AN UNDERGRADUATE THESIS
THE CORRELATION BETWEEN EXTRINSIC MOTIVATION AND THE STUDENTS’ DESCRIPTIVE WRITING ABILITY AT THE SEVENTH GRADE OF MTS MA’ARIF NU 5 SEKAMPUNG
By : SEPTIANA STUDENT ID. 14122137
Tarbiyah and Teacher Training Faculty English Education Department
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES OF METRO
1440 H / 2018 M
THE CORRELATION BETWEEN EXTRINSIC MOTIVATION AND THE STUDENTS’ DESCRIPTIVE WRITING ABILITY AT THE SEVENTH GRADE OF MTS MA’ARIF NU 5 SEKAMPUNG
Presented as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd)
in English Education Department
By:
SEPTIANA
Student Number : 14122137
Sponsor : Dr. Umi Yawisah, M.Hum.
Co-sponsor : Trisna Dinillah Harya, M.Pd.
Tarbiyah and Teachers Training Faculty English Education Department
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES OF METRO
1440 H / 2018 M
ABSTRACT
THE CORRELATION BETWEEN EXTRINSIC MOTIVATION AND THE STUDENTS’ DESCRIPTIVE WRITING ABILITY AT THE SEVENTH GRADE OF MTS MA’ARIF NU 5 SEKAMPUNG
By:
SEPTIANA
Writing is one of four skills that should be mastered by students in learning English. In writing there are several kinds of text such as narrative, descriptive, argumentative, and persuasive. Descriptive text is one of text which has to be mastered by the seventh grade students of the Junior High School. But, there are some problems that faced by the seventh grade students of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung in writing descriptive text. In this research, it focus on the students have low motivation in descriptive writing. Therefore, the writer conducted this research in order to know whatever related the students to get the good score.This research was aimed at detecting the correlation between extrinsic motivation (X) and the students’ descriptive writing ability (Y) at the seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung.
This research is quantitative research. The population of this research was the seventh grade students. A sample of 29 students is established through the purposive sampling technique. The instruments that used in this research are test, that consist of making a descriptive paragraph essay and questionnaire. To analyze the data, the writer used the formulation of Correlation product moment.
The result of this reseacrh shows that Degree of freedom (DF) of this research is 27, the value of correlation product moment was 0,518 and the level of correlation between extrinsic motivation and students’ descriptive writing ability is 26,83%. Then, the data confirmed that “robserved” = 0,518 is higher than “rtable” = 0,381 in 5% and 0,487 in 1%. Therefore, it can be inferred that alternatif hyphothesis (Ha) is accepted there is a positive an sifnificant correlation between extrinsic motivation and the students’ descriptive writing ability at the seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung.
Keywords: Descriptive Writing, Extrinsic Motivation, Writing Ability.
ABSTRAK
HUBUNGAN ANTARA MOTIVASI EKSTRINSIK
DAN KEMAMPUAN SISWA DALAM MENULIS TEKS DESKRIPTIF DI KELAS TUJUH MTS MA’ARIF NU 5 SEKAMPUNG
Oleh:
SEPTIANA
Menulis adalah salah satu dari empat keterampilan berbahasa yang harus dikuasai oleh siswa didalam pembelajaran bahasa inggris. Di dalam menulis terdapat beberapa jenis teks, salah satunya adalah narasi, deskripsi, argumentasi dan persuasi. Teks deskripsi merupakan teks yang harus di kuasai oleh siwa kelas delapan sekolah menengah pertama. Namun, terdapat beberapa masalah yang dihadapi oleh siswa kelas tujuh MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung didalam menulis teks deskripsi. Dalam penelitian ini, fokus pada rendahnya motivasi siswa dalam penulisan deskriptif. Oleh karena itu, penulis melakukan penelitian ini untuk mengetahui apa saja yang dapat mempengaruhi siswa untuk mendapatkan nilai yang bagus. Tujuan utama dari penelitian ini adalah mencari hubungan antara motivasi ekstrinsik (X) dan kemampuan menulis deskriptif siswa (Y) pada kelas VII MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung
Penelitian ini adalah penelitian kuantitatif, populasi dalam penelitian ini adalah siswa kelas VII. Sampel penelitian ini berjumlah 29 siswa, yang ditentukan dengan teknik purposive sampling. Instrumen yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah tes yang terdiri dari membuat sebuah esai deskriptif teks dan angket.
Untuk menganalisis data, peneliti menggunakan rumus korelasi produk momen.
Hasil penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa Degree of Freedom (DF) dari penelitian ini adalah 27, dan nilai korelasi produk momet adalah 0,518 dan level dari hubungan antara motivasi ekstrinsik dan kemampuan menulis siswa adalah 26,83%. Kemudian data konfirmasi yaitu “robserved” = 0,518 lebih tinggi dari
“rtable” = 0,381 pada 5% dan 0,487 pada 1%. Oleh karena itu, dapat disimpulkan bahwa hipotesis yang peneliti ajukan adalah alternatif hipotesis (Ha) di terima dan ada hubungan yang positif dan signifikan terhadap kemampuan menulis deskriptif siswa kelas VII MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung.
Kata Kunci: Karangan Deskriptif, Motivasi Ekstrinsik, Kemampuan Menulis.
v
iv
MOTTO
“Say : O My slaves who have been prodigal to their own hurt! Despair not of the mercy of Allah, Who forgiveth all sins. Lo! He is the Forgiving, the Merciful”
(QS. Az-Zumar : 53)
“A pessimist sees the difficulty in every opportunity; an optimist sees the opportunity in every difficulty.”
(Winston Churchill)
DEDICATION PAGE
I highly dedicated this undergraduate thesis to my gorgeous parents, Mr.Muhammad Arifin and Mrs. Sutimah, to my truly understanding friends, and to those who love me and those whom I love.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Thanks to Allah SWT, the Most Gracious, the Most Merciful, who always teach human being what we didn’t know before and has given us mercies and blessing especially to the writer so that she able to accomplish this undergraduate thesis. Shalawat and salaam be always given to our holy world leader Muhammad SAW, the man of true goodness of everything.
This undergraduate thesis is entitled “The Correlation between Extrinsic Motivation and The Students’ Descriptive Writing Ability at The Seventh Grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung”.
The researcher cannot stay alone, there are many people who contribute their meaningful hands in accomplishing this an undergraduate thesis, so the researcher would like to express her gratitude thanks to :
1. Mrs. Dr. Akla, M.Pd., as the Dean of Tarbiyah and Teacher Training Faculty IAIN Metro.
2. Mr. Ahmad Subhan Roza., M.Pd as the Head of English Education Department.
3. Mrs Dr. Umi Yawisah, M.Hum., as the first advisor,thank you so much for your kindness and valuable knowledge and for your support in finishing this undergraduate thesis.
4. Mrs. Trisna Dinillah Harya,M.Pd., as the second advisor, thank you so much for your kindness and valuable knowledge and for your guidance in finishing this undergraduate thesis.
5. Lectures and Administration Staff of English Education Department.
6. Headmaster, Teacher, staff and students of the MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung, who gives permission to the writer to conduct the research in this school.
7. All of her friends in IAIN Metro, thanks for everything in helping to finish this undergraduate thesis.
8. Mr. Muhammad Arifin and Mrs. Sutimah, as my parent and all of family, thank you so much for your best support, financial and your pray in finishing this undergraduate thesis.
Hopefully, this undergraduate thesis can be a meaningful benefit for the writer especially and for our campus and all readers generally.
Metro, November 2018 The Writer,
SEPTIANA 14122137
TABLE OF CONTENTS
COVER ... i
TITLE ... ii
ABSTRACT ... iii
ABSTRAK ... iv
APPROVAL PAGE ... v
NOTIFICATION PAGE ... vi
NOTA DINAS ... vii
RATIFICATION PAGE ... viii
STATEMENT OF RESEARCH ORIGINALITY ... ix
ORISINALITAS PENELITIAN ... x
MOTTO ... xi
DEDICATION PAGE ... xii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... xiii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... xv
LIST OF TABLES ... xix
LIST OF FIGURES ... xx
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xxi
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of Study ... 1
B. Problem Identification ... 4
C. Problem Limitation ... 5
D. Problem Formulation ... 5
E. Objective and Benefits of the Study ... 5
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF THE RELATED THEORIES ... 7
A. Theoretical Review ... 7
1. Concept of Writing ... 7
a. Definition of Writing ... 7
b. Writing Process ... 9
c. Types of Writing ... 10
2. Concept of Descriptive Writing ... 12
a. Definition of Descriptive Writing ... 12
b. Structure of Descriptive Writing ... 13
c. Language Features of Descriptive Writing ... 14
3. Concept of Extrinsic Motivation ... 14
a. Definition of Extrinsic Motivation ... 14
b. Types of Extrinsic Motivation ... 16
c. Extrinsic Motivational Factors ... 18
d. Advantages of Extrinsic Motivation ... 20
e. Indicators of Extrinsic Motivation ... 21
B. Theoretical Framework and Paradigm ... 22
1. Theoritical Framework ... 22
2. Paradigm ... 24
C. The Correlation of Extrinsic Motivation and The Students’ Descriptive Writing Ability ... 25
D. Hypothesis ... 26
1. Hypothesis Formulation ... 26
2. Statistical Hypothesis ... 26
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD ... 27
A. Research Design ... 27
B. The Operational Definition of Variables ... 28
1. Independent Variable ... 29
2. Dependent Variable ... 30
C. Population and Sampling Technique ... 31
1. Population ... 31
2. Sample ... 31
3. Sampling Technique ... 32
D. Data Collection Method ... 32
1. Test ... 32
2. Questionnare ... 33
3. Observation ... 34
4. Documentation ... 35
E. Research Instrument ... 36
1. Instrument Blue Print ... 36
2. Instrument Calibration ... 39
a. Validity ... 39
b. Reliability ... 47
F. Data Analysis Technique ... 52
CHAPTER IV RESULT OF THE RESEARCH AND INTERPRETATION A. Result of the Research ... 54
1. Description of Research Location ... 54
a. The History of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung ... 54
b. The Conditions of Teachers ... 55
c. The Quantity of Students ... 56
... d. The Organization Structure ... 57
e. The Building Condition and The Sketch ... 58
2. Description of the Research ... 60
a. The Students’ Extrinsic Motivation ... 60
b. Students’ Descriptive Writing Ability ... 63
B. Hypothesis Testing ... 65
C. Interpretation ... 68
1. Interpretation of “robserved” ... 68
2. Statistical Significance ... 68
D. Discussion ... 70
E. Limitation ... 71
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 72
A. Conclusion ... 72
B. Suggestion ... 73
BIBLIOGRAPHIES APPENDICES
CURRICULUM VITAE
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
1. The Data of Pre-Survey Research of Daily Tes 3
2. Criteria of Score 3
3. Instrument Grills 37
4. Instrument Grills of Research Variable 37
5. Questionnare Grills 38
6. The Score of Questionnare Items 38
7. The Result of Questionnaire Items Validity 41 8. The Calculation of Product Moment for Question Number 1 43 9. The Calculation of Product Moment for Question Number 2 44
10. Interpretation Table 46
11. Interpretation of Validity 46
12. List of Total Score Odd Items 48
13. List of Total Score Even Items 49
14. Reliability Test Odd and Even Score Questionnaire 49
15. The Writing Scoring Rubric 51
16. The Principles of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung 54 17. The Data Teachers of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung 55
18. The Students Quantity 57
19. Facilities in MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung 58
20. The Result of Students’ Extrinsic Motivation 61 21. The Frequency Distribution of Sudents’ Extrinsic Motivation Result 62 22. The Result of Students’ Descriptive Writing Ability Test 63 23. The Frequancy Distribution of The Students’ Decriptive Writing
Ability Result 64
24. The Table as the Authentication of the Correlation between
Extrinsic Motivation and the Students’ Descriptive Writing Ability 66 25. Interpretation to the Grade of “robserved” 68 26. The frequency Distribution of Extrinsic Motivation Questionnaire
and students’ Descriptive Writing Ability Test 71
LIST OF FIGURES
Table Page
1. Scheme of Correlation betweem Extrinsic Motivation and
Students’ Descriptive Writing Ability 24
2. The Organization Structure of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung 57 3. The Skecth Location of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung 59
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1 Instruments
Appendix 2 Documentation Picture Appendix 3 Students’ Observation Sheet Appendix 4 Curriculum Vitae
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. Background of Study
English has become an International language, so learning English is very important. Most countries in the world use English as primary language in communication. Every country has different language and culture. It is a reason why English has become International language, because every people can communicate each other. In addition, all of people can know the cultures in other countries. However, English has become the dominant language in many fields of activities in the world like industry, business, sports, and the others. It also has an important role in education field. On the other hand, English is a foreign language in Indonesia. It causes that Indonesian people use English rarely. Incomprehension is one of problems in listening, speaking, reading, and writing of English language. On the contrary, English is taught in some levels of education in Indonesia, like Elementary School, Junior High School, Senior High School and University. A language consists of language skills and language aspects. There are four skills of language, are listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Whereas, language aspects are phonology, structure and vocabulary. Writing is one of language skills that should be mastered by students, because they can show their ideas by written. Thus, writing is important to be learnt as early as possible especially in Junior High School.
Writing is a productive skill in language learning. It is one of four skills that has an importatnt role in teaching English as a foreign language. By writing, the students are able to show the ideas and share the information. The aim of writing is the students can transfer the information for the reader. To produce a good writing, the students must concentrate in the process of expressing their ideas, feeling, and thinking. In Junior High School, there are some texts which have been mastered by the students. One of the texts is descriptive text. Descriptive text is the text that describes about something, such as someone, place, situation, animal, and the others. Actually that descriptive text is a simple text, but there are students finding difficulties when they write this text.
In learning writing, students have some problems. Many students confused what should they write and many students have difficulties to express the ideas although they know about the topic that has been given by the teacher. It indicates that they have low ability in descriptive writing. Then, there are some students do not understand clearly about what the descriptive text is and how to describe person, place, animal, and the others. It causes they are not interest in learning descriptive text. In addition, learning writing is monotonous, so many students feel bored in the classroom. They also have low motivation. Everyday, they only get the explanation about the materials and task. Whereas, the students need to get the motivation in order to they interested in learning writing, especially descriptive writing.
In this case, the writer tried to study about the correlation between extrinsic motivation and the students’ descriptive writing ability that would be conducted at the seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung. The writer had conducted pre survey on April 20th 2017 in MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung. The data of the students’ Descriptive text writing are as follows:
Table 1
The Data of Pre Survey Research of Daily Test at The Seventh Grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung
Category Frequency Percentage
Excellent - -
Good 3 11%
Fair 6 21%
Poor 20 68%
Total 29 100%
Source : The English Teacher archive at Seventh Grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung
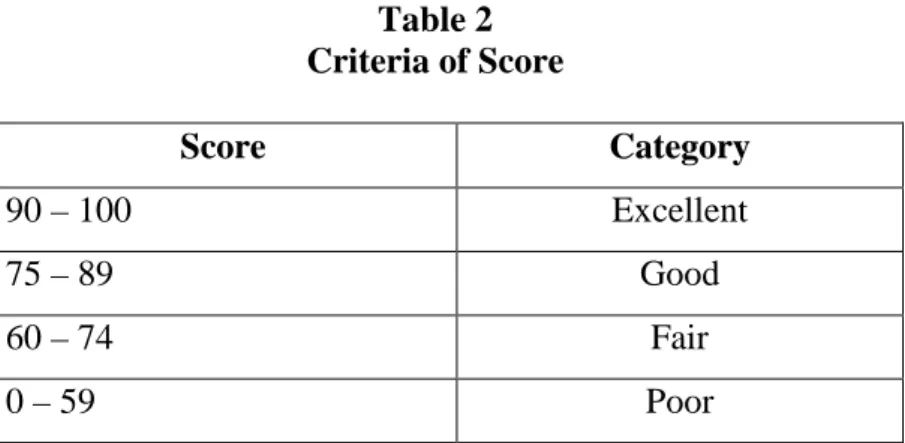
Table 2 Criteria of Score
Score Category
90 – 100 Excellent
75 – 89 Good
60 – 74 Fair
0 – 59 Poor
Source : Ledger of students’ English score at the seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung
(pre survey on April 20th 2017)
Based on the result data of pre-survey above, there are only 3 from 29 students who get good score, 6 students who get fair score, and the sudents who get poor score is 20 students. It is caused many factors, are the students do not have good writing, the students were passive during the learning process.
From the explanation above, the writer concluded that most of students have low ability in writing descriptive text. It is the problem that will be investigated by the writer. Therefore, the writer will conduct this research in order to know whatever related the students to get the good score.
Furthermore, teaching writing is not enough practice to write only.
Motivation is needed in teaching writing, to make the students more interest to learn in the class. By motivation like a reward, indirectly the students will interest to get that reward by studying seriously. Thus the writer wants to know is there any correlation between extrinsic motivation and the students’
descriptive writing ability at the seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung.
B. Problem Identification
Based on the background above, the writer identifies the problems as follows:
1. The students have low ability in writing, especially in descriptive text, 2. The students have difficulties to express their ideas,
3. The students are not interested in writing materials, 4. The students have low motivation in descriptive writing.
C. Problem Limitation
Based on the problems above, the writer limits the problem on the students have low motivation in descriptive writing. It is caused by there is no motivation in teaching learning writing, especially the extrinsic motivation.
Therefore, the writer will use extrinsic motivation on teaching descriptive writing at the seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung in order to the students can be more enthusiast in learning writing.
D. Problem Formulation
Concerning the background of the study, the writer formulates the problem of the study, as follows:
Is there any correlation between the extrinsic motivation and the students’
descriptive writing ability at the seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung?
E. Objective and Benefit of The Study 1. The objective of The Study
The objective of this research is to find out whether there is a correlation between the extrinsic motivation and the students’ descriptive writing ability at seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung.
2. The Benefit of The Study a. For the students
For the students, the writer expects that this study can make the students interest in learning writing and the students will have a good descriptive writing.
b. For the teachers
For the teachers, the writer expects that this study gives useful information in teaching English writing. In addition, the teacher can solve the problem of teaching and learning process by giving the motivation for the students to write descriptive text.
c. For the other researchers
This research can be one of the references for another researcher in English teaching learning process and it is expected to be useful to conduct further researchers.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF THE RELATED THEORIES A. Theoretical Review
This chapter contains the theories which support the research. It includes concept of writing, concept of descriptive writing. Moreover, it elaborates the concept of extrinsic motivation, types of extrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivational factors, advantages of extrinsic motivation and influences of extrinsic motivation in descriptive writing.
1. Concept of Writing a. Definition of Writing
According to Hamed, writing is a reflective activity requiring enough time to think about the specific topic and to analyse and classify any background knowledge. Then, in writing, a suitable language to structure these ideas in the form of a coherent discourse is needed.1 It means that, writing is the ability to show ideas and to transfer the information for the reader. It is a thought process as a medium of communicating writers’ thoughts to them and to others. In addition, Byrne declares that writing is arranging the words to be sentences.2 Developing and modifying the ideas are also needed to arrange the words or sentences. It can make the writing result is good. It same with Nunan and Carter’s opinion. They give an opinion that writing is limited to
1 Abdel Hamid Ahmed, “Students’ Problems with Cohesion and Coherence in EFL Essay Writing in Egypt: Different Perspectives”, in Literacy Information and Computer Education Journal (LICEJ), (copyright ), Volume 1, Issue 4, December 2010, p.211
2 Donn Byrne, Teaching Writing Skills, (New York: Longman, 1993), p.1
structuring sentences or combining sentences, and the result of which looked like a short piece of discourse.3 It is not only combining or arranging the sentences but also requiring concentration to get a good ideas.
Moreover, David Lodge states that writing is a peculiar activity, both easy and difficult. The more thinking about how to do it, the more difficult it becomes. Having an idea, then expressing it as a series of words and writing down on a piece of paper. It is a natural and effortless process.4 The ideas will proceed well if the writer ignore about grammar, punctuation, and spelling. It will proceed effectively. On the other hand, Gayle and Lawrence states that writing is important for the students. The reason is that the students being able to write well and express their thought.5 As we know that, writing has important role in education field.
It causes that the students can develop and explore their knowledge.
Based on the explanation above, the writer concludes that writing is an activity to show the information and the ideas by steps and purposes in written form. It is also to make the reader understand about the writer’s aim.
3 Ronald Carter and David Nunan, The Cambridge Guide to Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2001), p.28
4 David Lodge, How We Write, (London: Routledge, 1999), p.3
5 Gayle Feng & Lawrence, The Write Start Sentences to Paragraphs (4th Edition), (USA:
Wadsworth, 2010), p.1
b. Writing Process
Writing is a creative activity which needs the steps sistematically.
It is also need specific steps in proces of writing. According to Alice and Ann, there are four steps in writing. There are prewriting, organizing, writing, revising and editing.6
1) Prewriting
Prewriting is an essential step in the writing process. It is a way to get the ideas, choose a topic and collect ideas to explain the topic.
This step is the process to expand or narrow focus, and identify or organize ideas.
2) Organizing
This step involve the writer in organizing or drafting the ideas into coherent structure. It is also deciding the ideas. Choosing the idea which to talk about first, which to talk about next, and which to talk about last.
3) Writing
The next step is to write a rough draft, using the outline as a guide. Writing the rough draft as quickly as the writer can without stopping to think about grammar, spelling, or punctuation. Just get the ideas down on paper. The errors probably are seen in the rough draft.
However, it is better for the writer that ignoring these errors and revising it at the end.
6 Alice. O and Ann. H, Introduction to Academic Writing (3rd Ed), (New York: Pearson Education, 2007), p.15
4) Revising and Editing
The last step are revising and editing. In this step, the writer corrects what have written. This step is also called revising and editing. Correcting is most successful if the writer does it in two steps.
First, correcting the content and organization (revising). Then correcting of grammar, punctuation, and mechanics (editing).
Based on the explanation above, the writer can be conclude that many steps needed in writing. The writing process is not always linear. A writer may move back the steps. However, by paying attention process of writing carefully, the writer will get a good result.
c. Types of Writing
Thomas states that there are kinds of writing. There are exposition, description, narration, and persuasion. 7
1) Exposition
Exposition is a type of writing that intended to give information about an issue, subject or idea. In addition, it is also explaining about facts of everyday life, controversial issues laden with feelings, politics, religion. But whatever its subject, exposition reveals what a particular mind thinks or knows or believes. Exposition is constructed logically. It organizes around cause/effect, true/false, positive/negative, general/particular. Its movement is signaled by
7 Thomas S. Kane, The Oxford Essential Guide to Writing, (New York: Berkley Books, 2000), p.6
connectives like therefore, however, and so, besides, but, not only, more important, in fact, and the others.
2) Description
Description is the writing type that has principle purpose to elaborate the characteristic of the object from the object’s appearance that we can looks, smell, and taste. It is about sensory experience how something looks, sounds, taste. Mostly it is about visual experience. It deals with perceptions, most commonly visual perceptions. Its central problem is to arrange what we see into a significant pattern.
3) Narration
Narration is the form of writing used to relate the story of acts or events. Narration places occurrences in time and tells what happened according to natural time sequence. Types of narration include short stories, novels, and news stories, as well as large part of our everyday social interchange in the form of letters and conversation..
4) Persuasion
Persuasion is a type of non-fiction writing used to convince the reader to agree with the writer about an issue. The writer will rely heavily on facts to express their opinion. When using persuasive writing, the writer should never express their personal opinions, but instead ahould use facts to convince the reader to agree with them. In some cases, the writer will present information to the reader about two sides of an argument. This is done to show the reader that they have
thought about both sides and helps the writer shut down any counterargument that the reader may have about the issue. This type of writing style is commonly found in argumentative essays, articles, scripts for commercials and political campaigns, just to name of few.
It can change readers’s think or believe.
2. Concept of Descriptive Writing a. Definition of Descriptive Writing
According to Alice and Ann, descriptive writing appeals to the senses, so it tells how something looks, feels, smells, tastes, and/or sounds. A good descriptive text can make the readers imagine the object in their mind. A description usually follows a pattern of organization that we call spatial order. Spatial order is the arrangement of things in space.8 In short, descriptive writing is used to create sensory details as a means of enhancing the reading experience. If done effectively, the reader will be a draw connection through the use sensory details that include seeing, hearing, smelling, touching, and tasting. From the definition, it can be concluded that descriptive text is kind of writing that explain the detail characteristics of the object.
8 Ibid, Alice. O and Ann. H, p. 61
b. Structure of Descriptive Writing
Descriptive writing has two elements or generic structure, are identification and description.9
1. Identification : it identifies a particular person, place, or thing to be described. The identification can be in the form of definition. As usual, it is written at the beginning of teaxt or paragraph
2. Description : it contains subtopics. It describes parts, qualities, and characteristics os something.
Related to the explanation the generic structure above, the writer has the example of the descriptive text, as follows:
My Best Friend
John is one of my friends in the classroom.
His full name is John Marcell . He has tall body. His tall is about 170 cm. He has straight black hair. He has oval face. He has small eyes and pointed nose. He is kind smart, generous, dilligent, and he always wears black shirtt
Based on the explanation of the descriptive text above, the organization of the text consists of two parts; they are general classification and descriptions. General classification or sometimes called as
9Faisal and Krisna Suwandita, “The Effectiveness of FRESH Technique to Teach Descriptive Paragraph” in Journal of Education and Learning, (Purwokerto: University of Purwokerto Vol.7 (4)/ 2013), p.242..
Identification
Description
identification, introduces the topic being described (my besfriend). In the other hand, descriptions tell the topics more clearly (such as parts and its characteristics).
c. Language Features of Descriptive Writing
There are some language forms of Descriptive as follows:10 1. Using Linking verb or verb of sense as look, smell, taste, see, seem.
2. Using three parameter of sense: visual, auditory, and smell.
3. Using spatial order in which preposition precedes the verb and the subject.
4. Using multiple tenses based on the time: past, present, and future.
3. Concept of Extrinsic Motivation a. Definition of Extrinsic Motivation
According to Jeremy Harmer, extrinsic motivation is the result of some outside factors that influence the need of students to to do an exam, the hope of students to get financial reward or the possibility of students to achieve the future travel.11 On the other hand, Mahadi and Jafari declare that extrinsic motivation is a tendency to do an activities expecting the reward or gift and avoiding the punishment or sanction.12 By extrinsic motivation, the students will be more motivated and interested to do something.
10 Ibid, p.242.
11 Harmer. Jeremy, “The Practice of English Language Teaching, 4th Ed”, (England : Pearson Longman, 2007), p.98.
12 Tengku Sepora T. Mahadi and Moghaddas J. Sepideh, “Motivation. Its Types, and Its Impacts in Language Learning” in International Journal of Bussiness and Social Science, (Malaysia: Universiti Sains Malaysia Volume.3, No. 24, Special Issue / December 2012), p.232.
In other resources, Richard and Edward state that Extrinsic motivation is a concept discussing about an activity which is done to gain some separable outcome.13 For the example, the student afraid if his parents give him a punishment because he doesn’t finish his homework.
In addition, he tries to do his homework because he fears about the punishment. From this example, it is an extrinsic motivation because it can influence the student does homework in order to gain the separable outcome of avoiding punishment. Then, Fen and Kiat explain that motivation coming from the individual outside is extrinsic motivation.
Students are extrinsically got a motivation when learning is done for the sake of rewards such as grades or praise.14 Rewards are often used to control behaviour. This is especially true material rewards such as money and prizes.15 However, Extrinsic motivation is seen as motivation through rewards or factors external to the task. In higher education the external rewards most commonly cited are: the degree obtained, the job it can lead to, or the salary which results from it.16
13 Richard M. Ryan and Edward L. Deci, “Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivations: Classical definitions and New Directions” in Contemporary Educational Psychology, (Rochester: University of Rochester No.25/ 2000), p. 60..
14 Chiew Fen Ng and Poh Kiat Ng, ”A Review of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivations of ESL Learners” in International Journal of Languages, Literature and Linguistics, (Malaysia:
Volume. 1, No. 2, June 2015), p.98.
15 Carol Sansone & Judith M.Harackiewicz, Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation, (USA:
Academic Press, 2000), p.24
16 David Kember, Understanding The Nature of Motivation and Motivating Students through Teaching and Learning in Higher Education, (Australia: Springer, 2016), p.22.
The other experts, Katrina indicates that extrinsic is the activity which is doing for some reasons and getting the advantages.17 In addition, Brown declares that extrinsic motivation is carried out in expectation to get the reward from outside and beyond the self.18 As we know that, reward is the feed to get the students’ motivation. All of the students will mre enthuse to do something when the teacher give the rewards for them.
Based on the definition of some experts above, it can be concluded that the extrinsic motivation is the outside motivation influencing someone to do something to get some advantages or benefits and to avoid the sanctions.
b. Types of Extrinsic Motivation
Richard and Edward state that there are four types of extrinsic motivation. There are external regulation, introjection, identification, and integration. 19
1) External Regulation
External regulation is the type of motivation that occurs when the students participate in an activity only because they feel they have to, or because they may get a reward. Getting the reward is the main goal of the students when they perform this activity.
17 Katrina A. Korb, “Motivation in Education: Beyond Salary, Benefits, and Welfare” In Journal of Educational Foundations, (University of Jos, No 4, 2014), p.2.
18 Brown, H. Douglas. Teaching by Principles Second Editions: An Interactive Approach to Langueage Pedagogy, (New York: Addison Wesley Longman. Inc, 2001), p.76
19 Ibid, Richard M. Ryan and Edward L. Deci, p.61
2) Introjection
It occurs when the students participate in an activity because of various pressures or compulsions. Introjected regulation increases tension and anxiety. Introjection describes a type of internal regulation that is still quite controlling because people perform such actions with the feeling of pressure in order to avoid guilt or anxiety or to attain ego-enhancements or pride. Put differently, introjection represents regulation by contingent self-esteem. A classic form of introjection is ego involvement.
3) Identification
It occurs when the students participate in an activity because the activity is considered of high value and important for them, even if they do not enjoy the activity itself. The differences between identified regulation and integrated regulation, is that the identified regulation is limited to the particular activity itself. For example, going to school or doing the homework because it is a great way to learn about things which may be useful for the students. Here, the person has identified with the personal importance of a behavior and has thus accepted its regulation as his or her own.
4) Integration
It occurs when the students perform the activities to get the benefit different aspects of the activity which is performed by them, rather than the pleasure of participation itself. Integration occurs when
identified regulations have been fully assimilated to the self. This occurs through self-examination and bringing new regulations into congruence with one’s other values and needs.
c. Extrinsic Motivational Factors
According to Linberg and Lundmark extrinsic motivation is influenced by some factors, that are rewards, reputation, and personal need.20
1) Rewards
A tangible reward can be received as a payment in the form of money or prizes, but it can also be a symbolic item or a trophy that shows achievement for the students receive payment or other rewards for a performance it can motivate them to do the task in exchange for the reward. These rewards can be used to control the students’
behavior or strengthen an existing behavior, so the instance that students are given the reward, one can try to motivate the students to do something he otherwise wouldn’t do.
2) Reputation
There are students who chose to act with a certain behavior motivated by the possible gain of reputation, status and respect that one will receive from others when performing that action. When contributing content to programs or communities, some of the creators consider peer recognition as an incentive to contribute. They get an
20 Eric S. Linberg. & Joakim Lundmark, A quantitative study of product development in online communities, (Umea: Umea university, 2015), p.23-29.
ego boost from getting acknowledged by their peers and a desire to get their peers’ approval. Further creating or completing a task can also have the added benefit of getting recognized and approved from a personal authority.
Thus the motivation could come from a students’ desire for both peer and authority figures acknowledging the students’ contribution.
They retrieve their motivation by gaining statues among other in the community, and that other students like and use his content. Further unexpected feedback from others may not at all reduce intrinsic motivation but rather amplify it. This could mean that feedback from others may even boost both intrinsic and extrinsic motivation, which might increase motivation for the desired behavior further. But if the feedback is repeated and become a habit where the student expects to be complimented, it can like tangible rewards also be deleterious for intrinsic motivation. Therefore if the person expects to get positive feedback and compliments motivation for the behavior is increased extrinsic and reduced intrinsic.
3) Personal Need
Personal need is an extrinsic motivational factor which should be considered as an alternative to the extrinsic motivational factors rewards and reputation. The implication of personal need is that the contribution one provides will benefit or be useful to oneself in some way. Personal need may motivate the students to engage in virtual
versions of new knowledge development. Thus fulfilling students need is an immediate payoff resulting from participation. The students need has also been a source of innovation in fields ranging from scientific instruments find that students’ motivation to satisfy personal needs had a positive effect on participation. also find that the motivation of students need is correlated to participation
d. Advantages of Extrinsic Motivation
According to Katrina, there are primary advantages of Extrinsic Motivation.
1) Extrinsic rewards work more quickly and powerfully than intrinsic ones when teacher want students to learn new course information.
Students can be motivated to learn almost anything if promised a sufficiently attractive external reward. External reinforcement for engaging in a particular activity increases students' time on task, and performance is likely to improve as a result.
2) Extrinsic motivation may also focus on the social aspects of learning because learning is often a social activity. Learning often takes place in social settings. Students learn together in class, with friends, classmates, and study partners learn together outside of classroom.
Learning compliance is another social aspect of learning because of an external goal or requirement and because instructors require their students to learn new course information. These aspects of extrinsic
motivation are based primarily on the work of performance goals, as opposed to mastery or achievement goals, in the motivation literature.
3) Extrinsic motivation can persuade the students to engage in a specific behavior immediately, such as getting students to submit the homework on time by threatening punishment if they are late.
4) It can also be very useful for tasks that are just not interesting. For example, sometimes the students less enjoy the teaching learning process in the classroom. Therefore, one useful strategy in helping it is threathen the students who don’t pay attention will give a punishments, such reviewing what the teacher explains.21
e. Indicators of Extrinsic Motivation
Extrinsic motivation is an energy change within the person characterized by affective arousal and anticipatory goal reaction. It can be explain that extrinsic motivation is a psychologist condition that is drive someone to do something. As more specific learning extrinsic motivation can looked from the indicators as follow:
1) The students are enthusiasm in the learning activity 2) The students are active in the learning activity 3) The student attention in the learning process22
Extrinsic motivation as intensities and direction a behaviour that has correlation with the choice of decide someone to do something or to
21 Ibid, Korb Katrina A., p.2.
22 Marinda. P., et al, The Correlation between Students’ Motivation and Their Speaking Skill, (Rambah: University of Pasir Pangairan, 2016), p.8
blow a something, when do something and how the level of trying which they doing.
B. Theoretical Framework and Paradigm 1. Theoretical Framework
There are two variables in this paradigm in this research. There are independent variable (X) and dependent variable(Y). The independent variable (X) is extrinsic motivation and the dependent variable (Y) is students’ descriptive writing ability.
Descriptive writing ability receives no serious attention because many students think that descriptive writing is difficult. There are many factors that might influence the students’ quality of writing in descriptive text such as; students’ lack of grammar, vocabulary, ideas, and motivation to write. It has been known that it is hard enough to develop an idea into a long paragraph. These factors can cause the students unmotivated to start descriptive writing.. Motivation is the main problem for the students to start learning the second language especially writing of descriptive text. In other words, factor that might influence students to write is their motivation. As we know that, there are two kinds of motivation. They are instrinsic motivation and extrinsic motivation. In this research, it involves the extrinsic motivation.
However, many students did not pay attention to the teacher. On the contrary, some of them still paid attention to the teacher. Many of students
became passive when they were faced with a writing task. This phenomenon influenced the students’ descriptive writing ability achievement and as a consequence not all junior high school students’ scores were good in writing descriptive text.
According to Jeremy Harmer, extrinsic motivation is the result of some outside factors that influence the need of students to to do an exam, the hope of students to get financial reward or the possibility of students to achieve the future travel.23 It is very important in second language learning.
The primary motivation for learning a language is being able to communicate in the target. The students also have to pay attention whether they motivated from outside or inside. It means that extrinsic motivation can stimulate students to write descriptive text in order to improve their quality in evolving a text and it makes them become creative writers.
Moreover, extrinsic motivation is external factor to the individual and unrelated to the task they are performing. The examples are money, good grades, and other rewards. Extrinsically motivated students may have to be bribed to perform the same tasks.
The writer assumes that better giving extrinsic motivation in teaching descriptive writing ability because the students will be more interest in learning process. If extrinsic motivation is high in writing descriptive, it will be good effect to the students. On the contary, if extrinsic motivation is low, so it will be bad effect to the students’ descriptive writing ability.
23 Ibid, Jeremy Harmer, p.98.
2. Paradigm
Based on the theoretical framework above the writer describes the paradigm as following:
Figure 1.
Scheme of the correlation between the extrinsic motivation and the students’ descriptive writing ability at the seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung
Based on the paradigm above, the writer concluded that If the students have high extrinsic motivation in learning, so the students’ descriptive writing ability will be good. In the reverse, if the studets have low extrinsic motivation, so the students’ descriptive writing ability will be bad.
Extrinsic motivatio
Good Students’
descriptive writing
ability
Fair
Bad
H Y P O T H E S I S Hig
Fair
Low
C. The Correlation of Extrinsic Motivation and The Students’ Descriptive Writing Ability
Writing ability receives no serious attention because many students think that writing is difficult. There are many factors that might influence the students’ quality of writing such as; students’ lack of grammar, vocabulary, ideas, and motivation to write. It has been known that it is hard enough to develop an idea into a long paragraph. These factors can cause the students unmotivated to start writing. Motivation is the main problem for the students to start learning the second language especially in descriptive writing. In other words, factor that might influence students to write is their motivation.
However, The previous line of argument indicated that writing ability dealing mainly with expressing ideas, facts. Feeling, experience, and thought in written form. In writing, the aspects include the content, grammar, organization, vocabulary, and mechanics. Those aspects are important to master in order to be able to produce good writing. Not only the aspects above but also motivation is needed if the students want to start writing the descriptive text, especially extrinsic motivation such giving a reward. Extrinsic motivation is external factor to the individual and unrelated to the task they are performing. The examples are money, good grades, and other rewards.
Extrinsically motivated students may have to be bribed to perform the same tasks. Therefore, the higher students’ motivation, the higher students’
descriptive writing ability.
D. Hypothesis
1. Hypothesis Formulation
Paul S. Gary explains that hypothesis is a specific prediction that follows directly from theory.24 There are two kinds of hypothesis, such as alternative and null hypothesis.
Based on assumption above, hypothesis for this research can be formulated as follows:
a. Alternative Hypothesis (Ha)
There is a positive and significant correlation between extrinsic motivation and the students’ descriptive writing ability at the seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif Nu 5 Sekampung.
b. Null Hypothesis (Ho)
There is no positive and significant correlation between extrinsic motivation and the students’ descriptive writing ability at the seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif Nu 5 Sekampung.
2. Statistical Hypothesis
Based on the explanation above, the writer concludes that hypothesis are:
a. If “r observed (ro)” > r table (rt) alternative hypothesis (Ha) is accepted and null hypothesis (Ho) is rejected.
b. If “r observed (ro)” < r table (rt) alternative hypothesis (Ha) is rejected and null hypothesis (Ho) is accepted.
24 Paul S.Gray, The Research Imagination An Introduction to Qualitative and Quantitative Method, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007), p.4
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
A. Research Design
Yogesh Kumar Singh defines that reserach design is a mapping strategy which is based on sampling technique.25 It is essentially statement of the object of the inquiry, sampling, research strategy, tools and techniques for collecting the evidences, analysing the data and reporting the findings.
In this research, the writer uses quantitative research. According to Daniel Muijs, quantitative research is “explaining phenomena by collecting numerical data that are analyzed using mathematically based methods (in particular statistics)”.26 Moreover, C.R. Kothari stated that Quantitative research is based on the measurement of quantity or amount. It is applicable to phenomena that can be expressed in terms of quantity.27 Therefore, the writer concludes that this research is quantitative research because this research was using the numerical number that taken from the students.
Donald Ary decides that there are two main types of quantitative research design, experimental design and non-experimental design. Also, the writer will research by non-experimental design. The writer identifies variables
25 Yogesh Kumar Singh, Research Methodology and Statistics, (New Delhi: New Age International (P) Ltd, 2006), P
26 Daniel Muijs. Doing Quantitative Research in Education with SPSS. (London: Sage Publications, 2004). p.1
27 C.R Kathori. Research Methodology Methods and Technique. Second Revised Edition (New Delhi: New Age international publisher. 2004). p. 3
27
and may look for relationships among them but does not manipulate the variables.28
Furthermore the writer uses correlational research. It gathers data from individuals on two or more variables and then seeks to determine if the variables are related (correlated). Correlation means the extent to which the two variables vary directly (positive correlation) or inversely (negative correlation). The degree of relationship is expressed as a numeric index called the coefficient of correlation.
This research is intended to investigate whether there is any positive and significant correlation between extrinsic motivation and the students’
descriptive writing ability.
B. The Operational Definition of Variables
Mark and Peter defined variable as a general class of objects, events, situations, characteristics, and attributes that are of interest to the writer.29 They also added that the basic aim of any quantitative research is to investigate how variables interact with each other. By using operational definition, reseracher can proceed with investigations that might not otherwise be possible. There are two kinds of variable, namely:
28 Donald Ary, Introduction to Research in Education, (Wadsworth: Cengage Learning, 2010), p.26
29 Mark Balnaves and Peter Caputi. Introduction to Quantitative Research Methods.
(London: SAGE Publications Ltd. 2001),.p. 46
1. Independent Variable
Independent variable is a variable that stand alone. It is not changed by the other variable which the writer is trying to measure. Independent variable are those that the writer chooses to study in order to assess their possible affect(s) on one or more other variables. In this research, independent variable (Y) is extrinsic motivation. It encourages students’
writing ability especially in descriptive writing. Giving extrinsic motivation will help the students to increase students’ enthusiasm to write descriptive paragraph. It is not only make the students have high motivation but also make them produce a good descriptive paragraph.
In this research, the writer measures the correlation of extrinsic motivation and students’ descriptive writing ability. It would be implemented to the students at seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung. In addition, the writer measure by using observation to get the data. Then, the writer do the observation with gives questionnaire. So the writer get the result from the questionnaire and observation.
Moreover, based on the explanation above that was indicator of the extrinsic motivation as follow:
a) The students are enthusiasm in the learning activity b) The students are active in the learning activity c) The student attention in the learning process
2. Dependent Variable
According to John W. Creswell “Dependent variable are those that depend on the independent variable; they are the outcomes or result of the influence of the independent variables”.30
Dependent variable (Y) of this research is descriptive writing ability which the students able to express one idea, feeling, opinion by written. To measure descriptive writing ability of students, the writer uses a test. The writer gives the students by composing. The writer asks them to write the descriptive text. Then, each student will write the idea in their mind on the paper. It would be implemented to the students at seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung.
There are some indicators that should be gain by the students in writing descriptive ability based on this variable are:31
a. The students are able to express their ideas and arrange good sentences by giving extrinsic motivation.
b. The students interested in writing materials, especially in descriptive writing.
c. The students have high motivation in descriptive writing.
30 Creswell, John W. Research Design Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. (London: Sage Publications, 2014), p. 84
31 Ibid, Alice. O and Ann. H, p.15
C. Population and Sampling Technique 1. Population
According to Geoffrey Marczyk, the population is all individuals of interest to the writer.32 In addition, Paul S. Gray et-all defines population as all the possible cases of interest in a particular research project.33 The population of this research is the seventh grade of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung which consists of 119 students divided into four classes, are:
Class VII A = 29 students Class VII B = 30 students Class VII C = 32 students Class VII D = 28 students Total = 119 students 2. Sample
According to Paul “sample is the selection of a relatively small group of individuals from whom we obtain data in order to be able to generelize about a larger group”.34 It is subset of the population that is taken to be representative of the entire of the populations. Based on this explanation, the writer can be concluded that sample is the number of specific research subject taken from the population.
32 Geoffrey Marczyk R., et al, Essentials of Research Design and Methodology (United State of America: John Willey and sons Inc, 2005),p.18
33 Gray, Paul S. et-al. The Research Imagination, (Unites Stated of America: Cambridge University Press, 2007). p.103
34Ibid . p.102
The sample of the research is 29 students in the class VII A. The reason why the writer chooses the class VII A is that because most of students get low score of writing descriptive paragraph as in the pre survey result.
3. Sampling technique
Sample is needed in this describe population condition. In other hand, it is a group of individuals, items, or events that represents the characteristic of the larger group from which the sample is dawn. It can be presented the sample is the part of population which represents the population that will be researched.
The writer uses a purposive sampling in this research. Purposive sampling is the sample based on specific purpose.35 So the writer chooses one class that still low in writing ability.
D. Data Collection Method 1. Test
A test is a set of stimuli presented to an individual in order to elicit responses on the basis of which a numerical score can be assigned.36 Sometimes people complete tests as part of their research permitting the writer to describe performance of individuals or groups. Therefore, test is used as data collecting method to measure dependent variables in this research. The writer uses written test to measure students’ descriptive
35 Donald Ary, et al, Introduction to Research in Education Eighth Edition, (USA:
Wadsworth Cangage learning,, 2010), p.156
36 Ibid, p.201
writing ability. Furthermore, the writer measures teaching writing for the students through extrinsic motivation by test as data collecting method.
2. Questionnaire
Alison Mackey defines questionnaires (a subset of survey research) as
"any written instruments that present respondents with a series of questions or statements to which they are to react either by writing out their answers or selecting them among existing answers". It allows writer to gather information that learners are able to report about themselves, such as their beliefs and motivations about learning or their reactions to learning and classroom instruction and activities information that is typically not available from production data alone.
Specialized types of questionnaires have also been developed to address specific research areas or questions. For example, as noted previously, discourse completion questionnaires have been used to investigate interlanguage pragmatics.
There are two types of questionnaire items, are:
a. Closed questionnaire
A closed-item question is one for which the writer determines the possible answers, whereas an open-ended question allows respondents to answer in any manner they see fit. Closed-item questions typically involve a greater uniformity of measurement and therefore greater reliability. They also lead to answers that can be easily quantified and analyzed.
b. Open ended questionnaire
Open-ended items allow respondents to express their own thoughts and ideas in their own manner, and thus may result in more unexpected and insightful data. An example of a closed-item question is, "How many hours a week did you study to pass this test? Circle one: 3,4, 5, or 6 or more." An example of a more open-ended question is, "Describe ways that you found to be successful in learning a second language?".
The type of questions asked on a questionnaire naturally depends on the research questions being addressed in the study. For example, in relatively unstructured research, it may be more appropriate to ask openended questions and allow participant responses to guide hypothesis formation. Once hypotheses are formulated, writers can ask closed-item questions to focus in on important concepts. Of course questionnaires need not be solely closed or open ended, but can blend different question types depending on the purpose of the research and on what has previously been learned about the research phenomenon.37
3. Observation
According to Alison Mackey, Observation usually refers to "methods of generating data which involve the writer immersing (him or herself) in a research setting, and systematically observing dimensions of that setting, interactions, relationships, actions, events, and so on, within it".38 Observation is made for get the data of children activities such as students
37 Alison Mackey and Susan M. Gass, Second Language Research, Methodology and Design, (London: LEA Publisher, 2005), p.92.
38 Ibid, p.175
pay attention when learning process. Following the class ethusiastically, giving command, doing the physical action correctly, students’ ability in question and answer understand the material given. in this research, the writer uses systematic observation and it is organized by its category. The reason why the writer uses this observation, because to observe about the situation and development of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung and it also to observe about the students’ learning activity. This method is as complementary method.
4. Documentation
Jane Richie states that documentation will help the user of the research to understand the boundaries of the evidance in the term of any weder conclusion that can be drawn 39. In addition, Documentation method is looking for the data which concerned with the variables such as transcript note, books, newspaper, epigraphy, meeting notulen, Ledger, agenda and etc. Moreover, in this research the writer will use documentation method to know both the history of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung and all information which concerned with this research.
39 Jane Ritchie and Jane Lewis, Qualitative Research Practice, (London: Sage Publications , 2003), p.278.
E. Research Instrument
Gery Anderson defines “an instrument includes test and questionnaire, observations schedules and any other tool used to collect data.40Furthermore, the research instrument involves:
1. Instrument Blue Print
The research instrument in this research held the test which has explained follows:
The writer uses test instrument. The research about writing ability in descriptive text, so the research instrument which is used in present research is in the form of writing or composing descriptive text writing, There are the blue print:
a. The instrument which is used in observation method is observation guidance, as follow:
1) Observation the location sketch of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung 2) Observation the establishment of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung 3) Observation about building MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung
b. The instrument which is used in documentation method is documentation guidance, as follow:
1) Documentation about condition of the teachers and officials in MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung
2) Documentation about the students of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung
40 Gary Anderson, Fundamentals of Educational research, The Falmer Press Teachers Library, USA, 1998), p.94
3) Documentation about the organization structure of MTs Ma’arif NU 5 Sekampung
c. The instruments which are used in this research are test and questionnaire. The writer uses the objective test that is essay test.
Table 3 Instrument Grills
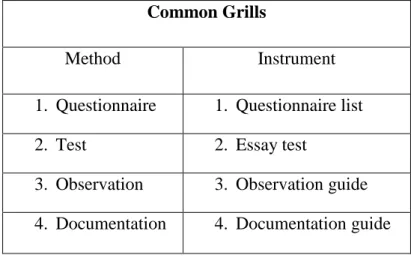
Common Grills
Method Instrument
1. Questionnaire 1. Questionnaire list 2. Test 2. Essay test
3. Observation 3. Observation guide 4. Documentation 4. Documentation guide
Table 4
Instrument Grills of Research Variable Research Variable Data
Source
Method Instrument
1. Independent variable extrinsic motivation
Students Questionnaire Questionnaire list
2. Dependent variable descriptive writing ability
Students Test Essay test
Specific Grills in this research as follow:
Table 5 Questionnaire Grills
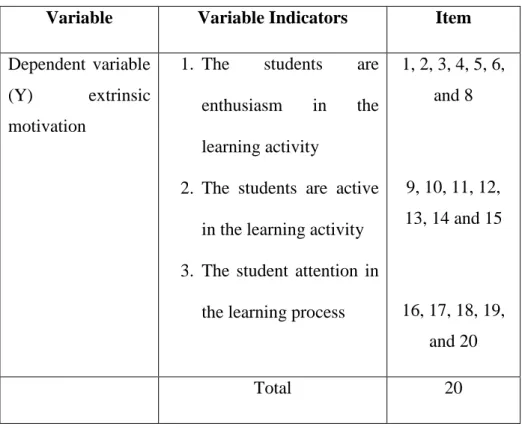
Variable Variable Indicators Item Dependent variable
(Y) extrinsic motivation
1. The students are enthusiasm in the learning activity
2. The students are active in the learning activity 3. The student attention in
the learning process
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8
9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15
16, 17, 18, 19, and 20
Total 20
Table 6
The Score of Questionnaire Item
Category Score
Yes Sometimes
No
3 2 1