During my time at the University of Mississippi, I joined The Sally McDonnell Barksdale Honors College (SMBHC) through the Junior Year Entry Program while studying accounting in The Patterson School of Accountancy. My performance and understanding led me to accept a full-time job at KPMG and further my academic career at the Patterson School of Accountancy's Data and Analytics Master's Program.
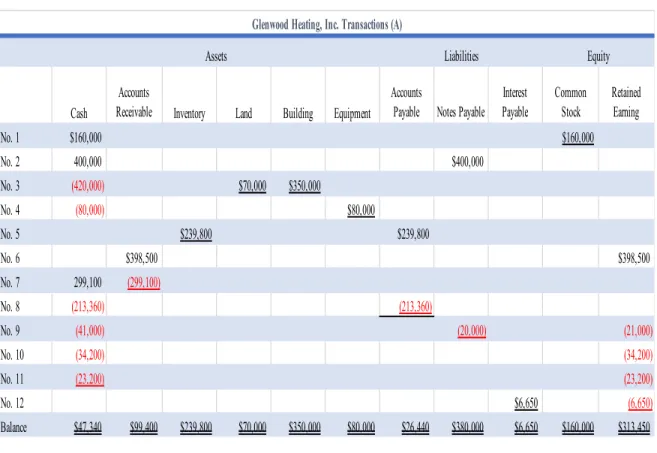
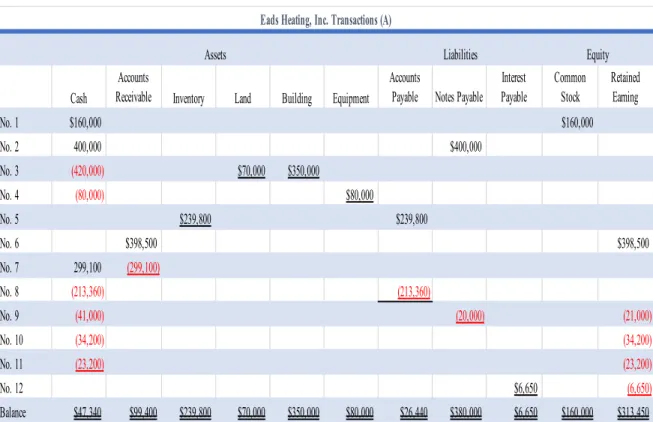
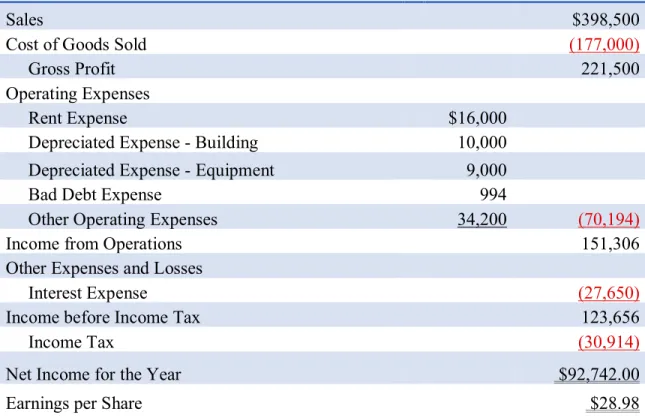
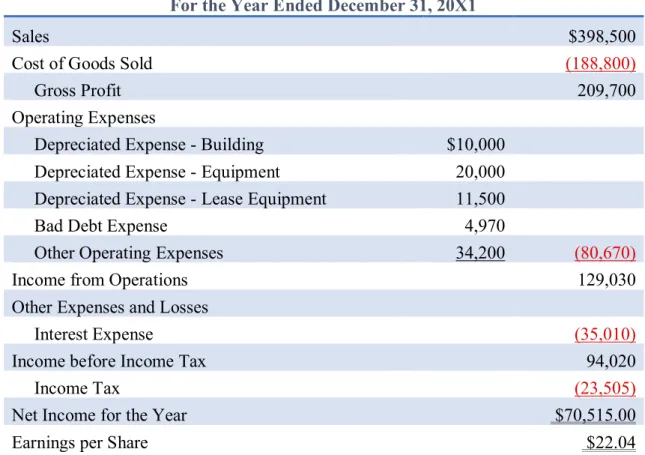
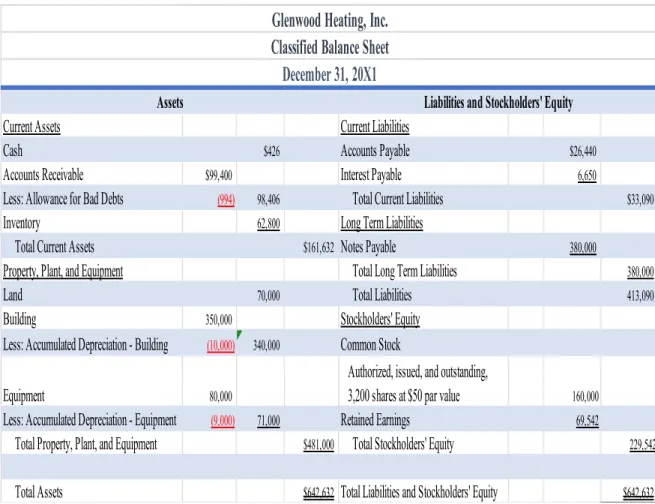
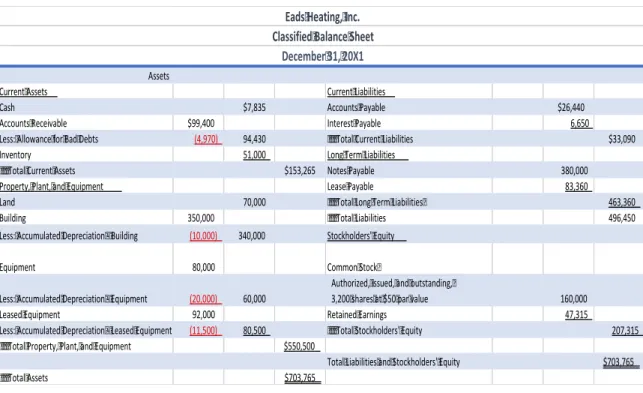
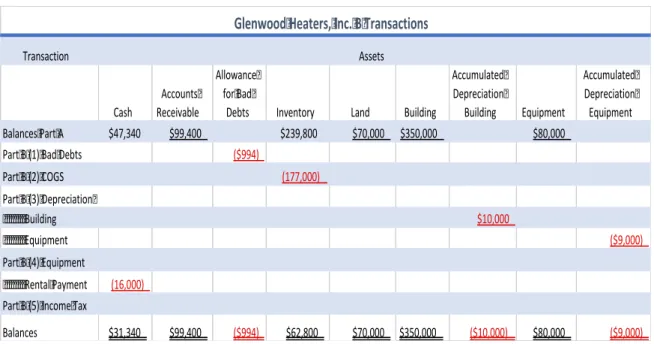
Analysis Comparing Glenwood and Eads Heating, Inc
With large account balances in the Leased Equipment and Lease Payable accounts, cash flows will be higher for Eads Heating, Inc. When we look at the cash balance, we see that Eads' cash balance is much larger than Glenwood's cash balance.

Profitability and Earnings Persistence
What is the difference between "Other income (expenses), net," which is classified as non-operating expenses, and "Special items, net," which Molson Coors classifies as operating expenses. The dirty surplus items are reported under "Other Comprehensive Income (Loss), Net of Taxes," which can be found in Molson Coors' comprehensive income statement.
Accounts Receivable
The actual amount of sales returns and allowances reduces the amount of the balance in the allowance account. Complete a T-account showing the activity in the sales returns allowance account during the year.
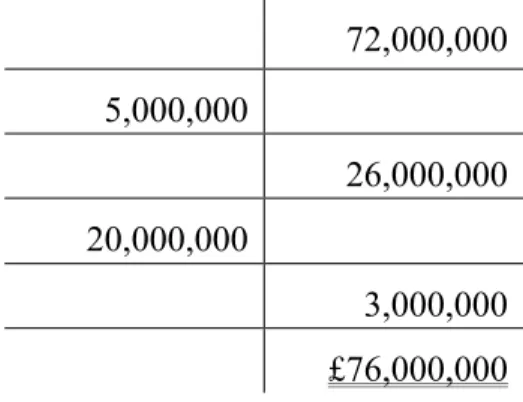
Diluted Earnings Per Share
A financial calculation entitled basic earnings per per share is a much simpler formula, net income minus preferred dividends divided by the weighted average number of shares outstanding, and is always presented on the face of the income statement. Diluted earnings per share includes the effect of all potentially dilutive common shares that were outstanding during the period. I realized when you use preferred stock dividend in the numerator and when you convert it to common stock to be used in the denominator.
Diluted earnings per share is a key financial statement factor that investors should consider for common circumstances, such as a company that must convert all securities for financial support. Know that the numerator is net income minus preferred stock dividends divided by the weighted average shares outstanding. We know that there are convertible, cumulative preferred shares and that the stock is 6% convertible into common.
To calculate the number of common shares outstanding, take the common stock price of six million and divide it by the price per share of $10. Multiplying by 3 shares shows that each convertible cumulative preferred share converts into 3 shares of common stock.
Property, Plant and Equipment
The net book value of the asset is the same regardless of whether the asset is debited or accumulated depreciation. What is the total income statement impact of the equipment for the two years Palfinger owned it. The income statement effect of the equipment for the two years Palfinger owned it is that the company will only record depreciation for one year until the gain or loss is placed under other gains and losses on income.
Compare the total two-year income statement impact of the equipment under the two depreciation policies. What is the amount of capitalized product and software development costs, net of accumulated depreciation at the end of fiscal year 2009. The T account on the next page shows the capitalization and amortization for 2009 for the intangible asset “Software Product and Development” . The initial balance of 12,381 kr is from the net carrying value of the 2008 account and the final balance of 11,409 kr comes from part i.
Market capitalization is the value of a company that is traded on the stock exchange. This reduction occurs because the value of the company decreases when dividends are paid. Note that the only difference is the classification of the unrealized gain or loss on the property.
This balance sheet represents the fair value of available-for-sale securities at the end of the year. 10,000 is stated in the company's financial statements, the balance sheet must show the percentage of the company's future investment as a deferred tax liability. The first deliverable for this contract is hardware and software essential to the operation of the phone.
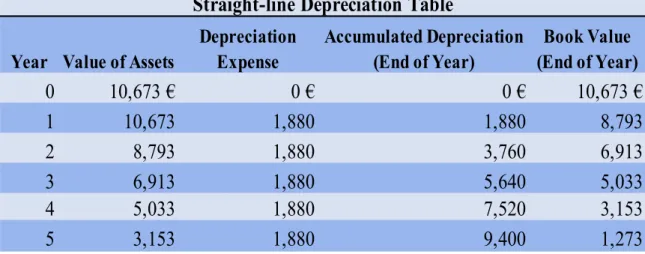
Research and Development Costs
Data Analytics
In the following pages, I will discuss the history, uses, and skills needed to take full advantage of the SAS tool. Once SAS became more popular, the creators left NCSU to form the SAS Institute Inc.
Below is a picture of the workbench, which was also found on the SAS website (SAS Institute— . Inventory Optimization). Using the SAS tool, tax auditors can monitor suspicious activity, document the process and report the reports. To help identify future or early-noticed problems, the SAS tool also pinpoints details that are responsible.
However, I find the most useful product for consulting accountants to be the SAS Risk Dimensions tool. I believe that accounting firms should invest in purchasing SAS because it is one of the first analytical programs.
Long-Term Debt
I also learned that dividing the current year's interest expense by the previous period's book value of the note can also determine the effective interest rate. To determine the annual interest expense, take the face value of the note and multiply by that note's stated interest rate of 7.5 percent. The face values and the carrying values are different because when Rite Aid purchased these notes, the cash proceeds of the notes were less than the face value of the notes.
Consider both the cash and discount portions of the interest expense from Part III above. According to note 11, the yield on the notes at the time of issue was 98.2% of the face value of the notes. According to Note 11, the yield on the notes at the time of issue was 98.2 percent of the face value of the notes, or a discount.
Based on your answer to part iv, what would the net book value of the debt securities be on February 27, 2010. This number is calculated by taking the book value of the securities as of the beginning of February 2010 and adding the current year's discount rate.
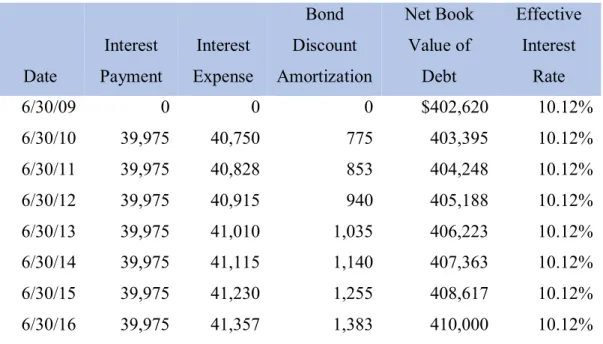
Shareholders’ Equity
I will explain Merck's financial statements, explain why companies pay dividends and repurchase treasury stock, and discuss the cash method for treasury stock. Reconcile the number of shares outstanding on December 31, 2007, with the dollar value of the common stock shown on the balance sheet. The purchase of own shares or shares of the company that are reacquired by the company itself reduces the equity capital and the number of outstanding shares.
The single entry summarizing Merck's common dividend activity for 2007 appears after the information shown. Numerical information is found in Merck's consolidated statement of cash flows and retained earnings. The cash account is credited for the number of dividends currently paid to shareholders, which is found in
Note that Merck's dividend price per share ratio represents the amount paid to shareholders each year. This is due to Merck paying less dividends in 2007 than in 2006, which also lowers Merck's dividend to total assets and dividend to operating cash flow ratio.
Marketable Securities
Trading and available-for-sale securities can be either debt or equity; However, held-to-maturity securities can only be debt, which is explained in further detail throughout the State Street case. A company must record $1 in dividends and interest received for available-for-sale securities in the same manner as trading securities. The next page shows a journal entry for the proper recording of dividends and interest received for available-for-sale securities.
If the market value of available-for-sale securities increased by $1 during the reporting period, what journal entry would the company record. What is the amount of net unrealized gains or losses on available-for-sale securities held by State Street as of December 31, 2012. What was the amount of net realized gains (losses) on sales of available-for-sale securities for 2012 .
Show the journal entry State Street made to record the purchase of available-for-sale securities for 2012. Show the journal entry State Street made to record the sale of available-for-sale securities for 2012.
Deferred Income Taxes
It can be complex at times; however, this case will show how to determine a deferred tax liability rather than a deferred tax liability. That said, the difference between a company's financial tax expense and their tax payable will determine whether the company has a deferred tax asset or liability. If a company pays more to the IRS in the future than is on their books, the company reports a deferred tax liability.
If a company pays less tax in the future than is due now, it reports a deferred tax asset such as a prepaid expense. However, the main common understanding is that the ASC requires entities to report deferred tax assets and liabilities as current or non-current balance sheet items. An example of a deferred tax asset is when a company reports a bad debt expense in the year it attributes the sale, but the company should not be able to claim the tax credit until it has written off a certain uncollectible amount.
Deferred tax liability is most often the result of different amortization methods for financial reporting and IRS rules. To determine the amount of the base for deferred tax receivables, we take the total balance of deferred tax receivables at the end of 2012, reduced by the balance from 2011 or
Revenue Recognition
This case furthered my knowledge of the new ASC 606 revenue recognition standards and taught me how to find a company's revenue recognition tactics that are presented in the company's 10-K. I also learned how to evaluate a company's revenue recognition policies by differentiating recognition tactics for different types of sales. For this particular case, I learned what four revenue recognition criteria Apple uses and how to determine tactics by looking through company records.
The specific accounts that are affected by the revenue recognition process are accounts receivable, cash and cash equivalents, sales revenue, and deferred revenue. Do they appear to meet the revenue recognition criteria you described in part b, above? In general, these revenue recognition tactics are fully consistent with the revenue recognition criteria described above in part b.
What are multi-element contracts and why they present revenue recognition problems for companies. Although these types of contracts often present revenue recognition difficulties for businesses due to the estimated selling price for a bundle of tangible products.
Analysis Comparing Glenwood and Eads Heating, Inc. 1
Accounts Receivable 20
Property, Plant and Equipment 37
Research and Development Costs 49
Long-Term Debt 67