The National Academy of Engineering was founded in 1964, under the charter of the National Academy of Sciences, as a parallel organization of outstanding engineers. This report would not have been possible without the tireless efforts of National Research Council staff, especially Robert P.
List of Abbreviations
About this PDF file: This new digital representation of the original work has been recomposed from XML files created from the original paper book, not from the original sentence files. Page breaks are true to the original; however, line lengths, word wraps, heading styles, and other typeface-specific formatting may not be preserved, and some typographical errors may have been accidentally inserted.
Summary
A series of animal bioassays have been developed to detect changes in the immune system caused by low oral doses of immunosuppressants. Studies of the interaction of the immune system and ultraviolet light can be particularly rewarding.
Biologic Makers in Immunotoxicology
Introduction
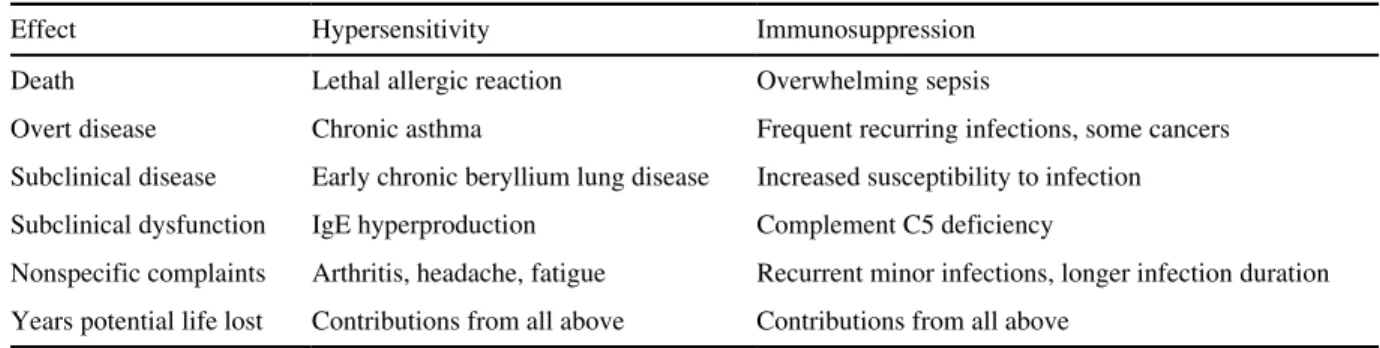
Immunological markers of effect include changes in components of the immune system itself (such as shifts in the distribution of lymphocyte subpopulations) and changes in other tissues caused by immune dysfunction (such as signs of renal failure caused by autoimmune kidney disease). . Stress of various kinds (loss of a spouse is often mentioned) can affect the immune system.
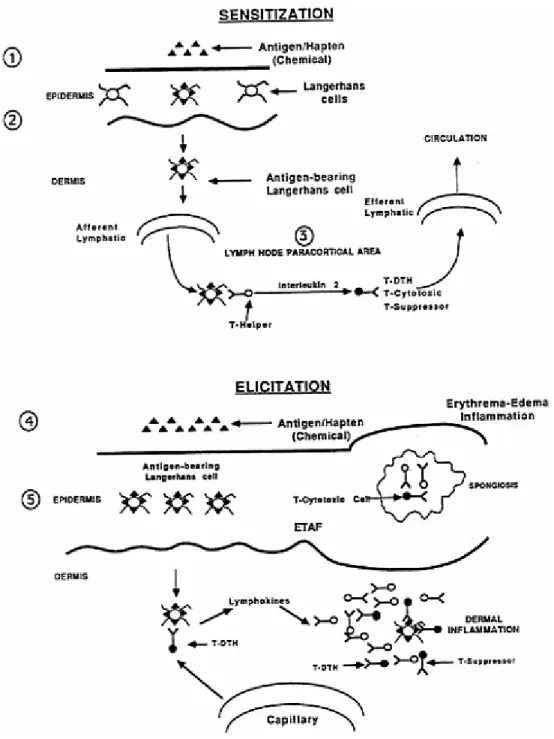
The Structure and Function Of the Immune System And Mechanisms of Immunotoxicity
Cell Reactions
Other biological markers that could be applied to the human immune system are discussed in subsequent chapters. The study and use of immune system markers in humans for the assessment of toxic environmental exposures is now in the initial stages.
Biologic Markers For Immune-Mediated Disease
Some of these antigens have adjuvant properties that may be important in the induction of these responses (Bice et al., 1977). It is difficult to distinguish between IgE-specific responses to chemical haptens and side effects that cause clinical symptoms through non-specific mechanisms (e.g. release of mediators).
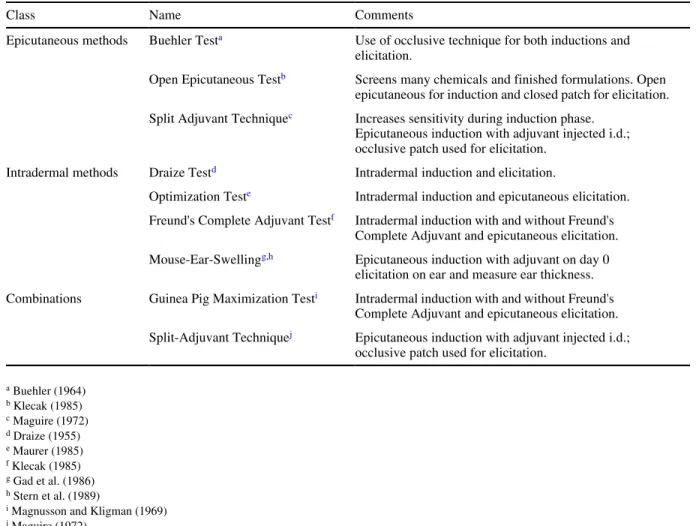
Autoimmune Diseases
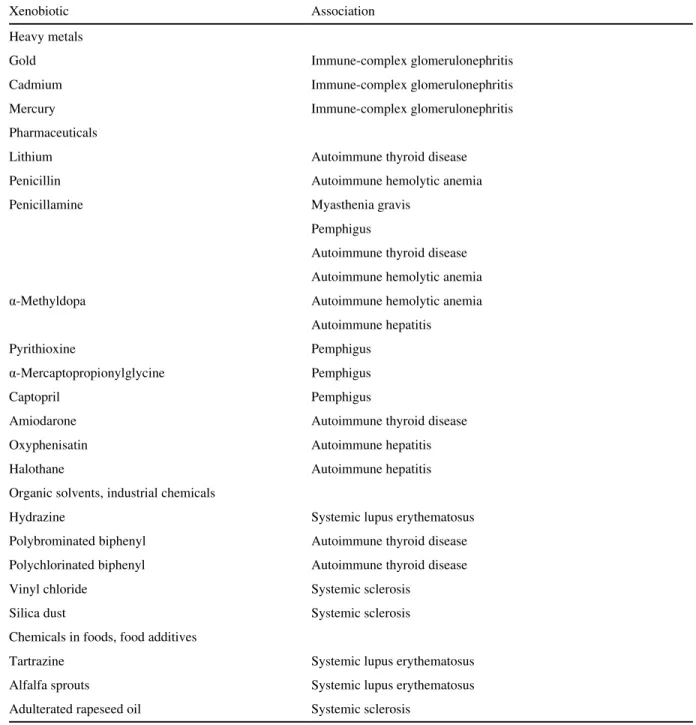
Several autoimmune diseases associated with the exposure of susceptible individuals to organic chemicals are listed in Table 4-2 (Bigazzi, 1988; Kammüller et al., 1988). Occupational exposure to the organic solvent hydrazine induces SLE in slow acetylators with the HLA-DR3 phenotype (Reidenberg et al., 1983). There was an increased incidence of the HLA-DR3 and HLA-DR4 phenotypes among those who developed chronic disease (Vicario et al., 1982; Kammüller et al., 1988).
A somewhat similar picture of progressive systemic sclerosis has been associated with trichlorethylene exposure (Lockey et al., 1987). An outbreak of disease with strikingly similar signs has been described in individuals consuming L-tryptophan preparations (Belongia et al., 1990). Some of these animals show liver damage similar to the hepatitis seen in some patients after halothane anesthesia (Hubbard et al., 1989).
Autoantibodies are found along with drug-dependent antibodies in patients with drug-induced immune neutropenia (Salama et al., 1989) and thrombocytopenia (Lerner et al., 1985). Canavanine occurs in alfalfa sprouts and causes a lupus-like autoimmune disease in primates (Malinow et al., 1982).
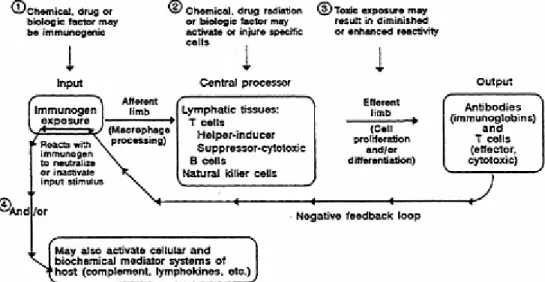
The Capacity of Toxic Agents to Compromise the Immune System (Biologic Markers of Immunosuppression)
Administration of CsA affected susceptibility to murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) infection by reducing the immune response (Selgrade et al., 1989). Reduced CD4:CD8 ratios and natural killer cell function have been reported in asbestos workers (Lew et al., 1986). Selected PAHs, including benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P), 7,12-dimethylbenzanthracene (DMBA), and 3-methylcholanthrene (3-MC), have been shown to produce immunosuppression and myelotoxicity; they are also carcinogenic (Dean et al., 1986).
HCB stimulates immune responses in rats after adult exposure (Vos and Luster, 1989) and perinatal exposure (Vos et al., 1983). Influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity in the lungs is suppressed after exposure to phosgene gas (Ehrlich et al., 1989). Injection or inhalation of isobutyl nitrite suppresses spleen and peripheral blood NK activity (Lotzová et al., 1984).
Suppressed pulmonary bactericidal activity was reported after a 4-hour exposure to ozone in mice (Goldstein et al., 1971). Exposure of human subjects to low ozone concentrations results in an increase in the appearance of neutrophils in BALF (Koren et al., 1988).
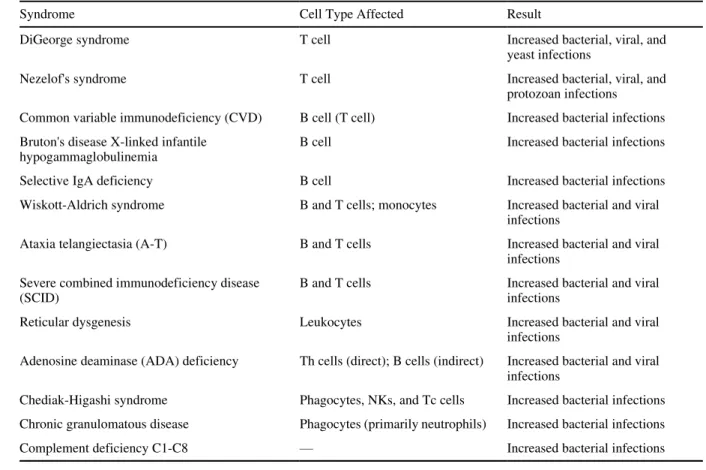
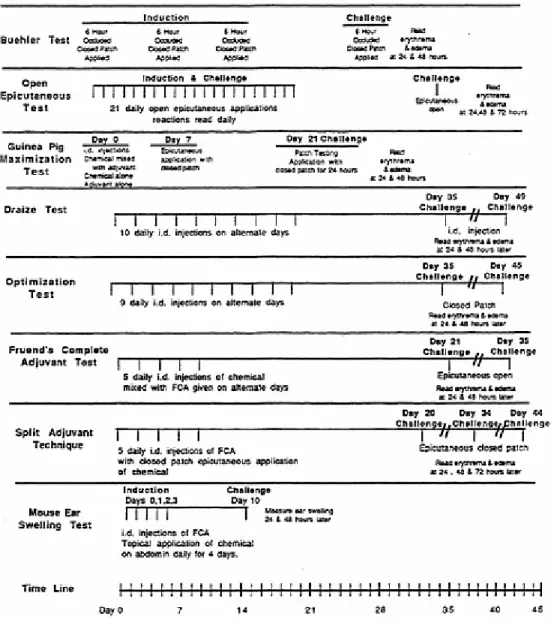
Animal Models for Use in Detecting Immunotoxic Potential And Determining Mechanisms of Action
Elucidating the mechanism by which a chemical affects the immune system provides important information for risk assessment. One is a determination of the number of cells that can form colonies in the spleen (CFU-S). Reversibility of effects on the immune system is related to the chemical and the age of the subject.
The reversibility of the effect on the immune system is important information for hazard assessment. Like other systems of the body, the immune system has many compensatory mechanisms and in a normal individual there is a large reserve. Minimal modulation of the nervous and endocrine systems can lead to an increase in effect in the immune system.
The results therefore give the best prediction of the potential actions of a xenobiotic substance on the immune system. This information is important in understanding the risk associated with changes in stratospheric ozone (De Fabo et al., 1990).
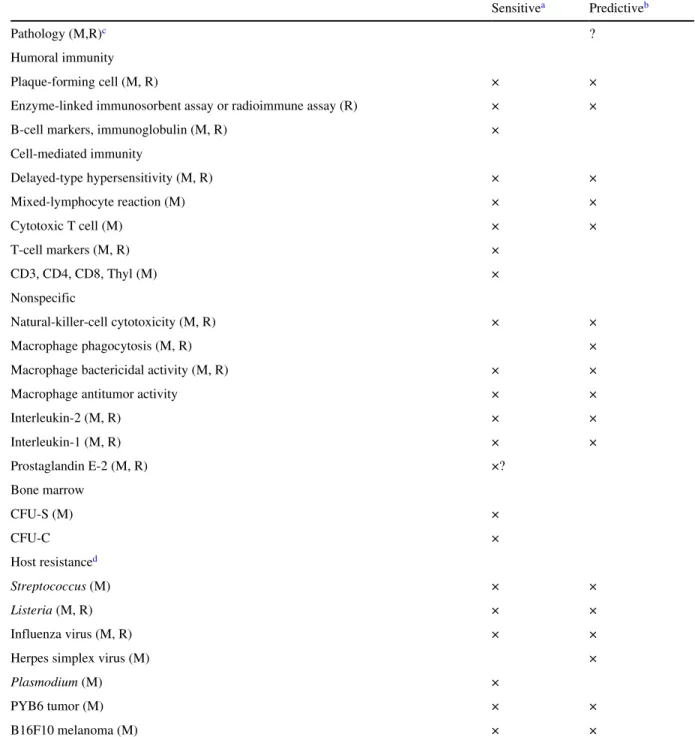
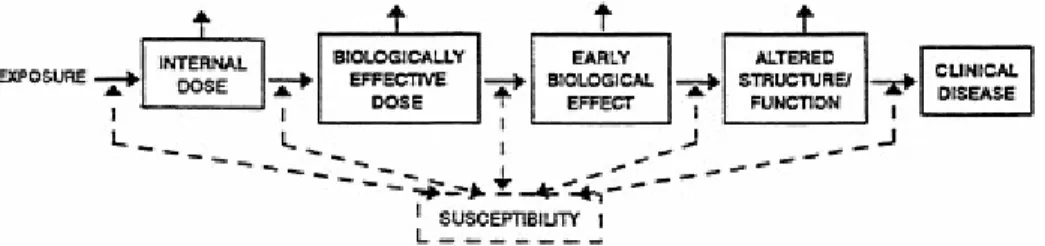
Human Immune-System Biologic Markers of Immunotoxicity
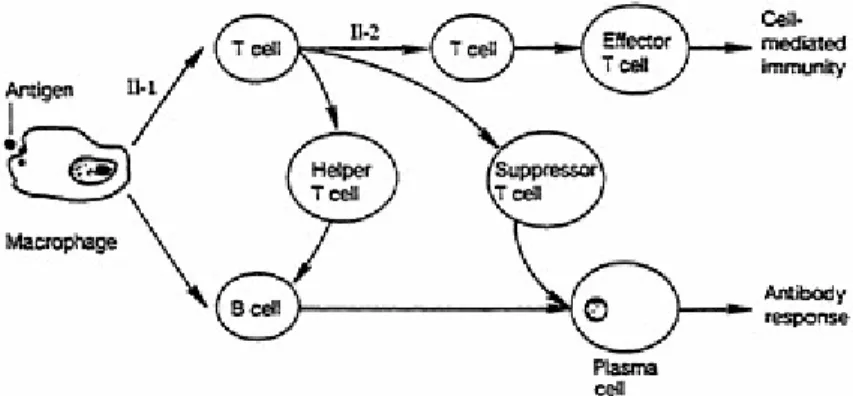
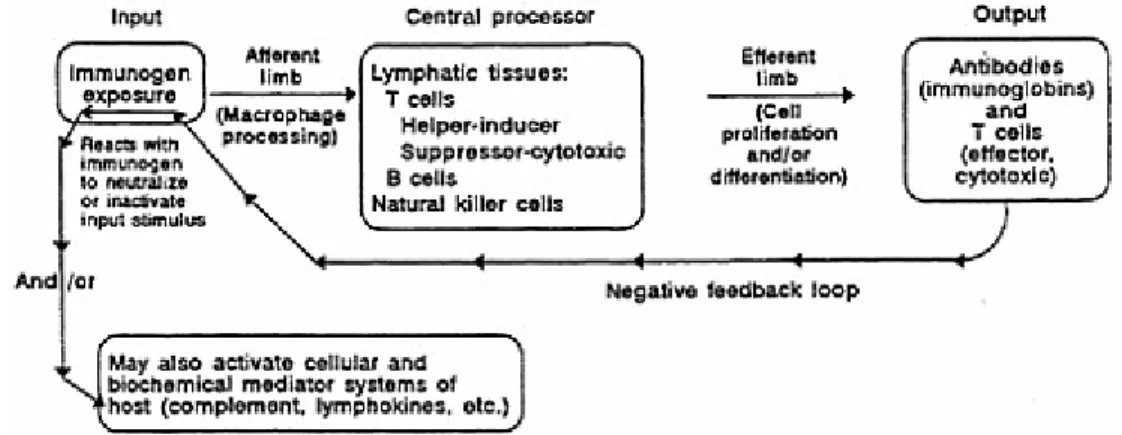
Such an approach should include evaluation of the humoral immune system (B cell system), of the cellular immune system (T cell system), and of non-specific resistance (polymorphonuclear leukocytes, natural killer cells, immune complement). The serum concentration of each of the major immunoglobulin classes, with the exception of IgD, which is predominantly cell-surface, should be determined. More information on the nature of the defects in immunoglobulin production can be obtained using in vitro immunoglobulin biosynthesis studies.
Modifications of the reverse hemolytic plaque assay have been used in attempts to determine helper and suppressor T cell activity. At least five of the antigens listed below should be used to determine impaired cell-mediated immunity. Concentrations of released receptors in serum can be assessed using an appropriate ELISA technique with two monoclonal antibodies that recognize distinct epitopes on the peptide.
Released forms of activation antigens (antigens expressed on activated but not normal resting cells), the 55-kD IL-2 receptor (CD25), CD8, CD23, CD30, and the transferrin receptor have been identified in the serum (Rubin) et al., 1985). An analysis of serum concentrations of the released form of these antigens should also be performed.
Application of Biologic Markers Of Immunotoxicity in Epidemiology
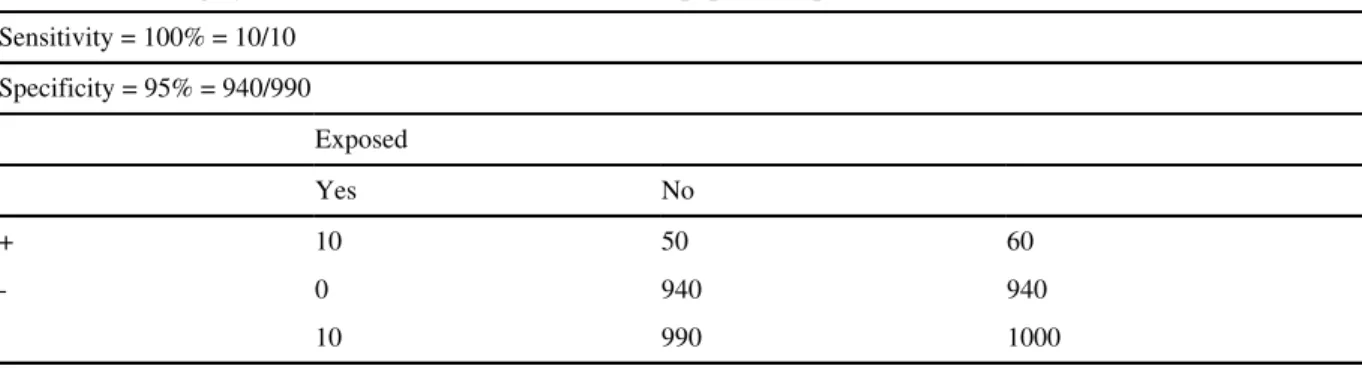
The use of the terms sensitivity and specificity when referring to populations under epidemiological research should be distinguished from their use in reference to laboratory methods (Griffith et al., 1989). Sensitivity and specificity as used in population studies are measures of the accuracy of a test. Predictive value is a measure of the test's potential utility in identifying an exposed individual in the population (positive predictive value) or identifying an unexposed individual in the population (negative predictive value).
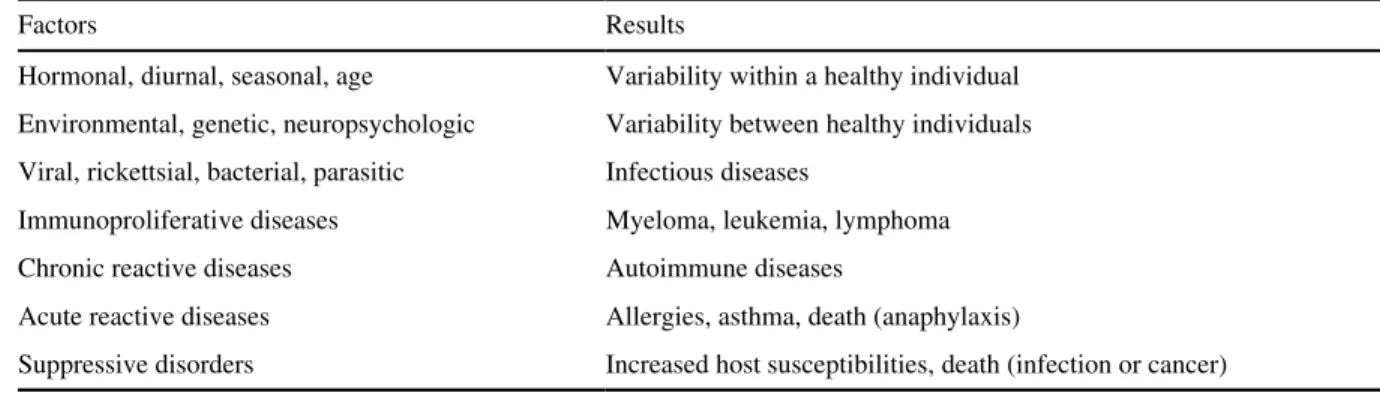
For biological markers of susceptibility, the condition must be defined in terms of the increased risk of a particular health effect (or of any step in the continuum between exposure and disease) for some defined exposure. Immunological markers can be used as dependent (outcome) or independent (risk factor) variables in exploratory epidemiological studies of the relationship between exposure and effect. Many of the clinics are members of the Association of Occupational and Environmental Clinics (Vogt et al., 1990).
The possibility of bias in the selection of the exposed cases cannot be ruled out. Studies on the prevalence of immunotoxicity and immunological markers should be performed to provide baseline and reference values.
Use of Biologic Markers In Controversial Areas Of Environmental Health
Ratios of CD4 to CD8 cells, measured by fluorescence-activated cell sorters or other instruments, have been proposed as biological markers of chemical sensitivity. 1982) suggest that this ratio is elevated for patients with some, but not all, diagnoses. A role for VOCs in the etiology of this syndrome is suggested, and the hypothesis that this syndrome is purely psychological in origin is inconsistent with existing data. The reported evidence is insufficient to define a distinct clinicopathological entity, MCS syndrome, distinct from the chemical-disease associations discussed above.
Well-designed clinical and epidemiologic studies using appropriate biomarkers of the immune system should be conducted to investigate the association between environmental chemicals and specific syndromes of uncertain origin, namely MCS. Information from this multicenter study should be used to study the prevalence of MCS in the general population. Page breaks are true yles, and other type-specific formatting, however, cannot be preserved and some typographical errors may have been accidentally introduced.
Although many patients describe the onset of this syndrome with an acute toxic chemical exposure, such an initial exposure is not necessary for inclusion. Patients' response to controlled exposure should be monitored with immunological, neurological, endocrinological, psychological and social markers and measures.
Summary and Recommendations
The immune system can be expressed bidirectionally; excessive stimulation can result in hypersensitivity, autoimmunity, or both. The use of these techniques should be preceded by validation of assays so that they are known to be sensitive to modulation by immunotoxic substances and the normal ranges are established. Special attention should be focused on susceptibility markers that aid in diagnosis and reveal the mechanistic aspects of environmental diseases.
Of particular importance may be the temporal relationship between suppression of the immune system and the development of clinical disease. Markers of susceptibility that can reveal the diagnostic and mechanistic aspects of environmental diseases need to be studied in laboratory models. Development of such guidelines should be developed for the investigation of the etiology, symptomatology and pathogenesis of this syndrome.
The public should be better informed about the risk to the immune system associated with exposure to chemicals. A case comparison study of patients claiming to be uniquely sensitive to workplace chemicals should be conducted.
Impairment of thymus-dependent immune functions by exposure of the developing immune system to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzone dioxin. Mechanism of intensification by complete Freund's adjuvant of the acquisition of delayed hypersensitivity in the guinea pig. Evaluation of the in vitro and in vivo effects of cyclosporine on the lung T-lymphocyte alveolitis of active pulmonary sarcoidosis.
Platinosis: A five-year study of the effects of soluble platinum salts on workers in a platinum laboratory and refinery. Beta-adrenoceptor mediation of the enhancing effect of norepinephrine on the mouse primary antibody response in vitro. Kinetics of the enhancing effect produced by norepinephrine and terbulatine on the mouse primary antibody response in vitro.
Laboratory evaluation of the immune system in individuals occupationally exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (2,3,7,8- TCDD): Quality control in a cross-sectional epidemiologic study. LFA-1, CD2 and LFA-3 molecules associated with lymphocyte function: Cell adhesion receptors of the immune system.