FISIKA
SUPERKONDUKTOR
oleh :
Fuad Anwar
LANJUTAN
SEJARAH DAN PERKEMBANGAN
S U P E R K O N D U K T O R
PENGERTIAN SUPERKONDUKTOR :
MUNCUL FENOMENA
SUPERKONDUKTIVITAS :
• = 0
• Efek Meissner
• dsb.
JIKA
T < T
cH < H
cDAN
SEJARAH PENEMUAN SUPERKONDUKTOR :
Tahun 1908 : Heike Kamerlingh Onnes dan Timnya (Leiden University) berhasil mencairkan Helium (suhu sekitar 1 K)
Tahun 1911 : Heike Kamerlingh Onnes dan Timnya
melakukan pengukuran hambatan merkuri sebagai fungsi suhu R(T).
Hasilnya :
R=0 pada T=4,2 K
Merkuri : jenis superkonduktor
Merkuri mempunyai suhu kritis
Tc =4,2 K
Heike Kamerlingh Onnes “the gentleman of absolute zero”, discovered Superconductivity on April 1911. Onnes won the Nobel Prize in 1913, just two years after his incredible discovery. Onnes died in 1926.
In 1898 Onnes’ rival, James Dewar, beat him in the race to liquefy hydrogen.
Onnes then moved on to a new goal, liquefying helium, and this time, Onnes beat Dewar in the race, producing the first liquid helium in July 1908.
Though he only liquefied a tiny amount of helium at that time, the liquefaction of helium made it possible to cool other substances to such low temperatures.
Onnes managed to cool the liquid to about one degree above absolute zero, at the time the coldest temperature ever achieved.
“The resistance of pure mercury at helium temperatures,” Communications from the Physical Laboratory at Leiden, April 1911.
“On the Sudden Change in the Rate at which Resistance of Mercury Disappears.” November 1911. Soon after finding the effect in mercury, Onnes showed that tin and lead also become superconducting at low temperatures.
In 1913 Onnes first used the term “supraconductivity,” to describe the effect;
later he changed it to “superconductivity.” By 1914 he had found another interesting feature: he started a supercurrent flowing in a lead wire, and a year later, found that it was still flowing, with no noticeable change. Onnes himself had believed that quantum mechanics would explain the effect, but he wasn’t able to produce a theory.
Heike Kamerlingh Onnes dan Timnya juga menemukan :
Beberapa unsur lain juga menunjukkan sifat superkonduktif dengan harga Tc yang berbeda.
Sifat superkonduktif akan hilang jika superkonduktor dikenai
medan magnet melebihi harga tertentu (disebut medan kritis Hc)
Superkonduktor unsur jenis lain :
Penemuan superkonduktor suhu tinggi
Muller dan Bednorz, 1987
Paul Chu, 1988
Penemuan superkonduktor suhu tinggi
Jenis Superkonduktor
No Jenis bahan T
c( K )
1. Unsur : Al
Nb 1,2
9,2 2. Paduan logam/senyawa biner :
Nb-Ti
MgB2 9
39 3. Superkonduktor heavy fermion :
UBe
13UPd
2Al
30,85 2 4. Superkonduktor organik :
β
L-(BEDT-TTF)
2I
3-(BEDT-TTF)
2Cu(NCS)
21,5 10,4 5. Superkonduktor oksida :
La
2-xSr
xCuO
4YBa
2Cu
3O
7-x38 92 6. Superkonduktor pnictide :
LiFeAs
GdFeAsO
1-x18
53,5
PERTEMUAN KE 3
LANJUTAN
SEJARAH DAN PERKEMBANGAN
S U P E R K O N D U K T O R
SIFAT MAGNET SUPERKONDUKTOR
Walter Meissner
GAMBARAN SIFAT SUPERKONDUKTOR :
lihat video 1-2
JENIS SUPERKONDUKTOR :
Superkonduktor
Superkonduktor Tipe I
Superkonduktor Tipe II
H
cH
c1H
c2(pada superkonduktor bongkahan/bulk)
SUPERKONDUKTOR BONGKAHAN ( BULK )
Ada 2 tipe superkonduktor :
• superkonduktor tipe I
• superkonduktor tipe II
Superkonduktor tipe I Superkonduktor tipe II B=0
-M
H
ekt-M
B0
keadaan campuran B=0
keadaan Efek Meissner
H
ektH
c2H
c1H
cH
ckeadaan
Efek
Meissner
SUPERKONDUKTOR TIPE II
(memperhatikan batas permukaan)
H ext
H
c1H
c2H
c3superkonduktivitas sempurna
superkonduktivitas sebagian
(mixed state)
superkonduktivitas permukaan
normal
fluks magnet dapat menerobos superkonduktor secara parsial fluks magnet terkuantisasi dalam bentuk vorteks
1 vorteks :
e e
h
0
2
APLIKASI SUPERKONDUKTOR :
penghantar arus listrik tanpa kehilangan energi
pembangkit medan magnet super tinggi dalam MRI
penyusun kumparan levitasi magnet MAGLEV
pengukur medan magnet sangat sensitif dalam SQUID
dan sebagainya
Gambaran Aplikasi Superkonduktor
GAMBARAN APLIKASI SUPERKONDUKTOR
lihat video 3
Teori Superkonduktor :
• Teori fenomenologi superkonduktor :
Teori London dan Teori Ginzburg-Landau
• Teori mikroskopis : Teori BCS
Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer (BCS)
Lev D. Landau and V. Ginzburg
Penemu Teori Superkonduktor
A.A. Abrikosov
Gambaran Teori BCS
Superconducting Gap in the electronic spectrum – Order parameter.
GAMBARAN ELEKTRON SUPER
lihat video 4
TEORI GINZBURG-LANDAU
Memperkenalkan Rapat Energi Bebas Gibbs Superkonduktor : Memperkenalkan konsep parameter benahan (ψ) :
• menunjukkan keberadaan sifat superkonduktivitas
• |ψ(r)|
2menyajikan rapat lokal elektron super
CATATAN :
dan A bergantung pada ruang saja
2 0
0 2 2
4 2
2 1 2
2 1
,
H
extB A
A
ss n s
i e m
T f
g
Keterangan :
g
s: rapat energi bebas Gibbs superkonduktor f
n: rapat energi bebas Gibbs keadaan normal ψ : parameter benahan
ћ : tetapan Planck dibagi 2π, μ
0: permeabilitas ruang hampa,
A : potensial vektor magnet di dalam superkonduktor B : induksi magnet di dalam superkonduktor
H
ext: intensitas medan magnet luar
e
sdan m
s: muatan dan massa elektron super
(T) dan : koefisien ekspansi rapat energi bebas Gibbs Catatan :
= konstanta positif, bukan fungsi T
0 1 , di mana 0 adalah pada 0 K
)
(
T
T T T
c
Minimisasi Rapat Energi Bebas Gibbs Superkonduktor terhadap ψ(r) dan A(r) menghasilkan :
Persamaan Ginzburg-Landau Pertama
Persamaan Ginzburg-Landau Kedua
J
s(r) : rapat arus super
r ie r
r r
r im r
e
r r
s s
s
A
A J
s2
22
) ( )
(
( ) 0
) 2 ( )
( )
(
2 2
2
e r r
m i r
r r
T
ss
A
PERSAMAAN SYARAT BATAS :
tanpa efek proksimitas
ada efek proksimitas
b : panjang ekstrapolasi
DARI TEORI GINZBURG-LANDAU, didefinisikan :
• panjang koherensi :
• panjang penetrasi London :
• parameter Ginzburg-Landau :
) ( ) 2
(
2
T T m
s
) ) (
(
20
e T
T m
s s
2 2 0
2
2) (
) (
s s
e m T
T
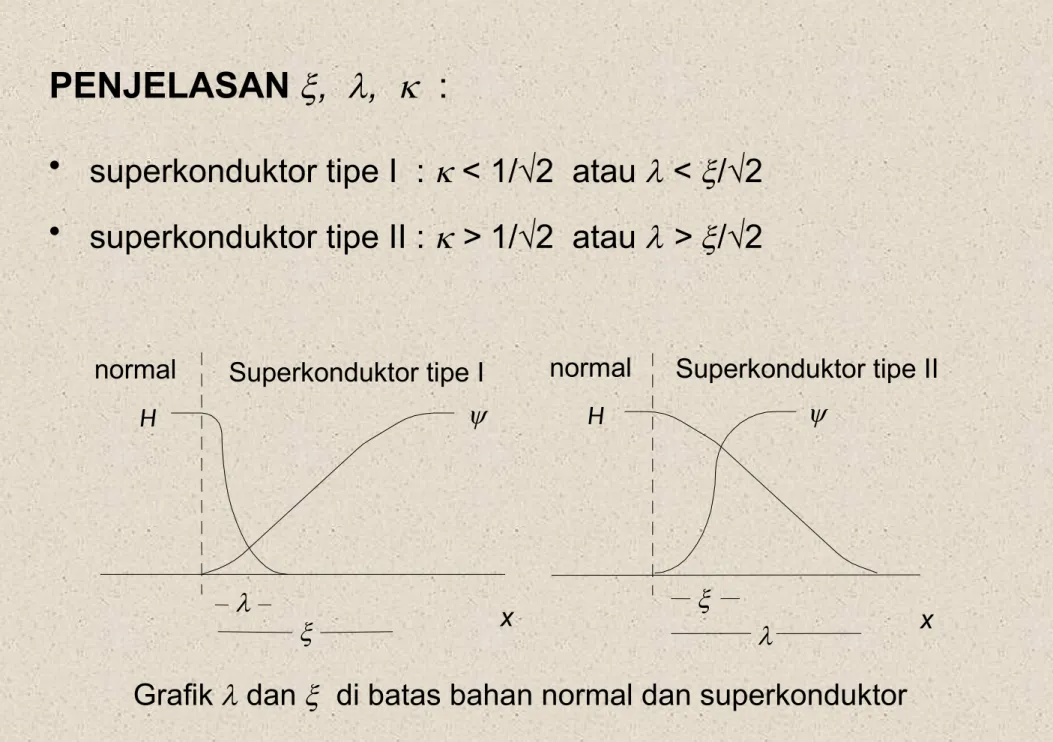
PENJELASAN , , :
• superkonduktor tipe I : < 1/√2 atau < /√2
• superkonduktor tipe II : > 1/√2 atau > /√2
Grafik dan di batas bahan normal dan superkonduktor
H
x H
Superkonduktor tipe I
normal normal Superkonduktor tipe II
x
DARI TEORI GINZBURG-LANDAU, diperoleh :
• Medan kritis rendah :
• Medan kritis tinggi :
• Hubungan antara Hc
1dan Hc
2:
• Medan kritis permukaan :
Hc
3//(T)=1,695 Hc
2(T) Hc
3 (T)=Hc
2(T)
di mana
H
extsejajar permukaan superkonduktor H
exttegak lurus permukaan superkonduktor
ln 2 ln
2
0 21
s s
s
m
T e
T T e
Hc
20 0 2
2
T e e
m T T
Hc
s s s
2 2 2
2
1
2
ln ln
Hc T T
Hc T T Hc
Hc
2
2 0
2
T Hc T T
Hc
GAMBARAN VORTEKS :
lihat video 3