INTRODUCTION
Background
Problem statement
Objective of the study
Significant of the study
Scope of the study
REVIEW OF THE RELATED LITERATURE
Reading
- Definition of reading
- Kinds of reading
- Step of reading
- Reading principle
- Reading rules
Tarin (1985) that reading is a process that the reader undertakes and uses to obtain the message, a method used to communicate with oneself and sometimes others, which communicates the meaning contained or implied in the written symbols. Anderson et al. (1985) state that reading is the process of constructing meaning from written texts. Davies (Sugiarto, 2001) provides an understanding of reading as a mental or cognitive process in which a reader must be able to follow and respond to the author's message.
Smith in Lamuhiddin (1988:22) explains that reading is a complex procedure in which the reader uses mental content to derive meaning from written material. Byrnes (1998:7) states that reading is an interactive process that takes place between the readers and the text, which leads to understanding. Based on the definition above, the researcher concludes that the definition of reading is interactive process of getting information and ideas from the author with the written text.
Aloud reading is a type of reading where a reader would say each word in the text orally. One of the main purposes of reading aloud is to recognize the sounds of words; . however, teachers can also modify their activities to develop their students' reading comprehension. The purpose of individual reading is to control pronunciation, reading individually stimulates students' ability to read. moreover, individual reading helps the teacher understand which of her students have reading difficulties.
According to Wood in Irawati (2008:28), the types of reading indicate an important category as follows. Based on explanation above, the research concludes that there are three types of reading proficiency. But during the lesson we will also do our best to ensure that they are engaged with the topic of a reading text and the activities they are asked to do while dealing with it.
Reading comprehension
- Definition of reading comprehension
- Levels of reading comprehension
It is also to determine whether there is a significant improvement in the students' reading comprehension before and after the use of Self-Question Strategy in the eight degree students of SMP Neg. Null hypothesis (H0): There is no significant improvement in the students' reading comprehension before and after giving using Self-Question Strategy. Alternative hypothesis (H1): There is a significant improvement of the students' reading comprehension before and after giving Self-Question Strategy.
If you ask the students to read the text, the students ask a question and answer it. The post-test was administered after the educational implementation, the students were given a post-test to determine the improvement of the students' reading comprehension. The indicator in the study was that after the learning process, students become better at reading a text using the self-questioning strategy that focuses on literal comprehension.
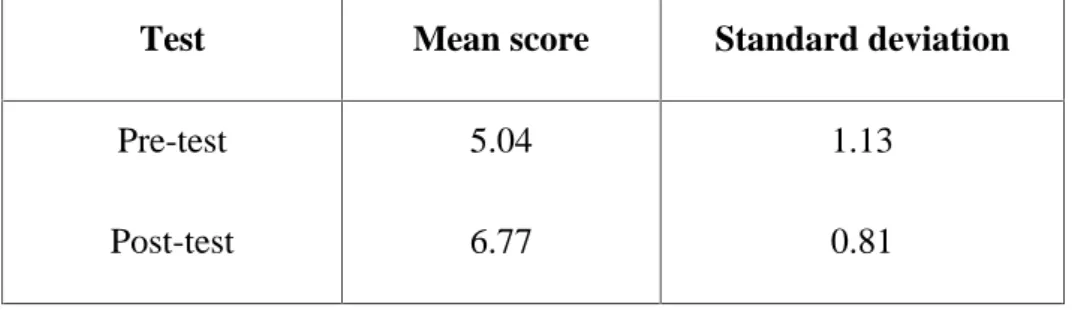
The mean post-test score of the students was higher than the mean pre-test score. It means that there is a significant difference between students' reading comprehension before and after intensive reading in teaching reading. The description of the data collected through the test, as explained in the previous section, shows that the students' reading comprehension improves significantly.
Based on the result of the students' answers, before and after the treatment, the researcher noticed that the students often did not understand the text questions. The self-questioning strategy that was implemented to be useful in motivating students to improve their reading comprehension. The result of the students' achievements in the literal level of understanding above shows that the students have improved in recognizing word-for-word statements in the text.
It was suggested that using this self-questioning strategy could improve students' reading comprehension. Reading material should be designed and presented using a self-questioning strategy so that students can study it in an engaging and effective way.
Question Technique
Self Question Strategy
Not only can teachers ask questions while students read, but students can also learn to ask their own questions while reading through self-questioning methods. The self-questioning skill is a type of self-management strategy that can be used to change behavior, complete tasks, provide instruction, gain insight, and much more (Heward. All self-questioning strategies help students generally understand more of what they want to know). read; however, it is important to note that self-examination strategies can serve several purposes.
Self-questioning is also considered a metacognitive strategy because it provides students with a way to test themselves; that is, it helps them check how well they are understanding what they are studying. Mark Pennington, asking questions about the text as you read. http://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/reading/how-to-improve-reading-comprehension-with-self-questioning/). In terms of question placement, pre-reading questions have been found to significantly improve recall of objective measures, ensuring that posttests measure the same information presented in the pre-questions.
It has not been found that remembering information that occurs in the text and on the post-test, but not in the preliminary questions, is improved. Of particular interest is the finding that trained and untrained questioners showed no difference in higher levels of reading ability, but that subjects with low or intermediate reading ability seemed to benefit from training in self-questioning, as the trained questioner compared the untrained group surpassed at this level. levels. Depending on the strategic approach, students are generally asked to use their prior knowledge of the topic and clues in the text (i.e. pictures, headlines) to predict what might happen in the upcoming story and to identify structural features (i.e. the main characters, the problem). , how the problem is solved).
Some models are student-mediated, where the teacher's direct teaching of the strategy itself has faded (Englert & Mariage, 1991; Fuchs D., Fuchs. This peer-mediated and reflective practice is designed to help students transfer self-regulated reading behaviors. Self-questioning during reading can be particularly effective for students with RD (Scruggs & Mastropieri, 1998).
Conceptual Framework
None of the texts presented to these older students in second grade were complex enough to challenge their understanding.
Hypothesis
METHOD OF RESEARCH
- Research design
- Population and sample
- Variable of research
- Research instrument
- Data collection
- Data analysis
Pre-reading activities were such activities before reading a text to activate the students' knowledge about the subject, help the students overcome key words and determine the purpose of the reading activities. Researcher asked the student to read the narrative test then ask the students a question and answer it. After performing the treatment, the researcher instructs the students to read the narrative text, after which the students ask a question and answer it.
Mean score and standard deviation of pretest and posttest test mean score Standard deviation. Using the self-questioning strategy is how students can understand the text and how students can ask and answer a question about the text. It shows that the background problem still exists, but the use of student self-questioning has been successfully increased.
The technique made the students creative, students became active with the text, had more opportunities to think about what they read, and acquired the skills to effectively reflect on what they read. From the data shown in the pre-test and post-test, the performance of the students on their literal level of understanding is increased where the data of post-test has improved significantly from the distribution frequency of the result and the average score in the test. The students can state the information given in the text explicitly or directly; for example main ideas, details, cause and effect and sequences written in the text.
It was proved by the t-test value that is 46.5 which was greater than the t-table (2.080) Which was classified as good score, the researcher also concludes that there was a significant difference between the reading comprehension of the students of SMP Neg. The teacher should present different strategies in reading instruction to make students more interesting in reading skills, especially in understanding a text and how to make questions from the text. The author suggests other researchers to conduct further research on self-questioning strategy to see which strategies are more useful for students in reading or make this strategy to be completeness in the learning process, especially in the teaching of reading.
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
Findings
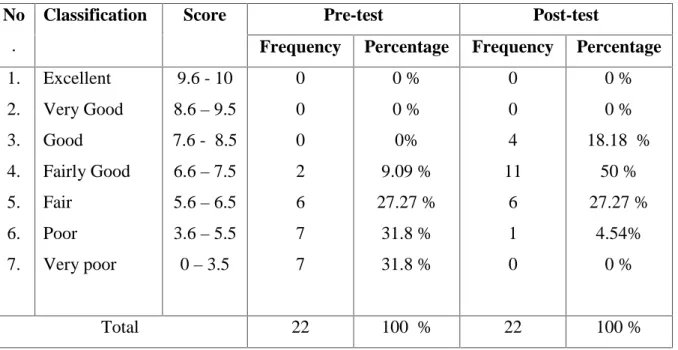
The score of the students on the pre- and post-test was divided into several criteria and percentages as follows. It can be concluded that the percentage of correctness in the post-test was greater than that in the pre-test. To know whether or not the difference between the average score of the test and the post-test is statistically significant, the statistical analysis of the t-test for nun is performed.
The result of the statistical analysis at the level of significance 0.05 with degrees of freedom (df) = n –1, where df = 22– 1 and df = 21 indicated that there was a significant difference between the mean scores of the post-test and the pre-test. -sample.
Discussion
Richards (1995) says that different types of reading comprehension are distinguished according to the readers' purposes and the type of reading they use. This chapter presents conclusions and suggestions based on the findings and discussions of data analysis. Based on the findings and discussion of the research, it can be concluded that teaching English reading through Self-Question can improve the reading comprehension of the second year students SMP Neg.
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
Conclusion
Suggestion
Diperoleh 25 Mei 2012, dari http://ezinearticles.com/?Improving-Reading-Strategies:-Literal-Reading Bernstein, Berg. Pedoman Pelaksanaan Proses Belajar Mengajar dan Pedoman Pelaksanaan Evaluasi Sekolah Menengah Negeri, Jakarta: Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan.