus and five naive sham-operated rats
mammillary nuclei, the hippocampal CA1 field was dam- were used. The procedure followed was identical to that
aged to various degrees in all the rats and CA2–CA3 fields described in Expt. 1 except for two aspects. First,
through-appeared partially damaged in two thirds of the animals. At out the training phase, a piece of sandpaper measuring
more posterior levels of the lesion, CA1 was partially 10360 cm (00 thickness) was placed on the floor of the
damaged in the majority of the rats and the dentate gyrus goal arm. Second, in two of the eight daily training trials
was partially affected in two thirds of the rats. the goal arm was positioned to the west, in two trials it was
Behavioral results showed that of the 12 hippocampal to the east, in two it was to the south and in two it was to
rats, only five reached the learning criterion before day 22 the north. The order in which the different goal arms were
of the training. Therefore, only the results obtained by used was randomized, and it was the same for all the
these five animals during the training and retraining phases animals. This created a situation in which the configuration
were included in the statistical analysis. A Student’s t-test of extramaze stimuli was not relevant, and in which it was
revealed that hippocampal rats committed significantly necessary for the animal to use a guidance versus a
more errors before reaching the criterion than the control cartographic strategy to effectively resolve the spatial
rats (t1257.16, P,0.00001, Table 1). Also, the mean problem. The procedure used during the retraining phase of
number of days required to reach the criterion was higher testing was identical to that of the acquisition phase.
in the HIP group (t1258.57, P,0.00001). However, During the acquisition phase, two Student’s t-test revealed
although the HIP group took longer to learn the task, the no significant differences between groups as far as the
level of performance during the last two days of training number of incorrect responses before criterion (t851.47,
was similar in both groups (t1251.07, P50.30). These P50.17) nor in the mean number of days to reach criterion
results indicate the same level of learning for the HIP and (t851.54, P50.15, Table 1). During the retraining phase,
CON groups at the end of the acquisition phase. the performance of the lesioned animals and the controls
During the retraining (retention), hippocampally dam- did not differ significantly in the number of errors before
aged rats performed significantly worse than the CON criterion (t850.89, P50.39) nor in the number of days of
group (Table 1). Thus, the HIP group committed more retraining before reaching criterion (t cannot be computed,
errors before reaching criterion (t1255.87, P,0.0001) and Table 1).
needed more days than the CON group to relearn the The central finding is that despite the fact that
over-spatial task (t1258.11, P,0.00001). Finally, upon analys- trained hippocampal animals can learn a cartographic task
ing the mean percentage of correct responses on the first at the same level of performance as the controls, 24 days
day of retraining, a Student’s t-test revealed that the HIP later lesioned rats show a profound deficit in the retention
group remembered the spatial information acquired during of the task. In contrast, no retention deficit was observed
the training phase significantly worse than the control rats when the spatial problem is learned using a guidance
(t1255.41, P,0.0002, Table 1). strategy. The type of strategy employed by the lesioned
Experiment 2 was performed to investigate whether animals in Expt. 1 is clearly very different from the one
hippocampal rats could retain spatial information in the employed in Expt. 2. Hippocampal rats in Expt. 1 probably
long term when the animals used a guidance versus a acquired the task by way of an allocentric / cartographic
cartographic strategy during the training. A total of five strategy. If they had used a guidance strategy, lesioned rats
naive male Wistar rats with electrolytic lesions to the would not have manifested any deficit in the retraining
Table 1
a Results of experiments 1 and 2
Acquisition Retention
Errors to criterion Mean days to criterion Mean percentage Errors to criterion Mean days to criterion Mean percentage
b c
Data are the mean6S.E.M. b
Mean percentage of correct responses on the last two days of training of the acquisition phase. c
J.M.J. Ramos / Brain Research 879 (2000) 200 –203 203
[4] E.J. Golob, J.S. Taube, Head direction cells and episodic spatial
phase. It is possible that in overtrained hippocampal rats,
information in rats without a hippocampus, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
the preserved hippocampal tissue and extra-hippocampal
USA 94 (1997) 7645–7650.
structures mediate in the acquisition of the task [14]. [5] J.J. Kim, R.E. Clark, R.F. Thompson, Hippocampectomy impairs
Supporting the last idea, electrophysiological studies have the memory of recently, but not remotely, acquired trace eye-blink
demonstrated location selective cells and head direction conditioned responses, Behav. Neurosci. 109 (1995) 195–203.
[6] J.L. Kubie, R.J. Sutherland, R.U. Muller, Hippocampal lesions
cells in various extrahippocampal structures [8,12]. It has
produce a temporally graded retrograde amnesia on a dry version of
been suggested that in hippocampally lesioned rats, head
the Morris swimming task, Psychobiology 27 (1999) 313–330.
cells are capable of creating a novel representation of the [7] C. Laurent-Demir, R. Jaffard, Temporally extended retrograde
animal’s environmental context [4]. Finally, our results amnesia for spatial information resulting from afterdischarges
suggest that the hippocampus is necessary for long-term induced by electrical stimulation of the dorsal hippocampus in mice,
Psychobiology 25 (1997) 133–140.
retention of cartographic information.
[8] R.U. Muller, J.B.Jr. Ranck, J.S. Taube, Head direction cells: properties and functional significance, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 6 (1996) 196–206.
Acknowledgements [9] L. Nadel, M. Moscovitch, Memory consolidation, retrograde am-nesia and the hippocampal complex, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 7 (1997) 217–227.
This research was supported by a grant from the
[10] G. Paxinos, C. Watson, The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates,
´ ´
Ministerio de Educacion y Cultura, Direccion General de
Academic Press, New York, 1998.
˜
Ensenanza Superior, Spain, PB96-1425. [11] J.M.J. Ramos, Retrograde amnesia for spatial information: a
dis-sociation between intra and extramaze cues following hippocampus lesions in rats, Eur. J. Neurosci. 10 (1998) 3295–3301.
[12] P.E. Sharp, Complimentary roles for hippocampal versus subicular /
References
entorhinal place cells in coding place, context, and events, Hip-pocampus 9 (1999) 432–443.
[1] P. Alvarez, L.R. Squire, Memory consolidation and the medial [13] E. Teng, L.R. Squire, Memory for places learned long ago is intact temporal lobe: a simple network model, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA after hippocampal damage, Nature 400 (1999) 675–677.
91 (1994) 7041–7045. [14] I.Q. Whishaw, L.E. Jarrard, Evidence for extrahippocampal in-[2] S.G. Anagnostaras, S. Maren, M.S. Fanselow, Temporally graded volvement in place learning and hippocampal involvement in path
retrograde amnesia of contextual fear after hippocampal damage in integration, Hippocampus 6 (1996) 513–524.
rats: within-subjects examination, J. Neurosci. 19 (1999) 1106– [15] S.M. Zola-Morgan, L.R. Squire, The primate hippocampal
forma-1114. tion: evidence for a time-limited role in memory storage, Science
[3] B. Bontempi, C. Laurent-Demir, C. Destrade, R. Jaffard, Time- 250 (1990) 288–290. dependent reorganization of brain circuitry underlying long-term