Based on the background of the above research, the writer will conduct a study titled 'An error analysis of the use of verbs - Ing form in writing recount text by the second grade students at the SMA Negeri 5 Medan. Based on the background of the research, the problem of the research is formulated as follows. The problems of the study focus on finding the type of error and the dominant type of error that occurs in the use of the verb tense made by the second grade students of SMA Negeri 5 Medan in writing Recount text.
The result of the study can be used as a choice in the procedures of teaching and learning English. The result of the study can be used as a model for those who want to conduct research in English teaching. In this case, for the purpose of the study, it is very important to state the following terms.
As Corder noted in Brown "a learner's errors are important in that they provide the researcher with evidence of how language is learned or acquired, what strategies or procedures the learner is using in language discovery." Addition errors usually occur in the later stages of second language acquisition, when the learner has already achieved a goal. Malformation errors are characterized by the incorrect use of a morpheme or structure.
English, you could compare the structure of the student's errors with that of the errors reported for children.
Communicative Effect Taxonomy
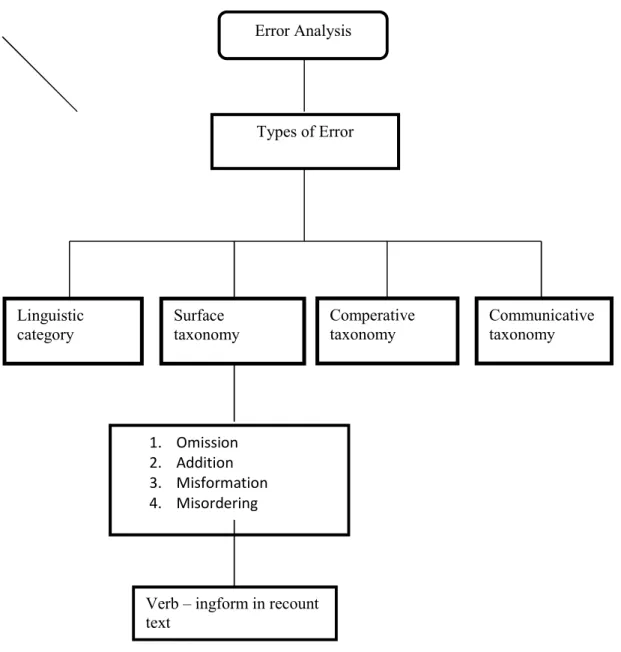
Error Analysis
- Goal of Error Analysis
- Procedures of Error Analysis
According to Carl James (1998:1), error analysis is the process of determining the occurrence, nature, causes and consequences of failed language. Brown Douglas said students make mistakes and these can be observed, analyzed and classified to reveal some of the system's overestimation of the student that led to an increase in the mistakes. Rod Ellis (1997:17) says that errors reflect gaps in a student's knowledge; they arise because the student does not know what is correct.
From the above definitions, the author concludes that error analysis is a process of specifying the nature, causes and consequences of learners' unsuccessful language, which can be observed and analyzed to reveal something from the overactive system in the learner that causes errors. Errors are believed to be an indicator of the learners' stages in their target language development. In error analysis, the goal is to determine accuracy, James says the goal of error analysis is to prevent obsessing over sample errors and prioritize the ones that really matter.
Based on the above definition, the author concludes that the goal of error analysis is to determine whether the learning process of teaching is successful or not. However, the teacher should know how to correct the students' mistake so that they do not repeat the same mistake. In other words, the teacher or researcher should improve or use a compatible technique to reduce the student's error.
There is no step in performing error analysis that we can properly call an analytical step, a step that coincides with data collection or interpretation. One engages in error analysis from the moment one systematically sets out to collect relevant data, using appropriate error extraction procedures. According to James, the four procedures of error analysis are: detecting, locating, describing, and classifying the error.
Most examples of language learners that have been used in error analysis include data collected from many speakers responding to the same kind of task or test (as in Morpheme Order Studies, discussed below). Based on some explanations of error procedures above, the writer concludes that the procedure of error analysis is a way to collect relevant data by examining and dealing with errors in students' sentences. They collect the result of the test, identify the mistakes from the test, describe the mistake in category and explain the reason why the student makes a mistake.
Writing
- Process of Writing
- The Purpose of Writing
- The Genre of Writing
Planning: First, the writer must consider the purpose of his writing not only the type of text, but also the use of language and the choice of information to include. Secondly, the experience of the writer think about the audience for which he is writing, as this will affect not only the form of writing, but also the choice of language. Third, the writer must list the facts, ideas, or arguments he has decided to include.
The writer represents these aspects of the writing process in a different way, so the process wheel below clearly shows the many directions that writers can take either by traveling backwards or forwards around the rim or going up and down the spokes. In what is written from the language, the author must give himself time to express the idea, meaning and message. Spoof is the way to distort some of the events in the process that used to create a humor and create a text.
Procedure is any written English text where the writer describes how something is accomplished through a series of actions or steps. Explanation is a written English text in which the writer explains the processes involved in the information or operation of natural or socio-cultural phenomena. It is written to expose the truth of the object's fact to the reader.
Hortatory exposition is a written English text in which the writer convinces people that something should not be the case. Discussion is a written English text in which the writer puts forward some points of view on a topic. The length of the text depends on the specific details of the object being described.
Anecdote is the tool of the writer to share the story of an unusual or funny accident with the others. A story is any written English text in which the writer aims to amuse, entertain, and deal with actual or vicarious experiences in various ways. Among the various genres of writing, the writer only focuses on report text.
Recount Text
- Generic Structure
- Language Features
Ing -form
- Present Participle
- Present Participle as Verb
- Present Participle as Adjective
- Gerund
- Gerund as a Subject
- Gerund as Subjective Complements
The gerund looks exactly the same as a present participle, but it's helpful to understand the difference between the two. According to Swan in Rafflis and Lase the gerund is a verb that ends in –ing and functions as a noun. It is one of the strangest constructions in the English language because it nominalizes the morpheme, turning a verb into a noun by adding the -ing form to the final verb.
In Indonesian, making a verb into a noun does not change the form, but in English the suffix –ing must be added to the word. Based on the above explanation, gerund is a verb that has –ing added to the end of the verb and acts as a noun. They can serve as subjects, objects, or even complement sentences, and they stand on their own, that is, unaided.
Smoking is a bad habit Singing makes me happy Cooking is a good hobby 2.6.2.2 Gerund as an object. Since gerunds can be used as nouns, they can also serve as subjective complements.
Previous of the Study
Pernilla (2018) in her research entitled The English −Ing Form from A Recapitulationist Hypothesis Perspective Seeing language as an evolutionary process can provide new insight into our understanding of historical change. In this paper, the English −ing form is examined from a recapitulationist hypothesis perspective, with the aim of elucidating the complexity surrounding the grammatical category membership of the various functions of this form. The study of the −ing form in children's language acquisition compared to its history will lead to the discussion of how the functions are related, both structurally and cognitively.
By looking beyond traditional grammatical approaches to grammatical categories, it is possible to clarify the identity of the form − ing.
Conceptual Framework
An Error Analysis of Verb Form Use in Writing Recounting Text by Second Grade Students in SMA Negeri 5 Medan (Artha Nelvita Naibaho).
Research Design
The Subject of the Study
The Instrument of Collecting Data
The Technique of Collecting Data
Technique of Analyzing the Data
Validity (Triangulation)
Data triangulation refers to the use of different data or information, including time, space, and person, in research. Data triangulation is the process of reviewing information by the writer and comparing it to observational data and interview data. The writer had to run the observation multiple times to make sure the data was valid.
Theory triangulation was related to the use of two or more theories which were combined when investigating situations and phenomena. Some theories support both the way of collecting and data should be created more complete to provide more comprehensive data. The goal of method triangulation was to complete a situation and a phenomenon by using some methods.
Triangulation of methodology was similar to the mixing of methods used in social science research, where the output from one method was used to enhance, argue and clarify the results of others. Relating to the use of a variety of data or information, including time, space and person in search.