commit to user
i
An Analysis of Translation Techniques and
Translation Quality of Flight Attendant Manual
THESIS
Submitted as a Partial Fulfillment of Requirement
For Sarjana Degree in English Department
By:
GERRY AGUSTINO
C0307028
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LETTERS AND FINE ARTS
SEBELAS MARET UNIVERSITY
commit to user
commit to user
commit to user
iv
PRONOUNCEMENT
Name : Gerry Agustino NIM : C0307028
In the name of God, the author states whole-heartedly that the thesis entitled “An Analysis of Translation Techniques and Translation Quality of Flight Attendant Manual” is originally made by the author. It is neither a plagiarism, nor made by others. The things related to other people’s work are written in quotation and included within bibliography.
If it is then proved that the author cheated, the researcher is ready to take the responsibility.
Surakarta, Desember 2011
commit to user
v
MOTTO
“It’s nice to be important, but it’s more important to be nice.”
(Cassis, John)
“
Start today with pray, hope, and smile. Close today with pray
and give thanks for HIS grace for our life.
”
(unknown)
“I can do all things through HIM who strengthens me.”
(Philippians 4:13)
“Do what you love, love what you do.”
commit to user
vi
DEDICATION
This thesis is dedicated to:
JESUS CHRIST
My beloved parents
My beloved brother and sister
commit to user
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Praise GOD for His blessing, love and guidance so that this thesis can be completed as a partial fulfillment of graduating requirement of the Sarjana Degree.
I realize that in accomplishing this thesis, I have acquired guidances, helps, supports and encouragements from many parties. Therefore, I would like to give my gratitude to all of them who have given contributions.
1. The Dean of Faculty of Letters and Fine Arts, Drs. Riyadi Santosa, M.Ed., Ph.D., for approving this thesis
2. The Head of Regular English Department, Prof. Dr. Djatmika, M.A., for giving me permission to write this thesis.
3. Prof. Drs. M.R. Nababan, M.Ed., M.A., Ph.D., my thesis supervisor, thank you for your advices, guidance, and helps. I would like to give my special thanks also for always giving me times to share my problems.
4. Ida Kusuma Dewi S.S., M.A., as my academic supervisor for her assistance during my study. Thank you also for always supporting me.
5. The Head of Academic of IIAM Surakarta, Dwi Liestyaningrum, S.T., thank you for helping me to get the Flight Attendant Manual and also thank you for your prayer.
commit to user
viii
7. My beloved parents. Thank you for always giving me support and praying for me during my study. Thank you for the love that you always give to me. 8. My beloved brother and sister. Thank you for always supporting me and
praying for me.
9. My sweetheart. Thank you for always giving me support and spirit to finish my study and also for being the one who always loves and cares for me. 10.All of the informants. Thank you for helping me during my research.
11.Lois Rosiana, Heigy Lingga, and Aditya Mewengkang. Thank you for helping me during my research and also praying for me.
12.All Members of Gerakan Pemuda GPIB Penabur Solo. Thank you for always supporting and praying for me during my research.
13.All Members of ED 07. Thank you for every beautiful moment we’ve shared. Thank you for always supporting me.
commit to user
ix
TABLE OF CONTENT
Approval of The Thesis Supervisor ………... ii
Approval of The Board of Examiners ………... iii
Pronouncement ……….. iv
Motto ……….. v
Dedication ……….. vi
Acknowledgement ………. vii
Table of Content ……… ix
List of Tables ………. xii
Abstract ……….. xiii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Research Background ... 1
B. Research Limitation ... 6
C. Problems Statements... 6
D. Research Objectives ... 6
E. Research Benefits ... 7
F. Thesis Organization ... 7
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW A. Definition of Translation ... 9
B. Problems in Translation ……… 9
C. Translation Techniques ... 12
commit to user
F. Research Procedures ... 26
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS A. Introduction……. ... 28
1.6 Established equivalence ... 39
1.7 Reduction ... 42
1.8 Transposition……... 44
1.9 Literal Translation ... 51
2. Translation Quality ………. ... 53
2.1 Accuracy ... 54
2.1.1 Accurate Translation ... 54
2.1.2 Less Accurate Translation ... 57
2.2 Acceptability ... 59
2.2.1 Acceptable Translation ... 59
commit to user
xi
2.3 Readability ... 62
2.3.1 Readable Translation ... 63
2.3.2 Less Readable Translation ... 64
C. Discussion ... 66
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS A. Conclusions ... 74
B. Recommendations ... 74
BIBLIOGRAPHY
commit to user
xii
LIST OF TABLES
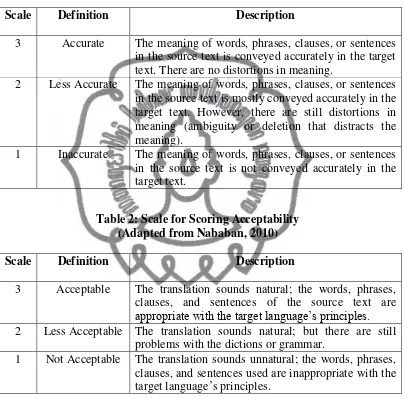
Table 1: Scale for Scoring Accuracy ……… 24
Table 2: Scale for Scoring Acceptability ……….. 24
Table 3: Scale for Scoring Readability ………. 24
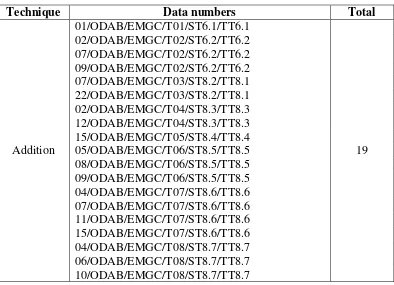
Table 4: Addition Technique ……… 30
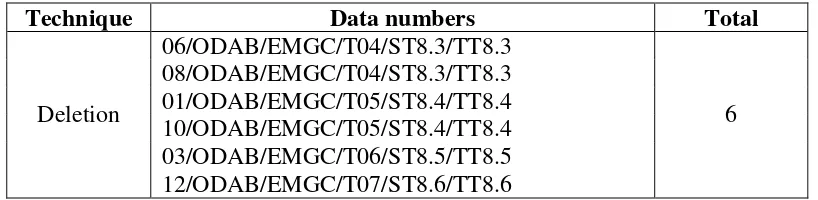
Table 5: Deletion Technique ………. 32
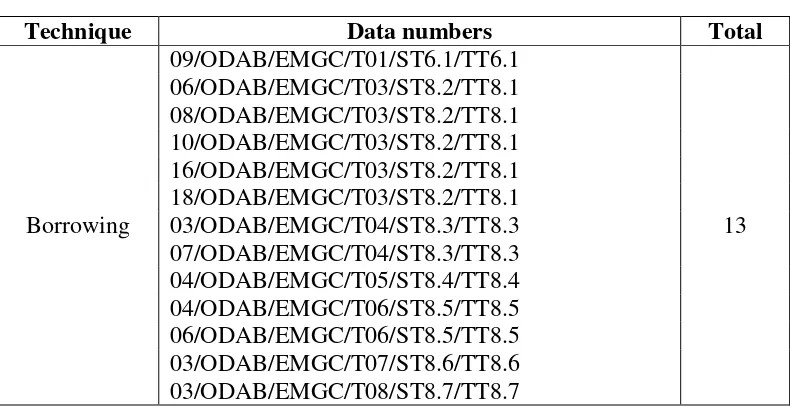
Table 6: Borrowing Technique ……… 34
Table 7: Amplification Technique ……… 36
Table 8: Modulation Technique ………... 38
Table 9: Established Equivalence Technique ………... 40
Table 10: Reduction Technique ……… 42
Table 11: Transposition Technique ……….. 45
Table 12: Literal Translation Technique ……….. 52
Table 13: Translation Techniques ………. 53
Table 14: The Result of Accuracy Assessment ……… 54
Table 15: The Result of Acceptability Assessment ……….. 59
Table 16: The Result of Readability Assessment ………. 62
commit to user
xiii ABSTRACT
Gerry Agustino C0307028. 2011. An Analysis of Translation Techniques and Translation Quality of Flight Attendant Manual. Thesis: English Department. Faculty of Letters and Fine Arts. Sebelas Maret University.
This research focuses on the analysis of translation techniques and translation quality of Flight Attendant Manual in terms of accuracy, acceptability, and readability. The source of data in this research is the Flight Attendant Manual entitled Operation Directorate Announcement Book. The objectives of this research are to find out the translation techniques applied by the translator in translating the Flight Attendant Manual and to know the impact of translation techniques applied by the translator toward the translation quality of the Flight Attendant Manual.
This research applied descriptive-qualitative method. The data were obtained by using content analysis and questionnaire. This research also used purposive sampling technique. This reseach only selected the emergency announcement as the data since this announcement is more important and influential compared to the other announcement in Flight Attendant Manual. The other data were the results of the translation quality assessments done by the informants. The translation techniques were analyzed in the level of micro unit, i.e. words, phrases, clauses, and sentences. Meanwhile, the translation quality was identified in the level of text.
The research findings show that the translator applies 9 types of translation techniques. They are: (1) addition, (2) deletion, (3) borrowing, (4) established equivalence, (5) literal translation, (6) reduction, (7) modulation, (8) amplification and (9) transposition. The results of the questionnaires show that the translation of Flight Attendant Manual is less accurate, less acceptable, and less readable.
An Analysis of Translation Techniques and Translation Quality of Flight Attendant Manual
Gerry Agustino1
Prof. Drs. M.R. Nababan, M.Ed., M.A., Ph.D.2
ABSTRACT
2011. Thesis: English Department. Faculty of Letters and Fine Arts. Sebelas Maret University.
This research focuses on the analysis of translation techniques and translation quality of Flight Attendant Manual in terms of accuracy, acceptability, and readability. The source of data in this research is the Flight Attendant Manual entitled Operation Directorate Announcement Book. The objectives of this research are to find out the translation techniques applied by the translator in translating the Flight Attendant Manual and to know the impact of translation techniques applied by the translator toward the translation quality of the Flight Attendant Manual.
This research applied descriptive-qualitative method. The data were obtained by using content analysis and questionnaire. This research also used purposive sampling technique. This reseach only selected the emergency announcement as the data since this announcement is more important and influential compared to the other announcement in Flight Attendant Manual. The other data were the results of the translation quality assessments done by the informants. The translation techniques were analyzed in the level of micro unit, i.e. words, phrases, clauses, and sentences. Meanwhile, the translation quality was identified in the level of text.
The research findings show that the translator applies 9 types of translation techniques. They are: (1) addition, (2) deletion, (3) borrowing, (4) established equivalence, (5) literal translation, (6) reduction, (7) modulation, (8) amplification and (9) transposition.
1
Mahasiswa Jurusan Sastra Inggris dengan NIM C0307028 2
Dosen Pembimbing
The results of the questionnaires show that the translation of Flight Attendant Manual is less accurate, less acceptable, and less readable.
commit to user
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Research Background
In human’s life, it is certain that language is a very important thing for human to live. It has a function as communication media for human beings. It is impossible for people to communicate without language because they will get problems in expressing their feelings, ideas, and thought. Samsuri in his book
Analisa Bahasa concerns this fact by saying that “Bahasa tidak terpisahkan dari manusia dan mengikuti dalam setiap pekerjaannya.” (1985:4). The statement describes that language is very useful and important for human’s life because people always use it every time and everywhere.
People must be able to use language as their communication media properly and correctly in order to communicate well. Along with the development of science and technology, people also try to develop themselves in many things. One of the evidences is the development of language. Language develops from time to time due to the development of human’s life.
In this globalization era, English has developed into international language not only in education and social life, but also in job. For instance, Indonesian people have started to teach English to children since they are in kindergarten or even playgroup. They realize that it is important to teach English to children because they will need it when they are adult and ready to work. The development
commit to user
of language also gives a great impact to some jobs in Indonesia. Some jobs in Indonesia are becoming internationally based, such as in aviation.
In aviation, a flight attendant should be able to communicate with the passengers both in English and Indonesia very well. Being a flight attendant is quite difficult because the job requires the best service which means no mistakes that can make inconvenience for the passengers. However, it is not easy for a flight attendant to do the entire job perfectly at anytime due to the human imperfection factors.
In order to minimize the mistake that might be conducted by a flight attendant, IIAM (Inti Ilmu Aviasi dan Manajemen), one of the best flight attendant school in Solo, has used Flight Attendant Manual, an announcement book for flight attendant when serving passengers on board. The book contains announcements that have to be explained by flight attendant to the passengers. The announcements are both written in English and Indonesia, considering that the passengers are not only Indonesian people but also some foreigners. Therefore, translation activities are badly needed. Translation does not only deal with the transfer of words from source language into target language, but also deal with the transfer of message from source language into target language. In this case, a translator has a great role as the bridge that link the author to the readers in transferring the message.
commit to user
In the process of translation, a translator will find some problems in transferring the message from source language into target language accurately. Translator should apply translation techniques in order to overcome these problems. Lorscher in Maharani (2006:2) defines translation technique as a global procedure that consists of a series of minimal problem–solving steps which the translator employs in making certain consideration about the text. It is necessary for a translator to decide which translation technique should be applied in transferring the message in order to produce an accurate, acceptable, and readable translation product.
The following examples show some translation qualities that are influenced by translation technique used by the translator.
Example 1:
ST: We have just executed an emergency descent caused by a rapid decompression in the cabin.
TT: Baru saja kita melakukan penurunan ketinggian secara darurat karena
terjadi dekompresi yang mendadak pada tekanan kabin pesawat ini.
commit to user
in order to make the translation more accurate because these words are quite common for the passengers and they can easily understand it.
Example 2:
ST: The fog coming out from the conditioning system is caused by condensation process the cabin airconditioning.
TT: Kalau saat ini anda melihat banyak kabut di dalam kabin pesawat ini, hal
ini disebabkan oleh proses kondensasi udara.
The example above is an emergency announcement telling the passengers that the fog coming out from the conditioning system is caused by condensation process of the cabin air conditioning. The source text in the example consists of one sentence, but the translator then transposes the sentence into two clauses. It can be seen that the translator wants to make the translation more readable and easy to understand by transposing the source text into two clauses and the message are still the same. This example is accurate because the messages are transferred well, but there are some mistakes in the source text. The word
airconditioning in the source text should be given a space, likes air conditioning. The other mistake in the source text is about the grammar. The words
condensation process the cabin airconditioning should be revised into
commit to user
According to the phenomena, the researcher is interested in examining the translation techniques and the translation quality of the Flight Attendant Manual in terms of accuracy, acceptability, and readability because almost all of airlines have an international standard today, which mean that they apply English in everything and it requires them to provide the information both in English and Indonesian very well. The researcher chooses to examine both translation quality and translation techniques because those two things are related each other. It means that the translation techniques influence the translation quality of the product. The use of precise techniques will produce a high quality of translation product. The Flight Attendant Manual contains announcements about flight operations and instructions in serving the passengers on the plane. The researcher chooses the Flight Attendant Manual as the data because the announcements and instructions in the manual text are very important for the flight attendant. The flight attendant must be able to explain all of the announcements and instructions to the passengers very well. This condition requires the translator of the Flight Attendant Manual to be able to transfer the message accurately due to the content of the Flight Attendant Manual is very important for the flight attendant.
In this case, the role of message transfer ability is very important. The original message should be transferred accurately to the target language in terms
commit to user
B. Research Limitation
The researcher only analyzed the translation techniques and translation quality of the Flight Attendant Manual. The analysis of translation quality dealt with readability, acceptability, and accuracy of the translation product.
C. Problem Statements
According to the research background, the researcher raised two problems. The problems are these below:
1. What translation techniques are used by the translator to translate the Flight Attendant Manual?
2. How is the impact of the translation techniques applied by the translator toward the translation quality of the Flight Attendant Manual in terms of accuracy, acceptability, and readability?
D. Research Objectives
The research was aimed:
1. To find out the translation techniques used by the translator to translate the Flight Attendant Manual.
commit to user
E Research Benefits
This thesis was expected to have some benefits for: 1. English Department Students
The results of the research can be used as additional reference for the English Department students, especially students who take translation subject.
2. Lecturers
The results of the research can give more information about the application of English in aviation, especially in flight attendant, for the lecturers and also can be used as additional reference in order to increase the quality of a translation.
3. Students of IIAM (Ilmu Inti Aviasi dan Manajemen)
The results of the research can be used as additional reference for the students of IIAM.
4. Translator of Flight Attendant Manual
The results of this research can help the translator to evaluate the quality of the product in terms of accuracy, acceptability, and readability.
F. Thesis Organization
The thesis consists of five chapters organized as follows:
commit to user
Chapter II is LITERATURE REVIEW. It consists of Definitions of Translation, Problems in Translation, Translation Techniques, and Translation Quality Assessment.
Chapter III is RESEARCH METHODOLOGY. It consists of Research Type and Design, Data and Sources of Data, Sampling Technique, Method of Data Collection, Technique of Data Analysis, and Research Procedures.
Chapter IV is RESEARCH FINDINGS. It consists of Introduction, Analysis, and Discussion.
commit to user
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
A. Definitions of Translation
Translation has so many definitions which are described by the experts. Newmark (1988: 28) states “Translation is rendering the meaning of a text into another language in the way that the author intended the text”. Simplify, Larson
defines that, “Translation consists of transferring the meaning of the source
language in the receptor language.” (1984:3). Catford in his book Linguistic
Theory of Translation says, “Translation is the replacement of textual material in
one language by equivalent textual material in another language.” (1965:20). Bell
(1991:6) states, “Translation is the replacement of a representation of a text in one
language by a representation of an equivalent text in a second language.” All of the definitions about translation are correct and they are completing each other. According to all of the definitions, it can be concluded that translation is about transferring message from source language into target language.
B. Problems in Translation
In translating a text, a translator often meets problems dealing with transferring the message or meaning from source language into target language. Nababan (1999:54-55) in his book Teori Menerjemahkan Bahasa Inggris states,
“…kesulitan-kesulitan yang kerap timbul dalam praktek menerjemahkan, yang
commit to user
disebabkan oleh beberapa faktor, seperti perbedaan sistem bahasa sumber
dengan sistem bahasa sasaran, kompleksitas semantik dan stilistik bahasa
sumber dan bahasa sasaran, perbedaan tingkat kemampuan penerjemah dan
tingkat kualitas tulisan bahasa sumber.” It can be seen that the problems in translation have something to do with the different system of the source language and target language, the semantics and stylistics complexity, quality of the source text, and the translator’s competence. The following are some explanations about the factors above:
1. The different systems of the source language and target language
The different systems between the source language and target language are one of the factors that cause problems of translation. It cannot be denied that every language in the world has a different system, either in terms of syntactical, lexical, or morphological structure. A further explanation about the different systems of the source language and target language is given by Nababan, “…kenyataan
bahwa tidak ada satu pun bahasa yang mempunyai sistem yang sama, baik
ditinjau dari sudut struktur sintaksis, leksikal, dan morfem.” (1999:55). One of
the examples is the English system of language. English has an agreement to refer
plural noun by adding “s” such as books, but there is no agreement like that in
Indonesian language.
2. The semantics and stylistics complexity
commit to user
equivalence with another language, such as Sekaten in Javanese. This word is a social cultural terms and it will be difficult for the translator to translate it into English since there is no such social culture in the England.
Stylistics complexity is also one of the factors that make the translator difficult in transferring the message. A brief explanation about stylistics complexity is given by Nababan, “Karena budaya bahasa sumber dan budaya
sasaran berbeda satu sama lain, gaya bahasa yang digunakan oleh kedua bahasa
itu tentu saja berbeda.” (1999:59). One of the examples is literature texts, such as
prose, poem, and drama which are expressed in their own style. They are different from the style of scientific texts.
3. The quality of the source text
The low quality of the source text could also make a problem in translation. The quality of the source text defines as low due to many mistakes like wrong grammar, ambiguous sentences, poor coherency within sentences or paragraph, miss punctuation, and etc. Nababan explains, “Pesan yang terkandung
dalam bahasa sumber akan sulit ditangkap atau dipahami apabila kualitas teks
tersebut tidak baik, seperti gramatikalnya tidak benar, kalimatnya taksa,
pengungkapan idenya tidak runtut, banyak kesalahan ejaan dan fungtuasi, dan
lain sebagainya.” (1999:60).
4. The translator’s competence
commit to user
different. Nababan describes, “…si penerjemah adalah pelaku utama dalam
proses penerjemahan, tingkat kemampuannya menjadi faktor penentu berhasil
tidaknya penerjemahan itu dilakukan.” (1999:59-60). The more higher the
competence mastered by a translator, the more easier the translator solves the problems in translation. In contrast, a beginner translator, which has limited competence and experience, will get many problems in translating a text. A good translator requires more than just able or have knowledge of languages. A good translator should have language competence, cultural competence, subject competence, textual competence, transfer competence and sufficient experiences in translating practice.
C. Translation Techniques
Nababan in his paper Teknik-Teknik Penerjemahan Teks defines translation techniques by saying, “Tehnik penerjemahan merupakan prosedur untuk menganalisa dan mengklasifikasikan bagaimana kesepadanan terjemahan
berlangsung dan dapat diterapkan pada berbagai satuan lingual, misalnya,
kalimat, klausa, frasa dan/atau kata.” Molina and Albir (as cited in Ikke, 2011)
defines translation techniques as procedures to analyse and classify how translation equivalence works. There are many translation techniques explained by experts. Nababan (2010:6-10) in his paper Tehnik-Tehnik Penerjemahan Teks
commit to user
1. Borrowing
In this technique, the translator borrows some words or idiom from source language. There are two kind of borrowing, pure borrowing and naturalized borrowing.
For example:
- Pure borrowing - Naturalized borrowing
SL: Flashdisk SL: Computer
TL: Flashdisk TL: Komputer
2. Calque
In this technique, the translator translates the phrase in source language literally.
For example:
SL: Secretariat general TL: Sekretaris jendral
3. Literal translation
In this technique, the translator translates the source language word by word.
For example: SL: I go to airport.
TL: Saya pergi ke bandara.
4. Transposition
commit to user
For example: SL: Observable
TL: Yang dapat diamati
In this research, the researcher only emphasizes on transposition which is explained by Catford (cited in Venutti, 2002:143) since the discussion of transposition theory are very wide. Catford calls it as “category shift”. It includes class shift (shift of word classes), unit or rank shift (shift of units), and intra system shift (shifting from singular to plural and vice versa). Meanwhile, the researcher does not include structural shift, which is actually also one type of category shift, because the difference of language structures between English and Indonesian would automatically cause structural adjustments in translation.
5. Adaptation
In this technique, the translator replaces the element of source language culture with the same element in the target language culture, and the target language is familiar to the target readers.
For example:
SL: As white as snow TL: Seputih kapas
6. Amplification
In this technique, the translator paraphrases implicit information in source language.
commit to user
TL: Month of fasting for Moslem
7. Established equivalent
In this technique, the translator uses a specific terms or idiom that is familiar for people in a society.
For example: SL: Cabin TL: Kabin
In the example, the word kabin is understandable than ruangan pesawat
because people in aviation are familiar with the word kabin. 8. Generalization
In this technique, the translator uses a neutral or general terminology in target language (from subordinate to super ordinate).
For example: SL: Penthouse TL: Tempat tinggal
9. Particularization
In this technique, the translator uses more concrete or precision terms. This technique is the opposite of generalization technique.
For example:
SL: Air transportation TL: Helikopter
10.Modulation
commit to user
For example: SL: I cut my finger TL: Jariku tersayat
11.Reduction
This technique is the opposite of amplification technique. In this technique, the information in source text is partially omitted in target text.
For example:
SL: He is very smart TL: Dia itu pandai
12.Deletion
In this technique, the translator deletes the word or information in the source language. Both deletion and reduction techniques are omitting some words, but there is a difference between deletion and reduction. Deletion technique omits the whole information, while the reduction only omits the information partially.
For example:
SL: He is very smart and handsome. TL: Laki-laki itu sangat pintar
13.Addition
In this technique, the translator adds more information to clarify the concept in source language to the target readers.
For example:
SL: He came late to the party
commit to user
14.Variation
In this technique, the translator changes the linguistic or paralinguistic elements which affect the linguistic variation such as dialect, language style, etc.
For example:
SL: I don’t care what you are talking about
TL: Gue nggak peduli elu ngomong apa
D. Translation Quality Assessment
A good translation has to transfer the message from source language to target language very well. The readers sometimes only read the translation product without paying attention to the translation quality. Translation quality assessment is very important for translation product. Translation quality assessment is an activity to give value to a translation product whether the product is having good quality or not. Assessing or criticizing a translation is not an easy matter because it needs an extraordinary ability (Nababan, 2003). The translation product is not always good. Sometimes there are many mistakes in the translation product when it is compared to the original one. Assessment towards translation quality focuses in three things namely accuracy, acceptability, and readability.
1. Accuracy
commit to user
message in source language should be conveyed to the target language correctly and also easy to be understood by the readers.
Sadtono (1985: 9) also explains that a translator should maintain the meaning of a text. He states that a translator should attempt to produce translation which has the same meaning as the source text. He explains further that the most important thing in translating a text is how the message is expressed in target
language, not how to maintain source text’s original form.
Based on the statement above, it can be seen that the maintenance of meaning is a very important aspect in translation. Therefore, a translator must be able to maintain the meaning or message of the source text. The translator has to transfer the message in a thorough and faithful manner, giving consideration to linguistic variations in both languages. Besides, the translator has to make sure that the readers understand what is meant by the original writer.
The translators also must have ability to provide accurate information because the accuracy aspect also related to the readers understanding and affect to readers expectation.
2. Acceptability
commit to user
3. Readability
A translation is produced to be read by the target reader. Readability deals with how natural and easy a translation can be read by the target readers. Nababan (1999: 61) states that readability is important in translation because translation cannot be separated from reading activity. Therefore, a translator should consider this aspect in translating a text. Readability influences the readers’ understanding of the content of a translation.
commit to user
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Research Type and Design
In the research, the researcher uses a descriptive qualitative method. It means that the researcher only collected, classified, and analyzed the data and then drew conclusion according to the analysis without making generalization. Sutopo explains about descriptive qualitative research by saying that “Penelitian kualitatif melibatkan kegiatan ontologis. Data yang dikumpulkan berupa
kata-kata, kalimat atau gambar yang memiliki arti lebih daripada sekedar angka atau
frekuensi.” (2002:35). According to the explanation, it can be seen that the data are collected in the form of words or sentences.
This research only focused on certain characteristics of the data that was the analysis of translation techniques and translation quality of the Flight Attendant Manual. In this case, it can be seen that the researcher also employed a single-embedded case study. Sutopo adds an explanation about single-embedded case study by saying that “Suatu penelitian disebut sebagai studi kasus tunggal, bilamana penelitian tersebut terarah pada satu karakteristik.” (2002:112).
B. Data and Source of Data
Source of data is a subject that is used in the research to obtain the data. Afterwards, the data are analyzed in order to draw conclusion. The language units
commit to user
in this research are texts. As stated by Sutopo (2002:50-54) that source of the data in qualitative research can be informant, event, place, and document, the researcher uses various sources of data in this research. The sources of the data in this research are these below:
1. Document
In this research, the researcher uses documents as a written source of data. Documents contain notes and records that are related to the problems of the research. The documents used in this research as source of data are the Flight Attendant Manual. From the Flight Attendant Manual, then the researcher collects the data. The data are the emergency announcements.
2. Informants
In this research, the researcher involves informants in order to assess the quality of translation product. The informants consist of three raters and three respondents who have an important role in providing data about translation qualities; in terms of accuracy, acceptability, and readability.
The researcher involves three raters in this research. The three raters are asked to assess the accuracy and acceptability of the translation. In this case, they must be people who experts in translation because they have an important role in determining the equivalence between source language and target language.
Dealing with this, Sutopo states, “Dalam penelitian kualitatif posisi sumber data
manusia (nara sumber) sangat penting perannya sebagai individu yang memiliki
informasi.” (2002:50). It can be seen that the researcher and the raters have the
same role in determining the source text and target text.
commit to user
Mastering both languages, English and Indonesian.
Having knowledge of translation.
Having practical experiences in translation.
Understanding the announcements in aviation.
Willing to participate in this research.
In this research, the researcher also uses three respondents. Unlike raters, the respondents are the people who do not have access to the source text. The respondents have a role in determining the quality of the translation product in terms of readability. The respondents used in this research were people who have an experience in travelling by using plane, mastering Indonesian language and willing to take part in this research.
C. Sampling Technique
commit to user
dipandang lebih mampu menangkap kelengkapan dan kedalaman data di dalam
menghadapai realitas yang tidak tunggal.” (2002:36). In purposive sampling
technique, the researcher also tends to choose informants who have experience with the central phenomenon and knows the information about the problems deeply. The informants must also be reliable as the valid source of data.
D. Method of Data Collection
In collecting the data, the researcher applied two methods. The methods were content analysis and questionnaire. Content analysis helped the researcher findings the translation techniques. The researcher analyzed the translation techniques used in the Flight Attendant Manual and then gave numbers for each datum. The researcher classified all of the translation techniques and finally drew conclusions.
commit to user
acceptability, accuracy, and readability of the translation based on the scales determined by the researcher. The following scales are the scoring scales of the quality assessment.
Table 1: Scale for Scoring Accuracy (Adapted from Nababan, 2010)
Scale Definition Description
3 Accurate The meaning of words, phrases, clauses, or sentences in the source text is conveyed accurately in the target text. There are no distortions in meaning.
2 Less Accurate The meaning of words, phrases, clauses, or sentences in the source text is mostly conveyed accurately in the target text. However, there are still distortions in meaning (ambiguity or deletion that distracts the meaning).
1 Inaccurate The meaning of words, phrases, clauses, or sentences in the source text is not conveyed accurately in the target text.
Table 2: Scale for Scoring Acceptability (Adapted from Nababan, 2010) problems with the dictions or grammar.
1 Not Acceptable The translation sounds unnatural; the words, phrases, clauses, and sentences used are inappropriate with the target language’s principles.
Table 3: Scale for Scoring Readability (Nababan, 2010)
Scale Definition Description
3 Readable The translation is very easy to understand.
2 Less Readable The translation is quite easy to understand; the readers need to read some parts more than once in order to understand the translation.
commit to user
After gathering data from the informants, the researcher calculated the results and categorized it into three types for each criterion. The categories of translation quality are composed as follows:
1. Accuracy
Category A = accurate (with mean score 2,66 - 3,0)
Category B = less accurate (with range mean score 1,34 – 2,65) Category C = inaccurate (with mean score 1,0 – 1,33)
2. Acceptability
Category A = acceptable (with mean score 2,66 - 3,0)
Category B = less acceptable (with range mean score 1,34 – 2,65) Category C = not acceptable (with mean score 1,0 – 1,33)
3. Readability
Category A = readable (with mean score 2,66 - 3,0)
Category B = less readable (with range mean score 1,34 – 2,65) Category C = not readable (with mean score 1,0 – 1,33)
E. Technique of Data Analysis
The obtained data were analyzed as follows:
commit to user
Flight Attendant manual. After the analysis was done, the researcher made classification based on translation techniques.
2) Second, the collected data were observed and compared between the original messages with the translation version. Then, the researcher asked the informants to analyze the quality of the translation in terms of accuracy, readability, and acceptability. After the analysis was accomplished, the researcher made classification based on the quality assessment of the translation.
3) After the researcher had finished analyzing all the data, the next step was counting the percentage of each classification.
4) Finally, the researcher drew the conclusion of the results of the analysis. Before the researcher made a conclusion based on what have been found in analyzing the data, the researcher asked the thesis advisor to check the conclusion which has been made.
F. Research Procedures
This research was conducted in the following procedures below: 1) Determining the manual text wanted to be analyzed.
2) Reading the manual text that has been decided and its translation. 3) Collecting the data from the Flight Attendant Manual.
4) Numbering the data obtained from the Flight Attendant Manual. The code of the data is composed as follows:
commit to user
01 : data number 1
ODAB : Operation Directorate Announcement Book (The name of the book from which the data are taken.)
T01 : text number (announcement text number 1) ST6.1 : the text is taken from the source text, page 6.1 TT6.2 : the text is taken from the target text, page 6.2
5) Distributing the questionnaire to the informants in order to assess the quality of translation in terms of accuracy, acceptability, and readability. 6) Analyzing the translation techniques which occurred in the translation of
the manual text.
7) Classifying the results of the data analysis into some classifications. The data was calculated in order to get the percentage and then the results were put in tables.
commit to user
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS
A. Introduction
This research is conducted to analyze the translation quality and translation techniques of Flight Attendant Manual. This chapter consists of three main parts. The first part is introduction, which provides description of what would be analyzed. The second one is analysis, which provides the analysis of both translation techniques applied by the translator and the quality of the translation in terms of accuracy, acceptability, and readability. The last part is discussion, which discusses about the impact of translation techniques toward the quality of translation. Based on the problem statements in chapter I, there are two questions that this research attempts to answer.
1. What translation techniques are used by the translator to translate the Flight Attendant Manual?
2. How is the impact of the translation techniques applied by the translator toward the translation quality of the Flight Attendant Manual in terms of accuracy, acceptability, and readability?
First, the analysis deals with the techniques used by the translator in translating the Flight Attendant Manual. Then, the last analysis will be about the quality of the translation in terms of accuracy, acceptability, and readability. The quality of translation will describe the data finding based on the questionnaires distributed to informants.
commit to user
B. Analysis
1. Translation Techniques
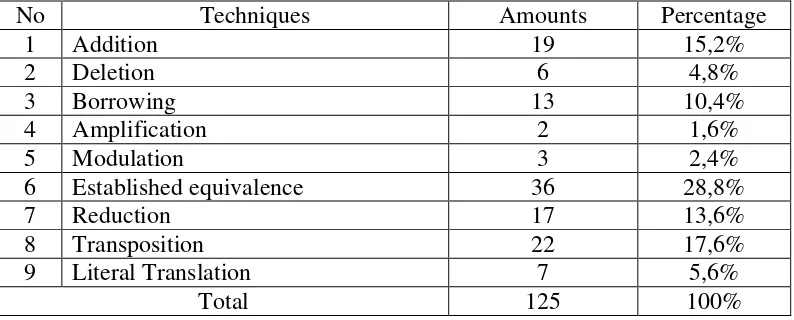
In transferring the message of a text from source language into target language, a translator needs some translation techniques in order to produce a good quality of translation. In this research, the researcher uses the theory of translation technique stated by Nababan in his paper Teknik-Teknik Penerjemahan Teks to analyze the data. The researcher decides to use this theory because the researcher considers that the theory is very appropriate for analyzing the data since the data are in the level of macro-unit or text. After analyzing the data, the researcher finds nine translation techniques used by the translator in translating the source text. They are addition, deletion, borrowing, established equivalence, literal translation, reduction, modulation, amplification and transposition or
category shift (Catford’s term). In this analysis, one datum could use one or more
translation techniques.
1.1.Addition
commit to user
Table 4: Addition Technique
Technique Data numbers Total
Addition
The examples of addition technique are as follows: Example 1: 01/ODAB/EMGC/T01/ST6.1/TT6.1 ST: Diversion
TT: Pengalihan Penerbangan
From the example above, it can be seen that there is an addition in the target text. It is Penerbangan. The translator adds Penerbangan to make the translation clear. If the translator does not add this word, it will be confusing for the target readers because they do not know what is being diverted.
Example 2: 22/ODAB/EMGC/T03/ST8.2/TT8.1
commit to user
TT: Segala sesuatu dalam keadaan aman dan terkendali, kami mohon anda untuk tetap tenang.
This example shows that the word aman in the target text was added by the translator in order to emphasize that the condition is already safe and nothing to be worried. This addition information also has a purpose to help the flight attendant as the target reader to make the passengers stay calm and not getting panic although the situation is in emergency.
Example 3: 12/ODAB/EMGC/T04/ST8.3/TT8.3
ST: This is quite normal and harmless; the fog will disappear in a shortwhile. TT: Keadaan ini normal dan tidak berbahaya, dalam beberapa saat lagi kabut
tsb akan hilang dengan sendirinya.
Based on the example above, it can be analyzed that the translator adds
commit to user
1.2.Deletion
In translating text, translators are allowed to delete some words in order to make the translation obvious. If the meaning conveyed in the source text is not very crucial and confuse the reader, translators can delete it as long as the message is still accurate. The data numbers of this technique are in the table below:
Table 5: Deletion Technique
Technique Data numbers Total
Deletion
The examples of deletion technique are as follows: Example 1: 06/ODAB/EMGC/T04/ST8.3/TT8.3
ST: The fog coming out from the conditioning system is caused by condensation process the cabin airconditioning.
TT: Kalau saat ini anda melihat banyak kabut di dalam kabin pesawat ini, hal ini disebabkan oleh proses kondensasi udara.
From the example above, it can be seen that the translator does not translate the words conditioning system in the target text. In this case, the translator deletes the words conditioning system because these words are quite difficult to understand by the reader. Although the translator deletes the words
commit to user
Example 2: 10/ODAB/EMGC/T05/ST8.4/TT8.4
ST: If you need any assistance please do not hesitate to call our flight attendant.
TT: Bagi penumpang yang membutuhkan bantuan silahkan menghubungi awak kabin.
The datum above uses deletion technique since there are some words that are deleted from the source text. The translator deletes the words do not hesitate that can be translated into jangan ragu-ragu. However, the deletion of the words do not hesitate does not make the message of the source text becomes incomplete. The words do not hesitate are not too influential for the readers because the keywords of the information are call our flight attendant. The words
do not hesitate only give such explanation that the passengers are allowed to call the flight attendant directly when they need any assistance.
Example 3: 12/ODAB/EMGC/T07/ST8.6/TT8.6
ST: To improve your safety during evacuation, we kindly request you to stay calm and not to panic. In the meantime, please follow closely instructions given by your flight attendant.
TT: Demi keselamatan anda dan penumpang-penumpang lain, kami harap anda tetap tenang dan tidak panik serta ikutilah petunjuk-petunjuk
commit to user
The datum above shows that the translator uses deletion technique. The decision of the translator in deleting the words during evacuation is not appropriate. The words during evacuation are influential to the message of the text because it contains message that shows the condition when the passengers have to follow the instruction. The deletion of the words during evacuation makes the translation becomes less accurate. It will be much better if the translator translates the words during evacuation to the target text to clarify the target readers that the instructions should be followed by the passengers during evacuation.
1.3.Borrowing
Borrowing is a technique used by the translator in translating a text if there are no words that can define the source language. Borrowing can be pure and naturalized. The data numbers of this technique can be seen in the table below:
Table 6: Borrowing Technique
Technique Data numbers Total
commit to user
The examples of borrowing technique are as follows: Example 1: 09/ODAB/EMGC/T01/ST6.1/TT6.1
ST: We have a very ill passenger onboard who needs emergency medical care, therefore we have to divert our flight to …. the (International) airport of
…. to get immediate assistance.
TT: Karena adanya seorang penumpang yang sakit dan memerlukan perawatan darurat, kami harus mengalihkan penerbangan ini ke bandar
udara (Internasional) …. di …. untuk mendapatkan pertolongan.
From the datum above, it can be seen that the translator uses borrowing (naturalized) in order to find the equivalence of meaning between the text in source language and target language. In the datum above, the word
International is absorbed into Indonesian as Internasional. The Indonesian absorbs this word by changing the middle consonant –t- into –s-.
Example 2: 06/ODAB/EMGC/T03/ST8.2/TT8.1
ST: We have just executed an emergency descent caused by a rapid decompression in the cabin.
TT: Baru saja kita melakukan penurunan ketinggian secara darurat karena terjadi dekompresi yang mendadak pada tekanan kabin pesawat ini.
commit to user
dekompresi. The translator decides to borrow the term because the translator cannot find the equivalence of meaning of the word.
Example 3: 08/ODAB/EMGC/T03/ST8.2/TT8.1
ST: We have just executed an emergency descent caused by a rapid decompression in the cabin.
TT: Baru saja kita melakukan penurunan ketinggian secara darurat karena terjadi dekompresi yang mendadak pada tekanan kabin pesawat ini.
The word cabin in the datum above also shows that the translator uses borrowing (naturalized) technique. In Indonesian, there is no term that refers to the word cabin. In order to solve this problem, the word cabin is absorbed into Indonesian as kabin. The decision of the translator in applying this technique is very appropriate because the word kabin is familiar for the people in aviation, both the flight attendant and the passengers, so people can understand it very well.
1.4.Amplification
In this technique, the translator paraphrases implicit information in source language. The data numbers of this technique can be seen in the table below:
Table 7: Amplification Technique
Technique Data numbers Total
Amplification 03/ODAB/EMGC/T01/ST6.1/TT6.1 2
commit to user
The examples of amplification technique are as follows: Example 1: 03/ODAB/EMGC/T01/ST6.1/TT6.1
ST: Illness
TT: Penumpang Sakit Selama Penerbangan
The datum above shows that the translator applies amplification technique. The word illness is being paraphrased into penumpang sakit selama penerbangan. Actually, the meaning of illness is sakit but the translator tries to see the implicit information from the word illness and then the translator paraphrases it by considering the context (during the flight).
Example 2: 08/ODAB/EMGC/T08/ST8.7/TT8.7
ST: At the moment, emergency equipments are being prepared near the runway just in case we need them.
TT: Saat ini alat-alat darurat telah disiapkan di landasan untuk mencegah
segala kemungkinan.
commit to user
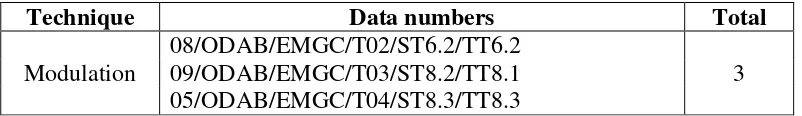
1.5.Modulation
Modulation is a translation technique where the translator changes the point of view, focus or cognitive category in relevance with the source language. The data numbers of this technique are in the table below:
Table 8: Modulation Technique
Technique Data numbers Total
Modulation
08/ODAB/EMGC/T02/ST6.2/TT6.2
3 09/ODAB/EMGC/T03/ST8.2/TT8.1
05/ODAB/EMGC/T04/ST8.3/TT8.3
The examples of modulation technique are as follows: Example 1: 08/ODAB/EMGC/T02/ST6.2/TT6.2
ST: You are kindly requested to stay calm and seated with your seatbelt fastened.
TT: Kami berharap anda tetap tenang dan duduk ditempat masing-masing
dengan mengenakan sabuk pengaman.
commit to user
Example 2: 09/ODAB/EMGC/T03/ST8.2/TT8.1
ST: (Due to oxygen contamination in the cabin you are kindly requested not to smoke until we have landed.)
TT: (Karena banyaknya oksigen di dalam kabin, kami harap anda jangan
merokok sampai pesawat ini mendarat nanti.)
The datum above also uses modulation technique. It is similar to the datum number 08/ODAB/EMGC/T02/ST6.2/TT6.2. The translator changes the focus of the text from you (the passenger) into kami (the flight attendant). The translation is more acceptable and readable because the translator changes the focus of the source text rather than translates it into anda diharap jangan merokok. In other words, the decision of the translator in applying this technique is very appropriate.
1.6.Established equivalence
commit to user
Table 9: Established Equivalence Technique
Technique Data numbers Total
Established
The examples of established equivalence technique are as follows: Example 1: 04/ODAB/EMGC/T01/ST6.1/TT6.1
ST: Ladies and Gentlemen,
commit to user
The datum above applies established equivalence technique. It can be seen from the target text that the translator tends to translate idiom in the source text into Penumpang kami yang terhormat because these words are commonly used by the flight attendant when she wants to announce information to the passengers in the plane.
Example 2: 10/ODAB/EMGC/T06/ST8.5/TT8.5
ST: Please accept our apology for this inconvenience. TT: Kami mohon maaf atas ketidaknyamanan ini.
From the datum above, it can be seen that the translator uses established equivalence technique. The translator tends to translate the source text into Kami mohon maaf atas ketidaknyamanan ini instead of Terimalah permohonan maaf kami atas ketidanyamanan ini because the first version is commonly used by the flight attendant in aviation. It has become such an idiom in aviation. If the translator translates the source text into the second version, the translation will not be acceptable for the passengers.
Example 3: 02/ODAB/EMGC/T08/ST8.7/TT8.7
ST: We have a technical abnormality in our …. system, therefore we have to take a precautionary preparation on landing.
commit to user
The datum above also uses established equivalence technique. It can be seen from the target text that the translator tends to translate the words We have a technical abnormality in our ...system into Karena kelainan tekhnis pada sistem ...pesawat ini. The translator does not translate those words literally into Kita mengalami kelainan teknis pada system pesawat ini because this translation version is not commonly used by the flight attendant on the plane. The flight attendant usually uses the first translation version. It is more acceptable and readable for the passengers on the plane.
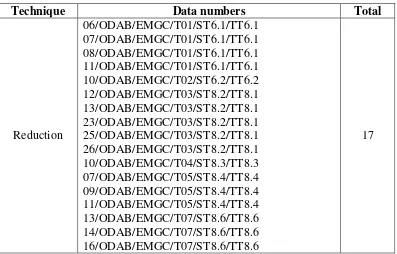
1.7.Reduction
In this technique, the information in source text is partially omitted in target text. The data numbers of this technique are in the table below:
Table 10: Reduction Technique
Technique Data numbers Total
commit to user
The examples of reduction technique are as follows: Example 1: 06/ODAB/EMGC/T01/ST6.1/TT6.1
ST: We have a very ill passenger onboard who needs emergency medical care, therefore we have to divert our flight to …. the (International) airport of
…. to get immediate assistance.
TT: Karena adanya seorang penumpang yang sakit dan memerlukan perawatan darurat, kami harus mengalihkan penerbangan ini ke bandar
udara (Internasional) …. di …. untuk mendapatkan pertolongan.
The datum above shows that the translator uses reduction technique. It can be seen from the word very in the source text. This word is actually explaining the words ill passenger. The complete information is a very ill passenger, but the translator reduces the information by omitting very. It means that the translator deletes the information partially.
Example 2: 10/ODAB/EMGC/T04/ST8.3/TT8.3
ST: This is quite normal and harmless; the fog will disappear in a shortwhile. TT: Keadaan ini normal dan tidak berbahaya, dalam beberapa saat lagi kabut
tsb akan hilang dengan sendirinya.
In the datum above, the word quite is omitted by the translator. In this case, the translator does not delete the whole information because the word quite
commit to user
Example 3: 13/ODAB/EMGC/T07/ST8.6/TT8.6
ST: To improve your safety during evacuation, we kindly request you to stay calm and not to panic. In the meantime, please follow closely instructions given by your flight attendant.
TT: Demi keselamatan anda dan penumpang-penumpang lain, kami harap anda tetap tenang dan tidak panik serta ikutilah petunjuk-petunjuk
keselamatan yang diberikan oleh awak kabin.
It can be seen from the datum above that the translator uses reduction technique. The word kindly in the source text is omitted in the target text. In this case, the translator does not delete the whole information because the word kindly
is explaining the word request, so the translator is only omitting the information partially.
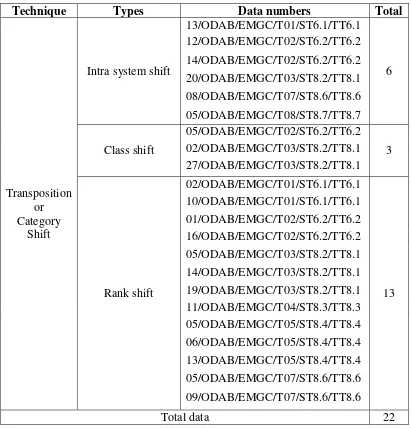
1.8.Transposition
commit to user
language structures between English and Indonesian would automatically cause structural adjustments in translation. In this analysis, the researcher finds that the translator also uses this technique in order to make a qualified translation. The data numbers of this technique can be seen as follows:
Table 11: Transposition Technique
Technique Types Data numbers Total
commit to user
The examples of intra system shift are as follows: Example 1: 12/ODAB/EMGC/T02/ST6.2/TT6.2
ST: Meanwhile please avoid touching or lifting anything until this aircraft has been completely inspected by security officers.
TT: Sementara itu kami mohon anda tidak menyentuh atau mengangkat barang apapun sampai pesawat ini selesai diperiksa oleh petugas
keamanan.
Example 2: 08/ODAB/EMGC/T07/ST8.6/TT8.6 ST: We shall be landing in …. minute(s).
TT: Kita akan mendarat kira-kira dalam waktu …. menit.
In the two examples above, it can be seen that the translator uses intra system shift. The translator changes the plural forms into the singular forms. In the first example, the word officers (plural) is translated into petugas (singular). It also happens in the second example. The word minute(s) (plural) is rendered into
menit (singular).
Example 3: 05/ODAB/EMGC/T08/ST8.7/TT8.7
ST: We have a technical abnormality in our …. system, therefore we have to take a precautionary preparation on landing.
commit to user
In the third example, it can be seen that the translator also applies intra system shift. The words a precautionary preparation in the source text are singular, but the translator decides to translate those words into langkah-langkah pencegahan. The words langkah-langkah pencegahan in the target text are plural. In this case, the translator transposes some words in the source text from singular into plural while in the first and second examples the translator transposes from plural into singular.
The examples of class shift are as follows: Example 1: 02/ODAB/EMGC/T03/ST8.2/TT8.1 ST: Emergency Descent
TT: Menurunkan Ketinggian Secara Darurat
Example 2: 27/ODAB/EMGC/T03/ST8.2/TT8.1
ST: Our flight attendant would be very happy to serve your needs.
TT: Awak kabin akan senang hati membantu apabila anda memerlukan
bantuan.
commit to user
Example 3: 05/ODAB/EMGC/T02/ST6.2/TT6.2
ST: We have just been informed that an explosive may have been placed on this aircraft.
TT: Baru saja kami mendapat informasi bahwa kemungkinan didalam pesawat ini telah dipasang bahan peledak.
In the third example, the word informed in the source text is a verb. The translator tends to translate this word into informasi (noun) rather than translate it into diinformasikan (verb). It can be seen that the translator decides to choose the word informasi (noun) because the translator wants to make the translation more readable. The decision of the translator in applying this technique is very appropriate. In this datum, the translator shifts the word in source text from verb into noun.
The examples of rank or unit shift are as follows: Example 1: 02/ODAB/EMGC/T01/ST6.1/TT6.1 ST: Illness
TT: Penumpang Sakit Selama Penerbangan
Example 2: 16/ODAB/EMGC/T02/ST6.2/TT6.2 ST: We apologize for this inconvenience.
commit to user
In the datum number 03/ODAB/EMGC/T01/ST6.1/TT6.1, the word
Illness is translated by the translator into a phrase Penumpang Sakit Selama Penerbangan. The word Illness in the source text is a noun. In the target text, it can be seen that the translator shifts the word Illness into noun phrase. In the datum number 16/ODAB/EMGC/T02/ST6.2/TT6.2, the translator also transposes word into phrase. The word inconvenience in the source text is a noun. In the target text, the translator shifts the word inconvenience (noun) into kejadian yang tidak menyenangkan (noun phrase). From the two examples, it can be seen that the translator applies this technique in order to make an accurate, readable, and acceptable translation. The researcher considers that the decision of the translator in applying this technique is very precise. In the two examples, it can be seen that the translator applies rank or unit shift from word into phrase.
Example 3: 05/ODAB/EMGC/T07/ST8.6/TT8.6
ST: We regret to announce that due to technical malfunction in our …. system, we are forced to make an emergency landing on (the runway/land/water). TT: Dengan sangat menyesal kami beritahukan bahwa karena adanya
kerusakan tekhnis pada sistem …. pesawat ini, kita terpaksa melakukan
pendaratan darurat di (landasan/daratan/air).
commit to user
this example, the researcher finds that the translator applies unit shift from phrase into word.
Example 4: 05/ODAB/EMGC/T05/ST8.4/TT8.4
ST: Now everything is under control and we request you to stay calm and remain seated then follow the instruction from our flight attendant.
TT: Pada saat ini keadaan sudah dapat dikendalikan. Kami mohon kepada anda untuk tetap tenang dan tetap duduk serta mengikuti arahan awak
kabin kami.
The datum above also shows that the translator applies rank or unit shift. It can be seen that the source text is a compound sentence which contains
two independent clauses joined by a coordinator “and”. The first clause is the
words Now everything is under control. The second clause is the words we request you to stay calm and remain seated then follow the instruction from our
commit to user
researcher finds that the translator uses rank shift from compound sentence into simple sentence.
Example 5: 09/ODAB/EMGC/T07/ST8.6/TT8.6
ST: To improve your safety during evacuation, we kindly request you to stay calm and not to panic. In the meantime, please follow closely instructions given by your flight attendant.
TT: Demi keselamatan anda dan penumpang-penumpang lain, kami harap anda tetap tenang dan tidak panik serta ikutilah petunjuk-petunjuk
keselamatan yang diberikan oleh awak kabin.
In the datum above, the source text consists of two simple sentences, but in the target text the translator transposes those two simple sentences into a compound sentence. In this case, the translator applies rank shift from simple sentence into compound sentence.
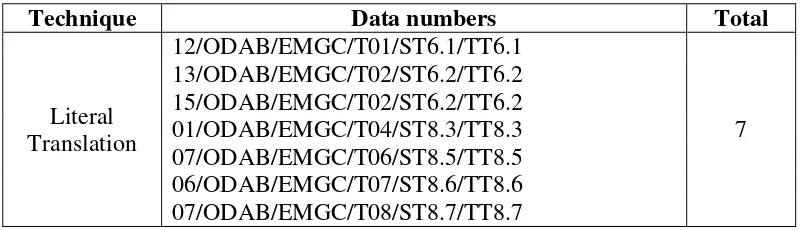
1.9.Literal Translation