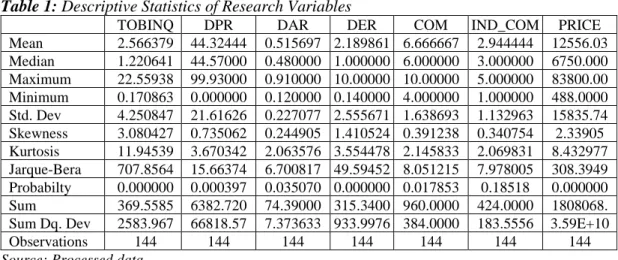
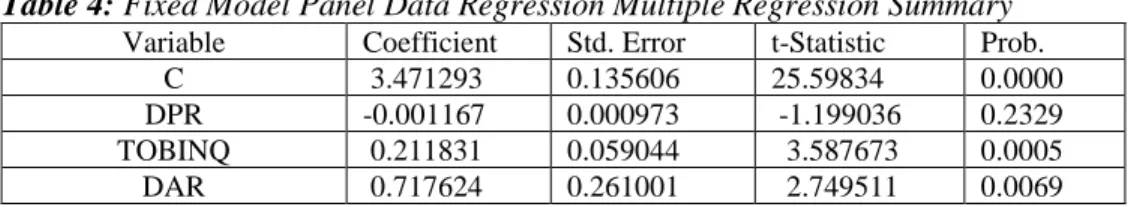
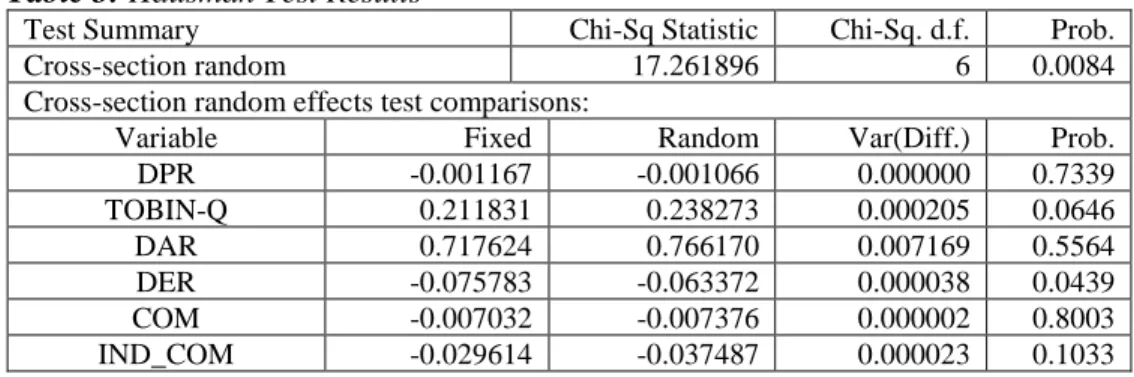
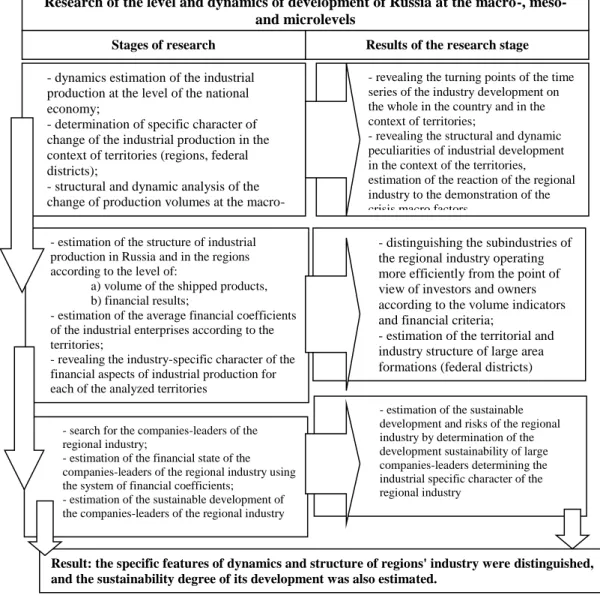
The rising share prices can be interpreted as the increasing value of the company and also increasing shareholder value. The indicator is the ratio between the market value of the company and the book value equity so that the.
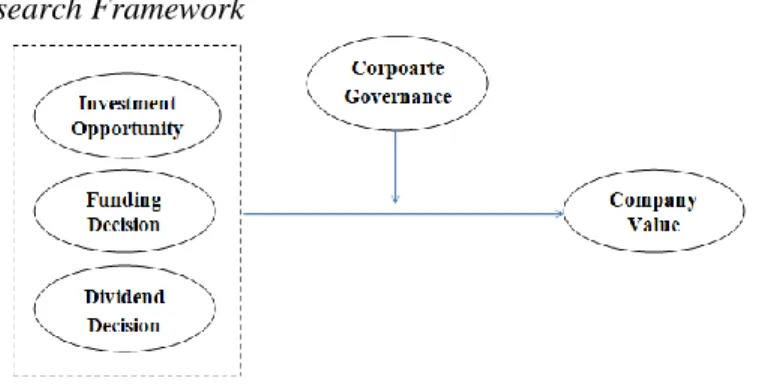
Hypothesis development
Discussion
DAR positively and significantly affects the value of the company, it means that the higher the source of debt funds used by the company, the higher the share prices. The higher the DER, the higher the level of risk, so that the value of the company decreases with the share price.
Conclusion
The mediating effect of leverage and dividend policy on the influence of corporate governance on firm value. The mediating effect of leverage and dividend policy on the influence of corporate governance on firm value.
European Research Studies Journal
Evolution of the total number of journal citations and self-citations received by a journal's published papers over the previous three years. External citations are calculated by subtracting the number of self-citations from the total number of citations received by the journal's papers.
EUROPEAN RESEARCH STUDIES JOURNAL
SJR 2018: 0.297 SNIP 2018: 2.169
Call for Papers
Conferences
Workshops
Synergy effect of innovative activities and their accounting in the technological competences of a company. Transformation of the Russian tax system as part of the integration of the economy into the international high-tech production field of socio-economic systems. Prospects for the use of cryptocurrency in Kazakhstan's economy and the attitude of the National Bank.
Assessment of small business development potential in the northern region of Russia based on correlation analysis. Analysis of Investment Activity Regulation in Priority Sectors of the Economy: A Case Study of China. Incentives of interest groups to cooperate in the production of information in the context of EU policy-making.
Women's entrepreneurship in the innovative regions of Russia in the mirror of qualitative sociological research.
Russian Banking in the Global Economic System: Historical Experience of Integration (1991-2017)
- Introduction
- Methods
- Results
- Conclusion
The state policy of the Russian Federation for the period 2001-2017 included a consistent implementation of a series of organizational and technological measures aimed at ensuring the protection of national interests in the context of the integration of Russian banking institutions in the global financial market. Until now, the Russian banking sector remains quite sensitive to the influence of the international financial and economic market, which requires new innovative approaches in the implementation of the banking construction and the rise of the stock market. This process has significant implications for the institutionalization and functional development of the Russian banking system.
The increasing integration of the Russian banking system into the global virtual banking services market and the latest information technologies in the financial field were important trends in its development in the early first century. The process of integrating the Russian banking system into the global financial and economic space and its institutionalization within the new world financial architecture includes addressing the problem of the efficient adaptation of financial institutions established in accordance with international standards to contemporary Russian socio-economic and technological developments. conditions. Formation of the legal framework for Russian banking policy in the context of modernization on the eve of the XX-XXI centuries.
Rusland i den globaliserende verdensøkonomi: Proceedings of the International Research-to-Practice Conference, Rostov-on-Don.
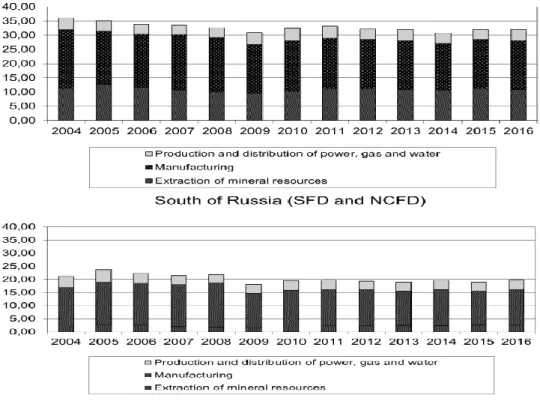
Dynamics, Peculiarities and Financial Factors for the Industrial Development of the South of Russia
Discussion
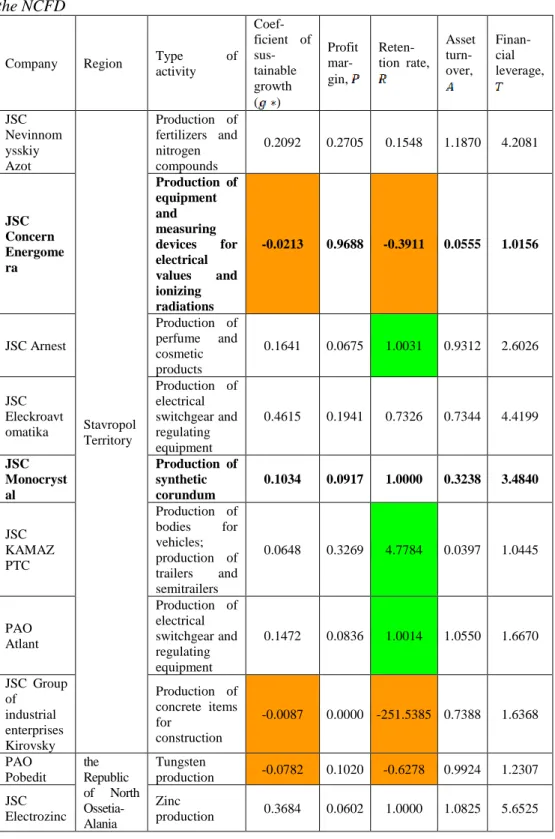
The further elaboration and expansion of the methodology of research of the regional industry of Russia requires the use of the multidimensional methods, which are determined by a large amount of data in the context of the regions, industrial sectors and industrial companies of the regions. In particular, the authors present the development of the benchmark system at the meso-level using the tools of the comparative analysis and algorithms of classification, especially the tools of the analysis of data shim and cluster analysis that allow the to reveal the most successful of the homogeneous. entities and the use of their experience for the implementation of the optimal, strategic scenarios of low-performing entities (regions, industrial complexes, single-industry cities, companies, etc.).
Conclusion
The methodology of implementing the systematic and derivative analysis of the development conditions of the local market of raw materials. The use of plant resources of the Astrakhan region as a basis for the development of the feed base of the livestock industry in the region.
Geographical Economics and Income Disparities Across
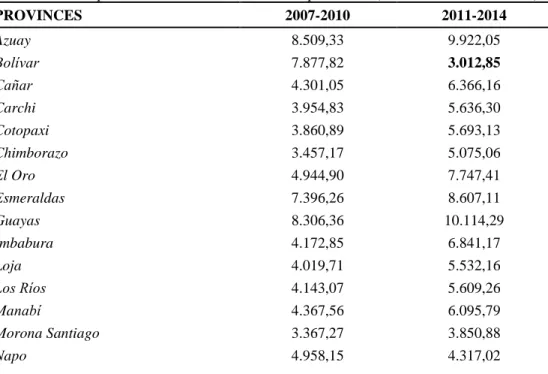
The geography of income disparities across provinces in Ecuador The levels of per capita income in the Ecuadorian provinces differ by significant
- Market potential: construction and summary statistics
Therefore, we will build six different measures of market potential for distances measured in km. The market potential measures using distances expressed in truck travel times will be labeled as PMYAT (market potential based on GDP, truck travel times and dii = 1/3), PM3YAT (market potential based on GDP, truck travel times and dii = 2 /3), PMVYAT (market potential based on GVA, truck driving times and dii = 1/3), PM3VYAT (market potential based on GVA, truck driving times and dii = 2/3), PMPT (market potential based on population, truck driving times and dii = 1/3) y PM3PT (market potential based on population, truck travel times and dii = 2/3). According to expression (2), the total market potential is divided into a domestic component and a foreign component and according to a weighting scheme based on a distance matrix expressed in kms (table 2) and a distance matrix expressed in minutes of truck driving times (table 3).
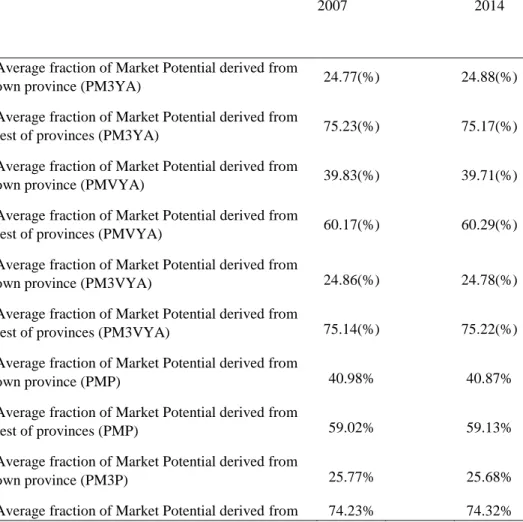
However, internal distances play a role in the distribution of domestic and foreign shares of market potential when we use GVA and Population as proxies for economic activity. As regards the relationship between the geographical distribution of income per per capita and the distribution of the market potential, figure 2 reveals a correlation between the two sizes, even if it is far from perfect. In general, provinces with high market potential are also provinces with high income levels per capita. inhabitant.
It can be observed that there are provinces with rather low values of market potential (for example the oil producing provinces of Sucumbios and Orellana) but with high levels of income per capita. per capita due to oil revenues.
Geographical economics explanation: Income and Geography
D is an aggregate of industrial varieties where mi,j(z) means the consumption of each available variety sin place j and produce in place i and ni is the number of varieties produced in place i. The consumer's problem solution gives the final demand in location j for each variety of produce in location i. Technology in the increasing returns to scale manufacturing sector is given by the usual linear cost function: lDij =F+cxijD, where lDij, represents the industrial workers used for the production of a variety in location i and sold in location j,.
6 This index of industrial prices at location j measures the minimum cost of purchasing a unit of the composite index of manufactured goods D, so that it can be interpreted as a function of expenditure. F represents the fixed cost of production, c is the variable cost per unit and xijD is the quantity of the differentiated good that is demanded at location j and produced at location i ( .. x represents the total amount of output produced by the firm in location i and sold at different j locations) and wiD is the nominal wage paid to production workers at location i. Equation (6) shows that the nominal wage level at location i depends on the weighted sum of the purchasing power of the surrounding locations, where the weighted scheme is a distance function that decreases with increasing distance between i and j.
Estimation of the Baseline Model 1 Panel data
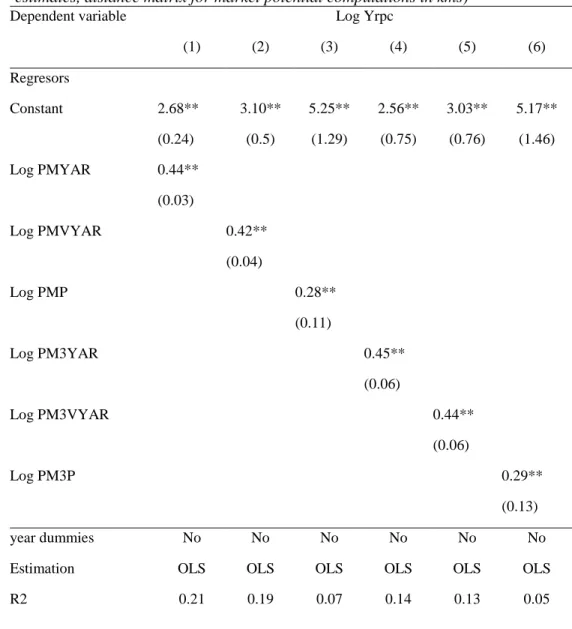
However, there is considerable variation in the values of the coefficient estimates depending on the definition of market potential used in the regression. Estimation results of the base model OLS pooled estimate, distance matrix for market potential calculations in km). Base model estimation results, pooled OLS estimates, distance matrix for market potential calculations in minutes of travel time).
Doubling the market potential would lead to an increase in average per capita income of approximately 47%-48%. The estimates in the first two columns take into account the definition of market potential (PMYAR) and the two defined sets of instruments (according to the two measures of distances) and the estimates in the last two columns correspond to the definition of market potential (PMVYAR). It is clear that the estimates of the elasticity of income per capita with respect to market potential in both cases are in line with the model's theoretical predictions and are very high.
The independent variable is the log of market potential (PMYAR) columns 1 and 2 and log market potential (PMVYAR) columns 3 and 4.
Missing Links (Disentangling Channels of Influence): Human capital The core-periphery geographical economics model sketched in section 3 provides a
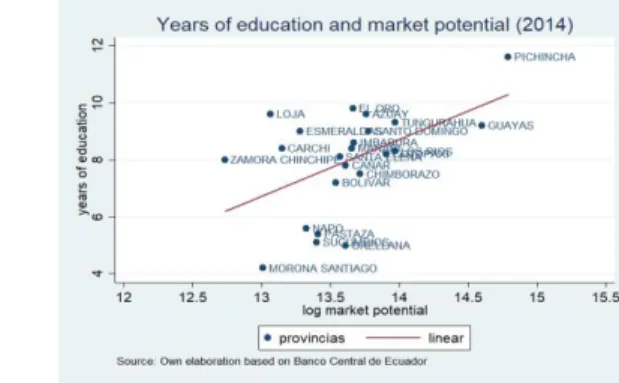
Missing links (disentangling channels of influence): human capital The geographic economic model of the core-periphery outlined in Chapter 3 offers a. At this point it is worth noting a major driver of income levels, which is related to and influenced by market potential: human capital. On the other hand, from the perspective of the geographic economics literature (Redding and Schott, 2003), we have shown that locations with high market potential also provide long-term incentives for human capital accumulation by increasing the premium for skilled labour.
The graphs show that the allocation of human capital is on average higher in the places which have high values of market potential. Thus, assuming that the accumulation of human capital across the Ecuadorian provinces is largely influenced by their relative access to markets, a natural way is to test the importance of market potential as a key factor in explaining the geographic distribution of income levels in Ecuador by incorporating human capital stocks as an additional regressor in the previously estimated baseline specification. Regarding the coefficients associated with the human capital proxy by average years of education, the signs are consistent with theoretical expectations.
The independent variable is the log of market potential (PMYAR) columns 1, 2 and the log of market potential (PMVYAR) columns 3 and 4.
Conclusions
The results of the IV estimations yielded slope parameter estimates for market potential that were in the range 0.23-0.25 and b) using lagged values for market potential. The results of the extended baseline estimates that have human controls showed that market potential retains its importance with elasticity estimates in the range 0.13-0.15. The market as a factor in the localization of industry in the United States, Annals of the Association of American Geographers.
The first page should be designed to contain, along with a portion of the text, the following (in the order listed, read from top to bottom): (a) the title of the paper and potential subtitle(s), (b) the name and author(s) ) institution(s), (c) an abstract not exceeding 100 words, in letter format size 10, (d) a footnote with detailed information related to the author(s) (name, full address, institution where the author(s) work i, telephone and fax numbers, e-mail address and any other relevant information), (e) a footnote marked with an asterisk containing potential acknowledgements. References in the main text must include the author(s) surname and the year of publication in parentheses, e.g. Formulas should be numbered with consecutive Arabic numerals (such as (1), (2), etc.), placed on the right side of the page.
They should be placed on separate pages at the end of the text after potential appendices and bibliography.